BP神经网络训练分类器——【机器学习与算法分析 精品资源池】
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:4.35 MB
- 文档页数:13

BP神经网络分类器优化技术研究BP神经网络是一种常用的深度学习模型,具有强大的非线性映射能力和自适应学习能力。
然而,其性能受到多种因素影响,如网络结构、学习率、迭代次数等。
因此,研究如何优化BP神经网络分类器的性能,提高其准确率和泛化能力,具有重要意义。
BP神经网络分类器是一种有监督学习算法,通过反向传播算法调整网络权重,使输出结果更接近目标值。
然而,传统的BP神经网络分类器存在一些问题,如易陷入局部最小值、过拟合等。
因此,研究如何优化BP神经网络分类器的性能,提高其鲁棒性和泛化能力,具有重要意义。
为了提高BP神经网络分类器的性能,许多研究者提出了各种优化算法和技巧。
例如,有些人通过改变网络结构,增加隐藏层或神经元数量,以提高模型的表达能力。
有些人通过采用不同的激活函数,如ReLU、sigmoid等,以提高模型的非线性映射能力。
还有些人通过引入正则化项,如LL2正则化,以减少过拟合现象。
本文提出了一种基于遗传算法的BP神经网络分类器优化方法。
该方法采用遗传算法自动调整网络结构、学习率、迭代次数等超参数,以获得最佳的网络性能。
具体实现步骤如下:初始化BP神经网络分类器的超参数,如学习率、迭代次数等。
利用遗传算法自动调整超参数,以获得最佳的网络性能。
具体来说,通过交叉、变异等操作,生成新的超参数组合,并计算其适应度值(即网络性能的评价指标,如准确率、召回率等)。
选择适应度值较高的超参数组合进行进一步优化,直到达到预设的停止条件(如迭代次数或准确率阈值)。
通过对比实验,我们发现采用遗传算法优化的BP神经网络分类器在处理多种数据集时,均取得了比传统BP神经网络分类器更好的性能。
具体来说,实验结果显示,优化后的BP神经网络分类器在准确率、召回率等指标上均有显著提高,同时过拟合现象也得到了有效控制。
尽管我们采用遗传算法优化了BP神经网络分类器的性能,但是仍存在一些问题需要进一步探讨。
例如,如何更有效地评价网络性能,以及如何处理不同类型的数据集等问题。

基于BP神经网络的隐写分析分类器设计作者:李红蕾吴汉炜谭毓银来源:《信息安全与技术》2014年第09期【摘要】设计并实现了基于BP神经网络的隐写分析分类器。
首先对图像库中的图像进行格式变换,并使用扩展修改方向和钻石编码两种隐写方法进行不同嵌入率的隐写嵌入,然后计算载体图像和载密图像中平面域、DCT域和小波域的一些属性值作为特征。
利用Matlab的模式识别工具箱搭建BP神经网络,用已知类别的图像特征训练分类器并进行分类测试。
实验结果表明,多域综合特征可以实现良好的分类效果,能以较高的准确率识别出载体图像和载密图像。
【关键词】 BP神经网络;隐写分析;分类器【中图分类号】 TP309 【文献标识码】 AA Classifier of Steganalysis based on BP Neural NetworksLi Hong-lei Wu Han-wei Tan Yu-yin(School of Information Science and Technology,Hainan University HainanHaikou 570228 )【 Abstract 】 A classifier of steganalysis based on back propagation neural network is designed and realized. Firstly,the images in image database are turned into gray-scale images, then some attribute values of carrier images and stego-images are computed from the images’ spatial domain,DCT domain and wavelet domain. And the Matlab pattern recognition toolbox is adopted to establish the BP neural?network classifier. The results show that the BP neural?network classifier based on three domains attribute values performs well in classifying.【 Keywords 】 back propagation neural network ; steganalysis ; classifier1 引言信息隐藏是目前信息安全领域的一个重要研究方向,其目的是在载体中隐藏秘密信息而不被人察觉。

「精选参考」BP神经网络预测模型算法解析,助您轻松掌握"Selected Reference" BP Neural Network Prediction Model Algorithm Analysis, Helping You Master it EasilyAbstract:In recent years, with the rapid development of artificial intelligence and big data technology, the BP neural network prediction model has become an important tool for data analysis and prediction. This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the BP neural network prediction model algorithm, including its basic principles, training process, and application scenarios. By understanding the algorithm in depth, readers can easily grasp its concepts and apply it to solve real-world problems.Introduction:The BP neural network prediction model algorithm is based on the concept of a feedforward neural network. It is widely used in various fields such as finance, weather forecasting, and stock market analysis. The algorithm is designed to learnfrom historical data and make predictions based on the learned patterns. Its ability to handle complex nonlinear relationships and adapt to changing environments makes it a powerful tool for prediction tasks.Basic Principles:The BP neural network prediction model consists of an input layer, hidden layers, and an output layer. Each layer contains a certain number of neurons, and the connections between neurons are weighted. The algorithm works by iteratively adjusting these weights to minimize the prediction error. This process is known as the backpropagation algorithm, which involves two main steps: forward propagation and backward propagation.During forward propagation, input data is fed into the network, and each neuron calculates its output based on the weighted sum of the inputs and a non-linear activation function. The outputs of the neurons are then passed to the next layer until reaching the output layer. The predicted output is compared with the actual output, and the prediction error is calculated.In the backward propagation step, the prediction error is used to update the weights of the connections in a way that reduces the error. This is done by calculating the gradient of the error with respect to each weight and adjusting the weight in the opposite direction of the gradient. This process is repeated for multiple iterations until the prediction error reaches an acceptable level.Training Process:To train the BP neural network prediction model, a dataset with known input-output pairs is required. The dataset is divided into a training set and a validation set. The training set is used to update the weights of the network, while the validation set is used to monitor the model's performance and prevent overfitting.During the training process, the network learns to generalize from the training data and make accurate predictions on new, unseen data. The model's performance is evaluated using metrics such as mean squared error or accuracy rate. If the performance is not satisfactory, the network architecture ortraining parameters can be adjusted to improve the results.Application Scenarios:The BP neural network prediction model algorithm has been successfully applied in various fields. In finance, it can be used to predict stock prices, exchange rates, and credit risk. In weather forecasting, it can be used to predict temperature, rainfall, and other meteorological variables. In marketing, it can be used to predict customer behavior and optimize advertising campaigns. The possibilities are endless, and the algorithm's flexibility allows it to be adapted to different domains.Conclusion:In conclusion, the BP neural network prediction model algorithm is a powerful tool for data analysis and prediction. By understanding its basic principles and training process, one can effectively apply it to solve real-world problems. However, it is important to note that the performance of the algorithm heavily depends on the quality of the dataset, network architecture, and training parameters. Continuous research and improvement are necessary to fully unleash its potential.摘要:近年来,随着人工智能和大数据技术的快速发展,BP神经网络预测模型已成为数据分析和预测的重要工具。


B P神经网络算法原理BP网络模型处理信息的基本原理是:输入信号X i通过中间节点(隐层点)作用于输出节点,经过非线形变换,产生输出信号Y k,网络训练的每个样本包括输入向量X和期望输出量t,网络输出值Y与期望输出值t之间的偏差,通过调整输入节点与隐层节点的联接强度取值W ij和隐层节点与输出节点之间的联接强度T jk以及阈值,使误差沿梯度方向下降,经过反复学习训练,确定与最小误差相对应的网络参数(权值和阈值),训练即告停止。
此时经过训练的神经网络即能对类似样本的输入信息,自行处理输出误差最小的经过非线形转换的信息。
一 BP神经网络模型BP网络模型包括其输入输出模型、作用函数模型、误差计算模型和自学习模型。
(1)节点输出模型隐节点输出模型:O j=f(∑W ij×X i-q j) (1)输出节点输出模型:Y k=f(∑T jk×O j-q k) (2)f-非线形作用函数;q -神经单元阈值。
(2)作用函数模型作用函数是反映下层输入对上层节点刺激脉冲强度的函数又称刺激函数,一般取为(0,1)内连续取值Sigmoid函数: f(x)=1/(1+e-x) (3)(3)误差计算模型误差计算模型是反映神经网络期望输出与计算输出之间误差大小的函数: E p =1/2×∑(t pi -O pi )2 (4)t pi - i 节点的期望输出值;O pi -i 节点计算输出值。
(4)自学习模型神经网络的学习过程,即连接下层节点和上层节点之间的权重拒阵W ij 的设定和误差修正过程。
BP 网络有师学习方式-需要设定期望值和无师学习方式-只需输入模式之分。
自学习模型为△W ij (n+1)= h×Фi ×O j +a×△W ij (n) (5)h -学习因子;Фi -输出节点i 的计算误差;O j -输出节点j 的计算输出;a-动量因子。
二 BP 网络模型的缺陷分析及优化策略(1)学习因子h 的优化采用变步长法根据输出误差大小自动调整学习因子,来减少迭代次数和加快收敛速度。


bp神经网络算法原理BP神经网络算法(Backpropagation algorithm)是一种监督学习的神经网络算法,其目的是通过调整神经网络的权重和偏置来实现误差的最小化。
BP神经网络算法基于梯度下降和链式法则,在网络的前向传播和反向传播过程中进行参数的更新。
在前向传播过程中,输入样本通过网络的各个神经元计算,直到达到输出层。
每个神经元都会对上一层的输入进行加权求和,并经过一个非线性激活函数得到输出。
前向传播的结果即为网络的输出。
在反向传播过程中,首先需要计算网络的输出误差。
误差是实际输出与期望输出的差异。
然后,从输出层开始,沿着网络的反方向,通过链式法则计算每个神经元的误差贡献,并将误差从输出层反向传播到输入层。
每个神经元根据自身的误差贡献,对权重和偏置进行调整。
这一过程可以看作是通过梯度下降来调整网络参数,以最小化误差。
具体而言,对于每个样本,BP神经网络算法通过以下步骤来更新网络的参数:1. 前向传播:将输入样本通过网络,计算得到网络的输出。
2. 计算误差:将网络的输出与期望输出进行比较,计算得到输出误差。
3. 反向传播:从输出层开始,根据链式法则计算每个神经元的误差贡献,并将误差沿着网络反向传播到输入层。
4. 参数更新:根据每个神经元的误差贡献,使用梯度下降方法更新神经元的权重和偏置。
5. 重复以上步骤,直到达到预设的训练停止条件,例如达到最大迭代次数或误差小于某个阈值。
总的来说,BP神经网络算法通过计算输出误差和通过反向传播调整网络参数的方式,实现对神经网络的训练。
通过不断迭代优化网络的权重和偏置,使得网络能够更准确地进行分类、回归等任务。
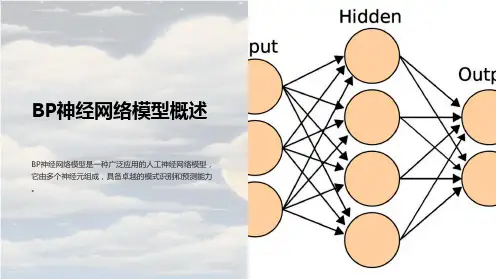


BP神经网络——王晓菲BP(Back Propagation)网络是1986年由Rumelhart和McCelland为首的科学家小组提出,是一种按误差逆传播算法训练的多层前馈网络,是目前应用最广泛的神经网络模型之一。
BP网络能学习和存贮大量的输入‐输出模式映射关系,而无需事前揭示描述这种映射关系的数学方程。
它的学习规则是使用最速下降法,通过反向传播来不断调整网络的权值和阈值,使网络的误差平方和最小。
BP神经网络模型拓扑结构包括输入层(input layer )、隐层(hide layer)和输出层(output layer)。
后向传播如何工作?后向传播迭代地处理训练元组数据集,将每个元组的网络预测与实际已知的目标值比较。
目标值可以是训练元组的已知类标号(对于分类问题)或连续值(对于预测)。
对于每个训练样本,修改权重使网络预测和实际目标值之间的均方误差最小。
这种修改“后向”进行,即由输出层,经由每个隐藏层,到第一个隐藏层(因此称作后向传播)。
一般地,权重将最终收敛,学习过程停止。
(1)初始化权重:网络的权重初始化为很小的随机数(例如由‐1.0~1.0,或由‐0.5~0.5)。
每个单元有一个关联的偏倚(bias),偏倚也类似地初始化为小随机数。
(2)向前传播输入:首先,训练元组提供给网络的输入层。
输入通过输入单元,不发生变化。
也就是说,对于输入单元j,它的输出O j等于它的输入值I j。
然后,计算隐藏层和输出层每个单元的净输入和输出。
隐藏层或输出层单元的净输入用其输入的线性组合计算。
事实上,每个单元有许多输入,是连接它的上一层各单元的输出。
每个连接都有一个权重。
为计算该单元的净输入,连接该单元的每个输入都乘以其对应的权重,然后求和。
给定隐藏层或输出层的单元j,到单元j的净输入Ij是:I j=∑i w ij O i+θj其中,wij 是由上一层的单元i到单元j的连接的权重;Oi是上一层的单元i的输出;而θj是单元j的偏倚。

BP神经⽹络的数据分类BP 神经⽹络的数据分类——语⾳特征信号分类1. BP神经⽹络是⼀种多层前馈神经⽹络,该⽹络的主要特点是信号前向传递,误差反向传播。
在前向传递中,输⼊信号从输⼊层经隐含层逐层处理,直⾄输出层. 每⼀层的神经元状态只影响下⼀层神经元状态。
如果输出层得不到期望输出,则转⼊反向传播, 根据预测误差调整⽹络权值和阔值,从⽽使BP 神经⽹络预测输出不断逼近期望输出。
2. 语⾳特征信号识别是语⾳识别研究领域中的⼀个重要⽅⾯, ⼀般采⽤模式匹配的原理解决。
语⾳识别的运算过程为:⾸先,待识别语⾳转化为电信号后输⼊识别系统,经过预处理后⽤数学⽅法提取语⾳特征信号,提取出的语⾳特征信号可以看成该段语⾳的模式E 然后,将该段语⾳模型罔已知参考模式相⽐较,获得最佳匹配的参考模式为该段语⾳的识别结果。
3. 本代码选取了民歌、古筝、摇滚和流⾏四类不同⾳乐, ⽤BP 神经⽹络实现对这四类⾳乐的有效分类。
每段⾳乐都⽤倒谱系费⽴法提取500 组24 维语⾳特征信号。
4. BP 神经⽹络构建根据系统输⼊输出数据特点确定BP 神经⽹络的结构,由于语⾳特征输⼊信号有24 维,待分类的语⾳信号共有4类,所以BP 神经⽹络的结构为24-25-4 ,即输⼊层有24 个节点,隐含层有25 个节点,输出层有4 个节点。
BP 神经⽹络训练⽤训练数据训练BP 神经⽹络。
共有2 000 组语⾳特征信号,从中随机选择1 5 00 组数据作为训练数据训练⽹络, 5 00 组数据作为测试数据测试⽹络分类能⼒。
BP 神经⽹络分类⽤训练好的神经⽹络对测试数据所属语⾳类别进⾏分类。
算法流程图为:5. 程序实现%% 该代码为基于BP⽹络的语⾔识别%% 清空环境变量clcclear%% 训练数据预测数据提取及归⼀化%下载四类语⾳信号load data1 c1load data2 c2load data3 c3load data4 c4%四个特征信号矩阵合成⼀个矩阵data(1:500,:)=c1(1:500,:);data(501:1000,:)=c2(1:500,:);data(1001:1500,:)=c3(1:500,:);data(1501:2000,:)=c4(1:500,:);%从1到2000间随机排序k=rand(1,2000);[m,n]=sort(k);%输⼊输出数据input=data(:,2:25);output1 =data(:,1);%把输出从1维变成4维output=zeros(2000,4);for i=1:2000switch output1(i)case 1output(i,:)=[1 0 0 0];case 2output(i,:)=[0 1 0 0];case 3output(i,:)=[0 0 1 0];case 4output(i,:)=[0 0 0 1];endend%随机提取1500个样本为训练样本,500个样本为预测样本input_train=input(n(1:1500),:)';output_train=output(n(1:1500),:)';input_test=input(n(1501:2000),:)';output_test=output(n(1501:2000),:)';%输⼊数据归⼀化[inputn,inputps]=mapminmax(input_train);%% ⽹络结构初始化innum=24;midnum=25;outnum=4;%权值初始化w1=rands(midnum,innum);b1=rands(midnum,1);w2=rands(midnum,outnum);b2=rands(outnum,1);w2_1=w2;w2_2=w2_1;w1_1=w1;w1_2=w1_1;b1_1=b1;b1_2=b1_1;b2_1=b2;b2_2=b2_1;%学习率xite=0.1;alfa=0.01;loopNumber=10;I=zeros(1,midnum);Iout=zeros(1,midnum);FI=zeros(1,midnum);dw1=zeros(innum,midnum);db1=zeros(1,midnum);%% ⽹络训练E=zeros(1,loopNumber);for ii=1:loopNumberE(ii)=0;for i=1:1:1500%% ⽹络预测输出x=inputn(:,i);% 隐含层输出for j=1:1:midnumI(j)=inputn(:,i)'*w1(j,:)'+b1(j);Iout(j)=1/(1+exp(-I(j)));end% 输出层输出yn=w2'*Iout'+b2;%% 权值阀值修正%计算误差e=output_train(:,i)-yn;E(ii)=E(ii)+sum(abs(e));%计算权值变化率dw2=e*Iout;db2=e';for j=1:1:midnumS=1/(1+exp(-I(j)));FI(j)=S*(1-S);endfor k=1:1:innumfor j=1:1:midnumdw1(k,j)=FI(j)*x(k)*(e(1)*w2(j,1)+e(2)*w2(j,2)+e(3)*w2(j,3)+e(4)*w2(j,4)); db1(j)=FI(j)*(e(1)*w2(j,1)+e(2)*w2(j,2)+e(3)*w2(j,3)+e(4)*w2(j,4));endendw1=w1_1+xite*dw1';b1=b1_1+xite*db1';w2=w2_1+xite*dw2';b2=b2_1+xite*db2';w1_2=w1_1;w1_1=w1;w2_2=w2_1;w2_1=w2;w2_2=w2_1;w2_1=w2;b1_2=b1_1;b1_1=b1;b2_2=b2_1;b2_1=b2;endend%% 语⾳特征信号分类inputn_test=mapminmax('apply',input_test,inputps); fore=zeros(4,500);for ii=1:1for i=1:500%1500%隐含层输出for j=1:1:midnumI(j)=inputn_test(:,i)'*w1(j,:)'+b1(j);Iout(j)=1/(1+exp(-I(j)));endfore(:,i)=w2'*Iout'+b2;endend%% 结果分析%根据⽹络输出找出数据属于哪类output_fore=zeros(1,500);for i=1:500output_fore(i)=find(fore(:,i)==max(fore(:,i)));end%BP⽹络预测误差error=output_fore-output1(n(1501:2000))';%画出预测语⾳种类和实际语⾳种类的分类图figure(1)plot(output_fore,'r')hold onplot(output1(n(1501:2000))','b')legend('预测语⾳类别','实际语⾳类别')%画出误差图figure(2)plot(error)title('BP⽹络分类误差','fontsize',12)xlabel('语⾳信号','fontsize',12)ylabel('分类误差','fontsize',12)%print -dtiff -r600 1-4k=zeros(1,4);%找出判断错误的分类属于哪⼀类for i=1:500if error(i)~=0[b,c]=max(output_test(:,i));switch ccase 1k(1)=k(1)+1;case 2k(2)=k(2)+1;case 3k(3)=k(3)+1;case 4k(4)=k(4)+1;endendend%找出每类的个体和kk=zeros(1,4);for i=1:500[b,c]=max(output_test(:,i));switch ccase 1kk(1)=kk(1)+1;case 2kk(2)=kk(2)+1;case 3kk(3)=kk(3)+1;case 4case 4kk(4)=kk(4)+1; endend%正确率rightridio=(kk-k)./kk; disp('正确率')disp(rightridio);6.点击7.结果如下图。
神经网络学习之 BP神经网络/u013007900/article/details/50118945目录第一章概述第二章BP算法的基本思想第三章BP网络特性分析3.1 BP网络的拓扑结构 (4)3.2 BP网络的传递函数 (5)3.3 BP网络的学习算法 (6)第四章BP网络的训练分解4.1前向传输(Feed-Forward前向反馈) (8)4.2逆向反馈(Backpropagation) (9)4.3 训练终止条件 (10)第五章BP网络运行的具体流程 (10)5.1网络结构 (10)5.2变量定义 (10)5.3误差函数: (11)第六章BP网络的设计 (14)6.1 网络的层数 (14)6.2 隐层神经元的个数 (15)6.3 初始权值的选取 (15)6.4 学习速率 (15)BP网络的局限性 (15)BP网络的改进 (16)第一章概述神经网络是1986年由Rumelhart和McCelland为首的科研小组提出,参见他们发表在Nature 上的论文Learning representations by back-propagating errors。
BP神经网络是一种按误差逆传播算法训练的多层前馈网络,是目前应用最广泛的神经网络模型之一。
BP网络能学习和存贮大量的输入-输出模式映射关系,而无需事前揭示描述这种映射关系的数学方程。
它的学习规则是使用最速下降法,通过反向传播来不断调整网络的权值和阈值,使网络的误差平方和最小。
第二章BP算法的基本思想多层感知器在如何获取隐层的权值的问题上遇到了瓶颈。
既然我们无法直接得到隐层的权值,能否先通过输出层得到输出结果和期望输出的误差来间接调整隐层的权值呢?BP算法就是采用这样的思想设计出来的算法,它的基本思想是,学习过程由信号的正向传播与误差的反向传播两个过程组成。
•正向传播时,输入样本从输入层传入,经各隐层逐层处理后,传向输出层。
若输出层的实际输出与期望的输出(教师信号)不符,则转入误差的反向传播阶段。
BP神经网络分类器摘要本文主要介绍了BP神经网络的分类器使用方法,结合USPS手写数字集,对该数据集进行了训练和分类,对结果做了分析。
手写体数字识别是模式识别中一个非常重要和活跃的研究领域,数字识别也不是一项孤立的技术,它所涉及的问题是模式识别的其他领域都无法回避的;应用上,作为一种信息处理手段,字符识别有广阔的应用背景和巨大的市场需求。
因此,对数字识别的研究具有理论和应用的双重意义。
语音识别分为说话人识别和语义识别,这里介绍说话人识别,说话人识别提取出特征参数之后,需要采用分类器对特征空间进行分类。
人工神经网络识别方法是近年该研究领域的一种新方法,该方法具有一些传统技术所没有的优点:良好的容错能力、分类能力强、并行处理和自学习能力,并且是离线训练和在线识别的。
这些优点使它在手写体字符的识别中能对大量数据进行快速实时处理,并达到良好的识别效果。
本文主要介绍了BP神经网络的分类器使用方法,结合USPS手写数字集,语音识别一节他人论文。
关键词: USPS手写数字,BP人工神经网络,语音识别1 人工神经网络人工神经网络(Artificial Neural Networks,NN)是由大量的、简单的处理单元(称为神经元)广泛地互相连接而形成的复杂网络系统,它反映了人脑功能的许多基本特征,是一个高度复杂的非线性动力学系统。
神经网络具有大规模并行、分布式存储和处理、自组织、自适应和自学习能力,特别适合处理需要同时考虑许多因素和条件的、不精确和模糊的信息处理问题。
神经网络的发展与神经科学、数理科学、认知科学、计算机科学、人工智能、信息科学、控制论、机器人学、微电子学、心理学、微电子学、心理学、光计算、分子生物学等有关,是一门新兴的边缘交叉学科。
神经网络具有非线性自适应的信息处理能力,克服了传统人工智能方法对于直觉的缺陷,因而在神经专家系统、模式识别、智能控制、组合优化、预测等领域得到成功应用。
神经网络与其他传统方法相组合,将推动人工智能和信息处理技术不断发展。
BP神经网络目录[隐藏][编辑本段]概述BP (Back Propagation)神经网络是一种神经网络学习算法,全称基于误差反向传播算法的人工神经网络。
[编辑本段]人脑与人工神经网络“人脑是如何工作的?”“人类能否制作模拟人脑的人工神经元?”多少年以来,人们从医学、生物学、生理学、哲学、信息学、计算机科学、认知学、组织协同学等各个角度企图认识并解答上述问题。
在寻找上述问题答案的研究过程中,近年来逐渐形成了一个新兴的多学科交叉技术领域,称之为“神经网络”。
神经网络的研究涉及众多学科领域,这些领域互相结合、相互渗透并相互推动。
不同领域的科学家又从各自学科的兴趣与特色出发,提出不同的问题,从不同的角度进行研究。
心理学家和认知科学家研究神经网络的目的在于探索人脑加工、储存和搜索信息的机制,弄清人脑功能的机理,建立人类认知过程的微结构理论。
生物学、医学、脑科学专家试图通过神经网络的研究推动脑科学向定量、精确和理论化体系发展,同时也寄希望于临床医学的新突破;信息处理和计算机科学家研究这一问题的目的在于寻求新的途径以解决目前不能解决或解决起来有极大困难的大量问题,构造更加逼近人脑功能的新一代计算机。
[编辑本段]人工神经网络基本元件人工神经网络是由大量的简单基本元件——神经元相互联接而成的自适应非线性动态系统。
每个神经元的结构和功能比较简单,但大量神经元组合产生的系统行为却非常复杂。
人工神经网络反映了人脑功能的若干基本特性,但并非生物系统的逼真描述,只是某种模仿、简化和抽象。
与数字计算机比较,人工神经网络在构成原理和功能特点等方面更加接近人脑,它不是按给定的程序一步一步地执行运算,而是能够自身适应环境、总结规律、完成某种运算、识别或过程控制。
[编辑本段]起源于脑神经元学说人工神经元的研究起源于脑神经元学说。
19世纪末,在生物、生理学领域,Waldeger等人创建了神经元学说。
人们认识到复杂的神经系统是由数目繁多的神经元组合而成。