药物化学构效关系
- 格式:docx
- 大小:22.68 KB
- 文档页数:3




第一章药物化学结构与构效关系药物化学结构与构效关系是研究药物分子结构与其生物活性之间关系的重要学科之一、了解药物分子的结构特征以及其与生物活性之间的相互作用对于新药的研发和优化具有重要意义。
本章将从药物分子的结构与活性关系的概念、分子结构对活性的影响、构象与构效关系等方面进行论述。
药物分子的结构与活性关系是以药物分子的结构特征为基础,通过对药物分子的结构与活性进行定性和定量的研究,从而提高药物的活性、选择性和毒性。
药物分子的结构特征包括分子量、电荷分布、功能团、立体构型等。
药物分子的活性受多种因素的影响,例如药物分子与靶点的相互作用方式、药物分子的生物转化、药物分子的分布与代谢等。
因此,通过研究药物分子的结构与活性关系,可以揭示药物分子与靶点之间的相互作用机制,为药物设计提供理论依据和指导。
药物分子的结构对活性的影响可以从药物内部结构、药物分子与靶点相互作用等角度进行分析。
药物内部结构中,有机化合物的骨架结构、取代基的位置和类型等对于药物分子的活性具有重要影响。
骨架结构的特定形状可以影响药物分子在靶点上的识别和结合,在保持药物分子与靶点相互作用的基础上,通过改变骨架结构来提高药物的活性和选择性。
取代基的位置和类型也可以影响药物分子的立体构型和电荷分布,从而影响药物与靶点之间的相互作用。
药物分子与靶点相互作用是药物发挥生物活性的基础,通过研究药物与靶点之间的相互作用方式,可以揭示药物分子活性的机制,并为药物的设计和优化提供指导。
药物分子的构象与构效关系是研究药物分子构象特征与其生物活性之间的关系。
药物分子的构象是指药物分子在空间中的排列方式,包括键角、键长、手性等方面的信息。
药物分子的构象特征对于药物的活性和选择性具有重要影响。
例如,药物分子的手性结构可以影响药物分子与靶点的亲和力和选择性,手性药物分子的活性常常和其对映异构体(对映体)的结构密切相关。
此外,药物分子的构象特征还可以通过分子模拟等方法进行预测和研究,为药物的设计和优化提供指导。

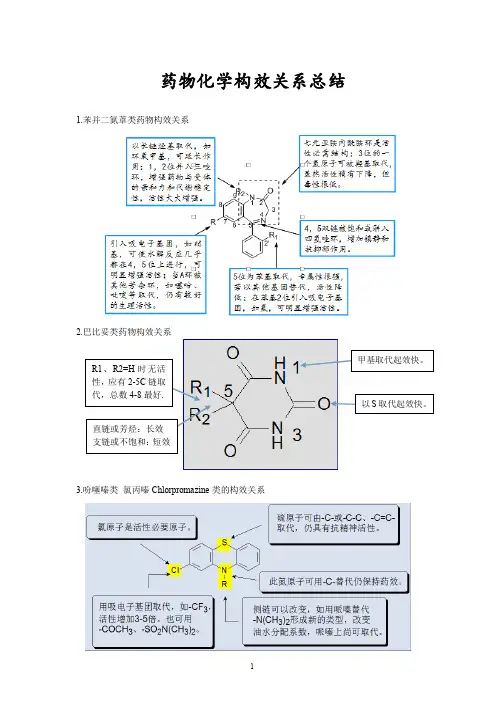
药物化学构效关系1.局部麻醉药的构效关系:①亲脂性部分:可变范围较大,可为芳环或芳杂环,但以苯环的作用较强,是局麻药物的必需部位。
当酯类药物苯环的邻位或对位引入给电子集团,如氨基、烷氧基时,局麻作用均较未取代得苯甲酸衍生物强;对氨基苯甲酸酯类苯环的邻位上若再有其他取代基如氯、氨基、烷氧基时,由于位阻作用而延长了酯的水解,因此活性增强,作用时间延长。
②中间连接部分:由羰基部分和烷基部分共同组成。
羰基部分与麻醉药持效时间及作用强度有关,作用持续时间为:酮﹥酰胺﹥硫代酯﹥酯;麻醉作用强度:硫代酯﹥酯﹥酮﹥酰胺。
烷基部分碳原子数以2~3个为好,当烷基部分为—CH2CH2CH2—时,麻醉作用最强。
③亲水性部分:大多数为叔胺,易形成可溶性的盐类。
氮原子上取代基的碳原子总和以3~5时作用最强,也可为酯环胺,其中以哌啶的作用最强。
2. 苯二氮卓类药物的构效关系:① 1、2位拼入三氮唑环,使代谢稳定性增加,提高与受体的亲和力,活性显著增加;② 3位引入手性碳,分子构想更稳定,对受体亲和力增强;③ 4、5位引入恶唑环,增强稳定性;④7位有吸电子取代基时,药物活性明显增强,且吸电子性越强,活性增加越明显,NO2>Br>CF3>Cl;⑤ 5位苯环的2’位引入体积较小的吸电子基团如F、Cl,可使活性增强。
①镇静作用的强度和起效快慢,与药物的理化性质有关。
【酸性解离常数pKa】巴比妥酸和5位取代的巴比妥类有较强的酸性,在生理pH=7.4几乎全都电离成离子状态,不易透过血脑屏障,无镇静催眠作用;5,5-二取代的巴比妥类,酸性减弱,生理pH条件下不易电离,易进入脑中发挥作用,显效快,作用强。
【脂水分配系数】5位无取代基时,分子有一定极性,亲脂性强,不易透过血脑屏障,无镇静催眠作用;5位取代基碳原子总数在7~8之间作用最强,若亲脂性过强,作用下降甚至出现惊厥。
药物有最适当的的脂溶性,有利于药物透过细胞膜和血脑屏障,起效快,作用强。

药物化学中构效关系的教学方法研究摘要:构效关系是先导化合物修饰、新型药物设计的基础,在药物化学教学中具有至关重要的作用。
由于其多样性和复杂性,学生的掌握情况不理想。
本文针对这一问题对药物的构效关系进行归纳分类,总结为“三部分一核心多构型”三类,每一类都进行举例讲解,为学生更好地理解与掌握药物化学的构效关系提供一种可行的方式。
关键词:药物化学;构效关系;三部分;一核心;多构型药物是一类特殊的有机化合物,对应的化学结构反应了药物的本质[1],药物的化学结构对其生理功能和效应起决定性作用[2]。
药物化学是一门着重研究药物的构效关系,并通过研究生物体与化合物之间的相互作用过程,从分子水平上解析药物作用方式和作用机理的学科[3~5],为药剂学、药理学、药物分析等提供理论支撑[6,7]。
因此,掌握各大类化学药物的构效关系是制药工程专业本科生学习药物化学的基本要求[3]。
药物的构效关系是探寻药物的生物活性与其化学结构间依赖关系规律的依据。
通过研究药物(包括激动剂和拮抗剂,底物和抑制剂)的构效关系,来推测药物的作用机制和受体(及酶)的结构,并在此基础上进行合理的药物设计,从而提高研究药物的成功率[8]。
除了生物活性与化学结构存在关系,药物的体内吸收、分布、排泄等药物动力学性质[8],药物的体内代谢和药物的毒副作用方面与化学结构也存在着密切的关系。
例如,药物的化学结构与药物动力学性质具有一定的关联,药物分子进入体内先进行氧化、还原、水解、羟基化,而引入或使分子暴露极性基团(羟基、羧基、巯基、氨基等),再与内源性分子(葡萄糖醛酸、硫酸、甘氨酸、谷胱甘肽等)共价键结合生成水溶性的物质,排出体外。
因此,药物功效与结构之间的一一对应关系,在药物的研发与应用中具有重要作用[9~11]。
依据文献报道以及同行之间的交流发现,在国内各大高校的药物化学教学过程中,由于课时较少、课程内容较多等原因,药物的构效关系的讲解时间不足,本科生的药物专业知识有限,学生只能死记硬背,经常出现不同药物的构效关系混淆的情况。



药物化学构效关系(第二版尤启冬主编)主要药物的构效关系应用抗肿瘤作用机理:1、药物在体内能形成缺电子活泼中间体(碳正离子)或其他具有活泼的亲电性基团的化合物,进而与肿瘤细胞的生物大分子(DNA,RNA,酶)中富电子基团(氨基,巯基,羟基等)发生共价结合,使其丧失活性,致肿瘤细胞死亡。
2、属细胞毒类药物,在抑制和毒害增生活跃的肿瘤细胞的同时,对其它增生较快的细胞产生抑制。
如骨髓细胞、肠上皮细胞、毛发细胞和生殖细胞等。
副作用大:影响造血功能和机体免疫功能,恶心、呕吐、骨髓抑制、脱发等。
氮芥类药物脂肪氮芥:氮原子的碱性比较强,在游离状态和生理PH(7.4)时,易和β位的氯原子作用生成高度活泼的亚乙基亚胺离子,为亲电性的强烷化剂,极易与细胞成分的,亲核中心发生烷基化反应。
脂肪族氮芥:烷化历程是双分子亲核取代反应(SN2),反应速率取决于烷化剂和亲核中心的浓度。
脂肪氮芥属强烷化剂,对肿瘤细胞的杀伤能力也较大,抗肿瘤谱较广;但选择性比较差,毒性也较大。
芳香族氮芥:氮原子与苯环共轭,减弱了碱性,碳正离子中间体,单分子的亲核取代反应。
氮芥类药物及大多数烷化剂主要是通过和,DNA上鸟嘌呤或胞嘧啶碱基发生烷基化,产生DNA链内、链间交联或DNA蛋白质交联而抑制,DNA的合成,阻止细胞分裂。
β-内酰胺类抗生素的化学结构特点:1分子内有一个四元的β-内酰胺环,除了单环β-内酰胺外,该四元环通过N原子和邻近的第三碳原子与另一个五元环或六元环相稠合。
2除单环β-内酰胺外,与β-内酰胺环稠合的环上都有一个羧基。
3所有β-内酰胺类抗生素的β-内酰胺环羰基α-碳都有一个酰胺基侧链。
4β-内酰胺环为一个平面结构,但两稠环不共平面β-内酰胺类药物可抑制粘肽转肽酶的活性和青霉素结合蛋白青霉素构效关系(1)6位的侧链酰胺基团决定其抗菌谱。
改变其极性,使之易于透过细胞膜可以扩大抗菌谱。
例如,在芳环乙酰氨基的α位上引入-NH2、-COOH、和-SO3H等亲水性基团,可以扩大抗菌谱,增强亲水性有利于对革兰阴性菌的抑制作用并能增强对青霉素结合蛋白的亲和力。
药物的构效关系药物的构效关系(Structure-activity relationship, SAR)是指药物的结构与其生物活性之间的关系。
通过研究不同化合物的结构特征和生物活性数据,可以揭示药物分子的作用机制,指导药物设计和优化,提高研发效率和成功率。
药物的构效关系研究对于药物化学、药理学和药代动力学等领域都有重要的意义。
以下是一些常见的构效关系的参考内容:1. 功能团对药效的影响:研究表明,药物分子中的特定功能团如羟基、酰胺、酯等,可以影响药物的生物活性。
例如,对于抗菌药物,羟基和酰胺基团通常与细菌靶标结合,从而发挥药效。
2. 结构类似性对药效的影响:药物分子的结构类似性对于药效也有重要的影响。
通常来说,结构相似的化合物可能具有相似的生物活性。
因此,通过对已知药物结构进行改良和优化,可以获得具有更高活性和选择性的新化合物。
3. 空间构型对药效的影响:药物分子的空间结构对于其与靶标的相互作用和选择性也起着重要作用。
例如,药物分子的立体异构体可能具有不同的生物活性。
研究不同空间构型的药效差异,有助于设计和优化具有更好活性和选择性的药物。
4. 电子结构对药效的影响:电子结构指的是药物分子中原子和键的电荷分布和云密度。
电子结构的差异可以影响药物分子与靶标的相互作用和药效。
例如,芳香环的电子密度与药物的溶解度、生物利用度和靶标的亲和性有关。
5. 氢键和离子键对药效的影响:氢键和离子键是药物分子与靶标相互作用的常见方式。
氢键的强度和方向性可以影响分子的亲和性和选择性。
离子键的形成可以改变药物分子的溶解度和稳定性。
6. 毒性与构效关系:药物的构效关系研究中还要考虑药物的毒性和副作用。
通过研究药物结构与毒性之间的关系,可以优化药物的安全性和耐受性,减少不良反应。
总的来说,药物的构效关系研究可以从多个角度考察药物分子的结构与生物活性之间的关系。
通过深入理解药物分子的作用机制,可以为药物设计和优化提供重要的理论指导。
药学综合考研之药物化学构效关系总结一、概述药物化学构效关系,即药物化学结构与生物活性之间的关系,是药学领域的重要研究方向之一。
在药学综合考研中,药物化学构效关系的学习和理解对于理解药物作用机制、药物设计与优化、新药研发等方面具有至关重要的意义。
药物化学构效关系研究主要关注药物分子结构与其生物活性之间的相互影响和关联。
通过系统研究药物化学结构的变化如何影响其生物活性,我们可以更好地理解药物作用的本质,为新药的设计和研发提供理论基础和实践指导。
药物化学构效关系不仅涉及到化学结构的知识,还需要深入理解生物学、生理学、病理学等领域的知识,是一个多学科交叉的领域。
随着现代科学技术的发展,尤其是计算机技术和生物技术的不断进步,药物化学构效关系的研究方法也在不断发展和完善。
从传统的合成、提取、筛选等实验方法,到现代的计算机模拟、大数据分析等高科技手段,药物化学构效关系的研究正在逐步深入。
对药物化学构效关系的考研复习者来说,不仅需要掌握基础的理论知识,还需要具备跨学科的综合能力,以适应这个领域的研究和发展。
药物化学构效关系是药学研究的重要基础,对于指导新药设计、优化药物作用机制等方面具有重要意义。
本文旨在对药学综合考研中的药物化学构效关系进行总结,以期为考研学生提供系统的学习资料和复习指导。
1. 简述药物化学构效关系的重要性。
药物化学构效关系,作为药物设计与研发领域中的核心原理,具有极其重要的地位。
其重要性主要体现在以下几个方面:药物化学构效关系是药物研发的基础。
药物的疗效与其化学结构之间有着密切的联系,通过对药物分子结构的深入研究,可以预测和优化药物的生物活性,从而有针对性地设计合成新药物。
构效关系研究有助于提高药物研发的效率。
随着现代医药产业的飞速发展,药物研发已经进入了一个竞争激烈的时代,如何快速、高效地发现和优化具有优良药效的药物成为了一个重要的挑战。
而药物化学构效关系的研究,可以指导科研人员快速筛选出具有潜力的药物分子,从而大大提高药物研发的效率。
构效关系的名词解释
构效关系的名词解释是:药物或其他生理活性物质的化学结构与其生理活性之间的关系,是药物化学的主要研究内容之一。
狭义的构效关系研究的对象是药物,广义的构效关系研究的对象则是一切具有生理活性的化学物质,包括药物、农药、化学毒剂等。
最早期的构效关系研究以直观的方式定性推测生理活性物质结构与活性的关系,进而推测靶酶活性位点的结构和设计新的活性物质结构,随着信息技术的发展,以计算机为辅助工具的定量构效关系成为构效关系研究的主要方向,定量构效关系也成为合理药物设计的重要方法之一。
药物的构效关系:
例如拟胆碱药的化学结构与乙酰胆碱相似,都有季胺或叔胺基团,都能与胆碱受体结合,形成具有活性的复合物,因而表现出相似的作用。
又如,磺胺药与对氨基苯甲酸化学结构相似,因而能与对氨基苯甲酸竞争二氢叶酸合成酶而影响细菌叶酸的代谢。
在具有基本结构的任何一类药物中,药理作用的类型是由它们的基本结构决定的,而它们的药理作用的相对强度,是由基本结构上各个取代基团的性质决定的,如磺胺类药物。
但也有化学结构相似而作用相拮抗的情况,如磺胺与对氨基苯甲酸、氨丙啉与硫胺等。
同时,也有化学结构不同而药理作用相似的情况,如麻黄碱与茶碱。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表本人。
本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容请联系客服!。
药物化学构效关系(Pharmacochemical structure-activityrelationship)barbituratesBarbiturates are structural nonspecific drugs.Structure nonspecific drugs: the biological activity of the drug is not related to the chemical structure of the drug.Structural specific drugs: the effects of drugs depend on the specific chemical structure and spatial alignment of drug molecules.The function of barbiturates and the fast and slow time of the drug are closely related to the dissociation constant, PKa, and the distribution coefficient of lipid water.Dissociation constant: the drug ACTS as an ion in the form of molecules through the biofilm.Oil and water distribution coefficient: the drug can be transported both in body fluids and through the blood-brain barrier.The category 5 is active, there are two substituents on the total number of carbon atoms when two substituent between 4 to 8, the distribution coefficient is moderate, active best. When the total number of carbon atoms in more than eight, effect is strong, easy to produce convulsion. The structure of the N atoms on the methyl on the imide replaced can reduce acidity andincrease the fat soluble, work fast. Use of C - 2 O S alternative. Increase lipid solubility and easy through the blood brain barrier, it works fast.The metabolism of barbiturates is associated with the metabolic time of the drug.2. Benzodiazepines (diazepam)A ring is necessary for the activity.B ring can be replaced by other aromatic rings, and it retains its activity.One is generally n-ch3. - CH3 can be removed in metabolism, but retains its activity1.2 bits can be added to the heterocyclic ring (triazolam: increased stability and increased activity)Three of the H atoms can be reduced slightly by -oh, but very low toxicity.4, 5 for the double bond to be saturated. The activity decreases, and incorporation into oxazole to increase sedation and antidepressant effect.The 2 bits of 5 - phenyl are introduced into the electron base (F, Cl, Br...). Increased activity.7 bits were introduced into the electron base, and the activity significantly enhanced NO2 > CF3 > Br > Br > ClThree. Aryl propionic acid (ibuprofen)One or more carbon atoms are spaced between a benzene ring and a carboxyl group.The carboxyl group of a is another - CH3, which limits the free rotation of carboxyl group, keeping it fit for the binding of the receptor or enzyme to increase the anti - inflammatory analgesic effect.Because of carboxyl a bit - the introduction of CH3, make its produce the asymmetric center, is usually a S - configuration activity is higher than R - configuration, can mutual transformation between chiral isomers in the body, is normally inactive R - S - configuration into active configuration.Another hydrophobic base, cyclohexyl and allyl oxide, can be introduced in the aromatic ring.The interposition of benzene ring carboxyl group is introduced into a suction electron base such as F.C l, etc.Anti-inflammation activity is good.Iv. The constitutive effect of cholinergic receptor agonists (choline choline)Positively charged amino 1, quarter. (1) the nitrogen atom is must be active. If the As, Se replace activity. (2) methyl instead As well on the nitrogen atoms, if replace with larger groups such As ethyl activity decreased, if three ethyl into choline active resistance.2 acetoxyl group. (1) when the acetyl or butyl acyl replace activity, (2) on the acetyl hydrogen is replaced by aromatic ring or larger groups to fight choline activity. (3) the rapid hydrolysis of ester base for acetylcholine effect time short and unstable factors, so it not easy to replace acetyl groups can increase the stability of the hydrolysis and action time. Such as acetyl ammonia formyl replaced, because in the nitrogen lone pair electrons, carbonyl carbon is electrophilic acetyl is low, not easy to hydrolysis.3, ethylidene bridge. (1) ethylidene has key influence on activity of the length of the bridge, two carbon for the best. With the extension of carbon chain, the activity is gradually reduced. (2) the quaternary ammonia nitrogen atom of a bit have replaced by methyl, overall activity decreased, but lack of the sample N greater than M. (season 3 of ammonia nitrogen atom B have replaced by methyl, can prevent the effect of cholinesterase, extend the action time, effect on the acetylcholine M sample, sample N effect greatly abate, be selective M receptor agonist.The constitutive effect of adrenal receptor agonistThe basic structure of phenylethylamine is the activity and the elongation or shortening of the carbon chain reduces the effect.Phenol hydroxyl groups in benzene ring significantly enhanced the role of pseudo adrenalin, especially in the 3 or 4 digits, but the effect time was brief.The peripheral function was retained and the central excitation decreased.N substituent on the relative strength of a and B receptor effect have a significant impact. The alternative to base from methyl tert-butyl, a receptor effect weakened. B receptor effect increase, and the selective increase of B2 receptor.B - carbon usually has hydroxyl group. Its absolute configuration is R - configurational.The constitutive relationship of anesthetics.The adjacent position gives the electron base substitution, which is beneficial to the formation of the amphoteric ion and the activity is enhanced. If there is an electron absorption, the activity decreases.It can be aromatic ring, aromatic heterocyclic, the modification of this part has a great influence on the activity, the active sequence is the benzene ring > pyrrol > furanIt's usually best to have 2 or 3 carbonsThere are secondary amine, tertiary amine or pyrrolidine, piperidine, etc., and tertiary amine is the most common.Insert - CH2, between benzene ring and carboxyl - O - groups, such as damage to the formation of zwitterionic. Activity. If connected to conjugate groups can be formed, such as - CH2 =CH2 -. Activity can remain the same. Amide also can form the amphoteric ion.In this part, the stability of the drug is determined, and the time sequence of carbonyl + -o->... + - S - >... + - NH - >... + - CH2 -; The order of strength: -s-> - o->-ch2 - > - NHThe constitutive relationship of beta blockers (figure of figure).Phenylethanolamine and aromatic propanolamineIt can be benzene, naphthalene, heterocyclic, dense ring, and fatty unsaturated heterocyclic. It can be substituted for methyl, chlorine, nitro, methoxide, etc., with the best activity in 2, 4 and 2, 3 and 6 positions.When substituted with S, CH2, -nch3, the activity decreases.The activity of s-configurational isomers increased, and the activity of r-configurational isomers decreased or disappeared.The activity of r-configurational isomers increased, and the activity of s-configurational isomers decreased or disappearedTertiary butyl and isopropyl instead at best, the hydrogen atoms on the methyl for less than 3 or N - N double replaced, activity decreased. Due to the structure of great B receptor blockers, so its solubility also have bigger difference, which related to its side effects and the location of the positionto eliminate. Pro fatty liver metabolism - rate faster. The hydrophilic - renal eliminationStructure-effect relationship of dihydropyridine drugs (nifedipine)The activity of dihydropyridine ring is necessary for the activity. If the activity of pyridine ring or hexahydropyridine ring is lost, the NH in the ring is not replaced, and the activity remains the best.2, 6 substituents are low - grade alkanesThe 3, 5 carboxylic acid lipid is necessary for the activity, and if it becomes acetyl or cyano, the activity decreases, and if it becomes nitro, the calcium channel can be activated.The 3, 5 carboxylic acid is different, the C4 is chiral center, the size of the ester group has little influence on the activity, but the asymmetric fat affects the part.C4 is stereoscopic for chiral carbonThe relationship between the four substituents and the activity: phenyl or substituted phenyl > ring alkyl > methyl > HIn the adjacent Spaces of the benzene ring, there is a better activity of the electron base substitutionThe constitutive effect of H2 receptor antagonist (ranitidine).The structure of the H2 receptor antagonist consists of three parts: the basic aromatic ring structure, and the four atomic chain and the polar group.Alkaline aromatic heterocyclic and alkaline groups substituted aromatic heterocyclic are necessary to active, imidazole ring as the proton transfer mechanism, by different thiazole, pbo replacement after alkaline, activity also decreases. By lipophilic aromatic heterocyclic (benzene) replaced activity. Was replaced by the alkaline groups, furan, thiazole, after displacement is good H2 receptor antagonist.Planar polar groups. It is the structure of guanidine and amidine. In the physiological PH condition, the polar groups with low ionization degree can form more than one hydrogen bond with the receptor forming one of the hydrogen bonds.The chain length is 4 atoms long. The chain length is related to antagonism. Free rotation and restriction make its activity fall, and the chain of intermediate connection can be replaced by the steel ring.The constitutive effect of penicillin(1) six side chain of amide groups mainly decided its antibacterial spectrum, change its polarity, makes it easy to through the cell membrane, can enlarge its antibacterial spectrum. For example, in a place of aromatic ring ethyl amide group introduced polarity - NH2, - COOH, - SO2 hydrophilic groups, such as antibacterial spectrum. Increase thehydrophilicity. Is advantageous to the bacteriostatic action of bacterium of negative of glen, and can enhance the affinity of binding protein to penicillin.The position of the three-dimensional resistance group is introduced in the appropriate position of the molecule.As in the side chain is introduced into the three-dimensional steric larger groups and introduced in six methoxyl and formamide, because of its three-dimensional steric effect reduces the passivation enzyme structure adaptability, protect B - lactam ring from B - lactamase attack. So get resistance to antibiotics of enzyme.Penicillin thiazole ring of carboxyl is basic reactive group, although can be replaced by sulfur acid and amide activity. If the reduction of carboxyl of alcohol, antimicrobial activity was lost. For fat carboxyl made available before the medicine principle, improve the oral absorption and pharmacokinetic properties.The configuration of three chiral carbons in penicillium is essential for its activity, but the two methyl groups on the thiazole ring of penicillin are not necessary for the activity.The constitutive effect of semi-synthetic cephalosporinIn seven side chain introduction of lipophilic groups, such as phenyl, dilute base, thiophene and nitrogen heterocyclic. Can be enhanced antibacterial activity, expand its antibacterial spectrum. Change 3 substituent at the same time, theintroduction of heterocyclic, can improve the oral absorption distribution also can expand its antibacterial spectrum.A position of 7 amides was introduced into the hydrophilic - SO3H, -nh2, -cooh, isopolar group. The antibacterial spectrum could be expanded to change 3 substituents, and the introduction of -cl, CH3, and nitrogen-containing heterocyclic could enhance oral absorption and expand the antibacterial spectrum.With 7 B as the side chain of ammonia oxime "conveniently" can improve the stability of B - lactamase, expand the antibacterial spectrum. This is mainly due to the introduction of oxime, methoxy occupy the position near the B - lactam ring. Prevents the enzyme molecules of B - lactam ring close to, so that drug resistant enzymes, the nature of broad spectrum.5 S with biological electronic body O, CH2, etc, respectively called cephalosporins cephalosporin and carbon, oxygen activity is not reduced. 3 substituent of transformation, such as acetoxyl group can be methyl, chloride to replace you can expand the antibacterial spectrum and change the absorption of drug in the body distribution and pharmacokinetic properties of the permeability of drugs.2-3 double - bond shift inactivation. 2 - COOH can be made into premedication to increase oral absorption.The constitutive effect of quinolone drugs.A ring (pyridine keto acid) is the basic therapeutic effectsof antibacterial action necessary to group. One of the three carboxyl and four ketone group is with its target enzyme binding sites, is A crucial part of the antimicrobial activity.The B ring part can be changed greatly, and can be incorporated into the benzene ring, pyridine ring and pyrimidine ring.The substitution of the N1 position substituents for the antibacterial activity was greater, and if the hydroxyl group was replaced by the hydroxyl group, the activity was better than that of ethyl, fluoroethyl and cyclopropyl.Two substituents were introduced to reduce or disappear the substituents, possibly due to space resistance blocking the binding of receptors.The carboxyl group and the 4-digit ketones are indispensable part of antibacterial activity.Five amino substituted activity increased. Other groups replaced the activity.Six substituent effect on the activity is very important. Active replace order: F > Cl > > CN = CH2 > = h. introduced F than H antibacterial activity of 30 times. Because the F generation and DNA spiral enzyme enhanced affinity 2-17 times. The penetration enhancement 1-70 times of bacterial cell walls.The order of 7 substituents to be substituted for base enhancement is piperazine > dimethylamine > methylamine > hydrogen, which is the best substitute for piperazine.The 8 bits were replaced by F, Cl and -och3, but they were also enhanced by the substitution of F instead of the phototoxicity. If 1, 8 rings, the photochemical isomers produced by the other were also significantly different.。
局部麻醉药构sheng效关系
1.分类
芳酸酯类、酰胺类、氨基醚类、氨基酮类、其他类
2.构效关系
亲酯部分中间链亲水部分
⑴亲脂部分:
芳烃或芳杂环,这一部分修饰对理化性质变化大,但苯环作用较强。
苯环上引入给电子取代基,麻醉作用增强,而吸电子取代基则作用减弱。
⑵中间部分:此部分决定药物稳定性,和局麻作用持续时间有关
⑶亲水部分:常为仲胺和叔胺,仲胺刺激性较大;烃基链3~4个碳原子作用最强,杂环以哌啶环作用最强
巴比妥类药构效关系
(1)、分子中5位上应有两个取代基。
(2)、5位上的两个取代基的总碳数以4—8为最好(3)、5位上的两个取代基的总碳数以4—8为最好. (4)、在酰亚胺氮原于上引入甲基,可降低酸性和增加脂溶性。
(5)、将C2上的氧原子以硫原子代替,则脂溶性增加,起效快,作用时间短。
苯二氮卓类药物的构效关系
(1)1,3-二氢-5-苯基-2H-1,4-苯二氮卓-2-酮是此类药物基本结构;(2)环A7位引入吸电子取代基活性增加(3)环B为七元亚胺-内酰胺结构是产生药理作用的必要结构(4)5位苯环上的取代基时产生药效的重要结构之一,(5)1,2位的酰胺键和4,5位的亚胺键在酸性条件下易水解开环.
吩噻嗪类药构效关系
R1 部分必须由三个成直链的碳原子组成,若为支链,与多巴胺受体B 部分立体上不匹配,抗精神病活性明显下降,抗组胺作用增强。
顺式吩噻嗪类药物与多巴胺的优势构象能部分重叠,活性高(当侧链与氯取代的苯环同侧时,成为顺式构象)。
丁酰苯类药物的构效关系
(1)丁酰苯基为必需的基本骨架(2)侧链末端连一碱性叔胺(3)苯环的对位一般具
有氟取代(4)侧链湠基于碱基之间以三个碳原子最好
镇痛药的一般特征
(1)分子中具有一个平坦的芳香结构(2)有一个碱性中心能在生理PH条件下大部分电离为阳离子(3)含有哌啶或类似于哌啶的空间结构
吗啡的构效关系(半合成类镇痛药)
叔胺是镇痛活性的关键基团,氮原子引入不同的取代基可使μ 受体激动剂转变为拮抗剂。
酚羟基被醚化和酰化后,活性及成瘾性均降低。
羟基被烃化、酯化、氧化或去除后,活性及成瘾性均增加。
解痉药构效关系
(1)该部分可以为叔胺或季胺(2)中间脂肪连接部分n在2-4之间(3)一般来讲,X为酯键,醚键和烷基(4)R1和R2为饱和的碳环或杂环,也可以为芳环或芳杂环
氢氯噻嗪结构改造药的构效关系
(1)一位取代基必须呈酸性(2)5位氨磺酰基是必需的(3)4位的为氯或三氟甲基取代时,活性增加(4)对5-氨磺酰基-3-氨基苯甲酸类利尿药,氨基可为单取代和双取代的烷基。
肾上腺素受体激动剂的构效关系
(1)取代苯环结构部分(Ⅰ)苯环是与β受体作用的关键结构(2)中间碳链部分(Ⅱ)β-羟基是与受体结合的基团,β-碳的绝对构型对机动效应影响较大,其R构型的活性远高于S构型的活性。
(3)氨基部分(Ⅲ)氨基部分是与α受体作用的关键结构,可在生理PH条件下形成氮正离子,与α受体阴离子部位结合,产生激动效应.
钙通道阻滞剂1,4-DHP类药构效关系
1,4-二氢吡啶环是活性必须结构。
2,6 位取代基应为低级烷烃。
3,5 位羧酸酯基取代活性最好,且两个酯基不同者冠脉扩张或降压作用优于相同者。
4位常为苯环取代,若以其他芳环取代,任能保持效应.
3,5 位若为其他吸电基取代,可由拮抗作用转为激动作用。
β受体阻滞剂的构效关系
(1)一般n=0或1:n=0为苯乙醇胺类结构类型,n=1为芳氧丙醇胺类结构类型.(2)芳环和苯环上的取代基类型对阻断作用影响不大.(3)侧链α碳上无取代若有甲基取代,阻断β2受体的作用选择性增加(4)侧链β碳为手性碳原子,两个光学异构体的活性相差较大.(5)氮原子上的取代基R为不同烃基活性不同,活性为:叔丁基>异丙基>仲丁基、异丁基
ACE 抑制剂的构效关系:(1)ACEI 分子中有三个基团与ACE 的结合点相结合:与ACE 的锌离子结合的基团,如巯基、羧基、次磷酰基,与ACE 的正电荷以离子键结合的阴离子部分,即末端氨基酸部分的羧基,与ACE 的供氢部位以氢键结合的基团,即酰胺部分的羰基
他汀类药物构效关系
(1)3,5-二羟戊酸结构部分(Ⅰ)是抑制HMG-CoA还原酶的活性必须结构(2)手性脱氢萘(Ⅲ)是疏水结合的重要基团,有一定的平面要求。
(3)中间连接桥(Ⅱ)应是两个碳原子的距离,若以乙烯型碳链连接仍能保持活性。
青霉素的构效关系
6 位碳原子上的氢用甲基或甲氧基取代,将导致活性降低,基团体积较大时,则活性消失。
但甲氧基的取代可增加药物对β-内酰胺酶的抵抗能力。
2 位羧基是活性必需基团,若将其转化成硫代羧酸或酰胺,活性不变,但羧基被还原为醇时,失去活性。
对其羧基可利用前药原理进行结构修饰,如酯化可增加口服吸收和提高生物利用度。
6 位氨基的侧链可用不同的杂环进行取代,其活性可以得到增强。
当侧链的取代基含有
极性基团,可扩大抗菌谱,增强其活性。
引入吸电子基团能提高药物对酸的稳定性,引入位阻基团能增加药物对β-内酰胺酶的抵抗能力。
磺胺类药物的构效关系:
对氨基苯磺酰胺为活性必需基团,邻、间位无效;苯环若被其他芳环或芳杂环取代,或在苯环上引入其他基团,抑菌活性降低或丧失;N4 上一般无取代基,若有,则必须在体内易转化为游离氨基才有效,如RCONH-,RN=N-,-NO2,等;N1 上为单取代,大多为吸电基,可使活性加强,如酰基、芳杂环。
N1,N1-
双取代一般丧失活性;
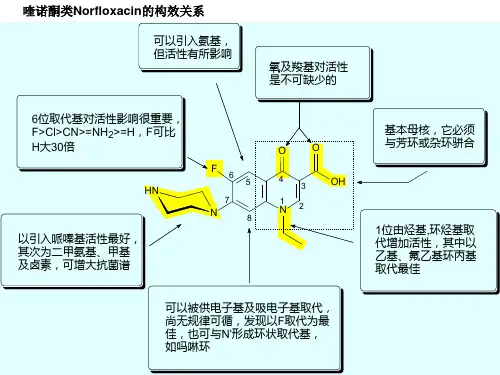
喹诺酮类抗菌药的构效关系
3 位COOH 和
4 位C=O 是活性必须基团,与DNA 螺旋酶和拓扑异构酶Ⅳ结合,不可缺少。
6 位:引入氟原子,与DNA 旋转酶结合力增大,对细菌细胞壁的穿透力增大
7 位取代活性增强(以取代或无取代的哌嗪、吡咯、吡咯烷基等五六原杂环较好)经典H1受体拮抗剂的构效关系
(1)Ar1可以是苯环。