高中英语时态总复习
- 格式:doc
- 大小:33.50 KB
- 文档页数:4


Tips:1. 一般过去时还可表示:1 . want, hope, think, intend等v. 的一般过去时往往表示“过去原……”e.g. I thought he was an honest man. 我原以为他是个老实人。
2 wonder 的一般过去时有时也可以表示现在的行为,但口气比一般现在时更委婉。
e.g. I wondered if you could do me a favour. 我不知道你能否帮我一个忙。
2. 一般将来时1 . will 表示事物的固有属性或必然趋势; 表示将来,有时含有偶然性、临时性决定的意思。
e.g. Fish will die without water.I will go and visit him right now.2 . be going to +v. 多用在口语中,表示“计划、打算做某事”;还可表示根据现在的迹象对未来进行推断。
e.g. He is going to speak on TV this evening. 他今晚要在电视上讲话。
Look at the dark clouds. It is going to rain. 看这些乌云,要下雨了。
3 . 有些动词如e, go, arrive, leave, begin, start等,其现在进行时表示按计划,安排近期将要发生的动作。
e.g. I am leaving for Beijing next week. 下周我要去北京。
4 . 有些动词的一般现在时可以表示计划、安排要做的事情,这种用法常常用于介绍火车时刻表、飞机时刻表、作息安排等内容。
e.g. We must hurry up. The first class begins at 8 o’clock.5 . be to +v. 原形表示“表示计划、安排要做的事情”e.g. The Queen is to visit Japan next month.表示“应该”,相当于should, ought to.e.g. You are to report it to the police. 你应该报警。

高中英语时态总结英语时态是英语语法中非常重要的一个部分,也是我们在学习和使用英语时需要掌握的重要知识点。
本文将高中英语中常见的时态进行总结,帮助大家更好地理解和掌握。
一、现在时态1、现在进行时:表示现在正在进行的动作或存在的状态。
结构为“be 动词(am/is/are)+动词的现在分词”。
例如:I am studying now.我正在学习。
2、现在完成时:表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果。
结构为“have/has+动词的过去分词”。
例如:I have finished my homework.我已经完成了我的作业。
二、过去时态1、过去进行时:表示过去正在进行的动作或存在的状态。
结构为“was/were+动词的现在分词”。
例如:They were playing football at that time.他们那时正在踢足球。
2、过去完成时:表示过去的过去发生的动作对过去造成的影响或结果。
结构为“had+动词的过去分词”。
例如:They had finished their work before we arrived.他们在我们到达之前已经完成了他们的工作。
三、将来时态1、将来进行时:表示将来某个时间正在进行的动作或存在的状态。
结构为“will+be动词+动词的现在分词”。
例如:I will be studying at 9 o’clock tomorrow.我明天9点将会在学习。
2、将来完成时:表示将来某个时间已经完成的动作或达到的状态。
结构为“will+have+动词的过去分词”。
例如:I will have finished my homework by 10 o’clock tonight.我将在今晚10点之前完成我的作业。
以上是高中英语中常见的时态总结,希望能够帮助大家更好地理解和掌握英语时态。
需要注意的是,不同的时态有着不同的用法和结构,大家在使用时需要根据语境选择合适的时态。

高考英语时态详解一、现在一般时1.表示普遍的事实或真理名言The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.太阳东升西落。
Time flies.时光飞逝。
Failure is the mother of success.失败是成功之母。
2.表示经常性的重复活动,包括动作和状态(常态)I often get up at 6 o’clock in the morning.我经常早晨六点起床。
I am an English teacher.我是一名英语老师。
二、现在进行时1.表示现在正在做的动作He is playing the piano now.他现在在弹钢琴。
2.表示即将发生的动作(come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return, die, take...) They are coming to dinner.他们要来吃晚餐。
I am leaving.我要走了。
3.表示现阶段正在进行的动作或者发生的事We are learning English this summer holiday.我这个暑假在学英语。
三、现在完成时表示到目前为止已经完成的动作,如果是延续性动词,表示持续到现在的动作或者状态I have received your letter.我已经收到了你的信。
He has been here for 10 years.他在这住了十年了。
四、现在完成进行时表示一直持续到现在,且可能继续持续下去I have been learning English in school for 7 years.我在学校学英语7年了。
It has been raining for 2 hours.雨下了两个小时了。
五、过去一般时过去的动作,习惯,事实I began to learn English five years ago.我五年前开始学英语。
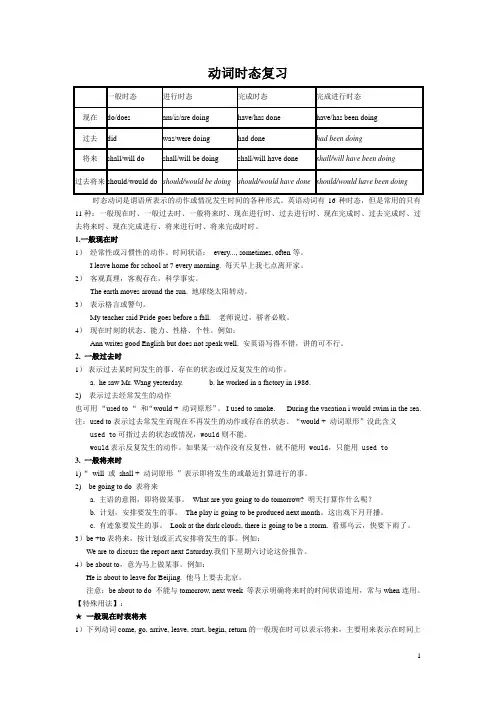
动词时态复习一般时态进行时态完成时态完成进行时态现在do/does am/is/are doing have/has done have/has been doing过去did was/were doing had done had been doing将来shall/will do shall/will be doing shall/will have done shall/will have been doing过去将来 should/would do should/would be doing should/would have done should/would have been doing时态动词是谓语所表示的动作或情况发生时间的各种形式。
英语动词有16种时态,但是常用的只有11种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、过去将来时、现在完成进行、将来进行时、将来完成时时。
1.一般现在时1)经常性或习惯性的动作。
时间状语:every..., sometimes, often等。
I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 每天早上我七点离开家。
2)客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。
The earth moves around the sun. 地球绕太阳转动。
3)表示格言或警句。
My teacher said Pride goes before a fall.老师说过,骄者必败。
4)现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。
例如:Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 安英语写得不错,讲的可不行。
2. 一般过去时1)表示过去某时间发生的事、存在的状态或过反复发生的动作。
a. he saw Mr. Wang yesterday.b. he worked in a factory in 1986.2) 表示过去经常发生的动作也可用“used to “和“would + 动词原形”。

时态时态(Tense)是表⽰⾏为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。
因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。
1. ⼀般现在时⽤法:A) 表⽰现在发⽣的动作、情况、状态和特征。
B) 习惯⽤语。
C) 经常性、习惯性动作。
例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别⼈。
)D) 客观事实和普遍真理。
E) 表⽰⼀个按规定、计划或安排要发⽣的动作,(仅限于某些表⽰“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表⽰未来时间的状语搭配使⽤。
常见的⽤法是:飞机、⽕车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运⾏的交通⽅式。
例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon.(下⼀趟⽕车今天下午3点开车。
)How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久⼀趟?)2. 现在进⾏时(be doing)⽤法:现在正在进⾏的动作。
3. 现在完成时(have done)⽤法:A) 表⽰动作到现在为⽌已经完成或刚刚完成。
B)表⽰从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。
此时经常⽤延续性动词。
时间状语常⽤since加⼀个过去的时间点,或for加⼀段时间,或by加⼀个现在时间。
例:Great as Newton was, many of his ideas ___________ today and are being modified by the work of scientists of our time.A) are to challenge C) have been challengedB) may be challenged D) are challengingC) 表⽰发⽣在过去,但对现在仍有影响的动作或情况。
通常⽤点动词,如:arrive, begin, find, give, lose等。
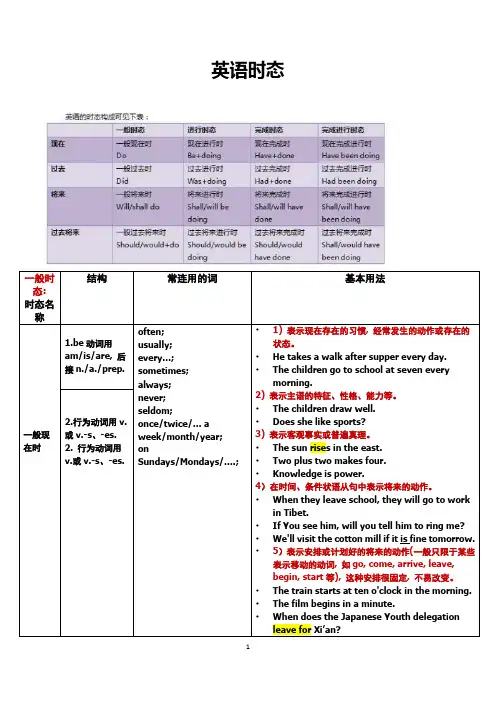
英语时态一般时态:时态名称结构常连用的词基本用法一般现在时1.be动词用am/is/are, 后接n./a./prep.often;usually;every…;sometimes;always;never;seldom;once/twice/… aweek/month/year;onSundays/Mondays/….;•1) 表示现在存在的习惯, 经常发生的动作或存在的状态。
•He takes a walk after supper every day.•The children go to school at seven everymorning.2)表示主语的特征、性格、能力等。
•The children draw well.•Does she like sports?3) 表示客观事实或普遍真理。
•The sun rises in the east.•Two plus two makes four.•Knowledge is power.4)在时间、条件状语从句中表示将来的动作。
•When they leave school, they will go to workin Tibet.•If You see him, will you tell him to ring me?•We'll visit the cotton mill if it is fine tomorrow.•5)表示安排或计划好的将来的动作(一般只限于某些表示移动的动词, 如go, come, arrive, leave,begin, start等), 这种安排很固定, 不易改变。
•The train starts at ten o'clock in the morning.•The film begins in a minute.•When does the Japanese Youth delegationleave for Xi’an?2.行为动词用v.或v.-s、-es.2. 行为动词用v.或v.-s、-es.1.________ a concert next Saturday?2. A.There will be B.Will there be C.There can be D.There are3.It’s good t o see you again, Agnes.— This has been our first chance to visit since from Iran.4. A.you return B.you returned C.you have returned D.returning5.If it ________ tomorrow, we’ll go roller-skating.A.isn’t rainB.won’t rainC.doesn’t rainD.doesn’t fine4.The reporter said that the UFO ___ east to west when he saw it.A.was travelingB.traveledC.had been travelingD.was to travel5.Sorry, I can’t open the door, for I the key to it.A.lostB.loseC.had lostD.have lost6.“What ' s the matter, Ali? You look sad.”“Oh, nothing much.As a matter of fact, I ___ of my friends back home.”A.just thoughtB.have just been thinkingC.was just thinkingD.have just thought7.—Did you expect Frank to come to the party? —No, but I had hoped .A.him comingB.him to comeC.that he comesD.that he would come8.—Bob must be very wealthy.—Yes, he more in one day than I do in a week.A.has been earnedB.had earnedC.earnsD.has earned9.I first met Lisa three years ago.She ___ at a radio shop at the time.A.has workedB.was workingC.had been workingD.had worked10.She _____her keys in the office so she had to wait until her husband ____home.A has left; comesB had left; would comeC had left; cameD left; had come11.Zhao Lan ______already ______in this school for two years.12.A.was ; studying B.will ; study C.has ; studied D.are ; studying---Mr Gorden asked me to remind you of the meeting this afternoon .Don’t forget it !---OK.I ______ .13.A.won't B.don't C.will D.do14.When I reached home, my parents __________their supper.15.A.are having B.have already had C.have had D.had already had16.She __________in this school ________the past ten years.A.was teaching, sinceB.had been teaching, since17.C.would teach, for D.has been teaching, forI first met Tom 10 years ago.He ______ in a radio factory at that time.18.A.had worked B.has worked C.was working D.has been working19.--- What ______ when I phoned you?--- I ______ my work, and I wanted to go out.A.have you done; finishedB.were you doing; have finished20.C.did you do; had just finished D.were you doing; had just finished21.I used to drink a lot of tea but these days I ______ coffee.22.A.prefer B.preferred C.had preferred D.am preferringJim talked for about half an hour yesterday.Never ______ him talk so much.23.A.I heard B.did I hear C.I had heard D.had I heard24.He ___ articles for our wall-newspaper these three years, and he ____ about fortyarticles.A.has been writing; has writtenB.had been writing; wrote25.C.is writing; has been writing D.has written; has written26.When he was alive, the old scientist used to say that knowledge ______ from practice andhe gained his experience by doing a lot of practical work.27.A.was coming B.had come es D.would come28.--- How are you planning to travel to Shanghai?--- I ______ yet, but I ______ taking a train.A.didn’t decide; am consideringB.haven’t decided; consider29.C.haven’t decided; am considering D.hadn’t decided; have considered30.--- Who’s the man over there?--- It’s Jack.--- Oh? ______ in Italy.A.I think he’sB.I’ve thought he’s been31.C.I thought he was D.I’d thought he’d beenI thought Jim would say something about his school report, but he ______ it.32.A.doesn’t mention B.hadn’t mentioned C.didn’t mention D.hasn’t mentioned33.—How long ________ each other before they ________ married?—For about a year.A.have they known; getB.did they know; getC.do they know; are going to getD.had they known; gotWe would like to go and thank him ourselves, but we ________ out his address yet,A.haven’t foundB.hadn’t foundC.didn’t findD.don’t find34.Shirley ________ a book about China last year but I don’t know whether she has finished.A.has writtenB.wroteC.had writtenD.was writing35.—Do you know when Tom ________ from abroad?—Perhaps it will be a long time before he ________ back.A.will come; will comees; will comeC.will come; comeses; comesThe pen I ________ I ________ is on my desk, right under my nose.A.think; lostB.thought; had lostC.think; had lostD.thought; lostHowever hard you ________, you will never succeed in pleasing her.A.tryB.will tryC.should tryD.would try36.By this time tomorrow we ________ the machine.A.have repairedB.shall have repairedC.will repairD.would repair37.I ________ the room to be empty but found it occupied.A.had thoughtB.have thoughtC.didn’t thinkD.was thinking。

高中16种英语时态总结归纳1. Simple Present Tense:- Used for regular actions or habits, and general truths.- Form: Base form of the verb (e.g. I go, he/she/it goes).2. Present Continuous Tense:- Used to describe actions happening at the moment of speaking, or for future arrangements.- Form: am/is/are + present participle (e.g. I am writing, he/she/it is reading).3. Present Perfect Tense:- Used for actions that happened at an unspecified timein the past, and have relevance to the present.- Form: has/have + past participle (e.g. I have seen,he/she/it has done).4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense:- Used for actions that started in the past and continue into the present, and emphasize duration.- Form: has/have been + present participle (e.g. I have been waiting, he/she/it has been working).5. Simple Past Tense:- Used for actions that started and finished at aspecific time in the past.- Form: Past form of the verb (e.g. I went, he/she/it played).6. Past Continuous Tense:- Used to emphasize the duration of an action in the past, or for two actions happening simultaneously in the past.- Form: was/were + present participle (e.g. I was sleeping, he/she/it was writing).7. Past Perfect Tense:- Used to describe an action that happened before another action in the past.- Form: had + past participle (e.g. I had seen, he/she/it had finished).8. Past Perfect Continuous Tense:- Used to show the duration of an action that happened before another action in the past.- Form: had been + present participle (e.g. I had been waiting, he/she/it had been studying).9. Simple Future Tense:- Used to talk about actions that will happen in the future.- Form: will/shall + base form of the verb (e.g. I will go, he/she/it will eat).10. Future Continuous Tense:- Used to describe actions that will be ongoing at a specific time in the future.- Form: will/shall be + present participle (e.g. I will be waiting, he/she/it will be working).11. Future Perfect Tense:- Used for actions that will be completed before another action in the future.- Form: will have + past participle (e.g. I will have finished, he/she/it will have left).12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense:- Used to emphasize the duration of an action that will be completed before another action in the future.- Form: will have been + present participle (e.g. I will have been waiting, he/she/it will have been studying).13. Present Unreal Conditional:- Used to talk about hypothetical situations in the present or future, expressing results that are unlikely or impossible.- Form: if + simple past, would + base form (e.g. If I were rich, I would travel the world).14. Past Unreal Conditional:- Used to talk about hypothetical situations in the past, expressing results that didn't happen.- Form: if + past perfect, would have + past participle(e.g. If I had studied harder, I would have passed the test).15. Mixed Tenses:- Used to describe actions that happen at the same time but in the past and present or future.- Form: Mix of different tenses.16. Future Time Clauses:- Used to indicate two actions happening in the future, with the main clause in the future and the time clause in the present.- Form: Present tense in the time clause, will/shall or other future tense in main clause (e.g. When I am 25, I will have graduated).。

高中英语的时态总结归纳时态是英语语法中的重要部分,它能够准确地表达动作的发生时间。
在高中英语学习过程中,掌握各种时态的用法对于正确表达和理解英文语境至关重要。
本文将对高中英语中常见的时态进行总结和归纳,旨在帮助读者加深对时态的理解和掌握。
一、一般现在时态(Simple Present Tense)一般现在时态表示经常性动作、客观真理、现象描述等。
其基本结构为主语 + 动词原形。
例如:1. I eat breakfast every morning.(我每天早上吃早饭。
)2. Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.(水在100摄氏度时沸腾。
)二、一般过去时态(Simple Past Tense)一般过去时态表示过去发生的动作或状态。
其基本结构为主语 + 动词过去式。
例如:1. He studied English in high school.(他在高中学习英语。
)2. They visited their grandparents last weekend.(他们上周末拜访了他们的祖父母。
)三、一般将来时态(Simple Future Tense)一般将来时态表示将来的动作或状态。
其基本结构为主语 + will +动词原形。
例如:1. We will have a party next week.(我们下周将举办派对。
)2. She will visit her friend tomorrow.(她明天将去拜访她的朋友。
)四、现在进行时态(Present Continuous Tense)现在进行时态表示正在进行的动作或现阶段的临时状态。
其基本结构为主语 + am/is/are + 动词ing形式。
例如:1. They are playing basketball in the park.(他们正在公园里打篮球。
)2. I am studying for the exam at the moment.(我现在正在备考。

高中英语时态总结在高中英语学习中,时态是一个至关重要的语法知识点。
掌握好时态,不仅能让我们更准确地表达自己的意思,还能帮助我们更好地理解英语文章。
下面就为大家详细总结一下高中英语中常见的时态。
一、一般现在时一般现在时表示经常发生的动作或存在的状态。
其构成是:主语+动词原形(当主语是第三人称单数时,动词要加“s”或“es”)。
例如:I go to school every day(我每天上学。
)He likes playing basketball(他喜欢打篮球。
)一般现在时的用法主要有以下几种:1、表示经常性或习惯性的动作,常与 often, always, usually, sometimes 等时间状语连用。
2、表示客观事实或普遍真理。
3、用于时间、条件、方式、让步等状语从句中,表示将来的动作。
二、一般过去时一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。
其构成是:主语+动词的过去式。
例如:I played football yesterday(我昨天踢足球了。
)一般过去时的用法:1、表示过去某个特定时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表示过去的时间状语连用,如 yesterday, last week, in 1998 等。
2、表示过去一段时间内经常或反复发生的动作。
三、一般将来时一般将来时表示将来要发生的动作或存在的状态。
其构成有多种形式,常见的有:“will +动词原形”和“be going to +动词原形”。
例如:I will go to Beijing next week(我下周将去北京。
)She is going to have a party tomorrow(她明天将举办一个派对。
)一般将来时的用法:1、表示将来要发生的动作或存在的状态。
2、表示将来的打算、计划或准备做某事。
四、现在进行时现在进行时表示正在进行的动作。
其构成是:主语+ be(am/is/are)+现在分词。
例如:I am reading a book now(我现在正在读一本书。
高中英语时态语法总结归纳英语时态是表示动作发生时间的一种语法形式,在高中英语学习中扮演着重要的角色。
正确使用时态可以使语言表达更加准确和流畅。
本文将对高中英语常用的时态进行总结归纳,以帮助学生更好地掌握时态的用法。
一、一般现在时 (Simple Present Tense)一般现在时用于表示经常性的动作、客观事实、真理、习惯和固定时间表等。
1. 结构:主语 + 动词原形(单数加s或es)+ 其他2. 示例:- He plays soccer every weekend.(他每个周末都踢足球。
)- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.(水在100摄氏度时沸腾。
)- I usually go to bed at 10 o'clock.(我通常十点钟上床睡觉。
)二、一般过去时 (Simple Past Tense)一般过去时用于表示过去某个时间发生的动作或状态。
1. 结构:主语 + 动词过去式(一般过去时动词过去式的变化规则多样)2. 示例:- They went to the park yesterday.(他们昨天去了公园。
)- She watched a movie last night.(她昨晚看电影了。
)- I played the guitar when I was young.(我年轻时弹吉他。
)三、一般将来时 (Simple Future Tense)一般将来时用于表示将来某个时间或情况下发生的动作或状态。
1. 结构:主语 + will/shall + 动词原形2. 示例:- We will study English tomorrow.(我们明天将学习英语。
)- He shall help you with your assignment.(他将帮助你完成作业。
)- They won't go to the party this weekend.(他们这个周末不会去参加派对。
高中16种英语时态总结归纳高中16种英语时态总结归纳16种英语时态总结归纳时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。
因此,当我们说时态构造的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。
英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进展时、完成时和完成进展时。
1.一般现在时用法:A)表示现在发生的动作、状况、状态和特征。
B)习惯用语。
C)常常性、习惯性动作。
例:Healwayshelpsothers.(他总是帮忙别人。
)D)客观事实和普遍真理。
尤其要留意,假如前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态全都。
E)表示一个按规定、规划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开头、完毕、连续”等的动词)可以与表示将来时间的状语搭配使用。
常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。
例:Thenexttrainleavesat3o“clockthisafternoon.(下一趟火车今日下午3点开车。
)Howoftendoesthisshuttlebusrun?(这班车多久一趟?)F)在时间和条件状语从句里常常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。
例:Whenyouhavefinishedthereport,Iwillhavewaitedforabout3hours.(等你完成这份报告的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。
)2.现在进展时(bedoing)用法:现在正在进展的动作。
3.现在完成时(havedone)用法: A)表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。
例:Iboughtanewhouse,butI_________myoldoneyet,soatthemomentIhavetwo houses.A)didn“tsellB)soldC)haven“tsoldD)wouldsell答案是C)haven “tsold。
高中英语时态总结英语时态是英语语法中的一个重要部分,掌握好英语时态对于英语语法的整体掌握至关重要。
作为学习英语基础中的重点内容,它们可以帮助我们明确一个句子或一段话所描述的动作发生的时间和状态。
下面我们来对高中英语时态总结一下,希望对大家有所帮助。
一、现在时态1. 简单现在时表示现在的状态或行为,或者频繁发生的事情。
基本结构:主语 + 动词原形或第三人称单数形式 + 其他补充例如:My sister and I go to school every day.2. 现在进行时表示现在正在发生的动作,或者表示不长时间的未来。
基本结构:主语 + be 动词 + 现在分词 + 其他补充例如:The children are playing with the ball inthe garden now.3. 现在完成时表示过去完成的动作对现在的影响或状态。
基本结构:主语 + have/has + 过去分词 + 其他补充例如:I have finished my homework, so I can goand play now.4. 现在完成进行时表示开始于过去并且一直持续到现在的动作。
基本结构:主语 + have/has been + 现在分词 + 其他补充例如:I have been learning English for ten years.二、过去时态1. 简单过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作。
基本结构:主语 + 过去式 + 其他补充例如:I studied math for three hours yesterday.2. 过去进行时表示一个过去的持续状态或动作正在进行着,其中常常带有"when"或"during"或"while"等时间状语。
基本结构:主语 + was/were + 现在分词 + 其他补充例如:They were talking on the phone while I was cooking dinner.3. 过去完成时表示在过去某个时间之前已经完成的动作。
常用英语时态总复习按构成和状态可分四类:一般时(单个V原/ V-ed,可借助于助动词do[多形] + V原构成否定句和疑问句)、进行时(借助于助动词be[多形]+V-ing)、将来时(借助于助动词will[多形]+ V原)、完成时(借助于助动词have[多形]+ V-ed)动词时态一:一般现在时①表示经常或习惯性的动作或存在的状态。
②表示主语通常的能力、兴趣爱好、和性格特征。
③表示客观的事实或真理。
④表示按照时刻表或已经计划安排好的将来行为。
(只限于是go, come, leave, arrive, begin, start, take off, stop, be等表示开始或移动意义的词。
)⑤在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,主句用一般将来时(will+动词原形),从句中用一般现在时表将来。
当主语是第三人称时,谓语动词要用第三人称单数形式,加-s/es。
除此之外都用动词原形。
1.He______(be, am, is, are) a teacher at No. 2 Middle School.2.He______(have, has) classes in the afternoon.3.He______(get, gets) up at half past six every morning.4.He always _____(come, comes ) to school on time.5.He ______(study, studies) very hard at his lesson.6.One and two _____(be, is, are) three.7.Blue and yellow _____(make, makes) green.8.The earth _____(move, moves) round the sun.9.I will go there if I ____( be, will be, am, is, are) free tomorrow.10.I will go there when I _____(have, will have, has) time tomorrow.11.He won’t come to the party unless he _____(be, will be, am, is, are) invited.12.I’ll wait here until my mother ____(come, comes, will come) back.13.Please return the book to the library as soon as you ______(finish, finishes, will finish) reading it.14.Once you _____(see, sees, will see) him, you will never forget him.时间状语:--- sometimes/often/usually/always/now/never/seldom/every morning/once a month---动词时态二:一般过去时(提示:使用动词的过去式)表示具体的某个过去时间所发生的动作或所处的状态。
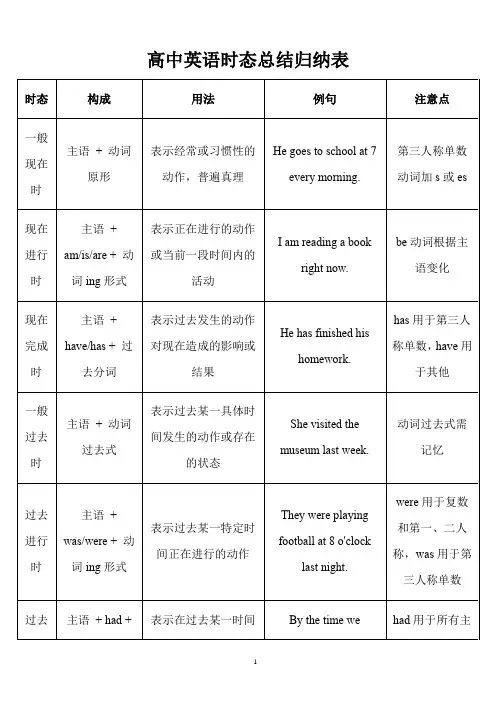
高中英语语法八个时态归纳总结英语语法中的时态是指动词形态变化来表示不同的时间状态。
在英语语法中,共有八个时态,包括一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、过去将来进行时、现在完成时和过去完成时。
这里将对这八个时态进行归纳总结,以帮助高中学生更好地理解和运用这些时态。
1. 一般现在时(Simple Present)一般现在时表示经常性、习惯性的动作或真理,也用于表示主语在现在的状态或职业。
例句:- I eat breakfast every morning.(我每天早上吃早餐。
)- The sun rises in the east.(太阳从东方升起。
)- She works as a teacher.(她是一名教师。
)2. 一般过去时(Simple Past)一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生或存在的动作或状态。
例句:- I studied English yesterday.(昨天我学习了英语。
)- They went to the beach last summer.(他们去年夏天去了海滩。
)- She lived in London for five years.(她在伦敦住了五年。
)3. 一般将来时(Simple Future)一般将来时表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态。
例句:- I will go shopping tomorrow.(我明天要去购物。
)- They are going to visit their grandparents next month.(他们下个月要去看望他们的祖父母。
)- She is going to study abroad after graduation.(她毕业后打算出国留学。
)4. 现在进行时(Present Continuous)现在进行时表示现在正在进行的动作或状态。
例句:- I am reading a book right now.(我现在正在读一本书。
高中英语九大时态总结归纳英语时态是英语语法中非常重要的一个概念,掌握好时态不仅对于学习英语的人来说是至关重要的,而且在日常交流中也非常实用。
在高中英语中,涉及的时态较多,本文将对高中英语九大时态进行总结归纳,以帮助读者更好地掌握和运用这些时态。
一、一般现在时(Simple Present Tense)一般现在时表示经常性的动作、习惯、真理等,常常使用的时间状语包括always, usually, often, sometimes等。
一般现在时的肯定句结构为:“主语 + 动词原形(第三人称单数加-s)+ 其他”,否定句为:“主语 + do not / does not + 动词原形”,疑问句为:“Do / Does + 主语 + 动词原形”。
例句:1. He always studies hard for exams.(他总是努力学习备考。
)2. We don't like to eat spicy food.(我们不喜欢吃辣的食物。
)3. Does she live in New York?(她住在纽约吗?)二、一般过去时(Simple Past Tense)一般过去时用于表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常常使用的时间状语有yesterday, last night, ago等。
一般过去时的肯定句结构为:“主语 + 动词过去式 + 其他”,否定句为:“主语 + did not + 动词原形”,疑问句为:“Did + 主语 + 动词原形”。
1. I visited my grandparents last weekend.(我上周末去看望了我的祖父母。
)2. They didn't go to the cinema yesterday.(他们昨天没去电影院。
)3. Did you finish your homework?(你完成作业了吗?)三、一般将来时(Simple Future Tense)一般将来时表示将来时态,常常使用的时间状语有tomorrow, next week, in the future等。
动词时态复习时态动词是谓语所表示的动作或情况发生时间的各种形式。
英语动词有16种时态,但是常用的只有11种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、过去将来时、现在完成进行、将来进行时、将来完成时时。
1.一般现在时1)经常性或习惯性的动作。
时间状语:every..., sometimes, often等。
I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 每天早上我七点离开家。
2)客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。
The earth moves around the sun. 地球绕太阳转动。
3)表示格言或警句。
My teacher said Pride goes before a fall.老师说过,骄者必败。
4)现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。
例如:Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 安英语写得不错,讲的可不行。
2. 一般过去时1)表示过去某时间发生的事、存在的状态或过反复发生的动作。
a. he saw Mr. Wang yesterday.b. he worked in a factory in 1986.2) 表示过去经常发生的动作也可用“used to “和“would + 动词原形”。
I used to smoke. During the vacation i would swim in the sea. 注:used to表示过去常发生而现在不再发生的动作或存在的状态。
“would + 动词原形”没此含义used to可指过去的状态或情况,would则不能。
would表示反复发生的动作。
如果某一动作没有反复性,就不能用 would,只能用 used to3. 一般将来时1)“will 或shall + 动词原形”表示即将发生的或最近打算进行的事。
2) be going to do 表将来a. 主语的意图,即将做某事。
What are you going to do tomorrow? 明天打算作什么呢?b. 计划,安排要发生的事。
The play is going to be produced next month。
这出戏下月开播。
c. 有迹象要发生的事。
Look at the dark clouds, there is going to be a storm. 看那乌云,快要下雨了。
3)be +to表将来,按计划或正式安排将发生的事。
例如:We are to discuss the report next Saturday.我们下星期六讨论这份报告。
4)be about to,意为马上做某事。
例如:He is about to leave for Beijing. 他马上要去北京。
注意:be about to do 不能与tomorrow, next week 等表示明确将来时的时间状语连用,常与when连用。
【特殊用法】:★一般现在时表将来1)下列动词come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return的一般现在时可以表示将来,主要用来表示在时间上已确定或安排好的事情。
例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. 火车明天上午六点开。
2)以here, there等开始的倒装句,表示动作正在进行。
例如:Here comes the bus. = The bus is coming.3)在时间或条件句中。
例如:When Bill comes, ask him to wait for me. 比尔来后,让他等我。
4)在动词hope, make sure that等的宾语从句中。
例如:I hope they have a nice time next week. 我希望他们下星期玩得开心。
★现在进行时代替将来时1)表示即将发生的或预定中计划好的活动。
例如:Are you staying with us this weekend? 和我们一起度周末好吗? We are leaving soon.我们马上就走。
2)渐变动词,如get, run, grow, become, begin以及瞬间动词die等。
例如:He is dying. 他要死了。
4.现在进行时a. 表示现在(指说话人说话时)正在发生的事情。
例如:We are waiting for you. 我们正在等你。
b. 习惯进行:表示长期的或重复性的动作,说话时动作未必正在进行。
例如:Mr. Green is writing another novel.他在写另一部小说。
(说话时并未在写,只处于写作的状态。
)c. 表示渐变,这样的动词有:get, grow, become, turn, run, go, begin等。
例如:The leaves are turning red. 叶子在变红。
It's getting warmer and warmer. 天越来越热了。
d. 与always, constantly, forever 等词连用,表反复、持续发生的动作或状态,带有说话人的主观色彩。
You are always changing your mind. 你老是改变主意。
★不用进行时的动词1)表示事实状态的动词,如have, belong, possess, cost, owe, exist, include, contain, matter, weigh, measure等。
例如:I have two brothers. 我有两兄弟。
This house belongs to my sister. 这房子是我姐的。
2)表示心理状态的动词,如know, realize, think see, believe, suppose, imagine, agree, recognize, remember, want, need, forget, prefer, mean, understand, love, hate等。
例如:I need your help. 我需要你的帮助。
3)瞬间动词,如accept, receive, complete, finish, give, allow, decide, refuse等。
例如:I accept your advice. 我接受你的劝告。
4)系动词,如seem, remain, lie, see, hear, smell, feel, taste, get, become, turn等。
例如:You seem a little tired. 你看上去有点累。
5. 过去将来时表示从过去的某个时间看来将要发生的动作或存在的状态。
如:The discovery of gold in Australia led thousands to believe that a fortune was to be made (将会发财)。
6. 过去进行时表示过去某一时刻、某一阶段正进行的动作,In 1980 he was studying in a university. He was reading a novel when I came in.与过去进行时连用的时间词:at that moment, at this time yesterday, then….7. 将来进行时表将来某一时刻,某一段时间正在进行的动作。
Eg. I will be sleeping at this time tomorrow.8. 现在完成时1)表示的动作在说话之前已完成,但对现在有影响。
句中没有具体时间状语。
I have seen the film.(表示已经知道电影内容)2)表示的动作开始于过去,持续到现在,也许还会持续下去。
区别:I have learned English for 10 years.(表示过去10年学过,还可能继续学下去)I learned English for 10 years.(表示曾经学过10年)3)现在完成时通常与模糊的时间状语连用。
常用for 和since表示一段时间的状语或never ,so far , now, today, this week (month, year ,), in/during/over+the last/past+时间, up to now, yet , already, recently, lately, ever, just,till/until,in recent years等。
★用于现在完成时的句型1)It is the first / second time.... thatIt is the first time that I have visited the city. 这是我第一次访问这城市。
2)This is +形容词最高级+thatThis is the best film that I've (ever)seen. 这是我看过的最好的电影。
注意:系动词是was时,从句用过去完成时9.过去完成时的用法1)概念:表示过去的过去----|----------|--------|----> 其构成是had +过去分词构成。
那时以前那时现在2)过去发生的两个动作,先发生的用过去完成时With their help I realized that I had been wrong.3)过去某时以前发生的动作或情况He hasn’t finished yet. He didn’t finish yesterday evening. He hadn’t finished by yesterday evening. 3)常用过去完成时的情况①No sooner…than….Hardly…when…“一...就...”No sooner had he begun his speech than he was interrupted②expect,hope,think,want,suppose等动词的过去完成时(或一般时)表示想做而未做的事I had planned to send him a telegram,but I didn’t manage it.4)常用过去完成时的时间主状语by the end of+过去时间; by+过去时间; by the time+过去时间; 过去时间+before10.将来完成时A. 表示在将来某一时刻将完成或在另一个未来的动作发生之前已经完成的动作。