外国人B类工作签证
- 格式:docx
- 大小:7.40 KB
- 文档页数:1

外国人申请工作签证流程以外国人申请工作签证流程为标题,我们来了解一下外国人申请工作签证的具体步骤和流程。
第一步:了解目标国家的政策和要求外国人申请工作签证首先需要了解目标国家的政策和要求。
不同国家对于外国人的工作签证政策和要求可能存在差异,因此需要仔细研究目标国家的相关规定。
第二步:选择合适的工作签证类型根据目标国家的政策和要求,外国人需要选择适合自己的工作签证类型。
常见的工作签证类型包括技术移民签证、工作签证、投资签证等,每种类型都有不同的申请条件和流程。
第三步:准备申请材料申请工作签证需要准备一系列的申请材料。
一般来说,申请人需要提供有效的护照、签证申请表、照片、工作合同或雇佣证明、教育和工作经历证明、财务证明等材料。
具体的申请材料清单可以向目标国家的使领馆或移民局查询。
第四步:递交申请准备好申请材料后,外国人需要将材料递交给目标国家的使领馆或移民局。
一般来说,申请人可以通过邮寄方式或亲自前往递交申请材料。
第五步:缴纳申请费用申请工作签证通常需要缴纳一定的申请费用。
费用金额和支付方式可能因目标国家的政策而有所不同。
申请人需要按要求缴纳申请费用,并保留好相关的支付证明。
第六步:面试和审理一些国家对于工作签证申请会进行面试和审理。
申请人可能需要参加面试,回答相关问题并提供进一步的证明材料。
审理过程可能需要一定的时间,申请人需要耐心等待结果。
第七步:签证结果和签发经过面试和审理后,目标国家会将签证结果通知申请人。
如果申请成功,申请人需要按要求前往使领馆或移民局领取签证。
签证的签发时间和有效期会根据目标国家的政策而有所不同。
第八步:抵达目标国家成功获得工作签证后,外国人可以按照签证的要求和有效期前往目标国家。
在抵达目标国家后,申请人需要按照签证要求进行工作或居留。
需要注意的是,不同国家的工作签证流程可能存在差异,以上是一般的申请流程。
建议申请人在进行具体申请前,仔细研究目标国家的政策和要求,并咨询相关专业人士或机构的建议。

美国签证种类一.非移民签证A----A1:大使,政府部长,外交官,及其家属A2:政府官员或职员及其家属A3:(A1A2)随员侍从及家属B----B1:商务考察人员----考察市场,推销或购买产品设备,洽谈合同和商务纠纷,参加商展或会议,短期培训。
签证特点:签发最多,提交材料简单,简便快捷。
要求:邀请方,中方,申请人自身的相关材料。
必须证明充足的赴美理由和返回的约束力。
B2:短期观光游客和短期探亲人员探亲----必须证明是美国公民永久居民的亲戚朋友未婚夫妻K,及F1 J1 M1 H1 H2 L1签证人的配偶及未满21岁子女,且希望单独去团聚。
要求:对方邀请信,身份证明,经公证的资产,经济担保书,申请人和对方关系感情,个人财产的证明。
旅游----观光,娱乐,访友,就医,参加会议,处理个人事务。
此类签证尚未对中国个人开放,且要求苛刻。
C----过境美国的人员D----海员或飞行人员E----E1:与美国有贸易协定国家的贸易商及配偶子女E2:与美国有贸易协定国家的投资人及配偶子女F----学者,大中小学校语言学校的学生。
程序:规划留学方案→联系学校→申请报名(填表,学校研究机构或单位领导的推荐信,个人简历,读书计划,成绩单及学历证明,财力证明,各种公证材料,申请费)→得到录取通知书或接收信,并取得I-20表→面签(材料审核:敏感专业和1%-5%材料抽查)→体检。
关键点:a. 为获得美国学生签证,申请人必须证明他们唯一的目的(而不是首要的目的)是学习。
b. 他们有能力并愿意做全日制学生。
c. 在不从事未经许可的工作的前提下,他们有足够的资金来支付学费、生活费以及应付突发事件的全部费。
d. 他们有不可分离的社会、经济和其它因素使其在完成计划的学业后离开美国。
e. 申请人必须证明他们已无条件地被有资格招收留学生的院校录取。
学校必须提供填写完整的SEVISI-20表和录取通知。
f. 申请人还应该证明他们有能力顺利地完成学业,并出具一些能证明自己学习能力和教育背景的资料,如:毕业证书、成绩单(包括所学的科目及成绩)以及学校所要求的其它成绩(如GRE、GMAT、TOEFL 等)。

(1)A类签证(即外交公务签证)的签发对象分别为:A-1:外国政府派驻美国的大使、公使、职业外交官员、领事官员及其家属成员;A-2:外国政府的其他官员、雇员及其家属成员;A-3:A-1和A-2类签证获得者的随从、仆人、私人雇员及其家属成员。
(2)B类签证(即商务旅游签证)的签发对象分别为:B-1:以经商贸易、考察访问等处理有关事务为目的的短期逗留人员;B-2:短期探亲访友、旅游观光者。
(3)C类签证(即过境签证)的签发对象分别为:C-1:过境的外国人;C-2:过境去联合国纽约总部的外国人;C-3:过境的外国政府官员、随从、仆人、私人雇员及其家属。
(4)D类签证(即机组人员,海员签证)的签发对象为:各国国际航班上的机组人员和轮船上的海员。
(5)E类签证(即国际条约或协议投资者签证)的签发对象分别为:E-1:根据国际条约或协议在美国经商者及其配偶和子女;E-2:根据国际条约或协议在美国投资者及其配偶和子女。
(6)F类签证(即留学签证)的签发对象分别为:F-1:留学者(即自费留学者);F-2:F-1签证获得者的配偶和子女。
(7)G类签证(即国际组织员工签证)的签发对象分别为:G-1:政府承认的外国政府派驻国际机构组织的首席常驻代表、代表下属的工作人员及上述人员的家属成员;G-2:政府承认的外国政府派驻国际机构组织的其他代表及其家属成员;G-3:政府未承认的外国政府国际机构组织的代表及其家属成员或者非国际机构组织成员的外国政府代表及其家属成员;G-4:国际机构组织官员,雇员及其家属成员;G-5:上述G1-G4签证获得者的随从、仆人、私人雇员及其家属成员。
(8)H类签证(即临时雇员及接受训练者签证)的签发对象分别为:H-1:有特殊专业技能的临时工作的外国人;H-2:因国内所缺乏的某种工种或职业而临时工作的外国人;H-3:接受各种培训的外国人;H-4:上述H-1~H-3签证获得者的配偶和子女。
(9)I类签证(即新闻从业人员签证)的签发对象为:驻美国的各国新闻、广播、电视等组织机构的代表、记者及其配偶和子女。

外国人来华工作签证申请的积分分类标准(试行)!最近很多客户咨询,什么条件能办理a类人才签证,外籍人有某个成就能不能作为申请签证的条件。
今天小编就这一类问题给大家一个标准的参考文件!建立科学、实用的外国人才评估体系,注重能力、实绩和贡献,突出市场评价、国际同行评价等市场需求导向,综合运用计点积分制、外国人在中国工作指导目录、劳动力市场测试和配额管理等,将来华工作外国人分为A、B、C三类,按标准实行分类管理。
一、外国高端人才(A类)中国经济社会发展急需的科学家、科技领军人才、国际企业家、专门特殊人才等“高精尖缺”外国高端人才,符合以下条件之一的,确定为A类,实行“绿色通道”和“容缺受理”服务。
(一)入选国内人才引进计划的经中共中央组织部、人力资源和社会保障部、国家外国专家局批准或备案同意的副省级以上人才主管部门认定的人才引进计划的入选者。
(二)符合国际公认的专业成就认定标准的1.诺贝尔奖获得者(物理、化学、生理或医学、经济学奖)。
2.以下奖项获得者:美国国家科学奖章、美国国家技术创新奖章;法国全国科研中心科研奖章;英国皇家金质奖章;科普利奖章;图灵奖;菲尔兹奖;沃尔夫数学奖;阿贝尔奖;拉斯克奖;克拉福德奖;日本国际奖;京都奖;邵逸夫奖;著名建筑奖;著名工业设计奖。
3.各国科学院院士、工程院院士。
4.担任过国际标准化组织(ISO)等国际知名学术机构和科教类国际组织委员、会员、理事的。
5.各国国立研究所或国家实验室主任负责人、高级研究员。
6.各国科技计划项目成果负责人、首席科学家或主要成员。
7.担任过国际高水平科技期刊(JCR一、二区)正、副总编和高级会员。
8.以第一作者或通讯作者(含同等贡献作者)在国际高水平科技期刊(所在专业领域《期刊引用报告》JCR一、二区)发表论文3篇。
9.曾任全球排名前200名大学中层以上管理职务或聘为教授、副教授的或曾任全球排名前500名大学高层以上管理职务或聘为教授的。
10.曾任世界500强企业总部高层管理职位和技术研发主要成员、二级公司或地区总部副总经理以上管理职位、技术研发负责人。

代号有些国家为了便于识别和管理,根据申请签证者的不同事由,用各种不同的字母代号标明在所签发的签证上。
这种字母代号就是签证代号。
目前使用签证代号最多的是美国,其中非移民签证代号有18种之多,每个种类再细分为多项。
简介如下:(1)A类签证(即外交公务签证)的签发对象分别为:A-1:外国政府派驻美国的大使、公使、职业外交官员、领事官员及其家属成员;A-2:外国政府的其他官员、雇员及其家属成员;A-3:A-1和A-2类签证获得者的随从、仆人、私人雇员及其家属成员。
(2)B类签证(即商务旅游签证)的签发对象分别为:B-1:以经商贸易、考察访问等处理有关事务为目的的短期逗留人员;B-2:短期探亲访友、旅游观光者。
(3)C类签证(即过境签证)的签发对象分别为:C-1:过境的外国人;C-2:过境去联合国纽约总部的外国人;C-3:过境的外国政府官员、随从、仆人、私人雇员及其家属。
(4)D类签证(即机组人员,海员签证)的签发对象为:各国国际航班上的机组人员和轮船上的海员。
(5)E类签证(即国际条约或协议投资者签证)的签发对象分别为:E-1:根据国际条约或协议在美国经商者及其配偶和子女;E-2:根据国际条约或协议在美国投资者及其配偶和子女。
(6)F类签证(即留学签证)的签发对象分别为:F-1:留学者(即自费留学者);F-2:F-1签证获得者的配偶和子女。
(7)G类签证(即国际组织员工签证)的签发对象分别为:G-1:政府承认的外国政府派驻国际机构组织的首席常驻代表、代表下属的工作人员及上述人员的家属成员;G-2:政府承认的外国政府派驻国际机构组织的其他代表及其家属成员;G-3:政府未承认的外国政府国际机构组织的代表及其家属成员或者非国际机构组织成员的外国政府代表及其家属成员;G-4:国际机构组织官员,雇员及其家属成员;G-5:上述G1-G4签证获得者的随从、仆人、私人雇员及其家属成员。
(8)H类签证(即临时雇员及接受训练者签证)的签发对象分别为:H-1:有特殊专业技能的临时工作的外国人;H-2:因国内所缺乏的某种工种或职业而临时工作的外国人;H-3:接受各种培训的外国人;H-4:上述H-1~H-3签证获得者的配偶和子女。

商务及旅游签证我们申请B-1签证。
B-1签证颁发给赴美从事短期商务活动、参加科技/教育/专业/商务领域的会议、处置房产或洽谈合同的申请人。
B-1申请人还必须证明有充足的资金支付在美停留期间的费用, 并证明其在祖国有牢固的社会、经济和其它方面的联系以迫使其在美短期、合法访问后如期返回。
所有签证申请人都应该提前做好准备, 以便能够在面谈时出示下列材料和其它任何与签证申请有关的支持材料。
如有可能,最好使用原件而不是影印件。
请勿通过传真、电子邮件或邮寄方式向使/领事馆递交任何支持性文件。
必要材料1、护照原件:至少有三张空白页,最后一页签名。
六个月以上有效期2、近期1张51mm*51mm白底彩色照片3、DS-160表格确认单页(可代填写),标注中文电码,联系方式并签名。
4、在读证明原件:包括学校联系方式,申请人的姓名、出生日期、护照号码、入学的时间,赴美国的目的、具体时间和回国保证,赴美国的费用由谁负担,在读证明信需要由相关负责人签字并加盖公章,并标明签字人的姓名及职务(最好是校长)。
5、英文邀请函原件:邀请函内容必须必须体现以下信息:美国主办方名称、地址、电话号码、传真号码,签证申请人的姓名、护照号码、计划在美国逗留的时间、赴美国的行程安排、由邀请单位法人代表签名,并注明签字人的姓名及职务。
辅助材料:1、身份证原件2、户口本原件(如和父母不在同一本户口本上,需提供父母户口本)3、父母结婚证原件4、父母房产证原件5、父母汽车行驶证原件6、申请人父母最近一年的银行出入账明细,及存折、存单原件7、父母公司营业执照副本原件及税务登记证副本原件或企业产权证、资产证明8、申请人父母的在职证明:说明职务、在此单位工作年数、每月收入及年总收入9、申请人父母的名片或工作证10、全家福照片(包括全体的家庭成员),能够证明有一个幸福的家庭说明:1. 有效护照:如果您的护照将在距您预计抵美日期的六个月内过期、或已损坏、或护照上已无空白的签证签发页, 请在前来面谈之前先申请一本新护照。

2022年美国h1b新政策规定美国h1b签证新政策美国移民局(USCIS)发布了一则最新规定,旨在改进职业移民(EB1、EB2、EB3)的相关规定,并且修改了相关法案,帮助美国雇主更好地雇用和留住高科技外国员工。
其中最大的亮点是H1B持有者在失去工作后,将有长达60天的宽限期寻找新的雇主或者延长合法身份。
这项法案将从2022年1月17日起生效。
这项法案主要包括:更好地帮助美国雇主雇用和留住高科技外国员工(I-140移民申请表获批者),同时为这些员工提供了稳定性和工作灵活度。
这项规则提高了这些员工发展自己职业生涯的可能性,他们可以接受升职,在公司内部改变目前职位,或者改变雇主,以及寻求其他就业机会。
确保I-140获批者的移民申请继续有效(只要I-140申请获批或调整身份申请在180天以上),不会因为雇主撤回申请或公司倒闭等其他因素而被DHS自动作废申请。
只要I-140申请未因欺骗、材料不实等原因被作废,申请人可在调整身份、申请合法永久居住权过程中保留其优先日期(prioritydate),方便申请人在此期间升职、换雇主,而不用担心失去移民签证排期。
允许具有E-3(澳洲公民工作签证),H-1B,H-1B1(智利和新加坡公民工作签证),L-1(跨国经理人签证)或O-1(特殊人才签证)非移民身份的高科技员工(包括适用于任何宽限期内)在以下情况下申请就业许可(employmentauthorization):是获批的I-140表格申请的主要受益人;其优先日期没有获得移民签证的发放;可以证明存在令人信服的情况下,DHS可以自行决定颁发就业许可。
注:这种就业许可只能在有限的情况下更新,并且必须每年申请延长。
为E-1(贸易商签证),E-2(投资人签证),E-3,L-1和TN(墨西哥和加拿大公民工作签证)非移民签证申请人设定两个长达10天的宽限期,为其准备开始在美国工作、离开美国或以其他方式维持合法身份提供充分时间。

美国非移民签证(B1-B2)须知美国驻华使馆地址:北京市朝阳区安家楼路55号关于B1-B2签证类型:该类型是一种组合签证类型,适用范围包括旅游、探亲、访友、商务等几种情况。
即无论您是以旅游、探亲、访友、商务之中的那种目的赴美,都是以B1-B2签证申请。
但具体资料则根据个人目的不同而有所区别。
签证领区划分:北京领区:北京、天津、河北、湖北、河南、山东、山西、陕西、甘肃、青海、内蒙、新疆、江西、湖南沈阳领区:辽宁、吉林、黑龙江成都领区:云南、贵州、四川、重庆、西藏广州领区:广东、广西、福建、海南上海领区:上海、江苏、浙江、安徽领区按常住地划分,请根据自身情况在相应的使领馆进行面试.美国B1-B2签证预约所需资料--所有人员均适用美国B1-B2签证面试所需资料――在职人员美国B1-B2签证面试所需资料――退休人员美国B1-B2签证面试所需资料――无业人员/家庭主妇/自由职业美国B1-B2签证面试所需资料――学生祝您签证顺利通过根据实际情况修改,公司抬头纸打印,领导签字盖章附件1:在职证明参考样本---在职人员使用TO: VISA SECTIONDear Sirs,Mr. / Ms. XXX (申请人姓名) works in our company from XX.XX.XXXX(现公司入职时间某年某月某日).He/She will be on travelling purposes visiting your country from XX.XX.XXXX to XX.XX.XXXX(出国时间). All the expenses include air tickets, transportation, accommodation and health insurance will be covered by himself / herself. He/She will be back ontime as per his/her schedule planned and shall continue to work in our company after his/her visit to America.Name Date of Birth Passport-No. Position Annual IncomeXXXX XXXXXX GXXXXXX XXXX RMB XXXXYour kind approval of this application will be highly appreciated.Best Regards,Name of the leader(领导人姓名拼音)Position of the leader(领导人职位)Signature (领导的签名)Company’s Stamp(公司盖章)Tel: XXX-XXXXXXE-Mail: XXXXXXAdd: XXXXXXCompany Name: XXXXXXThe registration number as which the company is registered in the business bureau(营业执照注册号):XXXXXX注:1. 在职证明需打印成英文,请删掉参考样本中所有中文的提示语,保持在职证明为全英文格式2. 凡样本中XX的地方,均需相应填写您的相关信息,不要保留XX在完成后的在职证明中3.()括号中为我们为您更加清晰在职证明的内容而标注的解释,不要保留在完成后的在职证明中4.请不要将“附件1:在职证明参考样本”字样保留在完成的在职证明中致:签证官XXX 先生/女士自X年X月X日(现公司入职时间某年某月某日)在我公司工作。

中国外国人工作签证积分制度
中国外国人工作签证积分制度是指2020年1月1日正式实施的中国外国人工作许可制度改革,将原来的按工作类型分为三类和等级制度改为按积分申请制度。
根据积分制度,外国人在中国申请工作签证时,需要根据一定的条件和要求来积累一定的积分,积分达到一定程度才能够获得工作签证。
积分制度主要包括以下几个方面的积分:
1. 学历背景:学士学位、硕士学位、博士学位等不同学历背景对应不同的积分。
2. 工作经历:工作年限越长,所获得的积分越高。
同时,具有国外知名企业工作经历也会加分。
3. 年龄:年龄在18岁至60岁之间,根据不同年龄段给予不同的积分。
4. 工作薪资:工作薪资越高,积分越高。
5. 中文水平:根据外国人的中文水平,分为A级、B级、C级和无中文水平四个等级,不同等级对应不同的积分。
6. 科技创新能力:对于在相关领域有突出贡献和专利或有较高技能的人才,可以额外加分。
外国人在申请工作签证时,需要满足一定的积分要求才能够被
批准签证。
根据积分制度,不同地区和行业对外国人的积分要求也可能有所不同。
中国外国人工作签证积分制度的实施,旨在吸引更多的高技能、高层次外国人才来华工作,促进人才流动和经济发展。

中国人去美国打工要有什么条件
中国人去美国打工,首先要满足美国移民局的要求,即必须拥有有效的签证。
美国移民局
提供了多种签证,其中最常见的是工作签证,也就是H-1B签证。
H-1B签证是一种专业移民签证,主要针对那些有特殊技能的外国人,如工程师、科学家、计算机专家等。
申请H-1B签证的外国人必须满足以下条件:
1、具有有效的技术文凭或学位,并且在技术领域有足够的经验;
2、有一家美国雇主,并且雇主已经向美国移民局提出了申请;
3、有足够的资金来支付在美国的生活费用;
4、有足够的英语能力,能够在美国社会中融入;
5、有足够的健康保证,不会对美国社会构成威胁。
此外,申请H-1B签证的外国人还需要提供一些其他的材料,如个人简历、学历证明、职
业资格证书等。
总之,中国人去美国打工,必须满足美国移民局的要求,并且提供有效的签证,以及其他相关的材料。
只有满足这些条件,中国人才能够在美国找到合适的工作,实现自己的梦想。
美国签证基本知识一、美国签证有多少种?(1) A类签证(即外交公务签证)的签发物件分别为:A-1:外国政府派驻美国的大使、公使、职业外交官员、领事官员及其家属成员;A-2:外国政府的其他官员、雇员及其家属成员;A-3:A-1和A-2类签证获得者的随从、仆人、私人雇员及其家属成员。
(2) B类签证(即商务旅游签证)的签发物件分别为:B-1:以经商贸易、考察访问等处理有关事务为目的的短期逗留人员;B-2:短期探亲访友、旅游观光者。
(3) C类签证(即过境签证)的签发物件分别为:C-1:过境的外国人;C-2:过境去联合国纽约总部的外国人;C-3:过境的外国政府官员、随从、仆人、私人雇员及其家属。
(4) D类签证(即机组人员,海员签证)的签发对象为:各国国际航班上的机组人员和轮船上的海员。
(5) E类签证(即国际条约或协议投资者签证)的签发对象分别为:E-1:根据国际条约或协定在美国经商者及其配偶和子女;E-2:根据国际条约或协定在美国投资者及其配偶和子女。
(6) F类签证(即留学签证)的签发物件分别为:F-1:留学者(即自费留学者);F-2:F-1签证获得者的配偶和子女。
(7) G类签证(即国际组织员工签证)的签发物件分别为:G-1:政府承认的外国政府派驻国际机构组织的首席常驻代表、代表下属的工作人员及上述人员的家属成员;G-2:政府承认的外国政府派驻国际机构组织的其他代表及其家属成员;G-3:政府未承认的外国政府国际机构组织的代表及其家属成员或者非国际机构组织成员的外国政府代表及其家属成员;G-4:国际机构组织官员,雇员及其家属成员;G-5:上述G1-G4签证获得者的随从、仆人、私人雇员及其家属成员。
(8) H类签证(即临时雇员及接受训练者签证)的签发物件分别为:H-1:有特殊专业技能的临时工作的外国人;H-2:因国内所缺乏的某种工种或职业而临时工作的外国人;H-3:接受各种培训的外国人;H-4:上述H-1~H-3签证获得者的配偶和子女。
H-1B常见问题解答1. 问:什麽是H-1B?答: H-1B是一种非移民签证,专门为在美国工作的专业技术人员设计。
在H-1B申请过程中,雇主为申请人,外籍员工为受益人。
该外籍员工最低必须拥有学士学位或者同等学历。
H-1B签证对于工程师、教授、研究员、软件设计师以及其他外籍专业人员来说是比较合适的。
一般情况下H-1B受益人可以在美国工作六年。
2. 问:想获得H-1B身份一般需要多长时间?答:通常情况下,移民局处理H-1B申请的时间大概是2-3个月。
外籍员工(受益人)或者雇主(申请人)在缴纳$1,225美元的加急处理费后,可以要求对申请进行加快处理。
加快处理程序可以保证在15天内得到最终处理结果,如果移民局没有在15天内给出处理结果,$1,225美元的加急处理费将会被退还。
请点击这里了解更多有关移民局的服务中心的处理时间的信息。
3.问:递交H-1B申请都需要哪些步骤?答:一般申请步骤如下:1. 获得美国雇主提供的工作机会;2. 通过查询State Wage Agency (SWA)或者其他调查获知工作的现行工资(Prevailing Wage);3. 递交Labor Condition Application (LCA)申请,并获得劳工部的批准;4. 填写移民局H-1B表格,准备好雇主出具的申请书;5. 将准备完毕的并已经签好字的所有申请资料递交到移民局。
我们协助客户准备的步骤是2、3、4和5。
4. 问:什麽是现行工资标准?确定现行工资标准的关键因素都有哪些?答:「现行工资标准」这一概念由劳工部的相关规则来定义,指在该工作所处的区域内,从事相同或相似的工作的工人的平均工资水平。
雇主必须保证支付H-1B雇员高于以下两条标准的报酬:1. 雇主支付给其他拥有类似经验和资格的员工的工资水平,或者2. 该工作所处地区的现行工资标准,由城市统计区(Metropolitan Statistical Area,或者MSA)和狭义的大城市统计区(Primary Metropolitan Statistical Area,或者PMSA)定义。
美国签证种类:A-1. 外国大使、高级长官、外交或领事官员以及他们的家庭成员A-2. 其他外国政府官员或职员以及他们的家庭成员A-3. A-1和A-2签证持有者的服务员、仆人或私人助理以及他们的家庭成员B-1. 短期商务访问B-2. 短期旅游C-1. 外国人过境C-2. 往返联合国总部和外国并且有资格的外侨过/转境C-3. 外国政府官员、家庭成员、服务员、仆人以及私人助理过境D- 乘务员E-1. 商人、配偶和未成年子女E-2. 投资者、配偶和未成年子女F-1. 进入合法学校全日制学习的学生F-2. 学生的配偶和未成年子女G-1. 国际组织的被认可的外国政府成员国的首席代表、成员和家庭成员G-2. 其他被认可的外国政府成员国的代表G-3. 国际组织的非被认可的外国政府的非成员国的首席代表、成员和家庭成员G-4. 国际组织的官员或职员以及家庭成员G-5. G-1、G-2、G-3和G-4签证持有者的服务员、仆人或私人助理以及家庭成员H-1A. 专业护士H-1B. 从事指定专业职业的短期专业工人H-2A. 从事短期或季节性的短期农艺工人H-2B. 从事短期服务或劳动的技术和非技术工人H-3. 受训者H-4. H-1、H-2和H-3的配偶和未成年子女I 外国媒体的代表、配偶和未成年子女J-1. 被核准项目的交流访问学者J-2. J-1交流访问学者的配偶和子女K-1. 美国公民的未婚夫(妻)移民美国K-2. K-1未婚妻的子女L-1A. 赴美国分公司的执行者和管理者L-1B. 专业知识雇员L-2. L-1的配偶和子女M. 学生在假期来美进行短期职业培训签证,这种培训不可以是语言学校,一般为大学N-8. 被指定为特殊移民的外侨子女的父(母)亲N-9. 被指定为特殊移民的父(母)亲的子女NATO-1. 北大西洋公约组织成员国的永久首席代表以及家庭成员NATO-2. 北大西洋公约组织成员国的其他代表以及家庭成员NATO-3. 北大西洋公约组织成员国的代表的协同官员以及家庭成员NATO-4. 北大西洋公约组织其他官员以及家庭成员NATO-5. 不符合NATO-4条件的,被代表北大西洋公约组织使团雇佣的专家和他们的随从NATO-6. 在北大西洋公约组织控制下,随从武力进入的工作人员和他们的随从NATO-7. NATO-1、 NATO-2、 NATO-3、 NATO-4、 NATO-5和 NATO-6的服务员、仆人或私人助理以及家庭成员O-1. 在科学、艺术、教育、商业方面有杰出能力的外国人或运动员O-2. 跟随O-1签证持有者的某些外国人O-3. O-1签证持有者的家庭成员P-1. 国际运动员或国际演艺团体P-2. 参加交流计划的艺术或演艺团体P-3. 参加特殊文化交流计划的艺术或演艺团体P-4. P-1、 P-2和 P-3的配偶或子女Q-1. 国际文化交流计划的参与者R-1. 宗教人士R-2. R-1的配偶或子女S-5. 提供违法组织或企业紧急信息的个人S-6. 提供与恐怖组织有关信息的个人TN. 北美自由贸易法案的从业人员TD. 北美自由贸易法案从业人员的配偶或子女。
留学生美国求职签证综述|F1、OPT、H1B、EB1(2、3、4、5)随着美国移民政策的日趋收紧,越来越多的赴美留学生关心在完成美国的学业后如何能够留在美国继续工作并最终获得美国绿卡。
一般情况下,留学生想通过国家利益豁免或者杰出人才这个途径实现移民的可能性极小,所以学生签证转为绿卡最常见且最传统的方式就是通过F1(学生签证)-H1B(工作签证)-绿卡这个流程来进行申请,以及其他几个途径。
看着很多前辈和同辈回国之后,因为不了解美国政策,毕业和课程结束之后就回国了,现在感觉十分可惜,下面给大家介绍一下OPT(免签实习期),H1B(美国专业技术人员工作签证),绿卡(美国永久居民卡),EB5,EB1,L1和O1等的相关知识。
F1转OPT美国F1学生在毕业之后有一年的Optional Practical Training时间,简称OPT。
申请OPT必须先由学校批准,然后再由美国国土安全局批准,最终获得OPT资格。
申请人必须持有效的F-1签证,并在完成学位前的90天内开始申请OPT;申请的OPT工作必须和本人所学的专业相关,否则视为非法工作;如果学生在毕业后60天内仍未申请到OPT,那么必须离开美国。
OPT是很多在美国的中国留学生在毕业之后继续留在美国的常用方式。
申请人可以在学生签证到期之后利用OPT的合法身份一边实习,一边寻找合适的工作。
OPT的6大问题释疑1. OPT的时间会被毕业前的实习占用吗?OPT严格意义上分为Pre-completion和Post-completion两种,即毕业前和毕业后。
Pre-completionOPT必须在本专业学习满一年以后才可以开始,且必须是做兼职,每周工作不可超过20小时,其工作天数也会计入OPT总时间。
不难发现Pre-completion OPT的要求和CPT是有许多相似之处的,所以作为学生来讲,毕业前最好使用CPT,以节约OPT的宝贵时间。
2. OPT期间只能做一份工作?NO! 在40小时/每周的法定工作时间内,你可以做多份兼职工作或一份全职工作;换工作也是相对灵活的,只要累计不工作时间保证在90天之内,都可以在EAD卡的保障下合法工作。
美国一直以来都是中国人选择的移民目的国。
尤其近几年,越来越多中国人在美国买房、来美国读书,美国移民,赴美生子都是挤破了头想来美国。
美国到底什么好,让中国人前仆后继移民到此呢?除了众所周知的,美国是世界第一的经济强国、拥有全球一流的教育水平外,美国的福利也是杠杠的。
在此也欢迎移友们加入美国移民交流群,与华人、律师、移民一起交流互助~H1B签证是一种非移民工作签证,发放给美国公司雇佣的外国籍有专业技能的工作人员,主要适用群体是美国留学生。
由于每年申请人数都是发放配额的几倍之多,所以移民局采取抽签的方式进行筛选,硕博学历要比本科抽中的几率更高。
H1B工作签证项目H-1B签证仅适用于从事特殊职业的工作、与国防部合作研究和开发项目有关的杰出优势和能力的工作、或者有杰出价值和能力的时尚模特工作的人群。
H1B工作签证三个类别的申请要求H1B工作签证申请流程1. 雇主向劳动部申请LCA(仅限H-1B特殊职业和H-1B3时尚模特)2. 雇主向美国移民局USCIS提交Form I-129,并附上劳动部批准的LCA(仅限H-1B特殊职业和H-1B3时尚模特);3. Form I-129批准以后,在美国境外的雇员通过美国驻海外领事馆申请H-1B签证,除此之外,入境时还必须向美国海关及边境保护局申请入境许可。
H1B工作签证对美国雇主的要求申请H-1B特殊职业和H-1B3时尚模特这两个类别的雇主必须向劳动部申请LCA(Labor condition application),申请中涉及宣誓,如果违反会导致雇主被罚款、监禁或其他制裁。
雇主需要宣誓遵守劳动法要求:1. 雇主为雇员支付的薪水不得低于相同水平的其他雇员,或者不能低于当地的现行工资;2. 雇主提供的工作条件不会对雇员产生负面影响,雇主申请LCA期间雇主经营场所没有罢工或停工行为,提交LCA的通知已经交给工会代表或者张贴在经营场所。
H1B签证有效期限H-1B签证有效期最多为3年,可以申请延长停留时间,但是最多停留时间不能超过6年。
H-1b Visa Petition General Steps/visas/h1b/h1b-visa-requirements.html1. 1 Discuss the wage and position /OESQuick.aspx /h1b-minimum-wage-or-lca-prevailing-wage-for-a-position-in-an-area-in-usa/1.2 The employer must demonstrate that the position is one requiring a professional in a specialty occupation and that the intended employee has the required qualifications. Definition of a specialty occupation is an that requires a theoretical and practical application of a body of highly specialized knowle dge, and the attainment of a bachelor’s or higher degree in the specific specialty or its equivalent as a minimum for entry into the occupation.2. Employer’s requirementsA U.S . employer is a person, firm, corporation, contractor or other association or organization in the United States with an IRS tax identification number. There must be an employer-employee relationship, as indicated by the fact that the employer may hire, fire, pay, supervise or otherwise control the work of the employee.In addition to showing that both the job requirements and the applican’s credentials or experience are “professional”, the employer must also meet the Department of Labor (“DOL”) requirements and file Form I-129 (H-1B petition”) with the USCIS for permission to employ the foreign national.Prior to filing the H-1B petition with the USCIS, an employer must file a labor condition application (“LCA”) with the Department of Labor. Employers affirm in the labor condition application that the wage offered to the applicant is at least as high as that paid by the employer for the same type of job, and the number equals or exceeds the prevailing wage for the job in the same geographical area; that working conditions will not adversely affect those workers similarly employed; that there is no strike or lockout at the employer’s premises and that the notice of the LCA has been given to current employees.3. After the company has successfully filed a LCA, they are free to apply for the visa. An employer is charged with the responsibility of filing for the visa on behalf of the employee as they are not allowed to self-petition.4. Waiting for approval by the USCIS is a torturous task for most. There are variousf actors the USCIS considers in order to approve a person’s H-1B visa. These factors may include:∙The person the employer wants to hire that is their level of education and expertise ∙The position the employer offers in the sense that it must require a degree holder for example, one cannot apply for a H-1B visa for the position of a cleaning lady.∙The employer is also a key factor since the company must be financially capable and be of adequate size in order for their employee to be granted a H-1B visa.Can my company make H1B visa applications?Any US employer can sponsor an H1B petition, provided it has an IRS Tax Number, also known as an IRS Number or Tax ID Number. This number is needed for obtaining approval of the Labor Condition Application (LCA), which is an essential preliminary to the H1B petition itself. However, employers should take note that sponsoring an H1B petition involves them making a number of undertakings, enforceable by heavy civil and criminal penalties: These undertakings are:-∙To pay the H1B worker at least the higher of the wage paid to similar workers in the same company or the "prevailing wage" (usually determined by the relevant State Employment Services Agency) for the occupation in the area the worker will be employed;∙That the recruitment of the H1B worker(s) will not adversely affect the conditions of the employer's US-resident employees in similar jobs;∙That there is no strike or lockout occurring at the time the Labor Condition Application is submitted, and that the approved LCA will not be used to support petitions for H1B aliens to be employed at the site of any subsequent strike or lockout;∙That a copy of the LCA form will be given to the H1B worker and either given to the bargaining representative of employees in similar occupations or (if there is no bargaining representative) posted in 2 conspicuous locations for at least 10 days in the place the H1B alien will be working;∙To maintain records of the LCA and the H1B alien's employment for inspection by the US Department of Labor.Note that the prevailing wage is generally lower for non-profit and academic/research organizations.H1B Beneficiary EligibilityIn order to qualify for an H1B visa, the alien must demonstrate that s/he is able to work in the 'speciality occupation' for which s/he is being hired by the sponsoring employer. This can be demonstrated by:-∙Possession of a relevant US college degree;∙Possession of a non-US college degree (and, generally, 3 years' relevant high-level work experience) independently evaluated as being equivalent to a relevant US college degree;∙Possession of at least 12 years' high-level work experience, independently evaluated as being equivalent toa US college degree; or∙Possession of any relevant State or Federal license that may be required in order to practice in a particular profession.NB: If there is a requirement for a State or Federal license in order to practice any 'speciality occupation', then the alien must generally possess such a license in order to qualify for an H1B visa. For example, doctors, lawyers, accountants and similar professionals must generally have passed the relevant state licensing examination and be in all other respects qualified to practice in the State of intended employment./us/investor_h-1b.htm#fein----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- How to Petition for an H-1B VisaFrom an employer perspective, H-1B eligibility is much more complex. The employer must file the petition for the visa on behalf of the employee, who is not allowed to self-petition. Every company, regardless of size or age, must petition for one of the 65,000 H-1B visasthat are made available every April 1st by U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services.The main factors affecting approval are:ØThe position offered. Does it require someone with at least a bachelor’s degree? For example, even if someone has a PhD, that person would not qualify for an H-1B visa based on work as a waiter.ØThe person. Does the H-1B beneficiary have a degree (or equivalent) which closely matches the company’s requirements and specific position offered? This has been an area of contention between the USCIS and practitioners of immigration law. USCIS has been requiring occupation-specific majors, while the law clearly supports granting of visas to applicants with degrees in multiple disciplines, as long as it reasonably qualifies the applicant to perform the work. For example, occupation specific degrees are required in law or medicine, but for marketing or IT positions, there are usually a number of academic disciplines which are acceptable.ØThe company. Is the company financially viable and of a sufficient size and complexity to justify hiring the H-1B candidate? Factors considered by the USCIS include the company’s stage of development, organizational complexity, ability to pay the required wage, current number of employees, gross income, and funding. Evidence provided to document company operations varies on a case-by-case basis. A comprehensive list is available in our H-1B Start Employer Questionnaire.H-1B Employer ObligationsØProtect wages in the region. Employers must pay every H-1B worker wages that are 100% of the wages paid to US workers in similar positions in the same geographical region. This wage is referred to as the prevailing wage.ØProtect wages in the workplace. Employers must pay every H-1B worker the actual wages paid to other employees in the same position, with normal variability for experience, merit, skills, etc. This wage is referred to as the actual wage.ØPost the proposed salary. Employers must post the prospective salary or the salary range for an H-1B position for 10 business days at the worksite in two conspicuous locations. Advertising required, only if the company is H-1B dependent - see below.ØProtect working conditions.Employers cannot use H-1B workers to break a strike and they must notify their U.S. workforce of the hiring of H-1B professionals.ØProvide benefits equally.Employers must provide benefits to H-1B employees in the same manner as provided to similar U.S. workers.ØFile a Labor Condition Application (LCA). Employers must file a Labor Condition Application attesting to the wages and the no-strike use of H-1B employees with the U.S. Department of Labor (DOL).ØPay the employee during benching. Employers who bench employees during non-productive status must continue to pay full salary and benefits as attested on the Labor Condition Application.ØBe subject to penalties for failures. Failure to comply with DOL regulations could result in civil penalties, a requirement to pay back wages, and even debarment from participating in key immigration programs. Audits are performed by US immigration authorities randomly.ØNo discrimination in hiring. The employer may decline employing any worker who is not legally eligible to work. Written offers should be contingent upon proof of eligibility to work for any employer in the U.S. If a candidate requests sponsorship for H-1B status, the company can decide to sponsor or not.ØReturn transportation. If an employer terminates an H1-B employee before the endof that employee’s period of authorized stay, the employer is liable for the “reasonable costs” of return transportation for the employee to his or her last country of residence. Immigration statutes and regulations suggest that the employer’s liability is limited to the reasonable cost of physically returning the H-1B employee, and does not extend to the cost of relocating family members or property.ØWithdrawal of H-1B after termination. Regulations require an H-1B employer to notify USCIS “immediately” of “any material changes in the terms and conditions of employment” affecting an H-1B employee. USCIS policy is that a termination is such a“material change.” Employers may satisfy this no tification obligation by sending a letter explaining the change or termination to USCIS office that approved the petition.H-1B Employee ObligationsØInform Lawyer of Travel. An employee who will be traveling in H-1B status should inform a lawyer in advance to make sure that all paperwork is in order and to ensure that H-1B status is still valid. He/she may need a trip to a US Embassy or Consulate abroad before returning to secure a visa stamp.ØQuitting a job is allowed. An employee may quit his/her employment in H-1B status at any time. He/she may be subject to contractual terms made specifically with the employer, outside the scope of the H-1B visa.ØLay-offs and leaving the U.S. An employee who is laid off or terminated is no longer considered to be maintaining H-1B status, despite having an I-94 document which might still be valid, on its face. The employee must leave the U.S. as quickly as possible, as is no official “grace period” or provision for continuing H-1B status while looking for another job.The Players in the H-1B Process and Their RolesA dual representation situation is created in the preparation of an H-1B petition, where our firm has the interests of both the US company petitioner and foreign national employee in mind, in representing both parties together, to obtain the desired visa from the US government.ØEmployer and employee participation. Both the US company petitioner (employer) and foreign national (employee) supply essential information to complete the needed paperwork, submitted to US immigration authorities. Paperwork includes numbered immigration forms, letters, and supporting documentation. Employer signs the immigration forms and a critical support letter, which confirms the temporary offer of employment, and summarizes eligibility for the H-1B. Employer also follows instructions from our firm to ensure compliance with applicable law surrounding hiring H-1B workers, including posting and maintenance of public access files (PAFs). Employer must update the Public Access File with information about benefits, salary changes. Information about recruitment is necessary only if the employer is dependent – see below.ØAttorney analysis and preparation. The attorney obtains the initial paperwork on a particular employee and determines if H-1B status will be viable based on information presented. The attorney informs the client about H-1B obligations and responsibilities. The attorney prepares the forms and files them with USCIS.ØDepartment of Labor. Reviews the Labor Condition Application (LCA) and certifies that the prevailing wage is being paid based on the information provided. DOL also may perform random audits to see if employer requirements in addition to the LCA disclosures are being upheld.ØUS Citizenship & Immigration Services. USCIS receives the filing and determines that the job requirements, the employee's credentials and the employer's viability are all sufficient for approval.ØDepartment of State/visits to US Embassy or Consulate abroad.If the employee is abroad after receiving approval of the petition, or is granted consular approval (as opposed to a change or extension of status) the employee must apply for an H-1B visa stamp at a US Embassy or Consulate abroad.Steps for EmployerThe Process of Sponsoring and Qualifying for an H-1B VisaThis process includes a few major components, which I will outline below:LCA application by a companyBefore an employer files for an initial petition for an H-1B visa, they have to file for a LCA with United States Department of Justice. The LCA is a form that contains statements that help protect US citizen workers due to the hiring of these new employees using the H-1B visa. It states the following; -∙The employee will be paid the prevailing wage as per their position∙The employee will receive equal benefits as other employees in the same position∙Hiring of the employee should not affect the working conditions of other employees.∙At the time of hiring, no active labor dispute or work stoppage is in place.Petition for an H-1B VisaAfter the company has successfully filed a LCA, they are free to apply for the visa. An employer is charged with the responsibility of filing for the visa on behalf of the employee as they are not allowed to self-petition. Usually, there is 65000 H-1B visas awarded each year that are up for grabs. However, 6800 visas are already set aside for Singapore and Chile while another 20000 are awarded to workers with advanced degrees such as a Mastersdegree or a PhD. After petition is done, one all has to do is wait for feedback from the USCIS. The fate of the employee then lies on the outcome of the lottery.The approving of the Visa by USCISWaiting for approval by the USCIS is a torturous task for most. There are various factors the USCIS considers in order to approve a person’s H-1B visa. These factors may include:∙The person the employer wants to hire that is their level of education and expertise∙The position the employer offers in the sense that it must require a degree holder for example, one cannot apply for a H-1B visa for the position of a cleaning lady.∙The employer is also a key factor since the company must be financially capable and be of adequate size in order for their employee to be granted a H-1B visa.Spouses/ ChildrenIn the event that the employee has a spouse and children, they are allowed to accompany the H-1B principal under H-4 status. They are not allowed to work but can study in the country.Employee ObligationsThere are various things that one has to take care of in the event that they are granted theH-1B visa.∙They have to inform their lawyer of their travel plans prior to the travelling date.∙They are allowed to quit their jobs but this may lead to termination of their visa∙In case of a layoff, their H-1B status is lost and they have to leave the country immediately as there is no grace period provided.The cost of acquiring an H-1B VisaIn order for one to acquire this visa, they must be prepared to meet the cost between $2000-$4000 to walk you through the maze and complete all the government filings.In case you are looking to either sponsor or acquire an H-1B visa, it would be helpful to understand all the steps mentioned above and thenvisit LawTrades for a free consultation with an experienced startupimmigration attorney.Specialty Occupation RequirementsThe occupation has to be a specialty occupation that generally requires a bachelor's degree or higher degree(or its equivalent) as a minimum for entry into the occupation. Fashion models of distinguished merit or ability may also apply for the H-1B program.A position that would normally not require a bachelor's degree may qualify as a specialty occupation if the position is so complex or unique that only an individual with a degree can perform the requisite duties. A position with specific duties that are so specialized and complex that the knowledge required to perform them is usually associated with the attainment of a bachelor’s or higher degree may also qualify as a specialty occupation.Positions that are normally considered professional positions would most likely qualify as a specialty occupation.Examples of specialty occupations include: architects, engineers, professors, teachers, researchers, medical professionals, dietitians, physicians, nurses, computer professionals, accountants, attorneys, social workers, economists, librarians and other professionals.Educational RequirementsThe employer must show that the alien worker meets the specific educational requirements to be engaged in the specialty occupation. As a general rule, the alien worker must possess a Bachelor's or higher degree from an accredited college or university and the degree must be a requirement to qualify for the specialty occupation.If the alien worker was awarded his/her degree from an institution not located in the U.S., that degree must be evaluated to determine if it can be consideredequivalent to a U.S. awarded degree. If the alien possesses a Bachelor’s degree or its equivalent, specific work experience is not required.If an alien does not meet the educational requirements, experience or training may be substituted, whereby three years of professional experience is considered equivalent to one year of college education (every 3 year of work experience = 1 year of University / College education). Pleasesee Using Experience to Meet the Advanced Degree Requirement for more details.For example:Neil is from India and has been working as a network analyst for more than 6 years. He only has an Associate’s degree with 2 years of college education, but wishes to apply for H-1B status so that he can work in the United States as a network analyst. The minimum educational requirement has been met because every 3 years of related work experience can substitute for 1 year of college education, and his 6 years of work experience make up for the 2 year shortage in terms of educational requirements. Therefore he may apply for an H-1B visa.Furthermore, if state law requires a worker(such as doctors, dentists, attorneys, CPAs, registered nurses) to obtain a license or professional certification to practice a specific specialty occupation, the alien must hold the appropriate license and be fully qualified to lawfully perform the duties of the position offered.DOL and USCIS RequirementsIn addition to both the Occupation requirements and the Education requirements, the employer must also adhere to the Department of Labor (DOL) requirements to obtain a Labor Condition Application (LCA). After the DOL certifies the LCA, the employer must submit Form I-129 to the USCIS for permission to employ the foreign worker under H-1B status, so that the alien worker may be hired.To successfully complete this process, the employer must first attest that the H-1B visa worker is being paid, at minimum, what is called the “prevailing wage” for the job. The “prevailing wage” is defined by DOL rules as the average rate of wages paid to workers similarly employed in the area ofintended employment. The prevailing wage is determined through the National Prevailing Wage Center (NPWC). The following factors determine one’s prevailing wage:1.Job title;cational and work experience requirements;3.Job description;4.Job location; and5.Type of employer, (i.e. academic, government or private.)Example 1:John and Ron are both professors of biochemistry who have the same educational experience and job description. John is employed by a university in New York City, while Ron works for a college inHouston, Texas. Everything else being equal, due to the differences in location and cost of living at these locations, the prevailing wage for John is higher than the prevailing wage for Ron.Example 2:Jen and Ryan are researchers in chemistry. Both livein Seattle, Washington and their jobs require the same level of education and work experience. The University of Washington hires Jen, while a private company employs Ryan. Since they are employed in different sectors (i.e. public v. private sectors), their prevailing wages will be different and Jen’s prevailing wage is much lower than Ryan’s prevai ling wage.Example 3:Jill and Greg are researchers in chemistry.Both livein Washington D.C. and have similar education and work experience. The same private company employs both of them, where Jill is a research scientist and Greg is just a post-doctoral researcher. Since Jill has a higher job title and her job description encompasses more duties, Jill’s prevailing wage will be higher than Greg’s.Next, the employer must attest to the following six conditions:1.The employer will pay the H-1B employee the higher of:a.The actual wage rate that it pays to all other individuals with similar experience and qualifications, orb.The prevailing wage level for the occupation in the “area of intended employment”, which is definedas the Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) and the narrower Primary Metropolitan Statistical Area (PSMA).2.Employment of the H-1B worker will not adversely affect the working conditions of workers similarlyemployed in the intended area of employment;3.There is no current strike/lockout involving the prospective H-1B worker’s position at his/herworkplace;4.The employer will provide notice of filing of the labor condition application to the employees’ collectivebargaining representative for the H-1B occupation or, lacking such a representative, willconspicuously post such notice at the work site onthe date the labor condition application is filed,or within 30 days before it is filed, and shall remain posted for 10 days;5.The employer will maintain for public examination:a. A copy of the Labor Condition Application filed,b.Documentation of the salary paid to the H-1B employee,c.An explanation of how the actual wage was determined, andd.Documentation of the basis used for the prevailing wage;6.The employer must agree to pay the alien the reasonable cost of transportation to return to his or herhome country if the employer terminates the alien’s employment prior to the end of the authorized employment period.U.S. Employer Sponsorship RequirementFor an alien to obtain an H-1B visa, an employer must make a job offer and be willing to sponsor the alien by filing a petition with the USCIS. Generally, individuals cannot apply for an H-1B visa to allow them to work in the US. The U.S. employer must petition for the entry of the employee.An employer seeking the services of an H-1B alien and filing the necessary papers to obtain such services must be a "U.S. employer." A U.S. employer is a person, firm, corporation, contractor or other association or organization in the United States with an IRS tax identification number known asa Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN). There must be an employer-employee relationship,as indicated by the fact that the employer may hire, fire, pay, supervise or otherwise control the work of the employee.There are two major requirements that the employer must fulfill:a.The employer must have the ability to pay the employee. For instance, John wants to hire a computerprogrammer for his start-up company. He promises to pay an alien worker $50,000 for a year of work;how ever he currently has only $800 in his company’s bank account. Under this circumstance, John fails the ability to pay test;b.The job offer to the intended H-1B beneficiary should be a bona fide offer. In other words, there mustbe a real business need for the position to be filled by the alien worker.On August 2, 2011, USCIS announced and outlined a series of policies to promote the US economy and investment by attracting foreign entrepreneurswith talent orexceptional ability who can create jobs, form start-up companies, and invest capital in areas of high unemployment. USCIS has clarifiedthat a nonimmigrant alien who is the owner of a petitioning company created in the US may establisha valid employer-employee relationship for the purposes of sponsoring an H-1B visa. Not all alien-owned companies can establish an employer-employee relationship, but it is possible to do so. There must be a degree of separation between the alien and his/her company as the employer. The alien cannot be self-employed in the traditional sense and be the beneficiary of an H-1B petition from his/her own company. There must be an independent company entity that can exerthiring/paying/supervising/firing authority outside of the alien-owner’s command in order for that same alien to be an H-1B beneficiary for his/her own company. For more information, please visit our article on “Starting a Business in Which an F-1 / H-1B Visa Holder is a Shareholder or Owner.”- See more at: /h-1b/h1b_requirements.html#sthash.DBbeMKVX.dpufH-1B RequirementsMinimum wage: /OesWizardStart.aspxRequirement 1 - You must have an employer-employee relationship with the petitioning U.S. employer.In general, a valid employer-employee relationship is determined by whether the U.S. employer may hire, pay, fire, supervise or otherwise control the work of the H-1B worker. In some cases, the sole or majority owner of the petitioning company or organization may be able to establish a valid employer-employee relationship, if the facts show that the petitioning entity has the right to control the beneficiary’s employment.Requirement 2 - Your job must qualify as a specialty occupation by meeting one of the following criteria:∙ A bachelor’s degree or higher degree or its equivalent is normally the minimum requir ement for the particular position;∙The degree requirement is common for this position in the industry, or the job is so complex or unique that it can only be performed by someone with at least a bachelor's degree in a fieldrelated to the position;∙The employer normally requires a degree or its equivalent for the position; or∙The nature of the specific duties is so specialized and complex that the knowledge required to perform the duties is usually associated with the attainment of a bachelor's or higher degree.How do I prove that my position within my business is in an occupation that normally requires a degree in a related field?USCIS often refers to the Occupational Outlook Handbook (OOH) from the Department of Labor (DOL) to help determine whether certain jobs require a degree. If the OOH does not indicate thata degree in a related field is normally the minimum requirement for the position, examplesof evidence you may submit to demonstrate that the position normally requires such a degree includes:。
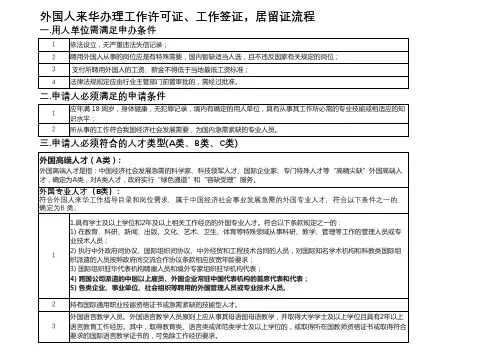
外国人B类工作签证
外国专业人才(B类)
符合外国人来华工作指导目录和岗位需求,属于中国经济社会事业发展急需的外国专业人才,符合以下条件之一的,确定为 B 类。
一、具有学士及以上学位和 2 年及以上相关工作经历的外国专业人才。
符合以下条款规定之
一的:
1.在教育、科研、新闻、出版、文化、艺术、卫生、体育等特殊领域从事科研、教学、管理
等工作的管理人员或专业技术人员。
2.执行中外政府间协议、国际组织间协议、中外经贸和工程技术合同的人员,对国际知名学
术机构和科教类国际组织派遣的人员按照政府间交流合作协议条款相应放宽年龄要求。
3.国际组织驻华代表机构聘雇人员和境外专家组织驻华机构代表。
4.跨国公司派遣的中层以上雇员、外国企业常驻中国代表机构的首席代表和代表。
5.各类企业、事业单位、社会组织等聘用的外国管理人员或专业技术人员。
二、持有国际通用职业技能资格证书或急需紧缺的技能型人才。
三、外国语言教学人员。
外国语言教学人员原则上应从事其母语国母语教学,并取得大学学
士及以上学位且具有2年以上语言教育工作经历。
其中,取得教育类、语言类或师范类学士
及以上学位的,或取得所在国教师资格证书或取得符合要求的国际语言教学证书的,可免除
工作经历要求。
四、平均工资收入不低于本地区上年度社会平均工资收入 4 倍的外籍人才。
五、符合国家有关部门规定的专门人员和实施项目的人员。
六、计点积分在 60 分以上的专业人才。