电子商务名词中英文对照
- 格式:doc
- 大小:16.00 KB
- 文档页数:4

电子商务英文名词解释————————————————————————————————作者:————————————————————————————————日期:1.e-commerce :The process of buying, selling, or exchanging products, services, or information via computer;2.e-business:A broader definition of EC that includes not just the buying and selling of goods and services, but also servicing customers, collaborating with business partners, and conducting electronic transactions within an organization;3.brick-and-mortar (old economy) organizations:Old-economy organizations (corporations) that perform their primary business off-line, selling physical products by means of physical agents;4.virtual (pure-play) organizations:Organizations that conduct their business activities solely online;5.click-and-mortar (click-and-brick) organizations:Organizations that conduct some e-commerce activities, usually as an additional marketing channel;6.electronic market (e-marketplace):An online marketplace where buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods, services, money, or information;7.Interorganizational information systems (IOSs):Communications systems that allow routine transaction processing and information flow between two or more organizations;8.Intraorganizational information systems:Communication systems that enable e-commerce activities to go on within individual organizations;9.intranet:An internal corporate or government network that uses Internet tools, such as Web browsers, and Internet protocols;10.extranet:A network that uses the Internet to link multiple intranets;11.business-to-business (B2B):E-commerce model in which all of the participants are businesses or other organizations;12.business-to-consumer (B2C):E-commerce model in which businesses sell to individual shoppers;13.business-to-business-to-consumer (B2B2C):E-commerce model in which a business provides some product or service to a client business that maintains its own customers;14.consumer-to-business (C2B):E-commerce model in which individuals use the Internet to sell products or services to organizations or individuals who seek sellers to bid on products or services they need;15.e-tailing:Online retailing, usually B2C;16.intrabusiness EC:E-commerce category that includes all internal organizational activities that involve the exchange of goods, services, or information among various units and individuals in an organization;17.business-to-employees (B2E):E-commerce model in which an organization delivers services, information, or products to its individual employees;18.consumer-to-consumer(C2C):E-commerce model in which consumers sell directly to other consumers;19.collaborative commerce (c-commerce):E-commerce model in which individuals or groups communicate or collaborate online;20.e-learning:The online delivery of information for purposes of training or education;21.e-government:E-commerce model in which a government entity buys or provides goods, services, or information from or to businesses or individual citizens;22.social computing:An approach aimed at making the human-computer interface more natural;23.Web 2.0:The second-generation of Internet-based services that let people collaborate and share information online in new ways, such as social networking sites, wikis, communication tools, and folksonomies;24.social network:A category of Internet applications that help connect friends, business partners, or individuals with specific interests by providing free services such as photo presentations, e-mail, blogging, and so on using a variety of tools;25.social network service (SNS):A service that builds online communities by providing an online space for people to build free homepages and that provides basic communication and support tools for conducting different activities in the social network;26.social networking:The creation or sponsoring of a social network service and any activity, such as blogging, done in a social network ;27.enterprise-oriented networks:Social networks whose primary objective is to facilitate business;28.virtual world:A user-defined world in which people can interact, play, and do business. The most publicized virtual world is Second Life;29.digital economy:An economy that is based on digital technologies, including digital communication networks, computers, software, and other related information technologies; also called the Internet economy, the new economy, or the Web economy;30.digital enterprise:A new business model that uses IT in a fundamental way to accomplish one or more of three basic objectives: reach and engage customers more effectively, boost employee productivity, and improve operating efficiency. It uses converged communication and computing technology in a way that improves business processes;31.corporate portal:A major gateway through which employees, business partners, and the public can enter a corporate Web site;32.business model:A method of doing business by which a company can generate revenue to sustain itself;33.revenue model:sales,transaction fees,subscription fees,advertising fees,affiliate fees,other revenue sources.1.e-marketplace:An online market, usually B2B, in which buyers and sellers exchange goods or services; the three types of e-marketplaces are private, public, and consortia;2.marketspace:A marketplace in which sellers and buyers exchange goods and services for money (or for other goods and services), but do so electronically;3.digital products:Goods that can be transformed to digital format and delivered over the Internet;4.front end:The portion of an e-seller’s business processes through which customers interact, including the seller’s portal, electronic catalogs, a shopping cart, a search engine, and a payment gateway;5.back end:The activities that support online order fulfillment, inventory management, purchasing from suppliers, payment processing, packaging, and delivery;6.intermediary:A third party that operates between sellers and buyers;7.sell-side e-marketplace:A private e-marketplace in which one company sells either standard and/or customized products to qualified companies;8.buy-side e-marketplace:A private e-marketplace in which one company makes purchases from invited suppliers;9.storefront:A single company’s Web site where products or services are sold;10.e-mall (online mall):An online shopping center where many online stores are located;11.Web portal:A single point of access, through a Web browser, to critical business information located inside and outside (via Internet) of an organization;Types of portals:commercial portal,corporate portals,publishing portals,personal portals12.mobile portal:A portal accessible via a mobile device;13.voice portal:A portal accessed by telephone or cell phone;mediaries:Electronic intermediaries that provide and/or control information flow in cyberspace, often aggregating information and selling it to others;15.e-distributor:An e-commerce intermediary that connects manufacturers with business buyers (customers) by aggregating the catalogs of many manufacturers in one place—the intermediary’s Web site;16.electronic catalogs (e-catalogs):The presentation of product information in an electronic form; the backbone of most e-selling sites;17.enterprise search:The practice of identifying and enabling specific content across the enterprise to beindexed, searched, and displayed to authorized users;18.desktop search:Search tools that search the contents of a user’s or organization’s computer files, rather than searching the Internet;19.search engine:A computer program that can access databases of Internet resources, search for specific information or keywords, and report the results;20.electronic shopping cart:An order-processing technology that allows customers to accumulate items they wish to buy while they continue to shop;21.auction:A competitive process in which a seller solicits consecutive bids from buyers (forward auctions) ora buyer solicits bids from sellers (backward auctions). Prices are determined dynamically by the bids;22.electronic auctions (e-auctions):Auctions conducted online;23.forward auction:An auction in which a seller entertains bids from buyers. Bidders increase price sequentially;24.reverse auction (bidding or tendering system):Auction in which the buyer places an item for bid (tender) ona request for quote (RFQ) system, potential suppliers bid on the job, with the price reducing sequentially, and the lowest bid wins; primarily a B2B or G2B mechanism;25.“name-your-own-price”model:Auction model in which a would-be buyer specifies the price (and other terms) he or she is willing to pay to any willing and able seller. It is a C2B model that was pioneered by ;26.double auction:An auction in which multiple buyers and their bidding prices are matched with multiple sellers and their asking prices, considering the quantities on both sides;27.bartering:The exchange of goods and services;28.e-bartering (electronic bartering):Bartering conducted online, usually in a bartering exchange;29.bartering exchange:A marketplace in which an intermediary arranges barter transactions;30.blog:A personal Web site that is open to the public to read and to interact with; dedicated to specific topics or issues;31.vlog (or video blog):A blog with video content;32.micro-blogging:A form of blogging that allows users to write messages (usually up to 140 characters) and publish them, either to be viewed by anyone or by a restricted group that can be chosen by the user;33.Twitter:A free micro-blogging service that allows its users to send and read other users’updates;34.tweets:T ext-based posts up to 140 characters in length posted to Twitter;35.tag:A nonhierarchical keyword or term assigned to a piece of information ;36.folksonomy :The practice and method of collaboratively creating, classifying, and managing tags to annotate and categorize content;37.social bookmarking:Web service for sharing Internet bookmarks. The sites are a popular way to store, classify, share, and search links through the practice of folksonomy techniques on the Internet and intranets;38.wiki (wikilog):A blog that allows everyone to participate as a peer; anyone may add, delete, or change content;39.avatars:Animated computer characters that exhibit humanlike movements and behaviors;40.customization:Creation of a product or service according to the buyer’s specifications;41.personalization:The ability to tailor a product, service, or Web content to specific user preferences;42.disintermediation:Elimination of intermediaries between sellers and buyers;43.reintermediation:Disintermediated entities or newcomers take on new intermediary roles;44.mass customization:A method that enables manufacturers to create specific products for each customer based on the customer’s exact needs;45.build-to-order (pull system):A manufacturing process that starts with an order (usually customized). Once the order is paid for, the vendor starts to fulfill it;1.direct marketing:Broadly, marketing that takes place without intermediaries between manufacturers and buyers; in the context of this book, marketing done online between any seller and buyer;2.virtual (pure-play) e-tailers:Firms that sell directly to consumers over the Internet without maintaining a physical sales channel;3.click-and-mortar retailers:Brick-and-mortar retailers that offer a transactional Web site from which to conduct business;4.brick-and-mortar retailers:Retailers who do business in the non-Internet, physical world in traditional brick-and-mortar stores;5.multichannel business model:A business model where a company sells in multiple marketing channels simultaneously;6.electronic(online) banking or e-banking:various banking activities conducted from home or the road using an internet connection;also known as cyberbanking,birtual banking,online banking ,and home banking7.birtual banks:have no physical location;only conduct online transactions8.shopping portals:gateways to e-storefronts and e-malls;may be comprehensive or niche oriented9.shopping robots:tools that scout the web on behalf of consumers who specify search criteria10.disintermediation:the removal of organizations or business process layers responsible for certain intermediary steps in a given supply chain11.reintermediation:the process whereby intermediaries take on new intermediary roles12.cybermediation(electronic intermediation):the use of software(intelligent) agents to facilitate intermediation13.channel conflict:situation in which an online marketing channel upsets the taditional channels due to real or perceived damage from competitionproduct brokering: Deciding what product to buymerchant brokering: Deciding from whom (from what merchant) to buy a productmarket segmentation:The process of dividing a consumer market into logical groups for conducting marketing research and analyzing personal informationone-to-one marketing (relationship marketing): Marketing that treats each customer in a unique waypersonalization:The matching of services, products, and advertising content with individual consumers and their preferencesuser profile:The requirements, preferences, behaviors, and demographic traits of a particular customercookie:A data file that is placed on a user’s hard drive by a remote Web server, frequently without disclosure or the user’s consent, which collects information about the user’s activities at a sitebehavioral targeting:Targeting that us es information collected about an individual’s Web-browsing behavior, such as the pages they have visited or the searches they have made, to select an advertisement to display to that individualcollaborative filtering:A market research and personalization method that uses customer data to predict, based on formulas derived from behavioral sciences, what other products or services a customer may enjoy; predictions can be extended to other customers with similar profilese-loyalty:Customer loyalty to an e-tailer or loyalty programs delivered online or supported electronicallyinteractive marketing: Online marketing, facilitated by the Internet, by which marketers and advertisers can interact directly with customers, and consumers can interact with advertisers/vendorsCPM (cost per thousand impressions) : The fee an advertiser pays for each 1,000 times a page with a banner ad is shownadvertising networks: Specialized firms that offer customized Web advertising, such as brokering ads and targeting ads to select groups of consumersbanner: On a Web page, a graphic advertising display linked to the advertiser’s Web pagespot buying: The purchase of goods and services as they are needed, usually at prevailing market prices strategic (systematic) sourcing:Purchases involving long-term contracts that usually are based on private negotiations between sellers and buyersdirect materials:Materials used in the production of a product (e.g., steel in a car or paper in a book)indirect materials:Materials used to support production (e.g., office supplies or light bulbs)MRO (maintenance, repair, and operation) :Indirect materials used in activities that support productionvertical marketplaces:Markets that deal with one industry or industry segment (e.g., steel, chemicals)horizontal marketplaces:Markets that concentrate on a service, material, or a product that is used in all types of industriesprocurement management:The planning, organizing, and coordinating of all the activities relating to purchasing goods and services needed to accomplish the organization’s missionmaverick buying:Unplanned purchases of items needed quickly, often at non–pre-negotiated higher prices e-procurement:The electronic acquisition of goods and services for organizationsinternal procurement marketplace:The aggregated catalogs of all approved suppliers combined into a single internal electronic catalogbartering exchange:An intermediary that links parties in a barter; a company submits its surplus to the exchange and receives points of credit, which can be used to buy the items that the company needs from other exchange participantsdesktop purchasing:Direct purchasing from internal marketplaces without the approval of supervisors and without the intervention of a procurement departmentgroup purchasing:The aggregation of orders from several buyers into volume purchases so that better prices can be negotiatedconsortium trading exchange (CTE) :An exchange formed and operated by a group of major companies in an industry to provide industry-wide transaction servicespartner relationship management (PRM) :Business strategy that focuses on providing comprehensive quality service to business partnerssupply chain:The flow of materials, information, money, and services from raw material suppliers through factories and warehouses to the end customerssupply chain:A supply chain that is managed electronically, usually with Web technologiesprocurement:The process made up of a range of activities by which an organization obtains or gains access to the resources (materials, skills, capabilities, facilities) they require to undertake their core business activities supply chain management (SCM) :A complex process that requires the coordination of many activities so that the shipment of goods and services from supplier right through to customer is done efficiently and effectively for all parties concerned. SCM aims to minimize inventory levels, optimize production and increase throughput, decrease manufacturing time, optimize logistics and distribution, streamline order fulfillment, and overall reduce the costs associated with these activitiese-supply chain management (e-SCM) :The collaborative use of technology to improve the operations of supply chain activities as well as the management of supply chainsbullwhip effect:Erratic shifts in order up and down supply chainsradio frequency identification (RFID) :Tags that can be attached to or embedded in objects, animals, or humans and use radio waves to communicate with a reader for the purpose of uniquely identifying the object or transmitting data and/or storing information about the objectcorporate (enterprise) portal:A gateway for entering a corporate Web site, enabling communication,collaboration, and access to company informationinformation portals:Portals that store data and enable users to navigate and query the datacollaborative portals:Portals that allow collaborationgroupware:Software products that support groups of people who share common tasks or goals and collaborate on their accomplishmentvirtual team:A group of employees using information and communications technologies to collaborate from different work basesvirtual meetings:Online meetings whose members are in different locations, even in different countriesgroup decision support system (GDSS) :An interactive computer-based system that facilitates the solution of semistructured and unstructured problems by a group of decision makersernment-to-citizens (G2C):E-government category that includes all the interactions between a government and its citizens;ernment-to-business (G2B):E-government category that includes interactions between governments and businesses;ernment-to-government (G2G):E-government category that includes activities within government units and those between governments;ernment-to-employees (G2E):E-government category that includes activities and services between government units and their employees;5.mobile government (m-government):The wireless implementation of e-government mostly to citizens but also to business;6.e-learning:The online delivery of information for purposes of education, training, or knowledge management;7.distance learning:Formal education that takes place off campus, usually, but not always, through online resources;8.virtual university:An online university from which students take classes from home or other offsite locations, usually via the Internet;tainment:The combination of education and entertainment, often through games;10.online publishing:The electronic delivery of newspapers, magazines, books, news, music, videos, and other digitizable information over the Internet;11.e-book:A book in digital form that can be read on a computer screen or on a special device;12.knowledge management (KM):The process of capturing or creating knowledge, storing it, updating it constantly, disseminating it, and using it whenever necessary;13.consumer-to-consumer (C2C):E-commerce model in which consumers sell directly to other consumers;14.peer-to-peer (P2P):Applications that use direct communications between computers (peers) to share resources, rather than relying on a centralized server as the conduit between client devices;1.short message service (SMS):A service that supports the sending and receiving of short text messages on mobile phones;2.multimedia messaging service (MMS):The emerging generation of wireless messaging; MMS is able to deliver rich media;3.interactive voice response (IVR):A voice system that enables users to request and receive information and to enter and change data through a telephone to a computerized system;4.personal area network (PAN):A wireless telecommunications network for device-to-device connections within a very short range;5.Bluetooth:A set of telecommunications standards that enables wireless devices to communicate with eachother over short distances;6.wireless local area network (WLAN):A telecommunications network that enables users to make short-range wireless connections to the Internet or another network;7.Wi-Fi (wireless fidelity):The common name used to describe the IEEE 802.11 standard used on most WLANs;8.WiMax:A wireless standard (IEEE 802.16) for making broadband network connections over a medium-size area such as a city;9.wireless wide area network (WWAN):A telecommunications network that offers wireless coverage over a large geographical area, typically over a cellular phone network;10.location-based m-commerce (l-commerce):Delivery of m-commerce transactions to individuals in a specific location, at a specific time;work-based positioning:Relies on base stations to find the location of a mobile device sending a signal or sensed by the network;12.terminal-based positioning:Calculating the location of a mobile device from signals sent by the device to base stations;13.global positioning system (GPS):A worldwide satellite-based tracking system that enables users to determine their position anywhere on the earth;14.geographical information system (GIS):A computer system capable of integrating, storing, editing, analyzing, sharing, and displaying geographically-referenced (spatial) information;15.pervasive computing:Invisible, everywhere computing; computing capabilities embedded into the objects around us;1.social media:The online platforms and tools that people use to share opinions, experiences, insights, perceptions, and various media, including photos, videos, and music, with each other;2.disruptors:Companies that introduce a significant change in their industries, thus causing a disruption in normal business operations;3.virtual (Internet) community:A group of people with similar interests who interact with one another using the Internet;4.mobile social networking:Members converse and connect with one another using cell phones or other mobile devices;5.business network:A group of people who have some kind of commercial relationship; for example, sellers and buyers, buyers among themselves, buyers and suppliers, and colleagues and other colleagues;6.business social network:A social network whose primary objective is to facilitate business connections and activities;7.Semantic Web:An evolving extension of the Web in which Web content can be expressed not only in natural language, but also in a form that can be understood, interpreted, and used by intelligent computer software agents, permitting them to find, share, and integrate information more easily;1.business continuity plan:A plan that keeps the business running after a disaster occurs. Each function in the business should have a valid recovery capability plan;2.cybercrime:Intentional crimes carried out on the Internet;3.exposure:The estimated cost, loss, or damage that can result if a threat exploits a vulnerability;4.fraud:Any business activity that uses deceitful practices or devices to deprive another of property or other rights;5.malware:A generic term for malicious software;6.phishing:A crimeware technique to steal the identity of a target company to get the identities of itscustomers;7.social engineering:A type of nontechnical attack that uses some ruse to trick users into revealing information or performing an action that compromises a computer or network;8.click fraud:Type of fraud that occurs in pay-per-click advertising when a person, automated system, or computer program simulates individual clicks on banner or other online advertising methods;9.identity theft:Fraud that involves stealing an identity of a person and then the use of that identity by someone pretending to be someone else in order to steal money or get other benefits;10.spyware:Software that gathers user information over an Internet connection without the user’s knowledge;11.spam:The electronic equivalent of junk mail;1.smart card:An electronic card containing an embedded microchip that enables predefined operations or the addition, deletion, or manipulation of information on the card;2.purchasing cards (p-cards):Special-purpose payment cards issued to a company’s employees to be used solely for purchasing nonstrategic materials and services up to a preset dollar limit;3.card verification number :Detects fraud by comparing the verification number printed on the signature strip on the back of the card with the information on file with the cardholder’s issuing bank;4.Address Verification System (AVS):Detects fraud by comparing the address entered on a Web page with the address information on file with the cardholder’s issuing bank;5.Automated Clearing House (ACH) Network:A nationwide batch-oriented electronic funds transfer system that provides for the interbank clearing of electronic payments for participating financial institutions;6.order fulfillment:All the activities needed to provide customers with their ordered goods and services, including related customer services;7.back-office operations:The activities that support fulfillment of orders, such as packing, delivery, accounting, and logistics;8.front-office operations:The business processes, such as sales and advertising, which are visible to customers;9.e-logistics:The logistics of EC systems, typically involving small parcels sent to many customers’homes ;10.merge-in-transit:Logistics model in which components for a product may come from two (or more) different physical locations and are shipped directly to the customer’s location;11.rolling warehouse:Logistics method in which products on the delivery truck are not preassigned to a destination, but the decision about the quantity to unload at each destination is made at the time of unloading;12.enterprise resource planning (ERP):An enterprisewide information system designed to coordinate all the resources, information, and activities needed to complete business processes such as order fulfillment or billing;13.sealed-bid auction:Auction in which each bidder bids only once; a silent auction, in which bidders do not know who is placing bids or what the bid prices are;14.Vickrey auction:Auction in which the highest bidder wins but pays only the second highest bid;15.bundle trading:The selling of several related products and/or services together;Order fulfillment:all the activities needed to provide customers with their ordered goods and services,including related customer servicesBack-office operations:the activitees that support fulfillment of orders,such as packing,delivery,accounting,and logisticsFront-office operations:the business processes,such as sales and advertising,which are visible to customers e-logistics:the logistics of EC systems,typically involving small parcels sent to many customers’ homes(in。

电子商务常用名词解释电子商务常用名词解释缩写英文全称中文3D The three-dimensional 三维技术3G 3rd Generation 第三代数字通信AACH Automated Clearing Houses 自动交换中心Acquirer 收单行ADC Automated Data Collection 数据自动收集系统administration 管理ADSL Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line 非对称数字用户线路Advance Notification of Payment 支付前通知agentonlong - termbasis 长期代理AM agile manufacturing 敏捷制造ANSI American National Standards Institute 美国国家标准协会,是一个标准化组织。
ANSI X12API Application Programming Interface 应用编程接口ARP Address Resolation Protocol 地址解析协议ARPA Advanced Research Project Agency 美国国防部高级研究计划署article 物品AS/RS automated storage and retrieval system 自动化仓库系统ASN Advance Shipment Notice 装运前通知ASP Active Server PagesASP Application Service Provider 应用服务供应商asymmetrical encryption 非对称加密ATM Automated T eller Machine 自动柜员机Auditing 审计augmented product 延伸产品Authentication 身份认证Automotive industry Action Group 汽车产业行动联盟average inventory 平均存货BB/W/D Brower/WebServer/DBMSB2B Business to Business 商家对商家的电子商务。

电子商务名词解释电子商务(Electronic Commerce,简称EC)指的是通过网络进行商业活动的过程。
以下是一些常见的电子商务名词的解释:1. 电子商务平台(E-commerce platform):提供给商家进行在线交易的网站或应用程序,包括购物车、支付接口、订单管理等功能。
2. 电子商务网站(E-commerce website):通过互联网提供商品或服务的网站,包括商品展示、购买流程、客户服务等功能。
3. 商-to-consumer(B2C):指商家直接向消费者销售商品或服务的模式,如京东、天猫等。
4. 商-to-business(B2B):指企业之间进行的电子商务交易活动,如阿里巴巴等。
5. 用户体验(User experience,简称UX):指用户使用电子商务平台时的感受和反馈,包括界面设计、响应速度、易用性等。
6. 移动电子商务(Mobile e-commerce):指在移动设备上进行的电子商务活动,如手机上的在线购物、移动支付等。
7. 跨境电子商务(Cross-border e-commerce):指跨越国界进行的电子商务交易,如跨境网购、跨境支付等。
8. 电子支付(Electronic payment):通过互联网进行的资金交易,包括信用卡、支付宝、微信支付等。
9. 电子物流(Electronic logistics):指通过互联网进行的物流管理和运输服务,包括订单处理、物品追踪等。
10. 电子商务安全(E-commerce security):指保护电子商务平台和用户信息安全的技术和措施,包括SSL加密、多因素认证等。
11. 电子商务营销(E-commerce marketing):通过互联网进行的产品推广和销售活动,包括搜索引擎优化、社交媒体营销等。
12. 个性化推荐(Personalized recommendation):根据用户的行为和偏好,向其推荐相关的商品或服务。

电子商务名词解释电子商务是指通过电子方式进行的商业交易活动,它涵盖了通过互联网、电子邮件、移动通信等电子手段进行的买卖、支付、物流、客户服务等商业活动。
电子商务的兴起极大地改变了传统的商业模式,为消费者提供了更为便捷的购物方式,也为商家提供了更广阔的市场空间。
1. B2B(Business-to-Business):即企业对企业的电子商务模式,指的是企业之间通过互联网进行的交易活动。
这种模式通常涉及大宗交易,如批发、采购等。
2. B2C(Business-to-Consumer):即企业对消费者的电子商务模式,指的是企业通过互联网直接向消费者销售产品和服务。
这种模式是最常见的电子商务形式,如在线零售商。
3. C2C(Consumer-to-Consumer):即消费者对消费者的电子商务模式,指的是消费者之间通过互联网进行的交易活动。
这种模式通常出现在拍卖网站或二手交易平台上。
4. B2E(Business-to-Employee):即企业对员工的电子商务模式,指的是企业通过互联网向员工提供服务,如在线培训、内部采购等。
5. M-Commerce(Mobile Commerce):即移动电子商务,指的是通过移动设备如智能手机、平板电脑等进行的电子商务活动。
6. E-Marketplace:即电子市场,指的是通过互联网连接买卖双方的在线平台,如eBay、Amazon等。
7. E-Procurement:即电子采购,指的是企业通过互联网进行的采购活动,可以提高采购效率,降低成本。
8. E-Payment:即电子支付,指的是通过电子方式进行的支付活动,如使用信用卡、电子钱包、移动支付等。
9. E-Logistics:即电子物流,指的是利用信息技术优化物流流程,提高物流效率和降低成本。
10. CRM(Customer Relationship Management):即客户关系管理,指的是企业通过信息技术手段管理与客户之间的关系,以提高客户满意度和忠诚度。

电商专⽤术语-英⽂版电商常⽤术语中英对照CVR (Click Value Rate): 转化率,衡量CPA⼴告效果的指标CTR (Click Through Rate): 点击率CPC (Cost Per Click): 按点击计费CPA (Cost Per Action): 按成果数计费CPM (Cost Per Mille): 按千次展现计费CPS(Cost Per Sales):以实际销售产品数量来换算(淘客)PV (Page View): 流量PV单价: 每PV的收⼊,衡量页⾯流量变现能⼒的指标ADPV (Advertisement Page View): 载有⼴告的pageview流量ADimp (ADimpression): 单个⼴告的展⽰次数RPS (Revenue Per Search): 每搜索产⽣的收⼊,衡量搜索结果变现能⼒指标ROI:return on investment回报率(ROI)是指通过投资⽽应返回的价值,它涵盖了企业的获利⽬标。
利润投⼊的经营所必备的财产相关,因为管理⼈员必须通过投资和现有财产获得利润。
⼜称会计收益率、投资利润率。
?UV(独⽴访客):Unique Visitor PV(访问量):PageView,即页⾯浏览量或点击量,⽤户每次刷新即被计算⼀次。
SKU:SKU=Stock Keeping Unit(库存量单位)销售常⽤术语及释义1. 时间2. ⽣意衡量指标1) 销售指标GSV Gross Sales Value Sell-in的销售额NSV Net Sales Value Sell-in的销售额减去TPDistribution 分销率(ACN数据库可以查)2) 市场表现Sales Value 消费者购买POS⾦额(offtake), 销售额Sales Volume 消费者购买数量(offtake), 销量Market share 市场份额(可以是销售额的份额Value share, 也可以是销量的份额Volume share)3) 财务指标MAC margin after conversion 公司计算⽑利, NSV减去制造成本OP Operating profit 运营利润(看最后赚钱不赚…)4) 客户⾓度case-fill rate 订单满⾜率Category Management 品类管理Shopper traffic 客流量Basket value 客单价5) 品牌⾓度Awareness 品牌认知度Trail 尝试率Repeat 重复购买率Loyalty 忠诚度SOV 线上⼴告份额(在嘈杂的竞争品牌⼴告中, 我们的声⾳占了多少) * 从Awareness ⼀直到Loyalty, 是层层递进的6) ⽐较基数Benchmark 基准Vs. target 和⽬标相⽐Vs LY 和去年同期相⽐Vs competitor 和竞品相⽐3. 渠道1) Mega ⼤型Hyper 超⼤型(收银台Checkout超过20个)Cash & Carry 仓储式(如麦德龙, 收银台Checkout超过20个) ?Large supermarket ⼤超市(收银台Checkout 7-19个) 2) Middle 中型Smaller supermarket (ss) ⼩超(收银台Checkout7-19个)CVS 连锁便利店(⼀个收银台, 20家单店以上)Counter store 柜台店OSDO 批发市场Special channel 特渠, 如加油站, ⽕车站…3) IC Impulse channel 冲动渠道NCVS ⾮连锁便利店Small store 夫妻⽼婆店4) B2B 团购4. 销量分类同样是销量, 在公司的衡量指标中有很多不同的名称和定义, 具体如下:Sell-in, Offtake, DTS5. 产品分类1) Brand 分品牌Dove, SNK, Crispy, M&M’s2) Sub-Category 分品类Bulk 散装Sharing 分享装Self-consumption 独享装Gifting 礼盒6. 销售⼈员BDS Business development supervisor 销售主管FOTG Feet on the ground ⼀线同事BDR Business development representative 业务代表JBDR Junior business development representative 初级业务代表FLS Front Line Sales前线实地销售MER Merchandise executive representative 理货员7. 合作部门Franchise 品牌市场部(品牌建设和开发, 更多是线上的投⼊, 以及新品开发) Consumer Insight 消费者洞察部(为市场部提供消费者研究结果以及尼尔森等外部数据源) Trade marketing 市场推⼴部(设计线下推⼴策略)Channel marketing 渠道推⼴部(负责具体到活动SOP以及与销售同事沟通)Logistic 后勤(物流)Finance 财务8. 价格表中的常见语RSP (Retail selling price) 零售价如43g, 6.5元Listing Price 供价如43g, 5.42元Margin 利润如, 43g, 20%Configuration 箱柜如⼼随8*16, ⼀箱8盒, 每盒16个Excl VAT 不含增值税Incl VAT 含增值税9. 城市分类fortress city 堡垒城市(BJ, TJ, SH, HZ, GZ, SZ)developing city 发展中城市(全国共38个)conversion city 转化城市10. 费⽤TP trade expense 投⼊给渠道的费⽤, 渠道受益CP consumer promotion expense 投⼊给消费者促销的费⽤, 消费者受益TTR trade term rebate 合同返点ATL Above the line 线上投⼊(如电视⼴告, 平⾯媒体, 楼宇⼴告, 赞助…)BTL Below the line 线下投⼊(如店内促销, 派发, 形象…)11. 必胜战役Must Win Battle公司MTP中期计划中的策略⽅向, 资源分配和结果追踪都围绕这四⼤战役, 我们销售也应该了解我们为何⽽战…今年为四⼤战役, 缩写连起来是SIGN(标语)MWB S (SNK) ⼠⼒架战役MWB I (Impulse Channel) 冲动渠道战役MWB G (Gifting) 礼盒战役MWB N (New needs) 开发新需求(包括M&M’s以及新品)12. 销售衡量指标Sales MetricsUniverse 存在店数Coverage 覆盖店数Distribution Points 分销点Hero SKU 英雄SKUAverage product line 平均产品线A- Display A陈列Activity evaluation 活动评估Turnover ⼈员流动NSV Gr NSV增长率Channel P&L 渠道的财务状况13. 其他POP point of promotion 促销点(咱⽼说贴POP, 其实就是通过张贴促销信息让消费者认识到这个是促销点) ?POS point of sales 销售点。

电子商务专业术语商业模式B2B模式,Business to Business-企业对企业,例子:阿里巴巴,生意宝(网盛科技)、慧聪网。
B2C模式,Business to Customer-企业对个人,例子:亚马逊,当当,凡客,时尚起义,走秀网。
C2C模式,Customer to Customer-个人对个人,例子:ebay,淘宝,拍拍,易趣。
BMC模式,BMC是英文Business-Medium-Customer的缩写,率先集量贩式经营、连锁经营、人际网络、金融、传统电子商务(B2B、B2C、C2C、C2B)等传统电子商务模式优点于一身,解决了B2B、B2C、C2C、C2B等传统电子商务模式的发展瓶颈。
B=Business,指企业;C=Customers,指消费者,终端;M=Medium,在这里指的是在企业与消费者之间搭建的一个空中的纽带与桥梁。
B2B2C是一种电子商务类型的网络购物商业模式,B是BUSINESS的简称,C是CUSTOMER的简称,第一个B指的是商品或服务的供应商,第二个B指的是从事电子商务的企业,C则是表示消费者。
以亚马逊为代表。
O2O ,online to offline 团购模式,团宝网,美团网,高朋网为代表。
广告词汇植入式广告:在电影或电视剧或者其它场景插入相关的广告。
如变形金刚,非诚勿挠等。
SEM:Search Engine Marketing的缩写,意即搜索引擎营销。
EDM:Electronic Direct Marketing的缩写,就是电子邮件营销。
CPS:Cost Per Sales的缩写,即销售分成。
CPA :Cost Per Action,每次动作成本,即根据每个访问者对网络广告所采取的行动收费的定价模式。
对于用户行动有特别的定义,包括形成一次交易、获得一个注册用户、或者对网络广告的一次点击等。
CPM:(Cost Per Mille,或者Cost Per Thousand;Cost Per Impressions) 每千人成本。

电商专业名词一、基础概念类1. 电子商务(E - Commerce)- 定义:通过互联网等电子手段进行的商业活动,包括商品和服务的销售、购买、营销、客户服务等各个环节。
例如,淘宝、京东等平台上商家与消费者之间的交易活动就是电子商务的典型体现。
2. B2B(Business - to - Business)- 含义:企业对企业的电子商务模式。
即企业之间通过互联网进行产品、服务及信息的交换。
阿里巴巴国际站,众多的制造商、批发商在这个平台上进行原材料、零部件等的交易。
3. B2C(Business - to - Consumer)- 解释:企业对消费者的电子商务模式。
企业直接向消费者销售产品和服务。
像亚马逊、当当网,消费者可以直接在这些网站上购买书籍、电子产品等商品。
4. C2C(Consumer - to - Consumer)- 定义:消费者对消费者的电子商务模式。
个人之间通过网络平台进行商品的交易。
例如,闲鱼平台,用户可以将自己闲置的物品卖给其他个人用户。
5. O2O(Online - to - Offline)- 含义:线上到线下的电子商务模式。
将线上的商业机会与线下的实体店铺相结合。
大众点评网,用户可以在线上查看餐厅、酒店等商家的信息并进行预订,然后到线下实体店消费。
二、营销相关类1. 流量(Traffic)- 解释:指网站或电商平台的访问量,包括独立访客数量、页面浏览量等。
流量是电商运营的重要指标,更多的流量意味着更多的潜在客户。
例如,一个电商网站每天有1000个独立访客访问,这1000就是该网站的日流量的一部分。
2. 转化率(Conversion Rate)- 定义:在电商中,转化率是指进行了期望行为的访问者数量与总访问者数量的比率。
例如,如果一个电商网站有1000个访客,其中有100个访客购买了商品,那么该网站的转化率就是100÷1000 = 10%。
期望行为可以是购买、注册、订阅等。

电子商务常用术语及常识整理概念:电子商务,英文名Electronic Commerce,简称EC。
电子商务模式(常见类):B2B模式,Business to Business-企业对企业,例子:阿里巴巴,生意宝(网盛科技)、慧聪网。
B2C模式,Business to Customer-企业对个人,例子:亚马逊,当当,凡客,时尚起义,走秀网。
C2C模式,Customer to Customer-个人对个人,例子:ebay,淘宝,拍拍,易趣。
电子商务专业名词(常见类):SEM:Search Engine Marketing的缩写,意即搜索引擎营销。
EDM:Electronic Direct Marketing的缩写,就是电子邮件营销。
CPS:Cost Per Sales的缩写,即销售分成。
CPA : Cost Per Action,每次动作成本,即根据每个访问者对网络广告所采取的行动收费的定价模式。
对于用户行动有特别的定义,包括形成一次交易、获得一个注册用户、或者对网络广告的一次点击等。
CPM:(Cost Per Mille,或者Cost Per Thousand;Cost Per Impressions) 每千人成本。
CPC:(Cost Per Click;Cost Per Thousand Click-Through) 每点击成本。
ROI:Return On Investment的缩写,投资报酬率。
SEO:Search Engine Optimization的缩写,搜索引擎优化。
转化率:Conversion Rate的缩写,是指访问某一网站访客中,转化的访客占全部访客的比例。
UV:Unique Vister的缩写,独立访客。
AdWords:Google的关键词竞价广告。
Alexa:是专门发布网站世界排名的网站,网站排名有两种:综合排名和分类排名。
二跳率:二跳率,由99click最先提出,网站页面展开后,用户在页面上产生的首次点击被称为“二跳”,二跳的次数即为”二跳量”。

电子商务专业名词汇总:•企业间交易(B2B)•企业和消费者间交易(B2C)•个人间交易(C2C)•C2A:消费者对行政机构(Consumer-to-administrations)的电子商务,指的是政府对个人的电子商务活动;•B2A:商业机构对行政机构(Business-to-administrations)的电子商务指的是企业与政府机构之间进行的电子商务活动。
•B2M:Business to Marketing,面向市场营销的电子商务企业。
B2M电子商务公司根据客户需求为核心而建立起的营销型站点,并通过线上和线下多种渠道对站点进行广泛的推广和规范化的导购管理,从而使得站点作为企业的重要营销渠道。
相对于拥有站点的简单电子商务模式,B2M注重的是网络营销市场和企业网络营销渠道的建立,相对于B2B、B2C、C2C的一种全新的电子商务模式。
•M2C:Merchant to Consumer商家对消费者,商家通过网络平台发布该企业的产品或者服务,消费者通过支付费用获得自己想要的。
商家最终还是要将产品销售给最终消费者。
此模式是针对B2M的电子商务模式而出现的延伸概念。
在M2C环节中,经理人将面对Consumer,即最终消费者。
•SaaS:是Software-as-a-service(软件即服务),是一种基于互联网提供软件服务的应用模式。
该模式为中小企业搭建信息化所需要的所有网络基础设施及软件、硬件运作平台,并提供一系列服务,能大幅度降低中小企业信息化的门槛与风险。
SEM:Search Engine Marketing的缩写,意即搜索引擎营销;EDM:Electronic Direct Marketing的缩写,就是电子邮件营销;CPS:Cost Per Sales的缩写,即销售分成;CPA :Cost Per Action,每次动作成本,即根据每个访问者对网络广告所采取的行动收费的定价模式。
对于用户行动有特别的定义,包括形成一次交易、获得一个注册用户、或者对网络广告的一次点击等;CPM:(Cost Per Mille,或者Cost Per Thousand;Cost Per Impressions) 每千人成本;CPC:(Cost Per Click;Cost Per Thousand Click-Through) 每点击成本;ROI:Return On Investment的缩写,投资报酬率;SEO:Search Engine Optimization的缩写,搜索引擎优化;转化率:Conversion Rate的缩写,是指访问某一网站访客中,转化的访客占全部访客的比例;UV:Unique Vister的缩写,独立访客;AdWords:Google的关键词竞价广告;Alexa:是专门发布网站世界排名的网站,网站排名有两种:综合排名和分类排名;二跳率:二跳率,由99click最先提出,网站页面展开后,用户在页面上产生的首次点击被称为“二跳”,二跳的次数即为”二跳量”。

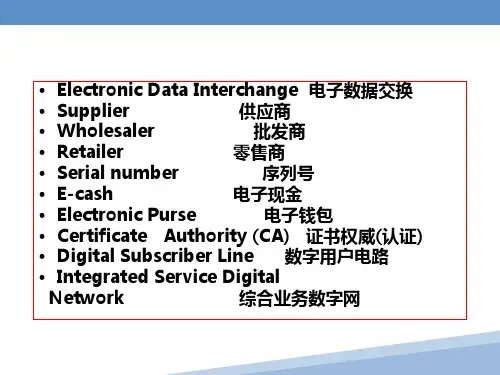
1.e-commerce :The process of buying, selling, or exchanging products, services, or information via computer;2.e-business:A broader definition of EC that includes not just the buying and selling of goods and services, but also servicing customers, collaborating with business partners, and conducting electronic transactions within an organization;3.brick-and-mortar (old economy) organizations:Old-economy organizations (corporations) that perform their primary business off-line, selling physical products by means of physical agents;4.virtual (pure-play) organizations:Organizations that conduct their business activities solely online;5.click-and-mortar (click-and-brick) organizations:Organizations that conduct some e-commerce activities, usually as an additional marketing channel;6.electronic market (e-marketplace):An online marketplace where buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods, services, money, or information;7.Interorganizational information systems (IOSs):Communications systems that allow routine transaction processing and information flow between two or more organizations;8.Intraorganizational information systems:Communication systems that enable e-commerce activities to go on within individual organizations;9.intranet:An internal corporate or government network that uses Internet tools, such as Web browsers, and Internet protocols;10.extranet:A network that uses the Internet to link multiple intranets;11.business-to-business (B2B):E-commerce model in which all of the participants are businesses or other organizations;12.business-to-consumer (B2C):E-commerce model in which businesses sell to individual shoppers;13.business-to-business-to-consumer (B2B2C):E-commerce model in which a business provides some product or service to a client business that maintains its own customers;14.consumer-to-business (C2B):E-commerce model in which individuals use the Internet to sell products or services to organizations or individuals who seek sellers to bid on products or services they need;15.e-tailing:Online retailing, usually B2C;16.intrabusiness EC:E-commerce category that includes all internal organizational activities that involve the exchange of goods, services, or information among various units and individuals in an organization;17.business-to-employees (B2E):E-commerce model in which an organization delivers services, information, or products to its individual employees;18.consumer-to-consumer(C2C):E-commerce model in which consumers sell directly to other consumers;19.collaborative commerce (c-commerce):E-commerce model in which individuals or groups communicate or collaborate online;20.e-learning:The online delivery of information for purposes of training or education;21.e-government:E-commerce model in which a government entity buys or provides goods, services, or information from or to businesses or individual citizens;22.social computing:An approach aimed at making the human-computer interface more natural;23.Web 2.0:The second-generation of Internet-based services that let people collaborate and share information online in new ways, such as social networking sites, wikis, communication tools, and folksonomies;24.social network:A category of Internet applications that help connect friends, business partners, or individuals with specific interests by providing free services such as photo presentations, e-mail, blogging, and so on using a variety of tools;25.social network service (SNS):A service that builds online communities by providing an online space for people to build free homepages and that provides basic communication and support tools for conducting different activities in the social network;26.social networking:The creation or sponsoring of a social network service and any activity, such as blogging, done in a social network ;27.enterprise-oriented networks:Social networks whose primary objective is to facilitate business;28.virtual world:A user-defined world in which people can interact, play, and do business. The most publicized virtual world is Second Life;29.digital economy:An economy that is based on digital technologies, including digital communication networks, computers, software, and other related information technologies; also called the Internet economy, the new economy, or the Web economy;30.digital enterprise:A new business model that uses IT in a fundamental way to accomplish one or more of three basic objectives: reach and engage customers more effectively, boost employee productivity, and improve operating efficiency. It uses converged communication and computing technology in a way that improves business processes;31.corporate portal:A major gateway through which employees, business partners, and the public can entera corporate Web site;32.business model:A method of doing business by which a company can generate revenue to sustain itself;33.revenue model:sales,transaction fees,subscription fees,advertising fees,affiliate fees,other revenue sources.1.e-marketplace:An online market, usually B2B, in which buyers and sellers exchange goods or services; the three types of e-marketplaces are private, public, and consortia;2.marketspace:A marketplace in which sellers and buyers exchange goods and services for money (or for other goods and services), but do so electronically;3.digital products:Goods that can be transformed to digital format and delivered over the Internet;4.front end:The portion of an e-seller’s business processes through which customers interact, including the seller’s portal, electronic catalogs, a shopping cart, a search engine, and a payment gateway;5.back end:The activities that support online order fulfillment, inventory management, purchasing from suppliers, payment processing, packaging, and delivery;6.intermediary:A third party that operates between sellers and buyers;7.sell-side e-marketplace:A private e-marketplace in which one company sells either standard and/or customized products to qualified companies;8.buy-side e-marketplace:A private e-marketplace in which one company makes purchases from invited suppliers;9.storefront:A single company’s Web site where products or services are sold;10.e-mall (online mall):An online shopping center where many online stores are located;11.Web portal:A single point of access, through a Web browser, to critical business information located inside and outside (via Internet) of an organization;Types of portals:commercial portal,corporate portals,publishing portals,personal portals12.mobile portal:A portal accessible via a mobile device;13.voice portal:A portal accessed by telephone or cell phone;mediaries:Electronic intermediaries that provide and/or control information flow in cyberspace, often aggregating information and selling it to others;15.e-distributor:An e-commerce intermediary that connects manufacturers with business buyers (customers) by aggregating the catalogs of many manufacturers in one place—the intermediary’s Web site;16.electronic catalogs (e-catalogs):The presentation of product information in an electronic form; the backbone of most e-selling sites;17.enterprise search:The practice of identifying and enabling specific content across the enterprise to be indexed, searched, and displayed to authorized users;18.desktop search:Search tools that search the contents of a user’s or organization’s computer files, rather than searching the Internet;19.search engine:A computer program that can access databases of Internet resources, search for specific information or keywords, and report the results;20.electronic shopping cart:An order-processing technology that allows customers to accumulate items they wish to buy while they continue to shop;21.auction:A competitive process in which a seller solicits consecutive bids from buyers (forward auctions) ora buyer solicits bids from sellers (backward auctions). Prices are determined dynamically by the bids;22.electronic auctions (e-auctions):Auctions conducted online;23.forward auction:An auction in which a seller entertains bids from buyers. Bidders increase price sequentially;24.reverse auction (bidding or tendering system):Auction in which the buyer places an item for bid (tender) ona request for quote (RFQ) system, potential suppliers bid on the job, with the price reducing sequentially, and the lowest bid wins; primarily a B2B or G2B mechanism;25.“name-your-own-price”model:Auction model in which a would-be buyer specifies the price (and other terms) he or she is willing to pay to any willing and able seller. It is a C2B model that was pioneered by ;26.double auction:An auction in which multiple buyers and their bidding prices are matched with multiple sellers and their asking prices, considering the quantities on both sides;27.bartering:The exchange of goods and services;28.e-bartering (electronic bartering):Bartering conducted online, usually in a bartering exchange;29.bartering exchange:A marketplace in which an intermediary arranges barter transactions;30.blog:A personal Web site that is open to the public to read and to interact with; dedicated to specific topics or issues;31.vlog (or video blog):A blog with video content;32.micro-blogging:A form of blogging that allows users to write messages (usually up to 140 characters) and publish them, either to be viewed by anyone or by a restricted group that can be chosen by the user;33.Twitter:A free micro-blogging service that allows its users to send and read other users’updates;34.tweets:Text-based posts up to 140 characters in length posted to Twitter;35.tag:A nonhierarchical keyword or term assigned to a piece of information ;36.folksonomy :The practice and method of collaboratively creating, classifying, and managing tags to annotate and categorize content;37.social bookmarking:Web service for sharing Internet bookmarks. The sites are a popular way to store, classify, share, and search links through the practice of folksonomy techniques on the Internet and intranets;38.wiki (wikilog):A blog that allows everyone to participate as a peer; anyone may add, delete, or change content;39.avatars:Animated computer characters that exhibit humanlike movements and behaviors;40.customization:Creation of a product or service according to the buyer’s specifications;41.personalization:The ability to tailor a product, service, or Web content to specific user preferences;42.disintermediation:Elimination of intermediaries between sellers and buyers;43.reintermediation:Disintermediated entities or newcomers take on new intermediary roles;44.mass customization:A method that enables manufacturers to create specific products for each customer based on the customer’s exact needs;45.build-to-order (pull system):A manufacturing process that starts with an order (usually customized). Once the order is paid for, the vendor starts to fulfill it;1.direct marketing:Broadly, marketing that takes place without intermediaries between manufacturers and buyers; in the context of this book, marketing done online between any seller and buyer;2.virtual (pure-play) e-tailers:Firms that sell directly to consumers over the Internet without maintaining a physical sales channel;3.click-and-mortar retailers:Brick-and-mortar retailers that offer a transactional Web site from which toconduct business;4.brick-and-mortar retailers:Retailers who do business in the non-Internet, physical world in traditional brick-and-mortar stores;5.multichannel business model:A business model where a company sells in multiple marketing channels simultaneously;6.electronic(online) banking or e-banking:various banking activities conducted from home or the road using an internet connection;also known as cyberbanking,birtual banking,online banking ,and home banking7.birtual banks:have no physical location;only conduct online transactions8.shopping portals:gateways to e-storefronts and e-malls;may be comprehensive or niche oriented9.shopping robots:tools that scout the web on behalf of consumers who specify search criteria10.disintermediation:the removal of organizations or business process layers responsible for certain intermediary steps in a given supply chain11.reintermediation:the process whereby intermediaries take on new intermediary roles12.cybermediation(electronic intermediation):the use of software(intelligent) agents to facilitate intermediation13.channel conflict:situation in which an online marketing channel upsets the taditional channels due to real or perceived damage from competitionproduct brokering:Deciding what product to buymerchant brokering:Deciding from whom (from what merchant) to buy a productmarket segmentation:The process of dividing a consumer market into logical groups for conducting marketing research and analyzing personal informationone-to-one marketing (relationship marketing): Marketing that treats each customer in a unique way personalization:The matching of services, products, and advertising content with individual consumers and their preferencesuser profile:The requirements, preferences, behaviors, and demographic traits of a particular customer cookie:A data file that is placed on a user’s hard drive by a remote Web server, frequently without disclosure or the user’s consent, which collects information about the user’s activities at a sitebehavioral targeting:Targeting that uses information collected about an individual’s Web-browsing behavior, such as the pages they have visited or the searches they have made, to select an advertisement to display to that individualcollaborative filtering:A market research and personalization method that uses customer data to predict, based on formulas derived from behavioral sciences, what other products or services a customer may enjoy; predictions can be extended to other customers with similar profilese-loyalty:Customer loyalty to an e-tailer or loyalty programs delivered online or supported electronically interactive marketing:Online marketing, facilitated by the Internet, by which marketers and advertisers can interact directly with customers, and consumers can interact with advertisers/vendorsCPM (cost per thousand impressions) :T he fee an advertiser pays for each 1,000 times a page with a banner ad is shownadvertising networks: Specialized firms that offer customized Web advertising, such as brokering ads and targeting ads to select groups of consumersbanner:On a Web page, a graphic advertising display linked to the advertiser’s Web pagespot buying: The purchase of goods and services as they are needed, usually at prevailing market prices strategic (systematic) sourcing:Purchases involving long-term contracts that usually are based on private negotiations between sellers and buyersdirect materials:Materials used in the production of a product (e.g., steel in a car or paper in a book) indirect materials:Materials used to support production (e.g., office supplies or light bulbs)MRO (maintenance, repair, and operation) :Indirect materials used in activities that support production vertical marketplaces:Markets that deal with one industry or industry segment (e.g., steel, chemicals)horizontal marketplaces:Markets that concentrate on a service, material, or a product that is used in all types of industriesprocurement management:The planning, organizing, and coordinating of all the activities relating to purchasing goods and services needed to accomplish the organization’s missionmaverick buying:Unplanned purchases of items needed quickly, often at non–pre-negotiated higher pricese-procurement:The electronic acquisition of goods and services for organizationsinternal procurement marketplace:The aggregated catalogs of all approved suppliers combined into a single internal electronic catalogbartering exchange:An intermediary that links parties in a barter; a company submits its surplus to the exchange and receives points of credit, which can be used to buy the items that the company needs from other exchange participantsdesktop purchasing:Direct purchasing from internal marketplaces without the approval of supervisors and without the intervention of a procurement departmentgroup purchasing:The aggregation of orders from several buyers into volume purchases so that better prices can be negotiatedconsortium trading exchange (CTE) :An exchange formed and operated by a group of major companies in an industry to provide industry-wide transaction servicespartner relationship management (PRM) :Business strategy that focuses on providing comprehensive quality service to business partnerssupply chain:The flow of materials, information, money, and services from raw material suppliers through factories and warehouses to the end customerssupply chain:A supply chain that is managed electronically, usually with Web technologiesprocurement:The process made up of a range of activities by which an organization obtains or gains access to the resources (materials, skills, capabilities, facilities) they require to undertake their core business activities supply chain management (SCM) :A complex process that requires the coordination of many activities so that the shipment of goods and services from supplier right through to customer is done efficiently and effectively for all parties concerned. SCM aims to minimize inventory levels, optimize production and increase throughput, decrease manufacturing time, optimize logistics and distribution, streamline order fulfillment, and overall reduce the costs associated with these activitiese-supply chain management (e-SCM) :The collaborative use of technology to improve the operations of supply chain activities as well as the management of supply chainsbullwhip effect:Erratic shifts in order up and down supply chainsradio frequency identification (RFID) :Tags that can be attached to or embedded in objects, animals, or humans and use radio waves to communicate with a reader for the purpose of uniquely identifying the object or transmitting data and/or storing information about the objectcorporate (enterprise) portal:A gateway for entering a corporate Web site, enabling communication, collaboration, and access to company informationinformation portals:Portals that store data and enable users to navigate and query the datacollaborative portals:Portals that allow collaborationgroupware:Software products that support groups of people who share common tasks or goals and collaborate on their accomplishmentvirtual team:A group of employees using information and communications technologies to collaborate from different work basesvirtual meetings:Online meetings whose members are in different locations, even in different countriesgroup decision support system (GDSS) :An interactive computer-based system that facilitates the solution of semistructured and unstructured problems by a group of decision makersernment-to-citizens (G2C):E-government category that includes all the interactions between agovernment and its citizens;ernment-to-business (G2B):E-government category that includes interactions between governments and businesses;ernment-to-government (G2G):E-government category that includes activities within government units and those between governments;ernment-to-employees (G2E):E-government category that includes activities and services between government units and their employees;5.mobile government (m-government):The wireless implementation of e-government mostly to citizens but also to business;6.e-learning:The online delivery of information for purposes of education, training, or knowledge management;7.distance learning:Formal education that takes place off campus, usually, but not always, through online resources;8.virtual university:An online university from which students take classes from home or other offsite locations, usually via the Internet;tainment:The combination of education and entertainment, often through games;10.online publishing:The electronic delivery of newspapers, magazines, books, news, music, videos, and other digitizable information over the Internet;11.e-book:A book in digital form that can be read on a computer screen or on a special device;12.knowledge management (KM):The process of capturing or creating knowledge, storing it, updating it constantly, disseminating it, and using it whenever necessary;13.consumer-to-consumer (C2C):E-commerce model in which consumers sell directly to other consumers;14.peer-to-peer (P2P):Applications that use direct communications between computers (peers) to share resources, rather than relying on a centralized server as the conduit between client devices;1.short message service (SMS):A service that supports the sending and receiving of short text messages on mobile phones;2.multimedia messaging service (MMS):The emerging generation of wireless messaging; MMS is able to deliver rich media;3.interactive voice response (IVR):A voice system that enables users to request and receive information and to enter and change data through a telephone to a computerized system;4.personal area network (PAN):A wireless telecommunications network for device-to-device connections within a very short range;5.Bluetooth:A set of telecommunications standards that enables wireless devices to communicate with each other over short distances;6.wireless local area network (WLAN):A telecommunications network that enables users to make short-range wireless connections to the Internet or another network;7.Wi-Fi (wireless fidelity):The common name used to describe the IEEE 802.11 standard used on most WLANs;8.WiMax:A wireless standard (IEEE 802.16) for making broadband network connections over a medium-size area such as a city;9.wireless wide area network (WWAN):A telecommunications network that offers wireless coverage over a large geographical area, typically over a cellular phone network;10.location-based m-commerce (l-commerce):Delivery of m-commerce transactions to individuals in a specific location, at a specific time;work-based positioning:Relies on base stations to find the location of a mobile device sending a signal or sensed by the network;12.terminal-based positioning:Calculating the location of a mobile device from signals sent by the device to base stations;13.global positioning system (GPS):A worldwide satellite-based tracking system that enables users to determine their position anywhere on the earth;14.geographical information system (GIS):A computer system capable of integrating, storing, editing, analyzing, sharing, and displaying geographically-referenced (spatial) information;15.pervasive computing:Invisible, everywhere computing; computing capabilities embedded into the objects around us;1.social media:The online platforms and tools that people use to share opinions, experiences, insights, perceptions, and various media, including photos, videos, and music, with each other;2.disruptors:Companies that introduce a significant change in their industries, thus causing a disruption in normal business operations;3.virtual (Internet) community:A group of people with similar interests who interact with one another using the Internet;4.mobile social networking:Members converse and connect with one another using cell phones or other mobile devices;5.business network:A group of people who have some kind of commercial relationship; for example, sellers and buyers, buyers among themselves, buyers and suppliers, and colleagues and other colleagues;6.business social network:A social network whose primary objective is to facilitate business connections and activities;7.Semantic Web:An evolving extension of the Web in which Web content can be expressed not only in natural language, but also in a form that can be understood, interpreted, and used by intelligent computer software agents, permitting them to find, share, and integrate information more easily;1.business continuity plan:A plan that keeps the business running after a disaster occurs. Each function in the business should have a valid recovery capability plan;2.cybercrime:Intentional crimes carried out on the Internet;3.exposure:The estimated cost, loss, or damage that can result if a threat exploits a vulnerability;4.fraud:Any business activity that uses deceitful practices or devices to deprive another of property or other rights;5.malware:A generic term for malicious software;6.phishing:A crimeware technique to steal the identity of a target company to get the identities of its customers;7.social engineering:A type of nontechnical attack that uses some ruse to trick users into revealing information or performing an action that compromises a computer or network;8.click fraud:Type of fraud that occurs in pay-per-click advertising when a person, automated system, or computer program simulates individual clicks on banner or other online advertising methods;9.identity theft:Fraud that involves stealing an identity of a person and then the use of that identity by someone pretending to be someone else in order to steal money or get other benefits;10.spyware:Software that gathers user information over an Internet connection without the user’s knowledge;11.spam:The electronic equivalent of junk mail;1.smart card:An electronic card containing an embedded microchip that enables predefined operations or the addition, deletion, or manipulation of information on the card;2.purchasing cards (p-cards):Special-purpose payment cards issued to a company’s employees to be used solely for purchasing nonstrategic materials and services up to a preset dollar limit;3.card verification number :Detects fraud by comparing the verification number printed on the signature strip on the back of the card with the information on file with the cardholder’s issuing bank;4.Address Verification System (AVS):Detects fraud by comparing the address entered on a Web page with the address information on file with the cardholder’s issuing bank;5.Automated Clearing House (ACH) Network:A nationwide batch-oriented electronic funds transfer system that provides for the interbank clearing of electronic payments for participating financial institutions;6.order fulfillment:All the activities needed to provide customers with their ordered goods and services, including related customer services;7.back-office operations:The activities that support fulfillment of orders, such as packing, delivery, accounting, and logistics;8.front-office operations:The business processes, such as sales and advertising, which are visible to customers;9.e-logistics:The logistics of EC systems, typically involving small parcels sent to many customers’homes ;10.merge-in-transit:Logistics model in which components for a product may come from two (or more) different physical locations and are shipped directly to the customer’s location;11.rolling warehouse:Logistics method in which products on the delivery truck are not preassigned to a destination, but the decision about the quantity to unload at each destination is made at the time of unloading;12.enterprise resource planning (ERP):An enterprisewide information system designed to coordinate all the resources, information, and activities needed to complete business processes such as order fulfillment or billing;13.sealed-bid auction:Auction in which each bidder bids only once; a silent auction, in which bidders do not know who is placing bids or what the bid prices are;14.Vickrey auction:Auction in which the highest bidder wins but pays only the second highest bid;15.bundle trading:The selling of several related products and/or services together;Order fulfillment:all the activities needed to provide customers with their ordered goods and services,including related customer servicesBack-office operations:the activitees that support fulfillment of orders,such as packing,delivery,accounting,and logisticsFront-office operations:the business processes,such as sales and advertising,which are visible to customers e-logistics:the logistics of EC systems,typically involving small parcels sent to many customers’ homes(in B2C)ERP:an enterprisewide information system designed to coordinate all the resources,information,and activities needed to complete business processes such as order fulfillment or billing.Sealed-bid auction:auction in which each bidder bids only once;a silent auction,in which bidders do not know who is placing bids or what the bid prices areVickrey auction:auction in which the highest bidder wins but pays only the second highest bidBundle trading:the selling of several related products and/or services together。
4,电子支付electronic payment电子支票electronic checks电子货币electronic money经常账户checking accounts数据加密data encryption客户认证client authentication智能卡smart cards计算机硬盘computer hard disks银行部门banking sector小额支付small value payment5.网上购物流程the flow of shopping/purchasing online 迅速发展rapid growth/development虚拟商店virtual stores/shops产品规格specification电子银行cyber bank购物中心shopping center在线付款payment online确认订单confirmation of the order总金额total amount批号date code6,最终产品finished goods相关信息related information产地the point of origin运输与配送transport &services国际供应链管理international supply chain management预售服务pre-retailing services军事策略military strategy战时物资生产wartime material production集中于centering on战略物资补给strategic commodities supply7,file transfer 文件传输digital cash 电子现金geographical location 地理位置on a global scale 在全球范围EDI 电子数据交换competition 竞争definition 定义manufacturer 生产商advertising 广告interaction 互动8 ,internet marketing 网络营销electronic mediu电子媒介affiliate marketing 会员营销merge…with…与…融为一体distribute products 配送产品community activities 社区活动marketing objectives 营销目的loyalty program 贵宾会员计划provide comprehensive information 提供综合信息commercialization 商业化9, virtual bank 虚拟银行online bank 在线银行physical bank 有形银行banking activities 银行业务credit unions 信用合作社credit card products 信用卡产品open a checking or savings account 开立支票或储蓄账户10, paper checks 纸质支票banking settlement system 银行结算系统payment data 支付数据secure communication protocols 安全通信协议secure payment protocols 安全支付协议server authentication 服务器认证prepaid cards 预付费卡electronic purses 电子钱包digital cash 数字现金access product 可存取的产品11, shopping online 在线购物business directories 企业名单purchasing process 采购流程authentication centre 认证中心surfing the internet 网上冲浪names of commodities 商品名称lead time 交货日期terms of payment 付款方式payment authentication 付款认证release the goods 发货12, the efficient and cost-efficient flow 有效而合算流动raw materials 原材料in-process inventory 半成品For the purpose of conforming to in motion and rest 为满足消费者需要the management of inventory in motion and rest 动态与静态的库存管理IT solutions 信息技术解决方案added-value 增值in military science 在军事科学方面the most crucial element 最关键的要素a network of transportation 运输网络二、句子翻译(1,2,14,17,18)(英→汉)1.1)in another word ,electronic commerce is the buying ,selling and trading of goods and services through private and public networks .换句话来说,电子商务是指通过私人或公众网络来买卖或交换货物和服务2)first stage of EC expansion is that with in the “connected ” or “online ” computer users .EC的首个发展阶段局限于“在线”计算机用户3)the second wave will come when more people get access to computers (via lowered computer prices or cheaper device )第二个高峰将会在更多人可以通过更低廉的价格或设备访问计算机的时候来临4)the third expansion is predicted to be from those with non-computer access to the global network :through broadcast TVs ,cable TVs ,telephone networks and new appliances .据预测,电子商务发展的第三次浪潮将会出现在不用电脑就能上网的技术发展方面,例如通过无线电视,有线电视,电话网络及新型的设备上网5)a widespread use of these cheaper access media represents the phase of “bringing workplace computers into living room ”低价的接入设备的广泛使用代表着进入了“家庭办公”的新时代2,1)the conveniences afforded by electronic commerce is limitless .电子商务提供的便利是无止境的2)more than 100 countries are linked into exchanges of data ,news and opinions .超过100个国家已经接入互联网,交换资料、新闻和言论。
电商专业名词大全在电子商务(电商)领域中,有许多专业术语被广泛使用。
本文将为您提供一个电商专业名词的大全,以帮助您更好地理解和应用这些术语。
1. 电子商务(E-commerce):指通过互联网等电子方式进行商业交易的活动。
2. 商业模式(Business Model):指企业用于创造和交付价值,并从中获取利润的方式。
3. B2B(Business-to-Business):指企业与企业之间进行的电商交易。
4. B2C(Business-to-Consumer):指企业与消费者之间进行的电商交易。
5. C2C(Consumer-to-Consumer):指消费者之间进行的电商交易。
6. O2O(Online-to-Offline):指线上与线下业务的结合,例如在线购买后到实体店自取商品。
7. 供应链管理(Supply Chain Management):指对物流、仓储和供应商之间的协作进行优化管理,以提高效率和降低成本。
8. 电子支付(E-payment):指在电子商务中使用电子形式完成货币交易的方式,如支付宝、微信支付等。
9. 电子数据交换(Electronic Data Interchange,EDI):指不同公司间通过计算机网络进行数据的交流和交换。
10. 网上商城(Online Marketplace):指由平台提供者在互联网上搭建的电商平台,供卖家和买家进行交易。
11. 虚拟商店(Virtual Store):指以虚拟现实技术为基础,通过计算机图形和仿真技术创造出的虚拟购物环境。
12. 网络营销(Internet Marketing):指通过互联网和其他数字渠道进行市场推广和销售的活动。
13. 网络推广(Online Promotion):指利用搜索引擎优化、社交媒体、在线广告等手段提升品牌知名度和销量。
14. 电子广告(Digital Advertising):指在互联网上使用文字、图像、音频和视频等形式进行广告宣传的行为。
电子商务术语翻译●B2C(参考答案:Business to Consumer企业与消费者之间;参见教科书1.2.2)●B2B(参考答案:Business to Business企业与企业之间;参见教科书1.2.2)●The World Business Agenda for Electronic Commerce(参考答案:世界电子商务会议;参见教科书1.2.1)●B2G(参考答案:Business to Government,企业与政府之间;参见教科书1.2.2)●EDI(参考答案:Electronic Data Interchange,电子数据交换;参见教科书1.2.2)●XML(参考答案:可扩展标识语言;参见教科书1.2.2)●CA(参考答案:认证机构;参见教科书1.4.4)●ISP(参考答案:Internet Service Provider,网络服务提供商;参见教科书1.5.5)●ICP(参考答案:Internet Content Provider,网络内容提供商;参见教科书1.5.1)●China Public Packet Switched Dada Network(参考答案:公用分组交换数据网;参见教科书2.2.2)●Paperless Trading(参考答案:无纸贸易;参见教科书2.5.2)●Electronic Data Interchange(参考答案:电子数据交换技术;参见教科书2.5.1)●Digital Subscriber Line(参考答案:数字用户线路;参见教科书3.1.4)●Integrated Service Digital Network(参考答案:综合业务数字网;参见教科书3.1.4)●Transport Control Protocol(参考答案:传输控制协议;参见教科书3.3.1)●Net Operation System(参考答案:网络操作系统;参见教科书3.1.3)●Internet Service Provider(ISP)(参考答案:因特网服务供应商;参见教科书4.2.1.1)●Application Service Provider(ASP)(参考答案:应用服务提供商;参见教科书4.2.1.1)●Internet Content Provider(ICP)(参考答案:网络内容提供商;参见教科书4.2.1.2)●Network Database(参考答案:网络数据库;参见教科书4.2.3.1)●Hyper Text Markup Language(HTTP)(参考答案:超文本标注语言;参见教科书4.3.5.1)●Extensible Markup Language(XML)(参考答案:可扩展置标语言;参见教科书4.3.5.2)●EDI(参考答案:电子数据交换;参见教科书6.3.3)●Soft goods(参考答案:软体商品;参见教科书7.2.3)●Brand Asset(参考答案:品牌资产;参见教科书7.3.1)●Continuity(参考答案:连续性;参见教科书7.5.4)●Coverage(参考答案:覆盖;参见教科书7.5.4)●Credit(参考答案:信用;参见教科书7.5.4)●Personal Data Assistants,PDAs(参考答案:个人数据助手;参见教科书7.7.1)●Page view(参考答案:网页浏览次数;参见教科书8.3.2)●Click-through Rate(参考答案:点进率;参见教科书8.3.2)●Cost Per Thousand Impressions(参考答案:千人广告成本;参见教科书8.3.2)●Cost Per Click-Through(参考答案:每点击成本;参见教科书8.3.2)●Partnership Marketing(参考答案:伙伴营销;参见教科书8.7.2)●Really Simple Syndication(参考答案:简易信息聚合;参见教科书8.7.6)●E-wallet(参考答案:电子钱包软件;参见教科书10.2.2)●E-cash(参考答案:电子现金;参见教科书10.2.2)●Electronic Purse(参考答案:电子钱包;参见教科书10.2.2)●Electronic Fund Transfer(参考答案:电子资金划拨;参见教科书10.2.2)●FSTC(Financial Services Technology Consortium)(参考答案:资金服务技术协会;参见教科书10.2.3)●SET(Secure Electronic Transaction)(参考答案:电子商务交易安全协议;参见教科书10.3.2)●Physical Distribution(参考答案:货物配送;参见教科书11.1.1)●Barcode technology参考答案:条码技术;参见教科书11.1.3)●Enterprise Resource Planning(参考答案:企业资源计划系统;参见教科书11.2.2)●Cross docking(参考答案:码头直接发运;参见教科书11.3.1)●Radio Frequency(参考答案:射频技术;参见教科书11.3.2)●Global Positioning System(参考答案:全球定位系统;参见教科书11.3.2)●Geographical Information System(参考答案:地理信息系统;参见教科书11.3.2)●Digita1TimeStampsever(参考答案:数字时间戳服务;参见教科书12.2.2)●Certificate Authority(参考答案:电子认证服务机构;参见教科书12.2.3)●functional-equivalent approach(参考答案:功能等同法;参见教科书12.5.2)●Public Key Infrastructure(参考答案:公钥基础设施;参见教科书12.2.3)。
电子商务英文名词解释1.e-commerce :The process of buying, selling, or exchanging products, services, or information via computer;2.e-business:A broader definition of EC that includes not just the buying and selling of goods and services, but also servicing customers, collaborating with business partners, and conducting electronic transactions within an organization;3.brick-and-mortar (old economy) organizations:Old-economy organizations (corporations) that perform their primary business off-line, selling physical products by means of physical agents;4.virtual (pure-play) organizations:Organizations that conduct their business activities solely online;5.click-and-mortar (click-and-brick) organizations:Organizations that conduct some e-commerce activities, usually as an additional marketing channel;6.electronic market (e-marketplace):An online marketplace where buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods, services, money, or information;7.Interorganizational information systems (IOSs):Communications systems that allow routine transaction processing and information flow between two or more organizations;8.Intraorganizational information systems:Communication systems that enable e-commerce activities to go on within individual organizations;9.intranet:An internal corporate or government network that uses Internet tools, such as Web browsers, and Internet protocols;10.extranet:A network that uses the Internet to link multiple intranets;11.business-to-business (B2B):E-commerce model in which all of the participants are businesses or other organizations;12.business-to-consumer (B2C):E-commerce model in which businesses sell to individual shoppers;13.business-to-business-to-consumer (B2B2C):E-commerce model in which a business provides some product or service to a client business that maintains its own customers;14.consumer-to-business (C2B):E-commerce model in which individuals use the Internet to sell products or services to organizations or individuals who seek sellers to bid on products or services they need;15.e-tailing:Online retailing, usually B2C;16.intrabusiness EC:E-commerce category thatincludes all internal organizational activities that involve the exchange of goods, services, or information among various units and individuals in an organization;17.business-to-employees (B2E):E-commerce model in which an organization delivers services, information, or products to its individual employees;18.consumer-to-consumer(C2C):E-commerce model in which consumers sell directly to other consumers;19.collaborative commerce (c-commerce):E-commerce model in which individuals or groups communicate or collaborate online;20.e-learning:The online delivery of information for purposes of training or education;21.e-government:E-commerce model in which a government entity buys or provides goods, services, or information from or to businesses or individual citizens;22.social computing:An approach aimed at making the human-computer interface more natural;23.Web 2.0:The second-generation of Internet-based services that let people collaborate and share information online in new ways, such as socialnetworking sites, wikis, communication tools, and folksonomies;24.social network: A category of Internet applications that help connect friends, business partners, or individuals with specific interests by providing free services such as photo presentations, e-mail, blogging, and so on using a variety of tools;25.social network service (SNS):A service that builds online communities by providing an online space for people to build free homepages and that provides basic communication and support tools for conducting different activities in the social network;26.social networking:The creation or sponsoring ofa social network service and any activity, such as blogging, done in a social network ;27.enterprise-oriented networks:Social networks whose primary objective is to facilitate business;28.virtual world:A user-defined world in which people can interact, play, and do business. The most publicized virtual world is Second Life;29.digital economy:An economy that is based on digital technologies, including digital communication networks, computers, software, and other related information technologies; also called the Interneteconomy, the new economy, or the Web economy;30.digital enterprise:A new business model that uses IT in a fundamental way to accomplish one or more of three basic objectives: reach and engage customers more effectively, boost employee productivity, and improve operating efficiency. It uses converged communication and computing technology in a way that improves business processes;31.corporate portal:A major gateway through which employees, business partners, and the public can enter a corporate Web site;32.business model:A method of doing business by which a company can generate revenue to sustain itself;33.revenue model:sales,transaction fees,subscription fees,advertising fees,affiliate fees,other revenue sources.1.e-marketplace:An online market, usually B2B, in which buyers and sellers exchange goods or services; the three types of e-marketplaces are private, public, and consortia;2.marketspace:A marketplace in which sellers and buyers exchange goods and services for money (or forother goods and services), but do so electronically;3.digital products:Goods that can be transformed to digital format and delivered over the Internet;4.front end:The portion of an e-seller’s business processes through which customers interact, including the seller’s portal, electronic catalogs, a shopping cart,a search engine, and a payment gateway;5.back end:The activities that support online order fulfillment, inventory management, purchasing from suppliers, payment processing, packaging, and delivery;6.intermediary:A third party that operates between sellers and buyers;7.sell-side e-marketplace:A private e-marketplace in which one company sells either standard and/or customized products to qualified companies;8.buy-side e-marketplace:A private e-marketplace in which one company makes purchases from invited suppliers;9.storefront:A single company’s Web site where products or services are sold;10.e-mall (online mall):An online shopping center where many online stores are located;11.Web portal:A single point of access, through aWeb browser, to critical business information located inside and outside (via Internet) of an organization;Types of portals:commercial portal,corporate portals,publishing portals,personal portals12.mobile portal:A portal accessible via a mobile device;13.voice portal:A portal accessed by telephone or cell phone;mediaries:Electronic intermediaries that provide and/or control information flow in cyberspace, often aggregating information and selling it to others;15.e-distributor:An e-commerce intermediary that connects manufacturers with business buyers (customers) by aggregating the catalogs of many manufacturers in one place—the intermediary’s Web site;16.electronic catalogs (e-catalogs):The presentation of product information in an electronic form; the backbone of most e-selling sites;17.enterprise search:The practice of identifying and enabling specific content across the enterprise to be indexed, searched, and displayed to authorized users;18.desktop search:Search tools that search thecontents of a user’s or organization’s computer files, rather than searching the Internet;19.search engine:A computer program that can access databases of Internet resources, search for specific information or keywords, and report the results;20.electronic shopping cart:An order-processing technology that allows customers to accumulate items they wish to buy while they continue to shop;21.auction:A competitive process in which a seller solicits consecutive bids from buyers (forward auctions) or a buyer solicits bids from sellers (backward auctions). Prices are determined dynamically by the bids;22.electronic auctions (e-auctions):Auctions conducted online;23.forward auction:An auction in which a seller entertains bids from buyers. Bidders increase price sequentially;24.reverse auction (bidding or tendering system):Auction in which the buyer places an item for bid (tender) on a request for quote (RFQ) system, potential suppliers bid on the job, with the price reducing sequentially, and the lowest bid wins; primarily a B2Bor G2B mechanism;25.“name-your-own-price”model:Auction model in which a would-be buyer specifies the price (and other terms) he or she is willing to pay to any willing and able seller. It is a C2B model that was pioneered by ;26.double auction:An auction in which multiple buyers and their bidding prices are matched with multiple sellers and their asking prices, considering the quantities on both sides;27.bartering:The exchange of goods and services;28.e-bartering (electronic bartering):Bartering conducted online, usually in a bartering exchange;29.bartering exchange:A marketplace in which an intermediary arranges barter transactions;30.blog:A personal Web site that is open to the public to read and to interact with; dedicated to specific topics or issues;31.vlog (or video blog):A blog with video content;32.micro-blogging:A form of blogging that allows users to write messages (usually up to 140 characters) and publish them, either to be viewed by anyone or by a restricted group that can be chosen by the user;33.Twitter:A free micro-blogging service thatallows its users to send and read other users’updates;34.tweets:Text-based posts up to 140 characters in length posted to Twitter;35.tag:A nonhierarchical keyword or term assigned to a piece of information ;36.folksonomy :The practice and method of collaboratively creating, classifying, and managing tags to annotate and categorize content;37.social bookmarking:Web service for sharing Internet bookmarks. The sites are a popular way to store, classify, share, and search links through the practice of folksonomy techniques on the Internet and intranets;38.wiki (wikilog):A blog that allows everyone to participate as a peer; anyone may add, delete, or change content;39.avatars:Animated computer characters that exhibit humanlike movements and behaviors;40.customization:Creation of a product or service according to the buyer’s specifications;41.personalization:The ability to tailor a product, service, or Web content to specific user preferences;42.disintermediation:Elimination of intermediariesbetween sellers and buyers;43.reintermediation:Disintermediated entities or newcomers take on new intermediary roles;44.mass customization:A method that enables manufacturers to create specific products for each customer based on the customer’s exact needs;45.build-to-order (pull system):A manufacturing process that starts with an order (usually customized). Once the order is paid for, the vendor starts to fulfill it;1.direct marketing:Broadly, marketing that takes place without intermediaries between manufacturers and buyers; in the context of this book, marketing done online between any seller and buyer;2.virtual (pure-play) e-tailers:Firms that sell directly to consumers over the Internet without maintaining a physical sales channel;3.click-and-mortar retailers:Brick-and-mortar retailers that offer a transactional Web site from which to conduct business;4.brick-and-mortar retailers:Retailers who do business in the non-Internet, physical world in traditional brick-and-mortar stores;5.multichannel business model:A business modelwhere a company sells in multiple marketing channels simultaneously;6.electronic(online) banking or e-banking:various banking activities conducted from home or the road using an internet connection;also known as cyberbanking,birtual banking,online banking ,and home banking7.birtual banks:have no physical location;only conduct online transactions8.shopping portals:gateways to e-storefronts and e-malls;may be comprehensive or niche oriented9.shopping robots:tools that scout the web on behalf of consumers who specify search criteria10.disintermediation:the removal of organizations or business process layers responsible for certain intermediary steps in a given supply chain11.reintermediation:the process whereby intermediaries take on new intermediary roles12.cybermediation(electronic intermediation):the use of software(intelligent) agents to facilitate intermediation13.channel conflict:situation in which an online marketing channel upsets the taditional channels due to real or perceived damage from competitionproduct brokering: Deciding what product to buymerchant brokering: Deciding from whom (from what merchant) to buy a productmarket segmentation:The process of dividing a consumer market into logical groups for conducting marketing research and analyzing personal informationone-to-one marketing (relationship marketing): Marketing that treats each customer in a unique waypersonalization:The matching of services, products, and advertising content with individual consumers and their preferencesuser profile:The requirements, preferences, behaviors, and demographic traits of a particular customercookie:A data file that is placed on a user’s hard drive by a remote Web server, frequently without disclosure or the user’s consent, which collects information about the user’s activities at a sitebehavioral targeting:Targeting that uses information collected about an individual’s Web-browsing behavior, such as the pages they have visited or the searches they have made, to select anadvertisement to display to that individualcollaborative filtering:A market research and personalization method that uses customer data to predict, based on formulas derived from behavioral sciences, what other products or services a customer may enjoy; predictions can be extended to other customers with similar profilese-loyalty:Customer loyalty to an e-tailer or loyalty programs delivered online or supported electronically interactive marketing: Online marketing, facilitated by the Internet, by which marketers and advertisers can interact directly with customers, and consumers can interact with advertisers/vendorsCPM (cost per thousand impressions) : The fee an advertiser pays for each 1,000 times a page with a banner ad is shownadvertising networks: Specialized firms that offer customized Web advertising, such as brokering ads and targeting ads to select groups of consumers banner: On a Web page, a graphic advertising display linked to the advertiser’s Web pagespot buying: The purchase of goods and services as they are needed, usually at prevailing market pricesstrategic (systematic) sourcing:Purchases involving long-term contracts that usually are based on private negotiations between sellers and buyers direct materials:Materials used in the production of a product (e.g., steel in a car or paper in a book)indirect materials:Materials used to support production (e.g., office supplies or light bulbs) MRO (maintenance, repair, and operation) :Indirect materials used in activities that support production vertical marketplaces:Markets that deal with one industry or industry segment (e.g., steel, chemicals) horizontal marketplaces:Markets that concentrate on a service, material, or a product that is used in all types of industriesprocurement management:The planning, organizing, and coordinating of all the activities relating to purchasing goods and services needed to accomplish the organization’s missionmaverick buying:Unplanned purchases of items needed quickly, often at non–pre-negotiated higher pricese-procurement:The electronic acquisition of goods and services for organizationsinternal procurement marketplace:The aggregatedcatalogs of all approved suppliers combined into a single internal electronic catalogbartering exchange:An intermediary that links parties in a barter; a company submits its surplus to the exchange and receives points of credit, which can be used to buy the items that the company needs from other exchange participantsdesktop purchasing:Direct purchasing from internal marketplaces without the approval of supervisors and without the intervention of a procurement departmentgroup purchasing:The aggregation of orders from several buyers into volume purchases so that better prices can be negotiatedconsortium trading exchange (CTE) :An exchange formed and operated by a group of major companies in an industry to provide industry-wide transaction servicespartner relationship management (PRM) :Business strategy that focuses on providing comprehensive quality service to business partnerssupply chain:The flow of materials, information, money, and services from raw material suppliersthrough factories and warehouses to the end customerssupply chain:A supply chain that is managed electronically, usually with Web technologiesprocurement:The process made up of a range of activities by which an organization obtains or gains access to the resources (materials, skills, capabilities, facilities) they require to undertake their core business activitiessupply chain management (SCM) :A complex process that requires the coordination of many activities so that the shipment of goods and services from supplier right through to customer is done efficiently and effectively for all parties concerned. SCM aims to minimize inventory levels, optimize production and increase throughput, decrease manufacturing time, optimize logistics and distribution, streamline order fulfillment, and overall reduce the costs associated with these activitiese-supply chain management (e-SCM) :The collaborative use of technology to improve the operations of supply chain activities as well as the management of supply chainsbullwhip effect:Erratic shifts in order up and downsupply chainsradio frequency identification (RFID) :Tags that can be attached to or embedded in objects, animals, or humans and use radio waves to communicate with a reader for the purpose of uniquely identifying the object or transmitting data and/or storing information about the objectcorporate (enterprise) portal:A gateway for entering a corporate Web site, enabling communication, collaboration, and access to company information information portals:Portals that store data and enable users to navigate and query the datacollaborative portals:Portals that allow collaborationgroupware:Software products that support groups of people who share common tasks or goals and collaborate on their accomplishmentvirtual team:A group of employees using information and communications technologies to collaborate from different work basesvirtual meetings:Online meetings whose members are in different locations, even in different countries group decision support system (GDSS) :An interactive computer-based system that facilitates thesolution of semistructured and unstructured problems by a group of decision makersernment-to-citizens (G2C):E-government category that includes all the interactions between a government and its citizens;ernment-to-business (G2B):E-government category that includes interactions between governments and businesses;ernment-to-government (G2G):E-government category that includes activities within government units and those between governments;ernment-to-employees (G2E):E-government category that includes activities and services between government units and their employees;5.mobile government (m-government):The wireless implementation of e-government mostly to citizens but also to business;6.e-learning:The online delivery of information for purposes of education, training, or knowledge management;7.distance learning:Formal education that takes place off campus, usually, but not always, through online resources;8.virtual university:An online university from which students take classes from home or other offsite locations, usually via the Internet;tainment:The combination of education and entertainment, often through games;10.online publishing:The electronic delivery of newspapers, magazines, books, news, music, videos, and other digitizable information over the Internet;11.e-book:A book in digital form that can be read on a computer screen or on a special device;12.knowledge management (KM):The process of capturing or creating knowledge, storing it, updating it constantly, disseminating it, and using it whenever necessary;13.consumer-to-consumer (C2C):E-commerce model in which consumers sell directly to other consumers;14.peer-to-peer (P2P):Applications that use direct communications between computers (peers) to share resources, rather than relying on a centralized server as the conduit between client devices;1.short message service (SMS):A service that supports the sending and receiving of short textmessages on mobile phones;2.multimedia messaging service (MMS):The emerging generation of wireless messaging; MMS is able to deliver rich media;3.interactive voice response (IVR):A voice system that enables users to request and receive information and to enter and change data through a telephone to a computerized system;4.personal area network (PAN): A wireless telecommunications network for device-to-device connections within a very short range;5.Bluetooth: A set of telecommunications standards that enables wireless devices to communicate with each other over short distances;6.wireless local area network (WLAN): A telecommunications network that enables users to make short-range wireless connections to the Internet or another network;7.Wi-Fi (wireless fidelity):The common name used to describe the IEEE 802.11 standard used on most WLANs;8.WiMax:A wireless standard (IEEE 802.16) for making broadband network connections over a medium-size area such as a city;9.wireless wide area network (WWAN): A telecommunications network that offers wireless coverage over a large geographical area, typically overa cellular phone network;10.location-based m-commerce (l-commerce):Delivery of m-commerce transactions to individuals in a specific location, at a specific time;work-based positioning:Relies on base stations to find the location of a mobile device sendinga signal or sensed by the network;12.terminal-based positioning:Calculating the location of a mobile device from signals sent by the device to base stations;13.global positioning system (GPS):A worldwide satellite-based tracking system that enables users to determine their position anywhere on the earth;14.geographical information system (GIS):A computer system capable of integrating, storing, editing, analyzing, sharing, and displaying geographically-referenced (spatial) information;15.pervasive computing:Invisible, everywhere computing; computing capabilities embedded into the objects around us;1.social media:The online platforms and tools that people use to share opinions, experiences, insights, perceptions, and various media, including photos, videos, and music, with each other;2.disruptors:Companies that introduce a significant change in their industries, thus causing a disruption in normal business operations;3.virtual (Internet) community:A group of people with similar interests who interact with one another using the Internet;4.mobile social networking:Members converse and connect with one another using cell phones or other mobile devices;5.business network:A group of people who have some kind of commercial relationship; for example, sellers and buyers, buyers among themselves, buyers and suppliers, and colleagues and other colleagues;6.business social network:A social network whose primary objective is to facilitate business connections and activities;7.Semantic Web:An evolving extension of the Web in which Web content can be expressed not only in natural language, but also in a form that can be understood, interpreted, and used by intelligentcomputer software agents, permitting them to find, share, and integrate information more easily;1.business continuity plan:A plan that keeps the business running after a disaster occurs. Each function in the business should have a valid recovery capability plan;2.cybercrime:Intentional crimes carried out on the Internet;3.exposure:The estimated cost, loss, or damage that can result if a threat exploits a vulnerability;4.fraud:Any business activity that uses deceitful practices or devices to deprive another of property or other rights;5.malware:A generic term for malicious software;6.phishing:A crimeware technique to steal the identity of a target company to get the identities of its customers;7.social engineering:A type of nontechnical attack that uses some ruse to trick users into revealing information or performing an action that compromises a computer or network;8.click fraud:Type of fraud that occurs in pay-per-click advertising when a person, automatedsystem, or computer program simulates individual clicks on banner or other online advertising methods;9.identity theft:Fraud that involves stealing an identity of a person and then the use of that identity by someone pretending to be someone else in order to steal money or get other benefits;10.spyware:Software that gathers user information over an Internet connection without the user’s knowledge;11.spam:The electronic equivalent of junk mail;1.smart card:An electronic card containing an embedded microchip that enables predefined operations or the addition, deletion, or manipulation of information on the card;2.purchasing cards (p-cards):Special-purpose payment cards issued to a company’s employees to be used solely for purchasing nonstrategic materials and services up to a preset dollar limit;3.card verification number :Detects fraud by comparing the verification number printed on the signature strip on the back of the card with the information on file with the cardholder’s issuing bank;4.Address Verification System (AVS):Detects fraudby comparing the address entered on a Web page with the address information on file with the cardholder’s issuing bank;5.Automated Clearing House (ACH) Network:A nationwide batch-oriented electronic funds transfer system that provides for the interbank clearing of electronic payments for participating financial institutions;6.order fulfillment:All the activities needed to provide customers with their ordered goods and services, including related customer services;7.back-office operations:The activities that support fulfillment of orders, such as packing, delivery, accounting, and logistics;8.front-office operations:The business processes, such as sales and advertising, which are visible to customers;9.e-logistics:The logistics of EC systems, typically involving small parcels sent to many customers’homes ;10.merge-in-transit:Logistics model in which components for a product may come from two (or more) different physical locations and are shipped directly to the customer’s location;11.rolling warehouse:Logistics method in which products on the delivery truck are not preassigned to a destination, but the decision about the quantity to unload at each destination is made at the time of unloading;12.enterprise resource planning (ERP):An enterprisewide information system designed to coordinate all the resources, information, and activities needed to complete business processes such as order fulfillment or billing;13.sealed-bid auction:Auction in which each bidder bids only once; a silent auction, in which bidders do not know who is placing bids or what the bid prices are;14.Vickrey auction:Auction in which the highest bidder wins but pays only the second highest bid;15.bundle trading:The selling of several related products and/or services together;Order fulfillment:all the activities needed to provide customers with their ordered goods and services,including related customer servicesBack-office operations:the activitees that support fulfillment of orders,such as packing,delivery,accounting,and logistics。
电子商务专业术语商业模式B2B 模式, Business to Business- 公司对公司,例子:阿里巴巴,买卖宝(网盛科技)、慧聪网。
B2C 模式, Business to Customer- 公司对个人,例子:亚马逊,当当,凡客,时髦起义,走秀网。
C2C 模式, Customer to Customer -个人对个人,例子: ebay ,淘宝,拍拍,易趣。
BMC 模式, BMC 是英文 Business-Medium-Customer的缩写,领先集量贩式经营、连锁经营、人际网络、金融、传统电子商务( B2B、B2C、C2C、 C2B)等传统电子商务模式长处于一身,解决了 B2B、B2C、C2C、C2B等传统电子商务模式的发展瓶颈。
B=Business,指公司; C=Customers,指花费者,终端;M=Medium ,在这里指的是在公司与花费者之间搭建的一个空中的纽带与桥梁。
B2B2C是一种电子商务种类的网络购物商业模式, B 是 BUSINESS的简称, C 是CUSTOMER的简称,第一个B 指的是商品或服务的供给商,第二个B 指的是从事电子商务的公司, C 则是表示花费者。
以亚马逊为代表。
O2O,online to offline团购模式,团宝网,美团网,贵客网为代表。
广告词汇如变形金刚,非诚植入式广告:在电影或电视剧或许其余场景插入有关的广告。
勿挠等。
SEM:Search Engine Marketing的缩写,意即搜寻引擎营销。
EDM:Electronic Direct Marketing 的缩写,就是电子邮件营销。
CPS: Cost Per Sales的缩写 ,即销售分红。
CPA : Cost Per Action,每次动作成本,即依据每个接见者对网络广告所采纳的行动收费的订价模式。
关于用户行动有特其余定义,包含形成一次交易、获取一个注册用户、或许对网络广告的一次点击等。
电子商务英语专业术语在当今数字化的时代,电子商务已经成为了一种不可忽视的商业模式。
随着全球市场的扩大和互联网技术的不断进步,电子商务的领域已经变得更加广阔和多样化。
作为电子商务从业者,掌握电子商务英语专业术语会给你带来极大的优势。
在这篇文章中,我们将会介绍一些电子商务中常用的英语专业术语。
1. eCommerce (电子商务):指通过互联网实现买卖商品或服务的商业活动。
2. B2B (Business-to-Business) :指企业之间进行电子商务的商业活动。
3. B2C (Business-to-Consumer) :指企业向消费者进行电子商务的商业活动。
4. C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer) :指消费者之间进行电子商务的商业活动。
5. E-Marketplace (电子市场):互联网上的一个平台,买家和卖家可以在该平台上进行交易。
6. Online Payment(在线支付):通过互联网进行支付的方式。
7. Mobile Payment(移动支付):通过手机或其他移动设备进行支付的方式。
8. Shopping cart(购物车):用于存储网上购物中所选商品的虚拟车,以方便消费者查看、修改商品和结算。
9. Shipping(配送):将商品从卖家处运送到买家处的过程。
10. Fulfillment(履行):从订单到发货的整个流程。
包括收货、检查商品、打包、配送等环节。
以上是电子商务常用的十个英语专业术语,虽然这些词汇看起来很简单,但是在实践过程中需要注意的细节很多。
另外,电子商务英语专业术语还有很多,如 SEO (搜索引擎优化)、CRM (客户关系管理)、ERP (企业资源计划)、EDI (电子数据交换)、P2P (点对点) 等,需要从业者们学习和掌握。
总之,在电子商务领域里,学习和掌握这些专业术语的重要性不言而喻。
通过深入了解电子商务中的专业术语,从业者们可以更好地沟通交流,理解客户需求,提高团队运作效率,进而推动企业不断发展。