生物工程专业英语期末复习资料
- 格式:doc
- 大小:49.50 KB
- 文档页数:7

Chapter OneFundamentals of MedicinePassage 1Anatomy of Mouse and Human Heart单词:Anatomy 解剖学anatomical 解剖的,解剖学的atria 心房atria chamber 心房腔cardiovascular 心血管系统genetical 遗传的conception 受孕diaphragm 横膈,横膈膜fetus 胎儿,胎gestational 妊娠的,妊娠期的morphological 形态学的murine 鼠类,鼠性的neonatal 新生的,新生期的,新生儿的,新生婴儿pericardial cavity 心包腔prenatal 产前的,出生前的pulmonary 肺的septation 分隔,中隔,隔膜thoracic cavity 胸腔句子:A fast-increasing number of genetically modified mouse models with structural and functional abnormalities in the cardiovascular system undoubtedly will contribute to an improved understanding of molecular and morphological mechanisms that regulate human heart development in health and disease.(5分)小鼠基因修饰模型是通过改变小鼠基因因而使其心血管系统结构和功能异常得到改变的一种动物模型。
这类模型的大量增加,无疑会促进我们理解人的心脏在健康及病理状态下的分子和形态学机制。
Developmentally, it is interesting to note that the gestational window during which the heart develops is quite different in the mouse and human. In the human it takes about 2 mo (from conception) for the heart to complete septation, followed by another 7 mo to further mature until the baby is born and the pulmonary circulation kicks in. In the mouse, however, it takes only 2 wk from the time of conception for cardiac septation to complete. After that, the mouse fetus has less than 1 wk of prenatal life before birth.Without going into any detail, it suffices to say that some of the developmental events that in the human are more or less completed at birth are still in progress in the neonatal mouse.人们有趣地发现小鼠与人的心脏在孕育其中的发育有很大不同。

生物专业英语试题及答案一、词汇题(每题2分,共20分)1. 以下哪个单词表示“细胞分裂”?A. Cell divisionB. Cell fusionC. Cell differentiationD. Cell metabolism答案:A2. “基因”在英文中的正确表达是?A. GeneB. GenusC. GenotypeD. Genomics答案:A3. 哪个术语与“光合作用”相关?A. PhotosynthesisB. RespirationC. FermentationD. Anaerobic respiration答案:A4. “遗传工程”的英文表达是什么?A. Genetic engineeringB. Genetic mutationC. Genetic selectionD. Genetic variation答案:A5. “酶”的英文单词是?A. EnzymeB. HormoneC. ProteinD. Lipid答案:A6. “生态系统”在英文中如何表达?A. EcosystemB. BiosystemC. EcosystemsD. Biosphere答案:A7. “进化”的英文对应词是?A. EvolutionB. DevolutionC. InvolutionD. Revolution答案:A8. “克隆”在生物学中的英文术语是什么?A. CloningB. CopyingC. DuplicationD. Replication答案:A9. “物种”的英文单词是?A. SpeciesB. GenusC. VarietyD. Type答案:A10. “微生物”的英文表达是?A. MicroorganismB. MacroorganismC. OrganismD. Microbe答案:A二、阅读理解题(每题5分,共30分)阅读以下段落,并回答问题。
Biotechnology is the use of living organisms and bioprocesses to develop or make products. It involves the use of organisms, cells, and cellular components to research and produce goods and services. Modern biotechnology provides breakthrough products and technologies to combat debilitating and rarediseases, reduce our environmental footprint, feed the hungry, use less and cleaner energy, and have safer, cleaner and more efficient industrial manufacturing processes.11. 根据段落,生物技术涉及哪些方面?A. 使用生物和生物过程开发产品B. 仅使用生物过程C. 仅使用生物D. 使用生物和非生物过程答案:A12. 现代生物技术提供了哪些突破性的产品和技术?A. 治疗罕见疾病B. 减少环境影响C. 提供食物D. 所有上述选项答案:D13. 根据段落,生物技术如何帮助环境?A. 减少环境足迹B. 增加污染C. 加剧气候变化D. 消耗更多资源答案:A14. 生物技术如何帮助解决饥饿问题?A. 提供更少的食物B. 提供更多的食物C. 提高食物价格D. 降低食物质量答案:B15. 生物技术在工业制造中的作用是什么?A. 提高效率B. 降低安全性C. 增加污染D. 减少清洁度答案:A三、完形填空题(每题3分,共15分)阅读以下短文,从所给选项中选择最合适的一项填入空白处。

生物工程专业英语The Origin of Species1.How Biologists Define a SpeciesModern biology generally define a species as group of actually or potenti ally interbreeding populationsthat is reproductively isolated from the such groups. Members of a species can interbreed with each other,but they ca nnot breed with organisms belonging to another species. One advantage of the standard ofreproductive isolation is that it is very precise. Notice, however, that it can only be applied to organismsthat reproduce sexually. Asexual reproducers, including most prokaryotes, many plants, and some animals, must be classified into species on the basis of physical (biochemi cal or morphological) traits.现代生物学大体将物种定义为实际上的一群或潜在的杂交群体,即从这个群体隔离繁殖的后代。
种族中个体可以互相交配,但种间不能。
这种繁殖隔离的一个优势是很精确。
但仅适用于性繁殖的生物。
非性繁殖,包括大多数原核生物,许多植物,某些动物,需要通过自然特征进行归类。
2.Preventing Gene ExchangeTwo general types of mechanisms operate to block the exchange of genes between individuals of relatedgroups. The first general type is made up of prezygotic isolating mechanisms that prevent the formation ofzygotes. Prezygotic isolation falls into two categories: ecological and behavioral. In the first case, tworelated group may become adapted to slightly differe nt environments-perhaps varying soil types or foodsources. Over time, th ese genetic differences become so great that successful cross-fertilization can nolonger take place. In behavioral isolation,related groups evolve differing behaviors such as specificmating rituals-that restrict the exchange of genes to members of the same group.两种基因型机制阻碍了相关群体中个体的基因交换。

GillCapHomozygous(纯合的):A diploid organism that has two identical alleles for particular characteristic.Heterozygous (杂合的):A diploid organism that has two different alletic forms of a particular gene.Phenotype(表型):The physical, chemical, and psychological expression of genes possessed by an organism.Genotype(基因型):The catalog of genes of an organism, whether or not these genes are expressed.Allele(等位基因):Alternative forms of a gene for a particular characteristic (e.g., attached earlobe genes and free earlobe genes are alternative alleles for ear shape).Monohybrid Crosses(单因子杂种):a hybrid produced by crossing parents that are homozygous except for a single gene locus that has two alleles.Dihybrid crosses(双因子杂种,双因子杂合子):A cross between individuals that differ with respect to two specified gene pairs.Law of independent assortment(独立分配定律,自由组合定律)::Members of one gene pair will separate from each otherindependently of the members of other gene pairs.Semiconservative replication(半保留复制):The method of replication of DNA in which the molecule divides longitudinally,each half being conserved and acting as a template for the formation of a new strand.Lagging strand(后随链):is synthesized in short stretches known as Okazaki fragments.DNA polymerase( DNA 聚合酶):An enzyme that brings new DNA triphosphate nucleotides into position for bonding onanother DNA molecule.Age structure(年龄结构):Of a population, the number of individuals in each of several or many age categories.Density-dependent factors(密度依赖因子,密度制约因子):population-limiting factors that become more effective as thesize of the population increases.1.As mitosis proceeds, the spindle microtubules play a crucial role in ensuring that both paired and separated chromatids move in the right directions at the proper times. Each half of the spindle forms as microtubules extend from each pole of a dividing cell to the region of the metaphase plate. During prophase, other microtubules, the centromeric fibers, extend outward from the spindle poles to structures on the chromosomes called kinetochores. During anaphase the fibers begin to shorten, and the chromatids begin to move apart.在有丝分裂过程中,是纺锤体微管确保了染色单体在适当时间以正确方向进行分离。


生物专业英语Biochemistry 生物化学essential element必需元素trace elements微量元素proteoglycan蛋白聚糖amino acid氨基酸primary structure 一级结构random coil无规卷曲structural domain 结构域subunit亚基degeneration变性adenine腺嘌呤guanine鸟嘌呤cytosine胞嘧啶thymine胸腺嘧啶uracil尿嘧啶nucleoside 核苷nucleotide核苷酸base pairing碱基配对base pair碱基对数base碱基数gyrase旋转酶nucleosome核小体 complementary DNA互补DNA plasmid质粒transposons转座子repetitive sequence重复序列exon外显子intron内含子variable loop可变环ribonuclease核糖核酸酶renaturation复性hyperchromic effect增色效应base stacking force碱基堆积力annealing退火melting-out temperature熔解温度hypochromic effect减色效应maltose麦芽糖sucrose蔗糖lactose乳糖starch淀粉glycogen糖原cellulose纤维素cellulase纤维素酶selectivity选择性substrate底物 holoenzyme全酶cofactor辅因子coenzyme辅酶oxidase氧化酶metabolism新陈代谢assimilation同化作用catabolism异化作用metabolite代谢产物biological oxidation 生物氧化cytochrome细胞色素rotenone鱼藤酮amytal阿密妥antimycin A抗霉素A cyanide氰化物glycolysis糖酵解ethanol乙醇citrate柠檬酸cis-aconitate 顺乌头酸succinic acid琥珀酸oxaloacetic acid草酰乙酸 acetyl-coenzyme乙酰辅酶fumarate延胡索酸glyoxylate cycle 乙醛酸循环malate苹果酸fatty acid 脂肪酸carbon unit一碳单位metabolic regulation代谢调feedback regulation反馈调节structural gene结构基因promoter gene启动基因operator gene操纵基因regulator gene调节基因termination factor终止因子triplet code三联体密码initiator codon起始密码termination codon终止密码replicon复制子core enzyme 核心酶primosome 引发体Okazaki fragment冈崎片段leading chain 前导链lagging strand后随链terminator终止子telomere端粒telomerase端粒酶replication fork复制叉vector载体promoter启动子terminator终止子operon操纵子codon密码子degeneracy简并性hormone激素citric acid cycle 柠檬酸循环Deamination 脱氨基作用urea cycle尿素循环euchromatin 常染色质messenger RNA信使RNAtransfer RNA 转移RNA ribosome RNA核糖体RNA secondary structure二级结构super-secondary structure超二级结构tertiary structure三级结构quaternary structure四级结构semiconservative replication 半保留复制ornithine cycle 鸟氨酸循环negative supercoil DNA负超螺旋DNA positive supercoil DNA正超螺旋DNA restriction endonuclease 限制性内切酶polymerase chain reaction 聚合酶链反应oxidative deamination 氧化脱氨作用transamination 转氨基作用reverse transcription 逆转录decarboxylation 脱羧作用semidiscontinuous replication半不连续复制reverse transcriptase 逆转录酶missense mutation 错义突变synonymous mutation 同义突变neutral mutation中性突变nonsense mutation 无义突变double-strand circular DNA 双链环形DNA phosphatidic acid 磷脂酸essential amino acids 必需氨基酸dihydrouracil loop 二氢尿嘧啶环anticodon loop 反密码子环superhelical DNA 超螺旋DNAopen circular DNA 开环DNA linear DNA 线形DNAbase stacking force 碱基堆积力glucogenic and ketogenic amino acid生糖兼生酮氨基酸ketogenic amino acid 生酮氨基酸glucogenic amino acid 生糖氨基酸Genetics遗传学heredity 遗传variation 变异pisum sativum 豌豆 segregation 分离gamete 生殖细胞zygote 合子allele 等位基因genotype 基因型phenotype 表现型test cross 测交oryza sativa 水稻diploid 二倍体haploid 单倍体centromere 着丝粒satellite 随体linker 连丝mitosis 有丝分裂mesoblast中胚层spindle 纺锤体interphase 间期spindle fiber 纺锤丝vicia faba 蚕豆nucleoplasm 核质spermatogenous 精原细胞oogonium 卵原细胞spermatid 精细胞Phenocopy 拟表型epistasis上位效应mutant突变型gametic lethal配子致死zygotic lethal合子致死autosome 常染色体dominant lethal显性致死carrier 携带者homozygote 纯合体heterozygote 杂合体genotype 基因型phenotype 表现型linkage group 连锁群interference 干涉coincidence 并发率genetic map 遗传学图wild type野生型secondary constriction 次级缢痕mutation 突变nucleolar organizer 核仁形成区induction 诱导first polar body 第一极体strain 菌株sister chromatids 姐妹染色单体recipient 受体female gametic nucleus 卵核donor 供体multiple alleles 复等位基因fragment 片段sex-chromosome性染色体heterokaryon 异核体sex-linked inheritance 伴性遗传auxotroph 营养缺陷型primary constriction 初级缢痕prophage 原噬菌体secondary constriction 次级缢痕transduction 转导complementary gene互补基因Mendel’s laws 孟德尔定律 law ofhomologous chromosome 同源染色体segregation 分离定律sister chromatids 姐妹染色单体first filial generation 子一代secondary oocyte 次级卵母细胞parental generation 亲代three-point testcross 三点测交dominant character显性性状primary spermatocyte 初级精母细胞recessive character 隐性性状secondary spermatocyte 次级精母细胞hereditary determinant遗传因子first division segregation 第一次分裂分离parental combination 亲组合second division segregation 第二次分裂分recombination 重组合离punnett square 棋盘法law of independent assortment 自由组合Mendelian character 孟德尔性状定律primary constriction 初级缢痕Microbiology微生物学living creatures 生物culture medium 培养基lawn菌苔culture plate 培养平板bacteria 细菌archaea 古生菌eukaryote真核生物prokaryote 原核生物protozoan 原生动物hypha 菌丝 mycoplasma 支原体yeast 酵母菌plasmolysis 质壁分离Escherichia Coli大肠杆菌murein胞壁质peptidoglycan 肽聚糖 mucopeptide 黏肽outer membrane外膜chromosome染色体nucleolus 核仁nucleoid 拟核chromatin 染色质 centromere 着丝粒telomere 端粒protoplast 原生质体mycoplasma 支原体glycoprotein 糖蛋白mesosome 间体 cytoplasm细胞质megnetosome磁小体nucleoid拟核glycocalyx 糖被capsule 荚膜flagellum 鞭毛lysosome 溶酶体chloroplast 叶绿体thylakoid类囊体inorganic salt 无机盐peptone 蛋白胨sulfur bacteria 硫细菌beef extract牛肉膏vitamin 维生素inclusion body 内含物lithotroph 无机营养型medium 培养基agar 琼脂organotroph 有机营养型antiport 逆向运输active transport 主动运输 pinocytosis 胞饮作用catabolism 分解代谢passive transport 被动运输 uniport 单向运输anabolism 合成代谢fermentation发酵batch culture 分批培养log phase 对数生长期stationary phase 稳定生长期lag phase 迟缓期decline phase衰亡期aerobe 好氧菌 antibiotic 抗生素antigenome 反基因组transformation 转化 genome 基因组plasmid 质粒transforming factor 转化因子diploid 二倍体haploid 单倍体transposable element 转座因子conjugation接合作用transposon转座子phenotype 表型genotype基因型auxotroph营养缺陷型wild-type野生型transition 转换transversion 颠换spontaneous mutation 自发突变reverse mutation 回复突变sexduction 性导transduction 转导 promoter 启动子operon 操纵子recombination repair 重组修复repressor 阻遏蛋白corepressor辅阻遏物clone 克隆 denaturation 变性annealing 退火extension 延伸cloning vector 克隆载体replicon 复制子telomere 端粒cohesive end 黏性末端promoter 启动子terminator 终止子gene therapy 基因治疗phylogeny 系统发育ammonification 氨化作用nitrification 硝化作用denitrification 反硝化作用expression vector 表达载体aerobic respiration有氧呼吸anaerobic respiration无氧呼吸origin of replication 复制起始点incompatibility 不亲和性gene mutation 基因突变synonymous mutation 同义突变chromosomal aberration 染色体畸变missense mutation 错义突变frame-shift mutation 移码突变lactose operon 乳糖操纵子negative transcription control 负转录调控 tryptophan operon 色氨酸操纵子 cytoplasmic inheritance 细胞质遗传 genetic engineering 基因工程 recombinant DNA technology 重组DNA技术palindromic structure 回文结构spread plate method 涂布平板法pour plate method 倾注培养法streak plate method 平板划线法shake tube method 稀释摇管法continuous culture 连续培养精品文档It was not evident, for example, whether or not a particular kind of protein has a consistent sequence of amino acids that would be the same in one individual molecule as it would be in another of that same kind of protein.例如,一类特定的蛋白质是否具有一致的氨基酸序列还是不明白的,同类蛋白质的单独一个分子与另一个分子的氨基酸序列也许是相同。
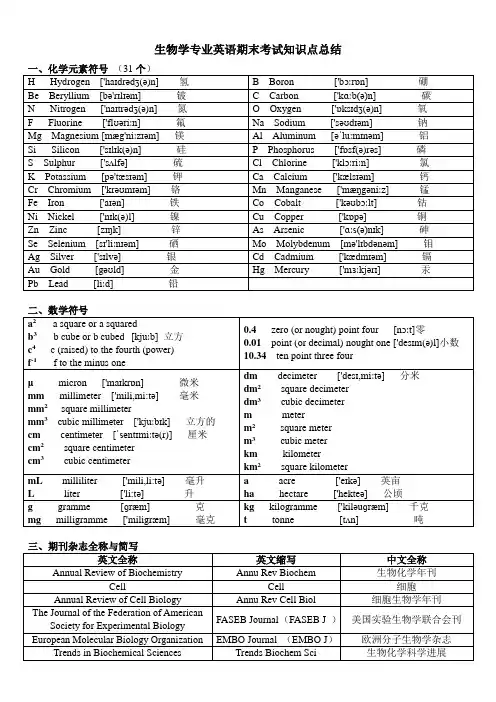
生物学专业英语期末考试知识点总结一、化学元素符号(31个)H Hydrogen ['haɪdrədʒ(ə)n] 氢 B Boron ['bɔːrɒn] 硼Be Beryllium [bə'rɪlɪəm] 铍 C Carbon ['kɑːb(ə)n]碳N Nitrogen ['naɪtrədʒ(ə)n] 氮O Oxygen ['ɒksɪdʒ(ə)n] 氧F Fluorine ['flʊəriːn] 氟Na Sodium ['səʊdɪəm] 钠Mg Magnesium [mæg'niːzɪəm] 镁Al Aluminum [əˈluːmɪnəm] 铝Si Silicon ['sɪlɪk(ə)n] 硅P Phosphorus ['fɒsf(ə)rəs] 磷S Sulphur ['sʌlfə] 硫Cl Chlorine ['klɔːriːn] 氯K Potassium [pə'tæsɪəm] 钾Ca Calcium ['kælsɪəm] 钙Cr Chromium ['krəʊmɪəm] 铬Mn Manganese ['mæŋgəniːz] 锰Fe Iron ['aɪən] 铁Co Cobalt ['kəʊbɔːlt] 钴Ni Nickel ['nɪk(ə)l] 镍Cu Copper ['kɒpə] 铜Zn Zinc [zɪŋk]锌As Arsenic ['ɑːs(ə)nɪk] 砷Se Selenium [sɪ'liːnɪəm] 硒Mo Molybdenum [mə'lɪbdənəm] 钼Ag Silver ['sɪlvə] 银Cd Cadmium ['kædmɪəm] 镉Au Gold [gəʊld] 金Hg Mercury ['mɜːkjərɪ] 汞Pb Lead [liːd] 铅二、数学符号a2 a square or a squaredb3 b cube or b cubed[kjuːb] 立方c4 c (raised) to the fourth (power)f-1 f to the minus one 0.4 zero (or nought) point four [nɔːt]零0.01point (or decimal) nought one ['desɪm(ə)l]小数10.34ten point three fourμ micron ['maɪkrɒn] 微米mm millimeter ['mili,mi:tə] 毫米mm2 square millimetermm3cubic millimeter ['kjuːbɪk] 立方的cm centimeter [ˈsentɪmiːtə(r)] 厘米cm2square centimetercm3cubic centimeter dm decimeter ['desɪ,miːtə] 分米dm2square decimeterdm3cubic decimeterm meterm2square meterm3cubic meterkm kilometerkm2square kilometermL milliliter ['mili,li:tə] 毫升L liter ['li:tə] 升a acre ['eɪkə] 英亩ha hectare ['hekteə] 公顷g gramme [ɡræm] 克mg milligramme ['miligræm] 毫克kg kilogramme ['kiləuɡræm] 千克t tonne [tʌn] 吨三、期刊杂志全称与简写英文全称英文缩写中文全称Annual Review of Biochemistry Annu Rev Biochem 生物化学年刊Cell Cell 细胞Annual Review of Cell Biology Annu Rev Cell Biol 细胞生物学年刊The Journal of the Federation of AmericanSociety for Experimental BiologyFASEB Journal (FASEB J )美国实验生物学联合会刊European Molecular Biology Organization EMBO Journal (EMBO J)欧洲分子生物学杂志Trends in Biochemical Sciences Trends Biochem Sci 生物化学科学进展Molecular and Cellular Biology Mol Cell Biol 分子与细胞生物学杂志Journal of Biological Chemistry J Biol Chem 生物化学期刊Plant Cell Plant Cell 植物细胞Molecular Pharmacology Mol Pharmacol 分子药理学DNA Cell Biology DNA Cell Biol DNA细胞生物学Journal of Molecular Biology J Mol Biol 分子生物学期刊Biochemistry Biochemistry 生物化学Cell Growth and Differentiation Cell Growth Differ 细胞生长与分化Methods in Enzymology Method Enzymol 酶学方法Molecular Microbiology Mol Microbiol 分子微生物学Journal of Neurochemistry J Neurochem 神经化学杂志Progress in Biophysics & MolecularBiologyProg Biophys Mol Biol 生物物理和分子生物学进展Advances in Microbial Physiology Adv Microb Physiol 微生物生理学进展Molecular Biology and Evolution Mol Bio Evol 分子生物学与进化Journal of Cellular Biochemistry J Cell Biochem 细胞生物化学杂志Molecular Biology and Medicine Mol Biol Med 分子生物学与药学Federation of European BiochemistrySociety FEBS Letters ( FEBS Lett)欧洲生物化学学会联合会杂志Plant Molecular Biology Plant Mol Biol 植物分子生物学Journal of Molecular Evolution J Mol Evol 分子进化杂志Analytical Biochemistry Anal Biochem 分析生物化学Molecular Immunology Mol Immunol 分子免疫学Neurochemical Research Neurochem Res 神经化学研究Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry Mol Cell Biochem 分子与细胞生物化学Molecular Biology Report Mol Biol Rep 分子生物学报告Proceedings of National Academy ofsciences USA PROC NATL ACADSCI USA美国国家科学院院刊四、作文1. Topic or title or head.2. Authors and their institutes.3. Abstract4. Introduction5. Materials and Methods6. Results7. Discussion8. References or literatures cited.How to write a report or paperA paperconsists of 8partsEnglish description英文叙述Chinese narrative中文叙述Part1.Topic or titleor head.(主题/标题/头)Concise and informative 简洁而信息量丰富Part2.Authors and their institutes. (作者及其所在研究机构)The name(s) of the auther(s)The affiliation(s) and address(es) of the auther(s)The e-mail address,telephone and fax numbers of the corresponding auther作者姓名作者的隶属机构和地址通讯作者的电子邮件地址,电话号码以及传真号。

1.( 多选题 | 2 分)根据Jordan(1997)二分法,ENGLISH teaching 包括A . ESPB . EGPC . EAPD . EGAPE . ESAP正确答案: A B2.( 单选题 | 2 分)ESP具有()特点A . 广泛性B . 工具性C . 应用性D . 人文性E . 基础性F . 以上都不是正确答案: B3.( 多选题 | 2 分)以下哪些属于原因和结果的标志性语言(signpost language)A . is due to B . whereasC . so to speakD . likewiseE . lead to正确答案: A E4.( 多选题 | 2 分)以下哪些属于分类的标志性语言(signpost language)A . such asB . for exampleC . such asD . that is to sayE . because正确答案: A B C选择哪一种阅读方式主要影响因素是()A . 文献长短B . 文献类型C . 专业背景D . 阅读目标E . 以上都不是正确答案: C6.( 多选题 | 2 分)Among these forms, dissimilatory sulfate–reducing bacteria use a restricted group of low-molecular-weight compounds (e.g., lactate) and generate biomass, carbon dioxide, and soluble end products.A . DefiningB . ClassificationC . SequenceD . Comparison and contrastE . Cause and effectF . Giving examplesG . Reformulation H . ListingI . Parenthetical statements正确答案: F H I7.( 单选题 | 2 分)Saxitoxin, a potent neurotoxin, is responsible for paralytic shellfish poisoning, a neurological disorder in humans resulting from the consumption of contaminated shellfish.A . DefiningB . ClassificationC . SequenceD . Comparison and contrastE . Cause and effectF . Giving examplesG . Reformulation H . ListingI . Parenthetical statements 正确答案: EAP写作的一般过程不包括A . 头脑风暴B . 草稿C . 与读者交流D . 了解读者E . 确定主题正确答案: C9.( 多选题 | 2 分)AP的学术语体基本特征包括A . 正式用语B . 客观性C . 学术性D . 主观性E . 以上都不是正确答案: A B C10.( 单选题 | 2 分)AP的过程顺序为 1.头脑风暴(讨论) 2.初稿 3.修改与语言润色 4.提炼出有价值的想法 5.明确读者和写作目的 6.确定主题7.围绕主题展开研究A . 6475123B . 4675123C . 1465723D . 1645723正确答案: B11.( 单选题 | 2 分)摘要重要组成部分BPMRC中的“R”代表A . 基础背景B . 研究目的C . 研究方法D . 研究结果E . 结论正确答案: D对于摘要的描述,错误的是A . 摘要内容没有要求,根据不同作者的写作风格而定B . 摘要是微型缩略版的论文C . 摘要不属于论文正文部分D . 摘要通常作为检索数据库的主要索引对象正确答案: A13.( 单选题 | 2 分)摘要重要组成部分BPMRC中的“B”代表A . 基础背景B . 研究目的C . 研究方法D . 研究结果E . 结论正确答案: A14.( 单选题 | 2 分)摘要重要组成部分BPMRC中的“M”代表A . 基础背景B . 研究目的C . 研究方法D . 研究结果E . 结论正确答案: C15.( 单选题 | 2 分)摘要重要组成部分BPMRC中的“P”代表A . 基础背景B . 研究目的C . 研究方法D . 研究结果E . 结论正确答案: B以下对于论文各部分正确的描述为A . 引言主要是对研究背景及研究进展进行阐述B . 结论部分是对实验结果进行描述与分析C . 讨论部分是对结果进行归纳和总结D . 参考文献不属于正文部分正确答案: A17.( 单选题 | 2 分)以下摘要括号部分请选择合适的词或词组。
单词整理a- 不,非aseptic 无菌的;apolar 非极性的;asymmetercal 不对称的ab- 去,离开,脱离abnormal 反常的;abuse 滥用;abduct 外展神经aceto- 乙酰acetolactate 乙酰乳酸;acetyl 乙酰(基);acetyl phosphate 乙酰磷酸actino- 光线,射线,放线菌acrinomycin 放线菌;actinometer 化学光度计acyl- 酰基acyltransferase 转酰基酶aden(o)- 腺adenovirus 腺病毒aer(o)- 空气的aerobic 需氧的;aeration 通气agro- 土壤;农业agrochemical 农用化学品;agronomical 农艺学的amidino- 脒基amidinotransferase 转脒基酶amylo- 淀粉amylopectin 支链淀粉;amylose 直链淀粉;amyloplastid 造粉粒an- 不,非anaerobic 厌氧的;analgesic 止痛的;anapepsia 胃蛋白酶缺乏ane- 烷methane 甲烷anti- 反对,对抗,取消,抑制,解除antagonistic 对抗的;antibody 抗体;antigen 抗原angio- 血管angiogenin 血管生成素;angioma 血管瘤aut(o)- 自己的,自动的autotroptic 自养的;autonomous 自发的;autosensitization 自身致敏bio- 生物的biochemistry 生物化学;bioamine 生物胺;biocatalyst 生物催化剂bromo- 溴的5-bromouracil 5-溴尿嘧啶bis- 双,二bisexualism 雌雄异体;bisphenols 双酚类brady- 缓慢hradycardia 心动过缓;bradykinin 缓激肽carb(o)- 碳的carbodiimide 碳二亚胺;carbohydrate 碳水化合物carboxy(l) 羧基carboxy methylcellulose 羧甲基纤维素carcin(o)- 癌carcinogen 致癌物cardio- 心脏cardiotonic 强心的cent(i)- 一百的,百分之一的,厘century 世纪;centimeter 厘米;centimorgan 厘摩chemo- 化学chemoautotrophy 化能自养;chemosynthesis 化能合成;chemoattractant 化学引诱物chlor- 氯,绿chloramphenicol 氯霉素;chlorobenzene 氯苯;chloroplast 叶绿体chrom(o)- (chromat(o)-) 颜色chromatid 染色单体;chromosome 染色体;chromatography 色谱法cis- 顺cistrion 顺反子;cis regulation 顺式调节;cis-isomer 顺式异构体co- 一起,共同cooperate 合作;coincide 重合;cognate 同源的con- (col-,com-,cor-)连同,一起complexant 络合剂;concentrate 集中;combine 结合contra- 反对,相反contrast 对照;contrary 相反的;contrasuppression 反抑制counter- 反,逆couner-circulation 逆向循环;counter-ecolution 逆进化;counter receptor 反受体cryo- 寒冷,冷冻cryopreservation 冷冻保藏;cryogen 冷冻剂;cryophile 适寒性cyano- 青,蓝,氰cyanobacteria 蓝细菌;cyanocobalamin 氰钴胺素;cyanogen bromide 溴化氰de- 否定,除去,离开,降低,脱debug 排除故障;deceleration 降速;degeneration 退化deca- 十,葵decahedron 十面体;decane 葵烷;decamer 十聚体deoxy- 脱氧deoxycytosine 脱氧胞嘧啶di- 二,二倍,二重diploid 二倍体;dimer 二聚体;divinylbenzene 二乙烯苯dia- 横穿diameter 直径;dialysis 透析;diaphragm 隔膜dis- 否定,分离disintegration 破碎;disagree 不同意;dissemination 散播dodeca- 十二dodecahedron十二面体;dodecane 十二烷;dodecamer 十二聚体eco- 生态,居处,宿主ecogentics 生态遗传学;ecology 生态学;ecomone 生态信息素ectoblast 外胚层;ectohormone 外激素;ectodomain 胞外结构electr(o)- 电electrodialysis 电渗析en-(em-) 使成为,置于……中enable 能够;encode 编码;embed 包埋end(o)- 内endergonic 吸能的;endospore 内生孢子enol 烯醇phosphoenolpyruvate 磷酸烯醇丙酮酸enter(o)- 肠enteroacteria 肠细菌;enterobactin 肠杆菌素;enterocyte 肠细胞epi- 表;变化epichlorohydrin 表氯醇;epimerase 差向异构体酶;epithelial cell 上皮细胞erythr(o)- 红,赤erythrose 赤藓糖;erythromycin 红霉素;erythrocyte 红细胞eu- 真正eukaryote 真核生物;eukaryocyte 真核细胞;eubacteria 真细菌e(x)- 向外,超出,完全,彻底explant 外植体;elongate 拉长;evaluate 评价ex(o)- 外,在外,产生exothermic 放热的;exergonic 放能的;exogenous gene 外源基因extra- 超出extracellular 胞外的;extract 抽提物;extracellular virus 胞外病毒ferri- 高铁ferricytochrome 高铁细胞色素;ferritin 铁蛋白;ferridoxin 铁氧还原蛋白ferro- 亚铁ferrocytochrome 亚铁细胞色素;ferroheme 血红素;ferrochelatase 亚铁螯合酶flavanol 黄烷酮;flavin 黄素;flavone 黄酮fluoro- 氟基,氟代,荧光fluorochrome 荧光染料;fluoroacetate 氟乙酸;fluorometer 荧光剂formyl- 甲酰formyltetrahydrofolate 甲酰四氢叶酸;formyl 甲酰基;formylation 甲酰化geo 土地geographical barrier 地理障碍;geographical isolation 地理隔离;geosmin 土腥味素glyc(o)- 糖glycoprotein 糖蛋白hem(o,a)-,haem(o,a)-,haemat(o)-血的hemoglobin 血红蛋白;haemagglutinin 血凝素;haem 血红素hemi- 半hemicellulase 半纤维素;hemizygote 半合子;hemiacetal 半缩醛heter(o)- 异,杂,异种heterogeneous 异质的,不均一的;heterotrophic 异养的;heteroantigen 异种抗原hepato- 肝hepatocarcinoma 肝癌;hepatocyte 肝细胞;hepatotoxin 肝脏毒素homeo- 同源,同祖homeotic gene 同源异形基因hom(o)- 相同homogeneous 同质的,均一的;homologous 同源的;homoeosis 同源异形hydr(o)- 水,液体,氢hydrocarbon 烃;hydrocolloid 水胶体;hydrobios 水生生物hydroxy(l) 羟基hydroxyapatite 羟磷灰石;hydroxylase 羟化酶hyper- 超出,过度hyperfiltration 反渗透;hypertension 高血压hypo- 低,(过)少sodium hypochlorite 次氯酸钠;hypoblast 下胚层;hypoimmunity 低免疫性imino- 亚胺基iminodiacetic acid 亚胺基二乙酸immuno- 免疫immunogenic 致免疫的;immunoassay 免疫分析in-(il-,im-,ir-)不,无;在内,入内insoluble 不能溶解的;insuperable 不能克服的;impermeable 不能渗透的infra- 下面,内部infrastructure 基础结构;infrared 红外线的inter- 相互,在……之间interact 相互作用;intergeneric 属间的;inter-particle 颗粒间的intra- 在内,向内intraspecific 种内的;intra-particle 颗粒内的;intravenous 进入静脉的iodo- 碘基,碘代iodometry 碘量法;iodouracil 碘尿嘧啶;iodoacetic acid 碘乙酸iso- 同,等,异isomer 同分异构体;isomerase 异构酶;isobutyl 异丁基kary(o)- 核,细胞核karyology 胞核学keto- 酮基ketohexulose 酮己酮糖;keto acid 酮酸;ketoamin 酮胺lacto- 乳lactobacillus 乳杆菌属;lactogen 催乳素;lactoglobulin 乳球蛋白leuco- 白,无色的leucocyte 白细胞lipo- 脂lipoprotein 脂蛋白;lipoxygenase 脂氧合酶lympho- 淋巴lymphocyte 淋巴细胞macro- 大的,宏观的macromolecule 大分子;macroporous 大孔的mal- 不当,不良malabsorption 吸收不良;malassimulation 同化不全;malnutrition 营养不良megal(o)- 巨大cytomegalovirus 巨细胞病毒mercapto- 巯基β-mercaptoethylamine β-巯基乙胺meso- 内消旋;中(间)meso inositol 内消旋肌醇;mesophilic 嗜温的meth- 甲基methacrylate 甲基丙烯酸methyl 甲基methyltroph 甲基营养菌micro- 微,微小的microscope 显微镜;microcarrier 微载体;microbe 微生物mono- 一,单,单一monoclonal 单克隆的;monolayer 单层multi- 多,多方面multistage 多级;multicellularity 多细胞性;myco- 真菌mycolytic 溶真菌的;mycotoxin 真菌毒素;mycoprotein 真菌蛋白myelo- 髓鞘,髓myeloblast 成髓细胞;myelocyte 髓细胞;myeloma 骨髓瘤myo- 肌myoalbumin 肌白蛋白;myoblast 成肌细胞;myocyte 肌细胞nano- 纳nanobacteria 微小细菌;nanosecond 纳秒;nanotechnology 纳米技术neo- 新neocarcinostatin 新制癌菌素;neocerebellum 新小脑;neomycin 新霉素neur(o)- 神经neural 神经的;neurotoxin 神经毒素nitro- 硝基nitrofuran 硝基呋喃;nitroalkane 硝基烷;nitrobacteria 硝化细菌nucle(o)- 核nucleoside 核苷;nucleophilic 亲核的non- 非,无,不non-newtonian fluid 非牛顿型流体;non-aqueous solution 非水溶液nor- 去甲,正noradrenalin 去甲肾上腺素;normal 正常,正交;normocyte 正红细胞over- 在上面,超过,过overshooting 过调节;overview 简明概述;overcooled 过冷的oligo- 寡oligosaccharide 寡糖,低聚糖onco- 肿瘤oncogene 致癌基因ovo- 卵ovocenter 卵中心体;ovorubin 卵红蛋白;ovum 卵细胞oxalo- 草酰,乙二酸-酰基oxalo acetate 草酰乙酸oxy- 氧;羟基deoxyguanosine 脱氧鸟苷;oxytetracycline 土霉素;oxyproline 羟脯氨酸path(o)- 病pathogen 病原菌para- 旁(位),对(位),副parabronchus 复支气管;parathyroid gland 甲状旁腺;paraoxon 对氧磷peri- 周,周围perimeter 周长;periplasmic space 周质间隙;periblast 胚周区per- 过peroxisome 过氧化质体phenyl 苯基phenylalanine 苯丙氨酸phospho- 磷酸基phosphofructokinase 磷酸果糖激酶phosphoryl- 磷酰基phosphorylation 磷酸化作用phyto- 植物phytoalexin 植物抗毒素;phytology 植物学;phytoplankton 浮游植物plasm(o)- 原生质,血浆plasmolemma 质膜pleio- 多pleiotropic 多效的;pleioxeny 多主寄生;pleiotropy 多效性poly- 多,聚polysaccharide 多糖;polystyrene 聚苯乙烯;polyacid 多酸post- 后post-transcriptional modification 转录后修饰作用;post-exponential growth phase 后对数生长期pre- 前,在前premature 过早的;precursor 前体;premise 前提pro- 原,前prokaryote 原核生物;prostate 前列腺proteo- 蛋白proteolipid 蛋白脂质;proteome 蛋白质组;proteolysis 蛋白酶解proto- 原始,初prototype 原型;protoplast 原生质体pseud(o)- 假的pseudo-plastic fluid 假塑性流体;psudodominance 假显性;pseudohypha 假菌丝pyro- 焦,火,热pyrophosphorylase 焦磷酸化酶;pyrogen 热源;progenic exotoxin 热源性外毒素quasi- 类似,准quasi-homogeneous 准均匀的radio- 辐射,放射autoradiography 放射自显影;radiotracer 放射性示踪物;radiology 放射学re- 再,重新,反复recirculation 循环;reversion 回复;reactivity 反应性retro- 后,向后,回复retrovirus 逆转录病毒ribo- 核糖riboflavin 核黄素;ribonucleic acid 核糖核酸;ribonucleotide 核糖核苷酸self- 自身的self-fertilization 自体受精semi- 半,部分semi-permeable membrane 半透膜;semi-synthetic 半合成的;semiconservative replication 半保留复制sero- 血清serological 血清学;seroconversion 血清转变soma- 体soma 体质,胞体;somatic cell 体细胞;somatization 体部分化somato- 生长somatocrinin 生长素释放肽;somatotroph 促生长素细胞;somatotropin 促生长素,生长激素sub- 下面,次于,近于subcellular 亚细胞的;subunit 亚基;subdivide 再分super- 上,上面,超,超级superior 上面的;supernatant 上清液的syn-(sym-) 共同,合synchronize 同步;symbiosis 共生现象;synergistic 协同作用的techn(o)- 技术,工艺technology 技术(学),工艺学;technique 技术therm(o)- 热thermistor 热敏电阻;themometer 温度计thi(o)- 硫,硫代thiamine 硫胺素;thioacylation 硫代酰化;thiokinase 硫激酶thym(o)- 胸腺thymosin 胸腺素toti- 全,全部,整个totipotency 全能性trans- 横穿,通过,转移transformation 转化;transcribe 转录;transposen 转位子tri- 三,三次,三级triplet 三联体;triangle 三角形;triacylglycerol 三酰甘油ultra- 超,极端,过分ultrasonic 超声波;ultracentrifugation 超离心un- 不,相反,出去unfold 展开under- 下面,低于,不足undergraduate 大学本科生;underpin 加固……的基础uni- 单,一,同一uninucleate 单核的;unique 独一无二的up- 向上,在上upstream 上游;upright 直立的uro- 尿urokinase 尿激酶vinyl- 乙烯基polyvinylchloride 聚氯乙烯后缀:-able(-ible) 可能的practicable 可行的;responsible 负责的-ability 能力acceptability 可接受性;permeability 渗透性-age 表示动作过程、量spillage 溢出;percentage 百分比-al 接在名词后形成形容词,接在动词后形成名词personal 个人的;exceptional 例外的;refusal 拒绝-aldehyde 醛glutaraldehyde 戊二醛-amin 胺methylamine 甲胺-ane 烷methane 甲烷-ant 动作者inactivant 失活剂;bioprotectant 生物保护剂-ase 酶protease 蛋白酶;polymerase 聚合酶-ate 盐,酯phosphate 磷酸盐;sebacate 奎二酸酯-cide 杀害,消灭suicide 自杀;bactericide 杀菌剂;amoebicide 抗阿米巴药-cyte 细胞leucocyte 白细胞-derm 皮,皮层blastoderm 胚层;dermadrone 内病性皮疹-ene 烯ethylene 乙烯-(e)ry 场所;一类事物bakery 面包房;circuitry 电路系统;poultry 家禽-fold 倍twofold 两倍-(i)fy 接名词或形容词后构成动词solidify 固化;simplify 简化-gen 原,剂antigen 抗原;mutagen 诱变剂;carcinogenic 致癌的-gram 图形;记录的东西chromatogram 色谱图;polarograph 极谱图-graphy 描绘、记录的方式、学科chromatography 色层分离法;autoradiography 放射自显影术-ic anhydride 酸酐sodium chloride 氯化钠-imine 亚胺iminodiacetic acid 亚胺基二乙胺-ish 略带一点的greyish 浅灰色的-ist ……的实行者,……专业人员(专家)scientist 科学家;geneticist 遗传学家-itis 炎,发炎hepatitis 肝炎;encephalitis 脑炎-ize(-ise) 使成为atomize 雾化;oxidize 使氧化-lactone 内酯β-propiolactone β-丙醇酸内酯-lemma 皮,壳,鞘膜basilemma 基底膜;lemmatoxin 鞘毒素-less 无,不,不能stainless 不锈的-like 如……样的sponge-like 海绵状的-(o)logy(-ological,形容词)学科biology 生物学;technology 技术学,工艺学;toxicology 毒理学的-lysis 分解作用,过程glycolysis 糖酵解作用;hydrolysis 水解作用;analysis 分析-lytic(形容词,分解的)-lyze(-lise)(动词,分解)-lysate(名词,分解液)hydrolytic 水解的;hydrolyze 水解;hydro-lysate 水解液-ment 在动词后构成名词development 发展;entrainment 夹带-meter 计,表spectormeter 发光剂;viscometer 粘度计-metric 测量的gravimetric (测定)重量的;volumetric (测定)体积的;potentiometric (测量)电位的-mycete 霉菌streptomycete 链霉菌-mycin 霉素,菌素mitomycin 丝裂霉素;actinomycin 放线菌素-nema 丝,线amphinema 偶线;chromonema 染色体;nemacicide 杀线虫剂-oid 类,似,……样、状的acidoid 似酸的;amyloid 淀粉样的;carotenoid 类胡萝卜素-ol 醇butanol 丁醇;inositol 肌醇-oma 瘤myeloma 骨髓瘤;hybridoma 杂交瘤-one 酮phenoxazinone 吩噁嗪酮-ory 构成形容词transitory 短暂的;respiratory 呼吸的;构成名词,表场所depository 储藏所-ose 糖heptose 庚糖;lactose 乳糖-oside 糖苷galactoside 半乳糖苷;cardiac glycoside 强心苷-osis 病,症;acalcicosis 缺钙症;hepatitis 肝炎-ous 构成形容词extraneous 外来的;rigorous 严格的-philic 亲……的lipophilic 亲脂性的;hydrophilic 亲水的-phobic 疏……的hydrophobic 疏水的-phoresis 移动electrophoresis 电泳-phil 亲,嗜,喜acidopil 嗜酸的;aerophil 好气的-plasm 血浆,原生质protoplasm 原生质-plast 原始细胞,(质)体,血浆centroplast 中心质体;hematoplast 成血细胞;plasmolemma 质膜-proof 耐……的flame-proof 耐火的;explosion-proof 防爆的-side 苷nucleside 核苷;glycoside 糖苷-sis 构成名词,表示作用,过程mutagenesis 诱变作用;mitosis 有丝分裂;meiosis 减速分裂-some 体,粒chromosome 染色体;idiosome 核旁体;ribosome 核糖体-stat 稳定装置chemostat 恒化器-taxis,tropism 趋向性aerotaxis 趋氧性;chemiotaxis 趋化性;lipotropism 亲脂性-tion(-ation,-ition,-sion) 构成名词instrumentation 仪表化;trypsinization 胰蛋白消化酶;adhesion 粘着-tide 甘酸,肽deoxyribotide 脱氧核苷酸;propeptide 前肽-troph ……营养生物,……营养型(-trophic 构成形容词)methanotroph 甲烷营养型;autotroph 自养生物;autotrophic 自养的-wise 接名词或形容词后构成副词batchwise 分批的;likewise 同样的。
专业英语整理一、绪论1、语法特点:〔1〕被动语态多中心是客观现象与事物本身,而非动作的发出者, 把论证说明的对象置于句子主语的位置,既能突出中心,又能吸引读者的注意.英语和汉语的逻辑表达有所差别.英语表达注重行为的结果;而汉语表达注重行为的主体.翻译时, 为符合汉语习惯,往往需要改变语序.例1:The effect of different concentrations of olive oil was studied on the production of lipase using free and alginate immobilized cell. Maximal lipase production was observed at 1% olive oil in both cases <4290 and 41400 U/l>, respectively.例2:The sample from the above step was loaded on pre-equilibrated Sephadex G-100 column with 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer pH 8.6. The protein elution wasdone with the same buffer at a flow rate of 0.2 ml/min. The active fractions were pooled, concentrated with lyophilizer and dialyzed against the Tris–HCl buffer <50 mM, pH 8.6>. This concentrated fraction wasstored at -20 ℃.〔2〕广泛使用非谓语形式非谓语动词在句子中可以起到名词,形容词或副词作用,动词的非谓语形式分为动名词,分词,动词不定式.①动名词用动名词短语取代时间从句或简化时间陈述句1>The gene should be cloned before it is expressed.The gene should be cloned before being expressed.表达基因前,应先对其进行克隆An object becomes hot. It is placed in the sun.Once being placed in the sun, an object becomes hot.物体放置在太阳下会变热.We must do various experiments before a new bio-product is designed.Before designing a new bioproduct we must do variousexperiments.在设计一个新的生物制品之前,我们必须做各种实验②分词过去分词短语替代从句中的被动语态现在分词短语替代从句中的主动语态The suspension of the mixture producted in stirred tank is led by the pump to the separating device, where the unreacted residues of cellulose and lignin are separated and led into the second tank of the unreacted solid phase.③动词不定式This paper outlines some of the key issues to be addressed to achieve optimal integration either by modification of preceding <or following> chemical steps, biocatalyst evolution or combinations of these approaches together with process engineering.〔3〕省略句使用频繁<精炼>省略成分:状语从句中的主语、全部或部分谓语;定语从句中的关系代词which和that、从句中的助词等;还常用介词短语替代从句.If it is possible, the open-loop control approach shouldbe used in this system.Ifpossible,theopen-loopcontrolapproachshouldbe used in this system.可能的话,这个系统应该使用开环控制方法.其他常用的省略形式:As already discussed 前已讨论, As explained before 前已解释, As described above 如上所示, If possible <necessary>如果可能〔必要〕,If so 倘若如此,As previously mentioned 前已提到, When needed <necessary, feasible> 必要时,Where feasible 在实际可行的场合,Where possible 在可能的情况下.〔4〕It句型和祈使句使用频繁〔准确、精炼〕It句型:it 充当形式主语,避免句子"头重脚轻〞祈使句: 无主语,精炼.It is very important <possible, necessary, natural, inevitable> to…It takes very much time learning…It is clear <possible, necessary, natural, inevitable> that…It happened that …It must be admitted that…Let A be equal to B.设A等于B.Consider a high-pressure chamber. 假如有一个高气压气候室.〔5〕复杂长句使用频繁〔准确、精炼〕为了完整、准确地表达事物内在联系,使用大量从句例1:Metabolic engineering is the practice of optimizing genetic and regulatory processes within cells to increase the cells’production of a certain substance. These processes are chemical networks that use a series of biochemical reactions and enzymes that allow cells to convert raw materials into molecules necessary for the cell’s survival.〔6〕后置定语多后置定语即位于其所修饰的名词之后的定语,汉语常用前置定语或多个简单句来说明某概念或术语,而专业英语则更多地使用后置定语.All radiant energies have wavelike characteristics, which are analogous to those of waves moving through water.All radiant energies have wavelike characteristics analogous tothose of waves moving through water.所有的辐射能都具有波的特性,与水中移动的波的特征相似.2、修辞特点:(1)广泛使用一般现在时(2)较多地使用图、表和公式(3)逻辑语法使用多although, because, but, if, once, only, suppose, as a result, because of, due to, so, therefore, thus, without等.3、词汇特点:(1)词汇构成:合成法〔由相互独立的两个或更多的词合成得到新词〕,派生法〔通过对词根加上各种前缀或后缀来构成新词〕二、词汇1、For thousands of years, microorganisms have been used to supply products such as bread, beer and wine. A second phase of traditional microbial biotechnology began during World War I and resulted in the development ofthe acetone-butanol and glycerol fermentations, followed by processes yielding, for example, citric acid, vitamins and antibiotics.数千年来,微生物一直被用来供应面包、啤酒和葡萄酒等产品.在第一次世界大战期间,传统微生物生物技术的第二阶段开始,导致丙酮-丁醇和甘油发酵的发展,接着是生产过程,例如柠檬酸、维生素和抗生素.2、In the early 1970s, traditional industrial microbiology was merged with molecular biology to yield more than 40 biopharmaceutical products, such as erythropoietin, human growth hormone and interferons. Today, microbiology is a major participant in global industry, especially in the pharmaceutical, food and chemical industries.在20世纪70年代早期,传统的工业微生物学与分子生物学结合,产生了40多种生物制药产品,如促红细胞生成素、人类生长激素和干扰素.今天,微生物学是全球工业的主要参与者,特别是在制药、食品和化学工业.3、Primary metabolites are the small molecules of living cells; they are intermediates or end products of the pathways of metabolism, buildingblocksforessentialmacromolecules, or are converted into coenzymes.主要代谢物是活细胞的小分子;它们是代谢途径的中间产物或最终产物,是基本大分子的基石,或转化为辅酶.4、Primary metabolites used in the food and feed industries include: alcohols <ethanol>, amino acids <monosodium glutamate, lysine, threonine, phenylalanine, tryptophan>, flavor nucleotides,初级代谢产物用于食品和饲料行业包括:醇<乙醇>,氨基酸<味精、赖氨酸、苏氨酸、苯丙氨酸、色氨酸>,味道核苷酸,5、Organic acids <acetic, propionic, succinic, fumaric, lactic>, polyols, <glycerol, mannitol, xylitol>, polysaccharides, <xanthan, gellan>, sugars <fructose, ribose, sorbose> and vitamins [biotin].有机酸<乙酸、丙酸、琥珀酸、富马酸、乳酸>、多元醇<甘油、甘露醇、木糖醇>、多糖、糖<果糖、核糖、山梨糖>、维生素<生物素>.6、Mutants During amino acid production, feedback regulation is bypassed by isolating auxotrophic mutants and partially starving them of their requirements. Another method is to produce mutants that are resistant to a toxic analog of the desired metabolite, that is, an antimetabolite. Combinations of auxotrophic and antimetabolite resistance mutations are common in primary metabolite- producing microorganisms.突变体在氨基酸生成过程中,通过分离营养缺陷突变体,部分抑制其需求,绕过反馈调节.另一种方法是产生一种突变体,这种突变体对所需要的代谢物的有毒类似物具有抵抗力,也就是一种抗代谢物.在产生初级代谢物的微生物中,常见的是营养缺陷和抗代谢物抗性突变的组合.7、Fermentation Another factor is the increase in outward permeability, whichis veryimportant in the production of L-glutamicacid, the major commercial amino acid.发酵另一个因素是向外渗透的增加,这在主要的商业氨基酸l -谷氨酸的生产中非常重要.8、Approximately 1.2 billion poundsof monosodium glutamate are made annually by fermentation usingvarious species of the genera Corynebacterium and Brevibacterium. Molar yields of glutamate from sugar are 50– 60% and broth concentrations reach over 100 g L−1.每年大约有12亿磅的谷氨酸钠是通过利用不同种类的短杆菌和棒状杆菌等细菌进行发酵制成的.从糖摩尔谷氨酸的产量50 - 60%和肉汤浓度达到超过100 g L−1.9、Glutamic acid Normally, glutamic acid overproduction would not occur because of feedback regulation. However, modification of the cell membrane can cause glutamate to be pumped out of the cell, thus allowing its biosynthesis to proceed unabated.谷氨酸正常情况下,由于反馈调节,不会发生谷氨酸过量生产.然而,对细胞膜的修饰可以使谷氨酸被泵出细胞,从而使其生物合成得以继续进行.10、This membrane alteration is intentionally effected by biotin limitation <all glutamic acid bacteria are biotin auxotrophs>, glycerol limitation of glycerol auxotrophs, oleate limitation of oleate auxotrophs, or addition of penicillin or fatty acid derivatives to exponentially growing cells. Apparently, all of these manipulations result in a phospholipid-deficient cytoplasmic membrane.这种膜的改变是由生物素的限制<所有谷氨酸的细菌都是生物素营养不良>,甘油营养缺陷,油酸营养缺陷,或加入青霉素或脂肪酸衍生物,以指数增长的细胞.显然,所有这些操作都会导致磷脂缺乏的细胞质膜.11、Lysine Most cereals are deficient inthe essential amino acid L-lysine. Lysine is a member of the aspartate family of amino acids and is produced in bacteria by a branched pathway that also produces methionine, threonine and isoleucine.赖氨酸大多数谷物都缺乏必需的l -赖氨酸.赖氨酸是天门冬氨酸家族的一员,在细菌中通过分支途径产生,也产生蛋氨酸、苏氨酸和异亮氨酸.12、This pathway is controlled very tightly in an organism such as Escherichia coli, which includes three aspartate kinases that are each regulated by a different end product.这种途径在大肠杆菌这样的生物体中受到非常严格的控制,大肠杆菌包含三种天冬氨酸激酶,每一种激酶都由不同的最终产物调控.13、Recombinant DNA technology is beginning to have a major impact on amino acid production. The major manipulation for lysine production is aimed at increasing the levels of feedback-resistant as partatekinase and dihydrodipicolinate synthase.重组DNA技术开始对氨基酸的生产产生重大影响.赖氨酸生产的主要操作是为了提高部分儿茶酸激酶和二氢吡啶合成酶的反馈抗性水平.14、FungiFilamentousfungi are widely used for the commercial productionof organic acids, for example, 1 billion pounds of citricacid are produced per year with a market value of US$1.4 billion. Citricacid is produced via the Embden-Meyerhof pathway and the first step of the tricarboxylic acid cycle;真菌丝状真菌广泛应用于有机酸的商业化生产,例如,每年生产10亿磅柠檬酸,市场价值14亿美元.柠檬酸通过糖酵解途径和三羧酸循环的第一步产生;15、the control of the process involves the inhibition of phosphofructokinase by citric acid. The commercial process uses Aspergillus niger in media deficient in iron and manganese 锰 . A high level of citric acid production is also associated with a high intracellular concentration of fructose 2,6-biphosphate, an activator of glycolysis.控制过程涉与柠檬酸对磷酸果糖激酶的抑制作用.商业流程使用黑曲霉在媒体缺乏铁和锰锰.高水平的柠檬酸生产也与细胞内高浓度的果糖2,6-二磷酸有关,它是糖酵解的激活剂.16、Other factors contributing to high citric acid production are the inhibition ofisocitrate dehydrogenase by citricacid and the low optimum pH <1.7–2.0>. Higher pH values <e.g. 3.0> lead to the production of gluconic acids, instead of citric acid.柠檬酸对异柠檬酸脱氢酶的抑制作用和对pH的抑制作用<1.7-2.0>.较高的pH值<如3.0>会产生葡萄糖酸,而不是柠檬酸.17、Alternative processes have been developed for the production of citric acid by Candida yeasts, especially from hydrocarbons. Such yeasts are able to convert n-paraffins 石蜡 to citric and isocitric acids in extremely high yields [150– 170% <w/w> of substrate used]; titers as high as 225 g L−1 have been reached.已经开发了由念珠菌生产柠檬酸的替代工艺,特别是从碳氢化合物中生产柠檬酸.这些酵母菌能够将正石蜡转化为柠檬酸和异柠檬酸的aci.DS产率[150%~170%<w/w>],效价可达225 g L−1.18、Secondary metabolites Microbially produced secondary metabolites are extremely important for health and nutrition. As a group that includes antibiotics, other medicinals, toxins, biopesticides and animal and plant growth factors, they have tremendous economic importance.次生代谢物是微生物产生的次生代谢物,对健康和营养极为重要.包括抗生素、其他药物、毒素、生物农药和安尼.MAL和植物生长因子,它们具有巨大的经济重要性.19、Secondary metabolites have no function in the growth of the producing cultures <although, in nature, they are essential for the survival of the producing organism>, are produced by certain restricted taxonomic groups of organisms and are usually formed as mixtures of closely related members of a chemical family.次级代谢物对培养物的生长没有作用<虽然在性质上,它们是生产生物体生存所必需的>,但它们是由某些限制产生的.有机体的分类群,通常是由一个化学家族的密切相关成员组成的混合物.20、Chemical Building Blocks of Cells Three major biopolymers are present in cells: proteins,composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds; nucleic acids, composed of nucleotides linked by phosphodiester bonds; and polysaccharides , composed of monosaccharides <sugars> linked by glycosidic bonds.细胞中存在三种主要生物聚合物:蛋白质,由肽键连接的氨基酸组成;核酸,由磷酸连接的核苷酸组成.ER键;和多糖,由单糖<糖>组成,由糖苷键连接.21、Many molecules in cells contain at least one asymmetric carbon atom, which is bonded to four dissimilar atoms. Such molecules can exist as optical isomers <mirror images>, designated D and L, which have different biological activities. In biological systems, nearly all sugars are D-isomers, while nearly all amino acids are L-isomers.细胞中的许多分子中至少有一个不对称碳原子,它与四个不同的原子相连.这些分子可以光学异构体<镜像>的形式存在,指定为D和L.有不同的生物活动.在生物系统中,几乎所有的糖都是D-异构体,而几乎所有的氨基酸都是L-异构体.22、Differences in the size, shape, charge, hydrophobicity, and reactivity of the side chains of amino acids determine the chemical and structural properties of proteins.氨基酸侧链的大小、形状、电荷、疏水性和反应性的差异决定了蛋白质的化学和结构性质.23、Amino acids with hydrophobic side chains tend to cluster in the interior of proteins away from the surrounding aqueous environment; those with hydrophilic side chains usually are toward the surface.带有疏水侧链的氨基酸倾向于聚集在蛋白质内部,远离周围的水环境;那些具有亲水侧链的氨基酸通常向表面聚集.24、The bases in the nucleotides composing DNA and RNA are heterocyclic rings attached to a pentose sugar. They form two groups: the purines—adenine <A> and guanine <G>—and the pyrimidines—cytosine <C>, thymine <T>, and uracil <U>. A, G, T, and C are in DNA, and A, G, U, and C are in RNA.组成DNA和RNA的核苷酸中的碱基是附在戊糖上的杂环.它们分为两组:嘌呤-腺嘌呤<A>和鸟嘌呤<G>-和嘧啶-胞嘧啶<C>,t海明<T>和尿嘧啶<U>.A、G、T和C在DNA中,A、G、U和C在RNA中.25、Glucose and other hexoses can exist in three forms: an open-chain linear structure, a six- member <pyranose> ring, and a five-member <furanose> ring. In biological systems, the pyranose form of D-glucose predominates.葡萄糖和其他己糖可以三种形式存在:一个开链线性结构,一个六元<吡喃>环和一个五元<呋喃糖>环.在生物系统中,D-葡萄糖的吡喃形式OSE占主导地位.26、Glycosidic bonds are formed between either the αorβ anomer 端基异构体 of one sugar and a hydroxyl group on another sugar, leading to formation of disaccharides and other polysaccharides.糖苷键是在一种糖的α或β失配体端基异构体与另一种糖上的羟基之间形成的,从而形成二糖和其他多糖.27、The long hydrocarbon chain of a fatty acid may contain no carbon - carbon double bond <saturated> or one or more double bonds <unsaturated>, which bends the chain.脂肪酸的长烃链可能不含碳-碳双键<饱和>或一个或多个双键<不饱和>,使链弯曲.28、Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules with a hydrophobic tail <often two fatty acyl chains> and a hydrophilic head.磷脂是具有疏水性尾〔通常是两个脂肪酰基链〕和亲水性头的两亲性分子.29、In aqueous solution, the hydrophobic effect and van der Waals interactions organize and stabilize phospholipids into one of three structures: a micelle, liposome, or sheet-like bilayer.在水溶液中,疏水效应和X德华相互作用将磷脂组织并稳定为三种结构之一:胶束、脂质体或片状双层.30、In a phospholipid bilayer, which constitutes the basic structure of all biomembranes, fatty acyl chains in each leaflet are oriented toward one another, forming a hydrophobic core, and the polar head groups line both surfaces and directly interact with the aqueous solution.在构成双层生物膜的基本结构的磷脂双层中,每个小叶中的脂肪酰基链彼此取向,形成疏水核心,以与极性头.基团使两面成直线,并与水溶液直接相互作用.31、The αhelix, βstrand and sheet, and turn are the most prevalent elements of protein secondary structure, which is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between atoms of the peptide backbone.α螺旋、β链和片状结构是蛋白质二级结构中最普遍的元素,它们是通过肽骨架原子间的氢键来稳定蛋白质二级结构的.32、Protein tertiary structure results from hydrophobic interactions between nonpolar side groups and hydrogen bonds between polar side groups that stabilize folding of the secondary structure into a compact overall arrangement, or conformation.蛋白质三级结构是由非极性侧基间的疏水相互作用和极性侧基间的氢键作用所致,使二级结构的折叠稳定在COMP中.采取整体安排,或构象.33、Large proteins often contain distinct domains, independently folded regions of tertiary structure with characteristic structural or functional properties or both.大蛋白通常包含不同的结构域,独立折叠的三级结构区域,具有独特的结构或功能特性,或两者兼具.34、The incorporation of domains as modules in different proteins in the course of evolution has generated diversity in protein structure and function.在进化过程中,将结构域作为不同蛋白质的模块结合在一起,在蛋白质结构和功能上产生了多样性.35、Cells contain large macromolecular assemblies in which all the necessary participants in complex cellular processes <e.g., DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis; photosynthesis; signal transduction> are integrated to form molecular machines.细胞含有大的大分子集合,其中所有参与复杂细胞过程<例如dna、rna和蛋白质合成;光合作用;信号转导>的参与者都是int.形成分子机器.36、The sequence of a protein determines its three-dimensional structure, which determines its function. In short, function derives from structure; structure derives from sequence.蛋白质的序列决定了它的三维结构,这决定了它的功能.简而言之,功能来源于结构,结构来源于序列.37、Enzymes and the Chemical Work of Cells The function of nearly all proteins depends on their ability to bind other molecules <ligands>. Ligand-binding sites酶和细胞的化学功几乎所有蛋白质的功能都取决于它们与其他分子<配体>结合的能力.配体结合位点38、The function of nearly all proteins depends on their ability to bind other molecules <ligands>. Ligand-binding sites on proteins and the corresponding ligands are chemically and topologically complementary.几乎所有蛋白质的功能都依赖于它们结合其他分子<配体>的能力.蛋白和相应配体上的配体结合位点在化学和拓扑结构上是互补的.39、The affinity of a protein for a particular ligand refers to the strength of binding; its specificity refers to the preferential binding of one or a few closely related ligands.蛋白质对特定配体的亲和力是指结合的强度;它的特异性是指一个或几个密切相关的配体的优先结合.40、Enzymes are catalytic proteins that accelerate the rate of cellular reactions by lowering the activation energy and stabilizing transition- state intermediates.酶是一种催化蛋白,通过降低活化能和稳定过渡态中间体来加速细胞的反应速度.41、An enzyme active site comprises two functional parts: a substrate-binding region and a catalytic region. The amino acids composing the active site are not necessarily adjacent in the amino acid sequence but are brought into proximity in the native conformation.酶的活性位点由两个功能部分组成:底物结合区和催化区.组成活性位点的氨基酸不一定在氨基酸序列中相邻,而是在天然构象中靠近.42、From plots of reaction rate versus substrate concentration, two characteristic parameters of an enzyme can be determined: the Michaelis constant Km, a measure of the enzyme’s affinity for substrate, and the maximal velocity Vmax, a measure of its catalytic power.从反应速率与底物浓度的图中可以确定酶的两个特征参数:米克里斯常数Km,这是酶对底物亲和力的度量;最大速度Vmax,这是它的催化能力的度量.43、Enzymes in a common pathway are located within specific cell compartments and may be further associated as domains of a monomeric protein, subunits of a multimeric protein, or components of a protein complex assembled on a common scaffold.共同途径中的酶位于特定的细胞隔间内,并可能进一步与单分子蛋白、多分子蛋白的亚基或在共同支架上组装的蛋白复合物的组成部分相关.三、荧光蛋白Fluorescent proteins as tools to aid protein productionIntroduction1、Expression of recombinant proteins from a variety of host organisms is now a common practice. However, production of properly folded proteins with high yield and purity may not always be achieved.2、Issues such as folding, solubility, protein stability, transcription and translation efficiency, post-translational processing, secretion, metabolic burden and other stress responses resulting from recombGiLnant protein production,3、as well as protein purification, need to be addressed in order to obtain biologically active recombinant proteins with high purity and yield. In this regard, genetically encoded fluorescent reporters provide ample new opportunities to better tackle these issues.4、Since the demonstration of the Aequorea victoria green fluorescent protein <GFP> as a versatile reporter, several additional GFP-like fluorescent proteins with various colors have been discovered and their genes cloned.5、Synthetic fluorescent protein variants have also been developed, exhibiting traits distinct from their wild-type counterparts. The properties of selected fluorescent protein variants derived from the A. victoria GFP and the Discosomared fluorescent protein <DsRed> are summarized in Table 1.6、Fluorescence spectra of enhanced GFP variants along with DsRed are shown in Figure 1, and fluorescence of purified protein variants derived from DsRed are shown in Figure 2.7、Readers are referred to the work of Labas et al. for information of additional fluorescent proteins. These GFP-like proteins each has its own unique properties, while sharing common structural, biochemical and photophysical characteristics.8、GFP-like proteins are relatively small <25–30 kDa> and their fluorescence mechanism is self-contained, requiring no cofactors. These unique properties make GFP-like proteins very attractive tools in non-invasive biological monitoring applications.9、As a tool to improve recombinant protein production, fluorescent proteins can be used to monitor the protein product or the cellular processes relevant to recombinant protein production.10、Monitoring protein production11、Fluorescent proteins are commonly used as a reporter for a protein of interest, normally by tagging the fluorescent protein reporter to the protein of interest via genetic fusion.12、Functional fusion ofAequoreaGFP to a broad range of protein partners at either N- or C- terminus has been reported, and a direct quantitative correlation between the GFP fluorescence intensity and the titer or even the functional activity of the fusion partner can often be established.13、To minimize potential interference by the GFP tag on its fusion partner, it is desirable and sometimes necessary to incorporate a peptide linker to allow sufficient spatial separation of the two protein moieties to assure fusion protein stability and functionality.14、Flexible linkers lacking large bulky hydrophobic residues <e.g. GSAGSAAGSGEF> are commonly used, while hydrophilic helix-forming linker peptides have been reported to be superior to flexible linkers in some cases.15、To allow removal of the GFP tag, an enzymatic cleavage site <e.g. enterokinase or Factor Xa cleavage sites> can be engineered into the linker. It is preferred to splice the GFP/linker to the N-terminus of the target protein, provided such fusion does not impair the target protein function and stability.16、With the majority of the enzymes commonly used for tag removal, this fusion orientation enables elimination of the tag without leaving extraneous amino acid residues on the target protein after cleavage.17、Alternatively, chemical cleavage based on cyanogen bromide, formic acid, or hydroxylamine may be considered, provided the target proteins are not susceptible to cutting by these chemical agents.18、Further information of tag removal can be found in a comprehensive review by Hearn and Acosta. In addition to tandem fusion, insertional fusion <i.e. by inserting the protein of interest into GFP or vise versa> may also be feasible.19、Recombinant protein production can be monitored non-invasively,in situ, and almost in real time, by monitoring culture fluorescence using on-line optical sensors.20、This information is useful in determining the optimal product harvest time to avoid product degradation and to devise process control strategies to optimize culture/operating conditions to improve recombinant protein production21、GFP has also been used to monitor recombinant virus titers in cell cultures, and cell density in microbial, animal, and plant cell cultures;22、the cell growth information can be used, in turn, to optimize the culture process for improved recombinant protein production <e.g. by optimizing the feeding profiles of the limiting nutrient or the promoter inducer, or by determining the optimal product harvest time>.23、Additionally, GFP-fusion coupled with flow cytometric analysis is useful for profiling recombinant protein expression among different cell subpopulations, and selection of highproducing cells.24、Monitoring protein purification25、The fact that GFP fluorescence is readily detectable makes it a very attractive tool for optimizing purification of recombinant proteins.26、Poppenborg et al. optimized immobilized metal affinity separation of a histidine-rich protein tagged with GFP by tracking the fluorescence of the fusion protein.27、Since GFP is a highly hydrophobic protein, recovery of GFP-fusion proteins can be facilitated by using hydrophobic interaction chromatography <HIC>.28、GFP has also been engineered to allow affinity purification. Paramban et al developed a chimeric GFP tag having an internal hexahistidine sequence.29、Such a GFP tag allows efficient purification of GFP-fusion proteins based on immobilized metal affinity separation, as well as maximum flexibility for protein or peptide fusions since both termini of the GFP are available.四、翻译技巧一1、单词转化〔1〕——词义引申〔1〕词义转译〔引申转译〕如遇无法直译或不宜直译的词〔组〕,应根据上下文和逻辑关系,引申转译.Oxygen forms about one fifth of the atmosphere.氧约占大气的五分之一.〔不译为"形成〞〕When suglight falls on the leaves of plants it is transformed into chemical energy.当阳光照在植物的叶子上时,就转变成化学能〔不译"落〞〕Laser is one of the most sensational developments in recent years.激光是近年来轰动一时的科学成就之一.〔不译为"发展〞〕More weight must be placed on the past history of Patients.必须更加重视患者的病史.〔不译为"过去的历史〞This medicine acts well on the heart.这种药治疗心脏病疗效很好.〔不译"对…起作用〞This kind of wood works easily.这种木材很容易加工.〔不译为"工作〞〕The patient had been given three transfusions <输血〕after he was admitted into the hospital.病人入院后已输过三次血了.〔不译为"给〞〕(2)词义具体化翻译时,根据汉语的表达习惯,把原文中某些词义较笼统的词引申为词义较具体的词.Other things being equal, iron heats up faster than aluminium 〔铝〕.其它条件相同时,铁比铝热的快.Hard metals can be easily cut with grinding wheels.硬金属可以很容易用砂轮磨削.When we speak, sound waves begin to travel and go in all directions.我们说话时,声波就开始传播,并向四面八方扩散.(3)词义抽象化翻译时,根据汉语的表达习惯,把原文中词义较为具体的词引申为较抽象,或词义较一般的词.Steel and cast iron also differ in carbon.钢和铸铁的含碳量也不相同.〔把"碳〞抽象化为"含碳量〞〕We have progressed a long way from the early days of electrical engineering.电气工程自从出现以来,已经有了很大的发展.〔不译为"已经前进了很长一段路〞〕Rocks made under water tell another story.水下形成的岩石说明另一个问题.〔不译为"讲另一个故事〞〕(4)词的搭配要注意动词与名词,以与形容词与名词的搭配, 遇到不合乎汉语的搭配习惯时,可以把动词或形容词的词义加以引申,以适合名词.Rubber, porcelain 〔陶瓷〕and glass are commonly used to resist electric current.橡胶、陶瓷和玻璃常常用来隔绝电流.〔不译为"抵抗电流〞〕Some plants have flowers but do not seed.有些植物开花而不结果.〔不译为"有花〞〕The sun's heat offers an almost limitless sourse of power.太阳热提供了一个几乎取之不尽的动力源泉.〔不译为"无限的动力源泉〞〕Americans every year swallow 15,000 tons of aspirin, one of the safest and most effective drugs invented by man.阿司匹林是人类发明的最安全、最有效的药物,美国每年要消耗15000吨.〔不译为"吞咽〞〕Alloys belong to a half-way house between mixtures and compounds.合金是介于混合物和化合物之间的一种中间结构.〔不翻译为"两地间中途歇脚的客栈〞〕Industrialization and environmental degradation seem to go hand in hand.工业化发展似乎伴随着环境的退化.〔不译为"携手〞〕In the microbial transformation of contaminants,organisms can either "eat〞the toxins or break them dow in the process of consuming other substances.在对污染物进行微生物转化的过程中,生物会清除毒素或在消耗其他物质时把这些毒素分解.〔吃掉〕The plan for launching the man-made satellite still lieson the table.那项发射人造卫星的计划仍被搁置,无法执行.〔放在桌子上〕The furnace eats up fuel at the rate of three tons per hour.炉子以每小时三吨的速度消耗燃料.〔吃光〕例题:试译下列各句,注意对划线词的词义作专业化引申:Rubber is not hard, it gives way to pressure.橡胶性软,受压变形.For millions of people suffering from arthritis <关节炎>, it is the only thing that works.对于千百万关节炎患者来说,这是惟一奏效的药物.Porcelain is commonly used to resist electric current.陶瓷常用来隔绝电流.Zinc is easy to obtain from its ore.锌容易从锌矿中提炼.There are three things we have to know about every force in order to be able to understand the effect it produced.要了解力的作用,我们必须懂得力的三要素.The purpose of a driller is to cut holes.钻床的功能是钻孔.The energy is so small that something must be done to prevent the complete loss of signal.由于能量太小,必须采取措施以防止信号完全丢失.The foresight <远见> and coverage shown by the inventor of the process aremost commendable〔值得称赞的〕.这种方法的发明者所表现的远见卓识和渊博知识,给人以良好的印象.The book is perhaps too high-powered for technician in general.这本书对一般技术员来说也许内容太深.The expense of such an instrument has discouraged its use.这种仪器很昂贵,使其应用受到限制.2、单词转化〔2〕——词类转换〔1〕非谓语译为汉语中的动词一个汉语的句子往往可以同时使用好几个动词, 而英语的句子一般只用一个谓语动词,其它的动词就得变成非谓语形式.例如:There are several types of mechanisms used for controlling the speed of a drilling machine.有几种机械可以用来控制钻床的转速.(2)名词译为汉语中的动词一般来源于动词名词化结构.Determination of FCC was conducted with flux data only.仅由流量数据确定FCC.。
单词整理a- 不,非aseptic 无菌的;apolar 非极性的;asymmetercal 不对称的ab- 去,离开,脱离abnormal 反常的;abuse 滥用;abduct 外展神经aceto- 乙酰acetolactate 乙酰乳酸;acetyl 乙酰(基);acetyl phosphate 乙酰磷酸actino- 光线,射线,放线菌acrinomycin 放线菌;actinometer 化学光度计acyl- 酰基acyltransferase 转酰基酶aden(o)- 腺adenovirus 腺病毒aer(o)- 空气的aerobic 需氧的;aeration 通气agro- 土壤;农业agrochemical 农用化学品;agronomical 农艺学的amidino- 脒基amidinotransferase 转脒基酶amylo- 淀粉amylopectin 支链淀粉;amylose 直链淀粉;amyloplastid 造粉粒an- 不,非anaerobic 厌氧的;analgesic 止痛的;anapepsia 胃蛋白酶缺乏ane- 烷methane 甲烷anti- 反对,对抗,取消,抑制,解除antagonistic 对抗的;antibody 抗体;antigen 抗原angio- 血管angiogenin 血管生成素;angioma 血管瘤aut(o)- 自己的,自动的autotroptic 自养的;autonomous 自发的;autosensitization 自身致敏bio- 生物的biochemistry 生物化学;bioamine 生物胺;biocatalyst 生物催化剂bromo- 溴的5-bromouracil 5-溴尿嘧啶bis- 双,二bisexualism 雌雄异体;bisphenols 双酚类brady- 缓慢hradycardia 心动过缓;bradykinin 缓激肽carb(o)- 碳的carbodiimide 碳二亚胺;carbohydrate 碳水化合物carboxy(l) 羧基carboxy methylcellulose 羧甲基纤维素carcin(o)- 癌carcinogen 致癌物cardio- 心脏cardiotonic 强心的cent(i)- 一百的,百分之一的,厘century 世纪;centimeter 厘米;centimorgan 厘摩chemo- 化学chemoautotrophy 化能自养;chemosynthesis 化能合成;chemoattractant 化学引诱物chlor- 氯,绿chloramphenicol 氯霉素;chlorobenzene 氯苯;chloroplast 叶绿体chrom(o)- (chromat(o)-) 颜色chromatid 染色单体;chromosome 染色体;chromatography 色谱法cis- 顺cistrion 顺反子;cis regulation 顺式调节;cis-isomer 顺式异构体co- 一起,共同cooperate 合作;coincide 重合;cognate 同源的con- (col-,com-,cor-)连同,一起complexant 络合剂;concentrate 集中;combine 结合contra- 反对,相反contrast 对照;contrary 相反的;contrasuppression 反抑制counter- 反,逆couner-circulation 逆向循环;counter-ecolution 逆进化;counter receptor 反受体cryo- 寒冷,冷冻cryopreservation 冷冻保藏;cryogen 冷冻剂;cryophile 适寒性cyano- 青,蓝,氰cyanobacteria 蓝细菌;cyanocobalamin 氰钴胺素;cyanogen bromide 溴化氰de- 否定,除去,离开,降低,脱debug 排除故障;deceleration 降速;degeneration 退化deca- 十,葵decahedron 十面体;decane 葵烷;decamer 十聚体deoxy- 脱氧deoxycytosine 脱氧胞嘧啶di- 二,二倍,二重diploid 二倍体;dimer 二聚体;divinylbenzene 二乙烯苯dia- 横穿diameter 直径;dialysis 透析;diaphragm 隔膜dis- 否定,分离disintegration 破碎;disagree 不同意;dissemination 散播dodeca- 十二dodecahedron十二面体;dodecane 十二烷;dodecamer 十二聚体eco- 生态,居处,宿主ecogentics 生态遗传学;ecology 生态学;ecomone 生态信息素ectoblast 外胚层;ectohormone 外激素;ectodomain 胞外结构electr(o)- 电electrodialysis 电渗析en-(em-) 使成为,置于……中enable 能够;encode 编码;embed 包埋end(o)- 内endergonic 吸能的;endospore 内生孢子enol 烯醇phosphoenolpyruvate 磷酸烯醇丙酮酸enter(o)- 肠enteroacteria 肠细菌;enterobactin 肠杆菌素;enterocyte 肠细胞epi- 表;变化epichlorohydrin 表氯醇;epimerase 差向异构体酶;epithelial cell 上皮细胞erythr(o)- 红,赤erythrose 赤藓糖;erythromycin 红霉素;erythrocyte 红细胞eu- 真正eukaryote 真核生物;eukaryocyte 真核细胞;eubacteria 真细菌e(x)- 向外,超出,完全,彻底explant 外植体;elongate 拉长;evaluate 评价ex(o)- 外,在外,产生exothermic 放热的;exergonic 放能的;exogenous gene 外源基因extra- 超出extracellular 胞外的;extract 抽提物;extracellular virus 胞外病毒ferri- 高铁ferricytochrome 高铁细胞色素;ferritin 铁蛋白;ferridoxin 铁氧还原蛋白ferro- 亚铁ferrocytochrome 亚铁细胞色素;ferroheme 血红素;ferrochelatase 亚铁螯合酶flavanol 黄烷酮;flavin 黄素;flavone 黄酮fluoro- 氟基,氟代,荧光fluorochrome 荧光染料;fluoroacetate 氟乙酸;fluorometer 荧光剂formyl- 甲酰formyltetrahydrofolate 甲酰四氢叶酸;formyl 甲酰基;formylation 甲酰化geo 土地geographical barrier 地理障碍;geographical isolation 地理隔离;geosmin 土腥味素glyc(o)- 糖glycoprotein 糖蛋白hem(o,a)-,haem(o,a)-,haemat(o)-血的hemoglobin 血红蛋白;haemagglutinin 血凝素;haem 血红素hemi- 半hemicellulase 半纤维素;hemizygote 半合子;hemiacetal 半缩醛heter(o)- 异,杂,异种heterogeneous 异质的,不均一的;heterotrophic 异养的;heteroantigen 异种抗原hepato- 肝hepatocarcinoma 肝癌;hepatocyte 肝细胞;hepatotoxin 肝脏毒素homeo- 同源,同祖homeotic gene 同源异形基因hom(o)- 相同homogeneous 同质的,均一的;homologous 同源的;homoeosis 同源异形hydr(o)- 水,液体,氢hydrocarbon 烃;hydrocolloid 水胶体;hydrobios 水生生物hydroxy(l) 羟基hydroxyapatite 羟磷灰石;hydroxylase 羟化酶hyper- 超出,过度hyperfiltration 反渗透;hypertension 高血压hypo- 低,(过)少sodium hypochlorite 次氯酸钠;hypoblast 下胚层;hypoimmunity 低免疫性imino- 亚胺基iminodiacetic acid 亚胺基二乙酸immuno- 免疫immunogenic 致免疫的;immunoassay 免疫分析in-(il-,im-,ir-)不,无;在内,入内insoluble 不能溶解的;insuperable 不能克服的;impermeable 不能渗透的infra- 下面,内部infrastructure 基础结构;infrared 红外线的inter- 相互,在……之间interact 相互作用;intergeneric 属间的;inter-particle 颗粒间的intra- 在内,向内intraspecific 种内的;intra-particle 颗粒内的;intravenous 进入静脉的iodo- 碘基,碘代iodometry 碘量法;iodouracil 碘尿嘧啶;iodoacetic acid 碘乙酸iso- 同,等,异isomer 同分异构体;isomerase 异构酶;isobutyl 异丁基kary(o)- 核,细胞核karyology 胞核学keto- 酮基ketohexulose 酮己酮糖;keto acid 酮酸;ketoamin 酮胺lacto- 乳lactobacillus 乳杆菌属;lactogen 催乳素;lactoglobulin 乳球蛋白leuco- 白,无色的leucocyte 白细胞lipo- 脂lipoprotein 脂蛋白;lipoxygenase 脂氧合酶lympho- 淋巴lymphocyte 淋巴细胞macro- 大的,宏观的macromolecule 大分子;macroporous 大孔的mal- 不当,不良malabsorption 吸收不良;malassimulation 同化不全;malnutrition 营养不良megal(o)- 巨大cytomegalovirus 巨细胞病毒mercapto- 巯基β-mercaptoethylamine β-巯基乙胺meso- 内消旋;中(间)meso inositol 内消旋肌醇;mesophilic 嗜温的meth- 甲基methacrylate 甲基丙烯酸methyl 甲基methyltroph 甲基营养菌micro- 微,微小的microscope 显微镜;microcarrier 微载体;microbe 微生物mono- 一,单,单一monoclonal 单克隆的;monolayer 单层multi- 多,多方面multistage 多级;multicellularity 多细胞性;myco- 真菌mycolytic 溶真菌的;mycotoxin 真菌毒素;mycoprotein 真菌蛋白myelo- 髓鞘,髓myeloblast 成髓细胞;myelocyte 髓细胞;myeloma 骨髓瘤myo- 肌myoalbumin 肌白蛋白;myoblast 成肌细胞;myocyte 肌细胞nano- 纳nanobacteria 微小细菌;nanosecond 纳秒;nanotechnology 纳米技术neo- 新neocarcinostatin 新制癌菌素;neocerebellum 新小脑;neomycin 新霉素neur(o)- 神经neural 神经的;neurotoxin 神经毒素nitro- 硝基nitrofuran 硝基呋喃;nitroalkane 硝基烷;nitrobacteria 硝化细菌nucle(o)- 核nucleoside 核苷;nucleophilic 亲核的non- 非,无,不non-newtonian fluid 非牛顿型流体;non-aqueous solution 非水溶液nor- 去甲,正noradrenalin 去甲肾上腺素;normal 正常,正交;normocyte 正红细胞over- 在上面,超过,过overshooting 过调节;overview 简明概述;overcooled 过冷的oligo- 寡oligosaccharide 寡糖,低聚糖onco- 肿瘤oncogene 致癌基因ovo- 卵ovocenter 卵中心体;ovorubin 卵红蛋白;ovum 卵细胞oxalo- 草酰,乙二酸-酰基oxalo acetate 草酰乙酸oxy- 氧;羟基deoxyguanosine 脱氧鸟苷;oxytetracycline 土霉素;oxyproline 羟脯氨酸path(o)- 病pathogen 病原菌para- 旁(位),对(位),副parabronchus 复支气管;parathyroid gland 甲状旁腺;paraoxon 对氧磷peri- 周,周围perimeter 周长;periplasmic space 周质间隙;periblast 胚周区per- 过peroxisome 过氧化质体phenyl 苯基phenylalanine 苯丙氨酸phospho- 磷酸基phosphofructokinase 磷酸果糖激酶phosphoryl- 磷酰基phosphorylation 磷酸化作用phyto- 植物phytoalexin 植物抗毒素;phytology 植物学;phytoplankton 浮游植物plasm(o)- 原生质,血浆plasmolemma 质膜pleio- 多pleiotropic 多效的;pleioxeny 多主寄生;pleiotropy 多效性poly- 多,聚polysaccharide 多糖;polystyrene 聚苯乙烯;polyacid 多酸post- 后post-transcriptional modification 转录后修饰作用;post-exponential growth phase 后对数生长期pre- 前,在前premature 过早的;precursor 前体;premise 前提pro- 原,前prokaryote 原核生物;prostate 前列腺proteo- 蛋白proteolipid 蛋白脂质;proteome 蛋白质组;proteolysis 蛋白酶解proto- 原始,初prototype 原型;protoplast 原生质体pseud(o)- 假的pseudo-plastic fluid 假塑性流体;psudodominance 假显性;pseudohypha 假菌丝pyro- 焦,火,热pyrophosphorylase 焦磷酸化酶;pyrogen 热源;progenic exotoxin 热源性外毒素quasi- 类似,准quasi-homogeneous 准均匀的radio- 辐射,放射autoradiography 放射自显影;radiotracer 放射性示踪物;radiology 放射学re- 再,重新,反复recirculation 循环;reversion 回复;reactivity 反应性retro- 后,向后,回复retrovirus 逆转录病毒ribo- 核糖riboflavin 核黄素;ribonucleic acid 核糖核酸;ribonucleotide 核糖核苷酸self- 自身的self-fertilization 自体受精semi- 半,部分semi-permeable membrane 半透膜;semi-synthetic 半合成的;semiconservative replication 半保留复制sero- 血清serological 血清学;seroconversion 血清转变soma- 体soma 体质,胞体;somatic cell 体细胞;somatization 体部分化somato- 生长somatocrinin 生长素释放肽;somatotroph 促生长素细胞;somatotropin 促生长素,生长激素sub- 下面,次于,近于subcellular 亚细胞的;subunit 亚基;subdivide 再分super- 上,上面,超,超级superior 上面的;supernatant 上清液的syn-(sym-) 共同,合synchronize 同步;symbiosis 共生现象;synergistic 协同作用的techn(o)- 技术,工艺technology 技术(学),工艺学;technique 技术therm(o)- 热thermistor 热敏电阻;themometer 温度计thi(o)- 硫,硫代thiamine 硫胺素;thioacylation 硫代酰化;thiokinase 硫激酶thym(o)- 胸腺thymosin 胸腺素toti- 全,全部,整个totipotency 全能性trans- 横穿,通过,转移transformation 转化;transcribe 转录;transposen 转位子tri- 三,三次,三级triplet 三联体;triangle 三角形;triacylglycerol 三酰甘油ultra- 超,极端,过分ultrasonic 超声波;ultracentrifugation 超离心un- 不,相反,出去unfold 展开under- 下面,低于,不足undergraduate 大学本科生;underpin 加固……的基础uni- 单,一,同一uninucleate 单核的;unique 独一无二的up- 向上,在上upstream 上游;upright 直立的uro- 尿urokinase 尿激酶vinyl- 乙烯基polyvinylchloride 聚氯乙烯后缀:-able(-ible) 可能的practicable 可行的;responsible 负责的-ability 能力acceptability 可接受性;permeability 渗透性-age 表示动作过程、量spillage 溢出;percentage 百分比-al 接在名词后形成形容词,接在动词后形成名词personal 个人的;exceptional 例外的;refusal 拒绝-aldehyde 醛glutaraldehyde 戊二醛-amin 胺methylamine 甲胺-ane 烷methane 甲烷-ant 动作者inactivant 失活剂;bioprotectant 生物保护剂-ase 酶protease 蛋白酶;polymerase 聚合酶-ate 盐,酯phosphate 磷酸盐;sebacate 奎二酸酯-cide 杀害,消灭suicide 自杀;bactericide 杀菌剂;amoebicide 抗阿米巴药-cyte 细胞leucocyte 白细胞-derm 皮,皮层blastoderm 胚层;dermadrone 内病性皮疹-ene 烯ethylene 乙烯-(e)ry 场所;一类事物bakery 面包房;circuitry 电路系统;poultry 家禽-fold 倍twofold 两倍-(i)fy 接名词或形容词后构成动词solidify 固化;simplify 简化-gen 原,剂antigen 抗原;mutagen 诱变剂;carcinogenic 致癌的-gram 图形;记录的东西chromatogram 色谱图;polarograph 极谱图-graphy 描绘、记录的方式、学科chromatography 色层分离法;autoradiography 放射自显影术-ic anhydride 酸酐sodium chloride 氯化钠-imine 亚胺iminodiacetic acid 亚胺基二乙胺-ish 略带一点的greyish 浅灰色的-ist ……的实行者,……专业人员(专家)scientist 科学家;geneticist 遗传学家-itis 炎,发炎hepatitis 肝炎;encephalitis 脑炎-ize(-ise) 使成为atomize 雾化;oxidize 使氧化-lactone 内酯β-propiolactone β-丙醇酸内酯-lemma 皮,壳,鞘膜basilemma 基底膜;lemmatoxin 鞘毒素-less 无,不,不能stainless 不锈的-like 如……样的sponge-like 海绵状的-(o)logy(-ological,形容词)学科biology 生物学;technology 技术学,工艺学;toxicology 毒理学的-lysis 分解作用,过程glycolysis 糖酵解作用;hydrolysis 水解作用;analysis 分析-lytic(形容词,分解的)-lyze(-lise)(动词,分解)-lysate(名词,分解液)hydrolytic 水解的;hydrolyze 水解;hydro-lysate 水解液-ment 在动词后构成名词development 发展;entrainment 夹带-meter 计,表spectormeter 发光剂;viscometer 粘度计-metric 测量的gravimetric (测定)重量的;volumetric (测定)体积的;potentiometric (测量)电位的-mycete 霉菌streptomycete 链霉菌-mycin 霉素,菌素mitomycin 丝裂霉素;actinomycin 放线菌素-nema 丝,线amphinema 偶线;chromonema 染色体;nemacicide 杀线虫剂-oid 类,似,……样、状的acidoid 似酸的;amyloid 淀粉样的;carotenoid 类胡萝卜素-ol 醇butanol 丁醇;inositol 肌醇-oma 瘤myeloma 骨髓瘤;hybridoma 杂交瘤-one 酮phenoxazinone 吩噁嗪酮-ory 构成形容词transitory 短暂的;respiratory 呼吸的;构成名词,表场所depository 储藏所-ose 糖heptose 庚糖;lactose 乳糖-oside 糖苷galactoside 半乳糖苷;cardiac glycoside 强心苷-osis 病,症;acalcicosis 缺钙症;hepatitis 肝炎-ous 构成形容词extraneous 外来的;rigorous 严格的-philic 亲……的lipophilic 亲脂性的;hydrophilic 亲水的-phobic 疏……的hydrophobic 疏水的-phoresis 移动electrophoresis 电泳-phil 亲,嗜,喜acidopil 嗜酸的;aerophil 好气的-plasm 血浆,原生质protoplasm 原生质-plast 原始细胞,(质)体,血浆centroplast 中心质体;hematoplast 成血细胞;plasmolemma 质膜-proof 耐……的flame-proof 耐火的;explosion-proof 防爆的-side 苷nucleside 核苷;glycoside 糖苷-sis 构成名词,表示作用,过程mutagenesis 诱变作用;mitosis 有丝分裂;meiosis 减速分裂-some 体,粒chromosome 染色体;idiosome 核旁体;ribosome 核糖体-stat 稳定装置chemostat 恒化器-taxis,tropism 趋向性aerotaxis 趋氧性;chemiotaxis 趋化性;lipotropism 亲脂性-tion(-ation,-ition,-sion) 构成名词instrumentation 仪表化;trypsinization 胰蛋白消化酶;adhesion 粘着-tide 甘酸,肽deoxyribotide 脱氧核苷酸;propeptide 前肽-troph ……营养生物,……营养型(-trophic 构成形容词)methanotroph 甲烷营养型;autotroph 自养生物;autotrophic 自养的-wise 接名词或形容词后构成副词batchwise 分批的;likewise 同样的。
Chapter 1Bacterium(Bacteria)细菌yeast 酵母fungus(fungi 真菌alga (algae)藻类cultured mammalian cells 哺乳动物培养细胞fermentation processes 发酵工程biomass 菌体biocatalyst生物催化剂antibiotics 抗生素amino acids氨基酸enzyme steroid 甾体,类固醇polysaccharides多糖vaccines 疫苗biochemical engineering生物化学工程immobilization 固定化genetic engineering基因工程genome 基因组mutation 突变gene 基因Comprehension1. What is biotechnology?what are its characteristics points?2. Name four developmental phases of biotechnology,denoting their chronological time,main products and techniques evolved?Sentence analysis and translation3.Biotechnology appears to be an area of expansion。
will become increasingly more expensive and in short supply.(翻译文章最后一段)中文译文:生物工程就如一个不断扩张和充满机遇的领域,它涉及了许多产业,包括农业、食品与饲料加工业、医药业、能源与水处理工业。
生物工程在新药、激素、疫苗和抗体生产方面,提供廉价可靠的能源以及(从长远来看)在化学饲料方面、环境控制体系的改进提高与废物管理方面都将扮演重要的角色。
P1 NO.1Biotechnology is an area of applied bioscience and technology which involves the practical application of biological organisms ,or their subcellular components to manufacturing and service industries and to environment management,biotechnology utilizes bacteria、yeast 、fungi 、algae、plant cells or cultured mammalian cells as constitutes of industrial processes。
Successful application of biotechnology will result only from the integration of a multiplicity of scientific disciplines and technologies,inclouding microbiology biochemistry,genetics ,molecular biology ,chemistry and chemical and process engineering。
生物工程是属于应用生物科学和技术的一个领域,它包含微生物或其亚细胞组份在制造业、服务业、和环境管理等方面的应用,生物工程利用细菌、酵母菌、真菌、藻类、植物细胞及培养的哺乳动物细胞作为工业生产的组成。
只有将微生物学、生物化学、遗传学、分子生物学、化学、和化学工程等多种学科和技术结合起来,生物工程的应用才能获得成功。
Biotechnological processes will normally involve the production of cells or biomass,and the achievement of desired chemical transformations.the latter may be further subdivided into:Formation of a desired end product decomposition of a given starting material生物学发展史四阶段:biotechnological production of food and beveragesbiotechnological processes initially developed under non-sterle conditionsthe introduction of sterility to biotechnological processesnew dimensions and possibilities forbiotechnological industriesrecombinant dna manipulationDNA重组tissue culture组培protoplast fusion原生质融合monoclonal antibody preparation 单克隆抗体protein structural modification蛋白结构修饰immobilized enzyme and cellcatalysis固定化酶和细胞技术sensing with the aid of biologicalmolecules生物传感computer linkage of reactors andprocesses计算机检测new biocatalytic reactor design新型生物反应器设计P9 summaryBiotechnology can be consideredto be the application ofbiological organisms andprocesses to manufacturingindustries 。
名词解释:发酵(fermentation):通过微生物或动植物细胞生长培养和化学变化大量产生和积累专门的代谢产物的过程。
生物固定化(immobilized):将具有一定生理更能的生物细胞,如微生物细胞、植物细胞、动物细胞等,用一定方法将其固定,作为固体催化剂加以利用的一门技术,固定化细胞与固定化酶技术共同组成了现代化的生物催化技术固体培养(solid culture):微生物生长在潮湿不溶于水的基质发酵,在固体发酵过程中几乎不含自由水。
腺病毒(adenovirus):一类DNA病毒主要引起呼吸系统急性感染,经改造的的腺病毒基因组可作为基因载体用于转染,也可用于基因治疗,潜在危险性较小。
在作为基因载体转染的过程中外源基因并整合到宿主靶细胞基因组中,并且表达一定时间自然降解。
佐剂(adjuvant):能非特异性的增强机体对抗原免疫应答的物质,其本身无抗原性,但与抗原结合后可以促进机体产生抗体,或延长抗体产生的时间,还能产生炎症反应,使抗体在组织局部聚集。
胰岛素(insulin):胰腺中的胰岛β细胞分泌的一种蛋白质激素含51个氨基酸其生物学作用包括参与糖代谢、脂代谢、蛋白质代谢的调节。
单克隆抗体(monoclonal antibody):抗体主要由B细胞合成,每个B细胞有合成一种抗体的遗传基因,动物脾脏有上百万种B细胞系,含遗传基因不同的B细胞合成不同的抗体,当机体受到抗原刺激时,抗原分子上的许多决定簇分别激活各个具有不同基因的B细胞,被激活的B细胞分裂增殖形成该细胞的子代细胞,有许多个被激活B细胞的分裂增殖,形成该细胞的子代细胞,有许多个被激活的B细胞的分裂增殖形成多克隆,并合成多种抗体,若能选出一个制造一种专一抗体的细胞进行培养,就可得到由单细胞经分裂增殖而形成的细胞群即单克隆、单克隆细胞将合成一种决定簇的抗体称为Ig。
单克隆抗体技术:要制备单克隆抗体须首先获得能合成转移抗体的单克隆B细胞。
但这种B 细胞不能在体外生长,实验发现骨髓瘤细胞可在体外生长繁殖,应用细胞杂交技术使骨髓瘤细胞与免疫系统的淋巴细胞融合,得到杂交骨髓瘤细胞,这种细胞既具有B细胞合成专一抗体的特性,又具有骨髓瘤细胞能在体外培养增值永存的特性。
单词:metabolic 新陈代谢的,fossil fuel 化石燃料,degrade 降解,fiber 纤维,cotton 棉花,wool 羊毛,hygienic 卫生的detergent 清洁剂,antibiotics 抗生素,component 组分,biodegradability 生物可降解性,intrinsic 固有的,perturb 扰动,thermochemistry 热化学,Biocatalysis 生物催化,enzyme 酶,genetics 遗传学,methodology 方法学,cellular 细胞的,extracellular 胞外的,isotope 同位素,Biotin 生物素,antibiotic 抗生素,penicillin 青霉素,2-oxoglutarate a酮戊二酸,trigger 引发,Flux 通量,transformant 转化株,plasmid 质粒,homologous 同源的,heterologous 异源的deficient 缺陷的,strain 菌株,sensitivity 灵敏度,steady state 稳态,infinitesimal 无穷小的,activity 活力,,mechanism 机制,attenuation 衰减,perturbation紊乱,kinetic 动力学的,glutamate 谷氨酸,composition 组分,medium培养基,perculture 预培养,deionize 去除离子,vitamin 维生素,soybean大豆,protein蛋白质,hydrolysate 水解产物,cholramphenicol 氯霉素,Kanamaycin 卡那霉素,batch 间歇式,fermentor发酵罐,dissolve溶解,oxygen 氧,concerntration浓度,agitation搅拌,revolution 旋转,aeration通气,buffer缓冲液,Sonication 超声波破碎法,supernatant上层液,absorption光吸收值,Branch point 分支点,glucose 葡萄糖,normalize 规格化,consumption 消耗,growth phas 生长期,specific activity 比活力,coefficient 系数,upstream 上游的,lysine 赖氨酸,inoculate 接种,agar 琼脂,bacteriophage 噬菌体,facultative兼性的,assimilate 吸收,saccharide糖类,fructose 果糖,ethanol乙醇,methanol甲醇,glycerol甘油,urea尿素,peptone蛋白胨,copper铜,aqueous水的,eluent 洗脱液,Phosphate 磷酸盐,redox 氧化还原,,modification修饰,host寄主,intermediate 中间体,respiration呼吸,consumption消耗,kinase激酶,isomerase异构酶,bisphophate 二磷酸盐,mass balance质量平衡,genome基因组,genomic基因组的,glycolysis糖消解,high throughput高通量,sequence测序仪,evolutionary进化的,tag标记,transcription转录,transduction传导,array阵列,proteomice蛋白组学,affinity亲和力,counterpart 对照物,amino acid氨基酸,promoter启动子,ligate链接,vector载体,plasmid质粒,base pair碱基对,homology同源性,codon密码子,excise切割下,primer引物,region区段,amplificatio 扩增,transform转化,template模板,strand链,SDS-PAGE十二烷基磺酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳,ORF coding 开放阅读框架编码,polymer聚合物,sterilize消毒,inoculate接种,batch fermentation间歇式发酵,continuous fermentation连续是发酵,recombinant重组子,secretion分泌,variant变体,in situ 原地,in vivo体内,ribosome核糖体,interface界面,crosslinking交联,entrapment包埋,encapsulation胶囊化,residue残基,cationic阳离子的,culture broth培养液,stabilization 稳定,hydrolytic水解的,actone丙酮,aromatic芳香族的,sediment沉淀,chiral 手性,pesticide 杀虫剂,aseptic无菌的,impair削弱,atringent严厉,shelf life贮存期,continuous stirred tank reactor连续搅拌釜式反应器,vessel容器,foam breaker 消泡器,condensate冷凝水,cascade control级联控制,ratio control 比率控制,feed forward control 前馈控制,parameter参数,carbon dioxide二氧化碳,hydrophilic polymers亲水聚合物,aqueous水质的,tissue组织,carbohydrate碳水化合物,density 密度,solubility溶解度,extraction萃取,centrifugation离心,filtration过滤,solvent溶剂,solute溶质,membrane 膜,adsorption吸附,evaporation 蒸发,sublimation 升华,vaporisation气化,dehydration 脱水,distillation蒸馏,latent heat潜热,streamlined层流的,turbulent湍流的,hyperfiltration 超滤,dialysis透析,electrophoresis电泳,flocculation絮凝,flotation浮选,milling碾碎,lysis细胞裂解,lipophilic亲脂的,crystallization结晶,chromatographic层析法的,heterotrophic 异养的,lag phase迟滞期,exponential growth phase指数期,stationary phase稳定期,deathphase衰亡期,specific growth rate比生长速率课后习题:1.以间歇式操作方式培养大肠杆菌XN-1。
使用5L的发酵罐,装液容量为3L。
温度控制在32度,用28%的氨水调节PH维持在7.0左右。
以每分钟180转的搅拌速度控制溶解氧浓度为3.0mg/L。
通气量控制在r2 vvm。
葡萄糖的初始浓度为20g/L,玉米浆初始浓度为15g/L. All cultivations were carried out in the batch mode.A 5L jar fermentor with a liquid working volume of 3L was used for cultivation.The temperature was controlled at 32 @,and the PH was maintained at 7.0 by adding 28%ammonia water.The dissolved oxygen concentration was maintained at above 3.0mg/L,by controlling the agitation speed in the range 180 revolutions per liter liquid volume per minute .The initial glucose was added intermittently.2.作为碳源,有糖类,如葡萄糖,果糖,蔗糖,糖蜜,淀粉和淀粉水解物;有机酸,如乙酸,富马酸,柠檬酸;醇类,如乙醇,甲醇和甘油。
As the carbon sources,saccharides such as glucase,fructose,sucrose,molasses,starch and starch hydrolyzate organic acids such as acetic acid,fumaric acid and citric acid,and alcohols such as ethanol,methanol and glycerol can be used.3.作为氮源,有氨水无机铵盐,如氯化铵,硫化铵,醋酸铵,磷酸铵;有机铵盐,如富马胺;胺,如乙胺;含氮化合物,如尿素;含氮有机物,如蛋白胨,肉膏,酵母膏,玉米浆,酪蛋白水解物,豆饼及水解物,氨基酸和核苷酸发酵生产的废细胞及其降解物。
As the nitrogen sources, ammonia, inorganic ammonium salts such as ammonium chloride, ammonium sulfate ammonium acetate and ammonium phosphate,organic,ammonium salts such as ammonium fumarate,amines such as ethylamine nitrogen-containing compounds such as urea,and nitrogenous organic substances such as peptone, meat extract,yeast extract,corn steep liquor, casein hydrolyzate, soybean and cakes and hydrolyzate thereof,and waste cells used for amino acid and nucleotide fermentation and its digested product thereof can be used.4.作为无机盐,有磷酸二氢钾,磷酸氢二钾,磷酸酶,硫酸镁,氯化钠,硫酸亚铁,硫酸锰,硫酸铜和碳酸钙。