语言学名词解释.英文
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:4.35 MB
- 文档页数:17

语言学名词解释语言学是研究语言的一门学科,涉及语言的结构、功能、变化和发展等方面的研究。
下面是一些常见的语言学名词及其解释。
1. 语音学(Phonetics):研究语言中各种语音的产生、传播和感知等方面的学科。
2. 语音语言学(Phonology):研究语音在特定语言中的音位(音素)和音位组合规则的学科。
3. 语法学(Grammar):研究语言的句法结构、词法结构和语义结构等方面的学科。
4. 句法学(Syntax):研究语言中句子的结构和组织方式的学科。
5. 语义学(Semantics):研究语言中词汇和句子的意义、概念和关系的学科。
6. 词汇学(Lexicology):研究语言中词汇的组成、形态、构词规则等方面的学科。
7. 词义学(Semantics):研究词汇中词义的构成、关系和词义的变化等方面的学科。
8. 语用学(Pragmatics):研究语言在具体语境中的使用方式以及语言的上下文相关性等方面的学科。
9. 文法学(Stylistics):研究语言使用中的文体、修辞手法、语言风格等方面的学科。
10. 母语(Mother tongue):一个人从小学会并用于日常交际的语言。
11. 第二语言(Second language):在学习者的母语之外学习的语言。
12. 语言接触(Language contact):不同语言之间在社会、文化接触中产生的相互影响和借用的现象。
13. 语言变异(Language variation):指同一个语言在不同社会、地理和使用者间发生的音、词、句法等方面的变化。
14. 语言变化(Language change):指语言在漫长的时间内逐渐变化和发展的过程。
15. 语言规范(Language standardization):制定和规范一个语言的正确用法、标准词汇和语法规则的过程。
16. 语言习得(Language acquisition):指儿童在自然环境中学习母语的过程。

名词解释nguage: language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication.2.Design features of language(语言的区别性特征) :i.Arbitrariness:the forms of linguistic signs bear no natural relationship to theirmeaning=language is arbitrary in the sense that there is no intrinsic connection between a word(e.g.pen) and the object it refers to .ii.Duality:the property of having two levels of structures, such that units of the primary level are composed of elements of the secondary level. By duality we mean that language system has two sets of structures, one of sounds and the other of meanings.指拥有两层结构的这种特性,底层结构是上层结构的组成成分。
指语言是声音和意义双重结构组成的系统。
举例:Sounds > syllables > words > phrases > clauses > sentences> texts/discoursesiii.Productivity: Language can be used to create new meanings because of its duality .语言可以理解并创造无限数量的新句子,是由双层结构造成的结果(Understand and create unlimited number with sentences)iv.Displacement:Human languages enable their users to symbolize something which are not present at the moment of communication.v.Cultural transmission: language is passed on from generation to generation through teaching and learning rather than instinct.3.Linguistics is the scientific study of language. It is a scientific study because it is based on thesystematic investigation of linguistic data, conducted with reference to some general theory of language structure.4.Psycholinguistics: It is the study of how language is acquired, understood and produced.ngue:F. de Saussure. Langue refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all themembers of a speech community.语言指语言系统的整体,这个整体相对是比较稳定的。

一、名词解释1.Diachronic历时的It refers to say of the study of developing of language and languages over time.研究语言随时间发展变化的方法。
2.Arbitrariness任意性Saussure first refers to the fact that the forms of linguistic signs bear no natural relationship to their meaning.任意性是指语言符号的形式与所表达的意义之间没有天然或逻辑的联系。
It is refers to absence of any physical correspondence between linguistic signals and the entities to which they refer.任意性是指语言符号和这些符号所指的实体间不存在任何物质的联系。
3.Parole言语It refers to the concrete utterances of a speaker.指语言在实际使用中的实现。
4.Creativity创造性By creativity we mean language is resourceful because of its duality and its recursiveness, which enables human beings to produce and understand an infinitely large number of sentences including the sentences that were never heard before.创造性是指语言具有能产型,因为语言有双重性和递归性,也就是说话者能够结合各个语言单位形成无尽的句子,其中很多句子是以前没有的或者没有听说过的。

Define the following terms:1。
Linguistics: Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language.2。
Phonology: The study of how sounds are put together and used in communication is called phonology.3. Syntax: The study of how morphemes and words are combined to form sentences is called syntax. .4. Pragmatics: The study of meaning in context of use is called pragmatics。
5. Psycholinguistics: The study of language with reference to the workings of mind is called psycholinguistics.6。
Language: Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication.7。
Phonetics: The study of sounds which are used in linguistic communication is called phonetics。
8. Morphology: The study of the way in which morphemes are arranged to form words is called morphology。
9. Semantics: The study of meaning in language is called semantics.10。

语言学名词语言学名词是用来描述和研究语言现象和语言结构的专门术语。
下面是一些常见的语言学名词及其解释:1. 语音学(Phonetics):研究语音产生、传播和接收的学科,包括音素的分类、语音能力和语音现象等。
2. 语音:语言中的基本声音单位,通过调节声带、口腔和喉咙等发音器官产生。
语音可以被分类为辅音和元音。
3. 辅音(Consonant):通过喉咙、口腔和鼻腔等部位的阻碍或摩擦,产生的声音单位。
4. 元音(Vowel):发音器官不受阻碍或摩擦,使空气顺畅通过口腔而产生的声音单位。
5. 语音形式学(Phonology):研究语音符号在特定语言中的组合和分布规律的学科。
6. 语音规则(Phonological rules):用来描述声音变化和音系结构的一套规则。
7. 语法学(Grammar):研究语言结构和组织的学科,包括句法、语义和语用等方面。
8. 句法(Syntax):研究句子结构和成分之间的关系,以及句子的形式和结构组织。
9. 语义(Semantics):研究词、短语和句子的意义和含义的学科。
10. 语用学(Pragmatics):研究语言在特定语用背景下的使用和理解方式。
11. 词汇学(Lexicology):研究词汇的起源、结构、使用和意义等方面。
12. 词(Word):语言中的基本意义单位,具有独立的意义和语法功能。
13. 词法(Morphology):研究词的内部结构、形态变化和构词法的学科。
14. 语素(Morpheme):语言中的最小意义单位,可以独立存在或者是其他词的构成组成部分。
15. 词义(Word meaning):词语所表达的概念或事物的内涵。
16. 语篇(Discourse):由句子和词组组成的扩展语言单位,表达完整的意义。
17. 修辞学(Rhetoric):研究语言如何用于说服和交流的学科。
18. 语族(Language family):具有共同源头和结构相似的一组语言。

1.Semantics: the study of meaning2.Synonymy: the sameness or close similarity of meaning.3.Polysemy: while different words may have the same or similar meaning, the same one word may have more than one meaning4.Homonymy: the phenomenon thea words having different meanings have same form, i.e.,different words are identical in sound or spelling, or in both5.Hyponymy: the sense relation between a more general, more inclusive word and a more specific word6.Antonymy: words that are opposite in meaning7.Pragmatics: it is the study of how speakers of a language ues sentences to effect successful communication8.Speech act theory: it is a philosopher explanation of the nature of linguistic communicatin. It is aim to answer the question “what do we do when suing lanfuage?”9.Constatives: either state or discribe, and were thus verifiable10. Performatives: did not state a face or describe a state, and were not verifiable11.Locutionary act: It is the act of utterance words,phrases,clauses. It is the act of conveying literal meaning by means of syntax, lexion and phonology.12.Illocutionary act: It is the act expressing the speaker’s intention; It is the act performed in saying something.13.Perlocutionary act: It is the act performed by or resulting from saying something: it is the consequence of, or the change brought about by the utterance; it is the act performed by saying something14.cooperative principle: in making conversation, the participants must first of all be willing to coopreate; otherwise, it would not be possible for them to carry on the talk15.historical linguistics:it is the subfield of linguistics that studies language change.16.blending: a way of forming a new word by combining parts of two other words17.semantic broadening:the process in which the meaning of a word becomes general or inclusive than its historically earlier meaning18.protolanguage: the original form of a language family which has ceased to existnguage family: a group of historically relate laguages that have developed from a common ancestral language20.socilinguistics: the subdiscipling of linguistics thet studies language variation and language ues in social contexts21.speech community: a group of people who form a community andshare at least one speech variety as well as similar linguistic norms22.lingua franca: a variety of language that serves as a sommon speech for social contact among groups of people who speak different native languages or dialects23.pidign:a marginal contact language with a limited vocabulary and reduced grammatical structures, used by native speakers of other languages as a means of business communication24.diglossia: a sociolinguistic situation in which two very different varieries of languag co-exist in a speech community, each serving a particular social function and used for a particular situation25.euphemism:a word or expression that is thought to be mild, indirect, or less offensive and used as a polite substitute for the supposedly harsh and unpleasant word or expression26.psycholinguistics: the study of language in relation to the mind, with focus on the processes of language production, comprehension and acquisition27.cerebral cortex: the outside surface of the brain which receives messages from all the sensory oragns and where human cognitive abilities reside28.brain lateralization: The localization of cognitive of cognitive and percpetual functions in a particular hemisphere of the brain29.linguistic lateralization: hemispheric specialization or dominance forlanguage30.the critieal period: an early period of one’s life extending to the age of puberty, during which the human brain is most ready to acquire language naturally and effortlessly, a period that coincides with the period of brain lateralization for language functions31.caretaker speech: simple, modified speech used by parents, baby-sitter, etc.when they talk to young children who are acquiring their native languagenguage transfer:the effect of one’s first language knowledge on the learning of a second language33.interlanguage:the aproximate language system that a second language learner constructs which represents his or her transitional competence in the target language34.acculturation: a process of adapting to the culture and value system of the second language communnity。

语言学名词解释英语Language is a complex system of communication used by humans to convey meaning. It consists of various components and structures that allow individuals to understand and generate language. In the field of linguistics, there are several important terms and concepts used to analyze and describe language. Here are explanations of some key linguistic terms in English:1. Phonetics: Phonetics is the study of the sounds of speech. It examines the physical properties of sounds, such as their production, transmission, and perception. Phonetics helps to understand the different speech sounds used in language.2. Phonology: Phonology refers to the organization and patterns of speech sounds in a particular language. It studies the sound system of a language, including the rules and constraints for combining and manipulating sounds.3. Morphology: Morphology is the study of the internal structure of words. It examines how words are formed from smaller units called morphemes, which are the smallest meaningful units of language. Morphology helps to analyze word formation processes and understand how words are related to each other.4. Syntax: Syntax is the study of the structure and arrangement of words to form meaningful sentences. It investigates the rules for combining words into phrases and sentences. Syntax helps to analyze sentence structure and understand how different grammatical structures are formed.5. Semantics: Semantics is the study of meaning in language. It analyzes how words, phrases, and sentences convey meanings and how different meanings are related. Semantics helps to understand how context, reference, and inference affect the interpretation of language.6. Pragmatics: Pragmatics is the study of how language is used in context and how meaning is influenced by social and cultural factors. It examines the principles of conversation, politeness, and the interpretation of implicatures and presuppositions. Pragmatics helps to understand the social and cultural aspects of language use.7. Sociolinguistics: Sociolinguistics is the study of how language varies and changes in different social groups and communities. It investigates the relationship between language and society, including language variation, language attitudes, and language in multilingual settings.8. Psycholinguistics: Psycholinguistics is the study of how language is processed and represented in the mind. It investigates the cognitive processes involved in language production, comprehension, and acquisition. Psycholinguistics helps to understand how we learn and use language.9. Historical linguistics: Historical linguistics is the study of how languages change over time. It examines the historical development of languages, language families, and language relationships. Historical linguistics helps to trace the evolution of languages and reconstruct their ancestral forms.10. Applied linguistics: Applied linguistics is the practical application of linguistic theories and principles to real-world problems. It includes areas such as language teaching, language planning, language assessment, and discourse analysis. Applied linguistics helps to address language-related issues in various contexts.These linguistic terms and concepts form the basis of studying and understanding language. Linguists use them to analyze language structure, usage, and evolution, and to gain insights into the intricacies of human communication.。

1. Linguistics: Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language.2. general linguistics: The study of language as a whole.3. applied linguistics: the application of linguistic theories and principles to language teaching, especially the teaching of foreign and second languages.4. prescriptive: If linguistic study aims to lay down rules for “correct and standard” behavior in using language, ,it is said to be prescriptive.( i.e. to tell people what they should and should not say).5. descriptive: If a linguistic study aims to describe and analyze the language people actually use, it is said to be descriptive.(09C)6. synchronic study: The description of language at some point of time in history is a synchronic study. (06C/ 04)7. diachronic study: It’s a historical study of language,it studies the historical development of language over a period of time. (06C)8. langue: Lange refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all the members of a speech community.9. parole :Parole refers to the realization of langue in actual use.10. competence : The ideal user’s knowledge of the rules of his language.(08F/09C)linguistic competence: universally found in the grammars of all human languages, syntactic rules comprise the system of internalized linguistic knowledge of a language speaker.11. performance : The actual realization of this knowledge in linguistic communication.12. language : Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication.13. design features : Design features refer to the defining properties of human language that distinguish it from any animal system of communication.14. arbitrariness: Arbitrariness refers to there is no logical connection between meanings and sounds.(08C)15. productivity: Language is creative in that it makes possible the construction and interpretation of new signals by it’s users.16. duality(double articulation): Language consists of two sets of structure, with lower lever of sound, which is meaningless, and higher lever of meaning.17. displacement: Language can be used to refer to contexts removed from the immediate situation of the speaker.( regardless of time or space) (04)18. cultural transmission: The capacity for language is genetically based while the details of any language system have to be taught and learned.( Language is culturally transmitted rather than by instinct).19.Sociolinguistics: the study of all social aspects of language and its relation with society from the core of the branch.20.Psycholinguistics: the study of language processing, comprehending and production, as well as language acquisition.municative competence:the ability to use language appropriately in social situations.Chapter 2: Phonology1. phonic medium : The limited range of sounds which are meaningful in human communication constitute the phonetic medium of language.(and the individual sounds within this range are speech sounds)2. phonetics : The study of phonic medium of language and it is concerned with all sounds in the world’s languages. (06C)3. articulatory phonetics : It studies sounds from the speaker’s point of view, i.e. how a speaker uses his speech organs to articulate the sounds. (03)4. auditory phonetics: The studies sounds from the hearer’s point of view, i.e. how the sounds are perceived by the hearer.5. acoustic phonetics: It studies the physical properties of the stream of sounds which the speaker issues.QR It studies the way sounds travel by looking at the sound waves, the physical means by which sounds are transmitted through the air from one person to another)6. voicing: the way that sounds are produced with the vibration of the vocal cords.7. voiceless: the way that sounds are produced with no vibration of the vocal cords.8. broad transcription: The use of letter symbols only to show the sounds or sounds sequences in written form.9. narrow transcription: The use of letter symbol, together with the diacritics to show sounds in written form.10. diacritics: The symbols used to show detailed articulatory features of sounds.11. IPA: short for International Phonetic Alphabets, a system of symbols consists of letters and diacritics, used to represent the pronunciation of words in any language.12. aspiration: A little puff of air that sometimes follows a speech sound.13. manner of articulation : The manner in which obstruction is created.14. place of articulation : The place where obstruction is created.15. consonant: a speech sound in which the air stream is obstructed in one way or another.16. vowel : a speech sound in which the air stream from the lung meets with no obstruction.17. monophthong : the individual vowel.18. diphthong : The vowel which consists of two individual vowels and are produced by moving one vowel position to another through intervening positions.(08F)19. phone: A phonetic unit,the speech sounds we hear and produce during linguistic communication are all phones.20. phoneme : An abstract phonological unit that is of distinctive value;it’s represented by a certain phone in a certain phonetic context. (06F/ 04)或者The smallest unit of sound in a language which can distinguish two sounds.21. allophone : the different phones which can represent the same phoneme in different phonetic enviroments are called allophones of that phoneme (07C/ 05)22. phonology : The description of sound systems of particular languages and how sounds form patterns and function to distinguish and convey meaning.(06C)23. phonemic contrast : two phonetically similar sounds occur in the same environment and distinguish meaning,they form phonemic contrast.24. complementary distribution : allophones of the same phoneme and they don’t distinguish meaning but complement each other in distribution.25. minimal pair: two different forms are identical in every way except forone sound segment which occurs in the same position.26. sequential rules: The rules to govern the combination of sounds in a particular language.27. assimilation rule: The rule assimilates one sound to another by copying a feature of a sequential phoneme, thus making the two phones similar.28. deletion rule: The rule that a sound is to be deleted although it is orthographically represented.29. suprasegmental features: The phonemic features that occur above the level of the segments(syllable, word, sentence),including stress tone intonation.(08F)30. tone: Tones are pitch variations, which are caused by the differing rates of vibration of the vocal cords.31. intonation: When pitch, stress and sound length are tied to the sentence rather than the word in isola tion, they’re collectively known as intonation.32. nucleus: It refers to the major pitch change in an intonation unit.32. minimal set: sound combinations which are identical in form except for the initial consonant together constitute a minimal set.。

Chapter 1: Introduction1. Linguistics: Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language.8. langue: Lange refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all the members of aspeech community.9. parole :Parole refers to the realization of langue in actual use.10. competence : The ideal user’s knowledge of the rules of his language.11.performance : The actual realization of this knowledge in linguistic communication.12. language : Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication.13.design features : Design features refer to the defining properties of humanlanguage that distinguish it from any animal system of communication.14. arbitrariness: Arbitrariness refers to no logical connection between meaning andsound.15. productivity: Users can understand and produce sentences t hat they have neverheard before.16. duality: Language consists of two sets of structure, with lower lever of sound,which is meaningless, and the higher lever of meaning.17. displacement: Language can be used to refer to the contexts removed from theimmediate situation of the speaker no matter how far away from the topic ofconversation in time or space.18. cultural transmission: Language is culturally transmitted. It is taught and learnedfrom one generation to the next, rather than by instinct.Chapter 2: Phonology1. phonic medium : The meaningful speech sound in human communication.2. phonetics : The study of phonic medium of language and it is concerned with allsounds in t he world’s languages.3. articulatory phonetics : It studies sounds from the speaker’s point of view, i.e. ha speaker uses his speech organs to articulate the sounds.the4. auditory phonetics: The studies sounds from the hearer’s point of view, i.e. how sounds are perceived by the hearer.5. acoustic phonetics: It studies the way sounds travel by looking at the sound waves,the physical means by which sounds are transmitted through the air from one personto another.6. voicing: the way that sounds are produced with the vibration of the vocal cords.7. voiceless: the way that sounds are produced with no vibration of the vocal cords.8. broad transcription: The use of letter symbols only to show the sounds or soundssequences in written form.9. narrow transcription: The use of letter symbol, together with the diacritics to showsounds in written form.10. diacritics: The symbols used to show detailed articulatory features of sounds.11. IPA: short for International Phonetic Alphabets, a system of symbols consists ofletters and diacritics, used to represent the pronunciation of words in any language.12. aspiration: A little puff of air that sometimes follows a speech sound.13. manner of articulation : The manner in which obstruction is created.14. place of articulation : The place where obstruction is created.15. consonant: a speech s ound in which the air stream is obstructed in one way or another.16. vowel : a speech sound in which the air stream from the lung meets with no obstruction.17. monophthong : the individual vowel.18. diphthong : The vowel which consists of two individual vowels, and functions as a single one.19. phone : The speech sound we use when speaking a language.20. phoneme : The smallest unit of sound in a language which can distinguish two sounds.21. allophone : any different forms of the same phoneme in different phonetic environments.22. phonology : The description of sound systems of particular languages and how sounds function to distinguish meaning.23. phonemic contrast : two similar sounds occur in the same environment and distinguish meaning.24. complementary distribution : allophones of the same phoneme and they don’t distinguish meaning but complement each other in distribution.25. minimal pair: two different forms are identical in every way except one sound and occurs in the same position. The two sounds are said to form a minimal pair.26. sequential rules: The rules to govern the combination of sounds in a particular language.27. assimilation rule: The rule assimilates one sound to another by copying a featureof a sequential phoneme, thus making the two phones similar.28. deletion rule: The rule that a sound is to be deleted although it is orthographically represented.29. suprasegmental features: The phonemic features that occur above the level of the segments----syllable, word, sentence.30. tone: Tones are pitch variations, which are caused by the differing rates of vibration of the vocal cords.31. intonation: When pitch, stress and sound length are tied to the sentence rather than the word in isolation, they are collectively known as intonation.Chapter 3: Morphology1. morphology: A branch of linguistics that studies the internal structure of words and rules for word formation.2. open class: A group of words, which contains an unlimited number of items, and new words can be added to it.3. closed class: A relatively few words, including conjunctions, prepositions and pronouns, and new words are not usually added to them.4. morpheme: The smallest unit of meaning of a language. It can not be divided without altering or destroying its meaning.5. affix: a letter or a group of letter, which is added to a word, and which changes themeaning or function of the word, including prefix, infix and suffix.6. suffix: The affix, which is added to the end of a word, and which usually changesthe part of speech of a word.7. prefix: The affix, which is added to the beginning of a word, and which usuallychanges the meaning of a word to its opposite.8. bound morpheme: Morpheme that can not be used alone, and it must be combinedwit others. E.g. –ment.9. free morpheme: a morpheme that can stand alone as a word.10. derivational morpheme: Bound morpheme, which can be added to a stem to forma new word.11. inflectional morpheme: A kind of morpheme, which are used to make grammatical categories, such as number, tense and case.12. morphological rules: The ways words are formed. These rules determine howmorphemes combine to form words.13. compound words: A combination of two or more words, which functions as asingle words14. inflection: the morphological process which adjusts words by grammatical modification, e.g. in The rains came, rain is inflected for plurality and came for pasttense.Chapter 4: Syntax1. syntax: A branch of linguistics that studies how words are combined to formsentences and the rules that govern the formation of sentences.2. category: It refers to a group of linguistic items which fulfill the same or similarfunctions in a particular language such as a sentence, a noun phrase or a verb.6. phrase: syntactic units that are built around a certain word category are calledphrase, the category of which is determined by the word category around which thephrase is built.8. head: The word round which phrase is formed is termed head.9. specifier: The words on the left side of the heads are said to function as specifiers.10. complement: The words on the right side of the heads are complements.11. phrase structure rule: The special type of grammatical mechanism that regulatesthe arrangement of elements that make up a phrase is called a phrase structure rule.14. coordination: Some structures are formed by joining two or more elements of thesame type with the help of a conjunction such as and or or. Such phenomenon isknown as coordination.15. subcategorization: The information about a word’s complement is included in the head and termed suncategorization.16. complementizer: Words which introduce the sentence complement are termed complementizer.17. complement clause: The sentence i ntroduced by the complementizer is called acomplement clause.18. complement phrase: the elements, including a complementizer and a complementclause is called a complement phrase.19. matrix clause: the contrusction in which the complement phrase is embedded iscalled matrix clause.20. modifier: the element, which specifies optionally expressible properties of headsis called modifier.21. transformation : a special type of rule that can move an element from one position to another22. inversion : the process of transformation that moves the auxiliary from the Infl position to a position to the left of the subject, is called inversion.23. Do insertion : In the process of forming yes-no question that does not contain an overt Infl, interrogative do is inserted into an empty Infl positon to make transformation work.24. deep structure : A level of abstract syntactic representation formed by the XP rule.25. surface structure : A level of syntactic representation after applying the necessary syntactic movement, i.e., transformation, to the deep structure. (05)26. universal grammar: the innateness principles and properties that pertain to the grammars of all human languages.Chapter 5: Semantics1. semantics: Semantics can be simply defined as the study of meaning.3. sense : Sense is concerned with the inherent meaning of the linguistic form. It is the collection of all the features of the linguistic form. It is abstract and de-contexturalized. It is the aspect of meaning dictionary compilers are interested in.4. reference : Reference means what a linguistic form refers to in the real, physical world. It deals with the relationship between the linguistic element and the non-linguistic world of experience.5. synonymy: Synonymy refers to the sameness or close similarity of meaning. Words that are close in meaning are called synonyms.6. dialectal synonyms: synonyms that are used in different regional dialects.7. stylistic synonyms: synonyms that differ in style, or degree of formality.8. collocational synonyms: Synonyms that differ in their colllocation, i.e., in the words they go together with.9. polysemy : The same word has more than one meaning.10. homonymy: Homonymy refers to the phenomenon that words having different meanings have the same form, i.e., different words are identical in sound or spelling, or in both.11. homophones: When two words are identical in sound, they are homophones.12. homographs: When two words are identical in spelling, they are homographs.13. complete homonymy: When two words are identical in both sound and spelling, they are complete homonyms.14. hyponymy: Hyponymy refers to the sense relation between a more general, more inclusive word and a more specific word.15. superordinate: The word which is more general in meaning is called the superordinate.16. co-hyponyms: Hyponyms of the same superordinate are co-hyponyms.17. antonymy: The term antonymy is used for oppositeness of meaning.20. relational opposites: Pairs if words that exhibit the reversal of a relationshipbetween the two items are called relational opposites. For example, husband---wife,father---son, buy---sell, let---rent, above---below.21. entailment: the relationship between two sentences w here the truth of one isinferred from the truth of the other. E.g. Cindy killed the dog entails the dog is dead.22. presupposition: What a speaker or writer assumes that the receiver of the massagealready knows. e.g. Some tea has already been taken is a presupposition of Take somemore tea.Chapter 6: Pragmatics1. pragmatics: The study of how speakers uses sentences to effect successful communication.2. context: The general knowledge shared by the speakers and the hearers.3. sentence meaning: The meaning of a self-contained unit with abstract andde-contextualized features.4. utterance meaning: The meaning that a speaker conveys by using a particularutterance in a particular context.5. utterance: expression produced in a particular context with a particular intention.6. Speech Act Theory: The theory proposed by John Austin and deepened by Searle,which believes that we are performing actions when we are speaking.7. constatives: Constatives are statements t hat either state or describe, and are thusverifiable.8. performatives: Pe rformatives are sentences that don’t state a fact or describe a state, and are not verifiable.9. locutionary act: The act of conveying literal meaning by virtue of syntax, lexiconand phonology.ntention and performed in10. illocutionary act: The act of expressing the speaker’s isaying something.11. perlocutionary act: The act resulting from saying something and the consequenceor the change brought about by the utterance.12. representatives: Stating or describing, saying what the speaker believes to be true.13. directives: Trying to get the hearer to do something.17. cooperative Principle: The principle that the participants must first of all bewilling to cooperate in making conversation, otherwise, it would be impossible tocarry on the talk.18. conversational implicature: The use of conversational maxims to imply meaningduring conversation.Chapter 7: Language Change8. acronyms: Acronyms are words derived from the initials of several words.9. protolanguage: The original form of a language family, which has ceased to exist.10. Language family: A group of historically related languages that have developedfrom a common ancestral language.Chapter 8: Language And Society1. sociolinguistics: The subfield of linguistics that study language variation andlanguage use in social contexts.2. speech community: A group of people who form a community and share at leastone speech variety as well as similar linguistic norms.3. speech varieties: It refers to any distinguishable form of speech used by a speakeror a group of speakers.4. regional dialect: A variety of language used by people living in the same geographical region.5. sociolect: A variety of language used by people, who belong to a particular socialclass.6. registers : The type of language which is selected as appropriate to the type of situation.dialect of an individual speaker that combines elements,7. idiolect : A person’sregarding regional, social, gender and age variations.8. linguistic reportoire : The totality of linguistic varieties possessed by an individualconstitutes his linguistic repertoire.9. register theory : A theory proposed by American linguist Halliday, who believedthat three social variables determine the register, namely, field of discourse, tenor ofdiscourse and mode of discourse.10. field of discourse : the purpose and subject matter of the communicative behavior..11. tenor of discourse: It refers to the role of relationship in the situation in question:who the participants in the communication groups are and in what relationship theystand to each other.12. mode of discourse: It refers to the means of communication and it is concernedwith how communication is carried out.13. standard dialect: A superposed variety of language of a community or nation,usually based on the speech and writing of educated native speakers of the language.14. formality: It refers to the degree of formality in different occasions and reflects the relationship and conversations. According to Martin Joos, there are five stages of formality, namely, intimate, casual, consultative, formal and frozen.15. Pidgin: A blending of several language, developing as a contact language ofpeople, who speak different languages, try to communication with one another on aregular basis.16. Creole : A pidgin language which has become the native language of a group ofspeakers used in this daily life.17. bilingualism : The use of two different languages side by side with each having adifferent role to play, and language switching occurs when the situation changes.(07C)18. diaglossia : A sociolinguistic situation in which two different varieties of languageco-exist in a speech community, each having a definite role to play.19. Lingua Franca : A variety of language that serves as a medium of communicationamong groups of people, who speak different native languages or dialects20. code-switching: the movement back and forth between two languages or dialectswithin the same sentence or discourse.Chapter 10: Language Acquisition1. language acquisition: It refers to the child’s acquisition of his mother tongue, i.e. how the child comes to understand and speak the language of his community.2. language acquisition device (LAD): A hypothetical innate mechanism every normalhuman child is believed to be born with, which allow them to acquire language.3. Universal Grammar: A theory which claims to account for the grammatical competence of every adult no matter what language he or she speaks.4. motherese: A special speech to children used by adults, which is characterized with slow rate of speed, high pitch, rich intonation, shorter and simpler sentence structures etc.----又叫child directed speech,caretaker talk.5. Critical Period Hypothesis: The hypothesis that the time span between early childhood and puberty is the critical period for language acquisition, during which children can acquire language without formal instruction successfully and effortlessly.6. under-extension: Use a word with less than its usual range of denotation.7. over-extension: Extension of the meaning of a word beyond its usual domain of application by young children.8. telegraphic speech: Childre n’s early multiword speech that contains content words and lacks function words and inflectional morphemes.9. content word: Words referring to things, quality, state or action, which have lexical meaning used alone.10. function word: Words with little meaning on their own but show grammatical relationships in and between sentences.11. taboo: Words known to speakers but avoided in some contexts of speech for reasons of religion, politeness etc.12. atypical development: Some acquisition of language may be delayed but followthe same rules of language development due to trauma or injury.Chapter 11 : Second Language Acquisition1. second language acquisition: It refers to the systematic study of how one person acquires a second language subsequent to his native language.2. target language: The language to be acquired by the second language learner.3. second language: A second language is a language which is not a native language ina country but which is widely used as a medium of communication and which is usually used alongside another language or languages.4. foreign language: A foreign language is a language which is taught as a school subject but which is not used as a medium of instruction in schools nor as a language of communication within a country.5. interlanguage: A type of language produced by second and foreign language learners, who are in the process of learning a language, and this type of language usually contains wrong expressions.6. fossilization: In second or foreign language learning, there is a process which sometimes occurs in which incorrect linguistic features become a permanent part ofthe way a person speaks or writes a language.14. overgeneralization: The use of previously available strategies in new situations, in which they are unacceptable.15. cross-association: s ome words are similar in meaning as well as spelling and pronunciation. This internal interference is called cross-association.16. error: the production of incorrect forms in speech or writing by a non-native speaker of a second language, due to his incomplete knowledge of the rules of thattarget language.17. mistake: mistakes, defined as either intentionally or unintentionally deviant formsand self-corrigible, suggest failure in performance.18. input: language which a learner hears or receives and from which he or she canlearn.19. intake: the input which is actually helpful for the learner.20. Input Hypothesis: A hypothesis proposed by Krashen , which states that in secondor the learner to understand input language whichlanguage learning, it’s necessary fpresent linguisticcontains linguistic items that are slightly beyond the learner’scompetence. E ventually the ability to produce language is said to emerge naturallywithout being taught directly.21. acquisition: Acquisition is a process similar to the way children acquire their firstlanguage. It is a subconscious process without minute learning of grammatical rules.Learners are hardly aware of their learning but they are using language to communicate. It is also called implicit learning, informal learning or natural learning.23. comprehensible input: Input language which contains linguistic items that aresent linguistic competence.slightly beyond the learner’s pre24. language aptitude: the natural ability to learn a language, not includingintelligence, motivation, interest, etc.25. motivation: motivation is defined as the learner’s attitudes and affective state or learning drive.26. instrumental motivation: the motivation that people learn a foreign language forinstrumental goals such as passing exams, or furthering a career etc.27. integrative motivation: the drive that people learn a foreign language because ofthe wish to identify with the target culture.28. resultative motivation: the drive that learners learn a second language for externalpurposes.29. intrinsic motivation: the drive that learners learn the second language forenjoyment or pleasure from learning.Chapter 12 : Language And Brain1. neurolinguistics: It is the study of relationship between brain and language. Itincludes research into how the structure of the brain influences language learning,how and in which parts of the brain language is stored, and how damage to the brainaffects the ability to use language.2. psycholinguistics: the study of language processing. It is concerned with theprocesses of language acqisition, comprehension and production.7. aphasia: It refers to a number of acquired language disorders due to the cerebrallesions caused by a tumor, an accident and so on.13. spoonerism: a slip of tongue in which the position of sounds, syllables, or words isreversed, for example, Let’s have chish and fips instend of Let’s have fish and ch 14. priming: the process that before the participants make a decision whether thestring of letters is a word or not, they are presented with an activated word.15. frequency effect: Subjects take less time to make judgement on frequently usedwords than to judge less commonly used words . This phenomenon is calledfrequency effect.16. lexical decision: an experiment that let participants judge whether a string of letter is a word or not at a certain time.18. priming effect: Since the mental representation is activated through the prime, when the target is presented, r esponse time is shorter that it otherwise would have been. This is called the priming effect.。

nguage: language can be defined as a system of arbitory vocal symbols used for communication.2.Duality: By Duality is meant the property of having two levels of structures, such that units of the primary level are composed of elements of the secondary level and each of the two levels has its own principle of organization.3.Displacement: Displacement means that human languages enable their users to symbolize objects, events and concepts which are not present ( in time and space) at the moment of communication.4.Vowel: a vowel is produced without such “stricture” so that air escapes in a relatively unimpeded way through the mouth or nose.petence and performance: A language user’s underlying knowledge about the system of rules is called his linguistic competence. And performance refers to the actual use of language in concrete situations.6.Phoneme: The word phoneme simply refers to a “unit of explicit sound contrast”: the existence of a minimal pair automatically grants phonemic status to the sounds responsible for the contrasts.7.Lexeme: A separate unit of meaning, usually in the form of a word.8.Bound morpheme: an element of meaning which is structually dependent on the word it added to.9.Inflection: inflection indicates grammatical relations by adding infectional affixes such as number, person, finiteness, aspect and case; the adding of inflectional affixes will not change the grammatical class of the stems ( to which they are attached).10.Positional relation: positional relation or word order refers to the sequential arrangement of words in a language.11.Endocentric: endocentric construction is one whose distribution is functionally equivalent to that of one or more of its constituents, i.e. a word or a group of words, which serves as a definable centre or head.12.Concep t: There is something behind the concrete thing we can see with our eyes. And that something is abstract, which has no existence in the material worldand can only be sensed in our minds. This abstract thing is usually called Concept.13.Categorization: categorization is the process of classifying our experiences into different categories based on commonalities and differences.14.Image schemas: Mark Johnson defines an image schema as a recurring, dynamic pattern of our perceptual interactions and motor programs that gives coherence and structure to our experience.15.Performatives: Sentences like the following do not describe things. They cannot be said to be true or false. The uttering of sentences is, or is a part of, the doing of an action.。
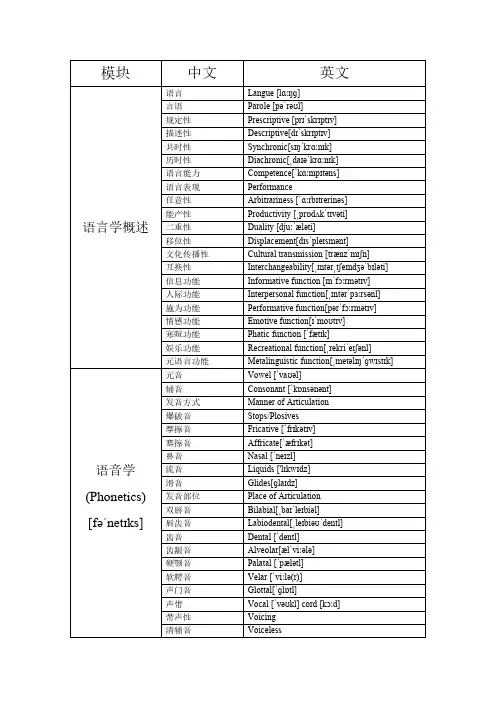
模块中文英文语言学概述语言Langue[lɑːŋɡ]言语Parole[pəˈrəʊl]规定性Prescriptive[prɪˈskrɪptɪv]描述性Descriptive[dɪˈskrɪptɪv]共时性Synchronic[sɪŋˈkrɑːnɪk]历时性Diachronic[ˌdaɪəˈkrɑːnɪk]语言能力Competence[ˈkɑːmpɪtəns]语言表现Performance任意性Arbitrariness[ˈɑːrbɪtrerinəs]能产性Productivity[ˌprɒdʌkˈtɪvəti]二重性Duality[djuːˈæləti]移位性Displacement[dɪsˈpleɪsmənt]文化传播性Cultural transmission[trænzˈmɪʃn]互换性Interchangeability[ˌɪntərˌtʃeɪndʒəˈbɪləti]信息功能Informative function[ɪnˈfɔːrmətɪv]人际功能Interpersonal function[ˌɪntərˈpɜːrsənl]施为功能Performative function[pərˈfɔːrmətɪv]情感功能Emotive function[ɪˈmoʊtɪv]寒暄功能Phatic function[ˈfætɪk]娱乐功能Recreational function[ˌrekriˈeɪʃənl]元语言功能Metalinguistic function[ˌmetəlɪŋˈɡwɪstɪk]语音学(Phonetics) [fəˈnetɪks]元音Vowel[ˈvaʊəl]辅音Consonant[ˈkɒnsənənt]发音方式Manner of Articulation爆破音Stops/Plosives摩擦音Fricative[ˈfrɪkətɪv]塞擦音Affricate[ˈæfrɪkət]鼻音Nasal[ˈneɪzl]流音Liquids['lɪkwɪdz]滑音Glides[ɡlaɪdz]发音部位Place of Articulation双唇音Bilabial[ˌbaɪˈleɪbiəl]唇齿音Labiodental[ˌleɪbiəʊˈdentl]齿音Dental[ˈdentl]齿龈音Alveolar[ælˈviːələ]硬颚音Palatal[ˈpælətl]软腭音Velar[ˈviːlə(r)]声门音Glottal[ˈɡlɒtl]声带Vocal[ˈvəʊkl]cord[kɔːd]带声性Voicing清辅音Voiceless浊辅音Voiced[vɔɪst]音系学(Phonology) [fəˈnɒlədʒi]音素Phone音位Phoneme[ˈfəʊniːm]音位变体Allophone[ˈæləfəʊn]互补分布Complementary[ˌkɒmplɪˈmentri]distribution 最小对立体Minimal pairs音位对立Phonemic[fəʊˈniːmɪk]contrast形态学(Morphology) [mɔːˈfɒlədʒi]词素Morphemes[ˈmɔːfiːmz]自由词素Free Morphemes粘着词素Bound Morphemes词根Root词缀Affix[əˈfɪks,ˈæfɪks]前缀Prefix[ˈpriːfɪks]后缀Suffix[ˈsʌfɪks]词干Stem屈折词缀Inflectional[ɪnˈflɛkʃən(ə)l]Affix派生词缀Derivational[ˌdɛrɪˈveɪʃən(ə)l]Affix 复合法Compound派生法Derivation发明法Invention混成法Blending['blendɪŋ]首字母连写法Initialism[ɪnˈɪʃəlɪzəm]首字母缩略法Acronym[ˈækrənɪm]借词法Borrowing逆构词法Back-formation[fɔːˈmeɪʃn]语义学(Semantics)[sɪˈmæntɪks]同义关系Synonymy[sɪˈnɒnɪmi]方言同义词Dialectal[ˌdaɪ.əˈlek.təl]synonyms[ˈsɪnənɪmz]文体同义词Stylistic[staɪˈlɪstɪk]synonyms情感同义词Emotive synonyms搭配同义词Collocational[ˌkɒləʊˈkeɪʃən(ə)l]synonyms 语义同义词Semantic synonyms反义关系Antonymy[æn‘tɒnɪmɪ]等级反义关系Gradable[ˈɡreɪdəbl]antonymy互补反义关系Complementary antonymy反向反义关系Converse antonymy上下义关系Hyponymy[haɪ'pɒnɪmɪ]上义词Superordinate[ˌsuːpər'ɔːdɪnət]下义词Hyponyms['haɪpəʊnɪm]一词多义Polysemy[pəˈlɪsɪmi]同音/同形异义关系Homonymy[ho'mɑnəmi]同音异义词Homophone[ˈhɒməʊfəʊn]同形异义词Homographs完全同音异义词Complete Homonyms[ˈhɒm.ə.nɪm]蕴含entailment[ɪnˈteɪl.mənt]预设Presuppose[ˌpriːsəˈpəʊz]语用学(Pragmatics) [præɡˈmætɪks]言内行为Locutionary[ləu'kju:ʃənəri]act言外行为Illocutionary[ˌɪləˈkjuːʃəneri]act言后行为Perlocutionary[ˌpɜːrləˈkjuːʃəneri]act直接言语行为Direct speech act间接言语行为Indirect speech act合作原则Cooperative principle数量准则Quantity maxim[ˈmæksɪm]质量准则Quality maxim关系准则Relation maxim方式准则Manner maxim会话含义Conversational implicature[ˈɪmplɪkətʃər]修辞学(Rhetoric)[ˈretərɪk]头韵Alliteration[əˌlɪtəˈreɪʃn]押尾韵End rhyme反韵Reverse rhyme准押韵(类韵)Assonance[ˈæsənəns]拟声Onomatopoeia[ˌɑːnəˌmætəˈpiːə]斯普纳现象Spoonerism[ˈspuːnərɪzəm]明喻Simile暗喻Metaphor转喻(借代)Metonymy[məˈtɑːnəmi]提喻Synecdoche[sɪˈnekdəki]隐喻(典故)Allusion[əˈluːʒn]拟人Personification[pərˌsɑːnɪfɪˈkeɪʃn]夸张Hyperbole[haɪˈpɜːrbəli]矛盾Oxymoron[ˌɑːksɪˈmɔːrɑːn]委婉语Euphemism[ˈjuːfəmɪzəm]反语Irony[ˈaɪrəni]双关Pun移就Transferred epithet[ˈepɪθet]。
英语语言学名词解释
英语语言学是语言学中的一个分支,研究英语的语言结构、语音、语法、语义、语用和历史演变等方面。
以下是一些英语语言学的名词解释:
1. Phonetics(音韵学):研究语音、发音和声音的学科。
它包括语音学和音系学。
2. Phonology(音系学):研究语音在语言中的系统性组织和规律性变化的学科。
3. Morphology(形态学):研究词形变化和词构成的学科。
4. Syntax(句法学):研究句子结构和语法规则的学科。
5. Semantics(语义学):研究语言意义的学科,包括词义和句子意义。
6. Pragmatics(语用学):研究语言在实际使用中的含义和功能的学科。
7. Discourse analysis(语篇分析):研究语言在实际使用中的连贯性和语篇结构的学科。
8. Historical linguistics(历史语言学):研究语言的演变和变化的学科。
9. Sociolinguistics(社会语言学):研究语言和社会、文化、地理和历史等因素之间的关系的学科。
10. Psycholinguistics(心理语言学):研究语言和心理过程之间的关系的学科,包括语言习得、记忆和理解等。
以上是一些常见的英语语言学名词解释,它们涵盖了英语语言学的主要领域和分支。
英语语言学名词解释2009-09-30 13:54Synchronic: said of an approach that studies language at a theoretical “point” in time. Diachronic: said of the study of development of language and languages over time. Arbitrariness: the absence of any physical correspondence between linguistic signals and the entities to which they refer.Duality: the structural organization of language into two abstract levels; meaningful units and meaningless segments .Competence: unconscious knowledge of the system of grammatical rules in a language. Performance: the language actually used by people in speaking or writing.Langue: the language system shared by a “speech community”.Parole: the concrete utterances of speaker.Morpheme: the smallest unit of language in terms of the relationship between expression and content, a unit that cannot be divided into further smaller units without destroying or drastically altering the meaning, whether it is lexical or grammatical.Inflection: is the manifestation of grammatical relationship through the addition of inflectional affixes such as number, person, finiteness, aspect and cases to which they are attached.Root: refers to the base form of a word that cannot be further analyzed without loss of identity. Stem:is any morpheme or combinations of morphemes to which an inflectional affix can be added.Acronym:is made up from the first letters of the name of an organization,which has a heavily modified headword.Syntax: the study of the interrelationships between elements in sentence structure. Subordination: the process or result of linking linguistic units so that they have different syntactic status, one being dependent upon the other, and usually a constituent of the other. Denotation: denotation involves the relationship between a linguistic unit and the non-linguistic entities to which it refers.Connotation: properties of the entity a word denote.Synonymy: synonymy is the technical name for one of the sense relations between linguistic units, namely the sameness relation.Hyponymy: the technical name for inclusiveness sense relation, is a matter of class membership. Entailment: This a logic relationship between two sentences in which the truth of the second necessarily follows from the truth of the first, while the falsity of the first follows from the falsity of the second.Traffic light does not have duality. Obviously, it is not a double-level system. There is onlyone-to-one relationship between signs and meaning but the meaning units cannot be divided into smaller meaningless elements further. So the traffic light only has the primary level and lacks the secondary level like animals’ call.Critical Period HypothesisThe critical period for language acquisition语言获得的关键期 Eric Lenneberg was a major proponent.The critical period hypothesis关键期假设It refers to a period in one’s life extending from about age two to puberty, during which the human brain is most ready to acquire a particular language and language learning can proceed easily, swiftly, and without explicit instruction. It coincides with the process of brain lateralization. Prior to this period, both hemispheres are involved to some extent in language and one can take over if the other is damaged.「语言学习关键期」(the critical period)的争议。
现代语言学一绪论1 Linguisitics : Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language2 Phonetics : The study of sounds which are used in linguistics communication is called phonetics.For example,vowels and consonants3 Phonology” : The study of how sounds are put together and used in communication is called phonology.For example,phone,phoneme,and allophone.4 Morphology :The study of the way in which morphemes are arranged to form words is called morphology.For example,boy and “ish”---boyish,teach---teacher.5 Syntax : The study of how morphemes and words are combined to form sentences is called syntax.For esample,”John like linguistics.”6 Semantics: The study of meaning in language is called semantics. For example,:The seal could not be f ound.The zoo keeper became worried.” The seal could not be found,The king became worried.” Here the word seal means different things.7 Pragmatics: The study of meaning in context of use is called pragmatics.For example, “I do” The word do means different context.8 Sociolinguistics: The study of language with reference to society is called sociolinguistics.For example,regional dialects,social variation in language.9Psycholinguistics: The study of language with reference to workings of mind is called psycholinguistics.二音系学1 Phonetics: The study of sounds that are used in linguistic communication is called phonetics.2 Phonology: The study of how sounds are put together and used in communication is called phonology.3 Phone: Phone can be simply defined as the speech sounds we use when speaking a language. A phone is a phonetic unit or segement. It does not necessarily distinguish meaning; some do,some don’t.4 Phoneme: Phonology is concerned with the speech sounds which distinguish meaning. The basic unit in phonology is called phoneme;it is a unit that is of distinctive value.5 allophone: The different phones which can represent a phoneme in different phonetic environment are called the allophones of that phoneme.6 Complementary distribution: These two allophones of the same phoneme are said to be in complementary distribution.7 Minimal pair: When two different forms are identical in every way except for one sound segement which occurs in the same place in the stings, the two words are said to form a minimal pair.8 Stress: When a certain syllable of a word is stressed, it means that the syllable is prounced with great force than the other or others.9 tones: Tones are pitch variation, which are caused by the different rates of vibration of the vocal cords. Pitch variations can distinguish meaning just like phoneme;therefore, the tone is a suprasegemental feature.10 intonation: When pitch, stress and sound length are tied to the sentence rather than the word in isolation, they are collectively known as intonation. Intonation plays an important role in conveying meaning in almost every language,especially in a language like English{$isbest}三形态学1 morphology: Morphology is a branch of grammer which studies the internal structure of words and the rules by which words are formed.2 inflectional morphology: Inflectional morphology studies the inflections of word-formation.3 derivational morphology: Derivational morphology is the study of word-formation.4 morpheme: Morpheme is the smallest meaningful unit of language.5 free morpheme: Free morpheme are the morphemes which are independent units of meaning and can be used freely all by themselces or in combination with other morphemes.6 bound morpheme: Bound morphemes are the morphemes which cannot be used independently but have to be combined with other morphemes, either free or bound, to form a word.7 root: A root is often seen as part of a word; it can never stand by itself although it bears clear,definite meaning; it must be combined with another root or an affix to forma word.8 affix: Affixes are of two types: inflectional and derivational.9 prefix: Prefix occur at the beginning of a word.10 suffix: Suffixes are added to the end of the stems; they modify the meaning of the original word and in many cases change its part of speech.11 derivation: Derivation affixes are added to an existing form to creat a word.Derivation can be viewed as the adding of affixes to stem to form nes words.12 compounding: Like derivation, compounding is another popular and important way of forming new words in English. Compounding can be viewed as the combination of two or sometimes more than two words to creat new words. {$isbest}四句法学1 linguistic competence: Comsky defines competence as the ideal user’s knowledge of the rules of his language,and performance the actual realization of this knowledge in linguistic communication.2 sentence : A sentence is a structurally independent unit that usually comprises a number of words to form a complete statement question or command.3 transformation rules: Syntactic movement is governed by transformational rules. The operation of the transformational rules may change the syntactic representation of a sentence.4 D-structure : A sentence may have two levels of syntactic representation. One exists before movement take place, the other occurs after movement take place. In formal linguistic exploration, these two syntactic representation are commonly termed as D-structure.5 Move а : Just as there is a general rule for all phrase structure rules,i,e. the X-bar schema, there is a general movement rule accounting for the syntactic behavior of any constituent movement. This movement rule is cal led Move а{$isbest}五语义学1 semantics: Semantics can be simply defined as the study of meaning in language.2 sense : Sense is concerned with the inherent meaning of the linguistic form. It is the collection of all the features of the linguistic form; it is abstract and decontextualized.3 reference : Reference means what a linguistic form refers to in the real, physical world; it deals with the relationship between the linguistic element and the non-linguistic world of experience.4 synonymy : Synonymy refers to the sameness or close similarity of meaning. Words that are close in meaning are called synonymy.5 polysemy : Polysemy refers to the fact that the same one word may have more than one meaning.A word having more than one meaning is called a polysemic word.6 antonymy : Antonymy refers to the oppositeness of meaning. Words that are opposite in meaning are called antonyms.7 homonymy :Homonymy refers to the phenomenon that words having different meanings have the same form,i.e. different words are identical in sound or spelling, or8 hyponymy : Hyponymy refers to the sense relation between a more general, more inclusive word and a more specific word.9 componential analysis : Componential analysis is a way to analyze wprd meaning. It was proposed by structural semanticists.10 grammatical meaning : The grammatical meaning of a sentence refers to its grammaticality,i.e. its grammatical well-formedness. The grammaticality of asentence is governed by the grammatical rules of the language.11 semantic meaning : The semantic meaning of a sentence is governed by rules called selectional restrictions.12 predication : In semantic analysis of a sentence, the basic unit is called predication. The predication is the abstraction of the meaning of a sentence.{$isbest}六语用学1 pragmatics: Pragmatics can be defined as the study of how speakers of a language use sentences to effect successful communication.2 context: The notion of context is essential to the pragmatic study of language. Generally speaking, it consists of the knowledge that is shared by the speaker and the hearer.3 utterance meaning: Utterance is based on sentence meaning; it is realization of the abstract meaning of a sentence in a real situation of communication, or simply in a4 locutionary act: A locutionary act is the act of utterance words,phrases,clauses. It is the act of conveying literal meaning by means of syntax, lexion and phonology.5 illocutionary act: An illocutionary act is the act expressing t he speaker’s intention; It is the act performed in saying something.6 perlocutionary act:A illocutionary act is the act performed by or resulting from saying something: it is the consequence of, or the change brought about by the utterance; it is the act performed by saying something.{$isbest}七历史语言学1 historical linguistics: Historical linguistics is the subfield of linguistics that studies language change.2 apocope: Another well-documented sound loss is the deletion of a word-final vowel segement, a phenomenon called apocope.3 epenthesis: A change that involves the insertion of a consonant or vowel sound to the middle of a word is known as epenthesis.4 metathesis: Sound change as a result of sound movement is known as metathesis.5 compounding: Compounding is a process of combining two or more words into one lexical unit.6 derivation: Derivation refers to the process by which new words are formed by the addition of affixes to the roots.7 blending: Blending is a process of forming a new word by combining parts of other words.8 back-formation: Back-formation is a process by which new words are formed by taking away the suffix of an existing word.9 semantic broadening: Semantic broadening refers to the process in which the meaning of a word becomes general or inclusive than its historically earlier denotation..10 semantic narrowing: Semantic narrowing is a process in which the meaning ofa word becomes less general or inclusive than its historically earlier meaning.11 semantic shift: Semantic shift is a process of semantic change in which a word loses its former meaning and acquire a new, sometimes related, meaning.12 protolanguage: It refers to a family of a language.A protolanguage is the original form of a language family that has ceased to exist.The proto form can be reconstructed by identifying and comparing similar linguistic forms with similar meanings across related languages.13 sound shift: It refers to the systematic modification of a series of phonemes. {$isbest}八社会语言学1 sociolinguistics: Sociolinguistics is the study of language in social context.2 speech community: A speech community is thus defined as a group of people who form a community and share the same language or a particular variety of language.3 speech variety: Speech variety, also known as language variety, refers to any distinguishable form of speech used by a speaker or group of speakers.4 language planning: One way out of the communication dilemma is language standardization known as language planning. This means that certain authorities, such as the government or government agency of a country, choose a particular speech variety and spread the use of it, including its pronunciation and spelling system, across regional boundaries.5 idiolect: Such a personal dialect is refered to as idiolect.6 standard language: The standard language is a superposed, socially prestigious dialect of language. It is the language employed by the government and the judiciary system,used by the mass media.7 nonstandard language: Language varieties other than the standard are called nonstandard, or vernacular, languages.8 lingua franca: A lingua franca is a variety of language that serves as a medium of communication among groups of people for diverse linguistic backgrounds.9 pidgin: A pidgin is a variety of language that is generally used by native speakers of other languages as a medium of communication.10 Creole: A Creole language is originally a pidgin that has become established asa native language in some speech communication.11 diglossia: Diglossia usually describes a situation in which two very different varieties of language co-exist in a speech communication, each with a distinct range of purely social function and appropriate for certain situations.12 bilingualism: Bilingualism refers to a linguistic situation in which two standard languages are used either by an individual or by a group of speakers, such as the inhabitants of a particular region or a nation.13 ethic dialect: An ethnic language variety is a social dialect of a language ,often cutting across regional differences.14 sociolect: Social dialect, or sociolects, are varieties of language used by people belonging to particular social classes.15 register: Registers are language varieties which are appropriate for use in particular speech situations, in contrast to language varieties that are associated with the social or regional grouping of their customary users. For that reason, registers are also known as situational dialects.16 slang: Slang is a causal use of language that consists of expressive but nonstandard vocabulary, typically of arbitrary, flashy and often ephemeral coinage and figure of speech characterized by spontaneity and sometimes by raciness.17 tabo A linguistic taboo refers to a word or expression that is prohibited by the “polite” society from general use.18 euphemism: Euphemism comes from the Greek word euphemismos, meaning “to speak with good words”. A euphemism, then ,is mild, indirect or less offensive word or expression substitute when the speaker or writer fears more direct wording might be harsh, unpleasantly direct, or offensive.{$isbest}九心理语言学1 psycholinguistics:Psycholinguistics is the study of language in relation to the mind. As the suggests, psycholinguistics is viewed as the intersection of psychology and linguistics, drawing equally upon the language we acquire, produce and comprehend.2 cerebral cortex: The most important part of the brain is the outside surface of the brain, called the cerebral cortex.3 brain lateralization: The localization of cognitive of cognitive and percpetual functions in a particular hemisphere of the brain is called lateralization.4 linguistic lateralization: In their research of brain lateralization, psycholinguistics are particulary interested in linguistic lateralization, which is the brain’s neurological specialization for language.5 dichotic listening: Evidence in support of lateralization for language in the left hemisphere comes from researches in dichotic listening tasks6 right ear advantage: Stimuli heard in the left ear are reported less accurately than those heard in the right car. This phenomenon is knowas the right ear advantage.7 critical period hypothesis: The critical period hypothesis refers to a period in one’s life extending from about age two to puberty during which the humanbrain is most ready to acquire a particular language and language learning can proceed easily, swiftly and without explicit instruction.8 linguistic determinism: Whorf proposed first that all higher levels of thinking are dependent on language. That is, language determines thought, hence the strong notion of linguistic determinism.9 linguistic relativism: Whorf also believed that speakers of different language perceive and experience the world differently, that is, relative to their linguistic background, hence the notion10 subvocal speech: When language and thought are identical or closely parallel to each other, we may regard thought as “subvocal speech”.of linguistic relativism.{$isbest}十语言习得1 language acquisition: Language acquisition is concerned with language development in humans. In general, language acquisition refers to children’s development of their first language, that is, the native language of the community in which a child has been brought up.2 telegraphic speech: The early multiword utterance of children have a special characteristic. They typically lack inflectional morphemes and most minor lexical categories. Because of their resemblance to the styly of language found in telegrams, utterance at this acquisition stage are often called telegraphic speech.3 holophrastic sentence: Children’s one-word utterance are also calledholophrastic sentences.4 acquisition: According to Krashen,acquisition refers to the gradual and subconscious development of ability in the first language by using it naturally in daily communicative situations.5 learning: Learning, however, is defined as a conscious process of accumulating knowledge of a second language usually obtained in school settings.6 language transfer: Learners will subconsciously use their L1 knowledge in learning a second language. This is known as language transfer.7 positive transfer: Presumably, positive transfer occurs when an L1 pattern is identical with, or similar to, a target-language pattern.8 negative transfer: Conversely, negative transfer occurs when an L1 pattern is different from the counterpart pattern of the target language.9 contrastive analysis: The Contrastive Analysis approach was founded on the belief that, by establishing the linguistic differences between the native and target language system, it was possible to predict what problems learners of a particular second language would face and the types of errors they would make.10 interlanguage: SLA is viewed as a process of creative construction, in which a learner constructs a series of internal representations that comprises the learner’s interim knowledge of the target language, known as interlanguage.11 formal instruction: Formal instruction occurs in classrooms when attempts are made to raise learner’s consciousnes s about the nature of target language rules in order to aid learning.12 instrumental motivation: Thus, instrumental motivation occurs when the learner’s goal is functional.13 integrative motivation: Integrative motivation occurs when the learner’s goal is social.14 acculturation: A related issue with integrative motivation has been the extent to which learners differ in the process of adapting to the new culture of the 12community. This adaptation process is called acculturation.。
DefinitionLanguage is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication.语言是一个用于人类交际的、具有任意性的语音符号系统。
Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language.语言学通常被定义为对语言进行科学性研究的学科。
Arbitrariness(任意性) There is no intrinsic(本质的) connection between the word and the thing it denotes(表示).Duality(双层性) Language is a system, which consists of two sets of structures, or two levels, and it enables its users to talk about anything within their knowledge.Creativity(创造性) It makes possible the construction(结构) and interpretation(翻译) of new signals by its users.Displacement(移位性) Language can be used to refer to things, which are not present, real or imagined matters in the past, present or future, or in far-away places.Phonetics(语音学) is defined as the study of the phonic medium of language; it is concerned with all the sounds that occur in the world's languages.语音学被定义为对语言的语音媒介的研究;它涉及所有出现在世界语言中的声音。
名词解释1.Prescriptive and Descriptive规定性的和描述性的Prescriptive and descriptive represent two kind of different types of linguistic study. If a linguistic study aims to describe and analyze the language people actually use, it is said to be descriptive; If the linguistic study aims to lay down rules for “correct and standard”behavior in using language, it is said to be prescriptive.描述性的研究主要以观察和描述人们实际所使用的语言为目的。
规定性的研究以制定语言使用的规范和标准为主要目的,即为使用者指出语言的标准用法,什么是正确的用法,什么是错误的用法,为语言使用者提供典范。
ngue and Parole 语言和言语Langue refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all the members of a speech community.Langue is the set of conventions and rules which language users all have to abide by.Parole refers to the realization of langue in actual use.Parole is the concrete use of the convention and the application of rules.语言是一种社会机制、是一种语言的理想形式、是为一个团体所有成员所接受的社会惯例的抽象的语言系统。
1)Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific or systematic study of (human) language.word language preceded by zero article in English implies that linguistics studies not any particular language, . English , Chinese , French and Japanese, but languages in general.word study does not mean “learn” but “investigate”.word scientific refers to the way in whichlanguage is studied.It is a science in the sense that it scientifically studies the rules,systems and principles of human languages. It deals with a wide range of linguistic phenomena,analyzes them,and makes general statements about them.2)Linguistics is always guided by the 3 canons of science:(e c e)exhaustiveness: it strives for thorough-goingness in the examination of relevant materials;consistency: there should be no contradiction between different parts of the total statementeconomy: other things being equal, a shorter statement or analysis is to be preferred to one that is longer or more complex. (e c e)3) The subject matter of linguistics is all natural language, living or dead.4) Linguistics has 2 main purposes:it studies the nature of language and tries to establish a theory of language, and describes languages in the light of the theory established.It examines all the forms of language in general and seeks a scientific understanding of the ways in which it is organized to fulfill the needs it serves and the functions it performs in human lifelinguistics differs from traditional grammar at least in 3 basic ways: Linguistics describes languages and does not lay down rules of correctness. Linguists are interested in what is said. So they are often said to be descriptive. Linguists regard the spoken language as primary. It is believed that speech came into being first for any human language and the writing system came along much later. Traditional grammar is based on Latin and it tries to impose the Latin categories and structures on other languages, while linguistics describes each language on its own merits.For a student of language, some knowledge of linguistics is of both interest and importance.For a teacher of foreign languages, he will definitely a great deal from the knowledge of linguistics.For a researcher, there is even more scope for displaying his abilities.Why study linguistics ?1. Linguistics takes an analytical approach to the study of language, andfocus on developing skills in data analysis, problem solving, and logical thinking that can be applied to many fields.2.It is an interdisciplinary subject.3.Linguistics is a science that is still in its infancy but undergoing rapiddevelopment, and it is “a pilot science”.What and how linguists study language?1. nature of language (focus on language itself)2. nature of acquisition (focus on learners)3. nature of teaching (focus on teachers)The process of linguistic study can be summarized as follows:.First, certain linguistic facts are observed, and generalizations are made about them;.Next, based on these generalizations, hypotheses are tested by further observations;.And finally a linguistic theory is constructed about what language is and how it works.General linguistics: The study of language as a whole. It deals with the basic concepts, theories, descriptions, models and methods applicable in any linguistic study.Microlinguistics(微观语言学)includes 6 branches, namely, phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics and pragmatics. It studies language itself. Macrolinguistics (宏观语言学)studies language in use--- practical usage. macrolinguistics includes:Sociolinguistics studies the relations between language and society: how social factors influence the structure and use of language. Another name for sociolinguistics is the sociology of language.Psycholinguistics is the study of language and mind: the mental structures and processes which are involved in the acquisition, comprehension and production of language.Neurolinguistics or neurological linguistics is the study of language processing and language representation in the brain.Stylistics is the study of how literary effects can be related to linguistic features. It usually refers to the study of written language, including literary texts, but it also investigates spoken language sometimes.Discourse analysis, or text linguistics is the study of the relationship between language and the contexts in which language is used.Computational linguistics is an approach to linguistics which employs mathematical techniques, often with the help of a computer.Cognitive linguistics is an approach to the analysis of natural language that focuses on language as an instrument for organizing, processing, and conveying information.Apart from the different branches of linguistics, there are some distinctions of linguistics, such as: functional linguistics vs formal linguistics; theoretical linguistics vs applied linguistics.Applied linguistics is primarily concerned with the application of linguistic theories, methods and findings to the elucidation of language problems which havearisen in other areas of experience.Phonetics(语音学):Phonetics is the scientific study of speech sounds.It studies how speech sounds are articulated, transmitted, and received. It is a pure science and examines speech sounds in general.Phonetics: The general study of the characteristics of speech sounds.Phonology(音系学/音位学): The description of the systems and patterns of speech sounds in a language.Phonology is the study of how speech sounds function in a language. It studies the ways speech sounds are organized. It can be seen as the functional phonetics of a particular language.Morphology(形态学,词法学):The study of the way in which morphemes are arranged to form words.Morphology is the study of the formation of words. It is a branch of linguistics which breaks words into morphemes.Syntax(句法学):The study of those rules that govern the combination of words to form permissible sentences.Syntax deals with the combination of words into phrases, clauses and sentences. It is the grammar of sentence construction.Semantics(语义学) is a branch of linguistics which is concerned with the study of meaning in abstraction.Pragmatics can be defined as the study of language in use. It deals with how speakers use language in ways which cannot be predicted from linguistic knowledge alone, and how hearers arrive at the intended meaning of speakers. In a broad sense, pragmatics studies the principles observed by human beings when they communicate with one another.Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication.This definition is widely accepted because it includes some of the important characteristics of human language.Language as system ---The key word in the definition is "system". Language is systematic. Otherwise we would not be able to learn or use it consistently. Each language system contains two subsystems: a system of sound and a system of meaning. Language is a system—elements in it are not arranged and combined randomly, but according to some rules and principles.Language as arbitrary ---There is no natural relationship between the sound and what it means in a certain language.The relation between sound and meaning is almost always arbitrary or conventional. The relation between sound and meaning is almost always arbitrary.A rose by any other name would smell as sweet.A rose by any other name would smell as sweet.Romeo and JulietThe relation between sound and meaning is almost always conventional《荀子·正名》:“名无固宜,约之以命,约定俗成谓之宜,异于约则谓之不宜。
大家论坛 英语专业考研资料
真题:
基础英语:各校基础英语真题资料汇总
英美文学各校英美文学真题汇总
二外:英研二外资料——日语法语德语俄语西班牙语等汇总
辅导书系列:
英语专业考研名校全真试题基础英语07到年真卷与解析下载
英语专业考研核心词汇.pdf.宫玉波.09版
星火英语专业考研名校全真试题精解英汉互译2012
2011英语专业考研名校全真题精解英汉互译.rar郭棲庆2010年出版
星火英语专业考研考点精梳与精炼英美文化
英语专业考研考点精梳与精练北京外国语大学英美文化.rar郭栖庆.2009年版
2010年英语专业考研考点精梳与精练英美文化.rar郭栖庆09年出版
星火英语专业考研考点精梳与精炼英美文学
2010年英语专业考研考点精梳与精练北京外国语大学英美文学.rar郭栖庆09年出版传播学原理2009年版张国良
孙亦丽--大学英语精读学习精要--第一二三册pdf下载
高级英语第二册教材及教师用书第一册rar下载
语言学资料:
英语专业考研考点精梳与精练上海外国语大学语言学.pdf.黄任.09版
《英语语言学基础》学习指南-温洪瑞主编1999年08月版pdf
[韩礼德语言学文集]唐纳德•韩礼德扫描版
英语句法与语用研究.rar下载
语言学名著选读pdf
英语专业考研考点精梳与精练上外语言学pdf下载
英语语言文学典型例题与全真题解析.rar下载英语语言学考点测评
英美概况导读中文版
胡壮麟《语言学教程》修订版笔记
新编英国文学教程——高等学校英语专业系列教材下载
英语语言学资料
华中师范大学语言学课本教程2010版
戴伟栋语言学笔记
liguistics--胡壮麟超赞的笔记
2007年上外英语语言文学专业英汉互译
2005年上外英语语言文学专业翻译试卷有答案
辽宁大学语言文学之英语专业基础课真题
英美文学、文化资料:
星火英语专业考研考点精梳与精炼英美文化
英语专业考研考点精梳与精练北京外国语大学英美文化郭栖庆09版
2010年英语专业考研考点精梳与精练英美文化郭栖庆09版
大家论坛-英语专业考研论坛-
公益论坛免费下载各种资料!
/thread-2407892-1-1.html
星火英语专业考研考点精梳与精炼英美文学
2010年英语专业考研考点精梳与精练北外英美文学.rar郭栖庆09版
漫话英美文学英美文学史考研指南常耀信
英语专业考研英语国家文化考点测评
王佐良:欧洲文化入门[1992][完整]DJVU
王守仁:英国文学选读[2001][完整]DJVU
陶洁:美国文学选读[2000][完整]DJVU
[美国文学经典].Classics of American Literature
英美文化基础教程学习手册—朱永涛—下载
新编英国文学教程——高等学校英语专业系列教材下载
《新编英国文学教程》下载
高教版《英美文学选读》课文译文
《英国文学简史》中文版
英国文学主要作家作品汇总
《英美文学史》之英国文学作家作品大全
《美国文学简史》上中文版
英国文学史考试要点
英美文学部分作家的介绍和评论
外国文学史图表版笔记整理
英国文学部分作品分析
英美文学超全题库
十套考研英美概况练习题含答案
南京师范大学2002年2003年语言学之英美文学考研真题.pdf
翻译资料:
全日制翻译硕士专业学位MTI研究生入学考试指南
外事翻译口译和笔译技巧.rar下载汉语成语典故谚语与歇后语英语翻译全国68所院校英汉互译试题分析
英语专业考研翻译超全面的笔记~
英语专业考研各大院校题型对比分析pdf
英语修辞手法
经济学人文本
许渊冲与翻译艺术.张智中.扫描版
散文佳作108篇汉英英汉对照
报刊英语单词精华
经济指标名词解释
大家论坛-英语专业考研论坛-
公益论坛免费下载各种资料!
/thread-2407892-1-1.html
真题:
基础英语:各校基础英语真题资料汇总
英美文学各校英美文学真题汇总
二外:英研二外资料——日语法语德语俄语西班牙语等汇总
辅导书系列:
英语专业考研名校全真试题基础英语07到年真卷与解析下载
英语专业考研核心词汇.pdf.宫玉波.09版
星火英语专业考研名校全真试题精解英汉互译2012
2011英语专业考研名校全真题精解英汉互译.rar郭棲庆2010年出版
星火英语专业考研考点精梳与精炼英美文化
英语专业考研考点精梳与精练北京外国语大学英美文化.rar郭栖庆.2009年版
2010年英语专业考研考点精梳与精练英美文化.rar郭栖庆09年出版
星火英语专业考研考点精梳与精炼英美文学
2010年英语专业考研考点精梳与精练北京外国语大学英美文学.rar郭栖庆09年出版传播学原理2009年版张国良
孙亦丽--大学英语精读学习精要--第一二三册pdf下载
高级英语第二册教材及教师用书第一册rar下载
语言学资料:
英语专业考研考点精梳与精练上海外国语大学语言学.pdf.黄任.09版
《英语语言学基础》学习指南-温洪瑞主编1999年08月版pdf
[韩礼德语言学文集]唐纳德•韩礼德扫描版
英语句法与语用研究.rar下载
语言学名著选读pdf
英语专业考研考点精梳与精练上外语言学pdf下载
英语语言文学典型例题与全真题解析.rar下载英语语言学考点测评
英美概况导读中文版
胡壮麟《语言学教程》修订版笔记
新编英国文学教程——高等学校英语专业系列教材下载
英语语言学资料
华中师范大学语言学课本教程2010版
戴伟栋语言学笔记
liguistics--胡壮麟超赞的笔记
2007年上外英语语言文学专业英汉互译
2005年上外英语语言文学专业翻译试卷有答案
辽宁大学语言文学之英语专业基础课真题
英美文学、文化资料:
星火英语专业考研考点精梳与精炼英美文化
英语专业考研考点精梳与精练北京外国语大学英美文化郭栖庆09版
2010年英语专业考研考点精梳与精练英美文化郭栖庆09版
大家论坛-英语专业考研论坛-
公益论坛免费下载各种资料!
/thread-2407892-1-1.html
星火英语专业考研考点精梳与精炼英美文学
2010年英语专业考研考点精梳与精练北外英美文学.rar郭栖庆09版
漫话英美文学英美文学史考研指南常耀信
英语专业考研英语国家文化考点测评
王佐良:欧洲文化入门[1992][完整]DJVU
王守仁:英国文学选读[2001][完整]DJVU
陶洁:美国文学选读[2000][完整]DJVU
[美国文学经典].Classics of American Literature
英美文化基础教程学习手册—朱永涛—下载
新编英国文学教程——高等学校英语专业系列教材下载
《新编英国文学教程》下载
高教版《英美文学选读》课文译文
《英国文学简史》中文版
英国文学主要作家作品汇总
《英美文学史》之英国文学作家作品大全
《美国文学简史》上中文版
英国文学史考试要点
英美文学部分作家的介绍和评论
外国文学史图表版笔记整理
英国文学部分作品分析
英美文学超全题库
十套考研英美概况练习题含答案
南京师范大学2002年2003年语言学之英美文学考研真题.pdf
翻译资料:
全日制翻译硕士专业学位MTI研究生入学考试指南
外事翻译口译和笔译技巧.rar下载汉语成语典故谚语与歇后语英语翻译全国68所院校英汉互译试题分析
英语专业考研翻译超全面的笔记~
英语专业考研各大院校题型对比分析pdf
英语修辞手法
经济学人文本
许渊冲与翻译艺术.张智中.扫描版
散文佳作108篇汉英英汉对照
报刊英语单词精华
经济指标名词解释
大家论坛-英语专业考研论坛-
公益论坛免费下载各种资料!
/thread-2407892-1-1.html。