【期末考试复习】计算机网络英文版
- 格式:doc
- 大小:220.50 KB
- 文档页数:13

【期末考试复习】计算机网络英文版第一章计算机网络概述●Identify the five components of a data communications system.(数据通信系统5个组成部分:报文发送方接受方传输介质协议) message,sender,receiver,transmission medium and protocol.●What are the three criteria necessary for an effective and efficient network?performance, reliability,and security.●What is an internet(互联网)? What is the Internet(因特网)?★ An internet is an interconnection of networks which is a collection of networks connected by internetworking devices such as routers.★The Internet is the name of a specific worldwide network that uses the TCP/IP protocol suite and is the largest internet in the world.第二章数据和信号●Which practical methods are used for analysis of a signal? And which is suitablefor network techniques? 研究电磁信号的方法是哪两种?适用于网络技术的?①Time domain and frequency domain②frequency domain●Why can't any digital signal be transferred with no distortion in communicationtransmission?(数字信号为什么不能无失真传输?)1.Because to receive an exact replica of the digital signal, all of the frequency components must be faithfully through the transmission medium, if certain harmonic cannot transfer successful, the signal we receive will be distorted. However, anymedium transfers signals only within certain frequency ranges, that is, has a limited bandwidth.2.Transmission impairments of signals (attenuation, distortion and noise) always exist, so signal errors unavoidable.●What's the bandwidth(带宽)? Explain briefly what correlation do bandwidth,data rate and cost have in communication process?带宽、数据率、成本之间的关系?The range of frequencies contained in a composite signal is its bandwidth.In networking, we use the term bandwidth in two contexts with two different measuring values: Bandwidth in Hertz is the range of frequencies in a composite signal or the range of frequencies that a channel can pass, usually used to present the performance of analog channels and transmission media. (Another is) Bandwidth in bits per second is the speed of bit transmission in a channel,a link,or even a network, usually used to present the performance of links and communication devices of a network.(课本P84)The greater the transmission bandwidth,the greater the data rate, and the higher the cost.●Q3-3: How can a composite signal be decomposed into its individual frequencies?复位信号如何分解成单独的频率成分?If the composite signal is periodic, we can ues Fourier Series decompose it into a series of signals with discrete frequencies;if the composite signal is nonperiodic, we can ues Fourier Transform decompose it into a combination of sine waves with continuous frequencies.●Q3-4: Name three types of transmission impairment. 三种传输减损?Attenuation, distortion,and noise. 衰减、失真和噪声●Q3-7: What does the Nyquist theorem have to do with communications?奈奎斯特公式在通信中的作用?Estimate the channel capacity of noise-free digital channels, , when the channel is greater than the data rate transmitted on channel capacity, it will be failure due to severe distortion.☆The Nyquist theorem defines the theoretical maximum bit rate of a noiseless channel.●Q3-8: What does the Shannon capacityhave to do with communications?香农容量原理在通信中的作用?Estimate the thermal noise interference channel capacity (theoretical upper limit), the data rate is higher, damage caused by noise will be more serious.☆ The Shannon capacity defines the theoretical highest data rate for noisy channel. 第三章传输介质●Briefly describe the main applications of three types of guided transmissionmedia. 三种重要的有向传输介质的应用总的说:Twisted-pair cable is used for voice and data communications. Coaxial cable is used in cable TV networks and traditional Ethernet LANs. Fiber-optic cable is used in backbone networks, cable TV networks, and Fast Ethernet networks.分别说:twisted-pair cable: 双绞线(广泛用于楼内布线)/doc/5611869427.html,ed as telephone lines to provide voice and data channels –connectingsubscribers to the central telephone office./doc/5611869427.html,ed as DSL (digital subscriber line) loop to provide high-data-rate Internet connection – the so called Family Broad Band./doc/5611869427.html,ed in LANs to provide high-data-rate baseband transmission (10 and 100 Mbps).coaxial cable: 同轴电缆(不用了,目前主要用于有线电视)1.Was widely used in analog telephone networks (10000 voice signals) and in digital telephone networks (data rate up to 600 Mbps).However, it has largely been replaced with fiber-optic cable.2.Was widely used in cable TV networksHowever, cable TV providers replaced most of coax with fiber-optic cable.3.Was widely used in early traditional Ethernet LANs.However, it has been replaced with UTP which has data rate up to 100 Mbps.☆ Now, mainly used for CATVfiber-optic cable: 光纤(广泛用于楼间布线和长途传输)widely used for wirings between buildings or long-distance transmission.such as:1.High-speed backbone networks because its wide bandwidth is cost-effective.2.Cable TV networks use usually a combination of optical fiber and coaxial cable.3.Backbone channels in LANs, CANs and W ANs4.Lightning-proof networks5.Secrecy networks against wiretapping●What types of optical fiber transmission modes are there?Which of them issuitable for long distance transmission?Types:sigal mode and multimode, and the multimode include two types:Step-index and Graded-index.The sigal mode is suitable for long distance transmission.第四章●What is Encoding? Why must encoding be used for data transmission?(1)【什么是编码?】Convert internal data of a sender into line signals suitable for transmission is called encoding.(2)【数据发送时为什么要编码?】1) Electromagnetic signals in information process devices are not allowed transmitting directly over communication lines.2) The signal type of a device differs from the signal type ofa communication line.3) The parameter requirements of device signals differs from the one of line signals.4) Specific requirements in synchronization, efficiency , error control, etc..★Because electromagnetic signals in information process devices are not allowed transmitting directly over communication lines, so encoding must be used for data transmission to converts internal data of a sender into line signals suitable for transmission.2.3.4.机内信号与线路类型不一样;机内信号参数与线路传输的要求不一样;同步、效率、纠错等方面的特殊要求●Which two techniques are used when analog data transmitted by digital signals?Which of them is the most important? Why?用数字信号传输模拟数据常用技术有哪两种?最常用的是?为什么?(1) Pulse Code Modulation(PCM) and Delta Modulation(DM).(2) Pulse Code Modulation(PCM) is the most important.(3) The principal advantage of DM over PCM is the simplicity of its implementation. In general, PCM exhibits better SNR characteristics at the same data rate.●What processes will be involved when analog data are digitized by PCMtechnique?用PCM技术将模拟数据数字化时,要经过哪些处理步骤?Sampling (PAM)---->quantization---->binary encoding---->digital to digital coding●Q4-1 List three techniques of digital-to-digital conversion.They are line coding,block coding and scrambling coding.●Q4-4 Define baseline wandering and its effect on digital transmission.(1)In decoding a digital signal, the receiver calculates a running average of the received signal power. This average is called the baseline.(2)The incoming signal power is evaluated against this baseline to determine the value of the data element.(3)A long string of 0s or 1s can cause a drift in the baseline (baseline wandering) and make it difficult for the receiver to decode correctly.●Q4-5 Define a DC component and its effect on digital transmission.(Define) When the voltage level in a digital signal is constant for a while, the specturm creates very low frequencies(results of Fourier analysis). These frequences around zero,called DC(derect-current) components, that present problems for a system that can not pass low frequencies or a system that uses electricalcoupling.(Effect) DC component means 0/1 parity that can cause base-line wondering. 直流分量的影响不仅仅是基线偏移,还有更重要的原因。

P63 #5 Consider sending a packet of F bits over a path of Q links. Each link transmits at R bps. The network is lightly loaded so that there are no queuing delays. Propagation delay is negligible.a.Suppose the network is a packet-switched virtual-circuit network. Denote the VC setup time by t s seconds. Suppose the sending layers add a total of h bits of header to the packet. How long does it take to send the file from source to destination?t s+[(F+h)/R]Qb.Suppose the network is a packet-switched datagram network and a connectionless service is used. Now suppose each packet has 2h bits of header. How long does it take to send the packet?[(F+2h)/R]Qc.Finally, suppose that the network is a circuit-switched network. Further suppose that the transmission rate of the circuit between source and destination is R bps. Assuming ts setup time and h bits of header appended to the packet, how long does it take to send the packet?t s+(F+h)/RP64 #6 This elementary problem begins to explore propagation delay and transmission delay, two central concepts in data networking. Consider two hosts, A and B, connected by a single link of rate R bps. Suppose that the two hosts are separated by m meters and suppose that the propagation speed along the link is s meters/sec. Host A sends a packet of size L bits to host B.[a] Express the propagation delay, d prop, in terms of m and s.[b] Determine the transmission time of the packet, d trans, in terms of L and R.[c] Ignoring processing and queueing delays, obtain an expression for the end-to-end delay.[d] Suppose Host A begins to transmit the packets at time t=0. At time t=d trans, where is the last bit of the packet?[e] Suppose d prop is greater than d trans. At time t=d trans, where is the first bit of the packet?[f] Suppose d prop is less than d trans. At time t=d trans, where is the first bit of the packet?[g] Suppose s=2.5 x 108, L=100 bits and R=28kbps. Find the distance m so that d prop = d trans.[a] d prop = m/s[b] d trans = L/R[c] end-to-end delay = d prop + d trans=m/s+L/R[d] The beginning position of the link.[e] On the channel between A and B.[f] On the host B.[g] m/s = L/R = > m = sL/R = > m = 892.86 kmP65 #10 Consider the queueing delay in a router buffer. Suppose that all packets are L bits, the transmission rate is R bps, and that N packets simultaneously arrive at the buffer every LN/R seconds. Find the average queueing delay of a packet (in terms of L, R and N). (Hint: The queueing delay for the first packet is zero; for the second packet L/R; for the third packet 2L/R. The Nth packet has already been transmitted when the second batch of packets arrives.)As the Nth packet has already been transmitted when the next batch of packets arrive, we only need to consider the delay for a single batch of packets.Average delay = Total delay / Number of packetsDelay for 1st packet = 0Delay for 2nd packet = L/RDelay for 3rd packet = 2L/R......Delay for Nth packet = (N-1)L/RTotal delay for N packets = (0 + 1 + 2 ... +(N-1) ) * (L/R)Using the formulas for sum of integer series, this can be written as: Total delay for N packets = (N-1) * (N/2) * (L/R)Therefore, average delay for N packets = ((N-1) * L) / 2RP170 #12 What is the difference between persistent HTTP with pipelining and persistent HTTP without pipelinning? Which of the two is used by HTTP/1.1?For the persistent connection without pipelining, the client issues a new request only when the previous has been received. In this case, the client experiences one RTT in order to request and receive each of the referenced objects.For the persistent connection with pipelining, the client issues a request as soon as it encounters a reference. It is possible for only RTT to be expended for all the referenced objects.P170 #14 Telnet into a Web server and send a multiline request message. Include in the request message theIf-modified-since: header line to force a response message with the 304 Not Modified status code.GET/somedir/exp.html HTTP/1.1Host: Connection: closeUser-agent: Mozilla/4.0If-Modified-Since: Thu, 30 May 2007 12:00:00 GMTAccept-language: frP172 #6 Suppose within your web browser you click on a link to obtain a web page. The IP address for the associated URL is not cached in your local host, so a DNS look-up is necessary to obtain the IP address. Suppose that n DNS servers are visited before your host receives the IP address from DNS; the successive visits incur an RTT (Round Trip Time) of RTT1, ... RTTn. Further suppose that the web page associated with the link contains exactly one object, consisting of a small amount of HTTP text. Let RTT0 denote the RTT between the local host and the remote server containing the object. Assuming zero transmission time of the object, how much time elapses from when the client clicks on the link until the client receives the object? (Hint: read pages 90 .. 93)Time to visit DNS servers and get IP address = RTT1 + RTT2 + ... + RTTnTime to establish TCP connection (SYN and SYNACK) = RTT0Time to send HTTP request and receive reply = RTT0Total time = 2 * RTT0 + (RTT1 + RTT2 + ... + RTTn)P171 #16 Suppose Alice with a Web-based e-mail account (such as Yahoo! Mail or Hotmail) sends a message to Bob, who accesses his mail from his mail server using POP3. Discuss how the message gets from Alice’s host to Bob’s host. Be sure to list the series of application-layer protocols that are used to move the message between the two hosts.The series of application-layer protocols: HTTP、SMTP、POP3Suppose that you send an e-mail message whose only data is a Microsoft Excel attachment. What might the header lines (including MIME lines) look like?From:***********To:***********Subject: helloMIME-Version: 1.0Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64Content-Type: Application/MS-ExcelP286 #5 Suppose host A sends two TCP segments back to back to host B over a TCP connection. The first segment has sequence number 90: the second has sequence number 110.a.How much data is in the first segment?a.20 bytesb.Suppose that the first segment is lost but the second segment arrives at B. In the acknowledgement that host B sends to host A, what will be the acknowledgement number?b.ACK90P291 #27 Consider the following plot of TCP window size as a function of time. (reproduced below for you) Assuming TCP Reno is the protocol experiencing the behavior shown above, answer the following questions. In all cases, you should provide a short discussion justifying your answer.a. Identify the intervals of time when TCP slow start is operating.b. Identify the intervals of time when TCP congestion avoidance is operating.c. After the 16th transmission round, is segment loss detected by a tripleduplicate ACK or by a timeout?d. After the 22nd transmission round, is segment loss detected by a triple duplicate ACK or by a timeout?e. What is the initial value of Threshold at the first transmission round?f. What is the value of Threshold at the 18th transmission round?g. What is the value of Threshold at the 24th transmission round?h. During what transmission round is the 70th segment sent?i. Assuming a packet loss is detected after the 26th round by the receipt of a triple duplicate ACK, what will be the values of the congestion-window size and of Threshold?Solution:a.1-6, 23-26b.6-16, 17-22c.a triple duplicate ACKd.timeoute.32f.21g.13h.7i.4, 4P293 #34 Consider sending an object of size O = 100 Kbytes from server to client. Let S = 536 bytes and RTT = 100 msec. suppose the transport protocol uses static windows with window size W. (See Section 3.7.2)a.For a transmission rate of 28 kbps, determine the minimum possible latency. Determine the minimum window size that achieves this latency.b.Repeat (a) for 100 kbps.tency=28.8s W=2tency=8.2s W=4P405 #8 Consider a datagram network using 8-bit host addresses. Suppose a router uses longest prefix matching and has t he following forwarding table:-----------------------------------------------------Prefix Match Interface-----------------------------------------------------00 001 110 211 3-----------------------------------------------------For each of the four interfaces, give the associated range of destination host addresses and the number of addresses in the range.6P407 #15 Consider sending a 3000-byte datagram into a link that has a MTU of 500 bytes. Suppose the original datagram is stamped with the identification number 422. How many fragments are generated? What are their characteristics?there are「2980/480」=7 fragments be generatedP408 #22 Consider the network shown in Problem 21 (reproduced below). Using Dijkstra’s algorithm, and showing your work using a table similar to Table 4.3, do the following:a. Compute the shortest path from s to all network nodesSteps D(t),P(t) D(u),P(u)D(v),P(v)D(w),P(w)D(x),P(x)D(y),P(y)D(z),P(z)0 1,s 4,s ∞∞∞∞∞1 3.t 10,t ∞∞5,t 3,t2 4,u 6,u ∞5,t 3,t3 4,u 6,u ∞5,t4 5,v 7,v 5,v5 6,w 5,v6 6,wPlease fill in the following tables using DV algorithm:For the node Z in the graph shown in the 22nd topic (P408), please fill in the following routing table in the router z about the initial distance-vector Destination node Next hop Current shortest distancevalue-DzS —∞T T 2U —∞V —∞W —∞X —∞Y Y 14Z Z 0following rout-ing table in the node z to update this routing tableDestination node Currentdistance-DyDestination node Current distance-DtS 5 S 1 T 4 T 0 U 2 U 2P493 #7 How big is the MAC address space?The IPv4 address space?The IPv6 address space?MAC address: 6 bytes, MAC address space 2^48IPV4 address: 4 bytes, IPV4 address space 2^32IPV6 address: 16 bytes, IPV6 address space 2^128P494 #4 Consider the 4-bit generator, G, shown in Figure 5.8, and suppose the D has the value 10101010. What is the value of R?G=1001, D=10101010, R=101。

计算机⽹络英⽂版——提供给学⽣部分习题答案Solution of Selected Exercises from the End of Chapter ExercisesChapter 1 - Introduction And Overview1.4 To what aspects of networking does data communications refer?Answer:Data communications refers to the study of low-level mechanisms and technologies used to send information acrossa physical communication medium, such as a wire, radio wave, or light beam.1.5 What is packet-switching, and why is packet switching relevant to the Internet?Answer: Packet switching divides data into small blocks, called packets, and includes an identification of the intended recipient in each packet. Packet switching changed networking in a fundamental way, and provided the basis for the modern Internet. Packet switching allows multiple senders to transmit data over a shared network.1.8 What is a communication protocol? Conceptually, what two aspects of communication does a protocol specify? Answer: A communication protocol refer to a specification for network communication.Major aspects of a protocol are syntax (format) and semantics (meaning) of the protocol.1.9 What is a protocol suite, and what is the advantage of a suite?Answer:protocols are designed in complete, cooperative sets called suites or families, instead of creating each protocol in isolation. Each protocol in a suite handles one aspect of communication; together, the protocols in a suite cover all aspects of communication. The entire suite is designed to allow the protocols to work together efficiently. 1.11 List the layers in the TCP/IP model, and give a brief explanation of each.(See Textbook)1.14 Give a brief explain of the layers in the ISO Open System Interconnection model.(See Textbook)Chapter 3 - Internet Applications And Network Programming3.1 What are the two basic communication paradigms used in the Internet?Answer: There are various approaches, but according to textbook, we can specify them as Stream Paradigm and Message Paradigm.3.2 Give six characteristics of Internet stream communication.(See Textbook)3.3 Give six characteristics of Internet message communication.(See Textbook)3.4 If a sender uses the stream paradigm and always sends 1024 bytes at a time, what size blocks can the Internet deliverto a receiver?Answer: stream paradigm does not provide any guarantees for block sizes, so all depends on individual transfer.3.6 What are the three surprising aspects of the Internet’s message delivery semantics?Answer:The Internet’s message delivery has the followi ng undesirable characteristics:* Messages can be lost* Messages can be duplicated* Messages can be delivered out-of-order3.8 When two applications communicate over the Internet, which one is the server?Answer: T he application that waits for some other applications to contact is called server, and the application that contact other one is called client.3.14 What two identifiers are used to specify a particular server?Answer: A particular server is identified by the following identifiers:* An identifier for the computer on which a server runs (IP Address)* An identifier for a particular service on the computer (Port Number)Chapter 4 - Traditional Internet Applications4.1 What details does an application protocol specify?(See Textbook)4.3 What are the two key aspects of application protocols, and what does each include?(See Textbook)4.6 What are the four parts of a URL, and what punctuation is used to separate the parts?Answer: The URL into four components: a protocol, a computer name, a document name, and parameters. The computer name and protocol port are used to form a connection to the server on which the page resides. And the document name and parameters are used to request a specific page.4.7 What are the four HTTP request types, and when is each used?(See Textbook)4.12 When a user requests an FTP directory listing, how many TCP connections are formed? Explain.Answer: FTP uses two types of connections to perform its functionality, namely* A control connection is reserved for commands. Each time the server needs to download or upload a file, the server opens a new connection.* A data connection is used to transfer files.4.16 List the three types of protocols used with email, and describe each.(See Textbook)4.17 What are the characteristics of SMTP?(See Textbook)4.20 What are the two main email access protocols?Answer: Two major email access protocols are:* Post Office Protocol (POP)* Internet Mail Access Protocol (IMAP)Chapter 6- Information Sources and Signals6.4 State and describe the four fundamental characteristics of a sine wave.(See Textbook)6.9 What is the analog bandwidth of a signal?Answer: Analog bandwidth of signal can be defined as to be the difference between the highest and lowest frequencies of the constituent parts (i.e., the highest and lowest frequencies obtained by Fourier analysis)6.11 Suppose an engineer increases the number of possible signal levels from two to four. How many more bits can be sent in the same amount of time? Explain.Answer: The number of levels that can be represented by n bits is given by 2n . So if number of levels changes from 2→4, it means number of bits goes from 1→2612. What is the definition of baud?Answer: Baud is defined as the number of times that a signal can change per second.6.14 What is the bandwidth of a digital signal? Explain.Answer: According to the definition of analog bandwidth, a digital signal has infinite bandwidth because Fourier analysis of a digital signal produces an infinite set of sine waves with frequencies that grow to infinity.6.18 What is the chief advantage of a Differential Manchester Encoding?Answer: The most important property of differential encoding is that the encoding works correctly even if the two wires carrying the signal are accidentally reversed.6.20 If the maximum frequency audible to a human ear is 20,000 Hz, at what rate must the analog signal from a microphone be sampled when converting it to digital?Answer: The sampling rate = 2 × f max, so the signal should be sampled at 2x20,000 = 40,000 HzChapter 7 - Transmission Media7.2 What are the three energy types used when classifying physical media according to energy used?Answer: Three types of energy used when classifying physical media are electrical, electromechanical (radio), and light7.4 What three types of wiring are used to reduce interference form noise?(See Textbook)7.10 List the three forms of optical fiber, and give the general properties of each.(See Textbook)7.21 What is the relationship between bandwidth, signal levels, and data rate?Answer: If a transmission system uses K possible signal levels and has an anal og bandwidth B, Nyquist’s Theorem states that the maximum data rate in bits per second, D, is: D = 2 B log2K7.22 If two signal levels are used, what is the data rate that can be sent over a coaxial cable that has an analog bandwidthof 6.2 MHz?Answer: Using the D= 2 B log2 K relationship, D = 2*6.2*log22 = 2*6.2*1 = 12.4 Mbps7.24 If a system has an input power level of 9000, and an output power level of 3000, what is the difference when expressed in dB?Answer: Decibel is expressed as 10log10(P out/P in) → 10log10(3,000/9,000) = to be determined by reader7.23 If a system has an average power level of 100, an average noise level of 33.33, and a bandwidth of 100 MHz, whatis the effective limit on channel capacity?Answer: Shannon theorem specify the maximum data rate that could be achieved over a transmission system that experiences noise: C = Blog2 (1 + S/N) = 100,000,000 * log2 (1 + 100/33.33) = 100,000,000 * log24 = 200,000,000 = 200 Mbps7.25 If a telephone system can be created with a signal-to-noise ratio of 40 dB and an analog bandwidth of 3000 Hz, how many bits per second could be transmitted?Answer: First we should convert 40 dB to a real number, namely if 40 = 10 log10S/N→S/N = 10,000 , Using the Shannon’s capacity expression C = B log2(1 + S/N) → C = 3,000 log2 (1+ 10,000) = to be determined by readerCh 8 - Reliability And Channel Coding8.1 List and explain the three main sources of transmission errors.(See Textbook)8.3 In a burst error, how is burst length measured?Answer: For a burst error, the burst size, or length, is defined as the number of bits from the start of the corruption to the end of the corruption.8.4 What is a codeword?Answer: We can define the set of all possible messages to be a set of datawords, and define the set of all possible encoded versions to be a set of codewords. So each possible code sequence is considered to be a codeword.8.8 Compute the Hamming distance for the following pairs: (0000, 0001), (0101, 0001), (1111, 1001), and ( 0001, 1110). (See Textbook)8.11 Generate a RAC parity matrix for a (20, 12) coding of the dataword 100011011111.(See Textbook)8.15 Express the two values in the previous exercise as polynomials.Answer:X10+ X7 + X5 + X3 + XX4+ X2+ 1Ch 9 - Transmission Modes9.1 Describe the difference between serial and parallel transmission.Answer: Transmission modes can be divided into two fundamental categories:* Serial: one bit is sent at a time* Parallel: multiple bits are sent at the same time9.2 What are the advantages of parallel transmission? What is the chief disadvantage?Answer: A parallel mode of transmission has two chief advantages:* High speed: Because it can send N bits at the same time, a parallel interface can operate N times faster than an equivalent serial interface.* Match to underlying hardware: Internally, computer and communication hardware uses parallel circuitry.Thus, a parallel interface matches the internal hardware well.The main disadvantage of parallel transmission is number of cables required, for long distance communication, this is an important consideration.9.4 What is the chief characteristic of asynchronous transmission?Answer:Asynchronous transmission can occur at any time, with an arbitrary delay between the transmission of two data items, it allows the physical medium to be idle for an arbitrary time between two transmissions.Chapter 11 - Multiplexing And Demultiplexing11.2 What are the four basic types of multiplexing?(See Textbook)11.4 What is a guard band?Answer: For proper communication without interference, we should choose a set of carrier frequencies with a gap between them known as a guard band. The guard band reduces or eliminates the possible interference between neighboring carrier signals.11.8 Explain how a range of frequencies can be used to increase data rate.Answer:To increase the overall data rate, a sender divides the frequency range of the channel into K carriers, and sends 1 /K of the data over each carrier.11.12 Suppose N users compete using a statistical TDM system, and suppose the underlying physical transport can sendK bits per second. What is the minimum and maximum data rate that an individual user can experience?Answer: If we neglect the overhead generated by statistical TDM, a system will have two possibilities: * Minimum: If all channels have equal data then the rate will be K/N bps* Maximum: If only one channel active and the others are passive, then rate will be K bpsChapter 13 - Local Area Networks: Packets, Frames, And Topologies13.1 What is circuit switching, and what are its chief characteristics?Answer: The term circuit switching refers to a communication mechanism that establishes a path between a sender and receiver with guaranteed isolation from paths used by other pairs of senders and receivers. The circuit switching has the following main characteristics:* Point-to-point communication* Separate steps for circuit creation, use, and termination* Performance equivalent to an isolated physical path13.3 In a packet switching system, how does a sender transfer a large file?Answer: The packet switching system requires a sender to divide each message into blocks of data that are known as packets . The size of a packet varies; each packet switching technology defines a maximum packet size. So, a large file will be divided into smaller pieces and sent.13.5 What are the characteristics of LANs, MANs, and W ANs?Answer: There are lots of details that can be said and discussed for categorization of network types based on geography, few points are highlighted below:* Local Area Network (LAN): Least expensive; spans a single room or a single building* Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) Medium expense; spans a major city or a metroplex* Wide Area Network (WAN) Most expensive; spans sites in multiple cities13.6 Name the two sublayers of Layer 2 protocols defined by IEEE, and give the purpose of each.Answer: The Layer 2 protocols defined by IEEE defines two sub-layers as mentioned below:* Logical Link Control (LLC) Addressing and demultiplexing* Media Access Control (MAC) Access to shared media13.8 What are the four basic LAN topologies?Answer: The four basic LAN topologies are star, ring, mesh and bus.13.10 In a mesh network, how many connections are required among 20 computers?Answer: The expression to calculate number of connections in a mesh network is given by n (n-1)/2. So for 20 computers then number of connections required will be = 20 (20 – 1)/2 =19013.15 Give a definition of the term frame .Answer: In a packet-switched network, each frame corresponds to a packet processed at data link layer.Chapter 14 - The IEEE MAC Sub-Layer14.1 Explain the three basic approaches used to arbitrate access to a shared medium.(See Textbook)14.3 List the three main types of channelization and the characteristics of each.(See Textbook)14.6 What is a token, and how are tokens used to control network access?Answer: A special control message is called a token. In a token passing system, when no station has any packets to send, the token circulates among all stations continuously. When a station captures the token, it sends its data, and when transmission completed, it releases the token.14.8 Expand the acronym CSMA/CD, and explain each part.Answer: The acronym CSMA/CD stands for Carrier Sense Multi-Access with Collision Detection, which means the following: * Carrier Sense: Instead of allowing a station to transmit whenever a packet becomes ready, Ethernet requires each station to monitor the cable to detect whether another transmission is already in progress.* Multiple Access: The system allows multiple users/hosts to make use of a common/shared media* Collision Detection. A collision can occur if two stations wait for a transmission to stop, find the cable idle, and both start transmitting.14.10 Why does CSMA/CD use a random delay? (Hint: think of many identical computers on a network.)Answer: Randomization is used to avoid having multiple stations transmit simultaneously as soon as the cable is idle.That is, the standard specifies a maximum delay, d, and requires each station to choose a random delay less than d after a collision occurs. In most cases, when two stations each choose a random value, the station that chooses the smallest delay willChapter 15 - Wired LAN Technology (Ethernet And 802.3)15.1 How large is the maximum Ethernet frame, including the CRC?Answer: According to Fig. 15.1 a conventional Ethernet frame has the following fields:* Header: 14 bytes (fixed)* Payload: 46-1500 bytes (there is a minimum frame size because of collision detection)* CRC: 4 bytes (fixed)Accordingly an Ethernet frame will be maximum 1518 bytes and minimum 64 bytes15.3 In an 802.3 Ethernet frame, what is the maximum payload size?Answer: The 802.3 Ethernet makes use of 8-bytes of the original/conventional Ethernet for Logical Link Control / Sub-Network Attachment Point (LLC / SNAP) header instead of extending/increasing the header. This is for sake of backward compatibility. So the maximum pay load is reduced from 1500 bytes to 1492 bytes.15.6 How did a computer attach to a Thicknet Ethernet?Answer: Hardware used with Thicknet was divided into two major parts:* Transceiver: A network interface card (NIC) handled the digital aspects of communication, and a separate electronic device called a transceiver connected to the Ethernet cable and handled carrier detection, conversion of bits into appropriate voltages for transmission, and conversion of incoming signals to bits.* AUI: A physical cable known as an Attachment Unit Interface (AUI) connected a transceiver to a NIC in a computer. A transceiver was usually remote from a computer.15.7 How were computers attached to a Thinnet Ethernet?Answer: Thinnet Ethernet (formally named 10Base2) uses a thinner coaxial cable that was more flexible than Thicknet. The wiring scheme differed dramatically from Thicknet. Instead of using AUI connections between a computer and a transceiver, Thinnet integrates a transceiver directly on the NIC, and runs a coaxial cable from one computer to another.15.8 What is an Ethernet hub, and what wiring is used with a hub?Answer: An electronic device that serves as the central interconnection is known as a hub. Hubs were available in a variety of sizes, with the cost proportional to size. The hubs are becoming old-fashioned, and being replaced with switches.15.3 What category of twisted pair wiring is needed for a 10 Mbps network? 100 Mbps? 1000 Mbps?Answer: The three major categories of Ethernet and their wiring is listed below:* 10 Mbps: 10BaseT (Ethernet) Category 5* 100 Mbps: 100BaseT (Ethernet Fast) Category 5E* 1 Gbps: 1000BaseT (Gigabit Ethernet) Category 6Chapter 20 - Internetworking: Concepts, Architecture, and Protocols20.2 Will the Internet be replaced by a single networking technology? Why or why not?Answer: Incompatibilities make it impossible to form a large network merely by interconnecting the wires among networks. The beauty of the Internet is interconnection of wide range of technologies from various manufacturers.Diversity of the products and solutions is a richness instead of limitation as long as they all adopt the same set of protocols.20.3 What are the two reasons an organization does not use a single router to connect all its networks?Answer:An organization seldom uses a single router to connect all of its networks. There are two major reasons: * Because the router must forward each packet, the processor in a given router is insufficient to handle the traffic passing among an arbitrary number of networks.* Redundancy improves internet reliability. To avoid a single point of failure, protocol software continuously monitors internet connections and instructs routers to send traffic along alternative paths when a network or router fails.20.6 In the 5-layer reference model used with the TCP/IP Internet protocols, what is the purpose of each of the five layers?(See 1.11)Chapter 21- IP: Internet Addressing21.3 In the original classful address scheme, was it possible to determine the class of an address from the address itself? Explain.Answer:Yes, since in the classful addressing scheme initial bit(s) gives indication about the class being used.21.7 If an ISP assigned you a /28 address block, how many computers could you assign an address?Answer: When an organization is assigned /28 CIDR address, it means 28 bits out of 32 bits are fixed, so 32-28 = 4 bits available for user space. So number of users 24-2 = 4, since the all 0s and all 1s address are having special use and can’t be assigned to a user.21.8 If an ISP offers a / 17 address block for N dollars per month and a / 16 address block for 1.5 N dollars per month,which has the cheapest cost per computer?Answer: Number of addresses in /17 block 232-17 = 215Price per address: N /215 = N / 215Number of addresses in /16 block 232-16 = 216Price per address: 1.5N /216 = 0.75N/215 So /16 address block will be cheaper in comparison with the price given for /17 block.21.10 Suppose you are an ISP with a / 24 address block. Explain whether you accommodate a request from a customer who needs addresses for 255 computers. (Hint: consider the special addresses.)Answer: For a/24 address block, number of available addresses will be 232-24 = 28 = 256. However, a suffix with all 0s address is reserved for network ID and a suffix with all 1s address is reserved for broadcast address, so number of addresses that can be assigned to computers/hosts will be 256 -2 = 254.21.11 Suppose you are an ISP that owns a / 22 address block. Show the CIDR allocation you would use to allocateaddress blocks to four customers who need addresses for 60 computers each.Answer: The /22 address block can be assigned as follows:ddd.ddd.ddd.00/26ddd.ddd.ddd.01/26ddd.ddd.ddd.10/26ddd.ddd.ddd.11/26Chapter 22- Datagram Forwarding22.1 What are the two basic communication paradigms that designers consider when designing an internet?Answer:* Connection-oriented service * Connectionless service22.2 How does the Internet design accommodate heterogeneous networks that each have their own packet format?Answer: To overcome heterogeneity, the Internet Protocol defines a packet format that is independent of the underlying hardware. The result is a universal, virtual packet that can be transferred across the underlying hardware intact. The Internet packet format is not tied directly to any hardware. The underlying hardware does not understand or recognize an Internet packet.22.5 What is the maximum length of an IP datagram?In the current version of the Internet Protocol (IP version 4), a datagram can contain at most 64 K (65535) octets, including the header.22.7 If a datagram contains one 8-bit data value and no header options, what values will be found in header fields H.LEN and TOTAL LENGTH?Answer: H. LEN indicated header in 32-quantities, since no options, then this value will be 5. The TOTAL LENGTH indicated the number of bytes in a datagram including the header. This means 5x4 bytes + 1 (8-bits) = 21 bytesChapter 23 - Support Protocols And Technologies23.1 When a router uses a forwarding table to look up a next-hop address, the result is an IP address. What must happenbefore the datagram can be sent?Answer: Each router along the path uses the destination IP address in the datagram to select a next-hop address, encapsulates the datagram in a hardware frame, and transmits the frame across one network. A crucial step of the forwarding process requires a translation: forwarding uses IP addresses, and a frame transmitted across a physical network must contain the MAC address of the next hop.23.2 What term is used to describe the mapping between a protocol address and a hardware address?Answer: Translation from a computer’s IP address to an equivalent hardware address is known as address resolution, and an IP address is said to be resolved to the correct MAC address. The TCP/IP protocol being used for this is called Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). Address resolution is local to a network.23.5 How many octets does an ARP message occupy when used with IP and Ethernet addresses?Answer: According to Fig 23.3 an ARP message has 7-lines of each being 32-bit (4 bytes or octets), therefore,number of octets in an ARP can be determined as 7x4 = 28 octets23.10 What types of addresses are used in layers below ARP?Answer:ARP forms a conceptual boundary in the protocol stack; layers above ARP use IP addresses, and layers below ARP use MAC addresses.23.17 What is the chief difference between BOOTP and DHCP?Answer:The main difference is that the BOOTP protocol required manual administration. So before a computer could use BOOTP to obtain an address, a network administrator had to configure a BOOTP server to know the computer’s I P address. Chapter 24 - The Future IP (IPv6)24.3 List the major features of IPv6, and give a short description of each.(See Textbook)24.4 How large is the smallest IPv6 datagram header?Answer: IPv6 datagram header consists of a base header + zero or more extension header. Since, smallest header is being asked, we assume zero extension header and consider IPv6 will have only base header. If we look at IPv6 header format in Fig. 24.3, it shows that 10x4 bytes = 40 bytes.Chapter 26 - TCP: Reliable Transport Service26.2 List the features of TCP.(See Textbook)26.6 When using a sliding window of size N, how many packets can be sent without requiring a single ACK to be received?Answer: If the size of the window is N, then it means a sender can transmit up to N packets without waiting for an ACK, as long as other controls are in place.26.9 What is the chief cause of packet delay and loss in the Internet?Answer: The main cause of packet delay and loss in the Internet is congestion.Chapter 28 - Network Performance (QoS and DiffServ)28.1 List and describe the three primary measures of network performance.(See Textbook)28.2 Give five types of delay along with an explanation of each.(See Textbook)Chapter 30 - Network Security30.1 List the major security problems on the Internet, and give a short description of each.(See Textbook)30.2 Name the technique used in security attacks.(See Textbook)30.8 List and describe the eight basic security techniques.(See Textbook)。
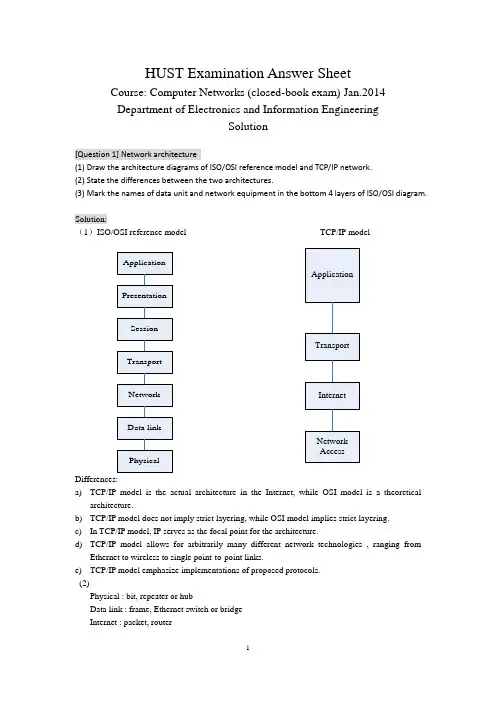
HUST Examination Answer SheetCourse: Computer Networks (closed-book exam) Jan.2014 Department of Electronics and Information EngineeringSolution[Question 1] Network architecture(1) Draw the architecture diagrams of ISO/OSI reference model and TCP/IP network. (2) State the differences between the two architectures.(3) Mark the names of data unit and network equipment in the bottom 4 layers of ISO/OSI diagram.Solution:(1)ISO/OSI reference model TCP/IP modelDifferences:a) TCP/IP model is the actual architecture in the Internet, while OSI model is a theoreticalarchitecture.b) TCP/IP model does not imply strict layering, while OSI model implies strict layering. c) In TCP/IP model, IP serves as the focal point for the architecture.d) TCP/IP model allows for arbitrarily many different network technologies , ranging fromEthernet to wireless to single point-to-point links.e) TCP/IP model emphasize implementations of proposed protocols. (2)Physical : bit, repeater or hubData link : frame, Ethernet switch or bridge Internet : packet, routerTransport : message, gateway[Question 2] Principles of network designSelect ONE of the following principles, tell its main ideas and provide an example. (1) Keep it simple and stupid(2) Complex edge and simple core (3) Smart sender and dumb receiverSolution:(1) KISS: Keep It Simple and StupidIt means that you should make things simple in the designing. One example following it : Ethernet(2) Complex edge and simple coreIt means that the hosts are very complex and have many functions while the nodes are very simple and have few functions.One example following it : The design of router, or the functions of TCP and IP(3) Smart sender and dumb receiverIt means that the function of sender is more complex than that of the receiver, which is help to improve the robustness and performance of communication protocol. One example following it: The flow control of TCP protocol[Question 3] Error detection(1) Tell the main idea of error detection and error correction in communication.(2) Given the CRC polynomial x 4 + x 3 + 1, if the original message is 10110011010, what is the CRC message to send?(3) Suppose the first bit of the message in (2) is inverted due to the noise in transmission. How can the receiver detect it via CRC verification?Solution:(1)1087431()M x x x x x x x =+++++, 43()1C x x x =++. So k=4.a) Multiply M(x) by 2kto get 141211875()T x x x x x x x =+++++,b) Then divide T(x) by C(x) to get the remainder 0000.c) The message that should be transmitted is 101100110100000.(2)The message received is 001100110100000.Divide it by C(x), then the remainder is 1100.So it is not divisible by C(x).So the receiver knows that an error has occurred.(1) What are the essential components to realize reliable transmission?(2) Suppose two computers are communicated via Stop-and-wait protocol. The link bandwidth is 5kbps, and the one-way propagation delay is 20ms. To reach 80% or higher link utilization, what is the minimal frame size for this communication?(3) If it is upgraded to Sliding-Window protocol. To reach the same goal with (2), what is the minimal window size, how many bits are required to describe the frame sequence in window? (Suppose the frame size is 1 or 100Byte)Solution:(1)ACK, and timerActual_throughput = Data / Total_DelayTotal_Delay = RTT + Data / BWLink_Utilization = 100 * Actual_throughput / BWSo: Data/throughput = RTT + Data/BW(BW/throughput - 1) Data = BW*RTTData = BW*RTT/(1/Utilization -1)For the stop-and-wait protocol, for each RTT only one frame is sent,Thus Frame_size = Data = BW*RTT/(1/Utilization - 1) = 5kbps * 40ms / (1/0.8 - 1)= 200 bit / 0.25 = 800 bit = 100 ByteIf the students ignore the data transmission delay, their answer isframe_size = BW*RTT*Utilization = 5000 bit/sec * 40 / 1000 sec * 0.8 = 160 bit = 20 ByteIn this case, at least -2 score.(3)For the sliding-window protocol, in each RTT the data window can be transmitted at most.Thus Window_size = Data = BW*RTT/(1/Utilization - 1) = 5kbps * 40ms / (1/0.8 - 1)= 200 bit / 0.25 = 800 bit = 100 ByteIf the frame size is 100Byte, 1 frames are allowed.To indicate the frames in both sides of sender and receiver, the sequence number should describe 2 frames, thus the [log2(2) ]=1 bitIf the students ignore the data transmission delay, their answer iswindow_size = BW*RTT*Utilization = 5000 bit/sec * 40 / 1000 sec * 0.8 = 160 bit = 20 ByteIf the frame size is 100Byte, 1 frames are allowed.To indicate the frames in both sides of sender and receiver, the sequence number should describe 2 frames, thus the [log2(2) ]=1 bitIn this case, at least -2 score.(1) What is the main idea of CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection) in traditional Ethernet? Can it be deployed for wireless local network, why?(2) Suppose one traditional Ethernet has 1km cable, the signal propagation speed is 2*105km/s, and the transmission rate is designed to be 100Mbps. What is the minimal frame size to support carrier sensing?Solution:(1) the main idea of CSMA/CD include two parts. One is carrier sensing, which means the node should detect the channel before sending any data. If the node finds the channel is idle, it begins to transmit. Otherwise, the node stop for next round. The second issues is collision detection, which means the node should detect the channel in the duration of its data transmission. If the node finds the channel become busy, or in other word, there is a collision, it should stop transmitting immediately.CSMA/CD cannot be deployed in wireless LAN, because the wireless radio transmitter and receiver can not work in dual mode. The wireless node cannot detect collision when it is transmitting data.(2)the minimal frame should be transmitted throughout the whole traditional Ethernet.Thus t = frame_size / transmit_rate = 2 * cable_length / prop_speed.Frame_size = 100 * 106 bits/sec * 2 * 103 m / (2 * 108)m/sec = 1000 bits = 125 Byte[Question 6] Switched network(1) What are the differences between circuit switching and packet switching?(2) For the following linear topology network, each link has 2ms propagation delay and 4 Mbps bandwidth.A B C DIf we use circuit switching, circuit setup requires a 1KB message to make one round-trip on the path, which incurs a 1ms delay at each switch after the message has been completely received. Then we can send the file as one contiguous bit stream. What is the delay for circuit switching to transmit n-byte from A to D?(3) If we use packet switching in the network of (2), we can break the file into 1KB packets, which has 24byte header and 1000byte payload. The switch takes 1ms process delay after receiving the packet, and then sent it continuously. What is the condition for packet switching to have less delay performance than circuit switching?Solution:(1)(2)T pkt = Packet_Size / Bandwidth = 1 KB / 4Mbps = 1024 *8 / (4 * 106) = 2.048 ms T p = 2 ms, T s = 1 ms,T t = n B / 4MbpsIn circuit switching, Total time duration:D = Singling_Delay + Transmission_Delay = 2 * Packet_Duration + Transmission_Delay = 2 * (T pkt * 2 + T p * 3 + T s * 2 + T pkt ) + (T p * 3 + T t ) = T pkt * 6 + T p * 9 + T s * 4 + T tThus, D = 2.048 * 6 + 2 * 9 + 1 * 4 + n * 8 bits / 4Mbps = 34.288 (ms) + 2n (us)(3)Main ideaThe reliability provided by endhost The reliability provided by thenetwork Information in packet Every packet has its dest-addrin header Every packet has its temp VCIlocally Forwarding action inswitch Every packet was treatedindependentlyThe packets are processed inthe manner of VCPackets received indestinationNot in sequenceIn sequenceT pkt = Packet_Size / Bandwidth = 1 KB / 4Mbps = 1024 *8 / (4 * 106) = 2.048 msT p = 2 ms,T s = 1 ms,T t = 1.024 * n B / 4MbpsIn packet switching, Total time duration:D = Delay_at_Switch * Switch_Num + Delay_at_last_hop= (T p + T pkt +T s)*2 + (T p + T t )= T pkt * 2 + T p * 3 + T s * 2 + T tThus, D = 2.048 * 2 + 2 * 3 + 1 * 2 + 1.024 * n B / 4Mbps= 12.096 (ms) + 2.048 n (us)In order to make34.288 (ms) + 2n (us) > 12.096 (ms) + 2.048 n (us)Thus 22.192(ms) > 0.048 n(us)n < 22.192 * 1000 / 0.048 = 462333 Byte = 451.5 KB[Question 7] Ethernet Switch(1) What are the differences between hub and switch in Ethernet?(2) Suppose one server and nine clients are connected via hub in 10Mbps Ethernet, what is the maximal bandwidth for the client-server connection?(3) If the hub is upgraded to switch, can the client-server connection obtain more bandwidth? if can, how much is it?Solution:(1)hub works in Layer2, it works as the shared media and relays the frames to all the nodes connecting to hub. Switch works in Layer2, it forwards the frames to the specific node according to the destination address embedded in the frame header.(2)the max bandwidth in client-server connection is 10Mbps/(1+9)= 1Mbps(3)the max bandwidth in client-server connection is 10Mbps/9 = 1.1111MbpsAdditional 0.1111 Mbps is obtained for each connection.[Question 8] Router(1) Somebody says that, ``the only difference between switch and router is that they do switch function based on the address in different layers.’’ Is it correct? Why?(2) If we obtain the following information from one router. What kind of routing protocol does itSolution:(1)it is not fully correct. The part talking about the forwarding function is correct, while it is not the only difference. Another but not the last difference is that, router has more functions on control plane, which do routing and find the paths for packets.(2)The routing protocol is RIP.The routing table is:Destination Next hop Interface192.168.1.0/24 * Fa 0/4192.168.2.0/24 * Fa 0/6192.168.10.0/24 192.168.1.1 Fa 0/4192.168.30.0/24 192.168.2.2 Fa 0/6[Question 9] Routing algorithm(1) State the main differences between distance vector routing and link state routing.(2) For the network given in the following figure, provide the steps of forward search in Dijkstra algorithm for node A finding the shortest path to node ESolution:(1) The idea of distance vector routing is to tell the neighbors about the learned topology to all the nodes in the network. The idea of link state routing is to tell all the nodes in network about the neighborhood topology.Step 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9Confirmed (A,0,-) (A,0,-) (A,0,-)(D,2,D)(A,0,-)(D,2,D)(A,0,-)(D,2,D)(B,4,D)(A,0,-)(D,2,D)(B,4,D)(A,0,-)(D,2,D)(B,4,D)(E,6,D)(A,0,-)(D,2,D)(B,4,D)(E,6,D)(A,0,-)(D,2,D)(B,4,D)(E,6,D)(C,7,D)Tentative (B,5,B)(D,2,D)(B,5,B) (B,4,D)(E,7,D)(E,7,D)(E,6,D)(C,8,D)(C,8,D) (C,7,D)A→E A→D→EA→D→B→EA→D→B→E[Question 10] IP address allocationA company has one C class IP address of 200.1.1.*. It has four departments.(1) If each department has less than 25 computers. Provide a kind of IP address allocation. Give the network address, subnet mask, and the available IP address range for each department. (2) If the four departments have 72, 35, 34, 20 computers respectively. Provide the IP address allocation scheme again.Solution:(1)Since each department has less than 25 computers, even considering the additional two more IP address for gateway and broadcast, the 64-computer subnet is enough for them.One IP address allocation scheme is to even divide the 256 IP addresses into 4 subnets, each subnet allows 64 hosts.Another IP address allocation scheme is to even divide the 256 IP addresses into 4 subnets, each subnet allows 32 hosts.(2) Since one of the department has more requirements than 64, then the even distribution scheme[Question 11] TCP protocol(1) Somebody says that, ``because of the reliable transmission service in layer 2, there is no need to provide such service again within TCP protocol in layer 4’’. Is it correct? Why?(2) State the main rules of TCP connection setup according to the following figure. Explain every word and number in the figure.Solution:(1) It is wrong. TCP is based on the un-reliable IP layer, which only provides best effort service. If TCP wants to provide reliable transmission service, it has to realize this by itself.(2)TCP use three hand-shakes to setup the connection.According to the figure, there are two nodes. The sender is with IP address of 192.168.1.163 and the receiver 192.168.1.165 respectively.●At first, the sender send a request ``SYN’’to the receiver to setup the connection. Thismessage is with the sequence number of 424CF1DC;●Secondly, the receiver reply an acknowledgment message ``SYN/ACK’’ to the sender. Thismessage has two sequence numbers. The seq in the ACK is 424CF1DD, which is to confirm the last ``SYN’’ from sender. The seq in the SYN is 30318555, which is a new message from the receiver.●Thirdly, the sender reply an acknowledgment message ``ACK’’ to the receiver. The seq in theACK is 30318556, which is to confirm the last ``SYN’’ from receiver.In the end, both the sender and receiver knows that the other side is ready for this TCP connection.[Question 12] TCP congestion control(1) Both flow control and congestion control in TCP are realized by window based packet control. How can TCP get the window sizes in these two mechanisms?(2) Assume that TCP implements an extension that allows window sizes much larger than 64 KB. Suppose that you are using this extended TCP over a 1Gbps link with a latency of 150ms. TCP packet size is 1KB, and the max receive window is 1 MB. Suppose there is no real congestion and packet loss in transmission. How many RTTs does it take until slow start opens the send window to 1 MB? How long does it take to send the complete file? ( Suppose file size is 10MB )Solution:(1) In flow control, TCP sender knows the window size by the field of advertise-window replied from the receiver. In congestion control, TCP sender learns the window size adaptively by AIMD( Additive Increase and Multiplicative Decrease) mechanism responding to the packet lossevent.(2)When TCP realizes congestion control mechanism, its effective send window size will be min (CongestionWindow, AdvertizedWindow). In original design of TCP header, the field of AdvertizedWindow is 16 bit, which is 216=26*210=64 KB. So the maximum effective window of original TCP sender is 64KB. The assumption of the first sentence in this question relaxes such constraint for TCP.In slow start, the send window starts from w0=1 packet, which is 1 KB. For each RTT after a successful transmission, the window size will be doubled. After i RTT, it will be 2i * w0. Let 2i * 1KB = 1MB, soi = log2(1MB/1KB) = log2(210) = 10.It will take 10 RTTs to reach 1MB send window.Case 1: if the receiver window remains as 1MBIn the first 10 RTTs, total (1 + 2 + 4 + … + 210) * 1KB has been transmitted.Which is (211 - 1) * 1KB = 2 MB - 1 KB, the rest file is 10MB - (2MB - 1KB) = 8MB + 1KBIn the reset transmission, each RTT can only support 1MB transmission.Thus, additional 9 RTTs are required. Total 19 RTT = 19 * 150ms = 2.85 sCase 2: if the receiver window can be changed.Since there is no congestion and loss, the maximum send window will be the bandwidth * delay for this TCP connection.w max= 1G bps * 150ms = 109 * 150 * 10-3= 150 *106 bit = 18.75 * 106 byte = 17.88 MB.So, this 10 MB file can be transferred before reaching w max. In another word, it can be sent in its slow start phase. Assume x RTT is required to send this file, then:(1 + 2 + 4 + … + 2x) * 1KB ≥ 10 MB2 * 2x–1 ≥ 10 * 1024x ≥ log2(10241) – 1 = 12.3Thus x = 13, it will take 13 RTTs to transfer this file. 13RTT = = sTotal delay = 13RTT + Filesize/BW = 13 * 150ms+ 10MB / 1Gbps =1.95 + 0.08 * 1.024^2=2.03 s11。

计算机⽹络英⽂复习题、英译汉(10分)1.TCP(Transmission Control Protocol) 传输控制协议2.IP(Internet Protocol) 互联⽹协议3.RFC(Requests for comments) 请求评议4.SMTP(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) 简单邮件传输协议5.Congestion-control 拥塞控制6.Flow control 流控制7.UDP (User Datagram Protocol) ⽤户数据报协议8.FTP(File Transfer Protocol) ⽂件传输协议9.HTTP( Hyper-Text Transfer Protocol ) 超⽂本传输协议10.TDM 时分复⽤11.FDM 频分复⽤12.ISP(Internet Service Provider) 互联⽹服务提供商13.DSL(Digital Subscriber Line) 数字⽤户线路14.DNS(Domain Name System) 域名系统15.ARQ(Automatic Repeat Request) ⾃动重发请求16.ICMP(Internet Control Message Protocol) ⽹间控制报⽂协议17.AS(Autonomous Systems) ⾃制系统18.RIP(Routing Information Protocol)\ 路由信息协议19.OSPF(Open Shortest Path First) 开放最短路径优先20.BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) 边界⽹关协议21.HFC 光纤同轴电缆混合⽹22.CRC(Cyclic Redundancy Check) 循环冗余检验23.CSMA/CD 带冲突检测的载波侦听多路存取24.ARP 地址解析协议25.RARP 反向地址解析协议26.DHCP 动态主机配置协议27.RTT 循环时间28.IETF(P5)互联⽹⼯程任务组29.URL(P88)统⼀资源定位30.API应⽤程序编程接⼝31.MIME多⽤途互联⽹邮件扩展1. DSL divides the communication link between the home and the ISP into three nonoverlapping frequency bands, a upstream channel is in _A_________.A)50 kHz to 1MHz band B) 1MHz to 2MHz bandC)4 kHz to 50kHz band D) 0 to 4kHz band2. As a data packet moves from the upper to the lower layers, headers are A .A) Added; B) subtracted; C) rearranged; D) modified3. What is the main function of the network layer? DA) node-to-node delivery; B) process-to-process message deliveryC) synchronization; D) updating and maintenance of routingtables4. Which of the following is the default mask for the address 168.0.46.201? BA) 255.0.0.0; B) 255.255.0.0; C) 255.255.255.0; D) 255.255.255.2555.A router reads theaddress on a packet to determine the next hop. AA) IP ; B) MAC; C) source; D)ARP6 .Which device can’t isolates the departme ntal collision domains. AA) Hub; B) switch; C) router; D) A and B7. Input port of a router don’t perform ____D____ functions.A) the physical layer functions B) the data link layer functionsC) lookup and forwarding function D) network management8. HTTP has a mechanism that allows a cache to verify that its objects are up to date. The mechanism is DA) persistent connections B) cookies C) Web Caching D) conditional GET9. A protocol layer can be implemented in ___D_____.A) software B) hardware C) a combination of the software and hardware D) All of the above10. A protocol has three important factors, they are_A______.A)syntax, semantics, order B) syntax, semantics, layerC)syntax, semantics, packet D) syntax , layer, packet11. There are two broad classes of packet-switched networks: datagram networks and virtual-circuit networks. The virtual-circuit networks forward packets in their switches use ___D___.A) MAC addresses B) IP addressesC) e-mail addresses D) virtual-circuit numbers12. TCP service model doesn’t provide ___D_______service.A) reliable transport service B) flow control serviceC) congestion-control service D) guarantee a minimum transmission rate service.13. Usually elastic applications don’t include____B______.A) Electronic mail B) Internet telephony14. A user who uses a user agent on his local PC receives his mail sited in a mail server by using _B___ protocol.A)SMTP B) POP3C)SNMP D) FTP15. Considering sliding-window protocol, if the size of the transmitted window is N and the size of the receiving window is 1,the protocol is BA) stop-and-wait protocol B) Go-Back-N protocolC) selective Repeat protocol D) alternating-bit protocol16. which IP address is effective___B______.A) 202,131,45,61 B) 126.0.0.1C) 192.268.0.2 D) 290.25.135.1217. if IP address is 202.130.191.33, subnet mask is 255.255.255.0,then subnet prefix is__D_____A) 202.130.0.0 B) 202.0.0.0C) 202.130.191.33 D)202.130.191.018.The command Ping s implemented with __B______messagesA) DNS B) ICMPC) IGMP D) RIP19. Which layer-function is mostly implemented in an adapter? __A________A) physical layer and link layer B) network layer and transport layerC)physical layer and network layer D) transport layer and application layer20. If a user brings his computer from Chengdu to Peking, and accesses Internet again. Now, __B_____ of his computer needs to be changed.A) MAC address B) IP addressC) e-mail address D) user address1. .traceroute is implemented with __B____messages.A) DNS B) ICMPC) ARP D) RIP2.A router reads the A address on a packet to determine the next hop.A. IP ;B. MAC;C. source;D.ARP3. There are two broad classes of packet-switched networks: datagram networks andvirtual-circuit networks. The virtual-circuit networks forward packets in their switches use ___D___.A) MAC addresses B) IP addressesC) e-mail addresses D) virtual-circuit numbersA) device interfaces with same subnet part of IP addressB) can’t physically reach each other without intervening a router.C)all of the devices on a given subnet having the same subnet address.D)A portion of an interface’s IP address must be determined by the subnet to which it is connected.5. if IP address is 102.100.100.32, subnet mask is 255.255.240.0,then subnet prefix is___A___A) 102.100.96.0 B) 102.100.0.0C) 102.100.48.0 D) 102.100.112.06 If a user brings his computer from chengdu to beijing, and accesses Internet again. Now,___B__ of his computer needs to be changed.A) MAC address B) IP addressC) e-mail address D) user address7.I nput port of a router don’t perform ____D___ functions.A) the physical layer functions B) the data link layer functionsC) lookup and forwarding function D) network management8.switching fabric is at the heart of a router, switching can be accomplished in a number of ways, donit include_D_A)Switching via memory B)Switching via crossbarC)Switching via a bus D) Switching via buffer9.if a host wants to emit a datagram to all hosts on the same subnet, then the datagram’s destination IP address is ___B__A)255.255.255.0 B) 255.255.255.255C)255.255.255.254 D) 127.0.0.110.The advantage of Circuit switching does not include________.A) small transmission delay B)small Processing costC) high link utilization D)no limited to format of message1.an ARP query sent to __A__A) local network B) all over the Internet.2. .packet-switching technologies that use virtual circuitsinclude__B___:A) X.25, ATM, IP B) X.25, ATM, frame relay.C) IPX, IP, ATM D) IPX, IP, TCP3. In Internet, _D_ protocol is used to report error and provide the information forun-normal cases.A) IP B) TCP C)UDP D) ICMP1.A is a Circuit-switched network.B. Datagram networkC. InternetD. virtual circuit network2.The store-and-forward delay is DA. processing delayB. queuing delayC. propagation delayD. transmission delay3.Which is not the function of connection-oriented service? DA. flow controlB. congestion controlC. error correctionD. reliabledata transfer4.The IP protocol lies in CA. application layerB. transport layerC. network layerD. link layer5.Which of the following is the PDU for application layer __B___A.datagram;B. message;C. frame;D.segment6.bandwidth is described in _B__A) Bytes per second B) Bits per secondC) megabits per millisecond D) centimeters7.A user who uses a user agent on his local PC receives his mail sited in a mail server by using __A__ protocol.A)SMTP B) POP3C)SNMP D) FTP8.As a data packet moves from the lower to the upper layers, headers are B.A)Added; B. subtracted; C. rearranged; D. modified三、填空题(每空1分,共22分 (注意:所有填空题不能写中⽂,否则中⽂答案对的情况1. link-layer address is variously called a LAN address, a MAC address, or a physical address.2 In the layered architecture of computer networking, n layer is the user of n-1 layer and the service provider of n+1 layer.A) n B) n+3 C) n+1 D) n-1四、判断题(每⼩题1分,共10分)1.√The services of TCP’s reliable data transfer founded on the services of theunreliable data transfer.2.√Any protocol that performs handshaking between the communication entitiesbefore transferring data is a connection-oriented service.3.× HOL blocking occur in output ports of router.4.√Socket is globally unique.5.√SMTP require multimedia data to be ASCII encoded before transfer.6.×The transmission delay is a function of the distance between the two routers.7.×IP address is associated with the host or router. SO one device only have one IPaddress.8. √In packet-switched networks, a session’s messages use the resources on demand, and Internet makes its best effort to deliver packets in a timely manner.9. ×UDP is a kind of unreliable transmission layer protocol, so there is not any checksum field in UDP datagram header.10.√Forwarding table is configured by both Intra and Inter-AS routing algorithmIP is a kind of reliable transmission protocol. F8.Forwarding table is configured by both Intra and Inter-AS routing algorithm.T9.Distance vector routing protocol use lsa to advertise the network which router10.RIP and OSPF are Intra-AS routing protocols T11.Packet switching is suitable for real-time services, and offers better sharing ofbandwidth than circuit switching F五、计算题(28 points)1.C onsider the following network. With the indicated link costs, use Dijkstra’s shortest-path algorithm to compute the shortest path from X to all network nodes.2 Given: an organization has been assigned the network number 198.1.1.0/24 and it needs todefine six subnets. The largest subnet is required to support 25 hosts. Please:●Defining the subnet mask; (2分) 27bits or 255.255.255.224●Defining each of the subnet numbers; which are starting from 0# (4分)198.1.1.0/27 198.1.1.32/27 198.1.1.64/27 198.1.1.96/27 198.1.1.128/27 198.1.1.160/27 198.1.1.192/27 198.1.1.224/27●Defining the subnet 2#’s broadcast address.(2分) 198.1.1.95/27Defining host addresses scope for subnet 2#. (2分) 198.1.1.65/27--198.1.1.94/273. Consider sending a 3,000-byte datagram into a link that has an MTU of 1500bytes.Suppose the original datagram is stamped with the identification number 422 .Assuming a 20-byte IP header,How many fragments are generated? What are their characteristics?(10分)。

Chapter 1 Computer Networks and the Internet1.The ( ) is a worldwide computernetwork, that is, a network that interconnectsmillionsofcomputing devices throughout theworld. ppt3 A public InternetB IntranetC switch netD television net2.Which kind of media is not a guidedmedia ( )A twisted-pair copper wireB a coaxial cableC fiber opticsD digital satellite channel3.Which kind of media is a guided media ( )A geostationary satelliteB low-altitude satelliteC fiber opticsD wireless LAN4.The units of data exchanged by a link-layer protocol are called ( ).A FramesB SegmentsC DatagramsD bit streams5.Which of the following optionbelongs to the circuit-switchednetworks ( )A FDMB TDMC VCnetworksD both A and B 6.( )makes sure that neither sideof a connection overwhelms theother side by sending too manypackets too fast.A Reliable data transferB Flow controlC Congestion controlD Handshaking procedure7.( ) means that the switch mustreceive the entire packet before it can begin to transmit the first bit of the packet onto the outbound link.A Store-and-forward transmissionB FDMC End-to-end connectionD TDM8.Datagramnetworksandvirtual-circuit networks differ in that ( ).A datagram networks are circuit-switched networks, and virtual-circuit networks are packet-switched networks.B datagram networks are packet-switched networks, and virtual-circuit networks are circuit-switched networks.C datagram networks use destination addresses and virtual-circuit networks use VC. numbers to forward packets toward their destination.D datagram networks use VC. numbers and virtual-circuit networks use destination addresses to forward packetstoward their destination.9.In the following options, which one is not a guided media ( )A twisted-pairwireB fiber opticsC coaxial cableD satellite10.Processing delay does not include the time to ( ).A examine the packet ’s headerB wait to transmit the packet onto the linkC determine where to direct thepacketD check bit-error in the packet 11.In the following four descriptions, which one is correct ( )A The traffic intensity must begreater than 1.B The fraction of lost packetsincreases as the trafficintensity decreases.C If the traffic intensity isclose to zero, the averagequeuing delay will be close tozero.D If the traffic intensity isclose to one, the averagequeuing delay will be close toone.12.The Internet’s network layer is responsible for movingnetwork-layer packets known as( ) from one host to another.A frameB datagramC segmentD message13.The protocols of various layersare called ( ).A the protocol stackB TCP/IPC ISPD network protocol14.There are two classes ofpacket-switched networks: ( )networks and virtual-circuitnetworks.A datagramB circuit-switchedC televisionD telephone15.Access networks can be looselyclassified into threecategories: residential access,company access and ( ) access.A cabledB wirelessC campusD city areaQuestion 16~17Suppose, a is the average rate at which packets arrive at the queue,R is the transmission rate, and all packets consist of L bits, then thetraffic intensity is ( 16 ), and it should no greater than ( 17 ).16. A LR /aB La /RC Ra /LD LR /a 17.A 2B 1C 0D -118.In the Internet, the equivalentconcept to end systems is ( ).A hostsB serversC clientsD routers19.In the Internet, end systems are connected together by ( ).A copper wireB coaxial cableC communication linksD fiber optics 20.End systems access to the Internet through its ( ). A modemsB protocolsC ISPD sockets21.End systems, packet switches,and other pieces of the Internet, run ( ) that control thesending and receiving ofinformation within theInternet.A programsB processesC applicationsD protocols22.There are many private networks,such as many corporate andgovernment networks, whosehosts cannot exchange messages with hosts outside of the private network. These private networks are often referred to as ( ).A internetsB LANC intranetsD WAN23.The internet allows ( ) runningon its end systems to exchangedata with each other.A clients applicationsB server applicationsC P2P applicationsD distributed applications24.The Internet provides two services to its distributed applications: a connectionlessunreliable service and ()service.A flowcontrolB connection-oriented reliableC congestion controlD TCP25.It defines the format and theorder of messages exchangedbetween two or morecommunicating entities, as wellas the actions taken on thetransmission and/or receipt ofa message or other event. Thesentence describes ( ).A InternetB protocolC intranetD network26.In the following options, which does not define in protocol ( )A the format of messagesexchanged between two or morecommunicating entitiesB the order of messagesexchanged between two or morecommunicating entitiesC the actions taken on thetransmission of a message orother eventD the transmission signals aredigital signals or analogsignals27.In the following options, which is defined in protocol ( )A the actions taken on thetransmission and/or receiptof a message or other event B the objects exchanged between communicating entities C the content in the exchangedmessagesD the location of the hosts28.In the following options, whichdoes not belong to the network edge( )A end systemsB routersC clientsD servers29.In the following options, whichbelongs to the network core ( )A end systemsB routersC clientsD servers30.In the following options, whichis not the bundled with theInternet’sconnection-oriented service( )A reliable data transferB guarantee of thetransmission timeC flow controlD congestion-control31.An application can rely on theconnection to deliver all of itsdata without error and in theproper order. The sentencedescribes ( ). A flow controlB congestion-controlC reliable datatransferD connection-oriented service 32.It makes sure that neither sideof a connection overwhelms theother side by sending too manypackets too fast. The sentence describes ( ). A flow controlB congestion-controlC connection-oriented serviceD reliable data transfer33.It helps prevent the Internetfrom entering a state of gridlock. When a packet switchbecomes congested, its bufferscan overflow and packet loss canoccur. The sentence describes( ).A flowcontrolB congestion-controlC connection-oriented serviceD reliable data transfer 34.TheInternet ’sconnection-oriented service has aname, it is ( ).A TCPB UDPC TCP/IPD IP35.In the following options, which service does not be provided to an application by TCP( )A reliable transportB flow controlC video conferencingD congestion control36.The Internet ’s connectionless service is called ( ).A TCPB UDPC TCP/IPD IP37.In the following options, which does not use TCP( )A SMTPB internet telephoneC FTPD HTTP38.In the following options, which does not use UDP( )A InternetphoneB video conferencingC streamingmultimediaD telnet39.There are two fundamentalapproaches to building a network core, ( ) and packet switching.A electrical current switchingB circuit switchingC data switchingD message switching40.In ( ) networks, the resourcesneeded along a path to provide for communication between the end system are reserved for theduration of the communicationsession.A packet-switchedB data-switchedC circuit-switchedD message-switched41.In ( ) networks, the resources are not reserved; a session’smessages use the resources ondemand, and as a consequence,may have to wait for access tocommunication link.A packet-switchedB data-switchedC circuit-switchedD message-switched42.In a circuit-switched network, if each link has n circuits, foreach link used by the end-to-endconnection, the connection gets( ) of the link’s bandwidthfor the duration of the connection.A a fraction 1/nB allC 1/2D n times43.For ( ), the transmission rateof a circuit is equal to theframe rate multiplied by thenumber of bits in a slot.A CDMAB packet-switched networkC TDMD FDM44.( ) means that the switch mustreceive the entire packetbefore it can begin to transmitthe first bit of the packet ontothe outbound link.A Queuing delayB Store-and-forwardtransmissionC Packet lossD Propagation45.The network that forwardspackets according to host destination addresses is called( ) network.A circuit-switchedB packet-switchedC virtual-circuitD datagram46.The network that forwardspackets according tovirtual-circuit numbers iscalled ( ) network.A circuit-switchedB packet-switchedC virtual-circuitD datagram47.In the following entries, whichis not a kind of access network( )A residentialaccessB company accessC wirelessaccessD local access48.Suppose there is exactly onepacket switch between a sendinghost and a receiving host. The transmission rates between thesending host and the switch and between the switch and the receiving host are R 1 and R 2,respectively. Assuming that theswitch uses store-and-forwardpacket switching, what is thetotal end-to-end delay to senda packet of length L (Ignorequeuing delay, propagationdelay, and processing delay.) ( ) A L /R 1+L /R 2B L /R 1C L /R 2D none of the above49.The time required to examine thepacket ’s header and determinewhere to direct the packet ispart of the ( ). A queuing delayB processing delayC propagation delayD transmission delay50.The time required to propagatefrom the beginning of the linkto the next router is ( ). A queuing delayB processing delayC propagation delayD transmission delay51.Consider sending a packet of3000bits over a path of 5 links. Eachlink transmits at 1000bps. Queuingdelays, propagation delay and processing delay are negligible. (6 points)(1).Suppose the network is apacket-switched virtual circuitnetwork. VC setup time is seconds.Suppose the sending layers add atotal of 500 bits of header to eachpacket. How long does it take to sendthe file from source to destination(2).Suppose the network is a packet-switched datagram networkand a connectionless service is used.Now suppose each packet has 200 bitsof header. How long does it take tosend the file(3).Suppose that the network is acircuit-switched network. Furthersuppose that the transmission rate of the circuit between source anddestination is 200bps. Assumingsetup time and 200 bits of header appended to the packet, how longdoes it take to send the packetS olution:(1).t=5*(3000+500)/1000+=( 2).t=5*(3000+200)/1000=16s( 3).t=(3000+200)/200+=。

家庭的外貌英语作文My Family's Appearance。
My family is a typical Chinese family with five members. My parents are both in their 50s, and they have three children. I am the youngest one, and my two elder sisters are both married and have their own families.My father is a tall and strong man with a round faceand a pair of big eyes. He has a full head of black hair, which is a little bit curly. He always wears a pair of glasses, which makes him look more intellectual. He likesto wear casual clothes, such as T-shirts and jeans, which are comfortable and easy to move in.My mother is a kind and gentle lady with a slim figure and a beautiful face. She has long black hair, which she always wears in a bun. She has a pair of big eyes, whichare always full of love and warmth. She likes to wear dresses and skirts, which make her look elegant andfeminine.My eldest sister is a tall and slim woman with a cheerful personality. She has a long face and a pair of bright eyes. She has short hair, which she likes to stylein different ways. She likes to wear fashionable clothes, such as high heels and tight dresses, which make her look sexy and confident.My second sister is a short and plump woman with a sweet smile. She has a round face and a pair of cute dimples. She has long hair, which she always wears in a ponytail. She likes to wear casual clothes, such as T-shirts and shorts, which are comfortable and easy to wear.As for me, I am a medium-sized girl with a lively personality. I have a round face and a pair of big eyes. I have long hair, which I like to wear in different styles. I like to wear comfortable clothes, such as T-shirts and jeans, which are easy to move in.In conclusion, my family members have differentappearances, but we all love each other and get along well. We are a happy and harmonious family.。

《计算机网络英语》期末复习试题及答案一选择题1.A ( ) protocol is used to move a datagram over an individual link.A application-layerB transport-layerC network-layerD link-layer2.The units of data exchanged by a link-layer protocol are called ( ).A datagramsB framesC segmentsD messages3.Which of the following protocols is not a link-layer protocol? ( )A EthernetB PPPC HDLCD IP4.In the following four descriptions, which one is not correct? ( )A link-layer protocol has the node-to-node job of moving network-layer datagrams over a single link in the path.B The services provided by the link-layer protocols may be different.C A datagram must be handled by the same link-layer protocols on the different links in the path.D The actions taken by a link-layer protocol when sending and receiving frames include error detection, flow control and random access.5.Which of the following services can not offered by a link-layer protocol? ( )A congestion controlB Link AccessC Error controlD Framing6.( ) protocol serves to coordinate the frame transmissions of the many nodes when multiple nodes share a single broadcast link.A ARPB MACC ICMPD DNS7.In the following four descriptions about the adapter, which one is not correct? ( )A The adapter is also called as NIC.B The adapter is a semi-autonomous unit.C The main components of an adapter are bus interface and the link interface.D The adapter can provide all the link-layer services.8.Consider CRC error checking approach, the four bit generator G is 1011, and suppose that the data D is 10101010, then the value of R is( ).A 010B 100C 011D 1109.In the following four descriptions about random access protocol, which one is not correct? ( )A In slotted ALOHA, nodes can transmit at random time.B In pure ALOHA, if a frame experiences a collision, the node will immediately retransmit it with probability p.C The maximum efficiency of a slotted ALOHA is higher than a pure ALOHA.D In CSMA/CD, one node listens to the channel before transmitting.10.In the following descriptions about MAC address, which one is not correct? ( )A The MAC address is the address of one node’s adapter.B No two adapters have the same MAC address.C The MAC address doesn’t change no matter where the adapter goes.D MAC address has a hierarchical structure.11.The ARP protocol can translate ( ) into ( ). ( )A host name, IP addressB host name, MAC addressC IP address, MAC addressD broadcast address, IP address12.The value of Preamble field in Ethernet frame structure is ( )A 10101010 10101010……10101010 11111111B 10101011 10101011……10101011 10101011C 10101010 10101010……10101010 10101011D 10101010 10101010……10101010 1010101013.There are four steps in DHCP, the DHCP server can complete ( ).A DHCP server discoveryB DHCP server offersC DHCP requestD DHCP response14.In CSMA/CD, the adapter waits some time and then returns to sensing the channel. In the following four times, which one is impossible? ( )A 0 bit timesB 512 bit timesC 1024 bit timesD 1028 bit times15.The most common Ethernet technologies are 10BaseT and 100BaseT. “10” and “100”indicate( ).A the maximum length between two adaptersB the minimum length between two adaptersC the transmission rate of the channelD the transmission rate of the node16.The principal components of PPP include but not( ).A framingB physical-control protocolC link-layer protocolD network-layer protocol17.In the following four options, which service can not be provided by switch? ( )A filteringB self-learningC forwardingD optimal routing18.In the following four services, which one was be required in PPP? ( )A packet framingB error detectionC error correctionD multiple types of link19.The ability to determine the interfaces to which a frame should be directed, and then directing the frame to those interfaces is( ).A filteringB forwardingC self-learningD optimal routing20.In ( ) transmission(s), the nodes at both ends of a link may transmit packets at the same time.A full-duplexB half-duplexC single-duplexD both full-duplex and half-duplex21.Consider the data D is 01110010001, if use even parity checking approach, the parity bit is( ①), if use odd parity checking approach, the parity bit is( ②). ( )A ①0 ②1B ①0 ②0C ①1 ②1D ①1 ②022.In the following four descriptions about parity checks, which one is correct? ( )A Single-bit parity can detect all errors.B Single-bit parity can correct one errors.C Two-dimensional parity not only can detect a single bit error, but also can correct that error.D Two-dimensional parity not only can detect any combination of two errors, but also can correct them.23.MAC address is ( ) bits long.A 32B 48C 128D 6424.Wireless LAN using protocol ( ).A IEEE 802.3B IEEE 802.4C IEEE 802.5D IEEE 802.1125.The following protocols are belonging to multiple access protocols except for ( ).A channel partitioning protocolsB routing protocolsC random access protocolsD taking-turns protocols26.Which of the following is not belonging to channel partitioning protocols? ( )A CSMAB FDMC CDMAD TDM27.In the following four descriptions about CSMA/CD, which one is not correct? ( )A A node listens to the channel before transmitting.B If someone else begins talking at the same time, stop talking.C A transmitting node listens to the channel while it is transmitting.D With CSMA/CD, the collisions can be avoided completely.28.( ) provides a mechanism for nodes to translate IP addresses to link-layer address.A IPB ARPC RARPD DNS29.A MAC address is a ( )address.A physical-layerB application-layerC link-layerD network-layer30.Which of the following is correct? ( )A No two adapters have the same MAC address.B MAC broadcast address is FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF.C A portable computer with an Ethernet card always has the same MAC address, no matter where the computer goes.D All of the above31.In the following four descriptions, which one is not correct? ( )A ARP resolves an IP address to a MAC address.B DNS resolves hostnames to IP addresses.C DNS resolves hostnames for hosts anywhere in the Internet.D ARP resolves IP addresses for nodes anywhere in the Internet.32.In the LAN, ( )protocol dynamically assign IP addresses to hosts.A DNSB ARPC DHCPD IP33.DHCP protocol is a four-step process: ①DHCP request. ②DHCP ACK. ③DHCP server discovery. ④DHCP server offer(s). The correct sequence is ( )A ①②③④B ③②①④C ③④①②D ①④③②34.In the Ethernet frame structure, the CRC field is ( )bytes.A 2B 4C 8D 3235.In the Ethernet frame structure, the Data field carries the ( ).A IP datagramB segmentC frameD message36.In the following four descriptions, which one is not correct? ( )A Ethernet uses baseband transmission.B All of the Ethernet technologies provide connection-oriented reliable service to the network layer.C The Ethernet 10Base2 technology uses a thin coaxial cable for the bus.D The Ethernet 10BaseT technology uses a star topology.37.Ethernet’s multiple access protocol is ( ).A CDMAB CSMA/CDC slotted ALOHAD token-passing protocol38.In the following four descriptions about CSMA/CD, which one is not correct? ( )A An adapter may begin to transmit at any time.B An adapter never transmits a frame when it senses that some other adapter is transmitting.C A transmitting adapter aborts its transmission as soon as it detects that another adapter is also transmitting.D An adapter retransmits when it detects a collision.39.Which of the following descriptions about CSMA/CD is correct? ( )A No slots are used.B It uses carrier sensing.C It uses collision detection.D All of the above.40.The Ethernet 10BaseT technology uses( )as its physical media.A fiber opticsB twisted-pair copper wireC coaxial cableD satellite radio channel41.For 10BaseT, the maximum length of the connection between an adapter and the hub is ( )meters.A 100B 200C 500D 1042.A ( )is a physical-layer device that acts on individual bits rather than on frames.A switchB hubC routerD gateway43.A hub is a ( )device that acts on individual bits rather than on frames.A physical-layerB link-layerC network-layerD ransport-layer44.A switch is a( )device that acts on frame.A physical-layerB link-layerC network-layerD transport-layer45.In the following four descriptions, which one is not correct? ( )A Switches can interconnect different LAN technologies.B Hubs can interconnect different LAN technologies.C There is no limit to how large a LAN can be when switches are used to interconnect LAN segments.D There is restriction on the maximum allowable number of nodes in a collision domain when hubs are used to interconnect LAN segments.46.The ability to determine whether a frame should be forwarded to some interface or should just be dropped is ( ).A filteringB forwardingC self-learningD optimal routing47.Which of the following devices is not a plug and play device? ( )A hubB routerC switchD repeater48.Which of the following devices is not cut-through device? ( )A hubB routerC switchD repeater49.In the following four descriptions, which one is not correct? ( )A Switches do not offer any protection against broadcast storms.B Routers provide firewall protection against layer-2 broadcast storms.C Both switches and routers are plug and play devices.D A router is a layer-3 packet switch, a switch is a layer-2 packet switch.50.Which device has the same collision domain? ( )A HubB SwitchC RouterD Bridge51.IEEE802.2 protocol belong to ( )layerA networkB MACC LLCD physical52.IEEE802.11 protocol defines ( )rules.A Ethernet BusB wireless WANC wireless LAND Token Bus53.In data link-layer, which protocol is used to share bandwidth? ( )A SMTPB ICMPC ARPD CSMA/CD54.When two or more nodes on the LAN segments transmit at the same time, there will be a collision and all of the transmitting nodes well enter exponential back-off, that is all of the LAN segments belong to the same( ).A collision domainB switchC bridgeD hub55.( )allows different nodes to transmit simultaneously and yet have their respective receivers correctly receive a sender’s encoded data bits.A CDMAB CSMAC CSMA/CDD CSMA/CA56.Because there are both network-layer addresses (for example, Internet IP addresses) and link-layer addresses (that is, LAN addresses), there is a need to translate between them. Forthe Internet, this is the job of ( ).A RIPB OSPFC ARPD IP57.PPP defines a special control escape byte, ( ). If the flag sequence, 01111110 appears anywhere in the frame, except in the flag field, PPP precedes that instance of the flag pattern with the control escape byte.A 01111110B 01111101C 10011001D 1011111058.The device ( ) can isolate collision domains for each of the LAN segment.A modemB switchC hubD NIC59.In the following four descriptions about PPP, which one is not correct? ( )A PPP is required to detect and correct errors.B PPP is not required to deliver frames to the link receiver in the same order in which they were sent by the link sender.C PPP need only operate over links that have a single sender and a single receiver.D PPP is not required to provide flow control.60.In the PPP data frame, the( ) field tells the PPP receivers the upper-layer protocol to which the received encapsulated data belongs.A flagB controlC protocolD checksum61.PPP’s link-control protocols (LCP) accomplish ( ).A initializing the PPP linkB maintaining the PPP linkC taking down the PPP linkD all of the above62.The PPP link always begins in the ( ) state and ends in the ( ) state. ( )A open, terminatingB open, deadC dead, deadD dead, terminating63.For( ) links that have a single sender at one end of the link and a single receiver at the other end of the link.A point-to-pointB broadcastC multicastD all of the above64.With ( )transmission, the nodes at both ends of a link may transmit packets at the same time.A half-duplexB full-duplexC simplex(单工)D synchronous65.With ( ) transmission, a node can not both transmit and receive at the same time.A half-duplexB full-duplexC simplex(单工)D synchronous66.Which of the following functions can’t be implemented in the NIC? ( )A encapsulation and decapsulationB error detectionC multiple access protocolD routing67.Which of the following four descriptions is wrong? ( )A The bus interface of an adapter is responsible for communication with the adapter’s parent node.B The link interface of an adapter is responsible for implementing the link-layer protocol.C The bus interface may provide error detection, random access functions.D The main components of an adapter are the bus interface and the link interface. 68.For odd parity schemes, which of the following is correct? ( )A 011010001B 111000110C 110101110D 00011011069.( )divides time into time frames and further divides each time frame into N time slots.A FDMB TMDC CDMAD CSMA70.With CDMA, each node is assigned a different ( )A codeB time slotC frequencyD link71.Which of the following four descriptions about random access protocol is not correct? ( )A A transmission node transmits at the full rate of the channelB When a collision happens, each node involved in the collision retransmits at once.C Both slotted ALOHA and CSMA/CD are random access protocols.D With random access protocol, there may be empty slots.72.PPP defines a special control escape byte 01111101. If the data is b1b201111110b3b4b5, the value is( )after byte stuffing.A b1b20111110101111110b3b4b5B b1b20111111001111101b3b4b5C b5b4b30111111001111101b2b1D b5b4b30111110101111110b2b173.MAC address is in ( ) of the computer.A RAMB NICC hard diskD cache74.Which of the following is wrong? ( )A ARP table is configured by a system administratorB ARP table is built automaticallyC ARP table is dynamicD ARP table maps IP addresses to MAC addresses75.NIC works in ( )layer.A physicalB linkC networkD transport76.In LAN, if UTP is used, the common connector is( ).A AUIB BNCC RJ-45D NNI77.The modem’s function(s) is(are) ( ).A translates digital signal into analog signalB translates analog signal into digital signalC both translates analog signal into digital signal and translates digital signal into analog signalD translates one kind of digital signal into another digital signal78.( )defines Token-Ring protocol.A IEEE 802.3B IEEE 802.4C IEEE 802.5D IEEE 802.279.( )defines Token-Bus protocol.A IEEE 802.3B IEEE 802.4C IEEE 802.5D IEEE 802.280.( ) defines CSMA/CD protocol.A IEEE 802.3B IEEE 802.4C IEEE 802.5D IEEE 802.281.The computer network that concentrated in a geographical area, such as in a building or on a university campus, is ( )A a LANB a MANC a WAND the Internet82.The MAC address is ( ) bits long.A 32B 48C 128D 25683.Which of the following four descriptions about MAC addresses is wrong? ( )A a MAC address is burned into the adapter’s ROMB No two adapters have the same addressC An adapter’s MAC address is dynamicD A MAC address is a link-layer address84.Which of the following four descriptions about DHCP is correct? ( )A DHCP is C/S architectureB DHCP uses TCP as its underlying transport protocolC The IP address offered by a DHCP server is valid foreverD The DHCP server will offer the same IP address to a host when the host requests an IP address85.The ( )field permits Ethernet to multiplex network-layer protocols.A preambleB typeC CRCD destination MAC address86.For 10BaseT, the maximum length of the connection between an adapter and the hub is ( ) meters.A 50B 100C 200D 50087.An entry in the switch table contains the following information excepts for ( )A the MAC address of a nodeB the switch interface that leads towards the nodeC the time at which the entry for the node was placed in the tableD the IP address of a node二、阅读理解The central processing unit (CPU) is the heart of the computer systems. Among other things, its configuration determines whether a computer is fast or slow in relation to other computers. The CPU is the most complex computer system component, responsible for directing most of the computer system activities based on the instructions provided. As one computer generation has evolved to the next, the physical size of the CPU has often become smaller and smaller, while its speed and capacity have increased tremendously. Indeed, these changes have resulted in microcomputers that are small enough to fit on your desk or your lap.The CPU comprises the control unit and the arithmetic / logic unit (ALU).The control unit is responsible for directing and coordinating most of the computer systems activities. It determines the movement of electronic signals between main memory and the arithmetic/logic unit, as well as the control signals between the CPU and input/output devices. The ALU performs all the arithmetic and logical (comparison) functions — that is, it adds, subtracts, multiplies, divides, and does comparisons. These comparisons, which are basically “less than”, “greater than”, and “equal to”, can be combined into several common expressions, such as “greater than or equal to”. The objective of most instructions that use comparisons is to determine which instruction should be executed next.Tell whether the following statements are true(T) or false(F) according to the passage A.(根据上文的内容判断下列句子的正误)1. With the development of computer, the physical size of the CPU has often become bigger and bigger. ( )2. The movement of electronic signals between main memory and the ALU as well as the control signal between the CPU and input /output devices are controlled by the control unit of the CPU. ( )3. The CPU comprises the control unit and memory. ( )4. The control unit performs all the arithmetic and logical (comparison) functions5. The central processing unit (CPU) is the heart of the computer systems. ( )三、翻译下面的文章。

计算机网络英文题库附答案c h a p t e r精编W O R D版IBM system office room 【A0816H-A0912AAAHH-GX8Q8-GNTHHJ8】Chapter 1 Computer Networks and the Internet 1.The ( ) is a worldwide computer network, that is, a network that interconnects millions of computing devices throughout the world.ppt3A public InternetB IntranetC switch netD television net2.Which kind of media is not a guided media ( )A twisted-pair copper wireB a coaxial cableC fiber opticsD digital satellite channel3.Which kind of media is a guided media ( )A geostationary satelliteB low-altitude satelliteC fiber opticsD wireless LAN4.The units of data exchanged by a link-layer protocol are called ( ).A FramesB SegmentsC DatagramsD bit streams5.Which of the following option belongs to the circuit-switched networks ( )A FDMB TDMC VC networksD both A and B6.( )makes sure that neither side of aconnection overwhelms the other side bysending too many packets too fast.A Reliable data transferB Flow controlC Congestion controlD Handshaking procedure7.( ) means that the switch must receive the entire packet before it can begin to transmit the first bit of the packet onto the outbound link.A Store-and-forward transmissionB FDMC End-to-end connectionD TDM8.Datagram networks and virtual-circuit networks differ in that ( ).A datagram networks are circuit-switchednetworks, and virtual-circuit networks arepacket-switched networks.B datagram networks are packet-switchednetworks, and virtual-circuit networks arecircuit-switched networks.C datagram networks use destinationaddresses and virtual-circuit networks useVC. numbers to forward packets towardtheir destination.D datagram networks use VC. numbersand virtual-circuit networks use destinationaddresses to forward packets toward theirdestination.9.In the following options, which one is not a guided media ( )A twisted-pair wireB fiber opticsC coaxial cableD satellite10.Processing delay does not include the time to ( ).A examine the packet’s headerB wait to transmit the packet onto the linkC determine where to direct the packetD check bit-error in the packet11.In the following four descriptions, which one is correct ( )A The traffic intensity must be greaterthan 1.B The fraction of lost packets increases asthe traffic intensity decreases.C If the traffic intensity is close to zero,the average queuing delay will be close tozero.D If the traffic intensity is close to one, theaverage queuing delay will be close to one.12.The Internet’s network layer isresponsible for moving network-layerpackets known as ( ) from one host toanother.A frameB datagramC segmentD message13.The protocols of various layers are called ( ).A the protocol stackB TCP/IPC ISPD network protocol14.There are two classes of packet-switched networks: ( ) networks and virtual-circuitnetworks.A datagramB circuit-switchedC televisionD telephone15.Access networks can be loosely classified into three categories: residential access,company access and ( ) access.A cabledB wirelessC campusD city areaQuestion 16~17Suppose, a is the average rate at which packets arrive at the queue, R is the transmission rate, and all packets consist of L bits, then the traffic intensity is ( 16 ), and it should no greater than ( 17 ).16.A LR/aB La/RC Ra/LD LR/a 17.A 2B 1C 0D -118.In the Internet, the equivalent concept to end systems is ( ).A hostsB serversC clientsD routers19.In the Internet, end systems are connected together by ( ).A copper wireB coaxial cableC communication linksD fiber optics20.End systems access to the Internet through its ( ).A modemsB protocolsC ISPD sockets21.End systems, packet switches, and other pieces of the Internet, run ( ) that controlthe sending and receiving of informationwithin the Internet.A programsB processesC applicationsD protocols22.There are many private networks, such as many corporate and government networks,whose hosts cannot exchange messageswith hosts outside of the private network.These private networks are often referredto as ( ).A internetsB LANC intranetsD WAN23.The internet allows ( ) running on its end systems to exchange data with each other.A clients applicationsB server applicationsC P2P applicationsD distributed applications24.The Internet provides two services to its distributed applications: a connectionlessunreliable service and () service.A flow controlB connection-oriented reliableC congestion controlD TCP25.It defines the format and the order of messages exchanged between two or morecommunicating entities, as well as theactions taken on the transmission and/orreceipt of a message or other event. Thesentence describes ( ).A InternetB protocolC intranetD network26.In the following options, which does not define in protocol ( )A the format of messages exchangedbetween two or more communicatingentitiesB the order of messages exchangedbetween two or more communicatingentitiesC the actions taken on the transmission ofa message or other eventD the transmission signals are digitalsignals or analog signals27.In the following options, which is defined in protocol ( )A the actions taken on the transmissionand/or receipt of a message or othereventB the objects exchanged between communicating entitiesC the content in the exchanged messagesD the location of the hosts28.In the following options, which does not belong to the network edge ( )A end systemsB routersC clientsD servers29.In the following options, which belongs to the network core ( )A end systemsB routersC clientsD servers30.In the following options, which is not the bundled with the Internet’s connection-oriented service( )A reliable data transferB guarantee of the transmission timeC flow controlD congestion-control31.An application can rely on the connection to deliver all of its data without error andin the proper order. The sentencedescribes ( ).A flow controlB congestion-controlC reliable data transferD connection-oriented service32.It makes sure that neither side of aconnection overwhelms the other side bysending too many packets too fast. Thesentence describes ( ).A flow controlB congestion-controlC connection-oriented serviceD reliable data transfer33.It helps prevent the Internet from enteringa state of gridlock. When a packet switchbecomes congested, its buffers canoverflow and packet loss can occur. Thesentence describes ( ).A flow controlB congestion-controlC connection-oriented serviceD reliable data transfer34.The Internet’s connection-oriented service has a name, it is ( ).A TCPB UDPC TCP/IPD IP 35.In the following options, which service does not be provided to an application by TCP( )A reliable transportB flow controlC video conferencingD congestion control36.The Internet’s connectionless service is called ( ).A TCPB UDPC TCP/IPD IP37.In the following options, which does not use TCP()A SMTPB internet telephoneC FTPD HTTP38.In the following options, which does not use UDP( )A Internet phoneB video conferencingC streaming multimediaD telnet39.There are two fundamental approaches to building a network core, ( ) and packetswitching.A electrical current switchingB circuit switchingC data switchingD message switching40.In ( ) networks, the resources needed along a path to provide forcommunication between the end systemare reserved for the duration of thecommunication session.A packet-switchedB data-switchedC circuit-switchedD message-switched41.In ( ) networks, the resources are not reserved; a session’s messages use theresources on demand, and as aconsequence, may have to wait for accessto communication link.A packet-switchedB data-switchedC circuit-switchedD message-switched42.In a circuit-switched network, if each link has n circuits, for each link used by theend-to-end connection, the connectiongets ( ) of the link’s bandwidth for theduration of the connection.A a fraction 1/nB allC 1/2D n times43.For ( ), the transmission rate of a circuit is equal to the frame rate multiplied by thenumber of bits in a slot.A CDMAB packet-switched networkC TDMD FDM 44.( ) means that the switch must receive the entire packet before it can begin totransmit the first bit of the packet onto theoutbound link.A Queuing delayB Store-and-forward transmissionC Packet lossD Propagation45.The network that forwards packetsaccording to host destination addresses iscalled ( ) network.A circuit-switchedB packet-switchedC virtual-circuitD datagram46.The network that forwards packetsaccording to virtual-circuit numbers iscalled ( ) network.A circuit-switchedB packet-switchedC virtual-circuitD datagram47.In the following entries, which is not a kind of access network()A residential accessB company accessC wireless accessD local access48.Suppose there is exactly one packet switch between a sending host and a receivinghost. The transmission rates between thesending host and the switch and betweenthe switch and the receiving host are R1and R2, respectively. Assuming that theswitch uses store-and-forward packetswitching, what is the total end-to-enddelay to send a packet of length L (Ignorequeuing delay, propagation delay, andprocessing delay.) ( )A L/R1+L/R2B L/R1C L/R2D none of the above49.The time required to examine thepacket’s header and determine where todirect the packet is part of the ( ).A queuing delayB processing delayC propagation delayD transmission delay50.The time required to propagate from the beginning of the link to the next router is( ).A queuing delayB processing delayC propagation delayD transmission delay51.Consider sending a packet of 3000bits over a path of 5 links. Each link transmits at 1000bps. Queuing delays, propagation delay and processing delay are negligible. (6 points) (1).Suppose the network is a packet-switched virtual circuit network. VC setup time is 0.1 seconds. Suppose the sending layers add a total of 500 bits of header to each packet. How long does it take to send the file from source to destination?(2).Suppose the network is a packet-switched datagram network and a connectionless serviceis used. Now suppose each packet has 200 bitsof header. How long does it take to send the file?(3).Suppose that the network is a circuit-switched network. Further suppose that the transmission rate of the circuit between sourceand destination is 200bps. Assuming 0.02s setuptime and 200 bits of header appended to the packet, how long does it take to send the packet?So lution:(1).t=5*(3000+500)/1000+0.1=17.6s( 2).t=5*(3000+200)/1000=16s( 3).t=(3000+200)/200+0.02=16.02s。

计算机网络(全英文版)期末复习As an AI language model, I can help you with the content of your article on "Computer Networks - Final Exam Review". However, please note that I am unable to format the document according to specific requirements, such as adding a word count or creating sections with headings. I will provide you with a comprehensive overview of computer networks in English, covering the essential concepts and topics that are typically covered in a final exam review. Here is the article:Computer Networks - Final Exam ReviewIntroduction:Computer networks are an integral part of modern society, facilitating communication and enabling the exchange of information between devices and users. Understanding the fundamentals of computer networks is crucial for professionals in the field of IT and related disciplines. This article aimsto provide a comprehensive review of key concepts and topics in computer networks to help you prepare for your final exam.Network Topologies:A network topology refers to the physical or logical layout of devices in a network. Several common network topologies include bus, star, ring, mesh, and hybrid topologies. Each topology has advantages and disadvantages, and understanding these can help network administrators design and maintain efficient networks.Network Protocols:Network protocols provide a set of rules and guidelines for devices to communicate with each other in a network. The TCP/IP protocol suite is the foundation of modern network communication, consisting of protocols such as IP (Internet Protocol), TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), and UDP (User Datagram Protocol). These protocols ensure reliable and efficient data transfer over networks.OSI Model:The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a conceptual framework that standardizes the functions of a network into several layers. These layers - physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application - define how data is transmitted, processed, and presented across a network. Understanding the OSI model aids in troubleshooting network issues and implementing effective network solutions.Network Addressing:In computer networks, devices are identified and addressed using unique addresses. IP addressing, specifically IPv4 and IPv6, allow devices to establish connections and route data packets across networks. IP addressing includes both network and host addresses, enabling efficient communication within and between networks.Routing and Switching:Routing involves determining the optimal path for data packets to travel from source to destination across interconnected networks. Routers, using routing tables and protocols such as OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and BGP (Border Gateway Protocol), facilitate this process. Switching, on theother hand, involves the efficient forwarding of data packets within a local area network (LAN) using MAC addresses.Network Security:As networks become increasingly complex and interconnected, ensuring network security is paramount. Network security measures include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, and authentication protocols. Protecting networks from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other threats is essential to maintain data integrity and user privacy.Wireless Networks:Wireless networks have revolutionized connectivity, allowing devices to communicate without physical cables. Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks are examples of wireless technologies widely used today. Understanding wireless networking protocols, security considerations, and challenges is important in a world where wireless connectivity is pervasive.Network Troubleshooting:Network administrators often encounter issues that require troubleshooting skills. Effective troubleshooting involves using diagnostic tools, analyzing network logs, and understanding common network issues such as connectivity problems, latency, and bandwidth constraints. By following logical steps and employing best practices, network administrators can identify and resolve network problems efficiently.Conclusion:Computer networks are the backbone of modern communication and information exchange. This article has provided an overview of key concepts and topics in computer networks, including network topologies, protocols, the OSI model, addressing, routing and switching, network security, wireless networks, and network troubleshooting. Remember to review these concepts thoroughly to prepare for your final exam.。

计算机网络英文题库(附答案) chapter 41. What is the purpose of the Network Layer in the OSI Model?The Network Layer, also known as the fourth layer in the OSI Model, is responsible for the logical addressing and routing of data packets between different networks. Its purpose is to enable the transfer of data between devices that may be located on different networks.2. What are the main functions of the Network Layer?The Network Layer performs the following main functions:•Logical Addressing: The Network Layer assigns logical addresses to devices, allowing them to be uniquelyidentified on a network. This is done using protocols suchas IP (Internet Protocol).•Routing: The Network Layer determines the optimal path for data packets to be transmitted from thesource to the destination. It uses routing algorithms andprotocols to make routing decisions and manage networktraffic.•Packet Switching: The Network Layer breaks data into smaller packets and adds control information to eachpacket. These packets are then transmitted independently over the network and reassembled at the destination.•Congestion Control: The Network Layer is responsible for managing network congestion andpreventing network resources from becomingoverwhelmed. It uses techniques such as traffic shapingand packet prioritization to ensure efficient and reliabledata transmission.•Network Interoperability: The Network Layer enables different types of networks to interconnect andcommunicate with each other. It provides mechanisms to facilitate the exchange of data between networks withdifferent protocols and technologies.3. What is IP addressing?IP addressing refers to the assignment and use of unique logical addresses, called IP addresses, to devices connected to an IP network. IP addresses are used by the Network Layer to identify and locate devices on a network.An IP address is a 32-bit binary number, typically represented in a dotted decimal notation (e.g., 192.168.0.1). It consists of two parts: the network part and the host part. The network part identifies the specific network to which the device is connected, while the host part identifies the individual device on that network.There are two types of IP addresses: IPv4 (32-bit) and IPv6 (128-bit). IPv4 is the most widely used addressing scheme and provides approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses. IPv6 is the next generation IP addressing scheme, designed to address the limitations of IPv4 and provide a significantly larger address space.4. What is routing? How does it work?Routing is the process of determining the optimal path for data packets to be transmitted from the source to the destination across a network. It is a key function of the Network Layer.When a device wants to send data to a destination device, it determines the destina tion’s IP address. It then consults its routing table, which contains information about the network topology and available paths. The routing table helps the device identify the next hop, which is the next device that will receive the data packet and forward it towards the destination.The routing table is populated through various methods, such as static routing (manually configured routes) and dynamic routing (automatically updated routes based on routing protocols). Routing protocols, such as RIP (Routing Information Protocol) and OSPF (Open Shortest Path First), are used to exchange information between routers and ensure accurate routing decisions.Routers use routing algorithms and metrics to calculate the best path for data packets. These algorithms consider factors such as the number of hops, link speeds, and network congestion to determine the most efficient route. Once the next hop is determined, the data packet is forwarded to that device, and the process is repeated until the packet reaches its destination.5. What is packet switching? How does it differ from circuit switching?Packet switching is a method of data transmission in which data is divided into smaller packets and transmitted independently over a network. It is the primary mode of transmission used in modern computer networks, including the Internet.In packet switching, data is broken into packets, each containing a portion of the original data and control information. Each packet is then labeled with the source and destination IP addresses. These packets are transmitted individually over the network and can take different paths to reach the destination. At the destination, the packets are reassembled to reconstruct the original data.Packet switching differs from circuit switching, which was commonly used in traditional telephone networks. In circuit switching, a dedicated communication path, known as a circuit, is established between the source and destination for the duration of the communication session. The entire message is transmitted along this dedicated circuit, without being divided into smaller units. This approach requires the reservation of network resources for the entire duration of the communication, even if no data is being transmitted.Packet switching offers several advantages over circuit switching, including better resource utilization, improved network efficiency, and the ability to handle variable network conditions. It allows multiple devices to share the same network resources and adapt to changing traffic patterns. Additionally, packet switching enables the transmission ofdiverse data types, such as voice, video, and text, over the same network.ConclusionThe Network Layer plays a crucial role in computer networks by facilitating the logical addressing, routing, and interconnectivity of devices across networks. It provides essential functions such as IP addressing, routing, packet switching, congestion control, and network interoperability. Understanding the concepts and principles of the Network Layer is vital for effective network design, management, and troubleshooting.This chapter has covered the purpose of the Network Layer, its main functions, IP addressing, routing, and packet switching. By grasping these concepts, you are now well-equipped to navigate the complexities of computer networks and ensure efficient data transmission.Keep learning and exploring the fascinating world of computer networking!。
计算机网络英文复习题1、请简述英文“network”是什么含义?并举出一个具体的网络应用实例。
“Network”的英文意思是网络。
网络是由多个节点(nodes)通过各种协议(protocols)进行连接,以实现信息的交换和共享的一种系统。
网络应用实例包括:电子邮件(Email)、万维网(World Wide Web)、文件传输(FTP)、远程登录(Telnet)等。
2、什么是局域网(Local Area Network,LAN)?请举例说明。
局域网(LAN)是一种在有限区域内(如一座大楼、一个校园或一个工厂等)连接计算机和其他设备的高速网络。
例如,家庭网络、办公室网络和校园网络等都是局域网的例子。
3、什么是广域网(Wide Area Network,WAN)?请举例说明。
广域网(WAN)是一种跨越较大地理范围的网络,通常由多个局域网组成,并通过各种传输媒介(如光纤、卫星等)连接在一起。
例如,因特网(Internet)就是一种广域网的例子。
4、请简述TCP/IP协议是什么?并列举其中两个主要的协议。
TCP/IP协议是一种在网络通信中广泛使用的协议套件,它包含了传输控制协议(TCP)和互联网协议(IP)。
这两个协议是TCP/IP协议的重要组成部分。
此外,TCP/IP协议还包括其他一些协议,如HTTP、FTP等。
5、什么是IP?请简述其结构。
IP是互联网协议(IP)中用来唯一标识网络主机或设备的。
它通常由四个数字组成,每个数字在0-255之间。
这些数字由点号分隔,形如 x.x.x.x。
例如,192.168.1.1就是一个IP的例子。
6、什么是DNS?请简述其作用。
DNS(Domain Name System)是域名系统,它可以将网站的域名解析为对应的IP,从而让用户可以通过域名访问网站。
DNS的作用是在用户访问网站时进行解析,将域名转化为对应的IP,这样用户就可以通过浏览器访问网站了。
计算机网络复习题一、选择题1、OSI模型将计算机网络分为几个层次?A. 4个B. 6个C. 7个D. 8个2、TCP/IP协议包含哪两个主要的协议?A. TCP和HTTPB. TCP和UDPC. HTTP和FTPD. FTP和SMTP3、以下哪个协议用于传输电子邮件?A. SMTPB. IMAPC. POP3D. FTP4、以下哪个网络设备用于将网络分成若干个子网?A.路由器B.交换机C.网关D.集线器5、以太网使用什么类型的传输方式?A.异步传输B.同步传输C.基带传输D.宽带传输二、填空题1、OSI模型的第一层是_________层,负责在计算机之间建立连接。
Chapter 3 Transport Layer1. A transport-layer protocol provides for logical communication between ____.A Application processesB HostsC RoutersD End systems2. Transport-layer protocols run in ____.A ServersB ClientsC RoutersD End systems3. In transport layer, the send side breaks application messages into ____, passes to network layer.A FramesB SegmentsC Data-gramsD bit streams4. Services provided by transport layer include ____.A HTTP and FTPB TCP and IPC TCP and UDPD SMTP5. Which of the following services is not provided by TCP?A Delay guarantees and bandwidth guaranteesB Reliable data transfers and flow controlsC Congestion controlsD In-order data transfers6. These two minimal transport-layer services----____ and ____----are the only two services that UDP provides!A process-to-process data delivery, error checkingB congestion control, reliable data transferC flow control, congestion controlD In-order data transfer, error checking7. Port number’s scop e is ____ to ____.A 0, 1023B 0, 65535C 0, 127D 0,2558. The port numbers ranging from ____to ____ are called well-known port number and are restricted.A 0, 1023B 0, 65535C 0, 127D 0,2559. UDP socket identified by two components, they are ____.A source IP addresses and source port numbersB source IP addresses and destination IP addressesC destination IP address and destination port numbersD destination port numbers and source port numbers10. TCP socket identified by a (an) ____.A 1-tupleB 2-tupleC 3-tupleD 4-tuple11. Which of the following applications normally uses UDP services?A SMTPB Streaming multimediaC FTPD HTTP12. Reliable data transfer protocol over a perfectly reliable channel is____.A rdt1.0B rdt2.0C rdt3.0D rdt2.113. Reliable data transfer protocol over a channel with bit errors and packet losses is _ ___.A rdt1.0B rdt2.0C rdt3.0D rdt2.114. Which of the following about reliable data transfer over a channel with bit errors i s not correct?A RDT2.0: assuming ACK and NAK will not be corruptedB RDT2.1: assuming ACK and NAK can be corruptedC RDT2.2: only use ACK-sD RDT2.2: use both ACK-s and NAK-s15. Which of the following protocols is not pipelining protocols?A TCPB rdt3.0C GO-BACK-ND selective repeat16. Which of the following is not correct about GBN protocol?A Only using ACK-sB Using cumulative ACK-sC Receiver discards all out-of-order packetsD It is not pipelined protocol17. Which of the following is not correct about SR protocol?A receiver individually acknowledges all correctly received packetsB sender only resends packets for which ACK not receivedC It limits sequence number of sent but un-ACK-ed packetsD It is not a pipelined protocol18. Which of the following about TCP connection is not correct?A It is a broadcast connectionB It is a point-to-point connectionC It is a pipelined connectionD It is a full duplex connection19. The SYN segment is used for____.A TCP connection setupB TCP flow controlC TCP congestion controlD Closing a TCP connection20. The FIN segment is used for____.A TCP connection setupB TCP flow controlC TCP congestion controlD Closing a TCP connection21.How does TCP sender perceive congestion?A Through a timeout eventB Through a receiving duplicate ACK-s eventC Both A and BD Either A or B22. Extending host-to-host delivery to process-to-process delivery is called transport-layer ____ and .A multiplexing and de-multiplexingB storing and forwardingC forwarding and filteringD switching and routing23. UDP is a ____ service while TCP is a connection-oriented service.A ConnectionlessB ReliableC Connection-orientedD In-order24. The UDP header has only four fields, they are____.A Source port number, destination port number, length and checksumB Source port number, destination port number, source IP and destination IPC source IP, destination IP, source MAC address and destination MAC addressD source IP, destination IP, sequence number and ACK sequence number25. There are two 16-bit integers: 1110 0110 0110 0110, 1101 0101 0101 0101. Their checksum is____.A 0100010001000011B 1011101110111100C 1111111111111111D 100000000000000026.The maximum amount of data that can be grabbed and placed in a segment is limited by the____.A Maximum segment size (MSS)B MTUC ChecksumD Sequence number27.The MSS is typically set by first determining the length of the largest link-layer frame that can be sent by the local sending host----the so-called____.A Maximum transmission unit (MTU)B MSSC ChecksumD Sequence number28. A File size of 500,000bytes, MSS equals 1000bytes. When we want to transmit this file with TCP, the sequence number of the first segment is 0, and the sequence number of the second segment is ____.A 1000B 999C 1001D 50000029.Because TCP only acknowledges bytes up to the first missing byte in the stream, TCP is said to provide____.A Cumulative acknowledgementsB Selective acknowledgementsC 3 duplicate ACKsD positive ACKs30. Provided α=0.125, current value of Estimated-RTT is 0.4s, Sample-RTT is 0.8s, then the new value of Estimated-RTT is ____s.A 0.45B 0.6C 0.7D 0.831.Provided RcvBuffer=20,LastByteRcvd=20,LastByteRead=15, thenRcvWindow=____.A 14B 15C 16D 1032. TCP service does not provide____.A Reliable data transferB Flow controlC Delay guaranteeD Congestion control33. There are two states in TCP congestion control, which are ____.A slow start and congestion avoidanceB safe start and congestion avoidanceC slow start and congestion abandonD safe start and congestion abandon34. The transport-layer protocol provides logical communication between ____, and the network-layer protocol provides logical communication ____.A hosts, processesB processes, hostsC threads, processesD processes, threads35. To implement the multicast services the Internet employs the ____ protocol.A FTPB TCPC IGMPD UDP36. If an application developer chooses ____ protocol, then the application process is almost directly talking with IP.A HTTPB RIPC CSMA/CDD UDP37. ____ maintains connection-state in the end systems. This connection state includes receive and send buffers, congestion-control parameters, and sequence and acknowledgment number parameters.A UDPB TCPC DNSD HTTP38. The host that initiates the session in the Internet is labeled as ____.A serverB user agentC clientD router39. With TCP there is no _____ between sending and receiving transport-layer entities.A flow controlB handshakingC. congestion control D VC setup40. The Internet’s ____service helps prevent the Internet from entering a state of gridlock.A datagramB congestion controlC sliding windowD timeout event41. Connection setup at the transport layer involves ____.A serverB only the two end systemsC clientD router42. A ____layer protocol provides for logical communication between applications.A transportB applicationC networkingD MAC43. In static congestion window, if it satisfies W*S/R > RTT + S/R, the Latency is ____.A W*S/R – ( RTT+ S/R)B 2RTT + O/RC 2RTT + O/R + (k-1)[W* S/R- (RTT + S/R)]D 2RTT + S/R44. The receive side of transport layer reassembles segments into messages, passes to ____layer.A ApplicationB NetworkingC PhysicalD MAC45. In the following four options, which one is correct?A The variations in the SampleRTT are smoothed out in the computation of the EstimatedRTTB The timeout should be less than the connection’s RTTC Suppose that the last SampleRTT in a TCP connection is equal to 1 sec. Then the current value of TimeoutInterval will necessarily be≥1 secD Suppose that the last SampleRTT in a TCP connection is equal to 1 sec. Then the current value of TimeoutInterval will necessarily be≤1 sec46. The port number used by HTTP is ____.A 80B 25C 110D 5347. The port number used by SMTP is ____.A 80B 25C 110D 5348. The port number used by pop3 is ____.A 80B 25C 110D 5349. The port number used by DNS is ____.A 80B 25C 110D 5350. The port number used by FTP is ____.A 20 and 21B 20C 21D 5351. A UDP socket identified by a ____ tuple(s).A 2B 4C 1D 352. A TCP socket identified by a ____ tuple(s).A 2B 4C 1D 353. A TCP socket does not include____.A Source MAC addressB Source port numberC Destination IP addressD Destination port number54. Which of following about UDP is not correct.A It is a reliable data transfer protocolB It is connectionlessC no handshaking between UDP sender, receiverD it is a best effort service protocol55. DNS uses ____ service.A TCPB UDPC Both TCP and UDPD None of above56. Which of following about UDP is correct?A Finer application-level control over what data is sent, and whenB No connection establishment (which can add delay), so no delay for establish a connectionC No connection state (so, UDP can typically support many active clients)D Large packet header overhead (16-B)57. Streaming media uses a ____ service normally.A TCPB UDPC Both TCP and UDPD None of above58. The UDP header has only ____ fields.A 2B 4C 1D 359. Which of the following does not included in UDP header.A Source port numberB Destination port numberC ChecksumD Sequence number60. Which of the following is not a pipelining protocol.A Rdt1.0B Go-Back-NC Selective repeatD TCP61. In the following four descriptions about MSS and MTU, which one is not correct?A The MSS is the maximum amount of application-layer data in the segmentB The MSS is the maximum size of the TCP segment including headersC The MSS is typically set by MTUD The MTU means the largest link-layer frame62. The job of gathering data chunks, encapsulating each data chunk with header information to create segments and passing the segments to the network is called ____.A multiplexingB de-multiplexingC forwardingD routing63. In the following four descriptions about the relationship between the transport layer and the network layer, which one is not correct?A The transport-layer protocol provides logical communication between hostsB The transport-layer protocol provides logical communication between processesC The services that a transport-layer protocol can provide are often constrained by the service model of the network-layer protocolD A computer network may make available multiple transport protocols64. Suppose the following three 8-bit bytes: 01010101, 01110000, 01001100. What’s the 1s complement of the sum of these 8-bit bytes?A 00010001B 11101101C 00010010D 1000100065. The following four descriptions about multiplexing and de-multiplexing, which one is correct?A A UDP socket is identified by a two-tuples consisting of a source port number and a destination port number.B If two UDP segment have different source port number, they may be directed to the same destination process.C If two TCP segments with different source port number, they may be directed to the same destination process.D If two TCP segments with same destination IP address and destination port number, they must be the same TCP connection.66. UDP and TCP both have the fields except ____.A source port numberB destination port numberC checksumD receive window67. If we define N to be the window size, base to be the sequence number of the oldest unacknowledged packet, and next-seq-num to be the smallest unused sequence number, then the interval [nextseqnum,base+N-1] corresponds to packet that ____.A can be sent immediatelyB have already been transmitted and acknowledgedC cannot be usedD have been sent but not yet acknowledged68. Which of the following about TCP is not correct?A It is a connectionless protocolB Point-to-point protocolC Reliable, in-order byte steam protocolD Pipelined protocol69. Which of the following about TCP is not correct?A It is a connectionless protocolB full duplex data transfer protocolC connection-oriented protocolD flow controlled protocol70. The maximum amount of data that can be grabbed and placed in a segment is limited by the ____.A Maximum segment size (MSS)B MTUC Sequence numberD Check sum71. The MSS is typically set by first determining the length of the largest link-layer frame that can be sent by the local sending host (the so-called____), and then will fit into a single link-layer frame.A Maximum segment size (MSS)B MTUC Sequence numberD Check sum72. The MSS is the maximum amount of ____layer data in the segment, not the maximum size of the TCP segment including headers.A ApplicationB TransportC NetworkingD Link73. Which of the following field is not used for connection setup and teardown?A Sequence numberB TSTC SYND FIN74. ____ is the byte stream number of first byte in the segment.A Sequence numberB ACK numberC ChecksumD port number75. ____ is the byte sequence numbers of next byte expected from other side.A Sequence numberB ACK numberC ChecksumD port number76. Because TCP only acknowledges bytes up to the first missing byte in the stream, TCP is said to provide ____ acknowledgements.A CumulativeB SelectiveC SingleD Negative77. Fast retransmit means in the case that ____ duplicate ACK-s are received, the TCP sender resend segment before timer expires.A 3B 4C 5D 678. TCP____ means sender won’t overflow receiver’s buffer by tran smitting too much, too fast.A Flow controlB Congestion controlC Reliable data transferD Connection-oriented service79. TCP provides flow control by having the sender maintain a variable called the ____.A Receive windowB Congestion windowC Sliding windowD buffer80. How does TCP sender perceive congestion?A TimeoutB 3 duplicate ACK-sC Both A and BD None of above81. Transport protocols run in ____.A ServersB ClientsC RoutersD End systems82. Which of the following services is not provided by TCP?A Delay guarantees and bandwidth guaranteesB Reliable data transfers and flow controlsC Congestion controlsD In-order data transfers83. Which service does UDP not provide?A multiplexingB de-multiplexingC error-detectionD error-correction84. There are three major events related to data transmission and retransmission in the TCP sender, which one is not in it?A data received from application aboveB de-multiplexing segmentC timer timeoutD ACK receipt85. Which of the following applications normally uses UDP services?A SMTPB Streaming multimediaC FTPD HTTP86. Which of the following about TCP connection is not correct?A It is a broadcast connectionB It is a point-to-point connectionC It is a pipelined connectionD It is a full duplex connection87. The SYN segment is used for____.A TCP connection setupB TCP flow controlC TCP congestion controlD Closing a TCP connection88. Which service helps prevent the internet from entering a state of gridlock?A reliable data transferB flow controlC congestion controlD handshaking procedure89. The Internet’s _____is responsible for moving packets from one host to another.A application layerB transport layerC network layerD link layer90.In the following applications, which one is a bandwidth-sensitive application?A E-mailB web applicationC real-time audioD file transfer91. In the following applications, which one uses UDP?A E-mailB web applicationC file transferD DNS92. In the following four descriptions, which one is correct?A If one host’s transport layer uses TCP, then its network layer must use virtual-circuit network.B Datagram network provides connection serviceC The transport-layer connection service is implemented in the routerD The network-layer connection service is implemented in the router as well as in the end system.93.____ is a speeding-matching service---matching the rate which the sender is sending against the rate at which the receiving application is reading.A congestion controlB flow controlC sliding-window controlD variable control94. In the following four descriptions about Rcv-Window, which one is correct?A The size of the TCP RcvWindow never changes throughout the duration of the connectionB The size of the TCP RcvWindow will change with the size of the TCP RcvBufferC The size of the TCP RcvWindow must be less than or equal to the size of the TCP RcvBufferD Suppose host A sends a file to host B over a TCP connection, the number of unacknowledged bytes that A sends cannot exceed the size of the size of the RcvWindow.95. There are 6 flag fields. Which one is to indicate that the receiver should pass the data to the upper layer immediately?A PSHB URGC ACKD RST96. Suppose the TCP receiver receives the segment that partially or completely fills in gap in received data, it will ____.A immediately send ACKB immediately send duplicate ACKC wait some time for arrival of another in-order segmentD send single cumulative97. _____ imposes constrain on the rate at which a TCP sender can send traffic into the network.A sliding windowB congestion windowC receive windowD variable window98. Flow control and congestion control are same at that they all limit the rate of the sender, but differ in that ____.A flow control limits its rate by the size of RcvWindow, but congestion control by the traffic on the linkB congestion control limits its rate by the size of RcvWindow, but flow control by the traffic on the linkC flow control mainly is accomplished by the sender, but congestion control by the receiver.D flow control mainly is accomplished by the receiver, but congestion control bythe link.99. This job of delivering the data in a transport-layer segment to the correct socket is called ____.A multiplexingB de-multiplexingC forwardingD routing100. If we define N to be the window size, base to be the sequence number of the oldest unacknowledged packet, and next-seq-num to be the smallest unused sequence number, then the interval [base, nextseqnum-1] corresponds to packet that ____.A can be sent immediatelyB have already been transmitted and acknowledgedC cannot be usedD have been sent but not yet acknowledged101. ____ are the two types of transport services that the Internet provides to the applications.A TCP and UDPB connection-oriented and connectionless serviceC TCP and IPD reliable data transfer and flow control102. In the following descriptions about persistent connection, which one is not correct?A The server leaves the TCP connection open after sending a responseB Each TCP connection is closed after the server sending one objectC There are two versions of persistent connection: without pipelining and with pipeliningD The default mode of HTTP uses persistent connection with pipelining103. The field of Length in UDP segment specifies the length of ____.A the UDP segment, not including the headerB the UDP segment, including the headerC the UDP segment’s headerD the Length field104. In TCP segment header, which field can implement the reliable data transfer?A source port number and destination port numberB sequence number and ACK numberC urgent data pointerD Receive window105. In the following four descriptions about TCP connection management, which one is not correct?A Either of the two processes participating in a TCP connection can end the connectionB If the FIN bit is set to 1, it means that it wants to close the connectionC In the first two step of the three-way handshake, the client and server randomly choose an initial sequence numberD In the three segments of the three-way handshake, the SYN bit must be set to 1 106. Suppose host A sends two TCP segments back to back to host B over a TCP connection. The first segment has sequence number 42, and the second has sequence number 110. If the 1st is lost and 2nd arrives at host B. What will be the acknowledgment number?A 43B ACK42C 109D ACK1101.Consider sending an object of size O=500,000bytes from server to client. LetS=500 bytes and RTT=0.2s. Suppose the transport protocol uses static windows with window size 5. For a transmission rate of 100Kbps, determine the latency for sending the whole object. Recall the number of windows K=O/ WS), and there is K-1 stalled state (that is idle time gaps).2.Consider the following plot of TCP congestion window size as a function of time.Fill in the blanks as follow:a) The initial value of Threshold at the first transmission round is ____. b) The value of Threshold at the 11st transmission round is ____. c) The value of Threshold at the 21st transmission round is ____. d) After the 9th transmission round, segment loss detected by ____.(A) Timeout(B) Triple duplicate ACKe) After the 19th transmission round, segment loss detected by ____.(A) Timeout(B) Triple duplicate ACKf) During ____ transmission round, the 18th segment is sent.3.Consider the TCP reliable data transfer in the given graph. If in Segment 1’s Sequence number =10,data=“AC”, please fill in the following blanks. a) In Segment 2, ACK number=____;b) In Segment 3, Sequence number =____; data=“0123456789”c) If there are some bits corrupted in segment 3 when it arrives Host B, then the ACK number in Segment 5 is ____; and the ACK number in Segment 6 is ____.14 180 26 3000 2 6 4 8 10 12 16 20 22 240 28 32Congestion window sizeTransmission round48121612345674. The client A wants to request a Web page from Server B. Suppose the URL of the page is 172.16.0.200/experiment, and also it wants to receive French version of object. The time-sequence diagram is shown below, please fill in the blanks.12345Packet① to Packet③are TCP connection’s segment, then:Packet ①: SYN flag bit= aACK flag bit= bSequence number= 92Packet ②: SYN flag bit=1ACK flag bit= c Sequence number=100 Packet ③: SYN flag bit= d ACK flag bit=1Sequence number= e5. Consider sending an object of size O=100 Kbytes from server to client. Let S=536 bytes and RTT=100msec. Suppose the transport protocol uses static windows with window size W.(1) For a transmission rate of 25 kbps, determine the minimum possible latency. Determine the minimum window size that achieves this latency. (2) Repeat (1) for 100 kbps.6. Consider the following plot of TCP congestion window size as a function of time. Please fill in the blanks as below.a) The initial value of Threshold at the first transmission round is____. b) The value of Threshold at the 11th transmission round is_____. c) The value of Threshold at the 21st transmission round is_____.14 18 26 30 0 2 6 4 8 10 12 16 20 22 24 28 32 Congestion window sizeTransmission round481216d) After the 9th transmission round, _____ occurs.e) After the 19th transmission round, ____ are detected.。
I.Choose the single correct answer from following choose. (1.5*20=30)[Correct checked:1.5; Other wise:0]1.Which physical media has high-speed operation and low error rate:A[] A.Fiber optic cable[] B.Coaxial cable[] C.Twisted pair[] D.Radio2.If no free buffers in router, the arriving packets will be: B[] A.dropped[] B.queued[] C.returned[] D.marked3.Which can provides delay measurement from source to router along end-end Internet path towards destination: A[] A.Ping[] B.Traceroute[] C.Ipconfig[] D.Nslookup4.In TCP/IP, which layer can make routing of datagrams from source to destination: C[] A.Applicaion[] B.Transport[] work[] D.Data Link5.Web page consists of ( ) which includes several referenced objects:A[] A.referenced HTML-file[] B.host HTML-file[] C.path HTML-file[] D.base HTML-file6.What is the default persistent model in HTTP/1.1:C[] A.Nonpersistent HTTP[] B.Persistent without pipelining[] C.Persistent with pipelining[] D.Nonpersistent with pipelining7.Web server maintains no information about past client requests, so HTTP is:B[] A.stateful[] B.stateless[] C.satisfied[] D.unsatisfied8.FTP client browses remote directory by sending commands over: D[] A.connection-less[] B.free connection[] C.data connection[] D.control connection9.Which can satisfy client request without involving origin server A[] A.Web caches[] B.Write caches[] C.TCP buffer[] D.Router buffer10.UDP socket identified by:B[] A.two-tuple (source IP address, source port number)[] B.two-tuple (dest IP address, dest port number)[] C.two-tuple (source IP address, dest port number)[] D.two-tuple (dest IP address, source port number)11.In GBN,when receiver receive a out-of-order packet,then discard and re-ACK the packet with:[] A. highest in-order sequence # A[] B. lowest in-order sequence #[] C. highest in-order port #[] D. lowest in-order port #12.In RDT Approachs, which is designed for performance: B[] A. checksum[] B. pipeline[] C. sequence #[] D. ACK or NAK13.Queued datagram at front of router’s queue prevents others in queue from moving forward is:A[] A.Head-of-the-Line (HOL) blocking[] B.Hops-of-the-Line (HOL) blocking[] C.Head-of-the-List (HOL) blocking[] D.Hops-of-the-List (HOL) blocking14.Wha t’s a network ? From IP address perspective they can physically reach each other without intervening router and the device interfaces with: C[] A. same IP address[] B. same TCP port #[] C. same network part of IP address[] D. same host part of IP address15. Large IP datagram divided (“fragmented”) within network,it will be reassembled:B[] A. only at last router[] B. only at final destination[] C. only at next router[] D. maybe at next router16.Which is not a common Intra-AS routing protocols:D[] A.RIP: Routing Information Protocol[] B.OSPF: Open Shortest Path First[] C.IGRP: Interior Gateway Routing Protocol[] D.ICMP: Interior Control Message Protocol17.Which is not a MAC Random Access protocol in Ethernet: D[] A.SCMA[] B.SCMA/CA[] C.SCMA/CD[] D.Slotted SCMA18.In DHCP client-server scenario, which message has DHCP-options field:D[] A. host broadcasts “DHCP discover”[] B. DHCP server responds with “DHCP offer”[] C. host requests IP address: “DHCP request”[] D. DHCP server sends a ddress: “DHCP ack”19.How to determine MAC address of host B, If knowing host B’s IP address?A[] A.ARP[] B.RARP[] C.RAP[] D.RIP20. Which device can break subnet into LAN segments: C[] A.IP mask[] B.NAT[] C.Router[] D.SwitchII.Choose the multiple correct answer from following choose. (2*10=20)[All correct checked:2; Part correct checked:1; No checked:0; Full checked:0]1.Which is the part of network structure: ABD[] work edge[] work core[] work user[] D.access networks2.How to connect end systems to edge router? BCD[] A.Microsoft access networks[] B.Residential access networks[] C.Institutional access networks[] D.Mobile access networks3.What kind of transport service does an application need? ABC[] A.Data loss[] B.Timing[] C.Bandwidth[] D.Security4.Electronic Mail three phases of transfer is: ABD[] A.handshaking (greeting)[] B.transfer of messages[] C.opens the 2nd TCP connection[] D.close5.In TCP Connection Management, initialize TCP variables include:AB[] A.sequence #[] B.buffers[] C.Sender MTU[] D.RcvWindow6.How does sender perceive congestion? AB[] A.timeout[] B.3 duplicate ACKs[] C.3 duplicate data[] D.slow start7.TCP Congestion Control use three mechanisms: ABC[] A.additive increase and multiplicative decrease[] B.slow start[] C.Conservative after timeout events[] D.additive decrease and multiplicative increase8.What are the Key Network-Layer Functions: ABC[] A.forwarding[] B.routing[] C.connection setup[] D.flow control9.Link Layer Services include: ABD[] A.Reliable delivery between adjacent nodes[] B.Flow Control between adjacent nodes[] C.Connection Manage[] D.Error Detection and Correction10.MAC Protocol’s taxonomy, three broad classes is: ABC[] A.Channel Partitioning[] B.Random Access[] C.Taking turns[] D.Peer-to-peerIII.Fill the blank from options. (1.5*16=24)1).The network protocols define format , order of message sent andreceived among network entities, and action taken on message transmission, receipt.(options: delay / format / policy / order / request / replay / actions taken / price / interface )2).InTCP Congestion Control, after 3 duplicate ACKs CongWin is cut in half and window then grows____linearly___. But after timeout event, CongWin instead set to 1 MSS , window then grows___exponentially____, when it up to a __threshold____ again, then grows linearly.(options: half / double / 1 MSS / 0 MSS / linearly / exponentially / threshold / top / bottom )3).Please fill the general format of Http request message:HTTP request message general format9.[Method] sp 10.[URL] sp 11.[version]12.[CR LP ]……13.[header field name ] : 14.[field value] 15. [Cr Lf ]16. [ Cr Lf ]Entity Body(options: header field name / URL / field value / version / method / Cr Lf/ 200 OK )IV.Question (26)1.As follow, LAN1 connect to LAN2 via a router:In session 1, Host A send a HTTP connection to WEB server D,if Host A initial TCP port 1025,Host D use TCP port 80;In session 2, Host A send a HTTP connection to WEB server B,if Host A initial TCP port 1026,Host B use TCP port 80;Session Step SourceMACDestinationMACSourceIPDestinationIPSourcePort#DestinationPort#Host A :1025 –> Host D:80 Host A –> ROUTER ROUTER–> Host DHost A :1026 –> Host B:80 Host A –> Host B2.Read and answer:(17)Two of the most important fields in the TCP segment header are the sequence number field and the acknowledgment number field. These fields are a critical part of TCP's reliable data transfer service. But before discussing how these fields are used to provide reliable data transfer, let us first explain what exactly TCP puts in these fields.TCP views data as an unstructured, but ordered, stream of bytes. TCP's use of sequence numbers reflects this view in that sequence numbers are over the stream of transmitted bytes and not over the series of transmitted segments. The sequencenumber for a segment is the byte-stream number of the first byte in the segment. Let's look at an example. Suppose that a process in host A wants to send a stream of data to a process in host B over a TCP connection. The TCP in host A will implicitly number each byte in the data stream. Suppose that the data stream consists of a file consisting of 500,000 bytes, that the MSS is 1,000 bytes, and that the first byte of the data stream is numbered zero. As shown in Figure 3.5-3, TCP constructs 500 segments out of the data stream. The first segment gets assigned sequence number 0, the second segment gets assigned sequence number 1000, the third segment gets assigned sequence number 2000, and so on.. Each sequence number is inserted in the sequence number field in the header of the appropriate TCP segment.Figure 3.5-3: Dividing file data into TCP segments.Now let us consider acknowledgment numbers. These are a little trickier than sequence numbers. Recall that TCP is full duplex, so that host A may be receiving data from host B while it sends data to host B (as part of the same TCP connection). Each of the segments that arrive from host B have a sequence number for the data flowing from B to A. The acknowledgment number that host A puts in its segment is sequence number of the next byte host A is expecting from host B. It is good to look at a few examples to understand what is going on here. Suppose that host A has received all bytes numbered 0 through 535 from B and suppose that it is about to send a segment to host B. In other words, host A is waiting for byte 536 and all the subsequent bytes in host B's data stream. So host A puts 536 in the acknowledgment number field of the segment it sends to B.As another example, suppose that host A has received one segment from host B containing bytes 0 through 535 and another segment containing bytes 900 through1,000. For some reason host A has not yet received bytes 536 through 899. In this example, host A is still waiting for byte 536 (and beyond) in order to recreate B's data stream. Thus, A's next segment to B will contain 536 in the acknowledgment number field. Because TCP only acknowledges bytes up to the first missing byte in the stream, TCP is said to provide cumulative acknowledgements.This last example also brings up an important but subtle issue. Host A received the third segment (bytes 900 through 1,000) before receiving the second segment (bytes 536 through 899). Thus, the third segment arrived out of order. The subtle issue is: What does a host do when it receives out of order segments in a TCP connection? Interestingly, the TCP RFCs do not impose any rules here, and leave the decision up to the people programming a TCP implementation. There are basically two choices: either (i) the receiver immediately discards out-of-order bytes; or (ii) the receiver keeps the out-of-order bytes and waits for the missing bytes to fill in the gaps. Clearly, the latter choice is more efficient in terms of network bandwidth, whereas the former choice significantly simplifies the TCP code. Throughout the remainder of this introductory discussion of TCP, we focus on the former implementation, that is, we assume that the TCP receiver discards out-of-order segments.In Figure 3.5.3 we assumed that the initial sequence number was zero. In truth, both sides of a TCP connection randomly choose an initial sequence number. This is done to minimize the possibility a segment that is still present in the network from an earlier, already-terminated connection between two hosts is mistaken for a valid segment in a later connection between these same two hosts (who also happen to be using the same port numbers as the old connection) .Question 1: Does TCP's use of sequence numbers over the series of transmitted segments? (3) Question 2: What does the sequence number for a segment means? For example. (4)Question 3: What does the acknowledgment number means, that host A puts in its segment to host B?(3)Question 4: How does TCPs to choose an initial sequence number? (3)Question 5: What does a host do when it receives out of order segments in a TCP connection? (4) (所有答案请填在答题卡上,答在试卷上的答案一律无效)。
Chapter 1 Computer Networks and the Internet 1.The The ( ( ) ) is is is a a a worldwide worldwide worldwide computer computer computer network, network, network, that that that is, is, is, a a a network network network that that interconnects millions of computing devices throughout the world. ppt3 A public Internet B Intranet C switch net D television net 2.Which kind of media is not a guided media? ( ) A twisted-pair copper wire B a coaxial cable C fiber optics D digital satellite channel 3.Which kind of media is a guided media? ( ) A geostationary satellite B low-altitude satellite C fiber optics D wireless LAN 4.The units of data exchanged by a link-layer protocol are called ( ). A Frames B Segments C Datagrams D bit streams 5.Which of the following option belongs to the circuit-switched networks? ( ) A FDM B TDM C VC networks D both A and B 6.( )makes sure that that neither neither neither side side side of of of a a a connection overwhelms connection overwhelms the the other other side by sending too many packets too fast. A Reliable data transfer B Flow control C Congestion control D Handshaking procedure 7.( ) means that the switch must receive the entire packet before it can begin to transmit the first bit of the packet onto the outbound link. A Store-and-forward transmission B FDM C End-to-end connection D TDM 8.Datagram networks and virtual-circuit networks differ in that ( ). A datagram networks are circuit-switched networks, and virtual-circuit networks are packet-switched networks. B datagram networks are packet-switched networks, and virtual-circuit networks are circuit-switched networks. C datagram networks use destination addresses and virtual-circuit networks use VC. numbers to forward packets toward their destination. D datagram networks use VC. numbers and virtual-circuit networks use destination addresses to forward packets toward their destination. 9.In the following options, which one is not a guided media? ( ) A twisted-pair wire B fiber optics C coaxial cable D satellite 10.Processing delay does not include the time to ( ). A examine the packet ’s header B wait to transmit the packet onto the link C determine where to direct the packet D check bit-error in the packet 11.In the following four descriptions, which one is correct? ( ) A The traffic intensity must be greater than 1. B The fraction of lost packets increases as the traffic intensity decreases. C If the traffic intensity is close to zero, the average queuing delaywill be close to zero. D If the traffic intensity is close to one, the average queuing delay will be close to one. 12.The The Internet Internet Internet’’s s network network network layer layer layer is is is responsible responsible responsible for for for moving moving moving network-layer network-layer packets known as ( ) from one host to another. A frame B datagram C segment D message 13.The protocols of various layers are called ( ). A the protocol stack B TCP/IP C ISP D network protocol 14.There are two classes of packet-switched networks: ( ) networks and virtual-circuit networks. A datagram B circuit-switched C television D telephone 15.Access networks can be loosely classified into three categories: residential access, company access and ( ) access. A cabled B wireless C campus D city area Question 16~17 Suppose, a is the average rate at which packets arrive at the queue, R is the the transmission transmission transmission rate, rate, rate, and and and all all all packets packets packets consist consist consist of of L bits, bits, then then then the the the traffic traffic intensity is ( 16 ), and it should no greater than ( 17 ). 16. A LR /aB La /RC Ra /L D LR /a 17.A 2 B 1 C 0 D -1 18.In the Internet, the equivalent concept to end systems is ( ). A hosts B servers C clients D routers 19.In the Internet, end systems are connected together by ( ). A copper wire B coaxial cable C communication links D fiber optics 20.End systems access to the Internet through its ( ). A modems B protocols C ISP D sockets 21.End systems, packet switches, and other pieces of the Internet, run ( ) that control the sending and receiving of information within the Internet. A programs B processes C applications D protocols 22.There are many private networks, such as many corporate and government networks, whose hosts cannot exchange messages with hosts outside of the private network. These private networks are often referred to as ( ). A internets B LANC intranets D W AN 23.The internet allows ( ) running on its end systems to exchange data with each other. A clients applications B server applications C P2P applications D distributed applications 24.The Internet provides two services to its distributed applications: a connectionless unreliable service and () service. A flow control B connection-oriented reliable C congestion control D TCP 25.It defines the format and the order of messages exchanged between twoor more communicating entities, as well as the actions taken on the transmission and/or receipt of a message or other event. The sentence describes ( ). A Internet B protocol C intranet D network 26.In the following options, which does not define in protocol? ( ) A the format of messages exchanged between two or more communicating entities B the order of messages exchanged between two or more communicating entities C the actions taken on the transmission of a message or other evenD the transmission signals are digital signals or analog signals 27.In the following options, which is defined in protocol? ( ) A the actions taken on the transmission and/or receipt of a message oother event B the objects exchanged between communicating entities C the content in the exchanged messages D the location of the hosts 28.In the following options, which does not belong to the network edge( ) A end systems B routers C clients D servers 29.In the following options, which belongs to the network core? ( ) A end systems B routers C clients D servers 30.In the following options, which is not the bundled with the Internet ’s connection-oriented service? ( ) A reliable data transfer B guarantee of the transmission time C flow control D congestion-control 31.An application can rely on the connection to deliver all of its data without error and in the proper order. The sentence describes ( ). A flow control B congestion-control C reliable data transfer D connection-oriented service 32.It makes sure that neither side of a connection overwhelms the other side by sending too many packets too fast. The sentence describes ( ). A flow control B congestion-control C connection-oriented service D reliable data transfer 33.It helps prevent the Internet from entering a state of gridlock. When a packet switch becomes congested, its buffers can overflow and packet loss can occur. The sentence describes ( ). A flow control B congestion-control C connection-oriented service D reliable data transfer 34.The Internet ’s connection-oriented service has a name, it is ( ). A TCP B UDP C TCP/IP D IP 35.In In the the the following following following options, options, options, which which which service service service does does does not not not be be be provided provided provided to to to an an application by TCP?( ) A reliable transport B flow control C video conferencing D congestion control 36.The Internet ’s connectionless service is called ( ). A TCP B UDP C TCP/IP D IP 37.In the following options, which does not use TCP?( ) A SMTP B internet telephone C FTP D HTTP 38.In the following options, which does not use UDP?( ) A Internet phone B video conferencing C streaming multimedia D telnet 39.There are two fundamental approaches to building a network core, ( ) and packet switching. A electrical current switching B circuit switching C data switching D message switching 40.In ( ) networks, the resources needed along a path to provide for communication between the end system are reserved for the duration ofthe communication session. A packet-switched B data-switched C circuit-switched D message-switched 41.In ( ) networks, the resources are not reserved; a session’s messages use the resources on demand, and as a consequence, may have to wait for access to communication link. A packet-switched B data-switched C circuit-switched D message-switched 42.In a circuit-switched network, if each link has n circuits, for each link used by the end-to-end connection, the connection gets ( ) of the link link’’s bandwidth for the duration of the connection. A a fraction 1/n B all C 1/2 D n times 43.For ( ), the transmission rate of a circuit is equal to the frame rate multiplied by the number of bits in a slot. A CDMA B packet-switched network C TDM D FDM 44.( ) means that the switch must receive the entire packet before it canbegin to transmit the first bit of the packet onto the outbound link. A Queuing delay B Store-and-forward transmission C Packet loss D Propagation 45.The network that forwards packets according to host destination addresses is called ( ) network. A circuit-switched B packet-switched C virtual-circuit D datagram 46.The network that forwards packets according to virtual-circuit numbers is called ( ) network. A circuit-switched B packet-switched C virtual-circuit D datagram 47.In the following entries, which is not a kind of access network?( ) A residential access B company access C wireless access D local access 48.Suppose there is exactly one packet switch between a sending host and a receiving host. The transmission rates between the sending host and the switch and between the switch and the receiving host are R 1 and R 2, respectively. Assuming that the switch uses store-and-forward packet switching, what is the total end-to-end delay to send a packet of length L ? (Ignore queuing delay, propagation delay, and processing delay.) ( )A L /R 1+L /R 2 B L /R 1C L /R 2D none of the above 49.The time required to examine the packet ’s header and determine where to direct the packet is part of the ( ). A queuing delay B processing delay C propagation delay D transmission delay 50.The time required to propagate from the beginning of the link to the next router is ( ). A queuing delay B processing delay C propagation delay D transmission delay 51.Consider sending a packet of 3000bits over a path of 5 links. Each link transmits transmits at at at 1000bps. 1000bps. 1000bps. Queuing Queuing Queuing delays, delays, delays, propagation propagation propagation delay delay delay and and and processing processing delay are negligible. (6 points) (1).Suppose (1).Suppose the the the network network network is is is a a a packet-switched packet-switched packet-switched virtual virtual virtual circuit circuit circuit network. network. network. VC VC setup time is 0.1 seconds. Suppose the sending layers add a total of 500 bits of header to each packet. How long does it take to send the file from source to destination? (2).Suppose the the network network network is is is a a a packet-switched packet-switched datagram datagram network network network and and and a a connectionless connectionless service service service is is is used. used. used. Now Now Now suppose suppose suppose each each each packet packet packet has has has 200 200 200 bits bits bits of of header. How long does it take to send the file? (3).Suppose that the network is a circuit-switched network. Further suppose that that the the the transmission transmission transmission rate rate rate of of of the the the circuit circuit circuit between between between source source source and and and destination destination destination is is 200bps. Assuming 0.02s setup time and 200 bits of header appended to the packet, how long does it take to send the packet? Solution: (1). t=5*(3000+500)/1000+0.1=17.6s(2). t=5*(3000+200)/1000=16s(3). t=(3000+200)/200+0.02=16.02s。
第一章计算机网络概述第二章数据和信号第三章传输介质第四章●What is Encoding? Why must encoding be used for data transmission?(1)【什么是编码?】Convert internal data of a sender into line signals suitable for transmission is called encoding.(2)【数据发送时为什么要编码?】1) Electromagnetic signals in information process devices are not allowed transmitting directly over communication lines.2) The signal type of a device differs from the signal type of a communication line.3) The parameter requirements of device signals differs from the one of line signals.4) Specific requirements in synchronization, efficiency , error control, etc..★Because electromagnetic signals in information process devices are not allowed transmitting directly over communication lines, so encoding must be used for data transmission to converts internal data of a sender into line signals suitable for transmission.2.3.4.机内信号与线路类型不一样;机内信号参数与线路传输的要求不一样;同步、效率、纠错等方面的特殊要求●Which two techniques are used when analog data transmitted by digital signals?Which of them is the most important? Why?用数字信号传输模拟数据常用技术有哪两种?最常用的是?为什么?(1) Pulse Code Modulation(PCM) and Delta Modulation(DM).(2) Pulse Code Modulation(PCM) is the most important.(3) The principal advantage of DM over PCM is the simplicity of its implementation. In general, PCM exhibits better SNR characteristics at the same data rate.●What processes will be involved when analog data are digitized by PCMtechnique?用PCM技术将模拟数据数字化时,要经过哪些处理步骤?Sampling (PAM)---->quantization---->binary encoding---->digital to digital coding●Q4-1 List three techniques of digital-to-digital conversion.●Q4-4 Define baseline wandering and its effect on digital transmission.(1)In decoding a digital signal, the receiver calculates a running average of the received signal power. This average is called the baseline.(2)The incoming signal power is evaluated against this baseline to determine the value of the data element.(3)A long string of 0s or 1s can cause a drift in the baseline (baseline wandering) and make it difficult for the receiver to decode correctly.●Q4-5 Define a DC component and its effect on digital transmission.(Define) When the voltage level in a digital signal is constant for a while, the specturm creates very low frequencies(results of Fourier analysis). These frequences around zero,called DC(derect-current) components, that present problems for a system that can not pass low frequencies or a system that uses electrical coupling.(Effect) DC component means 0/1 parity that can cause base-line wondering. 直流分量的影响不仅仅是基线偏移,还有更重要的原因。
看看教材和课件,或看看原书作业答案。
第五章●Which modulation techniques are used in analog transmission? Which of themis the most susceptible to noise? Which of them is the mechanism commonly used in all modern modems.1.Amplitude shift keying ( ASK)Frequency shift keying ( FSK )Phase shift keying ( PSK)Quadrature Amplitude Modulation(QAM)2.The most susceptible to noise of the four digital-to-analog conversion techniques is ASK.3.The mechanism commonly used in all modern modems of them is QAM.●Q5-1 Define analog transmission.●Q5-2 Define carrier signal and explain its role in analog transmission.(Define) A sender produces an analog signal as fundamental wave to carry digital signals. The fundamental wave is called carrier signal.(explain) Digital data are converted into modulated signals through changing one or more of three characteristics of a carrier signal: amplitude, frequency and phase.Most familiar application is for transmitting digital data through the public telephone network via a modem.(A carrier is a single-frequency signal that has one if its characteristic (amplitude, frequency, or phase) changed to represent the baseband signal.【In analog transmission, the sending device produces a high frequency analog signal that acts as a base for the information signals (data). The base signal is called the carrier signal. It is to represent the baseband signal.】)●Q5-3 Definne digital-to-analog conversion.Digital-to-analog conversion is the process of changing one of the characteristics of an analog signal based on the information in digital data. It is also called modulation of a digital signal. The baseband digital signal representing the digital data modulations the carrier to create a broadband analog signal.●Q5-4 Which of characteristics of an analog signal are changed to represent thedigital signal in each of the following digital-analog conversions?a.ASK changes the amplitude of the carrier.b.FSK changes the frequency of the carrier.c.PSK changes the phase of the carrier.d.QAM changes both the amplitude and phase of the carrier.QAM is the most efficient of these options and is the mechanism commonly used in all modern modems.●Q5-5 Which of the four digital-to-analog conversion techniques(ASK,FSK,PSKor QAM) is the most susceptible to noise?Defend your answer.(Answer) The most susceptible to noise of the four digital-to-analog conversion techniques is ASK.(Define) Noise usually affects the amplitude; therefore, ASK is the modulation technique most affected by noise than phase or frequency.第六章●Which of the four multiplexing techniques is (are) suitable for analog channels?Which of them is (are) suitable for digital channels? (See P181 Questions Q6-3) Frequency-division and wavelength-division multiplexing are suitable for analogchannelsSynchronous time-division multiplexing and asynchronous time-divisionmultiplexing are suitable for digital channels.●Which of the four multiplexing techniques is (are) suitable for electricallinks? Which of them is (are) suitable for optical links?Frequency-division , Synchronous time-division and asynchronous time-division multiplexingare suitable forelectrical links .Wavelength-division multiplexing is suitable for optical links.光传输信道都属于模拟信道,而时分复用只适用于数字信道。