快学scala第六章习题答案
- 格式:doc
- 大小:72.50 KB
- 文档页数:3

快学Scala课后习题答案分享⼀个之前做快学Scala的课后习题(2-21章节,19⽆)的Github链接,我把习题的⽂字写在了每个回答的注释上⾯,这样⽅便⼤家对照着看,省的回过头去对照着pdf看了,如果有做的不对的地⽅希望⼤家给予指正。
举⼀个第⼆章节的例⼦,抛砖引⽟:object charpter02 {/** 2.1* ⼀个数字如果为正数,则它的signum为1;* 如果是负数,则signum为-1;* 如果为0,则signum为0.编写⼀个函数来计算这个值* */def signum(x: Int): Int = {if (x > 0) { 1 }else if (x < 0) { -1 }else { 0 }}def signum(x: Int): Int = if (x > 0) 1 else if (x < 0) -1 else 0;def signum(x: Int) = { if (x > 0) 1 else if (x < 0) -1 else 0 }def signum(x: Int) = if (x > 0) 1 else if (x < 0) -1 else 0/** 2.2* ⼀个空的块表达式{}的值是什么?类型是什么?* */// def checkEmptyBlockType() = {// println({});// println({}.getClass())// }def checkEmptyBlockType { println({}); println({}.getClass()) }/** 2.3* 指出在Scala中何种情况下赋值语句x=y=1是合法的。
* (提⽰:给x找个合适的类型定义)*/def checkAssignLegal { var x: Unit = () println("x's type is: " + x.getClass) var y = 1 x = y = 1}/** 2.4* 针对下列Java循环编写⼀个Scala版本:* for(int i=10;i>=0;i–) System.out.println(i);*/def ScalaForeach { // 1.to(10).reverse.foreach { (i: Int) => Predef.println(i) } // 1.to(10).reverse.foreach { i => Predef println i } // 1.to(10).reverse.foreach { i => println(i) } // 1.to(10).reverse foreach { println _ } (1 to 10 reverse) foreach println}/** 2.5* 编写⼀个过程countdown(n:Int),打印从n到0的数字*/def countdown(n: Int) { n match { case n if n >= 0 => { (0 to n reverse) foreach println } case n if n < 0 => { n to 0 foreach println } }}/** 2.6* 编写⼀个for循环,计算字符串中所有字母的Unicode代码的乘积。

scala练习题库Scala是一种多范式编程语言,它结合了面向对象编程和函数式编程的特性。
通过练习,我们可以更好地理解和掌握Scala的各种语法和用法。
本篇文章将为大家提供一个Scala练习题库,帮助大家进行实战练习,加深对Scala的理解。
1. 变量和数据类型1.1 请编写一个程序,声明两个整型变量并计算它们的和,并打印结果。
1.2 请编写一个程序,声明一个字符串变量并将其内容逆序输出。
2. 函数2.1 请编写一个函数,接收一个整数作为参数,并判断该整数是否为偶数。
如果是偶数,返回true,否则返回false。
2.2 请编写一个函数,接收一个字符串作为参数,并返回该字符串的长度。
3. 条件语句和循环3.1 请编写一个程序,接收一个整数作为参数,判断它是否为正数、负数还是零,并打印相应的提示信息。
3.2 请编写一个程序,打印1到100之间所有的偶数。
4. 集合4.1 请使用列表(List)存储10个整数,并编写程序打印出列表中所有的偶数。
4.2 请使用集合(Set)存储10个不重复的整数,并编写程序打印出集合中的最大值和最小值。
5. 类和对象5.1 请定义一个Person类,包含姓名和年龄两个属性,以及一个打印信息的方法。
5.2 请定义一个Circle类,包含半径属性和计算面积的方法。
6. 模式匹配6.1 请编写一个程序,接收一个整数作为参数,判断该整数是奇数、偶数还是0,并打印相应的提示信息。
6.2 请编写一个程序,接收两个整数和一个操作符作为参数,实现加、减、乘、除四则运算,并打印结果。
通过完成以上练习题,可以加深对Scala编程语言的理解和掌握。
通过实际操作,我们可以更加熟悉Scala的语法和常用功能,并提升自己在Scala编程方面的能力。
希望本篇Scala练习题库能够为大家提供有效的学习工具,帮助大家在不断练习和实践中掌握Scala编程的技巧和规范。
祝愿大家在Scala编程的学习和实践中取得丰硕的成果!。
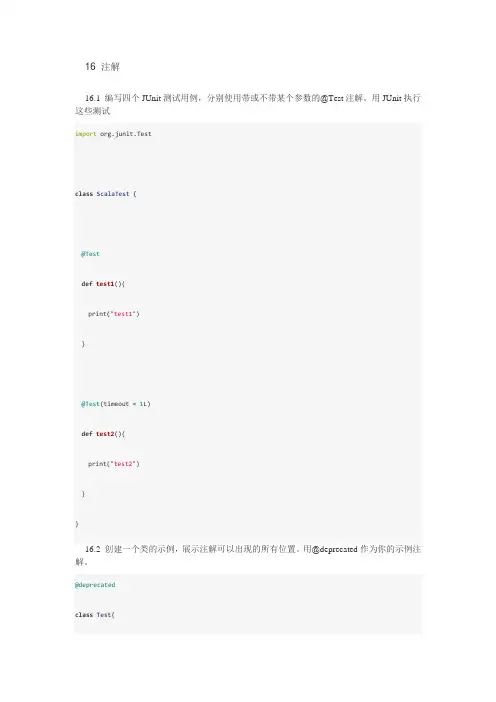
16 注解16.1 编写四个JUnit测试用例,分别使用带或不带某个参数的@Test注解。
用JUnit执行这些测试import org.junit.Testclass ScalaTest {@Testdef test1(){print("test1")}@Test(timeout = 1L)def test2(){print("test2")}}16.2 创建一个类的示例,展示注解可以出现的所有位置。
用@deprecated作为你的示例注解。
@deprecatedclass Test{@deprecatedval t = _;@deprecated(message = "unuse")def hello(){println("hello")}}@deprecatedobject Test extends App{val t = new Test()t.hello()t.t}16.3 Scala类库中的哪些注解用到了元注解@param,@field,@getter,@setter,@beanGetter 或@beanSetter?看Scala注解的源码就OK了16.4 编写一个Scala方法sum,带有可变长度的整型参数,返回所有参数之和。
从Java调用该方法。
import annotation.varargsclass Test{@varargsdef sum(n:Int*)={n.sum}}public class Hello {public static void main(String[] args){Test t = new Test();System.out.println(t.sum(1,2,3));}}16.5 编写一个返回包含某文件所有行的字符串的方法。
从Java调用该方法。
import io.Sourceclass Test{def read()={Source.fromFile("test.txt").mkString}}public class Hello {public static void main(String[] args){Test t = new Test();System.out.println(t.read());}}16.6 编写一个Scala对象,该对象带有一个易失(volatile)的Boolean字段。

快速入门Scala编程语言Scala编程语言是一种多范式编程语言,结合了面向对象编程和函数式编程的特点。
它的语法简洁优雅,适合用于大规模的软件开发项目。
本文将带你快速了解Scala编程语言。
一、Scala的基本语法1. 变量和常量:在Scala中,使用关键字`var`来声明一个可变的变量,使用关键字`val`来声明一个不可变的常量。
例如,`var x = 10`声明一个可变变量x,`val y = 5`声明一个不可变常量y。
2. 数据类型:Scala拥有丰富的数据类型,包括整数类型、浮点数类型、布尔类型、字符类型等。
例如,`Int`表示整数类型,`Double`表示浮点数类型,`Boolean`表示布尔类型,`Char`表示字符类型。
3. 控制流语句:Scala支持常见的控制流语句,如条件判断和循环。
例如,`if-else`语句用于条件判断,`for`循环用于迭代执行操作。
4. 函数:在Scala中,函数是一等公民,可以作为值进行传递和操作。
函数的定义使用关键字`def`,例如`def add(x: Int, y: Int): Int = x + y`定义了一个接受两个整数参数并返回它们的和的函数。
5. 类和对象:Scala是一种面向对象的语言,每个值都是一个对象。
类用于定义对象的蓝图,对象是类的实例。
通过使用`class`关键字定义类,使用`new`关键字来创建对象。
二、函数式编程特性Scala内置了许多函数式编程特性,使得函数的组合和操作更加简洁和灵活。
1. 高阶函数:Scala中的函数可以作为值进行传递和操作,因此可以使用函数作为参数或返回值。
这种函数接受其他函数作为参数或将函数作为返回值的函数称为高阶函数。
高阶函数可以极大地简化代码的编写和理解。
2. 不可变性:Scala鼓励使用不可变的数据结构和变量,在处理数据时避免副作用和数据竞争的发生。
不可变性使得代码更加安全和易于调试。
3. 模式匹配:模式匹配是一种强大的功能,用于根据数据的结构和属性进行分支处理。

9 继承扩展如下的BankAccount类,新类CheckingAccount对每次存款和取款都收取1美元的手续费class BankAccount(initialBalance:Double){ private var balance = initialBalance def deposit(amount:Double) = { balance += amount; balance} def withdraw(amount:Double) = {balance -= amount; balance} }继承语法的利用。
代码如下Scala代码 1.classCheckingAccount(initialBalance:Double) extends BankAccount(initialBalance){ 2. override def deposit(amount: Double): Double = (amount - 1) 3. 4. override def withdraw(amount: Double): Double = (amount + 1) 5.} 扩展前一个练习的BankAccount类,新类SavingsAccount每一个月都有利息产生(earnMonthlyInterest方式被挪用),而且有每一个月三次免手续费的存款或取款。
在earnMonthlyInterest方式中重置交易计数。
Scala代码 1.class SavingsAccount(initialBalance:Double) extends BankAccount(initialBalance){ 2. private var num:Int = _ 3. 4. def earnMonthlyInterest()={ 5. num = 3 6. (1) 7. } 8.9. override def deposit(amount: Double): Double = { 10. num -= 111. if(num < 0) (amount - 1) else (amount) 12. } 13.14. override def withdraw(amount: Double): Double = { 15. num -= 116. if (num < 0) (amount + 1) else (amount) 17. } 18.} 掀开你喜爱的Java或C++教科书,必然会找到用来讲解继承层级的实例,可能是员工,宠物,图形或类似的东西。

快学Scala习题解答—第三章数组相关操作3 数组相关操作3.1 编写⼀段代码。
将a设置为⼀个n个随机整数的数组,要求随机数介于0(包括)和n(不包括)之间random和yield的使⽤Scala代码1. import scala.math.random2.3. def randomArray(n:Int)={4. for(i <- 0 until n) yield (random * n).toInt5. }6.7. println(randomArray(10).mkString(","))3.2 编写⼀个循环,将整数数组中相邻的元素置换。
⽐如,Array(1,2,3,4,5)经过置换后变为Array(2,1,4,3,5)对数组⽅法的使⽤Scala代码1. def reorderArray(arr:Array[Int]):Array[Int]={2. val t = arr.toBuffer3. for(i <- 1 until (t.length,2);tmp = t(i);j <- i - 1 until i){4. t(i) = t(j)5. t(j) = tmp6. }7. t.toArray8. }9.10. println(reorderArray(Array(1,2,3,4,5)).mkString(","))3.3 反复前⼀个练习,只是这⼀次⽣成⼀个新的值交换过的数组。
⽤for/yieldScala代码1. def reorderArray(arr:Array[Int]):Array[Int]={2. (for(i <- 0 until (arr.length,2)) yield if (i + 1 < arr.length) Array(arr(i + 1),arr(i)) else Array(arr(i))).flatten.toArray3. }4.5. println(reorderArray(Array(1,2,3,4,5)).mkString(","))3.4 给定⼀个整数数组,产⽣⼀个新的数组,包括元数组中的全部正值,以原有顺序排列,之后的元素是全部零或负值。

scala课后习题答案Scala课后习题答案Scala是一种多范式编程语言,它结合了面向对象编程和函数式编程的特性。
在学习Scala的过程中,做课后习题是非常重要的,它可以帮助我们巩固所学的知识,提高编程能力。
下面我们来看一些常见的Scala课后习题及其答案。
1. 编写一个函数,计算给定数组的平均值。
```scaladef average(arr: Array[Int]): Double = {if (arr.isEmpty) 0else arr.sum.toDouble / arr.length}```2. 编写一个函数,将给定的字符串列表连接成一个字符串。
```scaladef concatStrings(strings: List[String]): String = {strings.mkString}```3. 编写一个函数,找出给定数组中的最大值和最小值。
```scaladef findMaxAndMin(arr: Array[Int]): (Int, Int) = {(arr.max, arr.min)}```4. 编写一个函数,将给定的整数列表按照奇偶分成两个列表。
```scaladef splitOddEven(nums: List[Int]): (List[Int], List[Int]) = {nums.partition(_ % 2 == 0)}```5. 编写一个递归函数,计算给定数字的阶乘。
```scaladef factorial(n: Int): Int = {if (n <= 1) 1else n * factorial(n - 1)}```以上是一些常见的Scala课后习题及其答案,通过做这些习题可以帮助我们更好地理解和掌握Scala编程语言。
希望大家在学习Scala的过程中能够多加练习,不断提升自己的编程能力。

中国大学慕课spoc第六章C++数组答案1最大值(100分)问题描述先输入一个正整数n(1到20之间),再输入n个整数,计算其中的最大值和相应下标。
输入描述先输入要处理的整数的个数n(1<=n<=20),再输入n个整数,并用空格分开。
输出描述依次输出n个整数中的最大值和相应下标(若多个整数与最大值相同,则从小到大输出相应下标),之间用空格分隔。
输入样例154 6 7 2 5输出样例17 2输入样例254 6 7 2 7输出样例27 2 4#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int main(){int n,i,j,a[20],max;cin>>n;for(i=0;i<n;i++){cin>>a[i];}max=a[0];for(i=0;i<n;i++){if(max<a[i])max=a[i];}cout<<max;for(i=0;i<n;i++){if(a[i]==max){cout<<" "<<i;}}}2峰值个数(100分)问题描述先输入一个正整数n(3到20之间),再输入n个整数,计算其中的峰值个数。
峰值是满足大于或小于左右两个元素的元素,例如12,45,32,0,14,25,62,48,51序列中,峰值有45,0,62,48,峰值个数为4。
输入描述先输入要处理的整数的个数n(3<=n<=20),再输入n个整数,并用空格分开。
输出描述一个整数,表示n个整数中有多少个峰值。
输入样例54 6 7 2 5输出样例2#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int main(){int n,i,a[20],j=0;cin>>n;for(i=0;i<n;i++){cin>>a[i];}for(i=1;i<n-1;i++){if((a[i]>a[i-1]&&a[i]>a[i+1])||(a[i]<a[i-1]&&a[i]<a[i+1]))j++;}cout<<j;}3互为相反数(100分)问题描述先输入一个正整数n(2到20之间),再输入n个数(可重复,可为浮点数),计算其中有多少对互为相反数(仅有符号不同的两数互为相反数)。
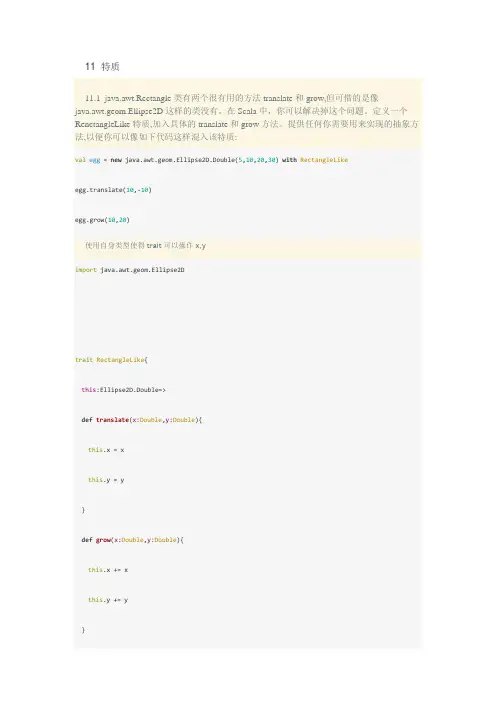
11 特质11.1 java.awt.Rectangle类有两个很有用的方法translate和grow,但可惜的是像java.awt.geom.Ellipse2D这样的类没有。
在Scala中,你可以解决掉这个问题。
定义一个RenctangleLike特质,加入具体的translate和grow方法。
提供任何你需要用来实现的抽象方法,以便你可以像如下代码这样混入该特质:val egg = new java.awt.geom.Ellipse2D.Double(5,10,20,30) with RectangleLikeegg.translate(10,-10)egg.grow(10,20)使用自身类型使得trait可以操作x,yimport java.awt.geom.Ellipse2Dtrait RectangleLike{this:Ellipse2D.Double=>def translate(x:Double,y:Double){this.x = xthis.y = y}def grow(x:Double,y:Double){this.x += xthis.y += y}}object Test extends App{val egg = new Ellipse2D.Double(5,10,20,30) with RectangleLikeprintln("x = " + egg.getX + " y = " + egg.getY)egg.translate(10,-10)println("x = " + egg.getX + " y = " + egg.getY)egg.grow(10,20)println("x = " + egg.getX + " y = " + egg.getY)}11.2 通过把scala.math.Ordered[Point]混入java.awt.Point的方式,定义OrderedPoint类。

6 类6.1 改进5.1节的Counter类,让它不要在Int.MaxValue时变成负数6.2 编写一个BankAccount类,加入deposit和withdraw方法,和一个只读的balance属性6.3 编写一个Time类,加入只读属性hours和minutes,和一个检查某一时刻是否早于另一时刻的方法before(other:Time):Boolean。
Time对象应该以new Time(hrs,min)方式构建。
其中hrs以军用时间格式呈现(介于0和23之间)6.4 重新实现前一个类中的Time类,将内部呈现改成午夜起的分钟数(介于0到24*60-1之间)。
不要改变公有接口。
也就是说,客户端代码不应因你的修改而受影响6.5 创建一个Student类,加入可读写的JavaBeans属性name(类型为String)和id(类型为Long)。
有哪些方法被生产?(用javap查看。
)你可以在Scala中调用JavaBeans的getter和setter方法吗?应该这样做吗?javap -c Student 后显示如下6.6 在5.2节的Person类中提供一个主构造器,将负年龄转换为06.7 编写一个Person类,其主构造器接受一个字符串,该字符串包含名字,空格和姓,如new Person("Fred Smith")。
提供只读属性firstName和lastName。
主构造器参数应该是var,val还是普通参数?为什么?必须为val。
如果为var,则对应的此字符串有get和set方法,而Person中的firstName和lastName为只读的,所以不能重复赋值。
如果为var则会重复赋值而报错6.8 创建一个Car类,以只读属性对应制造商,型号名称,型号年份以及一个可读写的属性用于车牌。
提供四组构造器。
每个构造器fc都要求制造商和型号为必填。
型号年份和车牌可选,如果未填,则型号年份为-1,车牌为空串。

Exercise6_2#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(){// Prompt the user to enter the first numbercout << "Enter an integer: ";int max;cin >> max;int count = 1;// Prompt the user to enter the remaining five numbers for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {cout << "Enter an integer: ";int temp;cin >> temp;if (temp > max) {max = temp;count = 1;}else if (temp == max)count++;}cout << "\n" <<"max is " << max << "\n" <<"the occurrence count is " << count;return 0;}Exercise6_4#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(){double scores[100];double sum = 0;int count = 0;do{cout << "Enter a new score: ";cin >> scores[count];sum += scores[count];}while (scores[count++] >= 0);double average = (sum - scores[count]) / (count - 1);int numOfAbove = 0;int numOfBelow = 0;for (int i = 0; i < count - 1; i++)if (scores[i] >= average)numOfAbove++;elsenumOfBelow++;cout << "Average is " << average << endl;cout << "Number of scores above or equal to the average " << numOfAbove << endl; cout << "Number of scores below the average " << numOfBelow << endl;return 0;}Exercise6_6#include <iostream>#include <cmath>using namespace std;int main(){const int NUM_OF_PRIMES = 50;// Store prime numbersint primeNumbers[NUM_OF_PRIMES];int count = 0; // Count the number of prime numbersint number = 2; // A number to be tested for primenessbool isPrime = true; // Is the current number prime?cout << "The first 50 prime numbers are \n";// Repeatedly find prime numberswhile (count < NUM_OF_PRIMES){// Assume the number is primeisPrime = true;// Test if number is primefor (int i = 0; i < count && primeNumbers[i] <= sqrt(1.0 * number); i++) {//If true, the number is not primeif (number % primeNumbers[i] == 0){// Set isPrime to false, if the number is not primeisPrime = false;break; // Exit the for loop}}// Print the prime number and increase the countif (isPrime){primeNumbers[count] = number;count++; // Increase the countif (count % 10 == 0){// Print the number and advance to the new linecout << number << endl;}elsecout << number << "\t";}// Check if the next number is primenumber++;}return 0;}Exercise6_8#include <iostream>#include <cmath>using namespace std;int average(int array[], int size) {int sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)sum += array[i];return sum / size;}double average(double array[], int size) { double sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)sum += array[i];return sum / size;}int main(){int list1[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};double list2[] = {5.0, 4.4, 1.9, 2.9, 3.4, 3.5};cout << average(list1, 6) << endl;cout << average(list2, 6) << endl;return 0;}Exercise6_10#include <iostream>#include <cmath>using namespace std;int minIndex(int list[], int size){int min = list[0];int minIndex = 0;for (int i = 1; i < size; i++)if (min > list[i]){min = list[i];minIndex = i;}return minIndex;}int main(){int list[] ={1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 100, 2, -22};cout << "The index of the min is " << minIndex(list, 8) << endl;return 0;}Exercise6_12#include <iostream>using namespace std;void reverse(int list[], int size){for (int i = 0, j = size - 1; i < size / 2; i++, j--){int temp = list[i];list[i] = list[j];list[j] = temp;}}int main(){int myList[] ={1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8};reverse(myList, 8);for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)cout << myList[i] << " ";return 0;}Exercise6_14#include <iostream>#include "LinearSearch.h"#include "BinarySearch.h"#include "SelectionSort.h"using namespace std;int main(){int list[100000];for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++){list[i] = rand();}int key = rand();long startTime = time(0);cout << linearSearch(list, key, 100000) << endl;long endTime = time(0);cout << "End time: " << endTime << endl;cout << "Start time: " << startTime << endl;long executionTime = endTime - startTime;cout << "Execution time for linear search is " << executionTime << endl; selectionSort(list, 100000);startTime = time(0);cout << binarySearch(list, key, 100000) << endl;endTime = time(0);executionTime = endTime - startTime;cout << "Execution time for binary search is " << executionTime << endl;return 0;}Exercise6_16#include <iostream>#include "LinearSearch.h"#include "BinarySearch.h"#include "SelectionSort.h"using namespace std;/** The method for printing numbers */void printList(double list[], int size){for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)cout << list[i] << " ";cout << endl;}void bubbleSort(double list[], int size) {bool changed = true;do{changed = false;for (int j = 0; j < size - 1; j++)if (list[j] > list[j + 1]){//swap list[j] wiht list[j+1]double temp = list[j];list[j] = list[j + 1];list[j + 1] = temp;changed = true;}}while (changed);}int main(){// Initialize the listdouble myList[] ={5.0, 4.4, 1.9, 2.9, 3.4, 3.5};// Print the original listcout << "My list before sort is: "; printList(myList, 6);// Sort the listbubbleSort(myList, 6);// Print the sorted listcout << "\nMy list after sort is: " << endl; printList(myList, 6);return 0;}Exercise6_18#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(){int m[4] [4] ={{1, 2, 4, 5},{6, 7, 8, 9},{10, 11, 12, 13},{14, 15, 16, 17}};int sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)sum += m[i] [i];cout << "Sum of diagonal is " << sum << endl;return 0;}Exercise6_20#include <iostream>using namespace std;/** The method for sorting the numbers */void sortAndKeepIndex(int list[], int indexList[], int size) { int currentMax;int currentMaxIndex;// Initialize indexListfor (int i = 0; i < size; i++)indexList[i] = i;for (int i = size - 1; i >= 1; i--) {// Find the maximum in the list[0..i]currentMax = list[i];currentMaxIndex = i;for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) {if (currentMax < list[j]) {currentMax = list[j];currentMaxIndex = j;}}// Swap list[i] with list[currentMaxIndex] if necessary;if (currentMaxIndex != i) {list[currentMaxIndex] = list[i];list[i] = currentMax;// Swap the index in indexList tooint temp = indexList[i];indexList[i] = indexList[currentMaxIndex];indexList[currentMaxIndex] = temp;}}}int main(){const int NUMBER_OF_WORKERS = 8;double workHours[NUMBER_OF_WORKERS][7] = {{2, 4, 3, 4, 5, 8, 8},{7, 3, 4, 3, 3, 4, 4},{3, 3, 4, 3, 3, 2, 2},{9, 3, 4, 7, 3, 4, 1},{3, 5, 4, 3, 6, 3, 8},{3, 4, 4, 6, 3, 4, 4},{3, 7, 4, 8, 3, 8, 4},{6, 3, 5, 9, 2, 7, 9}};// Create an array to store total weekly hoursint weeklyHours[NUMBER_OF_WORKERS] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0};for (int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_WORKERS; i++)for (int j = 0; j < 7; j++)weeklyHours[i] += workHours[i][j];int indexList[NUMBER_OF_WORKERS];// Sort weeklyHourssortAndKeepIndex(weeklyHours, indexList, NUMBER_OF_WORKERS);// Display resultfor (int i = NUMBER_OF_WORKERS - 1; i >= 0; i--)cout << "Employee " << indexList[i] << ": " <<weeklyHours[i] << endl;return 0;}Exercise6_22#include <iostream>using namespace std;const int COLUMN_SIZE = 5;/** The method for multiplying two matrices */void multiplyMatrix(int a[] [COLUMN_SIZE], int b[] [COLUMN_SIZE], int result[] [COLUMN_SIZE], int rowSize){for (int i = 0; i < COLUMN_SIZE; i++)for (int j = 0; j < COLUMN_SIZE; j++)for (int k = 0; k < COLUMN_SIZE; k++)result[i] [j] += a[i] [k] * b[k] [j];}/** Print result */void printResult(int m1[] [COLUMN_SIZE], int m2[] [COLUMN_SIZE], int m3[] [COLUMN_SIZE], char op, int rowSize){for (int i = 0; i < rowSize; i++){for (int j = 0; j < COLUMN_SIZE; j++)cout << " " << m1[i] [j];if (i == COLUMN_SIZE / 2)cout << " " << op << " ";elsecout << " ";for (int j = 0; j < COLUMN_SIZE; j++)cout << " " << m2[i] [j];if (i == COLUMN_SIZE / 2)cout << " = ";elsecout << " ";for (int j = 0; j < COLUMN_SIZE; j++)cout << " " << m3[i] [j];cout << endl;}}int main(){// Create two matrices as two dimensional arraysint matrix1[5] [5];int matrix2[5] [5];int result[5] [5];// Assign random values to matrix1 and matrix2for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++){matrix1[i] [j] = rand();matrix2[i] [j] = rand();}multiplyMatrix(matrix1, matrix2, result, 5);cout << "The multiplication of the matrices is " << endl; printResult(matrix1, matrix2, result, '*', 5);}Exercise6_24#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(){int board[8] [8];for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++){for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++){board[i] [j] = rand() % 2;cout << board[i] [j];}cout << endl;}// Check rowsfor (int i = 0; i < 8; i++){bool same = true;for (int j = 1; j < 8; j++){if (board[i] [0] != board[i] [j]){same = false; break;}}if (same) cout << "All " << board[i] [0] << "'s on row " << i << endl;}// Check columnsfor (int j = 0; j < 8; j++){bool same = true;for (int i = 1; i < 8; i++){if (board[0] [j] != board[i] [j]){same = false; break;}}if (same) cout << "All " << board[0] [j] << "'s on column " << j << endl; }// Check major diagonalbool same = true;for (int i = 1; i < 8; i++){if (board[0] [0] == board[i] [i]){same = false; break;}}if (same) cout << "All " << board[0] [0] << "'s on major diagonal" << endl;// Check subdiagonalsame = true;for (int i = 1; i < 8; i++){if (board[0] [7] == board[i] [7 - i]){same = false; break;}}if (same) cout << "All " << board[0] [0] << "'s on subdiagonal" << endl;return 0;}Exercise6_26#include <iostream>#include <cmath>using namespace std;int lcm(int number1, int number2);int pow(int a, int b);int getPrimeFactors(int number, int table[][2]);int main(){// Enter two integersint number1;cout << "Enter the first integer: ";cin >> number1;int number2;cout << "Enter the second integer: ";cin >> number2;cout << "The LCM for " << number1 << " and " << number2 << " is " << lcm(number1, number2) << endl;}int lcm(int number1, int number2){int table1[100][2];for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)table1[i][j] = 0;int i1 = getPrimeFactors(number1, table1);int table2[100][2];for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)table2[i][j] = 0;int i2 = getPrimeFactors(number2, table2);int result = 1;int i = 0;int j = 0;while (i < i1 && j < i2){if (table1[i] [0] < table2[j] [0]){result *= pow(table1[i] [0], table1[i] [1]);i++;}else if (table1[i] [0] == table2[j] [0]){result *= pow(table1[i] [0], max(table1[i] [1], table2[j] [1]));i++;j++;}else{result *= pow(table2[j] [0], table2[j] [1]);j++;}}while (i < i1){result *= pow(table1[i] [0], table1[i] [1]);i++;}while (j < i2){result *= pow(table2[j] [0], table2[j] [1]);j++;}return result;}int pow(int a, int b){int result = 1;for (int i = 1; i <= b; i++)result *= a;return result;}int getPrimeFactors(int number, int table[][2]) {int i = 0;int factor = 2;while (factor <= number){if (number % factor == 0){table[i] [0] = factor;while (number % factor == 0){number = number / factor;table[i] [1] ++;}i++;}else{factor++;}}return i;}。
scala编程练习题Scala是一种功能强大的编程语言,其结合了面向对象编程和函数式编程的特性。
对于学习和掌握该语言,进行编程练习是非常重要的。
在本文中,我们将介绍一些Scala编程练习题,旨在帮助读者提高他们的Scala编程技能。
练习题一:求列表的和编写一个函数,接受一个整数列表作为参数,然后返回该列表所有元素的和。
解答:```scaladef sumList(list: List[Int]): Int = {list.sum}```练习题二:计算列表中的偶数个数编写一个函数,接受一个整数列表作为参数,然后返回该列表中偶数的个数。
解答:```scaladef countEven(list: List[Int]): Int = {list.count(_ % 2 == 0)}```练习题三:查找列表中的最大值编写一个函数,接受一个整数列表作为参数,然后返回该列表中的最大值。
解答:```scaladef findMax(list: List[Int]): Int = {list.max}```练习题四:翻转列表编写一个函数,接受一个整数列表作为参数,然后返回一个翻转后的列表。
解答:```scaladef reverseList(list: List[Int]): List[Int] = {list.reverse}```练习题五:计算阶乘编写一个函数,接受一个正整数作为参数,然后返回该数的阶乘。
解答:```scaladef factorial(n: Int): Int = {if (n == 0) 1 else n * factorial(n-1)}```练习题六:判断字符串是否是回文编写一个函数,接受一个字符串作为参数,然后判断该字符串是否是回文。
解答:```scaladef isPalindrome(str: String): Boolean = {str == str.reverse}```以上是一些Scala编程练习题的示例解答。
8 包和引入8.1 编写示例程序,展示为什么package com.horstmann.impatient不同于package compackage horstmannpackage impatient8.2 编写一段让你的Scala朋友们感到困惑的代码,使用一个不在顶部的com包这样可以吗?8.3 编写一个包random,加入函数nextInt():Int,nextDouble():Double,setSeed(seed:Int):Unit。
生成随机数的算法采用线性同余生成器:后值= (前值* a + b)mod 2^n其中,a = 1664525,b=1013904223,n = 32,前值的初始值为seed8.4 在你看来Scala的设计者为什么要提供package object语法而不是简单的让你将函数和变量添加到包中呢?JVM不支持。
8.5 private[com] def giveRaise(rate:Double)的含义是什么?有用吗?除了com包可访问,其他包都不能访问。
8.6 编写一段程序,将Java哈希映射中的所有元素拷贝到Scala哈希映射。
用引入语句重命名这两个类。
8.7 在前一个练习中,将所有引入语句移动到尽可能小的作用域里8.8 以下代码的作用是什么?这是个好主意吗?import java._import javax._导入java和javax下的所有类。
而java和javax下是没有类的。
所以此代码无用8.9 编写一段程序,引入ng.System类,从系统属性读取用户名,从Console对象读取一个密码,如果密码不是"secret",则在标准错误流中打印一个消息;如果密码是"secret",则在标准输出流中打印一个问候消息。
不要使用任何其他引入,也不要使用任何限定词(带句点的那种)8.10 除了StringBuilder,还有哪些ng的成员是被scala包覆盖的?直接比对ng下的类和scala包下的类即可。
7 对象编写一个Conversions对象,加入inchesToCentimeters,gallonsToLiters和milesToKilometers方法Scala代码1.objectConversions{2.definchesToCentimeters(){}3.defgallonsToLiters(){}4.defmilesToKilometers(){}5.}前一个练习不是很面向对象。
提供一个通用的超类UnitConversion并定义扩展该超类的InchesToCentimeters,GallonsToLiters和MilesToKilometers对象Scala代码1.abstractclassUnitConversion{2.3.definchesToCentimeters(){}4.defgallonsToLiters(){}5.defmilesToKilometers(){}6.7.}8.9.objectInchesToCentimetersextendsUnitConversion{10.overridedefinchesToCentimeters(){}11.}12.13.objectGallonsToLitersextendsUnitConversion{14.overridedefgallonsToLiters(){}15.}16.17.objectMilesToKilometersextendsUnitConversion{18.overridedefmilesToKilometers(){}19.}定义一个扩展自的Origin对象。
为什么说这实际上不是个好主意(仔细看Point类的方法)Point中的getLocation方法返回的是Point对象,如果想返回Origin对象,需要Origin类才行Scala代码1.objectOriginextendsPointwithApp{2.3.overridedefgetLocation:Point=4.5.(2,3)6.println7.8.}定义一个Point类和一个伴生对象,使得我们可以不用new而直接用Point(3,4)来构造Point实例apply方法的使用Scala代码1.classPoint(x:Int,y:Int){2.overridedeftoString:String="x="+x+"y="+y3.}4.5.objectPointextendsApp{6.defapply(x:Int,y:Int)={7.newPoint(x,y)8.}9.10.valp=Point(1,2)11.println(p)12.}编写一个Scala应用程序,使用App特质,以反序打印命令行参数,用空格隔开。
第六章数据绑定技术6.5 课后习题6.5.1作业题6-1用C#编写一个方法,求1000!。
用javascript调用该方法并输出结果,同时绑定该方法到Label控件并显示结果,如图30所示。
(提示,因1000!结果太大,可采用BigInteger来求解)图30 数据绑定求1000!6-2 采用SqlDataSource控件,使DropDownList控件只显示College数据库Student 表中的男生姓名,如图31所示。
选中某男生后,在GridView控件中显示该生的详细资料,如图32所示。
图31 选中某男生图32 显示该男生详细信息见“课后习题源代码”文件夹下的“homework6-1——homework6-2”6.5.2思考题1.<%#%>、<%=%>与<%%>有什么区别?<%#数据源%>绑定数据源必须调用Page.DataBind()方法。
<%=数据源%>绑定数据源不需要调用Page.DataBind()方法。
<%--注释内容--%>是服务器端注释,允许开发人员在应用程序文件的任何部分(除了<script>代码块内部)嵌入代码注释。
服务器端注释元素的开始标记和结束标记之间的任何内容,不管是代码还是文本,都不会在服务器上进行处理或呈现在结果页上。
例如,使用服务器端注释对TextBox控件进行注释,代码如下:<%--<asp:TextBox ID="TextBox1" runat="server"></asp:TextBox>--%>执行后,浏览器上将不显示此文本框。
7 对象
7.1 编写一个Conversions对象,加入inchesToCentimeters,gallonsToLiters和milesToKilometers方法
7.2 前一个练习不是很面向对象。
提供一个通用的超类UnitConversion并定义扩展该超类的InchesToCentimeters,GallonsToLiters和MilesToKilometers对象
7.3 定义一个扩展自java.awt.Point的Origin对象。
为什么说这实际上不是个好主意?(仔细看P oint类的方法)
7.4 定义一个P oint类和一个伴生对象,使得我们可以不用new而直接用Point(3,4)来构造P oint实例
7.5 编写一个Scala应用程序,使用App特质,以反序打印命令行参数,用空格隔开。
举例来说,scala Reverse Hello World应该打印W orld H ello
7.6 编写一个扑克牌4种花色的枚举,让其toString方法分别返回♣,♦,♥,♠
7.7 实现一个函数,检查某张牌的花色是否为红色
7.8 编写一个枚举,描述RGB立方体的8个角。
ID使用颜色值(例如:红色是0xff0000)。