中国农业大学植物生理学本科课件 第一章 植物细胞
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:15.69 MB
- 文档页数:75
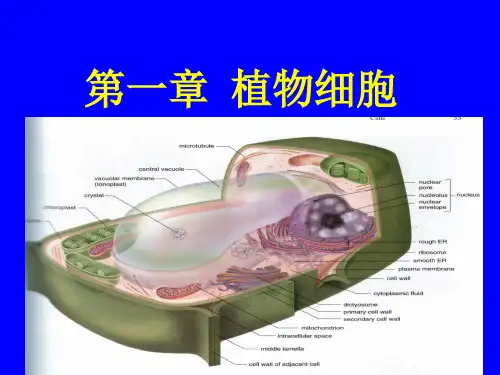








植物生理学——植物细胞## Plant Physiology Plant Cells.Introduction.Plant cells are the basic unit of life in plants. They are responsible for all of the plant's functions, from photosynthesis to reproduction. Plant cells are similar to animal cells in many ways, but they also have some unique features that allow them to thrive in their environment.Cell Structure.Plant cells have a cell wall, which is a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane. The cell wall protects the cell from its surroundings and helps to maintain its shape. The cell membrane is a thin layer of lipids that surrounds the cell wall and controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell.The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the cell. It contains all of the cell's organelles, which are small structures that perform specific functions. The nucleus is the largest organelle in the cell, and it contains the cell's DNA. The mitochondria are responsible for producing energy for the cell, and the chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis.Plant Cell Functions.Plant cells perform a variety of functions, including:Photosynthesis: Plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, which is a sugar that the plant uses for energy.Respiration: Plants use oxygen to break down glucose and produce energy.Transport: Plants transport water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves and other parts of the plant.Reproduction: Plants can reproduce sexually or asexually.Plant Cell Adaptations.Plant cells have a number of adaptations that allow them to thrive in their environment. These adaptations include:The cell wall: The cell wall protects the cell from damage and helps to maintain its shape.The vacuole: The vacuole is a large, fluid-filled space that helps to maintain the cell's turgor pressure.The chloroplasts: The chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, which allows plants to convert sunlightinto energy.## 植物生理学——植物细胞。