LG-VCS介绍资料(中文)
- 格式:pptx
- 大小:7.05 MB
- 文档页数:23
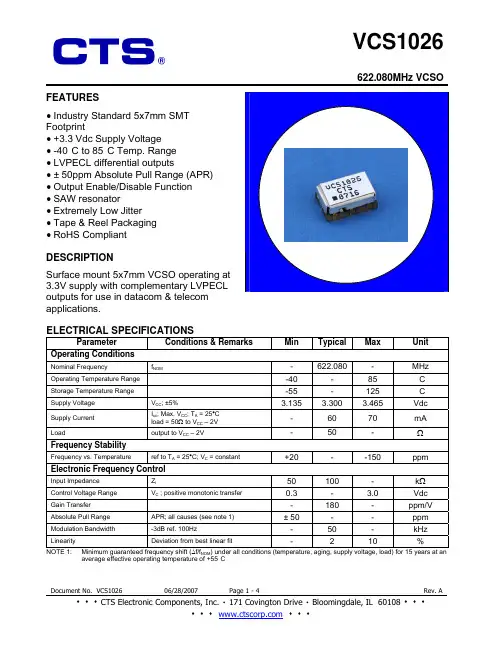
622.080MHz VCSO FEATURES• Industry Standard 5x7mm SMTFootprint• +3.3 Vdc Supply Voltage• -40°C to 85°C Temp. Range• LVPECL differential outputs• ± 50ppm Absolute Pull Range (APR)• Output Enable/Disable Function• SAW resonator• Extremely Low Jitter• Tape & Reel Packaging• RoHS CompliantDESCRIPTIONSurface mount 5x7mm VCSO operating at3.3V supply with complementary LVPECLoutputs for use in datacom & telecomapplications.ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONSParameter Conditions&RemarksMinTypicalMaxUnit Operating ConditionsNominal Frequency f NOM- 622.080 - MHz Operating Temperature Range -40 - 85 °C Storage Temperature Range -55 - 125 °C Supply Voltage V CC; ±5% 3.135 3.300 3.465 VdcSupply Current I cc; Max. V CC; T A = 25°Cload = 50Ω to V CC – 2V- 60 70 mALoad output to V CC – 2V - 50 - ΩFrequency StabilityFrequency vs. Temperature ref to T A = 25°C; V C = constant +20 - -150 ppm Electronic Frequency ControlInput Impedance Z i50 100 - kΩControl Voltage Range V C ; positive monotonic transfer 0.3 - 3.0 Vdc Gain Transfer - 180 - ppm/V Absolute Pull Range APR; all causes (see note 1) ± 50 - - ppm Modulation Bandwidth -3dB ref. 100Hz - 50 - kHz Linearity Deviation from best linear fit - 2 10 % NOTE 1: Minimum guaranteed frequency shift (∆f/f NOM) under all conditions (temperature, aging, supply voltage, load) for 15 years at an average effective operating temperature of +55°C622.080MHz VCSO ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)Parameter Conditions&RemarksMinTypicalMaxUnit Output ParametersOutput Signal LVPECLV OL- -V CC-1.620AmplitudeV OH V CC-1.025 - -VdcRise/Fall Times 20% to 80% - 250 400 ps Duty Cycle @ 50% of output signal 45 50 55 % Start up time to reach 90% of final amplitude - - 10 ms100Hz - -85 -75 dBc/Hz1kHz - -110 -100 dBc/Hz10kHz - -140 -130 dBc/Hz100kHz - -143 -140 dBc/Hz Phase Noise1MHz - -143 -140 dBc/Hz12kHz to 20MHz (calculated from Phase Noise) - 0.16 0.3 psRMSPhase Jitter50kHz to 80MHz (calculated from Phase Noise) - 0.16 0.3 psRMSLVPECL OUTPUT WAVEFORM TEST CIRCUIT, LVPECL LOADOUTPUT ENABLE/DISABLE LOGICPad 2 Pad 4 Pad 5Low ”0” outputs disabled HI Z HI ZOpen outputs enabled Output Comp. OutputHigh ”1” outputs enabled Output Comp. Output622.080MHz VCSO622.080MHz VCSOMAXIMUM SOLDERING PROFILETemperature217°C 260°C (Absolute max temperature) Time60-150 sec 10 sec. maxNote: Part is not designed to be reflowed in an inverted position.MSL Level: 1This product is fully compliant to RoHS Directive 2002/95/EC。

VCS的方案均采用了高性能的VERITAS存储软件作为存储管理和高性能数据访问软件。
鉴于提高数据库性能的考虑,我们配置了VERITAS Quick I/O 的Oracle数据库加速产品,使得数据库的处理能力大大提高。
作为系统安全的保障,我们配置了VERITAS群集管理(VERITAS Cluster Server,VCS)作为系统的高可用软件。
VCS能够对应用、系统、数据库系统、网络、备份等均提供高效快速的故障保护。
我们在各节点均采用了VERITAS V olume Manager 和VERITAS File System作为虚拟磁盘管理和高性能文件系统。
这两种产品各具优点,两者有机结合后,利用双方特有的对磁盘和数据的管理能力,能给企业的系统提供尽可能高的性能、可用性及可管理性。
---- VCS是一款高可用性多机应用软件,可以通过应用在各服务器之间的智能化灵活切换,使多台服务器协同工作,支持Unix和Windows NT环境。
作为多机的集群软件,VCS对应用的切换具有速度快、方式灵活的特点。
在SAN环境下,VCS可以支持最多32台服务器协同工作,在各种群集管理软件中优势突出,是目前扩展性最好高可用软件。
VCS还提供Windows NT控制工具和界面。
管理员可以做到无人现场值守即可监控群集的状态。
---- VERITAS Volume Manager为企业的应用提供了功能强大的磁盘和存储设备在线管理。
VERITAS V olume Manager提供虚拟设备机制(即逻辑卷),向用户应用和文件系统提供完全透明的设备在线管理,应用程序和文件系统无须直接管理物理设备,数据的安全性、完整性、I/O性能的调整、设备在线扩展由V olume Manager管理机制实现。
另外,服务器进行在线管理,不必因备份和维护而进行脱机。
VERITAS V olume Manager提供了磁盘的使用分析、RAID 配置和系统在线的情况下对磁盘进行动态配置。


abnormal vaginal bleeding requiring intervention had no statis-tical difference between VP and WVP patients group (p=0.3074)as other complications as well(table1).Median of related days of vaginal bleeding after the procedure were 7.4days(SD8.75)in VP group and7.34days(SD8.52)in WVP group,with no statistical difference(p=0.912). Conclusions Insert a vaginal pack or not,after LEEP,do not affect the number of postoperative gynecologic intervention due to vaginal bleeding or the amount of postoperative bleed-ing days.Previous pregnancies,hormonal status,cytology or LEEP specimen characteristics did not affect the disclosure. We also could not find any risk factor associated to abnormal bleeding.Based on that,the use of vaginal pack can be omit-ted with no further complications.IGCS19-0405382LATERALLY EXTENDED ENDOPELVIC RESECTION(LEER) AND NEOVAGINE,PATIENT WITH RECTALADENOCARCINOMA AND RECURRENCE IN CERVIX,VAGINA AND PELVIC WALL:A PURPOSE OF A CASE1J Torres*,2J Saenz,3O Suescun,3M Medina,4L Trujillo.1Especialista en entrenamiento–Universidad Militar Nueva Granada–Instituto Nacional de Cancerologia,Department of Gynecologic Oncology,Bogota D.C.,Colombia;2Especialista en entrenamiento–Universidad Militar Nueva Granada–Instituto Nacional de Cancerologia,Department of Gynecologic Oncology,Bogota D.C,Colombia;3Instituto Nacional de Cancerologia, Department of Gynecologic Oncology,Bogota D.C,Colombia;4Instituto Nacional de Cancerologia,Department of Gynecologic Oncology,Bogota D.C.,Colombia10.1136/ijgc-2019-IGCS.382Objectives Exenteration is used to treat cancers of the lower and middle female genital tract in the irradiated pelvis. Höckel described laterally extended endopelvic resection (LEER)as an approach in which the resection line extends to the pelvic side wall.Methods A49-year-old patient diagnosed with rectal adenocar-cinoma10years ago,managed with chemotherapy plus radio-therapy.T umor relapse at3years,management with low abdominoperineal resection and definitive colostomy.Second relapse4years later,compromising the posterior aspect of the coccyx and right side of the pelvis with irresecability criteria, management was decided with chemotherapy with capecita-bine,oxaliplatin and bevacizumab.New relapse at2years in the cervix,vagina and pelvic wall.Images without distance disease,type LEER management with extension of pelvic floor margins and resection of muscle pubococcygeus and right lat-eral iliococcygeus with neovagina(Singapore flap)and non-continent urinary derivation with bilateral cutaneous ureteros-tomy,achieving adequate lateral margin with curative intent. During follow-up with favorable evolution.Results LEER combines at least two procedures:total mesorec-tal excision,total mesometrial resection or total mesovesical resection.It may even require resection of the pelvic wall, internal obturator muscle,pubococcygeus,iliococcygeus,coccy-geus or internal iliac vessels.In combination with neovagina, it would offer better results in non-gynecological cancer relapses.Conclusions LEER with neovagina can be offered as a new therapy to a selected subset of patients with relapse in adja-cent gynecological organs with good oncological,functional and aesthetic results.Symptom Management–Supportive Cancer CareIGCS19-0706383PHOTOBIOMODULATION AND MANUAL LYMPHDRAINAGE FOR NIPPLE NECROSIS TREATMENT INBREAST CANCER:A CASE REPORT1J Baiocchi,2L Campanholi,3G Baiocchi*.1Oncofisio,Physical Therapy,Sao Paulo,Brazil;2CESCAGE,Physical Therapy,Ponta Grossa,Brazil;3AC Camargo Cancer Center, Gynecologic Oncology,Sao Paulo,Brazil10.1136/ijgc-2019-IGCS.383Objectives Recently,breast reconstruction after mastectomywith nipple preservation became an option of breast cancer surgery.Despite its efficacy and aesthetic superiority,the nip-ple preservation is associated with several complications in the postoperative period.The photobiomodulation therapy,for-merly known as low-intensity laser therapy,demonstrated tis-sue promotion repair by cellular repair biostimulation, angiogenesis and anti-inflammatory effects.These characteris-tics suggest a potential role for repair of chronic wounds andmay be applicable in necrosis treatment.Our aim was toreport the effects of the physiotherapeutic intervention through photobiomodulation therapy in a patient with nipple necrosis after risk reducing mastectomy.Methods We report a case of a breast cancer surgery with nip-ple necrosis treated with low-level laser therapy.The patientwas a36-year-old women who developed skin nipple necrosisin the right breast after bilateral reconstructive mastectomy.She had6sessions of low-level laser therapy.Results A female subject developed a nipple necrosis of morethan40%on the right breast after mastectomy and recon-struction.She was referred to Physical Therapy(PT)and thePT sessions were composed by manual lymph drainage,man-ual therapy for de AWS,exercises of strength and flexibility, followed by LLLT with laser660nm,2joules per point atevery1cm.Therapy was implemented for12times in total,from May2016to June2016.A re-evaluation was performed monthly from July13,2016to November2017.After18 months of follow-up,the sustained effects of LLLT were found.Conclusions Low-level laser therapy is effective for the skin cicatrization after nipple necrosis.IGCS19-0446384CONTRACEPTION AND FERTILITY COUNSELING INPATIENTS RECEIVING CHEMOTHERAPY1A Elnaggar*,2A Calfee,1LB Daily,2T Hasley,1T Tillmanns.1West Cancer Center and Research Institute,Gynecologic Oncology,Memphis,USA;2University of Tennessee Health Science Center,Obstetrics and Gynecology,Mempis,USA10.1136/ijgc-2019-IGCS.384Objectives Cancer care advances allow more patients to pursue fertility.Unfortunately,treatments may have detrimental effectson fertility and fetus should pregnancy occur.This study examines physician documentation and patient perceptions of fertility and contraception counseling. on December 24, 2023 by guest. Protected by copyright./ Int J Gynecol Cancer: first published as 10.1136/ijgc-2019-IGCS.384 on 18 September 2019. Downloaded fromMethods IRB approval obtained for a cross-sectional study of men and women,ages18–50,with newly diagnosed malig-nancy between May2017and2018.Prior sterilization,secon-dary or synchronous cancer,or prior chemotherapy were exclusionary.Consented patients received a survey regarding perception on receipt and quality of,counseling.Demographic, sexual,and social information was obtained.Differences were evaluated using chi-square tests.Results Fifty-three of179patients identified participated. Majority were women(75v25%).Patients were more likely to have perceived counseling for contraception and fertility than documented.The majority perceived counseling as suffi-cient regarding contraception and fertility.Men were more likely than women to be perceive counsel-ing regarding fertility(85v43%,p=0.010).However,both felt fertility counseling to be sufficient with similar rates of documentation.Caucasians were more likely to perceive receipt of fertility counseling(68v29%)and to perceive it to be sufficient(70v40%),then African Americans,with the same rate of documentation(35%).Conclusions Significant discrepancies in perception counsel-ing regarding contraception and fertility were seen.Gen-der and race were important factors for the perception of fertility counseling,while only race was a factor to qual-ity of perceived counseling.These differences occurred despite equal rates of physician documentation,across all groups.IGCS19-0430385WHO ARE YOU CALLING OLD?PRACTICE PATTERNS AND MANAGEMENT OF NONAGENARIANS PRESENTINGTO A GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGIST FOR INITIALCONSULTATIONE Ryan*,B Margolis,B Pothuri.New York University Langone Health,Obstetrics and Gynecology,New York,USA10.1136/ijgc-2019-IGCS.385Objectives T o describe the practice patterns and treatment of nonagenarians who initiated care with a gynecologic oncologist.Methods Retrospective chart review of women aged90or older who presented to a gynecologic oncologist between10/ 09and12/18at an urban academic medical center.Descrip-tive statistics utilized for variables of interest.Results We identified34nonagenarians(median age92,range 90–98):10(29%)had benign disease,8(24%)pre-malignancy or suspected malignancy,and16(47%)malignancy.Of these, 79%had age and/or functional status discussed in the care plan.Of the8with suspected malignancy,5declined further workup.The cancer distribution revealed5(31%)vulvar,5 (31%)uterine,4(25%)ovarian,1(6%)vaginal and1(6%) cervical bined,37%had stage I disease;6% stage3;6%stage4;13%recurrent;and25%unstaged.All received treatment plans:7(47%)with palliative intent and8 (53%)with curative intent.In the curative group,7under-went surgery(1adjuvant chemotherapy)and1chemotherapy/radiation.In the palliative group,4underwent radiation,1 chemotherapy and2declined/unknown.Overall,13(87%) completed the proposed treatment.T reatment-related complica-tions included1superficial skin infection and1thirty-day readmission.Conclusions Nonagenarians often presented with vulvar or endometrial cancer and87%successfully completed treatmentwith minimal adverse effects or toxicity.Age and/or functionalstatus were considered in the care plan for79%of women,but it did not preclude treatments that had the potential to preserve meaningful quality of life and/or cure patients oftheir disease.IGCS19-0646386RISK FACTORS COMPREHENSIVE GERIATRICASSESSMENT FOR EARLY DEATH IN ELDERLY PATIENTSWITH GYNECOLOGICAL CANCER.A PROSPECTIVECOHORT STUDY1J Sales*,2C Azevedo,2C santos,3L sales,4M Bezerra,5G Bezerra,4Z cavalcanti,6MJ Mello.1IMIP,Geriatric Oncology,Recife,Brazil;2IMIP,Oncology,Recife,Brazil;3FPS,Medical Course,Recife,Brazil;4IMIP,geriatric,Recife,Brazil;5HMV,oncology,caruaru,Brazil;6IMIP,post graduation,Recife,Brazil10.1136/ijgc-2019-IGCS.386Objectives T o determine risk factors for early death identifiedthe Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment(CGA)in elderly patients with gynecological cancer(EPGC).Methods Prospective cohort study.Participants with a recent diagnosis of cancer were from eight community hospitals andone cancer center in Northeast Brazil and were recruited dur-ing their first medical appointment at the outpatient oncologic clinic.A basal CGA was done before the treatment decision (ADL,Charlson Comorbidity Index-CCI,Karnofsky Perform-ance status–KPS,GDS15,IPAQ,MMSE,MNA,MNA-SF,PS,PPS,Polipharmacy,TUG).During the follow up of12 months,information about the treatments performed,the tar-geted interventions and early death was collected.Overall sur-vival was estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method,and survival curves were compared using the Log rank test for cat-egorical variables.A multivariate Cox proportional hazardsmodel was used.Results From2015–2017,84EPGC,mean age69,6±7,9;range60–96),were enrolled,25%were metastatic disease.tumor site:40,4%cervical uterine,36,9%endometrial,20,2%ovary and2,3vulva.Nine(10.7%)ECP died in less than12 months of follow-up.In our multivariate model,controlled byage,site of cancer and cancer stage,the remaining significantrisk factors were malnutrition/nonutrition determined byMNA-SF(HR3.70,95%CI1.81–5.99,p<0.001),Katz index(HR 3.60,CI 1.56–3.81,p<0.001)CCI>2(HR2,74,CI1.0.74–10.20,p=0.013)and Polipharmacy(HR2.65,CI0.71–9.81,p<0.001).Conclusions The CGA at admission identified risk factors (Nutritional risk,polypharmacy,functionality for Katz indexand comorbidity index)for premature death in EPGC.They can help to plan a personalized care. on December 24, 2023 by guest. Protected by copyright./ Int J Gynecol Cancer: first published as 10.1136/ijgc-2019-IGCS.384 on 18 September 2019. Downloaded from。

VCS检测技术名词解释
VCS检测技术原理是集三种物理学检测技术于一体,在细胞处于自然原始的状态下对其进行多参数分析。
V (Volume)代表细胞的体积,用低频电流准确分析细胞体积的测量方法;C (Conductivity)代表高频电导性,采用高频电磁探针原理测量细胞内部结构间的差异,即电流通过细胞膜传导过细胞,细胞核的化学组分使电流传导性产生变化从而反映出细胞内含物信息,进而区分体积相近而内部性质不同的细胞群体;S (Scatter)代表光散射,即细胞被一束激光在不同方向和角度测定各种白细胞产生散射光的特征,就是采用氯氖激光源发出的单色激光扫描每个细胞,收集细胞10°~70°出现的散射光信号,探测细胞内核分叶状况和胞浆中的颗粒情况,提供细胞的信息,区分出颗粒特性不同的细胞群体。


VCS参数什么是VCS?VCS是版本控制系统(Version Control System)的缩写。
它是一种用于记录和管理软件开发过程中代码版本变化的工具。
VCS允许多个开发者协同工作,并且可以跟踪每个开发者对代码的修改,以及恢复到之前的任何一个版本。
VCS参数的作用在使用VCS时,我们可以使用一些参数来控制和管理代码版本的变化。
这些参数可以帮助我们更好地管理代码库,追踪变更历史,并与其他开发者共享和合并代码。
以下是一些常见的VCS参数及其作用:1. commitcommit命令用于将当前修改保存为一个新的版本。
通过提交(commit)操作,我们可以记录下每次修改所引入的变化,并为每个版本添加注释说明。
$ git commit -m "Add new feature"在上面的示例中,-m参数用于添加提交消息。
提交消息应该清晰明了地描述这次提交所做的修改内容。
2. checkoutcheckout命令用于切换到不同的分支或恢复到之前某个版本。
通过checkout操作,我们可以在不同分支之间进行切换或回滚到先前的某个状态。
$ git checkout branch-name$ git checkout commit-hash在上面的示例中,branch-name是要切换到的分支名称,commit-hash是要恢复到的特定提交的哈希值。
3. branchbranch命令用于创建、查看和删除分支。
分支可以让我们在不影响主线开发的情况下,进行独立的实验和开发。
$ git branch new-branch$ git branch -d branch-to-delete在上面的示例中,new-branch是要创建的新分支名称,branch-to-delete是要删除的分支名称。
4. mergemerge命令用于将一个分支合并到另一个分支中。
通过合并操作,我们可以将不同分支上的修改合并为一个统一的版本。


vcs电解电容VCS(VariableCapacitanceSystem)电解电容是一种液体电解电容(LDC)的一种,属于变容量处理系统(VCS)的一种。
它是由一个金属容器内液体电解质,由一个金属膜组成的电容器,金属膜组构造形成双金属电容片,其中膜由一层氧化物分层,构成电解质电容组成液体电解电容。
VCS电解电容通常由一个容量电池或非线性电容连接而成,它的容量可根据需要以步进的方式进行调整。
VCS电解电容的特点VCS电解电容的特点在于它可以通过调整液体电解质的浓度来调节它的容量,从而达到电容器的可调容量的要求。
由于它的金属容器内充满液体电解质,其结构比传统固体电解电容更加复杂。
VCS电解电容由于拥有灵敏度高、工作电压低、温度稳定性高、稳定性佳、体积小、可靠性强等特点,在电子设备中得到了广泛的应用。
一般来说,VCS电解电容的容量可以在0.001-10uF之间进行调节,容量的调节范围比传统的固体电容要大得多。
VCS电解电容的应用VCS电解电容在电子设备中得到了广泛的应用,主要用于滤波器、放大电路、调节电路、噪声补偿、信号处理等电子设备中,也可用于高频开关电源、数字电路和精密仪器仪表中。
VCS电解电容的优势VCS电解电容是一种电解电容,其优点在于它可以根据电池的变化而调节它的容量,从而达到电路的需求,它的容量调节范围比传统的固定电容大得多,可以更好的满足电路的要求。
另外,VCS电解电容具有灵敏度高、工作电压低、温度稳定性高、稳定性佳、体积小、可靠性强等特点,在电子设备中的应用越来越广泛。
VCS电解电容的局限性VCS电解电容虽然有着许多优点,但它也存在一些局限性,首先,它的制作工艺比传统固定电容要复杂,生产成本更高;其次,由于VCS电解电容的金属容器内充满液体电解质,使得其焊接、安装、维护更加复杂,操作起来也更加麻烦。
最后,由于加工技术的限制,VCS 电解电容的容量只能在一定的范围内进行调整,无法进行大范围的调整。

vcs(鞘层电容电压
"VCS" 在电子学和半导体领域中并不是一个标准的术语或缩写,因此"VCS(鞘层电容电压)" 不是一个普遍认可的概念或术语。
不过,我可以尝试根据上下文来推测其可能的意义。
在半导体物理和器件模拟中,"鞘层"(Sheath)通常是指紧邻半导体表面的电荷耗尽区域,通常是由于表面态或界面态的影响而形成的。
而电容和电压之间的关系则是基础的电子学概念,通常用于描述电路中不同节点之间的电荷存储和电压变化。
如果"VCS" 是指某种特定的电压,那么它可能是与鞘层电容相关的电压。
例如,它可能是在某个特定条件下,鞘层电容所存储的电压值。
然而,这仅仅是一个猜测,没有更多的上下文信息,很难确定"VCS(鞘层电容电压)" 的确切含义。
为了更准确地理解"VCS(鞘层电容电压)" 的含义,建议查阅相关的专业文献、教科书或咨询相关领域的专家。
同时,如果"VCS" 是一个特定领域或技术中的术语,那么了解该领域或技术的背景知识也会有助于理解其含义。

vcs原理Version Control System(VCS)原理。
VCS(Version Control System)是一种用于跟踪和管理文件变化的系统,它可以记录文件的修改历史,并允许用户回溯到不同版本的文件。
VCS的使用范围非常广泛,不仅在软件开发中被广泛应用,也可以用于文档管理、设计图纸管理等领域。
本文将介绍VCS的原理,包括其基本概念、工作原理和常见的VCS系统。
1. 基本概念。
在介绍VCS的原理之前,首先需要了解一些基本概念。
VCS中最重要的概念之一是“版本”,它表示文件在某个特定时间点的状态。
当用户对文件进行修改时,VCS会创建一个新的版本,并记录这次修改的内容。
另一个重要的概念是“分支”,它允许用户在不影响主线开发的情况下,进行独立的修改和实验。
此外,“合并”是指将两个不同的分支或版本的修改合并到一起,以便形成一个新的版本。
2. 工作原理。
VCS的工作原理可以简单地分为三个步骤,提交、存储和检出。
首先,当用户对文件进行修改后,需要将这些修改提交到VCS中。
在提交过程中,VCS会记录这次修改的内容,并为其创建一个新的版本号。
其次,VCS会将所有的版本信息存储起来,通常是在一个中央服务器或者分布式系统中。
最后,当用户需要回溯到历史版本或者与其他人共享文件时,可以通过检出操作来获取所需的版本。
3. 常见的VCS系统。
目前,市面上有多种VCS系统可供选择,其中最流行的包括Git、SVN (Subversion)和Mercurial等。
这些系统在原理上有一些差异,但它们的基本功能和工作原理是相似的。
Git是一种分布式的VCS系统,它具有高效的分支和合并功能,因此在开源社区和企业中被广泛应用。
SVN是一种集中式的VCS系统,它侧重于文件和目录的版本控制,适用于一些传统的项目管理场景。
Mercurial是另一种分布式的VCS系统,它和Git类似,但在一些细节上有所不同。
总结。
VCS是一种用于跟踪和管理文件变化的系统,它通过记录文件的修改历史,允许用户回溯到不同版本的文件。
vcs使用手册版本控制系统(Version Control System,简称VCS)是软件开发中非常重要的工具,用于管理和跟踪代码的版本和变更。
本手册将介绍VCS的基本概念、常用命令和最佳实践,以帮助开发人员更好地使用版本控制系统。
一、基本概念1.1 仓库(Repository)仓库是VCS存储代码的地方,包括所有版本的代码和历史记录。
1.2 分支(Branch)分支是仓库中的一个独立的代码副本,用于开展不同的开发任务。
分支允许开发人员在不影响主线代码的情况下进行独立的开发工作。
1.3 提交(Commit)提交是指将代码的修改保存到版本控制系统中的操作。
每次提交都会生成一个唯一的标识符,用于跟踪代码的变更历史。
1.4 检出(Checkout)检出是指从版本控制系统中获取代码的操作。
开发人员可以在自己的工作环境中检出代码,并在本地进行修改和测试。
二、常用命令2.1 初始化仓库git initsvnadmin create2.2 克隆仓库git clone [仓库地址]svn checkout [仓库地址]2.3 添加文件git add [文件名]svn add [文件名]2.4 提交代码git commit -m "提交说明" svn commit -m "提交说明" 2.5 更新代码git pullsvn update2.6 创建分支git branch [分支名]svn copy [源路径] [目标路径] 2.7 切换分支git checkout [分支名]svn switch [分支路径]2.8 合并分支git merge [分支名]svn merge [源路径] [目标路径]2.9 查看提交历史git logsvn log2.10 撤销修改git revert [提交ID]svn revert [文件名]三、最佳实践3.1 分支管理为每个新功能或修复创建独立的分支,避免直接在主线代码上进行修改。
vcs血液细胞血细胞仪白细胞五分类法原理及质控血液细胞分析仪(VCS血细胞仪)是一种用于对血液中的细胞进行计数、测量和分类的仪器。
在白细胞的分类中,常用的是五分类法,即将白细胞分为:中性粒细胞、淋巴细胞、单核细胞、嗜酸性粒细胞和嗜碱性粒细胞。
VCS血细胞仪的原理是通过光学技术和电子学技术。
仪器会将采集到的血液样本通过流式细胞仪等装置进行传感器检测,并测量细胞的大小、形状和光散射特性。
光散射特性是指样本中细胞对光的散射效应,每个细胞的散射效应是不同的,根据这些差异就可以对细胞进行分类。
质控是指在使用血液细胞分析仪进行测试前,对仪器进行校准和验证,保证测试结果的准确性和可靠性。
质控是非常重要的步骤,它可以帮助发现仪器的偏差和误差,并及时进行调整和修正。
在白细胞五分类法中,常用的质控方法包括:
1. 使用稳定的标准化试剂,这些试剂具有已知的细胞浓度和特征,用于验证仪器的准确性,确保测试结果符合预期。
2. 定期进行质控样本的测试,这些样本是事先制备好的,其细胞数量和种类都已知,用于验证仪器是否能够正确分类和计数细胞。
3. 监测仪器的背景噪声水平,减少假阳性和假阴性的可能性。
总之,VCS血细胞仪白细胞五分类法的原理是通过光学技术和电子学技术对血液细胞进行测量和分类,质控则是保证仪器测试结果准确可靠的重要步骤。
VCS使用中文教程什么是VCS?VCS(Version Control System)是一种管理和追踪软件代码变更的工具。
它允许多个开发者在同一个项目中协同工作,并且记录和管理代码的变更历史。
通过使用VCS,开发者可以轻松地创建新的分支和合并已有的分支,方便团队合作和代码管理。
最常见的VCS工具是Git。
为什么要使用VCS?使用VCS有许多好处。
首先,VCS可以追踪和记录代码的变更历史,包括哪些文件被修改、何时被修改以及具体修改的内容。
这个功能很有用,可以帮助团队成员回顾和理解代码的演变过程,同时也方便排查代码错误。
其次,VCS可以支持并行开发。
多个开发者可以在同一个项目上并行工作,每个人都可以创建自己的分支,将自己的修改提交到主分支之前先合并。
这种并行开发的方式避免了多人同时修改同一个文件引发的冲突,提高了团队的工作效率。
此外,VCS也可以支持版本回滚。
如果在次代码提交后发现了问题,可以轻松地回退到之前的版本,修复问题后再次提交。
这样避免了错误代码的传播和部署。
VCS的基本操作使用VCS的第一步是在本地计算机上安装VCS工具,如Git。
安装完成后,可以通过以下几个基本操作来管理代码仓库:1. 创建代码仓库:在计算机中选择一个目录作为代码仓库的根目录,使用命令`git init`来初始化一个新的仓库。
2. 添加文件:将需要管理的文件复制到代码仓库中,使用命令`git add <file>`将文件添加到仓库的暂存区。
5. 创建分支:使用命令`git branch <branchname>`可以创建一个新的分支。
分支是用来开发新功能或修复错误的独立代码片段。
6. 切换分支:使用命令`git checkout <branchname>`可以切换到指定的分支上。
7. 合并分支:使用命令`git merge <branchname>`可以将指定分支的代码合并到当前分支上。
VCS使用中文教程Version Control System (VCS) 是一种用来管理和追踪代码变更的工具。
它允许开发人员在多个终端上协同工作,记录和恢复历史记录,并解决代码冲突。
本教程将介绍VCS的基本概念、工作流程以及如何使用常见的VCS工具,如Git。
1.为什么需要VCS?在软件开发过程中,代码的变化是无法避免的。
而VCS的存在可以让我们更好地管理和追踪这些变化。
它有以下优点:-历史记录追踪:VCS可以记录每次代码变更的详细信息,包括谁修改了代码、何时修改的以及修改了哪些部分。
这允许开发人员在需要时回溯历史并找到特定的代码状态。
-多人协作:VCS允许多个开发人员在同一个项目上协同工作,避免了手动合并代码带来的麻烦。
开发人员可以在各自的分支上工作,并通过合并操作将代码整合到主分支。
-冲突解决:当多个开发人员同时修改同一部分代码时,VCS可以帮助解决冲突。
它可以检测到冲突并提醒开发人员进行手动合并或选择合适的代码版本。
2.基本概念在使用VCS之前,我们需要了解一些基本概念:- 仓库(Repository):一个VCS仓库是存储代码和相关历史记录的地方。
它可以存储在本地或远程服务器上。
- 分支(Branch):分支是基于主分支或其他分支创建的独立开发线。
它允许团队成员在不同的分支上开发不同的功能,并在合适时将代码合并到主分支。
- 合并(Merge):合并是将一个分支上的代码变更合并到另一个分支的过程。
这通常涉及手动解决冲突。
- 冲突(Conflict):当两个分支同时修改了同一个文件的相同部分,就会发生冲突。
VCS会提示开发人员解决冲突。
3. Git的使用Git是目前最流行的VCS工具之一,下面是Git的基本使用教程:- 初始化仓库:首先,使用"git init"命令在本地创建一个新的仓库。
这将在当前目录下创建一个名为".git"的隐藏文件夹,它存储了Git仓库的相关信息。