湖南大学计算机体系结构期末复习题(含答案)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:93.00 KB
- 文档页数:6

2022年湖南科技大学数据科学与大数据技术专业《计算机系统结构》科目期末试卷B(有答案)一、选择题1、输入输出系统硬件的功能对()是透明的。
A.操作系统程序员B.应用程序员C.系统结构设计人员D.机器语言程序设计员2、在计算机系统设计中,比较好的方法是()。
A.从上向下设计B.从下向上设计C.从两头向中间设计D.从中间开始向上、向下设计3、下列说法正确的是()A."一次重叠"是一次解释一条指令B."一次重叠"是同时解释相邻两条指令C.流水方式是同时只能解释两条指令D."一次重叠"是同时可解释很多条指令4、推出系列机的新机器,不能更改的是( )A.原有指令的寻址方式和操作码B.系统总线的组成C.数据通路宽度D.存贮芯片的集成度5、以下说法不正确的是( )A.线性流水线是单功能流水线B.动态流水线是多功能流水线C.静态流水线是多功能流水线D.动态流水线只能是单功能流水线6、IBM360/91属于()A.向量流水机B.标量流水机C.阵列流水机D.并行流水机7、开发并行的途径有(),资源重复和资源共享。
A.多计算机系统B.多道分时C.分布式处理系统D.时间重叠8、与全相联映象相比,组相联映象的优点是( )A.目录表小B.块冲突概率低C.命中率高D.主存利用率高9、对汇编语言程序员透明的是()A.I/O方式中的DMA访问B.浮点数据表示C.访问方式保护D.程序性中断10、计算机组成设计不考虑()A.专用部件设置B.功能部件的集成度C.控制机构的组成D.缓冲技术二、填空题11、数据流机采用________,执行的操作序列取决于输入数据的可用性;归约机则采用________,执行的操作序列取决于对数据的要求,对数据的需求又来源于函数式程序设计语言对表达式的归纳。
12、一个程序在计算机上运行,花费的CPU时间为CPU的时钟周期乘以该程序所有机器指令使用CPU的时钟周期数,即CPU时间=________×________13、就目前的通用机来说,计算机系统结构的属性主要包括数据表示,________寄存器组织,________,存储系统。

2022年湖南科技大学软件工程专业《计算机系统结构》科目期末试卷B(有答案)一、选择题1、流水机器对全局性相关的处理不包括( )A.猜测法B.提前形成条件码C.加快短循环程序的执行D.设置相关专用通路2、非线性流水线是指( )A.一次运算中使用流水线中的多个功能段B.一次运算中要多次使用流水线中的某些功能段C.流水线中某些功能段在各次运算中的作用不同D.流水线的各个功能段在各种运算中有不同的组合3、不同系列的机器之间,实现软件移植的途径不包括( )A.用统一的高级语言B.用统一的汇编语言C.模拟D.仿真4、"一次重叠"中消除"指令相关"最好的方法是( )。
A.不准修改指令B.设相关专用通路C.推后分析下条指令D.推后执行下条指令5、系列机软件应做到( )。
A.向前兼容,并向上兼容B.向后兼容,力争向上兼容C.向前兼容,并向下兼容D.向后兼容,力争向下兼容6、对机器语言程序员透明的是( )。
A.中断字B.主存地址寄存器C.通用寄存器D.条件码7、计算机中优化使用的操作码编码方法是( )。
(书上为扩展编码法)A哈夫曼编码B ASCII码C BCD码D扩展操作码8、在计算机系统的层次结构中,机器被定义为()的集合体A.能存储和执行相应语言程序的算法和数据结构B.硬件和微程序(固件)C.软件和固件D.软件和硬件9、多处理机的各自独立型操作系统()。
A.要求管理程序不必是可再入的B.适合于紧耦合多处理机C.工作负荷较平衡D.有较高的可靠性10、若输入流水线的指令既无局部性相关,也不存在全局性相关,则()。
A.可获得高的吞吐率和效率B.流水线的效率和吞吐率恶化C.出现瓶颈D.可靠性提高二、填空题11、输入输出设备的异步性、实时性、与________三个特点是现代计算机系统必须具备的共同特性。
12、计算任何一个程序的执行时间的公式可表示为P=I•CPI•T,其中I是________ CPU是________T是一个周期的时间长度。

11.计算机系统结构的层次结构由高到低分别为应用语言机器级,高级语言机器级,汇编语言机器级,操作系统机器级,传统机器语言机器级,微程序机器级 12.计算机系统弗林分类法,把计算机系统分成单指令流单数据流(SISD)、单指令流多数据流(SIMD)、多指令单数据流和多指令多数据流四大类。
13.透明指的是客观存在的事物或属性从某个角度看不到,它带来的好处是简化某级的设计,带来的不利是无法控制。
22.数据结构和数据表示之间是什么关系?确定和引入数据表示的基本原则是什么?数据表示是能由硬件直接识别和引用的数据类型。
数据结构反映各种数据元素或信息单元之间的结构关系。
数据结构要通过软件映象变换成机器所具有的各种数据表示实现,所以数据表示是数据结构的组成元素。
(2分)不同的数据表示可为数据结构的实现提供不同的支持,表现在实现效率和方便性不同。
数据表示和数据结构是软件、硬件的交界面。
(2分)除基本数据表示不可少外,高级数据表示的引入遵循以下原则: (1)看系统的效率有否提高,是否养活了实现时间和存储空间。
(2)看引入这种数据表示后,其通用性和利用率是否高。
13.计算机组成指的是计算机系统结构的逻辑实现,包括机器级内的数据流和控制流的组成及逻辑设计等。
计算机实现指的是计算机组成的物理实现,。
21、软件和硬件在什么意义上是等效的?在什么意义上是不等效的? 逻辑上等效,性能、价格、实现难易程度上不一样。
22.说明翻译和解释的区别和联系.区别:翻译是整个程序转换,解释是低级机器的一串语句仿真高级机器的一条语句。
联系:都是高级机器程序在低级机器上执行的必须步骤。
19.计算机系统结构也称计算机体系结构,指的是传统机器级的系统结构。
它是软件和硬件/固件的交界面,是机器语言汇编语言程序设计者或编译程序设计者看到的机器物理系统的抽象。
15.引入数据表示的两条基本原则是:一看系统的效率有否提高;二看数据表示的通用性和利用率是否高。

2022年湖南大学计算机科学与技术专业《数据结构与算法》科目期末试卷A(有答案)一、选择题1、已知广义表LS=((a,b,c),(d,e,f)),用head和tail数取出LS中原子e 的运算是()。
A.head(tail(LS))B.tail(head(LS))C.head(tail(head(tail(LS))))D.head(tail(tail(head(LS))))2、下述文件中适合于磁带存储的是()。
A.顺序文件B.索引文件C.哈希文件D.多关键字文件3、连续存储设计时,存储单元的地址()。
A.一定连续B.一定不连续C.不一定连续D.部分连续,部分不连续4、已知有向图G=(V,E),其中V={V1,V2,V3,V4,V5,V6,V7}, E={<V1,V2>,<V1,V3>,<V1,V4>,<V2,V5>,<V3,V5>, <V3,V6>,<V4,V6>,<V5,V7>,<V6,V7>},G的拓扑序列是()。
A.V1,V3,V4,V6,V2,V5,V7B.V1,V3,V2,V6,V4,V5,V7C.V1,V3,V5,V2,V6,V7D.V1,V2,V5,V3,V4,V6,V75、下列关于AOE网的叙述中,不正确的是()。
A.关键活动不按期完成就会影响整个工程的完成时间B.任何一个关键活动提前完成,那么整个工程将会提前完成C.所有的关键活动提前完成,那么整个工程将会提前完成D.某些关键活动若提前完成,那么整个工程将会提前完成6、已知字符串S为“abaabaabacacaabaabcc”,模式串t为“abaabc”,采用KMP算法进行匹配,第一次出现“失配”(s!=t)时,i=j=5,则下次开始匹配时,i和j的值分别()。
A.i=1,j=0 B.i=5,j=0 C.i=5,j=2 D.i=6,j=27、下列选项中,不能构成折半查找中关键字比较序列的是()。
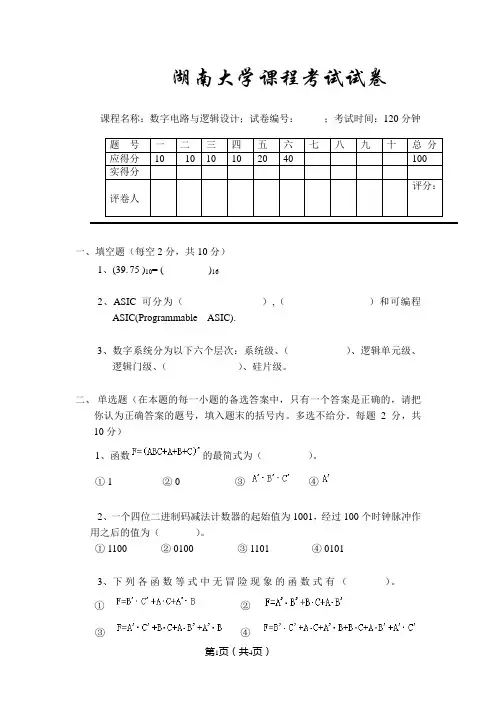
湖南大学课程考试试卷课程名称:数字电路与逻辑设计;试卷编号:;考试时间:120分钟一、填空题(每空2分,共10分)1、(39.75 )10= ( )162、ASIC可分为(),()和可编程ASIC(Programmable ASIC).3、数字系统分为以下六个层次:系统级、()、逻辑单元级、逻辑门级、()、硅片级。
二、单选题(在本题的每一小题的备选答案中,只有一个答案是正确的,请把你认为正确答案的题号,填入题末的括号内。
多选不给分。
每题2分,共10分)1、函数的最简式为()。
① 1 ② 0 ③④2、一个四位二进制码减法计数器的起始值为1001,经过100个时钟脉冲作用之后的值为()。
① 1100 ② 0100 ③ 1101 ④ 01013、下列各函数等式中无冒险现象的函数式有()。
①②③④4、用四选一数据选择器实现函数Y= A1A0+A1’A0,应使()。
①D0=D2=0,D1=D3=1 ②D0=D2=1,D1=D3=0③D0=D1=0,D2=D3=1 ④D0=D1=1,D2=D3=05、T触发器Q端的输出信号频率是输入信号频率的()倍。
① 1 ② 1/2 ③ 2 ④ 1/4三、判断题(下列各题,你认为正确的,请在题末的括号内打“√”,错的打“×”,并更正。
每题2分,共10分)1、不用的CMOS输入端绝不能悬空。
()2、对逻辑函数Y=A B’+A’B+B’C+B C’利用代入规则,令A=BC代入,得Y= BC B’+(BC)’B+B’C+B C’=B’C+B C’成立。
()3、处于三态输出的高阻态,因输出没和电路连上,所以输出端没有电流。
()4、由两个或非门构成的基本R S触发器,当R=S=0时,触发器的状态为不定。
()5、优先编码器的编码输入信号是相互排斥的,不允许有多个编码信号同时有效。
()四、简答题(任选2题,每题5分,共10分):1、格雷码和奇偶校验码的特点分别是什么?为什么说它们是可靠性编码?2、简述双稳态元件的亚稳定性概念及特点。

《计算机系统结构》期末考试复习题一、选择题:1、我们称由(B )实现的机器为虚拟机器。
A、硬件B、软件C、微程序D、固件2、计算机系统结构设计者所关心的是(C )所看到的的计算机结构。
A、硬件设计人员B、逻辑设计人员C、机器语言或汇编语言程序员D、高级语言程序员3、计算机组成是计算机系统结构的(B )。
A、硬件实现B、逻辑实现C、软件实现D、以上三种4、在计算机系统设计时,为了提高系统性能,应当注意(A )。
A、加快经常性使用指令的执行速度B、要特别精心设计少量功能强大的指令B、要减少在数量上占很小比例的指令的条数D、要加快少量指令的速度5、SIMD计算机可以处理(D )。
A、多指令流、单数据流B、单指令流单数据流C、多指令流多数据流D、单指令流多数据流6、在提高CPU性能的问题上,从系统结构角度,可以(C )。
A、提高时钟频率B、减少程序指令条数C、减少每条指令的时钟周期数D、减少程序指令条数和减少每条指令的时钟周期数7、冯.诺依曼计算机是(B )。
A、以存储器为中心B、以CPU为中心C、以处理输入/输出危重点D、以存储器与计算器为中心8、解决软件移植最好的办法就是(C )。
A、采用模拟方法B、采用仿真的方法C、采用统一高级语言D、采用统一标准设计计算机结构9、对计算机系统结构,下列透明的是(A )。
A、数据总线宽度B、浮点数表示C、CPU寄存器个数D、存储器的编址方法10、以下对系统程序员不透明的是(B )。
A、系列机各档不同的数据通路宽度B、虚拟存储器C、指令缓冲寄存器D、存储器读写缓冲寄存器11、在浮点数表示中,尾数的位数多少主要影响( B )。
A、表数范围B、表数精度C、表数效率D、运算实现容易程度12、当浮点数的尾数基值为(A )时,其表数效率最高(假如不考虑隐藏位)。
A、16B、8C、4D、213、当浮点数的尾数基值为( D )时,其表数精度最高,表数范围最大。
A、2B、8C、16D、2或414、当浮点数的尾数用原码表示,基值为2,阶码用移码表示,基值为2时,若尾数部分占23位(不含符号位),阶码占8位(含符号位),则表示的最大负数和最大正数分别为( C )。

2022年湖南大学计算机科学与技术专业《计算机系统结构》科目期末试卷A(有答案)一、选择题1、块冲突概率最高的Cache地址映象方式是( )A.段相联B.组相联C.直接D.全相联2、计算机系统结构不包括()A.主存速度B.机器工作状态C.信息保护D.数据表示3、外部设备打印机适合于连接到( )。
A.数组多路通道B.字节多路通道C.选择通道D.任意一种通道4、()属于MIMD系统结构。
A.各处理单元同时受同一个控制单元的管理B.各处理单元同时接受同一个控制单元送来的指令C.松耦合多处理机和多计算机D.阵列处理机5、与全相联映象相比,组相联映象的优点是( )A.目录表小B.块冲突概率低C.命中率高D.主存利用率高6、从计算机系统结构上讲,机器语言程序员所看到的机器属性是()A.计算机软件所要完成的功能B.计算机硬件的全部组成C.编程要用到的硬件组织D.计算机各部件的硬件实现。
7、下列说法中不正确的是()A.软件设计费用比软件重复生产费用高B.硬件功能只需实现一次,而软件功能可能要多次重复实现C.硬件的生产费用比软件的生产费用高D.硬件的设计费用比软件的设计费用低8、直接执行微指令的是( )A.汇编程序B.编译程序C.硬件D.微指令程序9、非线性流水线是指( )A.一次运算中使用流水线中的多个功能段B.一次运算中要多次使用流水线中的某些功能段C.流水线中某些功能段在各次运算中的作用不同D.流水线的各个功能段在各种运算中有不同的组合10、微指令由()直接执行。
A.微指令程序B.硬件C.汇编程序D.编译程序11、目前,MO由()实现,M1用()实现,M2至M5大多用()实现。
A.软件,固件,硬件B.固件,软件,硬件C.硬件,软件,固件D.硬件,固件,软件12、计算机系统多级层次中,从下层到上层,各级相对顺序正确的应当是()。
A.汇编语言机器级,操作系统机器级,高级语言机器级B.微程序机器级,传统机器语言机器级,汇编语言机器级C.传统机器语言机器级,高级语言机器级,汇编语言机器级D.汇编语言机器级,应用语言机器级,高级语言机器级13、系列机软件应做到( )。

《计算机体系结构》期末考试A卷(总分:100分,时间:100分钟)姓名:专业:学号:学习中心:一、填空题(每空1分,共14分)1.高速缓冲存储器的地址映象方式有三种,它们分别是:全向量方式,直接相联方式,组相连方式。
2.虚拟存储器的三种管理方式是段式管理,页式管理和段页式管理。
3.从主存的角度来看,“Cache—主存”层次的目的是为了提高速度,而“主存—辅存”层次的目的是为了扩大容量4.根据指令间的对同一寄存器读和写操作的先后次序关系,数据相关冲突可分为读与写(RAM)、写与读(WAR)和写与写(WAW)三种类型。
5.当代计算机体系结构的概念包括指令集结构、计算机组成和计算机实现三个方面的内容二、名词解释(每题2分,共16分)计算机体系结构:计算机体系结构是指根据属性和功能不同而划分的计算机理论组成部分及计算机基本工作原理、理论的总称。
其中计算机理论组成部分并不单与某一个实际硬件相挂钩,如存储部分就包括寄存器、内存、硬盘等。
兼容机:兼容机,就是由不同公司厂家生产的具有相同系统结构的计算机。
简单点说,就是非厂家原装,而改由个体装配而成的机器,其中的元件可以是同一厂家出品,但更多的是整合各家之长的计算机。
写直达法:写直达法一般指全写法。
全写法(write-through):又称写直达法、写穿法,透写法,Cache使用方式之一。
高速缓冲存储器:高速缓冲存储器(Cache)其原始意义是指存取速度比一般随机存取记忆体(RAM)来得快的一种RAM,一般而言它不像系统主记忆体那样使用DRAM技术,而使用昂贵但较快速的SRAM技术,也有快取记忆体的名称。
高速缓冲存储器是存在于主存与CPU之间的一级存储器,由静态存储芯片(SRAM)组成,容量比较小但速度比主存高得多,接近于CPU的速度。
在计算机存储系统的层次结构中,是介于中央处理器和主存储器之间的高速小容量存储器。
它和主存储器一起构成一级的存储器。
高速缓冲存储器和主存储器之间信息的调度和传送是由硬件自动进行的。

2023 年湖南工学院数据科学与大数据技术专业《计算机系统构造》科目期末试卷 A(有答案〕一、选择题1、对机器语言程序员透亮的是〔〕A.中断字B.主存地址存放器C.通用存放器D.条件码2、计算机系统构造不包括〔〕A.主存速度B.机器工作状态C.信息保护D.数据表示3、对汇编语言程序员透亮的是〔〕A.I/O 方式中的DMA 访问B.浮点数据表示C.访问方式保护D.程序性中断4、在尾数下溢处理方法中,平均误差最大的是〔〕A.截断法C.恒置“1“法D.ROM 查表法5、与流水线最大吞吐率凹凸有关的是( )A.各个子过程的时间B.最快子过程的时间C.最慢子过程的时间D.最终子过程的时间6、在计算机系统的层次构造中,机器被定义为〔〕的集合体A.能存储和执行相应语言程序的算法和数据构造B.硬件和微程序〔固件〕C.软件和固件D.软件和硬件7、不同系列的机器之间,实现软件移植的途径不包括( )A.用统一的高级语言B.用统一的汇编语言C.模拟D.仿真8、微指令由〔〕直接执行。
A.微指令程序C.汇编程序D.编译程序9、在操作系统机器级,一般用〔〕程序〔〕作业把握语句。
A.汇编程序,翻译B.汇编程序,解释C.机器语言,解释D.机器语言,翻译10、外部设备打印机适合于连接到( )。
A.数组多路通道B.字节多路通道C.选择通道D.任意一种通道二、填空题11、指令系统是软件设计人员与硬件设计人员之间的一个主要,也是他们之间相互沟通的一座桥梁。
在计算机系统的设计过程中,的设计是格外关键的,它必需由软件设计人员和硬件设计人员共同来完成。
12、页面替换是发生于页面失效,同时又发生的时候。
13、依据Flynn 分类法,依据指令流和数据流的不同组织方式,计算机系统的构造可以分为SISD〔单指令流单数据流〕、MISD、和14、解决Cache 与主存不全都性的方法有和15、向量处理机的构造主要有和两种。
16、一种机器的系统构造上实现另一种机器的指令系统,一般可承受方法或方法。


1.从执行程序的角度看,并行性等级从低到高分为那几级?从执行程序的角度看,并行性等级从低到高可分为:(1)指令内部并行:单条指令中各微操作之间的并行。
(2)指令级并行(Instruction Level Parallelism,ILP):并行执行两条或两条以上的指令。
(3)线程级并行(Thread Level Parallelism,TLP):并行执行两个或两个以上的线程,通常是以一个进程内派生的多个线程为调度单位。
(4)任务级或过程级并行:并行执行两个或两个以上的过程或任务(程序段),以子程序或进程为调度单元。
(5)作业或程序级并行:并行执行两个或两个以上的作业或程序。
2.计算机中提高并行性的技术途径有哪三种?(1)时间重叠。
多个处理过程在时间上相互错开,轮流重叠地使用同一套硬件设备的各个部分,以加快硬件周转而赢得速度。
(2)资源重复。
通过重复设置资源,尤其是硬件资源,大幅度提高计算机系统的性能。
(3)资源共享。
这是一种软件方法,它使多个任务按一定时间顺序轮流使用同一套硬件设备3.从当前计算机技术来看,CISC结构有什么缺点?(1)CISC结构的指令系统中,各种指令的使用频率相差悬殊。
(2)CISC结构指令系统的复杂性带来了计算机系统结构的复杂性,这不仅增加了研制时间和成本,而且还容易造成设计错误。
(3)CISC结构指令系统的复杂性给VLSI设计增加了很大负担,不利于单片集成。
(4)CISC结构的指令系统中,许多复杂指令需要很复杂的操作,因而运行速度慢。
(5)在CISC结构的指令系统中,由于各条指令的功能不均衡性,不利于采用先进的计算机系统结构技术来提高系统的性能。
4.根据Amdahl定律,系统加速比有哪两个因素决定?系统加速比依赖于两个因素:(1)可改进比例:可改进部分在原系统计算时间中所占的比例。
(2)部件加速比:可改进部分改进以后的性能提高。
5.从处理数据角度,并行性等级由低到高分为哪几级?从处理数据的角度来看,并行性等级从低到高可分为:(1)字串位串:每次只对一个字的一位进行处理。
第一题选择题1. SIMD是指(B)A、单指令流单数据流B、单指令流多数据流C、多指令流单数据流D、多指令流多数据流2.下列那种存储设备不需要编址?DA. 通用寄存器B. 主存储器C. 输入输出设备D. 堆栈3.按照计算机系统层次结构,算术运算、逻辑运算和移位等指令应属于(A)级机器语言。
A、传统机器语言机器B、操作系统机器C、汇编语言机器 D、高级语言机器4.早期的计算机系统只有定点数据表示,因此硬件结构可以很简单。
但是这样的系统有明显的缺点,下面哪一个不是它的缺点:BA.数据表示范围小B.单个需要的计算时钟周期多C.编程困难D.存储单元的利用率很低7.下面哪个页面替换算法实际上是不能够实现的?DA)随机页面替换算法B)先进先出替换算法C)最久没有使用算法D)最优替换算法9.指令优化编码方法,就编码的效率来讲,那种方法最好?CA. 固定长度编码B. 扩展编码法C. huffman编码法D. 以上编码都不是10.在早期冯·诺依曼计算机特征中,机器以(C)为中心。
A、存储器B、输入输出设备C、运算器D、控制器1.RISC 计算机的指令系统集类型是 ( C ) 。
A. 堆栈型B. 累加器型C. 寄存器—寄存器型D. 寄存器 - 存储器型2、相联存储器的访问方式是( D )。
A.先进先出顺序访问B.按地址访问C.无地址访问D.按内容访问3、假设—条指令的执行过程可以分为“取指令”、“分析”和“执行”三段,每—段分别只有—个部件可供使用,并且执行时间分别为Δt、2Δt和3Δt,连续执行n条指令所需要花费的最短时间约为( C )。
(假设“取指令”、“分析”和“执行”可重叠,并假设n足够大)A.6 nΔt B.2 nΔt C.3 nΔt D.nΔt6、下列计算机不属于RISC计算机的是( C )。
A.SUN:Ultra SPARCB.IBM:Power PC620C.IBM:PC/XTD.DEC:ALPHA211647、哪一点不是RISC的特点?( D )A. 减少指令的平均执行周期数B. 重视编译优化技术C. 减少指令和寻址方式的种类D. 增加指令的功能8、哪种兼容方式对系列机来说是必须要求做到的?( B )A. 向前兼容B. 向后兼容C. 向上兼容D. 向下兼容9、在计算机系统中,表征系统运行状态的部件是( D )。
计算机科学系《计算机系统结构》期末考试试卷(A卷)2、此试卷适用于计算机科学与技术本科专业。
一单选题:(10分,每题1分)1、."启动I/O"指令是主要的输入输出指令,是属于( B )A.目态指令B.管态指令C.目态、管态都能用的指令D.编译程序只能用的指令2、输入输出系统硬件的功能对(B )是透明的A.操作系统程序员B.应用程序员C.系统结构设计人员D.机器语言程序设计员3、全相联地址映象是指(A)A.任何虚页都可装入主存中任何实页的位置B.一个虚页只装进固定的主存实页位置C.组之间固定,组内任何虚页可装入任何实页位置D.组间可任意装入,组内是固定装入4、( C ) 属于MIMD系统结构A.各处理单元同时受一个控制单元的管理B.各处理单元同时受同个控制单元送来的指令C.松耦合多处理机和多计算机系统D.阵列处理机5、多处理机上两个程序段之间若有先写后读的数据相关,则(B )A.可以并行执行B.不可能并行C.任何情况均可交换串行D.必须并行执行6、计算机使用的语言是(B)A.专属软件范畴,与计算机体系结构无关B.分属于计算机系统各个层次C.属于用以建立一个用户的应用环境D.属于符号化的机器指令7、指令执行结果出现异常引起的中断是(C )A.输入/输出中断B.机器校验中断C.程序性中断D.外部中断8、块冲突概率最高的Cache地址映象方式是(A )A.直接 B.组相联 C.段相联 D.全相联9、组相联映象、LRU替换的Cache存储器,不影响Cache命中率的是(B ) A.增大块的大小 B.增大主存容量 C.增大组的大小 D.增加Cache中的块数10、流水处理机对全局性相关的处理不.包括(C)A.猜测法B.提前形成条件码C.加快短循环程序的执行D.设置相关专用通路1、 数据通路宽度就是 数据总线上一次并行传送的信息位数 。
2、 计算机仿真用 微程序 解释,计算机模拟用 机器语言 解释3、 阵列处理机按存贮器的组成方式可分为两种构形,分别为: 分布式存储器 和 集中共享式 。
填空题1.从2002年以来,计算机性能的年增长率下降到了约30%。
其主要原因是:①大功耗问题;②可以进一步有效地开发的指令级并行性已经很少;③存储器访问速度的提高缓慢。
2. 可移植性是指一个软件可以不经修改或者只需少量修改就可以由一台计算机移植到另一台计算机上运行。
实现可移植性的常用方法有3种:系列机,模拟和仿真,统一高级语言。
2.通用寄存器型指令集结构计算机在灵活性和提高性能方面有明显的优势。
主要体现在①寄存器的访问速度比存储器快;②对编译器而言,能更加容易有效地分配和使用寄存器;③寄存器可以用来存放变量。
3.MIPS的数据寻址方式只有立即数寻址和偏移量寻址。
4.向量处理机的结构由所采用的向量处理方式决定。
有两种典型的结构;存储器-存储器型结构和寄存器-寄存器型结构。
5.Cache-主存层次的工作由硬件实现,对系统程序员是透明的。
6.降低Cache不命中率最直接的方法是增加Cache的容量。
不过,这种方法不但会增加成本,而且还可能增加命中时间,这种方法在片外Cache中用得比较多。
7.大多数磁盘阵列的组成可以由以下两个特征来区分:数据交叉存放的粒度、冗余数据的计算方法以及在磁盘阵列中的存放方式。
8.时延和带宽是用来评估互连网络性能的两个基本指标。
时延包括通信时延和网络时延。
9.计算机系统可分为SISD、SIMD、MISD和MIMD四类,许多早期并行处理机是SIMD计算机,近年来,MIMD已经成为通用多处理机系统结构的选择。
这是因为MIMD具有灵活性,并且MIMD能充分利用现有微处理器的性价比优势。
判断题1.从计算机语言的角度,系统结构把计算机系统按功能划分成多级层次结构,其中,第2级是操作系统虚拟机,第3级是汇编语言虚拟机。
(错)2.计算机系统中提高并行性的3种途径中,资源重复是在并行性概念中引入时间因素,加快硬件周转而赢得时间。
(错)3.指令集结构中采用多种寻址方式可能会增加实现的复杂度和使用这些寻址方式的指令的CPI。
计算机体系结构期末考试试卷及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 计算机体系结构的研究对象是()A. 硬件系统B. 软件系统C. 硬件和软件系统D. 计算机网络答案:C2. 下面哪个不是计算机体系结构的基本特性?()A. 并行性B. 高效性C. 可扩展性D. 可靠性答案:D3. 下面哪个不是计算机体系结构的层次结构?()A. 物理层B. 逻辑层C. 指令层D. 系统层答案:A4. 下面哪个不是流水线技术的优点?()A. 提高指令执行速度B. 减少指令执行时间C. 提高硬件资源利用率D. 降低硬件成本答案:D5. 下面哪个不是超标量处理器的特点?()A. 多指令发射B. 多指令执行C. 高性能D. 低功耗答案:D6. 下面哪个不是精简指令集计算机(RISC)的特点?()A. 指令简单B. 执行速度快C. 指令复杂D. 硬件简化答案:C7. 下面哪个不是复杂指令集计算机(CISC)的特点?()A. 指令复杂B. 执行速度慢C. 硬件复杂D. 指令简单答案:D8. 下面哪个不是存储器层次结构的组成部分?()A. 寄存器B. 缓存C. 主存储器D. 硬盘答案:D9. 下面哪个不是虚拟存储器的作用?()A. 扩展物理内存B. 提高内存利用率C. 提高程序执行速度D. 减少程序占用空间答案:D10. 下面哪个不是计算机体系结构的发展方向?()A. 多核处理器B. 众核处理器C. 量子计算机D. 单核处理器答案:D二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. 计算机体系结构的五大部件是____、____、____、____、____。
答案:控制器、运算器、存储器、输入设备、输出设备2. 计算机体系结构的主要性能指标有____、____、____。
答案:吞吐量、执行时间、效率3. 流水线技术可以分为____、____、____三个级别。
答案:单级流水线、多级流水线、超流水线4.超标量处理器的主要技术有____、____、____。
2022年湖南大学软件工程专业《计算机组成原理》科目期末试卷B(有答案)一、选择题1、下列关于ROM和RAM的说法中,错误的是()。
I.CD-ROM是ROM的一种,因此只能写入一次ⅡFlash快闪存储器属于随机存取存储器,具有随机存取的功能Ⅲ.RAM的读出方式是破坏性读出,因此读后需要再生IV.SRAM读后不需要刷新,而DRAM读后需要刷新A.I、ⅡB.I、Ⅲ、ⅣC.Ⅱ、ⅢD.I、Ⅱ、lⅢ2、关于Cache的3种基本映射方式,下面叙述中错误的是()。
A.Cache的地址映射有全相联、直接和多路组相联3种基本映射方式B.全相联映射方式,即主存单元与Cache单元随意对应,线路过于复杂,成本太高C.多路组相联映射是全相联映射和直接映射的一种折中方案,有利于提高命中率D.直接映射是全相联映射和组相联映射的一种折中方案,有利于提高命中率3、冯·诺依曼型计算机的设计思想主要有()。
1.存储程序Ⅱ.二进制表示Ⅲ.微程序方式Ⅳ.局部性原理A. I,ⅢB.Ⅱ,ⅢC.IⅡ,IⅣD.I,IⅡ4、下列关于配备32位微处理器的计算机的说法中,正确的是()。
该机器的通用寄存器一般为32位Ⅱ.该机器的地址总线宽度为32位Ⅲ.该机器能支持64位操作系统IV.一般来说,64位微处理器的性能比32位微处理器的高A.I、ⅡB.I、ⅢC.I、ⅣD.I、IⅡ、Ⅳ5、CPU中的译码器要用()。
A.地址译码人B.指令译码C.数据译码1D.控制信号译码6、某同步总线的时钟频率为100MHz,宽度为32位,地址/数据线复用,每传输一个地址或数据占用一个时钟周期。
若该总线支持突发(猝发)传输方式,则一次“主存写”总线事务传输128位数据所需要的时间至少是()。
A.20nsB.40nsC.50nsD.80ns7、一次总线事务中,主设备只需给出一个首地址,从设备就能从首地址开始的若干连续单元读出或写入多个数据。
这种总线事务方式称为()。
A.并行传输B.串行传输C.突发传输D.同步传输8、某CPU主频为1.03GHz,采用4级指令流水线,每个流水段的执行需要1个时钟周期。
2022年湖南科技大学数据科学与大数据技术专业《计算机系统结构》科目期末试卷A(有答案)一、选择题1、下列关于虚拟存贮器的说法,比较正确的应当是( )A.访主存命中率随页面大小增大而提高B.访主存命中率随主存容量增加而提高C.更换替换算法能提高命中率D.在主存命中率低时,改用堆栈型替换算法,并增大主存容量,可提高命中率2、下列说法正确的是()A."一次重叠"是一次解释一条指令B."一次重叠"是同时解释相邻两条指令C.流水方式是同时只能解释两条指令D."一次重叠"是同时可解释很多条指令3、IBM360/91对指令中断的处理方法是()A.不精确断点法B.精确断点法C.指令复执法D.对流水线重新调度4、流水机器对全局性相关的处理不包括( )A.猜测法B.提前形成条件码C.加快短循环程序的执行D.设置相关专用通路5、最能确保提高虚拟存贮器访主存的命中率的改进途径是( )A.增大辅存容量B.采用FIFO替换算法并增大页面C.改用LRU替换算法并增大页面D.改用LRU替换算法并增大页面数6、与流水线最大吞吐率高低有关的是( )A.各个子过程的时间B.最快子过程的时间C.最慢子过程的时间D.最后子过程的时间7、以下说法不正确的是( )A.线性流水线是单功能流水线B.动态流水线是多功能流水线C.静态流水线是多功能流水线D.动态流水线只能是单功能流水线8、浮点数尾数下溢处理时,最大误差最大,但下溢处理不需要时间,平均误差又趋于0的方法是( )。
A.截断法B.舍入法C.ROM查表法D.恒置"1"法9、计算机系统结构不包括( )。
A.主存速度B.机器工作状态C.信息保护D.数据10、下列说法正确的是( )A.Cache容量一般不大,命中率不会很高B.Cache芯片速度一般比CPU的速度慢数十倍C.Cache本身速度很快。
但地址变换的速度很慢D.Cache存贮器查映象表和访问物理Cache其间可以流水,使速度与CPU匹配二、填空题11、按照Flynn分类法,根据指令流和数据流的不同组织方式,计算机系统的结构可以分为SISD(单指令流单数据流)、MISD、________和________12、三级存储系统是________、________、磁盘存储器。
1.从执行程序的角度看,并行性等级从低到高分为那几级?从执行程序的角度看,并行性等级从低到高可分为:(1)指令内部并行:单条指令中各微操作之间的并行。
(2)指令级并行(Instruction Level Parallelism,ILP):并行执行两条或两条以上的指令。
(3)线程级并行(Thread Level Parallelism,TLP):并行执行两个或两个以上的线程,通常是以一个进程内派生的多个线程为调度单位。
(4)任务级或过程级并行:并行执行两个或两个以上的过程或任务(程序段),以子程序或进程为调度单元。
(5)作业或程序级并行:并行执行两个或两个以上的作业或程序。
2.计算机中提高并行性的技术途径有哪三种?(1)时间重叠。
多个处理过程在时间上相互错开,轮流重叠地使用同一套硬件设备的各个部分,以加快硬件周转而赢得速度。
(2)资源重复。
通过重复设置资源,尤其是硬件资源,大幅度提高计算机系统的性能。
(3)资源共享。
这是一种软件方法,它使多个任务按一定时间顺序轮流使用同一套硬件设备3.从当前计算机技术来看,CISC结构有什么缺点?(1)CISC结构的指令系统中,各种指令的使用频率相差悬殊。
(2)CISC结构指令系统的复杂性带来了计算机系统结构的复杂性,这不仅增加了研制时间和成本,而且还容易造成设计错误。
(3)CISC结构指令系统的复杂性给VLSI设计增加了很大负担,不利于单片集成。
(4)CISC结构的指令系统中,许多复杂指令需要很复杂的操作,因而运行速度慢。
(5)在CISC结构的指令系统中,由于各条指令的功能不均衡性,不利于采用先进的计算机系统结构技术来提高系统的性能。
4.根据Amdahl定律,系统加速比有哪两个因素决定?系统加速比依赖于两个因素:(1)可改进比例:可改进部分在原系统计算时间中所占的比例。
(2)部件加速比:可改进部分改进以后的性能提高。
5.从处理数据角度,并行性等级由低到高分为哪几级?从处理数据的角度来看,并行性等级从低到高可分为:(1)字串位串:每次只对一个字的一位进行处理。
这是最基本的串行处理方式,不存在并行性;(2)字串位并:同时对一个字的全部位进行处理,不同字之间是串行的。
已开始出现并行性;(3)字并位串:同时对许多字的同一位(称为位片)进行处理。
这种方式具有较高的并行性;(4)全并行:同时对许多字的全部位或部分位进行处理。
这是最高一级的并行。
6.RISC的设计原则?(1)选取使用频率最高的指令,并补充一些最有用的指令。
(2)每条指令的功能应尽可能简单,并在一个机器周期内完成。
(3)所有指令长度均相同。
(4)只有load和store操作指令才访问存储器,其它指令操作均在寄存器之间进行。
(5)以简单、有效的方式支持高级语言。
7.控制指令中试用PC相对寻址方式有什么缺点?(1) 有效地缩短指令中表示目标地址的字段的长度。
(2) 使得代码在执行时与它被载入的位置无关。
8.指令中表示寻址方式的主要方法有哪些?表示寻址方式有两种常用的方法:(1)将寻址方式编于操作码中,操作码在描述指令功能的同时也描述了相应的寻址方式。
这种方式译码快,但操作码和寻址方式的结合不仅增加了指令的条数,导致了指令的多样性,而且增加了CPU对指令译码的难度。
(2)为每个操作数设置一个地址描述符,由该地址描述符表示相应操作数的寻址方式。
这种方式译码较慢,但操作码和寻址独立,易于指令扩展。
9.按流水级别来分,流水线分为哪三类?(1)部件级流水线(运算操作流水线):把处理机的算术逻辑部件分段,以便为各种数据类型进行流水操作。
(2)处理机级流水线(指令流水线):把解释指令的过程按照流水方式处理。
(3)处理机间流水线(宏流水线):由两个以上的处理机串行地对同一数据流进行处理,每个处理机完成一项任务。
10.按数据表示来分,流水线分为哪两类?(1)标量流水处理机:处理机不具有向量数据表示,仅对标量数据进行流水处理。
(2)向量流水处理机:处理机具有向量数据表示,并通过向量指令对向量的各元素进行处理。
11.预测分支失败方法的主要实现是什么?预测分支失败:沿失败的分支继续处理指令,就好象什么都没发生似的。
当确定分支是失败时,说明预测正确,流水线正常流动;当确定分支是成功时,流水线就把在分支指令之后取出的指令转化为空操作,并按分支目标地址重新取指令执行。
主要思想:当流水线译码到一条分支指令时,流水线继续取指令,并允许该分支指令后的指令继续在流水线中流动。
当流水线确定分支转移成功与否以及分支的目标地址之后,如果分支转移成功,流水线必须将在分支指令之后取出的所有指令转化为空操作,并在分支的目标地址处重新取出有效的指令;如果分支转移失败,那么可以将分支指令看作是一条普通指令,流水线正常流动,无需将在分支指令之后取出的所有指令转化为空操作。
12.定向技术主要思想是什么?在发生数据冲突时,后面的指令并不是立即就要用到前一条指令的计算结果。
如果能够将计算结果从其产生的地方直接送到需要它的地方,就可以避免暂停。
当定向硬件检测到前面某条指令的结果寄存器就是当前指令的源寄存器时,控制逻辑会将前面那条指令的结果直接从其产生的地方定向到当前指令所需的位置。
13.解释指令的静态调度与动态调度及二者区别?静态调度:当出现数据相关时,为了消除或者减少流水线空转,编译器确定并分离出程序中存在相关的指令,然后进行指令调度,并对代码进行优化动态调度:通过硬件重新安排指令的执行顺序,来调整相关指令实际执行的关系,减少处理器空转。
动态调度优点:(1)能够处理一些编译时情况不明的相关(比如涉及存储器访问的相关),并简化了编译器。
(2)能够使本来是面向某一流水线优化编译的代码在其他的流水线(动态调度)上也能高效地执行。
当然,动态调度的这些优点是以硬件复杂性的显著增加为代价的。
14.简述Tomasulo算法的思想。
核心思想是:①记录和检测指令相关,操作数一旦就绪就立即执行,把发生RAW冲突的可能性减小到最少;②通过寄存器换名来消除WAR冲突和WAW冲突。
寄存器换名是通过保留站来实现,它保存等待流出和正在流出指令所需要的操作数。
基本思想:只要操作数有效,就将其取到保留站,避免指令流出时才到寄存器中取数据,这就使得即将执行的指令从相应的保留站中取得操作数,而不是从寄存器中。
指令的执行结果也是直接送到等待数据的其它保留站中去。
因而,对于连续的寄存器写,只有最后一个才真正更新寄存器中的内容。
一条指令流出时,存放操作数的寄存器名被换成为对应于该寄存器保留站的名称(编号。
指令流出逻辑和保留站相结合实现寄存器换名,从而完全消除了数据写后写和先读后写相关这类名相关。
15.在存储层次中应解决哪四个问题?(1)映像规则:当把一个块调入高一层存储器时,可以放到哪些位置上。
(2)查找算法:当所要访问的块在高一层存储器中时,如何找到该块。
(3)替换算法:当发生失效时,应替换哪一块。
(4)写策略:当进行写访问时,应进行哪些操作。
16.在写回法中,用什么方法减少在替换时的写回?常采用“污染位”标志。
即为Cache中的每一块设置一个“污染位”(设在与该块相应的目录表项中),用于指出该块是“脏”的(被修改过)还是干净的(没被修改过)。
替换时,若被替换的块是干净的,则不必写回下一级存储器,因为这时下一级存储器中相应块的内容与Cache中的一致。
17.发生cache写失效时,是否调入相应块,有哪两种选择?(1)按写分配法:写失效时,先把所写单元所在的块调入Cache,然后再进行写入。
这种方法也称为写时取方法。
(2)不按写分配法:写失效时,直接写入下一级存储器而不将相应的块调入Cache。
这种方法也称为绕写法。
18.采用容量小且结构简单的cache有什么好处?(1)可以有效地提高Cache的访问速度。
因为硬件越简单,速度就越快。
小容量Cache可以实现快速标识检测,对减少命中时间有益。
(2)Cache足够小,可以与处理器做在同一芯片上,以避免因芯片外访问而增加时间开销。
(3)保持Cache结构简单可采用直接映像Cache。
直接映像Cache的主要优点是可以让标识检测和数据传送重叠进行,这样可以有效地减少命中时间。
19.增加cache块大小一定会降低失效率吗?不一定。
对于给定的Cache容量,当块大小增加时,失效率开始是下降,后来反而上升了。
主要因为增加块大小会产生双重作用。
一方面它减少了强制性失效;另一方面,可能会增加冲突失效。
20.DLX流水线寄存器的作用是什么?把数据和控制信息从一个流水段传送到下一个流水段。
21.流水线中有哪三种相关?是什么原因造成的?(1)结构相关:当硬件资源满足不了指令重叠执行的要求,而发生资源冲突时,就发生了结构相关(2)数据相关:当一条指令需要用到前面指令的执行结果,而这些指令均在流水线中重叠执行时,就可能引起数据相关。
(3)控制相关:当流水线遇到分支指令和其他能够改变PC值的指令时,就发生控制相关。
22.根据指令对寄存器的读写顺序,可将数据相关分为哪三类?(1)写后读相关(2)写后写相关(3)读后写相关23.什么是向量链接技术?当两条向量指令出现“写后读”相关时,若它们不存在功能部件冲突和向量寄存器(源或目的)冲突,就有可能把它们所用的功能部件头尾相接,形成一个链接流水线,进行流水处理。
24.根据CPU内部存储单元类型,将指令集结构分为哪几类?堆栈型指令集结构、累加器型指令集结构、通用寄存器型指令集结构。
26.现代大多数计算机均采用通用寄存器型指令集结构,为什么?主要有两个方面的原因,一是寄存器和CPU内部其他存储单元一样,要比存储器快;其次是对编译器而言,可以更加容易、有效地分配和使用寄存器。
27.通用寄存器指令集结构可以分为哪三类?寄存器-寄存器型。
寄存器-存储器型。
存储器-存储器型。
28.三种通用寄存器型指令集分别有哪些优缺点?29.计算机指令集结构所涉及的内容有哪些?(1) 指令集功能设计:主要有RISC和CISC两种技术发展方向。
(2) 寻址方式的设计。
(3) 操作数表示和操作数类型。
(4) 寻址方式的表示:可以将寻址方式编码于操作码中,也可以将寻址方式作为一个单独的域来表示。
(5) 指令集格式的设计:有变长编码格式、固定长度编码格式和混合型编码格式三种。
30.单级存储器主要矛盾是什么?采取什么方法解决?主要矛盾:(1) 速度越快,每位价格就越高。
(2) 容量越大,每位价格就越低。
(3) 容量越大,速度越慢。
采取多级存储层次方法来解决。
31.地址映像方法有哪几种?各有什么优缺点?(1)全相联映像。
实现查找的机制复杂,代价高,速度慢。
Cache空间的利用率较高,块冲突概率较低,因而Cache的失效率也低。
(2)直接映像。