中英文文献翻译—转向器
- 格式:doc
- 大小:34.50 KB
- 文档页数:5

附录 A一、课题国内外现状转向器又名转向机、方向机,它是转向系中最重要的部件。
转向器的作用是:增大转向盘传到转向传动机构的力和改变力的传递方向。
转向器按结构形式可分为多种类型。
目前较常用的有齿轮齿条式、蜗杆曲柄指销式、循环球-齿条齿扇式、循环球曲柄指销式、蜗杆滚轮式等。
如果按照助力形式,又可以分为机械式(无助力),和动力式(有助力)两种,其中动力转向器又可以分为气压动力式、液压动力式、电动助力式、电液助力式等种类。
转向器的工作原理就是,当驾驶员左右转动方向盘时,通过带有万向传动装置的转向柱转动,使转向螺杆转动,循环球在螺旋管状通道内滚动,形成“球流”。
钢球在管状通道内绕行两周后,流出转向螺母而进入导管的一端,再沿导管经导管的另一端流回螺旋管状通道。
故在转向器工作时,两列钢球在各自的封闭管道内循环,而不致脱出。
钢球流动的同时,推动螺母沿螺杆前后移动。
然后,齿条带动齿扇摆动,使摇臂轴发生转动。
最后,通过转向传动机构推动转向轮偏转,实现汽车转向。
近年来,我国汽车工业呈现出稳定快速增长的态势。
作为汽车关键部件之一的转向器也得到了较为快速地发展,在产销规模不断增长的同时,技术水平也得到了一定程度的提升。
在国内汽车配装的转向器产品中,商用车(主要是载货车)有95%以上是自主品牌转向器。
在中高档轿车中,2/3车辆使用的是中外合资企业或外商独资企业生产的转向器,1/3的车辆使用自主品牌转向器。
低档轿车则几乎全部使用自主品牌转向器[4]。
汽车转向器机构涉及整车的操纵性、稳定性和安全性,它的质量也反映了车辆的质量,是直接关系到车辆性能的关键部件。
对转向系统的要求,最主要的是转向的灵敏性和操纵的轻便性。
高的转向灵敏性,要求转向器具有小的传动比;好的操纵轻便性,则要求转向器具有大的传动比。
这个矛盾一直都以一个很难解决的问题。
而循环球式转向器的传动效率可达到75%~85%;转向器的传动比可以变化;工作平稳可靠;齿条和齿扇之间的间隙调整容易;适合用来做整体式动力转向器,达到矛盾的平衡。

1 IntroductionThe key task for the automobile industry and its suppliers in future lies in speedily developing and implementing ecologically sound and economically justifiable mobility systems. Light metals such as aluminum and magnesium along with glass and carbon fiber reinforced materials, ceramics and composites have opened up the potential for considerable weight reduction and for "green" vehicle concepts which can be realized economically. Aluminum in particular can provide the impetus for new designs for the next millennium. Decades ago, the use of aluminum in auto construction was seen as an "experiment"; Today it is a vital factor in reducing weight and thus lowering fuel consumption.The average passenger car today contains 60 to 70 kg of aluminum, and current developments point to a doubling of this amount in the next few years. Motor vehicles both now and in future must meet requirements for: greater performance, greater safety, comfort, low pollution. Lightweight construction is not just about reducing weight; it is a question of -striking the right balance between reduced weight and structural efficiency. In vehicle construction this normally means making the best use of the generally very tight space available for individual components so as to allow weight to be minimized while still meeting all stiffness, strength, natural frequency or acoustical requirements. To achieve this, stresses must be distributed throughout the structure as evenly as possible. Modern numerical analysis methods such as FEA allow a very detailed analysis of system behavior, provide cost-efficient support for the complex process of optimization and thus make a huge contribution to advances in lightweight construction. Packaging, safety considerations, reproducibility and price place restrictions on the degree of weight reduction achievable.The broad range of expertise available to Krupp Presta AG allows the company to analyze customer specifications for steering systems and provide appropriate solutions.2 Requirements to be met by steering systemsThe steering is an important part of the feel of a car. The steering system should make driving an enjoyable experience with no unpleasant vibration from the road surface while guaranteeing the required hand- sing. It is also important that high safety requirements be met, both under normal conditions and in crash situations. The key criteria for the steering system are thus as follows:rolling friction, torsional stiffness /strength, Damping, temperature, corrosion, durability / fatigue, weight. Crash kinematics and energy absorption steering column requirements:natural frequency / stiffness, mass, damping, space, strength (crash, misuse), ergonomics, handling, acoustics, crash kinematics and energy absorption. Other basic conditions:interfaces with adjacent components, installation, joining techniques, price.3 Materialsmaterial light weighting can be achieved by using either stronger or lighter material. When stiffness or natural frequency are Important sizing criteria, low density materials with a high modulus of elasticity by quired. Non-exotic materials must be selected which are readily recyclable, low in price and display good durability.Further requirements are set by the manufacturing and joining processes. Steel, aluminum, magnesium and a variety of plastics are the materials of choice for steering systems.Low specific gravity, high corrosion resistance, low fabricating costs, high energy absorption and good recycle ability make aluminum a favored light weighting material. Owing to its high energy content, up to 90% of the aluminum used in auto construction can be recycled (intelligent design / no mixing with other materials). The favorable energy balance of aluminum puts it at a great advantage over many other materials.In environmental terms aluminum scores highly. The large amounts of primary energy required to make raw aluminum are offset over the lifetime of the vehicle. Composites could also become a very attractive proposition on account of their extreme stiffness, low weight and energy absorption capabilities. At present, howler, price is a problem, as are joining and quality assurance.4 Reducing component weightA focused strategy to reduce component weight requires a lightweight approach to design (force distribution, stresses), material (material selection), specifications (modified, realistic specifications)Key factors in lightweight design include [1]: force flows, material properties, ambient conditions ® safety requirements, reliability of joints, manufacture ability. Practical experience has shown that car makers' specifications based on steel need to be revised for lightweighting. Requirements valid for a steel steering shaft, for example, can result in severe oversizing of an aluminum shaft. Reducing component weight requires material compatible designs combined with material- compatible specifications.5 Lightweight componentsAs part of its development program Krupp Presta is replacing conventional steel steering components such as steering rods , shafts or forks with corresponding aluminum components produced by new processes. Weight savings of 20-30% are achievable depending on the basic conditions stipulated by the customer. Aluminum and magnesium die castings are already being used in steering columns , and further opportunities for weight reduction are being investigated. The lightweight steering column (Fig. 1) produced by Krupp Presta for the Audi A6 is a good example. By using magnesium die castings it has been possible to limit the weight of the steering column to just 5kg, a reduction of 15-20% over conventional (steel) designs.6 Steering column designExperience has shown that it is possible to design steering columns for cars more or less on the basis of their natural frequency alone. Additional engineering work may be required to design critical parts which must not break in the case of a crash or misuse (e.g. theft). The main task when engineering a steering column is thus to achieve the highest possible natural frequencies while minimizing weight. Low-stiffness components are being analyzed and refined in an effort to achieve uniform loading of the structure. In solving this task, use is made of numerical methods such as FEA. The structure is divided into finite elements which are characterized by specific deformation assumptions. Using FE analysis it is possible to examine complex structures, analyze sensitivities and links, discuss variations or ways of making improvements and optimize the structure numerically. Topological optimization is carried out for the analysis of low-stress areas and for the basic design of ribs and beads. CAD geometrydata are processed in an FE pre-processor. Correct modeling of the following is essential, individual parts, stiffness, contact faces, kinematics mass. Modeling is followed by computation and evaluation of the data obtained. The deformation energy is a global measure for assessing stresses. Normalizing the element deformation energy by the element mass provides information on the stresses acting on the element relative to its mass. The kinetic energy is regarded as the influence of vibrating masses which have a negative effect on the natural frequency of the steering column. By evaluating stress and strain conditions, highly localized weak points or high-stress areas can be identified.7 ConclusionsExisting technologies must be continuously adapted and improved in line with the requirements of the auto industry. Systematic weight reduction is a major challenge and requires close cooperation between vehicle manufacturers and suppliers. Materials, fabricating and joining technologies must be further refined. One prerequisite for the continuing success of Krupp Presta is the flexibility to react to customer wishes and requirements.Reference[1] Klein, B.:Leichtbau-Konstruktion. Berech- nungsgrundlagen und Gestaltung.Braunschweig: Vieweg, 1997一、简介汽车工业及其供应商,在未来的关键任务在于迅速制定和实施无害生态和经济上合理流动系统。

中英文文献翻译—转向器的简单介绍附录Hyundai Motor on the stcering control of the request is lightweight,safe,reliable,and should have sufficient life. In order to meet these requirements,the design of the steering gear should have a reasonable transmission ratio characteristics,the correct gap cating together,a higher transmission efficiency,sufficient rigidiy and strength.If the steering gear in the design is reasonable,then the product is good and bad parts of the key issucs of manufacturing and assembly.How to control the quality of the product?The key problem is that a reasonable detection methods,the key to strictly control the passing rate of time,such products will be able to guarantee the quality of parts and components.First of all,the quality of shifting ASSY,should control the assenmbly and to ensure that turning the steering shaft torque and rotational axis and the transmission gap between components.Followed by testing the performance of steering gear,steering gear must also be adopted by all types of test-bed to verify the established angle transmission ratio,transmission efficiency,rotational torque,rigid.In addition to examination other than the above-mentioned steering performance,but also in the pilot stage of its life nuclear reliability and life expectancy that is static torsion test:a thin red hammer,hit test,fatigue life test.To determine whether the quality of the product in hand national standards.Noise from the steering angle repair cream,which is also a test method to detect and can learn from the J class machincry manufacturing industry in China “in the past only means to recognize the importance of detection,and the lack of”lack of testing and testing of the poorlaw awareness.So have some of the parts is a qualified products I materials,and assembly of products from the pilot test proved to be defective,or:The test can verify the quality of products and design for the steering gear (1) the accuracy of parts of the foot only, finish second,two-phase the location of the elite“Measuring the content of L steering shaf t loaded journal bearings.Department feet inch accuracy and smoothness,anti-worm or worm-inch accuracy.smoothness and surface hardness and magnetic---for testing;steering vertical axis arm journal dimensional accuracy and smoothness, the worm wheel roller bearing of the journal center hole distance,wheel bearing and the journal” hole angle from the Chinese side,the block size,finish and degree of asymmetry;circulating ball tooth-type radial fan,big-law length,journal hardness,the magnetic;browser to Min Xuan cochlear aperture wheel size precision,smoothness,tooth surface roughness,intermediate thick teech,tooth,tooth degree ofasymmetry; ball rolling circle diameter,smooth,cylindrical roller Road”degree of accuracy and bias,raccway adjacent pitch error,cumulative error section of grass lines and sub-racj section from Rolling Road Center,rack section Road center line and the roll of injustice;carburizing layer thickness,hardn ess’magnetic flaw detection;ahift steering shaft shell aperture,roughness,different degree of heart;shift towards vertical axis aperture arm flying finish,different degree of heart;chaos and stecring shaft steering arm hole down the center distance,steering shaft-hole axes and steering arm hole down the center line of the non-verticality.(2) parts of cleanliness.Detection of the site is turning-browser shell surface and the surface parts.Detection method is to use cleaning fluid to clean parts,and then the cleaning fluid with impurities,and vacuum membranc leaching;further 120 weeks of petrol industrial solvents the menbranc will be washed with inpurities.To be volatile after the membranc cleaning fluid,together with the impurities from weighing with the magne cellophane packets are sorted in the iron impurities said the weight of a scrap-iro, The iron filings and then 40 times on the microscope with a disability in most dogs measured particle size.(3)assembly of the leakage.. Does not allow any leakage of the phenomenon of steering.Because of internal lubricants in the steering gear is used to turn parts lubricated friction pair,and if as a result of damage caused by leakng seals,lubrication will be affected; resulting in increased friction and wear parts and reduce the life span of steering gera;transminssion efficiency at the same time will lower.The use of conventional vibration and temperature 40 under the conditions of inspection,the shell and shell cap shaft oil scal joints as well as whether the spill.,and water to observe whether there are leakages.(4) after a good tune stecring assembly should check the technical requirements flexible and comfortable when turning the steering wheel,there is no axial gap I turn the steering wheel of the total value of the number required to turn around a few cars in line with the original request.Steering gear shife, also known as machine,machine,machine direction.which is steering the most important parts. Its role ie to increase the spread to turn steering wheel and transmission mechanism to change the direction of power transfer.Hydraulic Steering Hydraulic steering vehicles are windelyused in marine hydraulicsteering and rudder.Drivers can be used through its ability to manipulate smaller shift power to achieve greater control and performance of safe,reliable,flexible manipulation,light.The manipulation of steering is hydraulic,that is in the steering column and steering wheel there is no mechanical connection between the steering gear is between the fuel tank and steering hydraulic pipes or hoses link.When turning the steering wheel,steering wheel rotation in accordance with the relative proportion of transport fuel,the fuel tank directly into the corresponding control side,while the other side of the oil back to tank.BZZ steering is a switch-type full-hydraulic steering valve with the following characteristics:the elimination of mechanical linkage device,the host can reduce costs,provide a reliable,lightweight structures,manipulation of a flexible lightweight,safe,reliable,and can be very small continuous torque stepless control of rotation, provided to the control loop,as well as a wide range of host size choice,able to shift and a variety of pumps and hydraulic supply system.Steering by the structure can be divided into many types.History,there have been many forms of steering,there is currently more commonly used rack and pinion,worm means crank pins,recycling the ball-rack fan gear type,recycling the ball crank pins means,such as worm-type wheel.The second,fourth,respectively, is the first,the third form of the deformation,and the worm wheel is even more rare type.If the form in accordance with assistance,but also can be divided into mechanical(no help),and power-style(with help) two types of power steering which can be divided into pressure andmotivation,hydraulic-power, Electric power-type,electro-hydraulic power types of blocks.It is a rack and pinion of steering one of the most common.The basic structure is a pair of mutually meshing rack and pinon.Pinon steering drive shaft rotates, rack linear motion would be done. In some cases,directly driven by the rack cross-bar,you can make of steering wheel shift. So,this is one of the most simple steering. Its advantage is simple structure,low-cost,steering sensitivity,small size,can be directly cross-link.In widely used vehicle.It is a worm for the active parts,crank pin for the steering gear follower.Worm has a trapezoidal thread,referring to a finger-shaped pin with tapered bearings in the crank bearings,the crank shaft and the shift into one arm.Shifted through steering wheel rotating worm,helical worm embedded in the cone-shaped slot means the marketing side of the rotation,the crank shaft and the shift into one arm.Shifted through steering wheel rotating worm,helical worm embedded in the cone-shaped slot means the marketing side of the rotation,the side rocker shaft to do around the shifted are movement,thereby stimulating and steering crank arm swing down and then turning to make shift transmission wheel deflection.This steering is usually used to turn power on a larger truck.Circulating ball-type:This device is turned by the gear mechanism from the steering wheel to slow down the rotation of power,so that the rotation of steering wheel movement into rotary movement of the turbine worm,ball screw and nut holding the ball engagement,which Ball screw linear motion into rotary movement,with the fan-shaoed nut meshing gears,linear motion into rotary movement,with the fan-shaped nut meshing gears,linear motion into rotary movement,with the fan-shapednut meshing gears,linear motion into rotary movement again to shake the rod arm,link arm moving again so that even the bar and cross bar to do a straight-line movement to change the wheels direction.This is a classical institutions,most modern cars no longer have to use,but the way was the latest by the application of power steering device.It is equivalent to the principle use of nuts and bolts in the rotation process of relative movement,and in between the thread and thrend the ball into the folder to reduce the resistance,all the ball,both connected in a closed loop of the spiral curve rolling ball club is named after the cycle.Hydraulic rack and pinion steering gear is relative to the case of rack and pinion steering gear machinery, mainly to increase the steering pump,steering oiler,steering pineline, steering valve,steering components,suan as fuel tanks,with a view to improve the pilot hand,the purpose of increasing power steering of the steering device.After 10 years of internal development,has become a mature R&D and manufacturing technology manufacturers have Yubei Koyo Steering Gear Co.Ltd.and other enterprises.With the rapid development of automobile industry,as well as for comfort,safety and continuous improvement in performance,steering systems are also changing with the advance of technology.For the time being,electric power steering systems is turning the forefront of the industry rescarch projects,in accordance with its distribution of the form of string can be divided into power,gear Power,power rack,power bar,the form of electro-hydraulic power. Ago in some sci-fi movies of the unmanned aircraft can occur,such as unmanned acrial vehicle is now a reality,steering systems are moving in the direction of the development of more advanced,such as rescarch anddevelopment from Japan JTEKT advanced by the steer-by-wire systems.In this paper,choice-bassed recycling the ball GX1608A gear-steering rack as a research topic,its main contents are: knowledge of automotive steering gear,ball-type steering gear cycle of the main paramenters and design choices.Design also includes the shift rocker shaft,involute spline,fan gear shaft and screw shaft design and verification.According to its own independent study completed by the steering shaft and screw shaft rocker design and verification,in other parts of the network,as well as through the school library to collect relevant information and fax to the future,in the papers have used information the mark.The design has been through a total of about 16 Chinese and foreign-related literature,and learn from the relevant parts of which the essence of the final design of the times.Because of its limited ability to learn and,I urge teachers and experts have pointed out that less than one.中文现代汽车对转向器的要求是操纵轻便,安全、可靠、,并应具有足够的使用寿命。

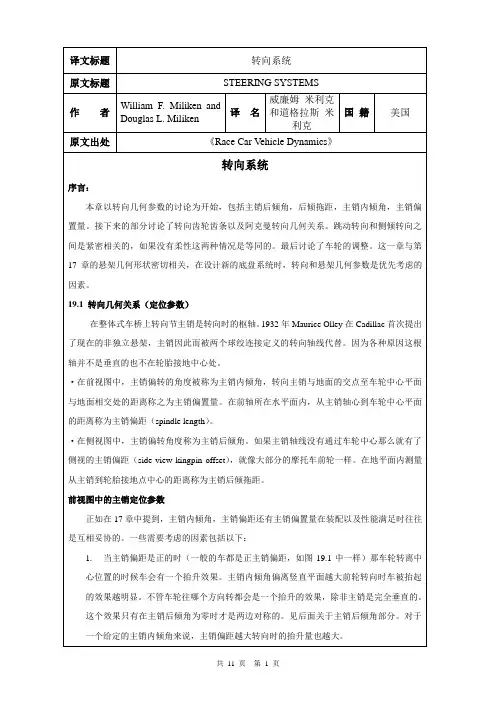
作者:William F. Miliken and Douglas L. MilikenSteering systemsIntroductionThis chapter begins with a discussion of steeringgeometry¡ªcasterangle ,trail ,kingpin inclination ,and scrub radius .The next section discuss Ackermann geometry followed by steering racks and gears .Ride steer (bump steer ) and roll steer are closely related to each other ;without compliance they would be thechapter is tied to chapter 17 onsame .Finally ,wheel alignment is discussed .this¨C when designing a new chassis ,steering and suspension suspension geometrygeometry considerations are high priorities .19.1 steering geometryThe kingpin in a solid front axle is the steering pivot .In modern independent suspensions , introduced by Maurice olley at Cadillac in 1932,the kingpin is replaced by two (or more ) ball joints that define the steering axis .This axis is not vertical or centered on the tire contact patch for a number of reason .see figure 19.1 to clarify how kingpin location is measured .In front view ,the angle is called kingpin inclination and the offset of the steering axis from the center of the tire print measured along the ground is called scrub (or scrub radius ). The distance from the kingpin axis to the wheel center plane , measured horizontally at axle height ,is the spindle length .In side view the kingpin angle is called caster angle ; if the kingpin axis does not pass through the wheel center then side view kingpin offset is present ,as in most motorcycle front ends .The distance measured on the ground from the steering axis to the center of the tire print is the trail (called caster offset in ref .1 )作者:William F. Miliken and Douglas L. MilikenSteering systemsIntroductionThis chapter begins with a discussion of steeringgeometry¡ªcasterangle ,trail ,kingpin inclination ,and scrub radius .The next section discuss Ackermann geometry followed by steering racks and gears .Ride steer (bump steer ) and roll steer are closely related to each other ;without compliance they would be thechapter is tied to chapter 17 onsame .Finally ,wheel alignment is discussed .this¨C when designing a new chassis ,steering and suspension suspension geometrygeometry considerations are high priorities .19.1 steering geometryThe kingpin in a solid front axle is the steering pivot .In modern independent suspensions , introduced by Maurice olley at Cadillac in 1932,the kingpin is replaced by two (or more ) ball joints that define the steering axis .This axis is not vertical or centered on the tire contact patch for a number of reason .see figure 19.1 to clarify how kingpin location is measured .In front view ,the angle is called kingpin inclination and the offset of the steering axis from the center of the tire print measured along the ground is called scrub (or scrub radius ). The distance from the kingpin axis to the wheel center plane , measured horizontally at axle height ,is the spindle length .In side view the kingpin angle is called caster angle ; if the kingpin axis does not pass through the wheel center then side view kingpin offset is present ,as in most motorcycle front ends .The distance measured on the ground from the steering axis to the center of the tire print is the trail (called caster offset in ref .1 )作者:William F. Miliken and Douglas L. MilikenSteering systemsIntroductionThis chapter begins with a discussion of steeringgeometry¡ªcasterangle ,trail ,kingpin inclination ,and scrub radius .The next section discuss Ackermann geometry followed by steering racks and gears .Ride steer (bump steer ) and roll steer are closely related to each other ;without compliance they would be thechapter is tied to chapter 17 onsame .Finally ,wheel alignment is discussed .this¨C when designing a new chassis ,steering and suspension suspension geometrygeometry considerations are high priorities .19.1 steering geometryThe kingpin in a solid front axle is the steering pivot .In modern independent suspensions , introduced by Maurice olley at Cadillac in 1932,the kingpin is replaced by two (or more ) ball joints that define the steering axis .This axis is not vertical or centered on the tire contact patch for a number of reason .see figure 19.1 to clarify how kingpin location is measured .In front view ,the angle is called kingpin inclination and the offset of the steering axis from the center of the tire print measured along the ground is called scrub (or scrub radius ). The distance from the kingpin axis to the wheel center plane , measured horizontally at axle height ,is the spindle length .In side view the kingpin angle is called caster angle ; if the kingpin axis does not pass through the wheel center then side view kingpin offset is present ,as in most motorcycle front ends .The distance measured on the ground from the steering axis to the center of the tire print is the trail (called caster offset in ref .1 )no diagonal weight jacking will occur .3. Caster angle affects steer-camber but ,unlike kingpin inclination ,the effect is favorable . With positive caster angle the outside wheel will camber in a negative direction (top of the wheel toward the center of the car ) while the inside wheel cambers in a positive direction , again learning into the turn .(steer out of the turn ) is used and in this case In skid recovery , ¨Dopposite lock ¡¬the steer¨Ccamber resulting from caster angle is in the ¨Dwrong ¡¬ direction for increased front tire grip . conveniently ,this condition results from very low lateral force at therear so large amounts of front grip are not needed .4. As discussed in chapter 2, tires have pneumatic trail which effectively adds to (and at high slip Angles subtracts from ) the mechanical trail . This tire effect is nonlinear with lateral force and affects steering torque and driver feel .In particular ,the fact that pneumatic trail approaches zero as the tire reaches the limit will result in lowering the self-centering torque and can be s signal to the driver that the tire is near breakaway .The pneumatic trail ¨Dbreakaway signal¡¬ will be swamped out by mechanical trail if the mechanical trail is large compared to the pneumatic trail .5.Sometimes the trail is measured in a direction perpendicular to the steering axis (rather than horizontal as shown in figure 19.1) because this more accurately describes the lever (moment ) arm that connects the tire lateral forces to the kingpin . Tie rod locationNote that in figure 19.1 a shaded area is shown for the steering tie rod location . Camber compliance under lateral force is unavoidable and if the tie rod is located as noted ,the effect on the steering will be in the understeer ( steer out of the turn ) direction becomes much more complex than can be covered here .19.2 Ackerman steering geometryAs the front wheels of a vehicle are steered away from the straight-aheadposition ,the design of the steering linkage will determine if the wheels stay parallel orif one wheel steers more than the other .This difference in steer Angles on the left and right wheels should not be confused with toe-in or toe-out which are adjustments and add to ( or subtract from ) Ackerman geometric effects .For low lateral acceleration usage (street cars) it is common to use Ackerman geometry . as seen on the left of figure 19.2, this geometry ensures that all the wheels roll freely with no slip Angles because the wheels are steered to track a common turn center . Note that at low speed all wheels are on a significantly different radius , the inside front wheel must steer more than the outer front wheel . A reasonable approximation to this geometry may be as shown in figure 19.3.According to ref .99, Rudolf Ackerman patented the double pivot steering systemin 1817 and in 1878, Charles Jeantaud added the concept mentioned above to eliminate wheel scrubbing when cornering . Another reason for Ackermanngeometry ,mentioned by Maurice olley , was to keep carriage wheels from upsetting smooth gravel driveways .High lateral accelerations change the picture considerably . Now the tires alloperate at significant slip Angles and the loads on the inside track are less than on the outside track . Looking back to the tire performance curves ,it is seen that less slip angle is required at lighter loads to reach the peak of the cornering force to a higher slip angle than required for maximum side force . Dragging the inside tire along at high slip Angles ( above for peak lateral force ) raise the tire temperature and slows the car down due to slip angle ( induced ) drag .For racing , it is common to use parallel steering or even reverse Ackermann as shown on the center and right side of figure 19.2.It is possible to calculate the correct amount of reverse Ackermann if the tire properties and loads are known . In most cases the resulting geometry is found to be too extreme because the car must also be driven (or pushed ) at low speeds , for example in the pits .Another point to remember is that most turns in racing have a fairly large radius and the Ackermann effect is very small . In fact , unless the steering system and suspension are very stiff ,compliance (deflection ) under cornering loads may steer the wheels more than any Ackermann (or reverse Ackermann ) built into the geometry .The simplest construction that generates Ackermannn geometry is shown in figure 19.3 for ¨Drear steer ¡¬ . Here ,the rack (cross link or relay rod in steering box systems ) is located behind the front axle and lines staring at the kingpin axis , extended through the outer tie rod ends , intersect in the center of the rear axle . The angularity of the steering knuckle will cause the inner wheel to steer more than the outer (toe-out on turning ) and a good approximation of ¨Dperfect Ackermann ¡¬ will be achieved .The second way to design-in differences between inner and outer steer Angles is by moving the rack (or cross link ) forward or backward so that it is no longer on a line directly connecting the two outer tie rod ball joints .This is shown in figure 19.4. with ¨Drear steer ¡¬ , as shown in the figure ,moving the rack forward will tend more toward parallel steer (and eventually reverse Ackermann ), and moving it toward the rear of the car will increase the toe-out on turning .A third way to generate toe with steering is simply to make the steering arms different lengths . A shorter steering arm (as measured from the kingpin axis to the outer tie rod end ) will be steered through a larger angle than one with a longer knuckle. Of course this effect is asymmetric and applies only to cars turning in one direction¡ªoval track cars .RecommendationWith the conflicting requirements mentioned above , the authors feel that parallel steer or a bit of reverse Ackermann is a reasonable compromise . With parallel steer , the car will be somewhat difficult to push through the pits because the front wheels will be fighting each other . at racing speeds , on large-radius turns , the front wheels are steered very little , thus any ackermann effects will not have a large effect on the individual wheel slip angles , relative to a reference steer angle , measured at the centerline of the car .》 文献翻译 摘自《Race Car Vehicle Dynamics第19章 转向系统 序言: 本章以转向几何参数的讨论为开始,包括主销后倾角,后倾拖距,主销内倾角,主销偏置量。

转向器基础知识中英文转向器基本原理介绍Fundamental Principles of Steering Gear 目录Contents一、汽车液压动力转向系统的组成I . Hydraulic power steering system二、循环球动力转向器基本原理II . Recirculating Ball Steering Gear三、齿轮齿条转向器基本原理III .R&P Power Steering Gear四、转向系统发展的先进技术IV . Advanced T echnology of Steering System五、我厂的技术优势及特点V . Our Advantages for developing Technology六、先进驾驶辅助系统ADAS Advanced Driver Assistant System汽车液压转向系统的组成Hydraulic Power Steering System汽车转向系统的组成Steering System汽车的跑、转、停是它的基本性能,他们中的一个重要机能则由转向装置来承担。
Basic capability of vehicle is to run, turn or stop. Turning device assumes this responsibility.机械转向系统Manual Steering Gear 动力转向系统Power Steering Gear汽车液压动力转向系统的组成Hydraulic Power Steering System 方向盘及管柱、中间轴Steering Wheel, Column and Intermediate Shaft转向器及摇臂Steering Gear and Pitman Arm 油泵Pump 油罐Reservoir 油管Pipe支架及其它附件Bracket and Other Accessories 拉杆系统Linkage 主销及车轮Pin and Wheels1-方向盘Steering Wheel 2-中间传动轴Intermediate Shaft 3-进油管Inlet Pipe4-回油管Outlet Pipe 5-油罐Reservoir 6-油泵Pump 7-转向器Steering Gear8-摇臂Pitman Arm 泵与油管组件Pump and Pipe Assembly 油泵Pump高、低压油管High and low Pressure Pipes 油箱Reservoir 回油管Outlet Pipe 油泵Pump循环油管Recycle Pipes 进油管Inlet Pipe R&P式油压动力转向器R&P Power Steering Gear转阀式循环球动力转向器基本原理Recirculating Ball Power Steering Gear转阀式动力转向器简介General Overview转向器是构成汽车转向系统的主要部件之一,由于特殊的作用,在性能和可靠性方面要求苛刻。
的动态特征时,以低段参数效果不是很好,如果没有,目标车辆液压系统也必须在发动机驱动。
因此,能源消耗,增加燃料发动机,现有的液压油泄漏问题应该不仅污染环境,而且容易影响其他组件。
针对低温,液压系统性能很差。
近年来,随着电子技术的广泛应用,转向系统也越来越多的使用电子设备。
因此,变成使用电子控制系统出现相应的电动液压助力转向系统。
电动液压动力转向系统可以分为两类:电动液压操舵系统(电液压动力(EHPS)和电动液压转向电子控制转向(液压动力转向)。
电动液压操舵系统在液压动力系统的基础上开发的液压增压系统,不同的是,电动液压系统液压系统的电源,但不是由汽车发动机汽车驱动液压系统,节约能源,降低发动机油耗。
电动液压操舵装置是在传统的液压助力系统的基础上开发,所不同的是,电动液压操舵系统,电子控制设备增加。
电子控制单元可以根据转向速度,速度的汽车液压系统的操作参数,改变液压增压速度不同的大小,从而实现变化,动态特征。
但根据电机驱动液压系统,反过来,电机停止转动,从而减少能源消耗。
虽然电动液压动力转向液压操舵系统克服了缺点。
但由于液压系统的存在,它的存在液压油泄漏问题,和电动液压助力转向系统,介绍了电机驱动系统更复杂,成本和可靠性。
为了区别电动液压转向系统、电动助力转向系统电动助力转向(EPS)。
现在应该知道各种各样的转向系统,最大的区别在于电动助力转向系统没有液压系统。
最初由液压操舵系统的电动机。
电动助力转向系统一般由扭矩传感器和微处理器、电机、等的基本原理是:当司机将方向盘驱动轴旋转,安装在转动轴的扭矩传感器和扭矩信号到电信号微处理器,微处理器基于其他车辆运行速度和扭矩信号的参数,根据治疗的程序集电力汽车助推器方向和大小的助推器。
自1988年以来,第一次在日本铃木Cervo汽车装备转向系统、动力转向系统被广泛承认的人。
转向系统主要体现在以下方面:动力转向系统可以提供不同在不同速度下的动态特性。
低,方向盘,增加更多的光,在高速转向减少,甚至为了提高道路增加潮湿。

中英文对照资料外文翻译文献Spin control for carsStability control systems are the latest in a string of technologies focusing on improved diriving safety. Such systems detect the initial phases of a skid and restore directional control in 40 milliseconds, seven times faster than the reaction time of the average human. They correct vehicle paths by adjusting engine torque or applying the left- or-right-side brakes, or both, as needed. The technology has already been applied to the Mercedes-Benz S600 coupe.Automatic stability systems can detect the onset of a skid and bring a fishtailing vehicle back on course even before its driver can react.Safety glass, seat belts, crumple zones, air bags, antilock brakes, traction control, and now stability control. The continuing progression of safety systems for cars has yielded yet another device designed to keep occupants from injury. Stability control systems help drivers recover from uncontrolled skids in curves, thus avoiding spinouts and accidents.Using computers and an array of sensors, a stability control system detects the onset of a skid and restores directional control more quickly than a human driver can. Every microsecond, the system takes a "snapshot," calculating whether a car is going exactly in the direction it is being steered. If there is the slightest difference between where the driver is steering and where the vehicle is going, the system corrects its path in a split-second by adjusting engine torque and/or applying the cat's left- or right-side brakes as needed. Typical reaction time is 40 milliseconds - seven times faster than that of the average human.A stability control system senses the driver's desired motion from the steering angle, the accelerator pedal position, and the brake pressure while determining the vehicle's actual motion from the yaw rate (vehicle rotation about its vertical axis) and lateral acceleration, explained Anton van Zanten, project leader of the Robert Bosch engineering team. Van Zanten's group and a team of engineers from Mercedes-Benz, led by project manager Armin Muller, developed the first fully effective stability control system, which regulates engine torque and wheel brake pressures using traction control components to minimize the difference between the desired and actual motion.Automotive safety experts believe that stability control systems will reduce the number of accidents, or at least the severity of damage. Safety statistics say that most of the deadly accidents in which a single car spins out (accounting for four percent of all deadly collisions) could be avoided using the new technology. The additional cost of the new systems are on the order of the increasingly popular antilock brake/traction control units now available for cars.The debut of stability control technology took place in Europe on the Mercedes-Benz S600 coupe this spring. Developed jointly during the past few years by Robert Bosch GmbH and Mercedes-Benz AG, both of Stuttgart, Germany, Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC). in Bosch terminology, or the Electronic Stability Program (ESP), as Mercedes calls it, maintains vehicle stability in most driving situations. Bosch developed the system, and Mercedes-Benz integrated it into the vehicle. Mercedes engineers used the state-of-the-art Daimler-Benz virtual-reality driving simulator in Berlin to evaluate the system under extreme conditions, such as strong crosswinds. They then put the system through its paces on the slick ice of Lake Hornavan near Arjeplog, Sweden. Work is currently under way to adapt the technology to buses and large trucks, to avoid jack-knifing, for example.Stability control systems will first appear in mid-1995 on some European S-Class models and will reach the U.S. market during the 1996 model year (November 1995 introduction). It will be available as a $750 option on Mercedes models with V8 engines, and the following year it will be a $2400 option on six-cylinder 鉣俕嶏핤딿냷 $1650 of the latter price is for the traction control system, a prerequisite for stability control.Bosch is not alone in developing such a safety system. ITT Automotive of Auburn Hills, Mich., introduced its Automotive Stability Management System (ASMS) in January at the 1995 North American International Auto Show in Detroit. "ASMS is a quantum leap in the evolution of antilock brake systems, combining the best attributes of ABS and traction control into a total vehicle dynamics management system," said Timothy D. Leuliette, ITT Automotive's president and chief executive officer."ASMS monitors what the vehicle controls indicate should be happening, compares that to what is actually happening, then works to compensate for the difference," said Johannes Graber, ASMS program manager at ITT Automotive Europe. ITT's system should begin appearing on vehicles worldwide near the end of the decade, according to Tom Mathues, director of engineering of Brake & Chassis Systems at ITT Automotive North America. Company engineers are now adapting the system to specific car models from six original equipment manufacturers.A less-sophisticated and less-effective Bosch stability control system already appears on the 1995 750iL and 850Ci V-12 models from Munich-based BMW AG. The BMW Dynamic Stability Control (DSC) system uses the same wheel-speed sensors as traction control and standard anti-lock brake (ABS) systems to recognize conditions that can destabilize a vehicle in curves and corners. To detect such potentially dangerous cornering situations, DSC measures differences in rotational speed between the two front wheels. The DSC system also adds a sensor for steering angle, Utilizes an existing one for vehicle velocity, and introduces its own software control elements in the over allantilock-brake/traction-control/stability-control system.The new Bosch and ITT Automotive stability control systems benefit from advanced technology developed for the aerospace industry. Just as in a supersonic fighter, the automotive stability control units use a sensor-based computer system to mediate between the human controller and the environment - in this case, the interface between tire and road. In addition, the system is built around a gyroscopelike sensor design used for missile guidance.BEYOND ABS AND TRACTION CONTROLStability control is the logical extension of ABS and traction control, according to a Society of Automotive Engineers paper written by van Zanten and Bosch colleagues Rainer Erhardt and Georg Pfaff. Whereas ABS intervenes when wheel lock is imminent during braking, and tractioncontrol prevents wheel slippage when accelerating, stability control operates independently of the driver's actions even when the car is free-rolling. Depending on the particular driving situation, the system may activate an individual wheel brake or any combination of the four and adjust engine torque, stabilizing the car and severely reducing the danger of an uncontrolled skid. The new systems control the motion not only during full braking but also during partial braking, coasting, acceleration, and engine drag on the driven wheels, circumstances well beyond what ABS and traction control can handle.The idea behind the three active safety systems is the same: One wheel locking or slipping significantly decreases directional stability or makes steering a vehicle more difficult. If a car must brake on a low-friction surface, locking its wheels should be avoided to maintain stability and steerability.Whereas ABS and traction control prevent undesired longitudinal slip, stability control reduces loss of lateral stability. If the lateral forces of a moving vehicle are no longer adequate at one or more wheels, the vehicle may lose stability, particularly in curves. What the driveɲ逾半쀹ᾩ쏪 ﲢ끣 "fishtailing" is primarily a turning or spinning around the vehicle's axis. A separate sensor must recognize this spinning, because unlike ABS and traction control, a car's lateral movement cannot be calculated from its wheel speeds.SPIN HANDLERSThe new systems measure any tendency toward understeer (when a car responds slowly to steering changes), or over-steer (when the rear wheels try to swing around). If a car understeers and swerves off course when driven in a curve, the stability control system will correct the error by braking the inner (with respect to the curve) rear wheel. This enables the driver, as in the case of ABS, to approach the locking limit of the road-tire interface without losing control of the vehicle. The stability control system may reduce the vehicle's drive momentum by throttling back the engine and/or by braking on individual wheels. Conversely, if the hteral stabilizing force on the rear axle is insufficient, the danger of oversteering may result in rear-end breakaway or spin-out. Here, the system acts as a stabilizer by applying the outer-front wheel brake.The influence of side slip angle on maneuverability, the Bosch researchers explained, shows that the sensitivity of the yaw moment on the vehicle, with respect to changes in the steeringangle, decreases rapidly as the slip angle of the vehicle increases. Once the slip angle grows beyond a certain limit, the driver has a much harder time recovering by steering. On dry surfaces, maneuverability is lost at slip-angle values larger than approximately 10 degrees, and on packed snow at approximately 4 degrees.Most drivers have little experience recovering from skids. They aren't aware of the coefficient of friction between the tires and the road and have no idea of their vehicle's lateral stability margin. When the limit of adhesion is reached, the driver is usually caught by surprise and very often reacts in the wrong way, steering too much. Oversteering, ITT's Graber explained, causes the car to fishtail, throwing the vehicle even further out of control. ASMS sensors, he said, can quickly detect the beginning of a skid and momentarily activate the brakes at individual wheels to help return the vehicle to a stable line.It is important that stability control systems be user-friendly at the limit of adhesion - that is, to act predictably in a way similar to normal driving.The biggest advantage of stability control is its speed - it can respond immediately not only to skids but also to shifting vehicle conditions (such as changes in weight or tire wear) and road quality. Thus, the systems achieve optimum driving stability by changing the lateral stabilizing forces.For a stability control system to recognize the difference between what the driver wants (desired course) and the actual movement of the vehicle (actual course), current cars require an efficient set of sensors and a greater computer capacity for processing information.The Bosch VDC/ESP electronic control unit contains a conventional circuit board with two partly redundant microcontrollers using 48 kilobytes of ROM each. The 48-kB memory capacity is representative of the large amount of "intelligence" required to perform the design task, van Zanten said. ABS alone, he wrote in the SAE paper, would require one-quarter of this capacity, while ABS and traction control together require only one half of this software capacity.In addition to ABS and traction control systems and related sensors, VDC/ESP uses sensors for yaw rate, lateral acceleration, steering angle, and braking pressure as well as information on whether the car is accelerating, freely rolling, or braking. It obtains the necessary information on the current load condition of the engine from the engine controller. The steering-wheel anglesensor is based on a set of LED and photodiodes mounted in the steering wheel. A silicon-micromachine pressure sensor indicates the master cylinder's braking pressure by measuring the brake fluid pressure in the brake circuit of the front wheels (and, therefore, the brake pressure induced by the driver).Determining the actual course of the vehicle is a more complicated task. Wheel speed signals, which are provided for antilock brakes/traction control by inductive wheel speed sensors, are required to derive longitudinal slip. For an exact analysis of possible movement, however, variables describing lateral motion are needed, so the system must be expanded with two additional sensors - yaw rate sensors and lateral acceleration sensors.A lateral accelerometer monitors the forces occurring in curves. This analog sensor operates according to a damped spring-mass mechanism, by which a linear Hall generator transforms the spring displacement into an electrical signal. The sensor must be very sensitive, with an operating range of plus or minus 1.4 g.YAW RATE GYROAt the heart of the latest stability control system type is the yaw rate sensor, which is similar in function to a gyroscope. The sensor measures the speed at which the car rotates about its vertical axis. This measuring principle originated in the aviation industry and was further developed by Bosch for large-scale vehicle production. The existing gyro market offers two widely different categories of devices: $6000 units for aerospace and navigation systems (supplied by firms such as GEC Marconi Avionics Ltd., of Rochester, Kent, U.K.) and $160 units for videocameras. Bosch chose a vibrating cylinder design that provides the highest performance at the lowest cost, according to the SAE paper. A large investment was necessary to develop this sensor so that it could withstand the extreme environmental conditions of automotive use. At the same time, the cost for the yaw rate sensor had to be reduced so that it would be sufficiently affordable for vehicle use.The yaw rate sensor has a complex internal structure centered around a small hollow steel cylinder that serves as the measuring element. The thin wall of the cylinder is excited with piezoelectric elements that vibrate at a frequency of 15 kilohertz. Four pairs of these piezo elements are arranged on the circumference of the cylinder, with paired elements positionedopposite each other. One of these pairs brings the open cylinder into resonance vibration by applying a sinusoidal voltage at its natural frequency to the transducers; another pair, which is displaced by 90 degrees, stabilizes the vibration. At both element pairs in between, so-called vibration nodes shift slightly depending on the rotation of the car about its vertical axis. If there is no yaw input, the vibration forms a standing wave. With a rate input, the positions of the nodes and antinodes move around the cylinder wall in the opposite direction to the direction of rotation (Coriolis acceleration). This slight shift serves as a measure for the yaw rate (angular velocity) of the car.Several drivers who have had hands-on experience with the new systems in slippery cornering conditions speak of their cars being suddenly nudged back onto the right track just before it seems that their back ends might break away.Some observers warn that stability controls might lure some drivers into overconfidence in low-friction driving situations, though they are in the minority. It may, however, be necessary to instruct drivers as to how to use the new capability properly. Recall that drivers had to learn not to "pump" antilock brake systems.Although little detail has been reported regarding next-generation active safety systems for future cars (beyond various types of costly radar proximity scanners and other similar systems), it is clear that accident-avoidance is the theme for automotive safety engineers. "The most survivable accident is the one that never happens," said ITT's Graber. "Stability control technology dovetails nicely with the tremendous strides that have been made to the physical structure and overall capabilities of the automobile." The next such safety system is expected to do the same.汽车的转向控制控制系统稳定性是针对提高驾驶安全性提出的一系列措施中最新的一个。

汽车转向系统的历史汽车转向系统在车辆系统中是最基础的系统,驾驶员通过方向盘操纵和控制汽车的行驶方向,从而实现了他的行驶意图。
100多年里,汽车行业中机械和电子技术的发展。
如今,汽车已经不是纯粹的机械,它是机械、电子和其他材料等的综合产品。
汽车产业的转向系统的发展,经过了漫长的变革。
传统的转向系统是机械转向系统,汽车的方向盘通过试点,通过这样一系列的机械零件使方向盘实现偏转,从而实现转向的控制。
由于在20世纪50年代,液压助力转向系统在汽车上的应用,标志着转向系统又进入一个新的开始。
汽车转向系统的动力源从人力转变为液压助力转向。
转向系统增加了液压助力器,高压钠灯(液压助力转向)是基于机械和液压系统。
液压系统和发动机,发动机开始时一部分是汽车发动机的功率,另一部分的功率是液压系统的动能。
由于其工作可靠,成熟的技术已被广泛使用。
转向系统的主要特点是流体的压力,减少驾驶员在方向盘的支持,提高了转向灯和自动运行的稳定性。
但同时,也有一些液压动力系统的缺陷。
针对汽车设计和制造,完成后的车辆转向动态特性无法改变。
其直接后果是,在低功率时汽车的部分的动力特性可以得到很好的发挥,但在高速期间有良好的方式来检测,因为是不可调整的动力特性,没有更好的方式驱动,当动力学特征高功率时,而不是非常善于低段的效果好。
如果没有看准车辆的液压系统,还必须是发动机驱动。
因此,能源消耗提高燃油发动机,现有的液压油泄漏问题不仅污染环境,容易到其他组件,针对气温低,液压系统的性能较差。
近年来,随着电子技术的广泛应用,转向系统也越来越多地使用电子设备。
变成电子控制系统,因此,相应的出现了电动助力转向系统。
电液动力转向可以分为两大类:电动液压转向系统(电液压动力 - EHPS)和电动液压转向,电控ECHPS转向(液压助力转向)。
电动液压助力转向系统是在液压系统的液压助力系统的发展的基础上,不同的是,在液压系统动力源的电动液压动力系统,但不是由汽车发动机电机驱动液压系统,节约能源和减少发动机的燃料消耗。

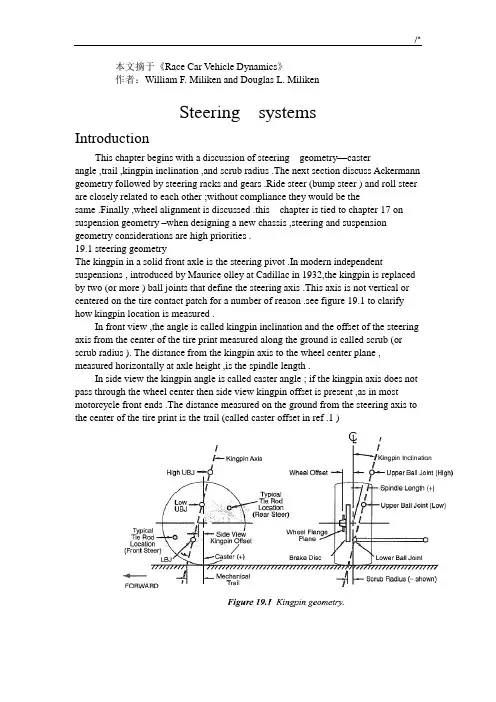
本文摘于《Race Car Vehicle Dynamics》作者:William F. Miliken and Douglas L. MilikenSteering systemsIntroductionThis chapter begins with a discussion of steering geometry—casterangle ,trail ,kingpin inclination ,and scrub radius .The next section discuss Ackermann geometry followed by steering racks and gears .Ride steer (bump steer ) and roll steer are closely related to each other ;without compliance they would be thesame .Finally ,wheel alignment is discussed .this chapter is tied to chapter 17 on suspension geometry –when designing a new chassis ,steering and suspension geometry considerations are high priorities .19.1 steering geometryThe kingpin in a solid front axle is the steering pivot .In modern independent suspensions , introduced by Maurice olley at Cadillac in 1932,the kingpin is replaced by two (or more ) ball joints that define the steering axis .This axis is not vertical or centered on the tire contact patch for a number of reason .see figure 19.1 to clarify how kingpin location is measured .In front view ,the angle is called kingpin inclination and the offset of the steering axis from the center of the tire print measured along the ground is called scrub (or scrub radius ). The distance from the kingpin axis to the wheel center plane , measured horizontally at axle height ,is the spindle length .In side view the kingpin angle is called caster angle ; if the kingpin axis does not pass through the wheel center then side view kingpin offset is present ,as in most motorcycle front ends .The distance measured on the ground from the steering axis to the center of the tire print is the trail (called caster offset in ref .1 )Kingpin front view geometryAs mentioned in chapter 17, kingpin inclination ,spindle length ,and scrub are usually a compromise between packaging and performance requirements .Some factors to consider include :1.With a positive spindle length (virtually every car is positive as shown in figure 19.1) the car will be raised up as the wheels are steered away from center .The more the kingpin inclination is tilted from vertical the more the car will be raised when the front wheels are steered .This effect always raises the car , regardless of which direction the wheel is steered ,unless the kingpin inclination is truevertical .the effect is symmetric side to side only if there is no caster angle .See the following section on caster angle .For a given kingpin inclination ,a longer positive spindle length will increase the amount of lift with steer .2.The effect of kingpin inclination and spindle length in raising the front end ,by itself ,is to aid centering of the steering at low speed .At high speed any trail will probably swamp out the effect that raise ad fall have on centering .3. Kingpin inclination affects the steer –camber characteristic .when a wheel is steered ,it will lean out at the top ,toward positive camber ,if the kingpin is inclined in the normal direction (toward the center of the car at the upper end ). Positive camber results for both left– and right-hand steer .the amount of this effect is small ,but significant if the track includes tight turns.4. When a wheel is rolling over a bumpy road ,the rolling radius is constantly changing ,resulting in changes of wheel rotation speed . This gives rise to longitudinal forces at the wheel center .The reaction of these forces will introduce kickback into the steering in proportion to the spindle length .If the spindle length is zero then there will be no kick from this source .Design changes made in the last model of the GM “P ”car (fiero ) shortened the spindle length and this resulted in less wheel kickback on rough roads when compared to early model “P ”cars.5. The scrub radius shown in figure 19.1 is negative ,as used on front-wheel–drive cars (see below ) . driving or braking forces (at the ground ) introduce steer torques proportional to the scrub radius . If the driving or braking force is different on left and right wheels then there will be a net steering torque felt by the driver (assuming that the steering gear has good enough rev erse efficiency ).The only time that this is not true is with zero scrub (centerpoint steering ) because there is no moment arm for the drive (or brake ) force to generate torque about the kingpin .With very wide tires the tire forces often are not centered in the wheel center plane due to slight changes in camber ,road surface irregularities ,tire nonuniformity (conicity ),or other asymmetric effects .These asymmetries can cause steering kickback regardless of the front view geometry .Packaging requirements often conflict with centerpoint steering and many race cars operate more or less okay on smooth tracks with large amounts of scrub .6. For front drive ,a negative scrub radius has two strong stabilizingeffects :first ,fixed steering wheel –if one drive wheel loses traction ,the opposingwheel will toe –out an amount determined by the steer compliance in the system .This will tend to steer the car in a straight line ,even though the tractive force is not equal side-to –side and the unequal tractive force is applying a yaw moment to the vehicle .Second ,with good reverse efficiency the driver’s hands never truly fix the steering wheel . In this case the steering wheel may be turned by the effect of uneven longitudinal tractive forces ,increasing the stabilizing effect of the negative scrub radius .Under braking the same is true .Negative scrub radius tends to keep the car traveling straight even when the braking force is not equal on the left and right side front tiresome (due to differences in the roadway or the brakes).Caster angle and trailWith mechanical trail ,shown in figure 19.1,the tire print follows behind the steering axis in side view .Perhaps the simplest example is on an office chair caster–with any distance of travel ,the wheel aligns itself behind the point .More trail means that the tire side force has a large moment arm to act on the kingpin axis .This produces more self-centering effect and is the primary source of self-centering moment about the kingpin axis at speed .Some considerations for choosing the caster angle and trail are :1.More trail will give higher steering force .with all cars ,less trail will lower the steering force .In some cases ,manual steering can be used on heavy sedans (instead of power steering ) if the trail is reduced to almost zero .2.Caster angle ,like kingpin inclination ,cause the wheel to rise and fall with steer .unlike kingpin inclination ,the effect is opposite from side to side .With symmetric geometry (including equal positive caster on left and right wheels ) ,the effect of left steer is to roll the car to the right ,causing a diagonal weight shift .In this case ,more load will be carried on the LF –RR diagonal ,an oversteer effect in aleft-hand turn .The diagonal weight shift will be larger if stiffer springing is used because this is a geometric effect .The distance each wheel rises (or falls ) is constant but the weight jacking and chassis roll angle are functions of the front and rear roll stiffness. This diagonal load change can be measured with the car on scales and alignment ( weaver ) plates .Keep in mind that the front wheels are not steered very much in actual racing , except on the very tightest hairpin turns . For example , on a 100-ft .radius (a 40-50 mph turn ), a 10-ft. wheelbase neutral steer car needs only about 0.1rad .(5.7)of steer at the front wheels (with a 16:1steering ratio this is about 90degree at the steering wheel ).For cars that turn in one direction only , caster stagger (differences in left and right caster ) is used to cause the car to pull to one side due to the car seeking the lowest ride height . caster stagger will also affect the diagonal weight jacking effect mentioned above .If the caster is opposite (positive on one side and negative the same number of degrees on the other side ) then the front of the car will only rise and fall with steer ,no diagonal weight jacking will occur .3. Caster angle affects steer-camber but ,unlike kingpin inclination ,the effect is favorable . With positive caster angle the outside wheel will camber in a negative direction (top of the wheel toward the center of the car ) while the inside wheel cambers in a positive direction , again learning into the turn .In skid recovery , “opposite lock ” (steer out of the turn ) is used and in this case the steer–camber resulting from caster angle is in the “wrong ” direction for increased front tire grip . conveniently ,this condition results from very low lateral force at the rear so large amounts of front grip are not needed .4. As discussed in chapter 2, tires have pneumatic trail which effectively adds to (and at high slip Angles subtracts from ) the mechanical trail . This tire effect is nonlinear with lateral force and affects steering torque and driver feel .In particular , the fact that pneumatic trail approaches zero as the tire reaches the limit will result in lowering the self-centering torque and can be s signal to the driver that the tire is near breakaway .The pneumatic trail “breakaway signal” will be swamped out by mechanical trail if the mechanical trail is large compared to the pneumatic trail .5.Sometimes the trail is measured in a direction perpendicular to the steering axis (rather than horizontal as shown in figure 19.1) because this more accurately describes the lever (moment ) arm that connects the tire lateral forces to the kingpin . Tie rod locationNote that in figure 19.1 a shaded area is shown for the steering tie rod location . Camber compliance under lateral force is unavoidable and if the tie rod is located as noted ,the effect on the steering will be in the understeer ( steer out of the turn ) direction becomes much more complex than can be covered here .19.2 Ackerman steering geometryAs the front wheels of a vehicle are steered away from the straight-ahead position ,the design of the steering linkage will determine if the wheels stay parallel or if one wheel steers more than the other .This difference in steer Angles on the left and right wheels should not be confused with toe-in or toe-out which are adjustments and add to ( or subtract from ) Ackerman geometric effects .For low lateral acceleration usage (street cars) it is common to use Ackerman geometry . as seen on the left of figure 19.2, this geometry ensures that all the wheels roll freely with no slip Angles because the wheels are steered to track a common turn center . Note that at low speed all wheels are on a significantly different radius , the inside front wheel must steer more than the outer front wheel . A reasonable approximation to this geometry may be as shown in figure 19.3.According to ref .99, Rudolf Ackerman patented the double pivot steering system in 1817 and in 1878, Charles Jeantaud added the concept mentioned above to eliminate wheel scrubbing when cornering . Another reason for Ackermann geometry ,mentioned by Maurice olley , was to keep carriage wheels from upsetting smooth gravel driveways .High lateral accelerations change the picture considerably . Now the tires alloperate at significant slip Angles and the loads on the inside track are less than on the outside track . Looking back to the tire performance curves ,it is seen that less slip angle is required at lighter loads to reach the peak of the cornering force to a higher slip angle than required for maximum side force . Dragging the inside tire along at high slip Angles ( above for peak lateral force ) raise the tire temperature and slows the car down due to slip angle ( induced ) drag .For racing , it is common to use parallel steering or even reverse Ackermann as shown on the center and right side of figure 19.2.It is possible to calculate the correct amount of reverse Ackermann if the tire properties and loads are known . In most cases the resulting geometry is found to be too extreme because the car must also be driven (or pushed ) at low speeds , for example in the pits .Another point to remember is that most turns in racing have a fairly large radius and the Ackermann effect is very small . In fact , unless the steering system and suspension are very stiff ,compliance (deflection ) under cornering loads may steer the wheels more than any Ackermann (or reverse Ackermann ) built into the geometry .The simplest construction that generates Ackermannn geometry is shown in figure 19.3 fo r “rear steer ” . Here ,the rack (cross link or relay rod in steering box systems ) is located behind the front axle and lines staring at the kingpin axis , extended through the outer tie rod ends , intersect in the center of the rear axle . The angularity of the steering knuckle will cause the inner wheel to steer more than the outer (toe-out on turning ) and a good approximation of “perfect Ackermann ” will be achieved .The second way to design-in differences between inner and outer steer Angles is by moving the rack (or cross link ) forward or backward so that it is no longer on a line directly connecting the two outer tie rod ball joints .This is shown in figure 19.4. with “rear steer ” , as shown in the figure ,moving the rack forward will tend mo re toward parallel steer (and eventually reverse Ackermann ), and moving it toward the rear of the car will increase the toe-out on turning .A third way to generate toe with steering is simply to make the steering arms different lengths . A shorter steering arm (as measured from the kingpin axis to the outer tie rod end ) will be steered through a larger angle than one with a longer knuckle. Of course this effect is asymmetric and applies only to cars turning in one direction—oval track cars .RecommendationWith the conflicting requirements mentioned above , the authors feel that parallel steer or a bit of reverse Ackermann is a reasonable compromise . With parallel steer , the car will be somewhat difficult to push through the pits because the front wheels will be fighting each other . at racing speeds , on large-radius turns , the front wheels are steered very little , thus any ackermann effects will not have a large effect on the individual wheel slip angles , relative to a reference steer angle , measured at the centerline of the car .文献翻译摘自《Race Car Vehicle Dynamics》第19章转向系统序言:本章以转向几何参数的讨论为开始,包括主销后倾角,后倾拖距,主销内倾角,主销偏置量。
附录Hyundai Motor on the steering control of the request is lightweight, safe, reliable, and should have sufficient life. In order to meet these requirements, the design of the steering gear should have a reasonable transmission ratio characteristics, the correct gap eating together, a higher transmission efficiency, sufficient rigidity and strength. If the steering gear in the design is reasonable, then the product is good and bad parts of the key issues of manufacturing and assembly. How to control the quality of the product? The key problem is that a reasonable detection methods, the key to strictly control the passing rate of time, such products will be able to guarantee the quality of parts and components. First of all, the quality of shifting ASSY, should control the assembly and to ensure that turning the steering shaft torque and rotational axis and the transmission gap between components. Followed by testing the performance of steering gear, steering gear must also be adopted by all types of test-bed to verify the established angle transmission ratio, transmission efficiency, rotational torque, rigid. In addition to examination other than the above-mentioned steering performance, but also in the pilot stage of its life nuclear reliability and life expectancy that is static torsion test: a thin red hammer, hit test, fatigue life test. To determine whether the quality of the product in hand national standards. Noise from the steering angle repair cream, which is also a test method to detect and can learn from the J class machinery manufacturing industry in China''in the past only means to recognize the importance of detection, and the lack of''lack of testing and testing of the poor law awareness. So have some of the parts is a qualified products l materials, and assembly of products from the pilot test proved to be defective, or: The test can verify the quality of products and design for the steering gear (1) the accuracy of parts of the foot only, finish second, two-phase - the location of the elite "Measuring the content of L ①steering shaft loaded journal bearings Department feet 'inch accuracy and smoothness, anti-worm or worm-inch accuracy, smoothness and surface hardness and magnetic → for testing; ②steering vertical axis arm journal dimensional accuracy and smoothness, the worm wheel roller bearing of the journal center hole distance, wheel bearing and the journal''hole angle from the Chinese side, the block size, finish and degree of asymmetry; ③circulating balltooth-type radial fan, big-law length, journal hardness, the magnetic; ④browser to Min Xuan cochlear aperture wheel size precision, smoothness, tooth surface roughness, intermediate thick teeth, tooth, tooth degree of asymmetry; ⑤ball rolling circle diameter, smooth, cylindrical roller Road''degree of accuracy and bias, raceway adjacent pitch error, cumulative error section of grass lines and sub-rack section from Rolling Road Center, rack section Road center line and the roll of injustice: line degrees; ® carburizing layer thickness, hardness; magnetic flaw detection; ⑦shift steering shaft shell aperture, roughness, different degree of heart; ⑧shift towards vertical axis aperture arm flying finish, different degree of heart; ⑨chaos and steering shaft steering arm hole down the center distance, steering shaft-hole axes and steering arm hole down the center line of the non-verticality(2) parts of cleanliness. Detection of the site is turning - browser shell surface and the surface parts.Detection method is to use cleaning fluid to clean parts, and then the cleaning fluid with impurities, and vacuum membrane leaching; further 120 weeks of petrol industrial solvents the membrane will be washed with impurities. To be volatile after the membrane cleaning fluid, together with the impurities from weighing, with the magnet cellophane packets are sorted in the iron impurities, said the weight of a scrap-iron. The iron filings and then 40 times on the microscope with a disability in most dogs measured particle size (length X width).(3) assembly of the leakage. Does not allow any leakage of the phenomenon of steering. Because of internal lubricants in the steering gear is used to turn parts lubricated friction pair, and if as a result of damage caused by leaking seals, lubrication will be affected, resulting in increased friction and wear parts and reduce the life span of steering gear; transmission efficiency at the same time will lower.The use of conventional vibration and temperature +40 ° C under the conditions of inspection, the shell and shell cap shaft oil seal joints as well as whether the spill, and water to observe whether there are leakages.(4) after a good tune steering assembly should check the technical requirements flexible and comfortable when turning the steering wheel, there is no axial gap I turn the steering wheel of the total value of the number required to turn around a few cars in line with the original request. Steering gear shift, also known as machine, machine direction, which is steering the mostimportant parts. Its role is to: increase the spread to turn steering wheel and transmission mechanism to change the direction of power transfer.Hydraulic Steering Hydraulic steering vehicles are widely used in marine hydraulic steering and rudder. Drivers can be used through its ability to manipulate smaller shift power to achieve greater control and performance of safe, reliable, flexible manipulation, light.The manipulation of steering is hydraulic, that is in the steering column and steering wheel there is no mechanical connection between the steering gear is between the fuel tank and steering hydraulic pipes or hoses link.When turning the steering wheel, steering wheel rotation in accordance with the relative proportion of transport fuel, the fuel tank directly into the corresponding control side, while the other side of the oil back to tank.BZZ steering is a switch-type full-hydraulic steering valve with the following characteristics: the elimination of mechanical linkage device, the host can reduce costs, provide a reliable, lightweight structures, manipulation of a flexible lightweight, safe, reliable, and can be very small continuous torque stepless control of rotation, provided to the control loop, as well as a wide range of host size choice, able to shift and a variety of pumps and hydraulic supply system.Steering by the structure can be divided into many types. History, there have been many forms of steering, there is currently more commonly used rack and pinion, worm means crank pins, recycling the ball - rack fan gear type, recycling the ball crank pins means, such as worm-type wheel. The second, fourth, respectively, is the first, the third form of the deformation, and the worm wheel is even more rare type. If the form in accordance with assistance, but also can be divided into mechanical (no help), and power-style (with help) two types of power steering which can be divided into pressure and motivation, hydraulic-power, electric power-type, electro-hydraulic power types of blocks. 1) It is a rack and pinion of steering one of the most common. The basic structure is a pair of mutually meshing rack and pinion. Pinion steering drive shaft rotates, rack linear motion would be done. In some cases, directly driven by the rack cross-bar, you can make of steering wheel shift. So, this is one of the most simple steering. Its advantage is simple structure, low-cost, steering sensitivity, small size, can be directly cross-link. In widely used vehicle.It is a worm for the active parts, crank pin for the steering gear follower. Worm has a trapezoidalthread, referring to a finger-shaped pin with tapered bearings in the crank bearings, the crank shaft and the shift into one arm. Shifted through steering wheel rotating worm, helical worm embedded in the cone-shaped slot means the marketing side of the rotation, the side rocker shaft to do around the shifted arc movement, thereby stimulating and steering crank arm swing down and then turning to make shift transmission wheel deflection. This steering is usually used to turn power on a larger truck.Circulating ball-type: This device is turned by the gear mechanism from the steering wheel to slow down the rotation of power, so that the rotation of steering wheel movement into rotary movement of the turbine worm, ball screw and nut holding the ball engagement, which Ball screw linear motion into rotary movement, with the fan-shaped nut meshing gears, linear motion into rotary movement again to shake the rod arm, link arm moving again so that even the bar and cross bar to do a straight-line movement to change the wheels direction. This is a classical institutions, most modern cars no longer have to use, but the way was the latest by the application of power steering device. It is equivalent to the principle use of nuts and bolts in the rotation process of relative movement, and in between the thread and thread the ball into the folder to reduce the resistance, all the ball, both connected in a closed loop of the spiral curve rolling ball club is named after the cycle.Hydraulic rack and pinion steering gear is relative to the case of rack and pinion steering gear machinery, mainly to increase the steering pump, steering oiler, steering pipeline, steering valve, steering components, such as fuel tanks, with a view to improve the pilot hand, the purpose of increasing power steering of the steering device. After 10 years of internal development, has become a mature R & D and manufacturing technology manufacturers have Yubei Koyo Steering Gear Co., Ltd. and other enterprises. [1] With the rapid development of automobile industry, as well as for comfort, safety and continuous improvement in performance, steering systems are also changing with the advance of technology. For the time being, electric power steering system is turning the forefront of the industry research projects, in accordance with its distribution of the form of string can be divided into power, gear Power, power rack, power bar, the form of electro-hydraulic power. Ago in some sci-fi movies of the unmanned aircraft can occur, such as unmanned aerial vehicle is now a reality, steering systems are moving in the direction of the development of more advanced, such as research and development from Japan JTEKT advancedby the steer-by-wire systems.In this paper, choice-based recycling the ball GX1608A gear - steering rack as a research topic, its main contents are: knowledge of automotive steering gear, ball-type steering gear cycle of the main parameters and design choices. Design also includes the shift rocker shaft, involute spline, fan gear shaft and screw shaft design and verification. According to its own independent study completed by the steering shaft and screw shaft rocker design and verification, in other parts of the network, as well as through the school library to collect relevant information and fax to the future, in the papers have used information the mark.The design has been through a total of about 16 Chinese and foreign-related literature, and learn from the relevant parts of which the essence of the final design of the times. Because of its limited ability to learn and, I urge teachers and experts have pointed out that less than one.现代汽车对转向器的要求是操纵轻便,安全、可靠,并应具有足够的使用寿命。
附录一:汽车的部件发动机发动机的作用是为汽车提供动力,人们形象的称之为汽车的动力工厂。
大多数汽车发动机都是利用空气和汽油混合物的爆炸能量推动活塞的。
活塞能够转动与它连接在一起的曲柄连杆。
从而,曲柄产生牵引力使车轮转动。
有些汽车是靠另一种发动机来提供动力的。
这种发动机因为它的旋转阀,旋转内燃机或者转子发动机而被人熟知。
这种旋转阀式发动机也能够吸入空气和燃料的混合物,然后将它们压缩并燃烧。
另外,发动机会在一个椭圆形腔室中旋转,它与驱动汽车后轮的后轴相连接。
绝大多数的汽车里,发动机会被安装在汽车的前部末端,离合器和变速箱在它的后面。
最后,发动机、离合器和变速箱会被装配成一个整体。
想要使一个发动机能够正常工作还需要很多系统的支持。
润滑系统可以用来减小摩擦,减轻发动机磨损。
冷却系统可以使发动机的工作温度在安全的范围之内。
另外,发动机还必须由供油系统提供适量的燃料和空气。
在气缸里,空气和燃料的混合物必须由点火系统在适当的情况下点燃。
而后,电子系统被用来控制启动发动机用的电动机和为发动机的附属部件提供电能。
润滑系统发动机的部件会因为它们之间的相互运动而逐渐导致磨损。
在这些部件中间存在着发动机循环油。
它可以避免金属间的相互摩擦而导致的磨损。
在润滑剂的润滑作用下,各部件会仅受到很小的摩擦力,这可以使它们更容易运动。
因此,润滑系统可以将由摩擦引起的能量损失降到最小。
润滑剂的第二个作用是可以发挥冷却剂的作用,也可以作为密封介质来防止泄漏。
还有在气缸上产生的润滑薄膜也可以有助于活塞环密封,改善发动机的压缩性能。
冷却系统在气缸中,燃料会在空气的作用下剧烈燃烧,从而导致发动机各部件的温度升高。
温度的上升将直接影响发动机的性能,也会缩短发动机零件的寿命。
而冷却系统则可以使发动机在适宜的温度下工作。
无论驾驶条件如何,该系统都要被设计用来防止机器过冷或过热。
燃料供给燃料供给系统的主要作用是在机动车辆所能遇到的所有条件下(包括负载,速度,温度压力的变化梯度等),提供足够的压力,以一定的速度为化油器或注油系统提供燃料,来满足发动机的燃料要求。
HOW CAR STEERING WORKSYou know that when you turn the steering wheel in your car, the wheels turn. Cause and effect, right? But a lot of interesting stuff goes on between the steering wheel and the tires to make this happen.In this article, we'll see how the two most common types of car steering systems work: rack-and-pinion and recirculating-ball steering. Then we'll examine power steering and find out about some interesting future developments in steering systems, driven mostly by the need to increase the fuel efficiency of cars. But first, let's see what you have to do turn a car. It's not quite as simple as you might think! recirculating ball.You might be surprised to learn that when you turn your car, your front wheels are not pointing in the same direction.For a car to turn smoothly, each wheel must follow a different circle. Since the inside wheel is following a circle with a smaller radius, it is actually making a tighter turn than the outside wheel. If you draw a line perpendicular to each wheel, the lines will intersect at the center point of the turn. The geometry of the steering linkage makes the inside wheel turn more than the outside wheel.There are a couple different types of steering gears. The most common are rack-and-pinion andRack-and-pinion steeringRack-and-pinion steering is quickly becoming the most common type of steering on cars, small trucks and SUVs. It is actually a pretty simple mechanism. A rack-and-pinion gearset is enclosed in a metal tube, with each end of the rack protruding from the tube. A rod, called a tie rod, connects to each end of the rack.The pinion gear is attached to the steering shaft. When you turnthe steering wheel, the gear spins, moving the rack. The tie rod at each end of the rack connects to the steering arm on the spindle (see diagram above).The rack-and-pinion gearset does two things: It converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into the linear motion needed to turn the wheels. It provides a gear reduction, making it easier to turn the wheels.On most cars, it takes three to four complete revolutions of the steering wheel to make the wheels turn from lock to lock (from far left to far right).The steering ratio is the ratio of how far you turn the steering wheel to how far the wheels turn. For instance, if one complete revolution (360 degrees) of the steering wheel results in the wheels of the car turning 20 degrees, then the steering ratio is 360 divided by 20, or 18:1.A higher ratio means that you have to turn the steering wheel more to get the wheels to turn a given distance. However, less effort is required because of the higher gear ratio. Generally, lighter, sportier cars have lower steering ratios than larger cars and trucks. The lower ratio gives the steering a quicker response -- you don't have to turn the steering wheel as much to get the wheels to turn a given distance -- which is a desirable trait in sports cars. These smaller cars are light enough that even with the lower ratio, the effort required to turn the steering wheel is not excessive.Some cars have variable-ratio steering, which uses a rack-and-pinion gearset that has a different tooth pitch (number of teeth per inch) in the center than it has on the outside. This makes the car respond quickly when starting a turn (the rack is near the center), and also reduces effort near the wheel's turning limits.Power Rack-and-pinionWhen the rack-and-pinion is in a power-steering system, the rack has a slightly different design. Part of the rack contains a cylinder witha piston in the middle. The piston is connected to the rack. There are two fluid ports, one on either side of the piston. Supplying higher-pressure fluid to one side of the piston forces the piston to move, which in turn moves the rack, providing the power assist.We'll check out the components that provide the high-pressure fluid, as well as decide which side of the rack to supply it to, later in the article. First, let's take a look at another type of steering.Recirculating-ball SteeringRecirculating-ball steering is used on many trucks and SUVs today. The linkage that turns the wheels is slightly different than on a rack-and-pinion system.The recirculating-ball steering gear contains a worm gear. You can image the gear in two parts. The first part is a block of metal with a threaded hole in it. This block has gear teeth cut into the outside of it, which engage a gear that moves the pitman arm (see diagram above). The steering wheel connects to a threaded rod, similar to a bolt, that sticks into the hole in the block. When the steering wheel turns, it turns the bolt. Instead of twisting further into the block the way a regular bolt would, this bolt is held fixed so that when it spins, it moves the block, which moves the gear that turns the wheels.Instead of the bolt directly engaging the threads in the block, all of the threads are filled with ball bearings that recirculate through the gear as it turns. The balls actually serve two purposes: First, they reduce friction and wear in the gear; second, they reduce slop in the gear. Slop would be felt when you change the direction of the steering wheel -- without the balls in the steering gear, the teeth would come out of contact with each other for a moment, making the steering wheel feel loose.Power steering in a recirculating-ball system works similarly to a rack-and-pinion system. Assist is provided by supplying higher-pressure fluid to one side of the block.Now let's take a look at the other components that make up a power-steering system.Power SteeringThere are a couple of key components in power steering in addition to the rack-and-pinion or recirculating-ball mechanism.PumpThe hydraulic power for the steering is provided by a rotary-vane pump (see diagram below). This pump is driven by the car's engine via a belt and pulley. It contains a set of retractable vanes that spin inside an oval chamber. As the vanes spin, they pull hydraulic fluid from the return line at low pressure and force it into the outlet at high pressure. The amount of flow provided by the pump depends on the car's engine speed. The pump must be designed to provide adequate flow when the engine is idling. As a result, the pump moves much more fluid than necessary when the engine is running at faster speeds. The pump contains a pressure-relief valve to make sure that the pressure does not get too high, especially at high engine speeds when so much fluid is being pumped.Rotary ValveA power-steering system should assist the driver only when he is exerting force on the steering wheel (such as when starting a turn). When the driver is not exerting force (such as when driving in a straight line), the system shouldn't provide any assist. The device that senses the force on the steering wheel is called the rotary valve.The key to the rotary valve is a torsion bar. The torsion bar is a thin rod of metal that twists when torque is applied to it. The top of the bar is connected to the steering wheel, and the bottom of the bar is connected to the pinion or worm gear (which turns the wheels), so the amount of torque in the torsion bar is equal to the amount of torque thedriver is using to turn the wheels. The more torque the driver uses to turn the wheels, the more the bar twists.The input from the steering shaft forms the inner part of a spool-valve assembly. It also connects to the top end of the torsion bar. The bottom of the torsion bar connects to the outer part of the spool valve. The torsion bar also turns the output of the steering gear, connecting to either the pinion gear or the worm gear depending on which type of steering the car has.As the bar twists, it rotates the inside of the spool valve relative to the outside. Since the inner part of the spool valve is also connected to the steering shaft (and therefore to the steering wheel), the amount of rotation between the inner and outer parts of the spool valve depends on how much torque the driver applies to the steering wheel.When the steering wheel is not being turned, both hydraulic lines provide the same amount of pressure to the steering gear. But if the spool valve is turned one way or the other, ports open up to provide high-pressure fluid to the appropriate line.It turns out that this type of power-steering system is pretty inefficient. Let's take a look at some advances we'll see in coming years that will help improve efficiency.The Future of Power SteeringSince the power-steering pump on most cars today runs constantly, pumping fluid all the time, it wastes horsepower. This wasted power translates into wasted fuel. You can expect to see several innovations that will improve fuel economy. One of the coolest ideas on the drawing board is the "steer-by-wire" or "drive-by-wire" system. These systems would completely eliminate the mechanical connection between the steering wheel and the steering, replacing it with a purely electronic control system. Essentially, the steering wheel would work like the one you can buy foryour home computer to play games. It would contain sensors that tell the car what the driver is doing with the wheel, and have some motors in it to provide the driver with feedback on what the car is doing. The output of these sensors would be used to control a motorized steering system. This would free up space in the engine compartment by eliminating the steering shaft. It would also reduce vibration inside the car.General Motors has introduced a concept car, the Hy-wire, that features this type of driving system. One of the most exciting things about the drive-by-wire system in the GM Hy-wire is that you can fine-tune vehicle handling without changing anything in the car's mechanical components -- all it takes to adjust the steering is some new computer software. In future drive-by-wire vehicles, you will most likely be able to configure the controls exactly to your liking by pressing a few buttons, just like you might adjust the seat position in a car today. It would also be possible in this sort of system to store distinct control preferences for each driver in the family.In the past fifty years, car steering systems haven't changed much. But in the next decade, we'll see advances in car steering that will result in more efficient cars and a more comfortable ride. For more information on steering systems and related topics, check out the links on the next page.汽车转向装置是怎样工作的当你转动汽车的方向盘时,为什么车轮会转动呢?我们可以在方向盘和使之转动的车轮之间发现一些有意思的东西。
附录附录A 英文文献Along with automobile electronic technology swift and violent development, the people also day by day enhance to the motor turning handling quality request. The motor turning system changed, the hydraulic pressure boost from the traditional machinery changes (Hydraulic Power Steering, is called HPS), the electrically controlled hydraulic pressure boost changes (Elect ric Hydraulic Power Steering, is called EHPS), develops the electrically operated boost steering system (Elect ric Power Steering, is called EPS), finally also will transit to the line controls the steering system (Steer By Wire, will be called SBW).The machinery steering system is refers by pilot's physical strength achievement changes the energy, in which all power transmission all is mechanical, the automobile changes the movement is operates the steering wheel by the pilot, transmits through the diverter and a series of members changes the wheel to realize. The mechanical steering system by changes the control mechanism, the diverter and major part changes the gearing 3 to be composed.Usually may divide into according to the mechanical diverter form: The gear rack type, follows round the world -like, the worm bearing adjuster hoop type, the worm bearing adjuster refers sells the type. Is the gear rack type and follows using the broadest two kinds round the world -like (uses in needing time big steering force).In follows round the world -like in the diverter, the input changes the circle and the output steering arm pivot angle is proportional; In the gear rack type diverter, the input changes the turn and the output rack displacement is proportional. Follows round the world -like the diverter because is the rolling friction form, thus the transmission efficiency is very high, the ease of operation also the service life are long, moreover bearing capacity, therefore widely applies on the truck. The gear rack type diverter with follows round the world -like compares, the most major characteristic is the rigidity is big, the structure compact weight is light, also the cost is low. Because this way passes on easily by the wheel the reacting force to the steering wheel, therefore has to the pavement behavior response keen merit, but simultaneously also easy to have phenomena and so on goon and oscillation, also its load bearing efficiency relativeweak, therefore mainly applies on the compact car and the pickup truck, at present the majority of low end passenger vehicle uses is the gear rack type machinery steering system.Along with the vehicles carrying capacity increase as well as the people to the vehicles handling quality request enhancement, the simple mechanical type steering system were already unable to meet the needs, the power steering system arise at the historic moment, it could rotate the steering wheel while the pilot to provide the boost, the power steering system divides into the hydraulic pressure steering system and the electrically operated steering system 2 kinds.Hydraulic pressure steering system is at present uses the most widespread steering system.The hydraulic pressure steering system increased the hydraulic system in the mechanical system foundation, including hydraulic pump, V shape band pulley, drill tubing, feed installment, boost installment and control valve. It with the aid of in the motor car engine power actuation hydraulic pump, the air compressor and the generator and so on, by the fluid strength, the physical strength or the electric power increases the pilot to operate the strength which the front wheel changes, enables the pilot to be possible nimbly to operate motor turning facilely, reduced the labor intensity, enhanced the travel security.The hydraulic pressure boost steering system from invented already had about half century history to the present, might say was one kind of more perfect system, because its work reliable, the technology mature still widely is applied until now. It takes the power supply by the hydraulic pump, after oil pipe-line control valves to power hydraulic cylinder feed, through the connecting rod impetus rotation gear movement, may changes the boost through the change cylinder bore and the flowing tubing head pressure size the size, from this achieved changes the boost the function. The traditional hydraulic pressure type power steering system may divide into generally according to the liquid flow form: Ordinary flow type and atmospheric pressure type 2 kind of types, also may divide into according to the control valve form transfers the valve type and the slide-valve type.Along with hydraulic pressure power steering system on automobile daily popularization, the people to operates when the portability and the road feeling request also day by day enhance, however the hydraulic pressure power steering system has many shortcomings actually: ①Because its itself structure had decided it is unable to guarantee vehicles rotates the steering wheel when any operating mode, all has the ideal operation stability, namely is unable simultaneously to guarantee time the low speed changes theportability and the high speed time operation stability;②The automobile changes the characteristic to drive the pilot technical the influence to be serious; ③The steering ratio is fixed, causes the motor turning response characteristic along with changes and so on vehicle speed, transverse acceleration to change, the pilot must aim at the motor turning characteristic peak-to-peak value and the phase change ahead of time carries on certain operation compensation, thus controls the automobile according to its wish travel. Like this increased pilot's operation burden, also causes in the motor turning travel not to have the security hidden danger; But hereafter appeared the electrically controlled hydraulic booster system, it increases the velocity generator in the traditional hydraulic pressure power steering system foundation, enables the automobile along with the vehicle speed change automatic control force size, has to a certain extent relaxed the traditional hydraulic pressure steering system existence question.At present our country produces on the commercial vehicle and the passenger vehicle uses mostly is the electrically controlled hydraulic pressure boost steering system, it is quite mature and the application widespread steering system. Although the electrically controlled hydraulic servo alleviated the traditional hydraulic pressure from certain degree to change between the portability and the road feeling contradiction, however it did not have fundamentally to solve the HPS system existence insufficiency, along with automobile microelectronic technology development, automobile fuel oil energy conservation request as well as global initiative environmental protection, it in aspect and so on arrangement, installment, leak-proof quality, control sensitivity, energy consumption, attrition and noise insufficiencies already more and more obvious, the steering system turned towards the electrically operated boost steering system development.The electrically operated boost steering system is the present mo tor turning system development direction, its principle of work is: EPS system ECU after comes from the steering wheel torque sensor and the vehicle speed sensor signal carries on analysis processing, controls the electrical machinery to have the suitable boost torque, assists the pilot to complete changes the operation. In the last few years, along with the electronic technology development, reduces EPS the cost to become large scale possibly, Japan sends the car company, Mitsubishi Car company, this field car company, US's Delphi automobile system company, TRW Corporation and Germany's ZF Corporation greatly all one after another develops EPS.Mercedes2Benz and Siemens Automotive two big companiesinvested 65,000,000 pounds to use in developing EPS, the goal are together load a car to 2002, yearly produce 300 ten thousand sets, became the global EPS manufacturer. So far, the EPS system in the slight passenger vehicle, on the theater box type vehicle obtains the widespread application, and every year by three million speed development.Steering is the term applied to the collection of components, linkages, etc. which allow for a vessel (ship, boat) or vehicle (car) to follow the desired course. An exception is the case of rail transport by which rail tracks combined together with railroad switches provide the steering function.The most conventional steering arrangement is to turn the front wheels using a hand–operated steering wheel which is positioned in front of the driver, via the steering column, which may contain universal joints to allow it to deviate somewhat from a straight line. Other arrangements are sometimes found on different types of vehicles, for example, a tiller or rear–wheel steering. Tracked vehicles such as tanks usually employ differential steering —that is, the tracks are made to move at different speeds or even in opposite directions to bring about a change of course.Many modern cars use rack and pinion steering mechanisms, where the steering wheel turns the pinion gear; the pinion moves the rack, which is a sort of linear gear which meshes with the pinion, from side to side. This motion applies steering torque to the kingpins of the steered wheels via tie rods and a short lever arm called the steering arm.Older designs often use the recirculating ball mechanism, which is still found on trucks and utility vehicles. This is a variation on the older worm and sector design; the steering column turns a large screw (the "worm gear") which meshes with a sector of a gear, causing it to rotate about its axis as the worm gear is turned; an arm attached to the axis of the sector moves the pitman arm, which is connected to the steering linkage and thus steers the wheels. The recirculating ball version of this apparatus reduces the considerable friction by placing large ball bearings between the teeth of the worm and those of the screw; at either end of the apparatus the balls exit from between the two pieces into a channel internal to the box which connects them with the other end of the apparatus, thus they are "recirculated".The rack and pinion design has the advantages of a large degree of feedback and direct steering "feel"; it also does not normally have any backlash, or slack. A disadvantage is that it is not adjustable, so that when it does wear and develop lash, the only cure is replacement.The recirculating ball mechanism has the advantage of a much greater mechanical advantage, so that it was found on larger, heavier vehicles while the rack and pinion was originally limited to smaller and lighter ones; due to the almost universal adoption of power steering, however, this is no longer an important advantage, leading to the increasing use of rack and pinion on newer cars. The recirculating ball design also has a perceptible lash, or "dead spot" on center, where a minute turn of the steering wheel in either direction does not move the steering apparatus; this is easily adjustable via a screw on the end of the steering box to account for wear, but it cannot be entirely eliminated or the mechanism begins to wear very rapidly. This design is still in use in trucks and other large vehicles, where rapidity of steering and direct feel are less important than robustness, maintainability, and mechanical advantage. The much smaller degree of feedback with this design can also sometimes be an advantage; drivers of vehicles with rack and pinion steering can have their thumbs broken when a front wheel hits a bump, causing the steering wheel to kick to one side suddenly (leading to driving instructors telling students to keep their thumbs on the front of the steering wheel, rather than wrapping around the inside of the rim). This effect is even stronger with a heavy vehicle like a truck; recirculating ball steering prevents this degree of feedback, just as it prevents desirable feedback under normal circumstances.The steering linkage connecting the steering box and the wheels usually conforms to a variation of Ackermann steering geometry, to account for the fact that in a turn, the inner wheel is actually traveling a path of smaller radius than the outer wheel, so that the degree of toe suitable for driving in a straight path is not suitable for turns.As vehicles have become heavier and switched to front wheel drive, the effort to turn the steering wheel manually has increased - often to the point where major physical exertion is required. To alleviate this, auto makers have developed power steering systems. There are two types of power steering systems—hydraulic and electric/electronic. There is also a hydraulic-electric hybrid system possible.A hydraulic power steering (HPS) uses hydraulic pressure supplied by an engine-driven pump to assist the motion of turning the steering wheel. Electric power steering (EPS) is more efficient than the hydraulic power steering, since the electric power steering motor only needs to provide assist when the steering wheel is turned, whereas the hydraulic pump must run constantly. In EPS the assist level is easily tunable to the vehicletype, road speed, and even driver preference. An added benefit is the elimination of environmental hazard posed by leakage and disposal of hydraulic power steering fluid.An outgrowth of power steering is speed adjustable steering, where the steering is heavily assisted at low speed and lightly assisted at high speed. The auto makers perceive that motorists might need to make large steering inputs while manoeuvering for parking, but not while traveling at high speed. The first vehicle with this feature was the Citroën SM with its Diravi layout, although rather than altering the amount of assistance as in modern power steering systems, it altered the pressure on a centring cam which made the steering wheel try to "spring" back to the straight-ahead position. Modern speed-adjustable power steering systems reduce the pressure fed to the ram as the speed increases, giving a more direct feel. This feature is gradually becoming commonplace across all new vehicles.Four-wheel steering (or all wheel steering) is a system employed by some vehicles to increase vehicle stability while maneuvering at high speed, or to decrease turning radius at low speed.In most four-wheel steering systems, the rear wheels are steered by a computer and actuators. The rear wheels generally cannot turn as far as the Alternatively, several systems, including Delphi's Quadrasteer and the system in Honda's Prelude line, allow for the rear wheels to be steered in the opposite direction as the front wheels during low speeds. This allows the vehicle to turn in a significantly smaller radius —sometimes critical for large trucks or vehicles with trailers.附录B 文献翻译随着汽车电子技术的迅猛发展,人们对汽车转向操纵性能的要求也日益提高。
汽车转向控制中英文对照外文翻译文献(文档含英文原文和中文翻译)中英文对照翻译汽车的转向控制控制系统稳定性是针对提高驾驶安全性提出的一系列措施中最新的一个。
这个系统能够在40毫秒内实现从制动开始到制动恢复的过程,这个时间是人的反应时间得七倍。
他们通过调整汽车扭矩或者通过应用汽车左侧或右侧制动,如果需要甚至两者兼用,来实现准确的行车路线。
这个系统已被应用于奔驰S600汽车了。
稳定的机械自动系统能够在制动时发现肇端,并且在驾驶人员发现能够反应以前实现车辆的减速。
安全玻璃,安全带,撞击缓冲区,安全气囊,ABS系统,牵引力控制系统还有现在的稳定调节系统。
汽车安全系统的连续升级,已经产生了一种为保护汽车所有者安全的设计模式。
稳定调节系统帮助驾驶员从不可控制的曲线制动中解脱出来,从而避免了汽车的摆动滑行和交通事故。
利用计算机和一系列传感器,稳定调节系统能够检测到制动轮的打滑并且比人更快的恢复对汽车的方向控制。
系统每百万分之一秒作出一次快速捕捉,以及断断汽车是否在按照驾驶员的路线行驶。
如果检测到汽车行驶路线和驾驶员驾驶路线存在一个微小的偏差,系统会在瞬间纠正发动机扭矩或者应用汽车左右制动。
过程的标准反应时间是40毫秒----人的平均反应时间的七分之一。
罗伯特博世工程系统负责人安东·范·桑特解释说:“一个稳定的控制系统能够‘感觉到”驾驶员想要运动的方向,通过控制转向角度,油门踏板的位置,制动板的状态来确定汽车实际运动路线的偏航比率(汽车偏离方向轴的角度)和横向加速度”。
项目负责人阿明·马勒领导着范桑特的工作小组和奔驰汽车公司的工程师发明了第一个完全有效的稳定调节系统,该系统由发动机扭矩控制系统,制动系统,牵引控制系统组成以实现理想与现实运动之间的最小差距。
汽车安全专家相信稳定调节系统能够减少交通事故的发生,至少是在伤亡严重的事故方面。
安全统计表明,多数的单车撞击事故伤亡(占伤亡事故发生的4%),事故能够通过应用这项新技术避免。
原文The basic steering system in most cars is the same. The steering gear of steering box is the heart of the steering system. This usually is next to the engine. A shaft extends from the back of the steering gear. This shaft is connected to the steering column or steering shaft. The steering wheel is at the top of the steering column. Another shaft comes from the bottom of the steering gear. This shaft connects to the arms, rods, and links. This parts assembly, called the steering linkage, connects the steering gear to the parts at the wheels. The wheels and tires mount to the steering knuckles. The knuckles are pivoted at the top and bottom. Thus, the wheels and tires can turn from side to side.While the steering system may look complicated, it works quite simply. When a driver drives a car straight down the road, the steering gear is centered. The gear holds the linkage centered so that the wheels and tires point straight ahead. When the driver turns the steering wheel, the steering shaft rotates and the steering gear moves toward that side. The shaft coming out the bottom of the steering gear turns, as well. When the shaft turns, it pulls the linkage to one side and makes the steering knuckles turn slightly about their pivot points. Thus, the steering knuckle, spindle, wheels, and tires turn to one side, causing the car to turn.To minimize tire wear the front wheels should be steered from the straight ahead to a position where they form an angle of 90ºto a line drawn from the instantaneous center to the wheel center. It means that the inner wheel turns through a larger angle than the outer wheel.It is obtained by making the track rod a different length to the distance between the king pins. The track rod length is set so that its connection to the track arm falls on an imaginary line taken from the king pin to a point on the vehicle center line just in front of the rear axle.Most heavy commercial vehicles use the recirculating ball type of steering gear. This steering gear is durable, with good steering response and good road feel for the driver.In the recirculating ball steering gear, the wormshaft is the input shaft. The wormshaft connects to the steering column in such a way that a mechanic can remove the steering gear or steering column independently of one another. The sector shaft (also called the pitman shaft) is like the output shaft of the steering gear. The main parts of the steering gear are the balls, ball nut, and the gear teeth on the ball nut.As the wormshaft turns, the balls move the ball nut up and down along the wormshaft. This turns the sector shaft, since the sector teeth mesh with the ball nut teeth. The sector shaft is connected through steering linkage to the front wheels.The rack-and-pinion system has two main parts-the pinion and the rack. The pinion is on the end of the steering column. The steering wheel turns the pinion. The rack is a long, flat bar with teeth on one side. The rack teeth mesh with the teeth on the pinion.Rack-and-pinion steering is used on many new smaller cars and on most cars with a transverse engine. This steering gear is small and lightweight. It provides good steering with minimum driver effort. Also, rack-and-pinion steering needs fewer parts in the steering gear and linkage. Thus, it is easy to service. Rack-and-pinion steering gives more feedback and road feel to the driver.翻译多数汽车的转向系基本上是一样的。
附录 A一、课题国内外现状转向器又名转向机、方向机,它是转向系中最重要的部件。
转向器的作用是:增大转向盘传到转向传动机构的力和改变力的传递方向。
转向器按结构形式可分为多种类型。
目前较常用的有齿轮齿条式、蜗杆曲柄指销式、循环球-齿条齿扇式、循环球曲柄指销式、蜗杆滚轮式等。
如果按照助力形式,又可以分为机械式(无助力),和动力式(有助力)两种,其中动力转向器又可以分为气压动力式、液压动力式、电动助力式、电液助力式等种类。
转向器的工作原理就是,当驾驶员左右转动方向盘时,通过带有万向传动装置的转向柱转动,使转向螺杆转动,循环球在螺旋管状通道内滚动,形成“球流”。
钢球在管状通道内绕行两周后,流出转向螺母而进入导管的一端,再沿导管经导管的另一端流回螺旋管状通道。
故在转向器工作时,两列钢球在各自的封闭管道内循环,而不致脱出。
钢球流动的同时,推动螺母沿螺杆前后移动。
然后,齿条带动齿扇摆动,使摇臂轴发生转动。
最后,通过转向传动机构推动转向轮偏转,实现汽车转向。
近年来,我国汽车工业呈现出稳定快速增长的态势。
作为汽车关键部件之一的转向器也得到了较为快速地发展,在产销规模不断增长的同时,技术水平也得到了一定程度的提升。
在国内汽车配装的转向器产品中,商用车(主要是载货车)有95%以上是自主品牌转向器。
在中高档轿车中,2/3车辆使用的是中外合资企业或外商独资企业生产的转向器,1/3的车辆使用自主品牌转向器。
低档轿车则几乎全部使用自主品牌转向器[4]。
汽车转向器机构涉及整车的操纵性、稳定性和安全性,它的质量也反映了车辆的质量,是直接关系到车辆性能的关键部件。
对转向系统的要求,最主要的是转向的灵敏性和操纵的轻便性。
高的转向灵敏性,要求转向器具有小的传动比;好的操纵轻便性,则要求转向器具有大的传动比。
这个矛盾一直都以一个很难解决的问题。
而循环球式转向器的传动效率可达到75%~85%;转向器的传动比可以变化;工作平稳可靠;齿条和齿扇之间的间隙调整容易;适合用来做整体式动力转向器,达到矛盾的平衡。
二、研究主要成果1、做成整体式动力转向器应用于各种工况的多种车辆中。
2、制成变传动比转向器解决转向灵敏度和转向力之间的矛盾。
3、可逆式转向器保证转向后转向轮和转向盘自动回证,减轻驾驶员疲劳,提高行驶安全性。
4、采用变厚齿扇简单了转向器的传动间隙调整机构,保证了转向的灵敏度。
三、发展趋势随着生产技术的发展,动力转向系统在体积、价格和所消耗的功率等方面都取得了惊人的进步。
电动助力转向技术得到迅速发展,其应用范围己经从微型轿车向大型轿车和客车方向发展。
日本的大发汽车公司、三菱汽车公司、木田汽车公司,美国Oelph 公司,英国Lueas公司,德国的ZF公司,都研制出了各白的EPS。
EPS技术日趋完善,并且其成本大幅度降低,为此其应用范围将越来越大。
在国内,越来越多的企业参与到转向器生产研发中来,江门兴江、沙市久隆、荆州恒隆等一些本土企业开始将液压动力转向器作为企业的战略重点来发展,而国内外资企业如上海采埃孚、广州昭和、一汽光洋等主要生产轿车用液压动力转向器。
2006年我国27家主要汽车转向器生产企业的产量达804.3万台。
出口规模超过进口,出口数量达3048.1万千克,实现创汇14451. 8万美元。
但需要注意到的是,我国本土企业采用国内设备为主,生产设备加工精度低,过程控制不规范,很多流程被简略掉了。
山于生产技术方而的积累和创新比较少,本土企业主要依靠引进和模仿国外的先进技术来改进产品。
所以提倡本土生产的国内汽车还广泛的应用传统的机械式转向器。
附录 BA situation at home and abroad, and subject.Steering gear and name to machine, machine, it is the direction of the most important to the parts. The role of steering gear is: increase steering wheel steering transmission mechanism to the force and change the direction of the force transmission.Steering gear in the form of the structure can be divided into DuoZhong type. At present the more commonly used have super-modulus gear type, worm crank refers to pin type, circulation ball-rack tooth fan type, circulation ball crank refers to pin type, worm wheel type, etc. If in power, can divide again to form (no power), the mechanical and the power type (help) two kinds, in power steering gear and can be divided into the air pressure power type, hydraulic power type, electric power type, such as type electric hydraulic booster species.The working principle of steering gear is, when the driver to turn right or left, through the steering wheel with universal transmission device of the rotation of the steering to screw rotation, circulation ball in a spiral tubular channels in rolling, and formed a "ball flow". Steel ball in tubular channels in around two weeks later, the outflow to one end of the catheter into the nuts, along with an catheter to the other end of the flow back to spiral tubular channels. So in the steering gear work, two columns of steel ball in their respective closed cycle, and do not send in the pipeline to get out. The flow of steel ball while pushing nuts along the screw moved back and forth. Then, rack drive teeth, make swing door lock shaft rotation happened. Finally, through the steering wheel drive mechanism to promote deflection, and to make the turn to.In recent years, automobile industry in our country present a steady and rapid growth trend. As one of the key components of the automobile redirector also obtained fast development, the scale of production and marketing in growing at the same time, the technical level also got some degree of ascension.In the domestic cars equipped with the steering gear products (mainly trucks, commercial vehicle) more than 95% is the independent brand steering gear. In the upscale cars, two-thirds of the vehicle use is a sino-foreign joint venture or a wholly foreign owned enterprise production of steering gear, a third of the vehicle use independent brand steering gear. Cheap car is almost all of the use of the independent brand steering gear [4].Automobile redirector agencies involved in the vehicle handling, stability and safety, its quality also reflect the quality of the vehicle, is directly related to vehicle performance of the key components.To turn to the requirements of the system, the most is to the sensitivity of theportability and manipulation. High sensitivity to request with small steering gear transmission ratio of; Good manipulate light sex, and the requirements of steering gear had transmission. The conflict has been a difficult to solve the problem. Ball type redirector and circulation of the transmission efficiency can reach 75% ~ 85%; The steering gear transmission ratio can change; Steady and reliable; Rack and tooth fan clearances between adjustment easily; Suitable for used to make integral power steering gear, achieve the balance of the contradiction.Second, the main research results.1. make integral power steering gear used in various modes of the DuoZhong vehicles2. variable transmission ratio steering gear to solve made the sensitivity and to force the contradiction between.3. reversible steering gear steering wheel and to ensure that after steering wheel to be automatic back to lighten the card, fatigue, improve road safety.4. the variable thick tooth fan simple steering gear transmission that gap adjusting structure, the sensitivity of the steering.Three, the development trend.As the production and the development of technology, power steering system in volume, price and the power consumption has made amazing progress. Electric power steering technology is rapidly developing, its application already from the small cars to large cars and buses direction. Japan's great car company, mitsubishi motor company, wood field automobile company, the United States, Britain Oelph company Lueas company, Germany's government, which is the company, developed the white of EPS. EPS technology improvement, and its cost greatly reduced, therefore the application area will more and more big.In China, more and more enterprises to participate in the r&d and production of steering gear, jiangmen and jiang, shashi JiuLong, jingzhou, some of the local enterprise started 5 hydraulic power steering gear as a key to development of enterprise strategy, and foreign-invested enterprise in China such as Shanghai, guangzhou numbered by ella has GuangYang, faw main production cars with hydraulic power steering gear. In 2006 in China's major automobile redirector 27 production enterprise production to 8.043 million units. Export import and export scale than the number of 30.481 million kg, and realize the exchange 14451. $80000.But need to note that our country local enterprises with domestic equipment is given priority to, the production equipment processing precision low, process control is not standard, many process was briefly away. Mountain in production technology party and accumulation and innovation is less, local enterprises rely mainly on the introduction and imitating foreign advanced technology to improve products. So advocate of local productiondomestic car also widely used the traditional mechanical steering gear.。