grammar—trans 英语语法翻译
- 格式:docx
- 大小:19.50 KB
- 文档页数:4

英语教学法之GrammarTranslationMethod<i>语法翻译法是最原始的英语教学方法。
</i>Approaches and Methods in Language Teaching<i>语法翻译法是最原始的英语教学方法。
</i>Grammar method / Grammar translation method Ollendorff’s method / Jacotot’s method Traditional method Classical method / Old method<i>语法翻译法是最原始的英语教学方法。
</i>Translation MethodGrammar Translation MethodLexicon Translation MethodTranslation Comparison MethodModern Translation Method<i>语法翻译法是最原始的英语教学方法。
</i>What is Grammar Translation Method?The Grammar-Translation Method is a method of foreign or second language teaching derived from the classical method of teaching Greek and Latin which uses translation and grammar study as the main teaching and learning activities.<i>语法翻译法是最原始的英语教学方法。
</i>BackgroundIn Middle Ages, Latin was the dominant language of education, commerce, religion, and government in the Western world. In the 16th century, however, French, Italian, and English gained in importance as a result of political changes in Europe, and Latin gradually became displaced as a language of spoken and written communication.The study of classical Latin and an analysis of its grammar and rhetoric became the model for foreign language studyfrom the 17th century to the 19th century.<i>语法翻译法是最原始的英语教学方法。
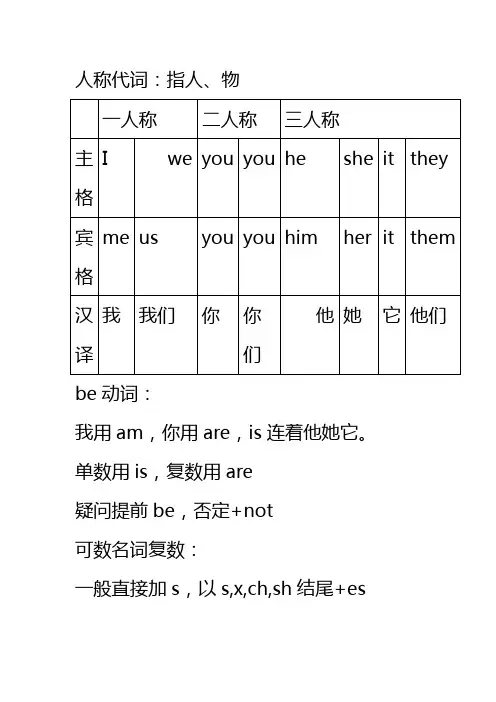
人称代词:指人、物be动词:我用am,你用are,is连着他她它。
单数用is,复数用are疑问提前be,否定+not可数名词复数:一般直接加s,以s,x,ch,sh结尾+eso结尾,有生命+es,无生命+s辅音+y结尾,y变i+esf,fe结尾,f,fe变v+esf,fe结尾,直接加s:giraffe,roof,handkerchief,scarf,golf可数名词有单复数,单数用a/an修饰,不可数名词无复数,常与a+量词+of+u.n. 两者都可用some修饰指示代词:this(这个),that(那个),these (这些),those(那些)所有格:表人:sb+’s表物:of(前后倒置)there be:有地点介词:里面in,上面on,over,under 上下方;between…and两者间,among用于3者间,紧挨next to,附近near,before 后面,in front of在外部前方,in the front of空间内部前方来自from,朝前to,里面穿过是through,表面穿过across,到里面into,到上面onto 一般现在时:表示经常反复、现在状态、客观真理助动词:do,does否定分别don’t,doesn’t 动词单三:一般+s,以s,x,ch,sh,o结尾,词尾+es,辅音+y结尾,y变i+es,have单三是has 一般疑问句把be、情态动词、助动词提前,谓语动词还原特殊疑问句=特殊疑问词+一般疑问句how many提问可数名词复数how much提问不可数名词年月季节前用in,日期前面可不行,具体几号要用on,上午下午又是in,具体某天上下午,要用on来不用inat用法真不少,正午午夜到黎明频度副词:always(100%),usually(90%),often(80%),sometimes(40%),seldom(30%) never(0%)现在进行时:表现在正在进行的动作结构:be+doing现在分词变化规则:一般直接+ing不发音e结尾,去e+ing重读闭音节结尾,双写词尾辅音字母+ing ie结尾,ie变y+ing形容词:系动词后,名词前;译为:…的方式副词:用在动词后,译为:…地形容词变副词规则:一般直接+ly,个别e结尾去e+ly,y结尾,y变i+ly情态动词:can,should,shall,would,could+v原;否定+not,疑问直接提前have to,would like to,+v原;否定前+don’t 疑问前+do一般过去时:表过去发生的事动词过去式变化规则:一般直接+ed,e结尾+d,辅音字母+y结尾,y变i+ed重读闭音节,双写辅音字母+ed过去时中,助动词用did,be的过去式为was(am,is),were(are)其他结构和现在时相同祈使句:表命令、警告、指示、建议肯定:v原+其他否定:don’t+v原+其他and表并列,多个成分用and连接,在最后两个成分之间,其余用逗号隔开or表选择,用法与and相同but表转折,连接相反意义的词some用于肯定句中,接可数名词复数或不可数名词any用于否定句和疑问句中,用法和some一样表委婉语气时,some在疑问句中不变any 形容词、副词的比较级和最高级变化规则:一般+er/est,e结尾,+r/st重读闭音节结尾,双写辅音字母+er/est 辅音字母+y结尾,y变i+er/est多音节词在前面+more/most一般将来时:表将要发生,或对未来打算三种表达方式:will/shall+v原be going to+v原be doing表将来过去进行时:表过去某一时间正在进行的动作构成:was/were+doing现在完成时:表发生在过去已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或后果结构:have/has+done一般动词过去分词与过去式变化相同一般疑问句把have/has提前其他不变,否定在have/has后+nothave been to曾经去过某地(已回)have gone to曾经去过某地(未回)already(已经)用在have/has和过去分词之间,用在句末表强调,常用于肯定句中yet用法和汉译与already相同,常用于否定或疑问句中since+时间点,译为自从…以来for+段时间,现在完成进行时:表开始于过去,现在仍进行或刚刚结束的动作现在完成进行时构成:have/has been doing 时间状语从句:1.when引导:表时间段或时间点,译为当…时候用法:主从同现/过,或主将从现2.while引导:表主、从动作同时进行用法:主从同现/过3.as soon as引导:译为一…就…4.not…until…引导:译为直到…才…条件状语从句:1.if引导:译为如果用法:主将从现2.unless引导:译为如果不/除非用法和if相同unless引导否定从句,与if…not不可互换,否则意思相反结果状语从句:so…that…引导:译为如此…以致于…原因状语从句:because引导:译为因为because和so不能连用because引导原因状语从句,从句一般在主句之后让步状语从句:although/though引导:译为虽然although/though不能和but/however连用直接引语:直接用别人原话,用引号标出间接引语:用自己的话转述别人的话,不用引号直接引语变间接引语要把现在时变为过去时,一人称变三人称,三人称一般不变附加疑问句:在陈述句之后,表对陈述内容提出质疑或通过反问以确定陈述句的一种疑问句构成:前肯后否,前否后肯陈述部分是I’m,附加部分用aren’t I答语用yes,肯定陈述部分;no否定陈述部分陈述句带有否定词,附加用肯定不定代词(表人)在正式语体中用he,非正式语体中用they不定代词(表物)用it。

grammar--过去分词做定语和⼀般过去式Grammar —The -ed form used as attributives and the simple past tense⼀. 过去分词(短语)做定语分词是动词的⼀种⾮谓语形式,在句中可做定语、状语、补⾜语和表语。
有两种形式,⼀种是现在分词(v.-ing),⼀种是过去分词(v.-ed)。
现在分词⼀般表⽰主动和进⾏的意思,过去分词⼀般表⽰被动和完成的意思。
以下主要是过去分词(短语)做定语的⼏点⽤法。
1. 及物动词的过去分词做定语,表被动和完成。
a broken cup ⼀个破杯⼦ a wounded soldier ⼀个受伤的⼠兵respected leaders 受⼈尊敬的领导们trained camels 受过训练的骆驼们an abandoned farm ⼀个废弃的农场2. 不及物动词的过去分词没有被动的意义,只表⽰动作的完成.a grown woman ⼀位成年妇⼥an escaped prisoner⼀名逃犯a fallen tree ⼀棵倒下的树the retired manager 退休经理fallen leaves 落叶the risen sun 已升起的太阳3. 过去分词可构成合成词作定语。
man-made satellite ⼈造卫星half-finished products 半成品highly-developed industry ⾼度发达的⼯业widely-used language ⼴泛应⽤的语⾔4. 过去分词或短语作定语时,相当于⼀个定语从句。
the color TV set produced last year =the color TV set that were produced last year 去年⽣产的彩⾊电视机a letter written by my daughter =a letter which/that is written by my daughter ⼀封我⼥⼉写给我的信a young girl dressed in white= a young girl who was dressed in white⼀个穿⽩⾐服的年轻⼥孩the food cooked by experts = the food which/that was cooked by experts 烹饪专家做的⾷物5. 过去分词做定语的位置:1)单个的过去分词作定语常放在所修饰的名词之前,叫前置定语。

主题:grammar translation教学法内容:1. 简介Grammar translation教学法是一种传统的语言教学方法,主要应用于教授外语的语法和翻译技巧。
这种教学法在欧洲和美国曾经很流行,在20世纪后期逐渐被认为是一种过时的教学方法。
然而,一些学者认为在特定情况下,这种教学法仍然有其独特的优势和适用性。
2. 原理Grammar translation教学法主要基于对语法规则和结构的学习,以及对文本的逐字逐句的翻译。
学生通过翻译文本来学习和掌握语法知识,建立起对目标语言的理解和掌握。
这种教学法偏重于语法的教学和语法知识的运用,对于学生的语法掌握和写作能力有一定的帮助。
3. 优点- 对语法规则的系统性学习:通过Grammar translation教学法,学生可以系统地学习目标语言的语法规则,掌握语言的结构和逻辑。
- 促进翻译技巧的培养:这种教学法通过翻译练习,可以帮助学生提高翻译和理解能力。
- 强调语法的正确应用:Grammar translation教学法注重语法的正确应用,可以帮助学生避免语法错误,提高写作质量。
4. 缺点- 忽略口语表达能力:由于Grammar translation教学法偏重于语法和翻译练习,对口语表达能力的培养并不充分,学生在实际交流中可能存在障碍。
- 缺乏实际应用:这种教学法偏重于文本的翻译和理解,缺乏实际语言运用的机会,学生对于语言的应用能力有所欠缺。
- 学习动机不足:由于翻译练习的单一性和语法学习的枯燥性,学生可能缺乏学习外语的动力和兴趣。
5. 适用性- 学习重点在于阅读和理解:对于需要重点培养阅读理解能力和写作能力的学生,Grammar translation教学法是一种有效的教学方法。
- 重视语法知识的掌握:对于需要系统学习语法知识的学生,这种教学法可以帮助他们建立起对语法规则的理解和掌握。
6. 结论尽管Grammar translation教学法在现代语言教学中逐渐被边缘化,但在特定情况下仍然有其独特的优势和适用性。

九年级英语《grammarfocus》翻译1. 引言在学习英语的过程中,语法始终是一个让学生感到棘手的问题。
特别是在九年级,学生们需要更加深入地理解和掌握英语语法知识,以便更自如地进行表达和交流。
本文将从九年级英语课程中的《grammarfocus》这一重要部分入手,深入研究和解析其内容,以期帮助同学们更好地掌握英语语法知识。
2. 什么是《grammarfocus》?《grammarfocus》是九年级英语课程中的一部分,其主要内容包括英语语法的重点知识点和难点,旨在帮助学生们理解和掌握这些知识,从而提高他们的英语表达能力和写作水平。
在学习过程中,学生们需要逐步学习和应用这些知识点,才能够真正掌握英语语法。
3. 《grammarfocus》中的重点内容在九年级的《grammarfocus》中,包括了诸多重要的知识点,比如动词的时态和语态,名词的单复数和所有格,形容词和副词的比较级和最高级,以及连接词的使用等。
这些内容涵盖了英语语法的基本要点,对于学生们打下扎实的语法基础至关重要。
《grammarfocus》还会涉及一些高级语法知识,如虚拟语气、倒装句等,这需要学生们更深入地理解和应用。
4. 《grammarfocus》的难点在九年级的英语课程中,学生们普遍会遇到一些比较难以理解和掌握的语法知识。
虚拟语气的运用、不同时态的转换、副词的用法等,都是学生们容易混淆和错误的地方。
而《grammarfocus》中也会针对这些难点进行重点讲解和练习,帮助学生们克服这些困难,从而更好地掌握英语语法。
5. 我对《grammarfocus》的理解在我看来,《grammarfocus》确实是一个非常重要而且有价值的部分。
通过系统的学习和实践,我逐渐明白了语法对于英语学习的重要性,也体会到了它的复杂和微妙之处。
在学习过程中,我要求自己多加练习,不断总结和归纳,以便更深入地掌握这些知识。
我也意识到语法的学习需要持之以恒,不能一蹴而就,需要不断地积累和提高,才能够真正做到熟练运用。


1。
If the earth suddenly ________spinning,we would all fly off it。
A。
stopped B。
had stopped C。
has stopped D. would stop 2。
“How should the city be run?” “If I ________a mayor,I would make the streets cleaner and hire more policemen。
"A. wouldB. wereC. would be D。
should3。
If the whole operation _________ beforehand, a great deal of time and money would have been lost.A。
was not planned B。
has not been plannedC。
had not been planned D. were not planned4。
Jean doesn’t want to work right away because she thinks that if she________ a job she probably wouldn’t be able to see her friends very often。
A。
has to get B。
were to getC. had got D。
could have got5. It is recommended that the project________ until all the preparations have been made.A。
is not started B. will not be startedC. not be started D。
is not to be started6。

英语语法(Grammar)一、一般疑问句(The General Question Sentence)1、句子中有am ,is ,are的,把am ,is ,are提前,句号(period /΄piəriəd/)变成问号(question mark)。
例:This is a boy. →Is this a boy?2、句子中有will ,can的,把will, can提前,句号(period /΄piəriəd/)变成问号(question mark)。
例:He can play ball. →Can he play ball?3、变一般疑问句时,把I we变成you,把am变成are 。
例:I am a boy. →Are you a boy?4、当句子中没有am ,is ,are ,will ,can时,需do , does帮忙⑴当句子人称是I , we, you , they等第一、第二人称或为复数名词(Birds)时,句子前加Do,句号变问号。
例:I know that man. →Do you know that man?⑵当句子人称是she, he, it等第三人称或为单数名词(a chair)时,句子前加Does,动词变成原形(has →have),句号变问号。
例:Lucy runs fast. →Does Lucy run fast?He has apen. →Does he have a pen?二、特殊疑问句(Special Interrogative Sentence)1、特殊疑问词:What(什么),Who(谁)What对thing提问(thing指职业、不明白的事或物), Who对person提问(person指人)。
结构:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句+?例:He is a doctor.用What代替a doctor, is提前到he前→What is he?This is a chair. →What is this?That woman is my mother. →Who is that woman?2、划线部分是地点(place):→用Where提问。

一、简介几种主要外语教学法及其语法教学观1、语法翻译法(Grammar-Translation Method/The Classical Method)语法翻译法是十八世纪创建的,直至十九世纪80年代之前的外语教学,它独领风骚。
其教学过程是先分析语法,然后把外语译成本族语,主张两种语言机械对比。
2、直接法(Direct Method)直接法是十九世纪下半叶始于西欧的外语教学改革运动的产物,是古典语法翻译法的对立面。
要求外语与思想直接联系,绝对不使用本族语,即完全不借助于翻译,语法降到完全不重要的地位。
3、听说法(The Audiolingual Method/ Oral Approach)听说法产生于第二世界大战爆发后的美国。
强调模仿、强记固定短语并大量重复,极其重视语音的正确,尤其强调语调训练,“There is little or no grammatical explanation: Grammar is taught by inductive analogy(归纳类推) rather than deductive(演绎的) explanation.”广泛利用对比法、在对比分析母语与外语的基础上学习外语的难点,并在教学中有针对性地加以解决。
但听说法过分重视机械性训练,忽视语言规则的指导作用,过分重视语言的结构形式,忽视语言内容和意义,存在流于“造作”的语言倾向。
4、视听法(Audio-Visual Method),又叫情景(Situational Method)视听法于20世纪五十年代首创于法国,它是以幻灯的视觉感受和录音的听觉感受相结合的一种教学法,是在直接法和听说法的基础上发展起来的。
主张听说训练必须同一定情景结合,在某一情景基础上进行。
视听法的缺点是过于重视语言形式,忽视交际能力的培养,过分强调整体结构,忽视语言分析、讲解和训练。
5、全身反应法(Total Physical Response)全身反应法是美国加州圣约瑟大学心理学教授詹姆士.阿歇尔(James Asher)于20世纪60年代提出的。

中学英语常见的教学方法介绍1.语法翻译法(grammar translation method)2.直接法(direct method)3.听说法(audio-lingual method4.视听法(audio--visual approach)一、语法翻译法(grammar translation method)(一)语法翻译法及其理论基础1.定义:语法翻译法(grammartranslationmethod),又称“翻译法”、“传统法”、“古典法”。
它是以系统的语法知识教学为纲,依靠母语,通过翻译手段,重在培养外语读写能力的教学法。
2.起源:起源于中世纪欧洲人教希腊文和拉丁文的方法,18世纪开始教英语、法语、意大利语等现代语言时,仍沿用这一古老的方法。
3.创始人:18世纪末、19世纪初,德国语言学家奥伦多夫等人对语法翻译法进行理论上的总结和阐述,才使语法翻译法成为一种具有完整系统的第二语言教学法。
4.理论基础:①语言学基础是历史比较语言学;②心理学基础是18世纪德国的官能心理学,创始人是德国哲学家沃尔夫。
(二)语法翻译法的主要特征语法翻译法的主要特征包括5个方面。
(1)以培养读写书面语能力以及发展智力为主要目标。
(2)以系统的语法知识为教学的主要内容,对语法规则进行详细的分析,要求学生熟记并通过翻译练习加以巩固。
(3)词汇的选择完全由课文内容决定,用对译的生词表进行教学,句子是讲授和练习的基本单位。
(4)用母语进行教学,母语和外语互相翻译是主要的教学手段、练习手段和评测手段。
(5)阅读领先,重视阅读能力和翻译能力的培养,强调学习规范的书面语,注重通过阅读外语名著来学习外语。
(三)语法翻译法评价1.主要优点:①有助于学生牢固掌握系统的语法知识,阅读和翻译水平较高;②采用母语讲授,可以减轻教师的压力,还可以节省课堂教学时间。
2.缺点:(5个)①忽视口语教学和语音教学,缺乏听说能力的训练;②过分地强调语法规则的教学,忽视语言技能的训练;③教学内容、教学过程比较枯燥(指经典文学作品);④利用母语教学,过分地强调翻译,不利于培养学生运用目的语进行思维和交际的能力;⑤以教师为中心,教学方式单一,学生缺少实践机会,课堂气氛沉闷。
grammar的用法Grammar(语法)是指语言中词语和句子的结构、形态和用法规则的总称。
良好的语法能够帮助我们准确地表达思想,避免歧义和误解。
在英语中,掌握正确的语法用法是学习和运用语言的关键之一。
下面将介绍一些常见的英语语法用法。
首先,我们来讨论名词的用法。
名词是用来表示人、事物、地方或概念的词语。
名词可以用于单数形式和复数形式。
通常,我们在表示一个人、事物或概念时使用单数形式,而在表示多个人、事物或概念时使用复数形式。
例如,单数形式的名词包括 "book"(书)和 "cat"(猫),而复数形式的名词包括 "books"(书籍)和"cats"(猫咪)。
其次,我们来谈谈动词的用法。
动词是用来表示行动、状态或存在的词语。
它可以用于不同的时态和语态。
时态包括过去时、现在时和将来时,表达动作发生的时间。
而语态包括主动语态和被动语态,分别表示主语是动作者还是动作的承受者。
例如,"run"(跑)是一个动词,可以用于不同的时态和语态。
比如,过去时形式为 "ran"(跑过),被动语态形式为 "is run"(正在被跑)。
此外,在英语中,形容词和副词的用法也十分重要。
形容词用来描述名词的特征或性质,而副词则用来描述动词、形容词或其他副词的程度或方式。
形容词通常位于名词前面,副词则位于动词或形容词之前。
例如,"beautiful"(美丽的)是一个形容词,它可以修饰名词,如 "beautiful flowers"(美丽的花朵);而 "quickly"(快速地)是一个副词,它可以修饰动词,如 "she runs quickly"(她快速地跑)。
最后,我们要注意代词的用法。
代词用来替代名词,以避免重复使用。
对中国产生过影响的教学法流派及其优缺点一、语法翻译法(the Grammar Translation Method)语法翻译法对近代和当代语言教学产生重大影响,对中国外语教学的影响达数十年。
语法翻译法也叫古典法,它因曾经用来教授古典语言希腊语和拉丁文而得名。
16 ~17 世纪,处于文艺复兴中心的欧洲人崇尚古典文化,学习拉丁文,通过阅读来继承文化遗产。
18 世纪以后,以英语和法语为代表的现代语言作为外语取代拉丁文,但其教学方法仍然沿用教授拉丁文时的方法,因为当时的语言学家认为:世界上大多数语言源于同一种语言,词汇概念和语法结构都是相同的,通过“等值翻译”可以实现不同语言之间的理解和沟通。
语法翻译法以翻译作为手段来处理课文教学:课堂上用母语来组织教学,用外语或母语来回答问题,将课文逐句翻译成本族语,培养学生阅读外语原文的能力;用演绎法处理语法,句子是教学与练习的基本单位,要求学生背诵语法规则和例句,通过母语和外语之间的比较来理解抽象词汇、句子意义和句法结构;用书面形式来设疑答问,问题的设计停留在语言的表层结构,答案直接从课文中找到;用直觉思维来应对检测,句子是练习的基本单位,借助“题海战术”进行单一的形式练习,就能获得“满意”的成绩。
语法翻译法从20 世纪初就开始影响我国的外语教学,经过几十年的实践运用,我国教师运用“语法翻译法”颇有心得,将其总结为“八字诀”,即“读( 课文) ”、“译( 句子) ”、“讲( 语法规则) ”、“问( 提问) ”、“背( 规则) ”、“练( 习) ”、“记 ( 单词) ”、“测 ( 试) ”。
上课之初,每个学生都有可能被要求朗读课文中的几行文字,然后将所读的内容逐句译成汉语。
当学生阅读完段落并将其翻译为母语之后,学生举手就所存在的问题提问,老师回答,讲解或造句示范。
解决学生存在的问题之后,教师开始讲解课文中重要的语法点,要求学生背记规则。
接着做课文后的练习题,练习的内容就课文设计的问题进行书面答问,英汉、汉英翻译练习,填空选择练习等,或是要求学生抢记单词,最后进行分课小测验。
人教版八年级上英语语法聚焦翻译全文档编制序号:[KK8UY-LL9IO69-TTO6M3-MTOL89-FTT688]Unit 1 Grammar Focus1、你去哪里度假了我去纽约市了。
2、你和别人一起出去了吗(对比:你和谁一起去了)不,没有人在这儿。
每个人都在度假。
3、你买特别的东西了吗是的,我为我爸爸买了些东西。
不,我没买任何东西。
4、食物怎么样所有的东西尝起来真的很好吃!5、大家都玩得很开心吗哦,是的。
一切都很棒。
Unit 2 Grammar Focus1、你周末通常做什么我总是锻炼。
2、他们周末做什么他们经常帮助做家务。
3、她周末做什么她有时候去购物。
4、你多久看一次电影我大概每月去看一次电影。
5、他多久看一次电视他几乎不看电视。
6、你去购物吗不,我从不去购物。
?Unit 3 Grammar?Focus1、?汤姆比萨姆聪明吗不,不是。
萨姆比汤姆聪明。
2、塔拉比蒂娜外向吗不,不是。
蒂娜比塔拉外向。
3、你和你姐姐一样友好吗不,不是。
我更友好。
4、塔拉学习和蒂娜一样努力吗是的,她是。
5、谁在学校谁更努力蒂娜认为她比我学习努力。
Unit 4 Grammar?Focus1、最好的电影院是哪家城镇影院。
它离家最近。
而且在那里你可以最快地买到电影票。
2、城镇上最差的服装店是哪家梦想服装店。
它比蓝月亮服装店更差。
它的服务最差。
3、你认为调幅970兆赫怎么样我认为调幅970兆赫相当差。
它的音乐最糟糕。
Unit 5 Grammar?Focus1、你想看新闻节目吗是的,我想看。
/不,我不想看。
2、今晚你打算看什么我打算看《我们过去的日子》。
3、你期待能从情景喜剧中学到什么你可以学到一些很棒的笑话。
4、你为什么喜欢看新闻节目因为我希望了解世界各地发生的事。
5、你认为谈话节目怎么样我不介意它们。
/我无法忍受它们!/我喜欢看它们!?Unit 6 Grammar?Focus1、?你长大以后打算做什么我想成为一名工程师。
英语教学法流派Schools of teaching methodsMain contents:1.grammar translation method 翻译法2. direct method 直接法3. audio-lingual approach 听说法4. audio-visual approach 视听法5. cognitive approach 认知法6. functional approach功能法/功能意念法/ 交际法( 沉默法/ 全身互动法/暗示法)7.task-based approach任务型教学法8.Natural approach 自然教学法Main aspects:1.Concepts概念2.Background历史背景3.Theory base理论基础4.Teaching principles 教学基本原则5.Teaching procedures教学过程6.Typical textbooks典型教材7.Evaluation 评价第一章翻译法Translation Method第一节翻译法的概念及其产生的背景The concept and background oftranslation method1.Concept 概念:翻译法是用母语来教授外语的一种语言教学方法。
2.特点(feature):在外语教学过程中本族语与所学外语经常并用。
法国语言学家兼教学法家Louis Marchand在《以科学方法教授现代外国语》一文中说:“Grammar translation method is to use your native language to teach a foreign language.翻译教授法,就是拿本国语言去译解外国言语。
”背景(background):1.在外语教学中运用翻译作为教学手段已有几千年的历史,但从理论上对翻译法进行概括和说明,使之成为一种科学的教学法体系却是近一百多年的事。
外语外文 课程教育研究·13·4.2教师要培养学生学习英语的兴趣 兴趣是最有效的方法,兴趣也是最好的老师。
爱因斯坦曾说:“兴趣与爱好是最大的动力”,因此我们不难看出培养学生学习英语的兴趣是激发学生英语学习动机的关键。
它可以激发学生求知欲的动力,也是学习动机中最活跃的因素。
学生一旦对英语学习产生并保持浓厚的兴趣,学习主动性性就会调动,自然而然地就会增强学习的动机。
因此教师应该采用各种有效手段,如清晰的教学思路、丰富的教学内容、灵活的教学方法、现代化的教学手段等来激发学生的好奇心,培养学生的英语学习兴趣,使其在学习英语的过程中感到无穷的乐趣,以达到激发中学生学习动机的目的。
4.3教师应培养学生的求异思维 教师要注意引导和鼓励学生打破思维定势,鼓励学生用自己独到的见解来回答老师的问题。
课堂气氛要自由活跃,这样有利于学生主动参与,更好的发挥学生的个性和主动性,使学生积极主动地探究知识,创造性地运用知识,培养学生的开拓精神与创新意识,逐步培养出其求异创造的能力和思维。
在课文教学中教师要善于设计新颖别致,并能唤起学生共鸣的问题,让学生在独立思维的基础上,再进行集体讨论,集思广益。
也可以用所教的知识,让学生自由地求异发散,相互启发,相互交流,从而用创新意识来灵活运用语言知识。
让学生凭自己的能力与摸索解决新产生的问题,掌握新知识。
在此过程中学生的创新能力得以真正提高,从而学生学习的动机也在这过程中得以增强。
4.4教师应提高自身专业素质并转变教学观念 教师的专业素质和教学观念,既会影响学生的学习兴趣,也会影响教学效果。
教师的专业素质低,教学观念陈旧,就会使课堂气氛沉闷、乏味,学生学习兴趣就会降低,相反,一个有一口流利标准的发音,专业水平特别高的教师,能无形中激发学生内在的求知动机,教学相长,整个英语教学工作就能良性循环。
教师也要不断给自己创造学习的坏境和机会,这样才能有足够的能量释放给学生,才能适应新时期英语教学的要求,才能在学生的心目中树立榜样。
English tenses 英语时态
1)the present tense 一般现在时
2)the past tense 一般过去时
3)the future tense 一般将来时
4)the past future tense 一般过去将来时
5)the present continuous tense 现在进行时
6)the past Continuous Tense 过去进行时
7)the future continuous tense 将来进行时
8)the past future continuous tense 过去将来进行时
9)the Present Perfect Tense 现在完成时
10)the Past Perfect Tense 过去完成时
11)the future perfect tense 将来完成时
12)the past future perfect tense 过去将来完成时
13)the present perfect continuous tense 现在完成进行时
14)the past perfect continuous tense 过去完成进行时
15)the future perfect continuous tense 将来完成进行时
16)the past future perfect continuous 过去将来完成进行时Passive voice 被动语态
parts of speech 词类
1)Nouns (n.) 名词
2)Adjectives (adj.) 形容词
3)Adverbs (adv.) 副词
4)Verbs 动词
5)Pronouns (pron.) 代词
6)Numerals (num.) 数词
7)Articles (art.) 冠词
8)Prepositions (prep.) 介词
9)Conjunction (conj.) 连词
10)Interjection (interj.) 感叹词
11)common noun 普通名词
12)proper noun 专有名词
13)class noun 类名词
14)collective noun 集体名词
15)material noun 物质名词
16)abstract noun 抽象名词
17)indefinite article 不定冠词
18)definite article 定冠词
19)Irregular Verbs 不规则动词
Adverbs (adv.) 副词
1)ordinary adverb 普通副词
2)interrogative adverb 疑问副词
3)relative adverb 关系副词
4)conjunctive adverb 连接副词
Pronouns (pron.) 代词
1) personal pronoun 人称代词
a) nominative case 主格
b) objective case 宾格
2) possessive pronoun 物主代词
a) Adjective possessive pronoun形容词性物主代词
b) Noun possessive pronoun名词性物主代词
3) self-pronoun自身代词
4) reciprocal pronoun 相互代词
5) demonstrative pronoun 指示代词
6) interrogative pronoun疑问代词
7) relative pronoun关系代词
8) indefinite pronoun不定代词
members of the sentence 句子成分
1)subject主语
2)predicate谓语
3)object 宾语
4)attributive (modifier) 定语
5)adverbial adjunct状语
6)complement补语
7)predicative 表语
case格
1)nominative case 主格
2)objective case 宾语
3)possessive case 所有格
Punctuation 标点符号
1)period;full stop句号
2)comma逗号
3)question mark问号
4)exclamatory mark感叹号
5)quotation mark引号
6)colon冒号
7)semicolon 分号
8)hyphen连字符
9)apostrophe 撇号
10)dash 破折号
11)ellipsis 省略号
12)italics 斜体
sentence 句子类型
1)simple sentence 简单句
2)compound sentence 并列句
3)complex sentence 复合句
4)compound complex sentence 并列复合句
5)declarative sentence 陈述句
6)interrogative sentence 疑问句
7)imperative sentence 祈使句
8)exclamatory sentence 感叹句
9)simple sentence 简单句
10)compound sentence 并列句
11)complex sentence 复合句
interrogative sentence 疑问句
1)general question 一般疑问句;yes-no question 是非疑问句2)special question 特殊疑问句
3)alternative question 选择疑问句
4)echo question 反问句
English mood 英文语气
1)indicative mood 直陈语气
2)imperative mood 祈使语气
3)subjunctive mood 虚拟语气
Clause 从句
1)subject clause 主语从句
2)predicative clause 表语从句
3)object clause 宾语从句
4)attributive clause 定语从句
5)adverbial clause 状语从句
6)if clause if从句
短语phrase
a)infinitive phrase不定式短语
b)gerundial phrase动名词短语
c)participial phrase分词短语
d)prepositional phrase介词短语。