自考05439考核知识点(中英版)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:27.50 KB
- 文档页数:4


2019年自学考试《管理学原理》复习资料(9)1.计划工作是指制定计划,就是根据组织内外部的实际情况权衡客观需要的主管可能,通过科学地预测,提出在未来一定时期内的组织所要达到的目标以及实现目标的方法2.计划工作中5W1H的具体含义:⑴what做什么:要明确组织的使命,战略,目标以及行动计划的具体任务和要求,明确一个时期的中心任务和工作重点⑵why为什么做:要论证组织的使命,战略,目标和行动计划的可能性和可行性,也就是说要提供制定的依据,实践表明,计划工作人员对组织和企业的宗旨,目标和战略了解得越清楚,理解得越深刻,就越有助于他们在计划工作中发挥主动性和创造性⑶when何时做:规定计划中各项工作的开始和完成的进度,以便实行有效的控制和对水平及资源实行平衡⑷where何地做:规定计划的实践地点或场所,了解计划实践的环境条件和限制,以便合理安排计划实践的空间组织和布局⑸who谁去做:计划不但要明确规定目标、任务、地点和进度,还应规定由哪个部门、那个人负责⑹how怎么做:制定实现计划的措施,以及相对应的政策和规则,对资源实行合理分配和集中使用,对人力,生产水平实行平衡,对各种派生计划实行综合平衡等3.计划工作的基本特征:⑴目的性⑵主导性⑶普遍性⑷经济性4.在管理中居于主导地位的工作是计划工作5.计划工作的核心是决策与产出之间的比例7.计划工作的经济性是指投入与产出之间的比例8.计划工作的意义:(⑴补充不肯定性和变化带来的问题⑵有利于管理人员把注意力集中与目标⑶有利于更经济地实行管理⑷有利于控制9.计划的种类:⑴按企业职能分类:生产计划,财务计划,供应计划,劳资计划,安全计划,人员培训计划等⑵按计划所涉及的范围分类:上层管理计划,中层管理计划基层管理计划⑶按计划的内容分类:专项计划和综合计划⑷按计划所涉及的时间分类:长期计划,中期计划,短期计划⑸按计划的表现形式分类:目的或使命,目标,战略,政策,程序,规则,规划,预算等10.计划工作的程序:①估量机会②确定目标③确定前提条件④确定可供选择的方案⑤评价各种方案⑥选择方案⑦制定派生计划⑧用预算形式使计划数字化。

2019年4月全国高等教育自学考试00015《英语(二》真题与答案解析第一部分:阅读判断(第1~10题,每题1分,共10分)下面的短文后列出了 10个句子,请根据短文的内容对每个句子作出判断:如果该句提供的是正确信息,选择A;如果该句提供的是错误信息,选择B;如果该句的信息文中没有提及,选择C。
在答题卡相应位置上将答案选项涂黑。
My BrotherMy brother is off at college, and at age 14, I miss him terribly. My brother is a rare kind of guy. He’s smart and kind. And my friends say he5s lovely. But it’s how he handles things and how he treats his friends and his family that make me feel more proud.He applied to 14 colleges. He was accepted by all but one, the one he wanted, Brown University. So he took his second choice, and off he went to a first year. When he came home for summer vacation, he said he’d move to Rhode Island near Brown, find a job, and do whatever he could to become known in the area. He'd work his heart out and do his best at everything. Someone, he was sure, would notice. This was a big deal for my parents as it meant agreeing to a year without college. But they trusted him and encouraged him to do whatever he thought it would take to realize his dream.It wasn’t long before he was hired as an amateur (业余的)play director at Brown. Now was his chance to shine, and shine he did. He put every bit of himself into the job. He met teachers and school officials, talked to everyone about his dream and never hesitated to tell them what he was after.And, sure enough, at the end of the year, when he reapplied to Brown, he was accepted. We were all happy, but for me the happiness went very deep. I had learned an important lesson—a lesson no one could have taught me with words. If I work hard for what I want, and if I keep trying after I’ve been turned down, my dreams can also come true. This is a gift I still hold in my heart.1.My brother had many good qualities.A.TrueB. FalseC. Not Given【答案】A【解析】题目中原句的意思是我的哥哥有很多好品质。

第一章管理与管理学※管理:是指组织中的管理者,通过实施计划、组织、人员配备、领导、控制等职能来协调他人的活动,使他们同自己一起实现既定目标的活动过程。
※管理的基本特征:1、管理是一种文化现象和社会现象;2、管理的主体是管理者;3、管理的任务、职能和层次;4、管理的核心是处理好人际关系※管理的五个基本职能:计划、组织、人员配备、领导、控制※管理的任务:设计和维持一种环境,使在这一环境中工作的人们能够用尽可能少的支出,实现既定的目标,层次分为上、中、下三个管理层次。
※管理是一种艺术,是强调管理的实践性※管理具有两重性:1、管理具有自然属性和社会属性,自然属性指管理的发展状况受到生产力和社会化大生产水平的制约,社会属性指管理的发展状况受到生产关系和社会制度的制约;反映出管理的必要性和目的性2、管理的两重性是马克思主义关于管理问题的基本观点。
管理的两重性反映出管理的必要性(即管理是有效组织劳动所必需的)和目的性(即管理反映了生产资料占有者组织劳动的目的)。
※掌握管理两重性的意义:1、认真总结我国在管理理论与实践上正反两方面的经验教训,更好地发挥社会主义制度的优越性;2、注意学习引进国外对我们有益的管理理论、技术和方法;3、要结合实际,随机制宜地学习与运用※管理学:是一门系统地研究管理过程的普遍规律、基本原理和一般方法的科学。
※管理学的特点:一般性、多科性、历史性、实践性※管理学研究的内容:1、根据管理活动总是在一定社会生产方式下进行的,可分为生产力方面、生产关系方面、上层建筑;2、从历史的角度研究管理实践,管理思想及管理理论的形成与演变过程;3、从管理者的基本职能或工作出发来系统研究管理活动的原理、规律和方法※学习研究管理学的原因:1、管理的重要性决定了学习研究管理学的必要性;2、是培养管理人员的重要手段之一;3、是未来的需要※学习与研究管理学的方法:1、唯物辩证法,总的方法论的指导;2、系统方法;3、理论联系实际的方法※系统:是指由相互作用和相互依赖的若干组成部分结合而成的,具有特定功能的有机整体,系统本身又是它从属的一个更大系统的组成部分。
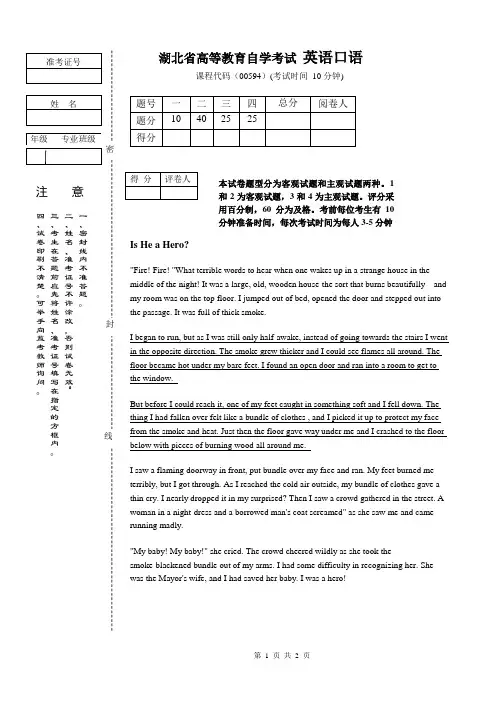
湖北省高等教育自学考试 英语口语课程代码(00594)(考试时间 10分钟) Is He a Hero? "Fire! Fire! "What terrible words to hear when one wakes up in a strange house in the middle of the night! It was a large, old, wooden house-the sort that burns beautifully---and my room was on the top floor. I jumped out of bed, opened the door and stepped out into the passage. It was full of thick smoke. I began to run, but as I was still only half-awake, instead of going towards the stairs I went in the opposite direction. The smoke grew thicker and I could see flames all around. The floor became hot under my bare feet. I found an open door and ran into a room to get to the window. But before I could reach it, one of my feet caught in something soft and I fell down. The thing I had fallen over felt like a bundle of clothes , and I picked it up to protect my face from the smoke and heat. Just then the floor gave way under me and I crashed to the floor below with pieces of burning wood all around me.I saw a flaming doorway in front, put bundle over my face and ran. My feet burned me terribly, but I got through. As I reached the cold air outside, my bundle of clothes gave a thin cry. I nearly dropped it in my surprised? Then I saw a crowd gathered in the street. A woman in a night-dress and a borrowed man's coat screamed" as she saw me and came running madly."My baby! My baby!" she cried. The crowd cheered wildly as she took thesmoke-blackened bundle out of my arms. I had some difficulty in recognizing her. She was the Mayor's wife, and I had saved her baby. I was a hero!本试卷题型分为客观试题和主观试题两种。

自考学位英语是中国自学考试的一门重要科目,主要针对那些希望通过自学获取学位证书的学习者。
这门课程旨在评估考生的英语水平,特别是他们在阅读、写作、听力和口语方面的能力。
以下是自考学位英语考试的一些关键知识点,帮助你更好地准备考试:1. **词汇与语法**:- 掌握一定数量的英语基础词汇及其用法,通常涉及日常生活、工作、学习等方面的词汇。
- 理解并运用基本的英语语法规则,包括时态、语态、直接和间接引语、条件句、虚拟语气等。
2. **阅读理解**:- 能够阅读并理解各种类型的英文材料,如新闻报道、散文、简短的评论文章等。
- 提高快速抓取文章大意、细节信息、作者观点和态度等能力。
- 分析和推断文章隐含的意义或信息。
3. **写作**:- 学会如何组织一篇逻辑清晰、结构合理的英语短文。
- 掌握基本的写作技巧,包括论点的提出、论据的支持、结论的总结等。
- 注意文章的一致性和连贯性,以及正确使用标点符号和段落划分。
4. **听力理解**:- 能够听懂英语新闻、讲座、日常对话等不同场景下的英语听力材料。
- 提高抓取关键信息、理解对话或讲话大意的能力。
- 练习根据听到的内容进行推理和判断。
5. **口语表达**:- 虽然自考学位英语可能不会严格测试口语能力,但提高口语表达能力对于全面掌握英语非常重要。
- 练习日常对话、表达个人观点和感受、进行简单的陈述或描述等。
准备自考学位英语时,建议广泛阅读英文材料,多听英语广播或观看英语视频,积极参与英语交流活动,同时可以通过做历年真题来熟悉考试形式和题型。
此外,合理安排复习计划,坚持每天学习,是成功的关键。

湖北省高等教育自学考试课程考试大纲课程名称:商务英语阅读课程代码:05439第一部分课程性质与目标一、课程性质与特点商务英语阅读课程是湖北省高等教育自学考试商务英语(专科)的一门专业基础课。
本课程以当代英语国家的原版教材、英语报纸、杂志和学术刊物中与经济和商务有关的文章为基础,材料内容涉及商贸英语的主要领域,如经济学、国际贸易、市场营销、企业管理、投资、证券、保险、广告等。
本课程是一门理论联系实际,应用性较强的课程。
二、课程目标与基本要求通过本课程的学习,学生既可学到地道的英语(包括大量的专业术语),又可以学到对外经济贸易知识,同时也能够掌握商务报刊文章的基本特点,提高阅读和分析能力,最终从整体上提高商贸英语语言水平以及语言欣赏和运用能力,达到商务英语专业专科生水平。
三、与本专业其他课程的关系商务英语阅读课程与商务英语口语、综合英语等课程同属于专业基础课,是商务英语写作、商务英语翻译、商务英语函电等课程的先修课程。
第二部分考核内容与考核目标第一单元财经一、学习目的与要求通过本单元学习,认知商贸英语文章的内在逻辑关系,帮助学生提高第 1 页阅读理解的能力,了解国际财经概况。
二、考核知识点与考核目标(一)课内训练(重点)识记:1. When Banker’s Bets Go Bad银行家的猜测落空名词解释:OCC: Office of the Comptroller of the Currency 通货监理局Alan Greenspan 艾伦·格林斯潘,美联储主席句子翻译:1)The bank had doubled profits in the past year viaa string of successful mergers, but on Apr. 21 itreported that its securities portfolio hadunrealized losses of nearly $131 million.2)We’re considering strategies that make the mostsense if rates are going up much more aggressivelyand sooner than anticipated.2. Creating Government Financing Programs for Small andMedium-sized Enterprises in China中国为中小型企业提供政府财政援助项目名词解释:Labor-intensive 劳动密集型SME: small and medium-sized enterprise 中小型企业SOE: state-owned enterprises 国有企业句子翻译:In China, as a result of the economic reforms and market opening measures, SMEs have enjoyed remarkabledevelopment and have grown to become an important forcein contributing towards sustained and rapid growth ofthe Chinese economic.(二)阅读技巧(次重点)应用:阅读的逻辑技巧(三)课外练习(一般)理解:1.Carlyle Group’s As ian Invasion加雷集团的亚洲扩张名词解释:Venture-capital 风险资本Carlyle Group 凯雷投资集团Citigroup 花旗集团2. Why the Dollar Is Blooming Again为什么美元再次复兴?名词解释:Greenback 美元(俚语)第 3 页Lehman Brothers Inc 雷曼兄弟公司European Central Bank 欧洲中央银行Federal Reserve Bank 美国联邦储备银行(四)拓展阅读(一般)理解:1. How Banks Pretty up the Profit Picture银行如何美化收益前景2. Thai Stocks What Goes Up泰国股市:到底是怎么了?3. Inventing to Order以市场为导向开发产品4. I t’s an Office Party in Hong Kong香港办公楼地价之争第二单元人力资源管理一、学习目的与要求通过本单元学习,掌握商务英语阅读中的快速阅读技巧,了解人力资源管理概况。

自考05439考核知识点《新编商务英语泛读2》Unit 1Definition of advertising,types of advertising,advertising media,considerations in choosing media.广告的定义、类型,广告媒体(媒介),对选择媒体的考虑。
Unit 2 The four functions of money;cashless ways of dealing with money.钱的四个功能,非现金处理钱的方式。
Unit 3 The five steps in entering business in China.在中国进入业务的五个步骤。
Unit 4 The reasons why Dell is so successful in China.戴尔在中国如此成功的原因。
Unit 5 Sources to investigate for information on employers;preparing the essential written materials,details about the resume and the cover letter.雇主的信息来源调查;准备必要的书面材料、详细的简历和求职信。
Unit 6 The definition of insurance,types of insurance.保险的定义,保险的类型。
Unit 7 The concepts behind consumers’actions;the 3 steps for the purchase process.基于消费者行为背后的概念;购买过程的3个步骤。
Unit 8 The personnel policy in management;the building up of Microsoft Co.人事政策管理;微软公司的建立。

英译汉1.Domestic business 国内商务国内商务2.economic 2.economic globalization 经济全球化球化3.host country 东道国东道国 intellectual4.property intellectual 4.property 知识产权知识产权5.non-tariff barriers 非关税壁垒非关税壁垒6.national product 国民产值国民产值7.per capita GDP人均国内生产总值8.Durable equipment耐用设备9.Staple goods大路货10.Creditor country债权国11.Customs union关税同盟12.Dual-Ministerial meetings 12.Dual-Ministerial meetings 双部长会议双部长会议13.European Commission 欧盟委员会anization of Petroleum Exporting Countries(OPEC)石油输出国组织 15.North American Free Trade Agreement(NAFTA)15.North American Free Trade Agreement(NAFTA)北美自由贸易协北美自由贸易协定16.Board of directors 董事会17.day to day running 日常管理18.the parent MNE 18.the parent MNE 多国公司目公司多国公司目公司19.national economic welfare 国家经济利益20.the legal jurisdiction 法律经管范围21.self-sufficient 21.self-sufficient 自给自足的自给自足的22.farm produce 农农品23.the endowments of nature 自然禀赋24.perfect competition 完全竞争25.output per many-year of labour人均年产量26.production capability 生产能力27.consumption preference 消费偏好28.cost advantage 成本优势rge-scale production大规模生产30.tariff barrier关税壁垒31.International Chamber of Commerce国际商会32.customs clearance结关33.EDI电子数据交换34.Incoterms国际贸易术语解释通则35.destination port目的港36.binding obligation有约束力的义务37.international trunk call国际长途38.the business line业务范围39.force majeure不可抗力40.cross-border contract进出口合同41.clearing system清算系统42.leverage杠杆作用43.trade credit account贸易信贷往来账户44.centrally planned economy中央计划经济45.financial status财务状况46.to open account开立账户47.Consignment transaction寄售交易48.a usance draft远期汇票49.documentary collection跟单托收50.impeccable documents正确无误单据51.correspondent bank往来行52.confirming bank保兑行53.transportation clause运输条款54.clean credit即期信用证55.deferred payment credit不可转让信用证56.freight prepaid运费预付57.prepare documents缮制单据58.consignor托运人59.consular invoice领事发票60.notify party被通知人61.contract carriers契约承运人62.intermediate product半成品63.ultimate consumers最终消费者64.natural product province产品自然领域65.time lag 时差66.claim on goods 对货物的索赔67.premium 保险费68.insurer 承保人69.insurable interest 可保利益70.settlement of a claim 理赔71.freight forwarder 货运代理行72.utmost good faith 最大诚信原则73.valued policies 有价保单74.exchange rate 买入价75.balance of payment 收支平衡76.direct quote 直接标价77.buying rate 买入价78.financial policies 金融政策79.financial policies 资金80.retained capital 预留资金81.grace period 优惠期82.a specialized mandate 特殊使命83.direct investment 直接投资84.tax holiday 免税期 85.greenfield strategy 绿地战略86.customer mobility 客户流动87.investment return 投资回报88.start from scratch 政府债券89.market maker 股票经营商90.standing committee 常务委员会91.underlying securities 基础证券92.global trade rules 世界贸易规则93.the reciprocal tariff concession list 互惠关税减让表94.a uniform tariff system 统一关税体系95.the non-discrimination principle 非歧视原则96.escape clause 豁免条款97.a new economic order 新经济秩序98.trade concession 贸易减让99.Special Drawing Rights 特别提款权100.maturity 100.maturity 到期日到期日101.certificate of deposit 101.certificate of deposit 大额大额102. cartel 102. cartel 卡特尔卡特尔汉译英1.1.国际商务国际商务international business2.2.无形贸易无形贸易invisible trade3.3.国内生产总值国内生产总值gross domestic products4.4.证券投资证券投资portfolio investment5.5.交钥匙工程交钥匙工程turnkey project6.6.国民生产总值国民生产总值Gross National product Gross National product((GNP GNP))7.7.收入分配收入分配income distribution8.经济合作与发展组织the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development9.9.基础储备基础储备infrastructure10.10.外汇储备外汇储备foreign currency reserves11.11.区域经济一体化区域经济一体化regional economic integration12.12.自由贸易区自由贸易区free trade area13.13.欧盟欧盟European Union14.14.亚太经合组织亚太经合组织Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation(APEC)16.16.部长理事会部长理事会Council of Ministers17.17.经济全球化经济全球化Economic Globalization 18.18.跨国企业跨国企业multinational economic environment19.19.生产设施生产设施manufacturing facilities20.20.自然资源分配自然资源分配the distribution of nature resources21.21.初级产品初级产品the primary commodities22.22.比较优势论比较优势论the theory of comparative advantage23.23.互利贸易互利贸易the mutual beneficial trade24.24.资源储备资源储备资源储备 the reserves of natural resources the reserves of natural resources25.25.技术创新技术创新technology innovation26.26.贸易方式贸易方式patterns of trade27.27.关税区关税区customs area28.28.自动出口限制自动出口限制voluntary export restraint29.29.名胜古迹名胜古迹places of historical interest30.30.贸易条款贸易条款trade terms31.31.修改信用证修改信用证amendment to the letter of credit32.32.集装箱运输集装箱运输container transport33.33.运费付至运费付至CPT34.34.报价报价quotation35.35.有效期有效期the validity period36.36.付款方式付款方式modeOf payment37.37.仲裁仲裁arbitration38.38.对销贸易对销贸易cunter trade39.39.实际头寸实际头寸net positions40.40.双边协议双边协议bilateral agreement41.41.易货贸易易货贸易barter42.42.垂直合并,纵向组合垂直合并,纵向组合vertical combination43.43.汇率浮动变化汇率浮动变化exchange rate fluctuation44.44.资信状况资信状况credit standing45.45.分期付款分期付款payment by installments46.46.即期汇票即期汇票sight draft47.47.付款交单付款交单document against payment document against payment((D/P D/P))48.48.商业信用证商业信用证commercial letter of credit49.49.开证行开证行the opening bank50.50.受益人受益人the beneficiary51.51.统一惯例统一惯例the uniform customs and practice52.52.循环信用证循环信用证revolving credit 53.53.保兑信用证保兑信用证confirmed credit54.54.远期信用证远期信用证usance credit55.55.票面价值票面价值face value56.56.资金周转资金周转capital turnover57.57.空运提单空运提单airway bill58.58.产地证书产地证书certificate of origin59.59.运输标记运输标记shipping marks60.60.装运港装运港port of shipment61.61.原始的生产方式原始的生产方式primitive mode of production62.62.竞争机制竞争机制competition system63.63.运输体系运输体系transportation system64.64.公共承运人公共承运人common carriers65.65.保证金保证金margin66.66.股票投资股票投资investment in stocks67.67.货物保险货物保险cargo insurance68.68.外汇储备外汇储备foreign exchange services69.69.共同基金共同基金the common pool70.70.代位追偿代位追偿subrogation71.71.近因原则近因原则the doctrine of proximate cause72.72.预约保单预约保单open policy73.73.平安险平安险F.P.A74.74.水渍险水渍险W.P.A75.75.金本位制金本位制gold standard76.76.平价平价par value77.77.布雷顿森会议布雷顿森会议the Bretton Woods Conference78.78.间接标价间接标价indirect quote79.79.储备货币储备货币reserve currency80.80.世界资本市场世界资本市场World capital market81.81.借贷成本借贷成本the cost of borrowing82.82.产权产权产权((股票股票))投资equity investment83.83.经济结构调整经济结构调整economic restructuring84.84.合资公司合资公司joint venture85.85.并购并购acquisition86.86.生物遗传学生物遗传学biogenetics87.87.自动出口限制自动出口限制Voluntary Export Restriction Voluntary Export Restriction((VER VER))88.88.证券交易所证券交易所the Stock Exchange Market 89.89.普通股普通股ordinary share90.90.补偿基金补偿基金compensation fund91.91.金边债券金边债券gilt92.92.期权期权option93.93.协商机制协商机制a consultative mechanism94.94.双边谈判双边谈判bilateral negotiation95.95.签约国签约国the signatory countries96.96.充分就业充分就业full employment97.97.多边贸易体制多边贸易体制multilateral trade system98.98.国际组织国际组织international organizations99.99.技术转让技术转让technology transfer100.100.商品协议商品协议commodity agreement101.101.国际货币体系国际货币体系international monetary system102.102.优惠关税优惠关税preferential preferential((customs customs))tariff103.103.承包生产承包生产Contract manufacturing104. tariff rates 关税率105. settlement 105. settlement 协议协议106.Shareholders 股东股东107.board of directors 董事会 108.parent company 母公司 109.affiliate 子公司 110.day-to-day running 日常管理 101.multinational corporation 跨国公司跨国公司102.home country 母公司所在国母公司所在国103.host country 东道国 术语解释1.affiliate MNC: a MNC which is associated or controlled by its parent MNC without losing its own identity.2.Absolute advantage: an advantage possessed by a country engaged in international trade when, using a given resource input, it is able to produce more output than other countries possessing the same resource input.3.Arbitration: the setting of a dispute by means of a neutral third party rather than by a court of law.4.A correspondent bank: a bank which acts 4.A correspondent bank: a bank which acts as an as an as an agent agent for another bank.5.All 5.All risks: risks: risks: extensive extensive extensive insurance coverage insurance coverage insurance coverage of cargo, of cargo, of cargo, including including coverage due to external causes such as fire, collision, pilferage etc., but usually excluding ”special” risk such as those resulting from acts of war, labor strikes and the perishing of good, and from internal damage due to faulty packaging, decay or loss of market.Buyback: an agreement by an export of plant and equipment to take back in the future part of the output produced by these goods as full or partial payment.Bill Bill of exchange: of exchange: of exchange: a a a signed signed signed document document document that that that orders orders orders a person a person a person or or or an an organization, such as a bank, to pay a fixed sum of money on demand or on a certain date to the person specified.Capital: the contribution to productive activity made by investment in physical capital and in human capital.Customs clearance: the formalities necessary to satisfy the customs officers before they will allow goods to the cleared from customs for dispatch or delay elsewhere.Banknotes circulation: movement of the printed paper money issued by a bank, usually the country’s central bank.Contract: a legally binding agreement made between two or more people.Clause: part of a legal document that deals with a particular item or condition in it.Confirmed credit: a letter of credit to which a number of other document such as shipping documents have been joined by the exporter to obtain payment from the bank.Commission: the amount paid to an agent, which may be an individual, a broker, or a financial institution, for consummating a transaction involving sale or purchase of assets or services.Commercial invoice: a document identifying numbers such as invoice number, date, shipping date, mode of transport, delivery and payment terms, and a complete listing and description of the goods or services being sold including prices, discounts and quantities.Common pool: a fund contributed by all insured parties in the name of premium against certain risk, outof which the claims if those suffering losses are paid.capital infrastructure: the basic physical requirements, without without which which which the the the industry industry industry cannot cannot cannot function effectively, function effectively, function effectively, water water and electricity installations, qualified and killed professionals in technology and administration.Capital market: markets where corporations and governments sell securities to investors in order to raise funds for long or short periods.Consumerism: considerable desire to make purchase for consumption.Distributor: a person who sends goods from those who produce them to them to those who use them.Documents against acceptance(D/A): documents are handed over to the importer upon his acceptance of the bill of exchange drawn by the importer upon his acceptance of the bill of exchange drawn by the exporter. Payment will be paid on a laterdate.Documentary credit: a letter of credit to which a number of other documents such as shipping documents have been joined by the exporter to obtain payment from the bank.Devaluation: the act of a government in reducing by law the exchange exchange value value value of of of its currency its currency its currency in in in units of units of units of gold gold gold or as or as or as compared compared with other currencies.Envisage: picture in the mind as a future possibility; imagine Economic of scale: the long-run reduction in average costs that occurs as the scale of the firm’s output is increased./the reduction in unit cost and increase in profit obtained when goods are produced in large quantities.EDI: an electronic system that sends specially-prepared document direct from the computer of one company to that of another, so avoiding delays and improving services to customers.Equity investment :a type of investment by buying the ordinary shares of a company.Exchange rate: the ratio between one currency unit and the number of number of units units units of another of another of another currency at currency at currency at which which which it it it is possible is possible is possible to to exchange the two at a given time.Economic integration: economic integration is a term used to describe how different aspects between economic are integrated. As economic integration increase, the barriers of trade between markets diminishes. The most integration economy today, between independent nations, is the European Union and its euro zone.FOB FOB: in foreign trade contracts, the seller’s delivers the : in foreign trade contracts, the seller’s delivers the goods on board the ship named by the buyer at the named port of of shipment. shipment. shipment. From From From that that that point, point, point, all all all charges charges charges and and and risks risks risks have have have to to to be be borne by the buyer.Fair trade: in international trade, the principle that maintains that there should only be free trade with those countries which themselves extend free trade.Full employment: an economic situation in which all persons physically and mentally capable of doing some kind of work, canfind employment.Gold reserves: the stock of gold coin and bullion held by a note-issuing bank in country on the gold standard. GNP : refers refers to to the market market value value of goods and services produced by by the the property property and and and labor owned by labor owned by labor owned by the the the residents residents residents of of of an economy an economy GDP : refers to the market value of all goods and services produced within the geographic area of an economy.Host country: in international trade, the country in which a multinational corporation is active, but which is not the home country of that corporation.Hyperinflation: an extreme form of inflation; the situation that exists in a Economy when the money supply is being increased very rapidly, resulting in an increase of over 20%in the annual growth of the money supply or of the price level. Infrastructure: large-scale public services, such as water and power supplies, road, rail and radio communication,etc. needed to support economic activity, esp. industry, trade and commerce.Integration: combine into a whole.Inflation: a general rise in prices within an economy, accompanied by a reduction of the value of money.International trade: the exchange of goods and services between countries through exports and imports.Irrevocable credit: a letter of credit to which the paying bank has added its guarantee that payment will be made against presentation of certain documents.Intermediate products: goods that enter into the production of other goods. In the manufacturing process, goods and materials pass through various states of production, frequently requiring transfer from one plant to another or sale by one firm to another.Indemnity: a basic idea in all branches of insurance that the insured should be in the same position after a loss as he as be was before it, i.e. neither richer nor poorer as a result of loss.Intellectual property: certain non-tangible assets held,principally covering the areas of patent protection,registered trade marks and designs, and copy right.Joint venture: a commercial undertaking by two or more people,differing from a partnership in that it relates to thedisposition of a single lot of goods or the termination of aspecific project.just-in-time inventory: making or ordering only just enoughparts or materials for the factory’s immediat immediate e needs, soavoiding the expense of keeping stocks.Liberalize: of trade, the act of government in lifting controlover import and exports.Letter of credit: A written instruction by a bank or some otherfinancial institution. To its agent or another bank, eitherlocal local or or or aboard, to aboard, to aboard, to lend lend lend the bearer the bearer the bearer of of of the letter certain sums the letter certain sumsof money for a fixed period of time.Loan: a commercial transaction between two legal entitieswhereby one party, known as lender agrees to put at the disposalof another known as a borrower certain property, usually money ,for its temporary use, with am understanding by both partiesthat the property will be returned. Money circulation: money in the hands of the public and beingused to pa for goods and services.Most-favored nation Most-favored nation clause: clause: clause: an an an understanding principle understanding principle understanding principle of the of theWTO whereby each country undertakes to apply the same rate oftariff to all its trade partners.Negotiable transport document: transport document can betransferred from one person to another by endorsement.Non-tariff barriers: all public regulations and governmentpractices that introduce unequal treatment for domestic andforeign goods of the same or similar production.North American free trade agreement(NAFTA 北美自由贸易协定):NAFTA is a trade agreement between Canada, Mexico, theunited states, which entered into force on january1,1994. Itwas preceded in 1988 by a trade agreement covering Canada andthe U.S.U.S.——the Canada –U.S. free trade agreement, which servedas a negotiating framework for the expanded agreement.Option: a contractual agreement between a buyer and a sellerto buy or sell a particular security commodity or currency ata specific price within a pre-determined period of time.Partnership: a contractual Partnership: a contractual relationship relationship relationship undertaking by undertaking by undertaking by two or two ormore people, differing from a partnership in that it relatesto to the the disposition of disposition of a a a single single single lot lot lot of of of goods or the termination goods or the terminationof a specific project.PPP: purchasing power parity.Protectionism: the deliberate use or encouragement ofrestrictions on imports to enable relatively inefficientdomestic producers to compete successfully with foreignproducers.Productivity: the relation between the output or amountproduced in a given period and one unit of the factors ofproduction employed in producing that output.Preferential customs tariff: a lower (or zero) tariff on aproduct from one country than is applied to imports from mostcountries. This violation of the MFN principle is permitted inspecial cases.Per capita income : It is calculated by dividing its nationalincome by its populationQuota: a Quota: a limit limit limit placed by placed by placed by a a a government government government on the on the on the amount amount amount of imports of importsor commodity.Revenue: the money received by a firm from selling its outputof goods or services or money earned by government fromtaxation.Reserves: in a business, amount set aside from profits to meetcontingencies or for future investment.Specialization Specialization: : to restrict one’s economic activities tocertain particular field.Subrogation: the legal right of an insurer to receive any moneyobtained by the insured as a result of his making use of hisrights against third parties; this reduces the cost of the lossto the insurer and prevents the insured from obtaining more thanhis full indemnity.Stock exchange: a markets where stocks and shares are boughtand sold under fixed rules, but at princes controlled by supplyand demand.Settlement: a payment of money claimed.Tariff Tariff: a form of tax that occurs as the scale of the firm’s : a form of tax that occurs as the scale of the firm’soutput is increased./the reduction in unit cost and increasein profit obtained when goods are produced in large quantities.Terms of payment: the terms agree upon between a sellers anda buyer regarding a transaction with respect to the mode andtime-table of payment.Trade fair: a big exhibition where manufactures and sellers anda similar or related products display their goods, meetcustomers and each other.Transfer Transfer of technology: of technology: of technology: a a a complicated complicated complicated aspect of international aspect of internationalbusiness. Technology can be divided into two types: non-tacitand tacit. It can be transferred through various modes, eitherexport of products and goods or though service. The mostimportant feature of technology transfer is it is a transferof the right to use, not the right to ownership.Terms of trade: a measure of the trading success of a countryby comparing the prices of its imports with the prices of its exports.Triad and Quad : A . United StatesB. Western EuropeC. JapanD. CanadaW.P.A: a wider coverage than the F.P.A. partial loss of ordamage to damage to the insured goods the insured goods the insured goods is is is excluded only excluded only excluded only where where where the loss the loss the loss to tothe insurer and prevents the insured from obtaining more thanhis full indemnity.简答1.Major difference between international business anddomestic business: A . differences in legal system; B.differences in currencies;C . differences in culturalbackground; D . differences in natural and economic conditions.2.Major types of international business: A. tradea. Commodity tradeb. Service tradeB. investmenta. foreign direct investmentb. portfolio investmentC. other typesa. licensing and franchisingb. management contract and contract manufacturingc. turnkey project and BOT3.Explain the concepts of GNP and GDP respectively and point out their major difference. Can we use them interchangeably? GNP refers to the market value of goods and services produced by the property and labor owned by the residents of an economy. GDP measure the market value of all goods and services produced within the geographic area of an economy. The difference between between GNP GNP GNP and and and GDP GDP GDP is that is that is that the the the former former former focuses om ownership focuses om ownership focuses om ownership of of the factors of production while the latter concentrates on the place where production while the latter concentrates on the place where production takes place. We can use them interchangeably.4. what is the free trade area? And what is Customs union? In what way is a customs union different from a free trade area. Free trade area is the first trade area is the first and loosest and loosest and loosest form of regional form of regional economic integration. Members of a free trade area area removes barriers to the flow of goods and services among themselves while each member still adopts its own policy as regards to trade with outsiders. Custom Union is the second form of regional economic integration that goes a step farther by adopting the same trade policy for all the members toward countries outsides their organization in addition to abolishing trade barriers among themselves . Since imports from other other countries countries are subject subject to to the same tariff no matter matter which which member they export export to, to, it is impossible for non-members to get into the market of the customs union in a detour as they possibly do in the case of trade with a free trade area.5. Describe briefly the characteristics of MNEs.①they are usually enormous in size in terms of the amount of annual sales and of resources it controls.②they have a wide geographical spread, and ②they have a wide geographical spread, and seek to set up an seek to set up an integrated production and distribution network in the world. ③MNEs enjoy longevity and rapid growth. They have a long development history and rapid growth record.6. how are MNEs usually usually operated? operated? operated? And And how are important decision made?①the operation ofMNES is under the control of parent MNE at their home countries. ②the affiliate MNEs also have their own decisionmaking mechanism, however the major decision, such as those on corporate goals, new investment and their location are made by parent MNEs.8. Which theory makes more sense, absolute absolute advantage advantage advantage or or comparative advantage. Comparative advantage sound more plausible .As it is very difficult to find for a country a product with absolute advantage, and also, a country still gains from trade for its products with comparative advantages.9. What are the important factors that one has to take into account when talking about the possibility of international specialization?Whether the internationalization will happen or not is decided by trade patterns, economic of scale, innovation.The production capacity and conditions decide what a country can produce and trade, the economies of scale decides if a country has a cost advantage for the traded product, and the innovation decides if the traded product is competitive in the foreign market.10. Why is it necessary to have Incoterms? And what is the purpose of making amendments and additions to Incoterms? The purpose of Incoterms is to provide a set of international rules for the interpretation of the most commonly used trade term in foreign trade, thus, the uncertainties of different interpretation of such terms in different countries can be avoided or at least reduced to a considerable degree.And the purpose of making amendments and additions is in orderto bring the rules in line with current international trade practices.11. What contents should be included in a firm offer?A firm offer s a promise to sell goods at a stated price. The major terms include time of shipment, made of payment, description of goods and validity period.12.Give the major item of the contract proper.This includes four major parts: the full name and address of the buyer and seller; the description of the commodities; the terms and conditions for the transaction; indication of the number of original copies of the contract and other additional terms.13. Please Please define define define counter counter counter trade. trade. trade. What What are the possible reasons for its attraction. An umbrella term for several sorts of trade in which the seller is required to accept goods or other instruments or trade, in partial or whole payment for its products. Counter trade transactions include barter, buyback, or compensation, compensation, offset offset requirements, and clearing agreements. Counter trade is allegedly popular in less development countries and in planned economies, it attracted much interest in the past. Now as the landscape od landscape od economic system economic system economic system drastically drastically drastically changed changed changed recently, recently, recently, it it attracts much more attention.14.What is the difference between a clean draft anda documentary draft?For a clean draft, it is a draft without attached additional documents; for a documentary draft, it is a draft supported supported by by title documents, such as an invoice, bill of lading or insurance policy. In fact everything having a real commercial value is know as a documentary draft.15.How dose L/C offer security to the buyer and the seller? ①it enable exporters obtain, through a correspondent bank,duarantees that the invoice for goods sent by them will actually be paid by the buyer actually be paid by the buyer——the importer.②it also provides the buyer with a guarantee that goods will be received in good order, for L/Cs are subject to appropriate。

WTO(世界贸易组织)一, 选择1, 1947年4月至8月,美国, 英国, 法国, 中国等23个国家在日内瓦召开了第二次筹委会会议。
就详细产品的关税减让进行了谈判。
2, 1947年11月至1948年3月,在哈瓦那实行的联合国贸易和就业会议,审议并通过了《国际贸易组织宪章》,又称《哈瓦那宪章》3, 1947年11月15日签署了关税与贸易总协定《临时适用议定书》,同意从1948年1月1日起实施关税与贸易总协定的条款。
4, 关税与贸易总协定从1948年1月1日开始实施,到1995年1月1日世界贸易组织正式运行,共存续了47年。
截止1994年底,关税与贸易总协定共有128个缔约方。
5, 1947年4月至10月,关税与贸易总协定第一轮多边贸易谈判在瑞士日内瓦实行。
下调关税的承诺是第一轮多边贸易谈判的主要成果。
6, 第五轮1960年9月至1962年7月,共有45个参与方,后称为“狄龙回合”。
前一阶段从1960年9月至12月,着重就欧洲共同体建立所引出的关税同盟等问题,与有关缔方进行谈判。
7, 第六轮1964年5月至1967年6月,共有54个缔约方参与,又称“肯尼迪回合”。
这次谈判首次涉及非关税壁垒。
这轮谈判还汲取波兰参与,开创了“中央支配经济国家”参与关税与贸易总协定的先例8, 第七轮又称“东京回合”。
历时5年多,取得的主要成果:⑴开始实行按既定公式削减关税,关税越高减让幅度越大⑵产生了只对签字方生效的一系列非关税措施协议⑶通过了对发展中缔约方的授权条款,允许发达缔约方赐予发展中缔约方普遍优惠制待遇。
9, 第八轮又称“乌拉圭回合”,从1986年9月到1994年4月,共历时8年。
10, 在启动“乌拉圭回合”的部长宣言中,明确了这轮谈判的主要目标:一是通过削减或取消关税, 数量限制和其他非关税措施,改善市场准入条件,进一步扩大世界贸易;二是完善多边贸易体制,将更大范围的世界贸易置于统一的, 有效的多边规则之下;三是强化多边贸易体制对国际经济环境变化的适应实力;四是促进国际合作,增加关税与贸易总协定同有关国际组织的联系,加强贸易政策和其他经济政策之间的协调。

1、国际贸易一般指不同国家的当事人进行的交易,它涉及到许多因素,因而此国内贸易要复杂得多。
International business refers to transaction between parties from different countries. It involves more factors and thus is morecomplicated than, domestic business.2、有形贸易是指将在一国生产或制造的商品,出口或进口到另一国消费或转售。
Visible trade refers to exporting and importing goods produced or manufactured in one country for consumption or resale in an-other.3、外国直接投资,简称FDI。
投资者通过控制其投资在他国的企业和资产获得回报。
Foreign direct investments of FDI for short is made for returns through controlling the enterprises or assets invested in a host country.4、国民生产总值指一个经济体凭借其居民拥有的资产和劳动力所生产的货物和服务的市场价值。
GNP refers to the market value of goods and services produced by the property and labor owned by the residents of an economy.5、日本和中国是重要贸易伙伴,两国经济互补,又是一衣带水的近邻。
中日贸易关系对两国都有重要的意义。
With mutually complementary economy, Japanand China are major trade partners, and the two countries are close neighbours separated only by a strip of water. Sino-Japanese relationsare therefore of great importance to both countries.6、加拿大和美国有很长的共同边境,而且大部分加拿大居民居住在边境地区。
本文部分内容来自网络整理,本司不为其真实性负责,如有异议或侵权请及时联系,本司将立即删除!== 本文为word格式,下载后可方便编辑和修改! ==自考英语二复习重点为帮助大家复习英语二,那么,下面是小编给大家整理收集的自考英语二复习重点,供大家阅读参考。
自考英语二复习重点:No.1名词复数的规则变化一般情况加词尾 -s,如 book / books, desk / desks等。
其读音规则是在清辅音后读[s],在元音和浊辅音后读[z]。
以 s, x, z, sh, ch 等结尾的名词,通常加词尾 -es:bus / buses, box / boxes, dish / dishes等。
以y 结尾的名词,其复数构成要分两种情况:以“辅音字母+y”结尾的名词,将 y 改为 ies;以“元音字母+y”结尾的名词,直接加词尾-s:city / cities, toy / toys, holiday / holidays 等。
No.2复数规则变化的几点说明以 ch 结尾的名词变复数时加词尾-es,指的是 ch 读音为[tF]时;若ch的读音为[k],则其复数应加词尾-s,如 stomach[tstQmEk]是 stomachs,而不是 stomaches。
以y结尾的专有名词,直接加词尾s变复数。
以 o 结尾的名词,有些加词尾 -s,有些加-es,但在中学英语范围内,以o结尾的名词变复数加词尾-es 的主要有以下4个:tomato(西红柿),potato(土豆),hero(英雄),Negro(黑人)。
注:有些以o 结尾的名词在变复数时加-s或-es均可,如zero /zero(e)s(零)等。
以 f 或 fe 结尾的名词,也有两种可能:即有些直接加词尾-s,有些则把f / fe 改为 ves:roof / roofs(屋顶),knife / knives(小刀)等。
但在中学英语范围内,要改 f / fe 为 ves 的只有以下10个词(它们都是日常生活中的常用词):wife(妻子),life(生命),knife(小刀),leaf(树叶),thief(贼),half(一半),self(自己),shelf(架子),loaf(面包),wolf(狼)。
2017年1月广东省高等教育自学考试商务英语阅读试题(课程代码 05439)I. Translate the following words or phrases into Chinese (10%)1. fiscal year2. mortgage bond3. cover letter4. job opening5. price discrimination6. modes of conduct7. legal tender 8. consumer preferences9. inflation 10. discount couponⅡ. Translate the following words or phrases Into English (10%)11.控股公司 12.账面利润 13.上市公司14.商业银行 15.流动资金 16.国有银行17.资金注入 18.货币贬值 19.提货单 20. 运营费用Ⅲ. Choose the best answer to fill in the blanks (10%)21. A______ is a letter tailored to a specific company explaining why you are the best candidate for a particular job.A. reference letterB. recommendation letterC. self-introduction letterD. cover letter22. If competitors get together to raise or lower prices, this act is_________.A. price discriminationB. deceptive pricingC. resale price maintenanceD. price fixing23. A (n) _________ is an accounting statement that shows a firm’s status on the last day of an accounting period.A. income statementB. net income sheetC. balance sheetD. income sheet24. On a loan that is legal, the courts will allow a lender to collect only his principal when_____.A. there is no fixed interest rateB. the interest rate is very lowC. the borrower can’t pay the interestD. the lender demands an interest more than the state law allows25. The insurance companies base their costs on _________.A. the pool of people sharing the riskB. the cost each member of the pool paysC. the theory of probabilityD. past experience26. Owners of_________ have rights to vote for directors at the annual meeting of the corporation and to share any profits or losses.A. preferred stocksB. deferred stocksC. stock certificatesD. common stocks27. _________is reached when the money from the sales of a product equals the total costs and expenses involved in producing and marketing it.A. The selling pointB. The ultimate pointC. The break-even pointD. The final goal28. Now more and more women go shopping with an incomplete shopping list or without list at all. It is mainly because _________.A. it is troublesome to make a complete shopping listB. there are too many kinds of merchandise for them to choose fromC. merchandise is usually displayed on open shelves, which will remind them of the items theywant to buyD. without a shopping list, they are free to buy whatever they want to buy29. When one buys a fund, the most important thing for him to do is_________.A. to read the fund’s prospectus carefullyB. to fill out some formsC. to pay a sales commission called “load”D. to match his personal objective with that of the fund30. For a company, the strength of publicity is _________.A. being flexibleB. reaching a larger number of audiencesC. avoiding media costsD. saving preparation timePart Ⅱ. Reading ComprehensionIV. In this part, there are some reading passages followed by 15 questions or unfinished statements. For each of them there are four answers marked A, B, C and D. You should decide on the best one according to your understanding (30%)Passage 1Parker Pen’s Globalization StrategyWhen Parker Pen Company decided to launch a global marketing strategy 20 years ago, some observers were puzzled. Although Parker’s name was well-known, the Wisconsin-based company brought limited resources to the task. Annual sales of Parker writing instruments had never exceeded $225 million, and the company had never budgeted more than $20 million a year for advertising. Still, Parker’s high-quality products were sold in 154 countries, and its marketingexecutives were eager to design and implement a global strategy for Parker Pen. In their view, cultural and competitive similarities would be more important than differences, meaning that the same product could be sold the same way in many different markets, and with much lower marketing costs. They believed, in short, that Parker Pen would provide a classic test of global marketing theory.Parker’s then president, James Peterson, also believed that global marketing would be crucial to the survival of the faltering company. The company’s weaknesses had been obscured for years by strong overseas sales and a weak U. S. dollar. At home, not only were competitors introducing mass-marketed, disposal pens, but even as Parker attempted to guard its reputation for quality, the company was losing its share of the domestic expensive-pen market to A. T. Cross Company and Sheaffer Eaton. Furthermore, Parker’s manufacturing process was inefficient. New-product development had been neglected, and advertising worldwide, which had been left to local marketers, was handled by more than forty different agencies. Profits were plunging, and most of the profits were generated by Manpower Temporary Services, a subsidiary of Parker Pen.Peterson’s first move was to streamline Parker’s operations by cutting the payroll by half, reducing the product line from 500 different writing instruments to 100, and spending $20 million to upgrade Parker’s manufacturing facilities. Then Peterson and his marketing team embarked on a two-pronged program with far-reaching consequences. They began production of cheap pens that could compete in the under- $3 market, and they standardized everything associated with Parker products under a “global umbrella”. From then on, all packaging and point-of-sale display materials would use the same striking block motif. The advertising budget would be centralized, and one advertising agency would handle accounts worldwide. A single theme-“Make your mark with a Parker”-would be used for all products and in all markets, and advertisements would feature the same graphics, photography, and typefaces; only the languages of the copy would vary. In addition, advertising would spotlight Parker’s new, inexpensive products instead of the quality pens that were the company’s trademark.These two decisions-to produce cheap pens and to use a uniform marketing strategy for all Parker products-were eventually considered major blunders by many inside Parker Pen. Long-time Parker Pen employees objected that the lower-quality pens ran counter to Parker’s carefully nurtured status image. Parker’s European manager argued that advertising should take into account the differences among markets.However, Parker’s new management insisted that the company’s future lay in high-tech. High-volume production of cheap pens for a global market, and implementation of new strategy proceeded. At first, sales of the new roller-ball pen and other writing instruments increased. Then, just as demand was picking up, the automated production line began to shut down repeatedly. Parker employees were forced to return to the assembly lines to take over for the malfunctioningsystems. The defect rate soared, and before the problems were resolved, the marketing division set aside strategies and forecasts and sold whatever products were available.A few months later, the global advertising campaign was launched. In accordance with the “one product, one market” policy, advertisements for different markets had identical layout, illustrations, and text; only the languages in which they were written were different. Because the theme was so general, the advertisements appealed to no one in particular, especially not to those buyers who viewed writing instruments as status symbols. Resentment against the global marketing strategy mounted within the company, and when the failure of the advertising campaign could no longer be ignored, Peterson resigned, followed by his hand-picked marketing executives. The pen business suffered a $500,000 loss and was purchased in 1986 by a group of Parker’s international managers and a British venture capital company.Now based in Newhaven, England, Parker Pen Ltd. is a profitable company, with 2000 pretax profits of 8 million. Although the reorganized firm used the now-functioning Wisconsin plant and owes some of its success to the greater operating efficiency the former management brought about, the new owners have instituted several policies of their own. Parker’s inexpensive pens receive less emphasis in advertising, and plans to produce disposable pens were dropped. The company is working to restore its reputation for quality and reliability. It intends to add perceived value, rather than volume, to its products. In addition, except for the marketing of the company’s Duofold Centennial model, a $312 18-carat goldnib fountain pen targeted to a tiny market segment, global advertising has been abandoned.31. Before the practice of its global marketing strategy, Parker Pen Company _________.A. was an international company with an increasingly large market shareB. had not been doing well and was at a critical momentC. had been eager to push up sales in the international marketD. enjoyed satisfactory sale performances and was ready for the new move32. What problem did Peterson fail to address in his two moves?A. Inadequate manufacturing facilitiesB. Specialized product rangeC. Employment of various advertising agenciesD. Neglect of quality product development33. Parker Pen’s top management insisted on producing lower-quality pens because________.A. they found quality pens did not sell as cheap onesB. they believed cheap pens would be more popular in the global marketC. they deemed quality pens responsible for the company’s declining market shareD. they found it more profitable to produce cheap pens34. We can learn from the passage that the global advertising campaign ________.A. was a moderate successB. was a total failureC. met with strong resistance from the company’s long-time employeesD. resulted in the company’s mergence with an American business35. Which of the following can NOT account for Peterson’s decision?A. He and his management were confident of the success of their new strategy.B. He intended to adopt a new strategy to help the company to prosper.C. He was eager to help the company to break free from its troubles.D. He failed to take timing into consideration.Passage 2Famous AmosToday, most of us recognize Wally “Famous”Amos, the man who gave his name to the original gourmet cookie. The company founded by Amos has achieved nationwide distribution of several flavors of its cookies in stores and has scattered retail stores world-wide, with franchises in Japan, Australia, and Canada, as well as the United States.In 1988, Wally Amos was just another talent agent trying to succeed in Hollywood. However, he soon developed another calling. Friends told him that the cookies he made were so good that he should sell them, and eventually Amos took their advice. Some of these friends backed up their advice by investing $25,000 in his venture, the Famous Amos Chocolate Chip Cookie Company, and the world’s first gourmet cookie shop opened in 1988. It was an instant success.News of Famous Amos spread by word of mouth, and in a classic example of great demand, consumers would walk into stores and ask the owners why they did not stock Famous Amos cookies. The company relied solely on this informal sort of marketing for its first five years.When Amos started his company, he had made no plans for such growth. His first retail “hot bake” shop appeared to be earning a profit and, after all, in his words, “All I wanted to do was make a living.” Consumer demand grew and requests began to pour in from other areas, but Amos did not have the funds to expand his cookie shop concept into a chain. He also wanted to avoid the risk of expanding through borrowing funds. Then the idea struck him just as it had McDonald’s Ray Kroc 30 years earlier: franchising. The firm distributed its frozen dough directly to the franchised “hot bake” shops located in suburban shopping centers and downtown walk-in locations.Amos also used other distribution alternatives to set the cookies into supermarkets, convenience outlets, “mom-and-pop”stores, and gift shops that make up the Famous Amos market, by contracting with an independent wholesale distributor. This distribution channel saved the company the cost of starting its own network, while giving it access to an already established distribution system, without which the young company might have failed. Even though many storeowners were unhappy about doing business with products offering such a low markup, consumer demand was so strong that retailer complaints soon fell to a trickle and distribution became more widespread.Famous Amos tailored its cookies to its markets. Frozen dough was shipped directly to the firm’s franchised “hot bake” shops. For supermarkets, it offered several different sizes of cookies, and set up racks for the packages in the fresh baked goods section, rather than on the cookie shelf. For convenience stores, one-and-two-ounce bags were created to save and to encourage impulse sales. It now makes several flavors of cookies (oatmeal-based cookies are the nation’s best sellers).Demand was created in part by the cookie’s taste. The gourmet cookie shop concept was entirely novel, and to outlast the novelty, Famous Amos cookies had to be good. But while consumers like the taste of the cookies (a recent Consumer Report’s test rated famous Amos’s chocolate chip cookies one of the best-tasting brands available), much of the success of FamousAmos is based on effective person marketing. Wally Amos’s winning grin gleams from each package of Famous Amos cookies, and his presence seems to give the cookies an identity that its competitors lack.John Rosica, a public relations executive with the company, called Wally “a perpetual promotion”. In recognition of his role in the company’s success, the Smithsonian’s collection of Advertising History includes his Panama hat and brightly patterned Indian gauze shirt.By the late I 990s, interest in the gourmet cookie had waned so that only a few locations could support bake shops devoted exclusively to cookies. Famous Amos decided to change its placement from gourmet cookie to high-quality family cookie. Package sizes were changed from 21/2-, 7-, and 16- ounce packages to 12-ounce size for wholesale distribution to grocery store outlets and a 30-ounce size for food-club stores. A 2-ounce package was also developed to be sold through vending machines. As of 2002, there were only a few bake shop franchises operating 15 stores, and Famous Amos was restricting itself to making finished cookies.Even though Amos sold his ownership interest in the firm in 1998, Famous Amos continued to rely solely on promotions that feature Wally. Among the most successful promotions have been its efforts at cause marketing. The company worked in conjunction with literacy councils in several American cities, having stores contribute a percentage of profits to literacy programs. Such promotions resulted in greatly increased sales, including a 38 percent sales jump in Philadelphia.36. Wally Amos is __________.A. the man who once a successful figure in HollywoodB. the man who originated the idea of gourmet cookieC. the man who had a cookie store in the United StatesD. the man who originated the idea of franchise operation37. Initially, Wally Amos started his business__________.A. to satisfy his interest in baking cookiesB. to build a chain of cookie shops eventuallyC. to help him make a livingD. to become a famous businessman38. Which of the following is NOT one of the reasons why Wally Amos’s company succeeds?A. Wide channels of distribution of its cookies.B. Adaptation of its cookies to different markets.C. Uniform taste of its cookies sold at all its outlets.D. Effective person marketing.39. In the development of the company, Wally Amos’s most important role is __________.A. using his image to promote the company’s cookiesB. using his influence to open more channels of distributionC. using his relationship to get more government fundsD. using his experience to develop different tastes of cookies40. What remained the same after Wally Amos sold his ownership interest in the company?A. Its management staff.B. Its line of product.C. Its sales volume.D. Its promotion methods.Passage 3As a manager in the service industry sector, I’ve looked at hundreds of CVs in my time. They are not necessarily the bland documents some bosses might think they are! They are full of little pointers towards individuals personalities and suitability for the job. The first thing I always look at is an applicant’s employment record. I check for continuity and stability. If somebody has a long list of previous jobs, all of varying length, alarm bells start ringing. Rather than an irregular route from job to job, what I hope to see is stable career progression. What does their career path look like-is it all steps forward, or are there a lot of sideways moves? And I am always pleased to find a family person with children, because in my experience they tend to be responsible and reliable.I never rely on CVs alone. We get applicants to fill in one of our own application forms. We ask why they’ve applied, what their aspirations and personal goals are, and also about their interests and hobbies and any clubs they belong to. That gives you a useful insight into their personality and lifestyle. The application form also enables us to test how much people have actually been progressing in their careers, because we ask for details of the salaries they have received for each job.It’s always worth looking at CVs and designing application forms with great care. Taking on employees might be rewarding, but it is also a big investment for any business. Mistakes in choosing staff can cost companies dear, so it makes sense to spend time ensuring you get the right person.In the service sector, one of the aims of companies is to maintain and improve customer service, and this is achieved partly through low staff turnover. You need to take on people who understand that, and will want to stay. That’s why, when you’ve taken staff on, the next thing is getting the best out of them.My management style comes from the days when I took over my first business, an ailing road haulage firm which I was certain I could turn into a profitable company. The first thing is to treat others as you’d like to be treated yourself. As soon as I took over the business, I talked to everybody individually, and looked for ways to make sure their particular skills benefited the company.I didn’t have much experience then of managing people, but above all I always tried to be fair and honest with everyone. As a result, I think the staff knew that and accepted my decisions, even if they didn’t agree with them all. Also, bosses must be able to communicate. You also need to create team spirit, and build on the strength of the team. I explained my plans for the company to all the staff, and let them all know what I needed from them. The lorry drivers responded brilliantly, and were the key to turning the business round. They understood that we had to develop a professional reputation, and from then on the days of poor quality deliveries were over.Lastly, I am a great believer in profit-sharing. It takes a team to make a company work, so profits should be shared by all. Job satisfaction is important, but it doesn’t pay the rent. Shared profit and bonuses help to strengthen team spirit by giving everyone a common goal that they work towards together.41. What fact does the writer hope to learn from applicants CVs?A. Whether they have experience of many different jobs.B. Whether their careers have developed steadily.C. The opinion their employers had of them.D. Whether they are married or single.42. The writer says the application form is useful because it________.A. reveals something of the applicant’s characterB. gives information about the applicant’s familyC. explains what skills the applicant has for the jobD. shows how much the applicant wants to earn43. According to the writer, why are CVs and application forms so important?A. Interviewing people is an expensive process.B. They indicate whether applicants really want the job.C. They indicate whether applicants are efficient or not.D. Employing the wrong people can be disastrous.44. One reason why the writer was successful in her first business was that ______.A. she was used to dealing with peopleB. she was open with the staffC. the business was already doing well when she startedD. the staff agreed with all her decisions45. Which would make the best title for this text?A. Profit-sharing as MotivationB. How I Turned a Business RoundC. People-the Key to Business SuccessD. The Importance of a Well-presented CVV. Read the following passages and finish the exercises of each one (40%):Passage 4The economic phenomena of the Barbie doll helped explain the reason why an increasing number of Chinese enterprises purchase well-known brands overseas. Like the recent case of a Chinese enterprise purchasing the Volvo.The viewpoint held by Taodong, economist from UBS, is frequently borrowed by Chinese government officials and enterprises. Tao claimed that the price of a plastic Barbie doll is $20, from which Chinese manufacturers could only gain 35 cents. The lesson we could learn from this case is that it is brand that can bring profits, not “working” for overseas enterprises.The large-scale overseas M&A of China are mostly carried out by state-owned business, and their main targets are mine and oil fields, by which the raw materials of the fast-developing economy of China could be assured. On the other hand, a trend has began several years before-in hope of catching up with international competition, the ambitious private-run businesses are busy purchasing overseas brands. However, analysts indicated that this fast- developing trend would probably -lead to the overseas rebound. Moreover, because those requiring enterprises lack experience of international M&A, it would cost an arm and a leg.“Many Chinese enterprises have ranked in the list of Fortune 500, and they wish to continue improving their fame world-wide.” He Yuxin, an analyst of Long Zhou Jing Financial Research and Consulting Institution said.For the past 10 years, China has been encouraging its enterprises to “go global fearlessly”and to realize the Economic Diversification. The statistics data given by Chinese CommerceDepartment showed that from 2007 to 2008, Chinese investments abroad had more than doubled, reaching 55.9 million dollars.The tide of merging in China reminds people of Japan in the 1980s. At that time, the Japanese’s purchase of “Pebble Beach” Golf Course in California and Rockefeller Center in NY stirred up American’s unrest-they feared that Japan would rule the world.Similar resist also impediment some large-scaled M&A deals. Disputes exist about whether China will commit the same mistake as Japan. Huo Jianguo, dean of the College of International Trade and Economic Coorporation of Chinese Commerce Department, said that Chinese government would continue objecting strongly to M&A deals in sensitive industries such as oil enterprises. “However,” he said, “if the project is based on mutual reciprocity and profits, and meantime drives local employments and tax income, it will surely be accepted and promoted.”Cash-starved enterprises give warm welcome to Chinese investers and mergering proposals. General Motors lapped at selling its Hummer to Teng Zhong Industry Coorporation in Sichuan province, China. Chinese government, however, rejected the deal.A. Mark the following statements true (T) or false (F) according to the passage.(10%)46. An increasing number of Chinese enterprises purchase well-known brands overseas in orderto develop domestic brand.47. Several overseas companies have already been successfully acquired by Chinese state-ownedenterprises.48. Chinese enterprises can offer lower prices in international acquisition.49. Japanese companies used to be very active in international acquisition during the 1980s.50. Chinese government is cautious towards international acquisition.Passage 5A report by Boston Consulting Group (B CC) says China represents the second largest market in Asia excluding Japan, with about US $1. 44 trillion in assets being managed for wealthy individuals defined as those whose annual income is above US $100, 000.BCG’s survey of retail banks reveals that the average private banking customer can be 10 times more profitable than an average mass market retail customer, a statistic that explains why banks are paying increasing attention to the wealthy.(56) Facing the emerging wealth management market, Chinese banks have made impressive headway in the creation of new wealth management products and services. There are now more than 20 kinds of wealth management products on offer at the state-owned big four banks and national joint-stock banks. The China Everbright Bank’s November 2005 financial report shows a 20 billion yuan (US $2.5 billion) wealth management revenue, up 50 per cent over last year.Chinese banks, especially the State-owned big four, have inherent advantages in wealth management. (57) They have a large customer base and an extensive service network that offers customers accessibility and convenience. Managers at the big banks also tend to have a good relationship with local customers.However, analysts believe that, although the level of personal assets held in financial institutions in China is significant, wealth management products and services offered by Chinese banks are still relatively unsophisticated.Deng Junhao, vice president and director of BCG points out that China’s typical wealth management offering as more “hardware” than “software”.(58) Key issues that continue to stymie domestic banks’ progress include a lack of properly-trained managers, limited differentiation of customers, limited products and similar brands.Despite having 20 kinds of products to choose between, there is actually little separating them. Brands do not have a sufficiently unique or differentiated product to target specific types of customers.Competitive threatThere is only one year left until the Chinese banking market is fully liberalized and foreign institutions are able to serve individual customers in renminbi-based business.(59) Foreign banks have already experimented and learned about the market despite regulatory limitations over the type of businesses they can operate. Standard Chartered Bank has offered an “SC Priority Banking” card for customers with quarterly average account balances of US $100,000 or the equivalent, while Citibank has launched its “Citigold” product for customers with monthly average account balances of US $100, 000 or the equivalent. Both banks have set up dedicated wealth management centres in key cities such as Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen.Foreign banks have many competitive advantages over local banks including brand names with internationally recognized prestige and trust, experience and expertise in a broader range of investment products and advisory models, established operational models, particularly processes, systems and policies, and capabilities to attract, train and retain the best talent.(60) Foreign banks will create tough competition in the wealth management market, as they enter the retail market and attempt to pick the most attractive customers. Unless Chinese banks can respond, there is a real and significant threat that many wealthy customers will be lured away by the highly-evolved products and services foreign banks can offer.B. Answer the following questions or complete the statements according to your understandingof the passage. (10%)51. In China, banks are paying increasing attention to the wealthy because ________.。
Ⅰ. Translate the following words or phrases into Chinese(10%)1. bearer bond2. mutual funds3. loan4. mass selling5. stock certificate6. venture capital7. real estate8. physical distribution9. limited liability10. capital injectionⅡ. Translate the following words or phrases into Chinese(10%)11.初次公开招股12.资产变现能力13.电话销售,电话推销14.期末存货15.独立法人16.盈亏平衡点17.股东18.逆差;赤字19.流动资金20.价格操纵Ⅲ. Choose the best answers to fill in the blanks(10%)21. Packaging has the responsibility to do all of the following EXCEPT __________.A. To attract the buyer’s attention.B. To explain the benefits of the good inside.C. To change the quantity of the product.D. To provide information of price,value,and uses.22. Insurance companies base their costs on __________.A. the pool of people sharing the riskB. the cost each member of the pool paysC. the theory of probabilityD. past experience23. Some Americans complain about the Japanese style of management because __________.A. they think the manager is too inhumanB. they think the manager is indecisiveC. they think the manager is too lenientD. they think the manager is too generous24. __________ belongs to “Marketing Mix”.A. Labor forceB. MachinesC. MaterialsD. Promotion25. Symbols play an important role in cross-cultural analysis because __________.A. symbols help one to understand one’s own culture betterB. the meanings of symbols vary from culture to cultureC. marketers may use symbols to please potential customersD. improper use of symbols may cause misunderstanding26. A dishonoured bill is __________.A. one which the importer is ashamed ofB. one which the importer fails to pay on the due dateC. one which the drawer fails to payD. one which the exporter fails to clear27. Mutual Savings Banks are __________.A. national banksB. state banksC. private banksD. thrift institutions28. __________ is the fastest method of money transfer.A. Telegraphic transferB. Mail transferC. ChequeD. International money order29. In promotion,__________ is the strength of publicity.A. being flexibleB. avoiding media costaC. saving preparation timeD. reaching a larger number of audiences30. Publicity is designed to familiarize the public with __________.A. the characteristics of a goodB. the features of a serviceC. the advantages of an ideaD. all of the aboveⅣ. In this part,there are three reading passages followed by 15 questions or unfinished statements. For each of them there are four choices marked A,B,C and D. You should decide on the best one according to your understanding(30%).Passage 1Customer RelationsCustomer relations describes the resources of a company-be it a store,manufacturer,or service industry-that are devoted to discerning and then serving the needs of customers. In earlier times,this was known as the complaint department,the part of the operation that dealt with negative customer comments,returns,and other concerns. Renaming this function customer relations is more than a word game. It reflects the proactive nature of the department in modern industry and retailing. Customer service extends beyond sales and advertising to ensure that the company understands its customer base and what its customers really want. Customer relationsworks within the business to direct the quality of the product or service,its delivery,and advertising strategy to meet that need. This part of a business operation responds to customer inquiries and complaints and resolves problems so as not to lose customers;at the same time,customer relations works with the marketing department to attract new customers.The short answer to why so much attention should be paid to customer needs and dissatisfied customers is that such attention has been found to support long-term success. Some of the earliest such endeavors began with concern over product reputation-as far back as the early days of the Industrial Revolution in the l89Os. Placing one’s name on a product was considered to be a bond of tie between the customer and the merchant and/or the manufacturers.Over the years,many firms developed a policy of “the customer is always right,” finding that it was more profitable to take a small loss and keep a customer than to argue with customers about alleged defective products or problems that occurred with staff. Firms developed complaint departments to deal with customers who had bad experiences with products or services.As consumer consciousness grew in the late twentieth century the focus of the industry shifted from dealing with dissatisfied customers as they complained,to a more active approach of reaching out to discover why the complaint was made ,to ensure that the dissatisfied customers remain customers,and to study each case and improve the product or service and the way in which it was delivered to customers. In the 1 960s the complaint department began to be known as the customer relations department. Customer relations departments still take on complaints. The advent of toll-free numbers makes it easier for people to register complaints-and praise. Customers who phone in praise for or complaints about a product are often offered free coupons and recipes for that product.Studies of the customer relations movement show that the shift to an aggressive policy of customer study is more than “nice”,it is profitable for business. Resources expended in the customer service area are more than offset by savings from customers not lost. Goodwill toward all customers reaps tangible rewards in the form of increased profits for business.In a study of service industries,Ron Zemke cited two studies by Technical Assistance Research Institute(TARI)in Washington D. C. ,on consumer complaints. TARI found that one in four customers was upset enough about a product or service or both to seek an alternative business for that product or service. Of those unhappy customers,however,only five percent had bothered to complain. The other 95 percent just voted with their cash by switching. To reduce the loss of customers in the future,customer relations tries to analyze the five percent who complained in order to understand the ninety-five percent who did not complain yet were unhappy. Customer relations must anticipate the needs of each individual Customer,up and down the social scale,across the racial and cultural lines that make up the American melting pot.Zemke and others offer many strategies for building a good customer relations department.The best strategies involve learning as much as possible about the customer base and training staff well as to what the customers want and the way they want it. Zemke and others show that a company with excellent service toward customers is one that understands the tie between employee relations and customer relations. A well-trained satisfied employee is better able to satisfy the needs of the customer.An acknowledged leader in customer service in the retailing field is Nordstrom’s department store. Nordstrom’s stresses quality in every aspect of its service and merchandise down to the last detail. A 1994 Washington Post article about a survey of the quality of women’s rest rooms inmetro-D. C. stores and malls reported that the heat overall was Nordstrom’s. Nordstrom’s was not seeking to highlight this area. When interviewed the Nordstrom local officials seemed not to understand the fuss. Maintaining their store rest rooms as one would maintain one’s home bathroom for expected guests is just one small part of Nordstrom’s total commitment to customer service. Nordstrom associates are encouraged to learn about their customers,to send thank-you notes,to send postcard reminders to customers when products they might like arrive and to give regular customers advance notification of Nordstrom’s infrequent sales.The conversion of complaint departments to customer relations departments became so widespread that in 1973 the Society of Consumer Affairs Professionals in Business was founded.Consisting of more than 3,000 members who are involved with the management of consumer affairs divisions of business,the society takes the cause of customer relations to a national level,promoting harmonious relationships between business,government,and consumers. The society works on ways to help businesses assess and compare their successes and failures in consumer relations and maintains a library and bookstore of materials on customer relations as well as publishing a magazine,Mobius Quarterly.31. Customer relations should be responsible for all of the following EXCEPT __________.A. the quality of product or serviceB. customer inquires and complaintsC. finding new resources for the companyD. attracting new customers32. A business should pay much attention to customer needs and dissatisfied customers because __________.A. customers are always rightB. a business’s success depends on theseC. customer needs are on the increaseD. customers are more and more difficult to satisfy33. According to the text,when dissatisfied customers complain,the most important thing a business should do is to __________.A. set up a complaint departmentB. deal with customers’ complaintsC. find out why they complainD. study some typical cases34. According to Zemke and others,a company with excellent service toward customers should be able to __________.A. find out why only a small percentage of unhappy customers make complaintsB. understand the tie between employee relations and customer relationsC. anticipate the needs of each individual customerD. understand that the American melting pot is made up of different races and cultures35. Which of the following is NOT true according to the text?A. Nordstrom’s department store is devoted to retailing.B. Keeping women’s rest rooms clean has made Nordstrom’s department store an acknowledged leader in customer service.C. Maintaining women’s rest rooms clean is only one example that shows Nordstrom’s stresses on quality in every aspect of its service and merchandise.D. The Nordstrom officials thought it fussy to be interviewed.Passage 2Japanese Style of ManagementTime clocks are banned from the premises. Mangers and workers converse on a first-name basis and eat lunch together in the company cafeteria. Employees are briefed once a month by a top executive on sales and production goals and are encouraged to air their complaints. Four times a year,workers attend company-paid parties. Says Betty Price,54,an assembly-line person:“Working for Sony is like working for your family.”Her expression,echoed by dozens of other American Sony workers in San Diego,is a measure of success achieved at the sprawling two-story plant,where both the Stars and Stripes and the Rising Sun fly in front of the factory’s glistening white exterior. In 1981 the San Diego plant turned over 700,000 color television sets,one-third of Sony’s total world production. More significantly,company officials now proudly say that the plant’s productivity approaches that of its Japanese facilities.Plant manager Shiro Yamada,58,insists that there are few differences between workers in the United States and Japan. Says he:“Americans are as quality conscious as the Japanese.But the question has been how to motivate them. ” Yamada’s way is to bathe his U. S. employees in personal attention. Workers with perfect attendance records are treated to dinner once a year at a posh restaurant downtown. When one employee complained that a refrigerator for storing lunches was too small,it was replaced a few days later with a larger one. Vice-President Masayoshi Morirnoto,known as Mike around the plant,has mastered Spanish so he can talk with his many Hispanic workers. The company has installed telephone hot lines on which workers can anonymously register suggestions or complaints. The firm strives to build strong ties with its employees in the belief that the workers will then show loyalty to the company in return,It carefully promotes from within,and most of the assembly-line supervisors are high school graduates who rose through the ranks because of their hard work and dedication to the company. During the 1973 1975 recession,when TV sales dropped and production slowed drastically,no one was fired. Instead,workers were kept busy with plant maintenance and other chores. In fact,Sony has not laid off a single employee since 1972,when the plant was opened. The Japanese managers were stunned when the first employee actually quit within one year. Says Richard Crossman,the plant’s human relations expert:“They came to me and wanted to know what they had done wrong. I had to explain that quitting is just the way it is sometimes in Southern California. ”This personnel policy has clearly been a success. Several attempts to unionize the work force have been defeated by margins as high as 3 to 1. Says Jan Timmerman,22,a parts dispatcher and former member of the Retail Clerks Union:“Union pay was better,and the benefits were probably better. But basically I’m more satisfied here. ”Sony has not forced Japanese customs on American workers. Though the company provides lemon-colored smocks for assembly-line workers,most prefer to wear jeans and running shoes.The firm doesn’t demand that anyone put on uniforms. A brief attempt to establish a general exercise period for San Diego workers,similar to the kind Sony’s Japanese employees perform,was dropped when managers saw it was not wanted.Inevitably,there have been minor misunderstandings because of the differences in languageand customs. One worker sandblasted the numbers 1 2 6 4 on a series of parts she was testing before she realized that her Japanese supervisor meant that she was to label them “1 to 64. ”Mark Dempsey,23,the plant’s youngest supervisor,admits that there is a vast cultural gap between the Japanese and Americans. Says he;“They don’t realize that some of us live for the weekend,while lots of them live for the week-just so they can begin to work again. ” Some workers grumble about the delays caused by the Japanese system of managing by consensus,seeing it instead as an inability to make decisions. Complains one American;“There is a lot of indecision. No manager will ever say do this or do that.”Most American workers,though,like the Japanese management style,and some do not find it all that foreign. Says supervisor Robert Williams:“A long time ago,Americans used to be more people-oriented,the way the Japanese are. It just got lost somewhere along the way.”36. What is the main idea of the passage?A. American employees working for Sony.B. How Sony established business in the United States.C. How Japanese manage their business.D. The difference between Americans and Japanese.37. We can learn from the passage that the relationship between the Japanese employers and their American employees at Sony is __________.A. detachedB. harmoniousC. unfriendlyD. very formal38. The phrase “to bathe his U. S. employees in personal attention” in paragraph three means __________.A. to personally look into the welfare of his American workersB. to show great concern for the personal needs of his employeesC. to direct his U. S employees’ attention to workD. to provide his U. S. employees with chances to go swimming in their bathing suits39. By building strong ties with its employees,the Sony company expects __________.A. its workers to work faster and longerB. its workers to be loyal to the companyC. to attract more employeesD. to complete more successfully with other companies40. What do the workers think of the Japanese style of management?A. They think it is far from being satisfactory.B. They think it is inefficient.C. They think it is family style.D. They prefer it anyway.Passage 3Making the Right ChoicesWith imports and exports accounting for nearly half of Chinese economic output last year,trade has become an essential part of its economy and society.China’s decision in 1999 to join the World Trade Organization was a vital catalyst in itsemergence as a major economic power. But since 2001,the WTO has been unable to finalize the new trade agreements(known as the Doha Round)that would enable the WTO system to keep pace with a globalizing world.Nevertheless,countries around the world,including China,have continued to reach out on their own for the benefits of free trade and investment,by arranging bilateral free trade agreements with other countries with whom they see advantages in developing economic ties.The economic benefits of free trade have been demonstrated time and again. One country’s economic strengths are often another country’s weaknesses. Removing import restrictions and duties encourages a country to buy products from another country that make them cheaper and better,while exporting more of its own competitive products.Free trade makes everyone better off,because greater specialization improves economic efficiency,which in turn encourages more trade and economic growth everywhere. History shows that trade between countries after they have signed a free trade agreement grows by as much as 100 percent.China has used its attractiveness as a large market and powerful Asian presence to establish FTAs around the world with other economies,such as ASEAN,Chile,Peru,Singapore,New Zealand and Costa Rica.In 2010,China decided it needed to build a free trade foothold in Europe,its largest market and a vital strategic partner,and opened FTA discussions with Switzerland in January 2011.The Swiss service-based and high-value-added economy is very complementary to China’s economy,although much smaller.But at first sight it would appear that Switzerland has much more to gain than China from a free trade agreement. The removal of Chinese import tariffs as high as 15 percent on machinery imports will further support Switzerland’s already strong Chinese trade position,while Switzerland’s world-leading banking and insurance companies are big investors in China. Only in certain agricultural products,where Switzerland maintains import duties of more than 20 percent,does China appear to enjoy a significant advantage from liberalizing its Swiss trade.But the discussions demonstrate a Chinese strategic interest that extends far beyond developing closer economic ties with a much smaller country. Switzerland is located in the center of Europe,and although independent of the European Union,is closely linked economically and by trade agreements to the euro economy,as Costa Rica is with the United States.With its road and rail links into Italy,France,Germany,Austria and beyond,Switzerland is an excellent place for Chinese companies to position themselves to develop the European market. Under a free trade agreement,China can export components and semi-finished products to Switzerland without paying any Swiss import duties.Under a Sino-Swiss FTA,some of China’s exports to Switzerland,if re-exported to European countries,could displace European agricultural and manufactured products,such as autos and household products. Similarly,some Swiss exports to China that escape import tariffs of 10 percent or more will displace competitors’ products from other major exporters of specialized machinery,chemicals and watches,such as Germany,Japan and the US.Since 2007 Europe has firmly embraced the bilateral free trade approach. Europe has just opened FTA negotiations with Japan,and is holding discussions with the US about developing free trade. China’s huge market and its average import duties of about 10 percent represent a very attractive prize for free traders.Switzerland’s example could encourage the EU to consider opening FTA discussions with China,which would have to decide whether to weaken its role as leader of the large group of emerging world countries at the WTO Doha Round discussions,in order to gain the economic benefits of a bilateral European free trade agreement.41. What is the purpose of Doha Round according to the passage?A. To reach some international trade agreements.B. To settle some illegal trade.C. To improve better relationship between countries.D. To solve some international political affairs.42. What is the most possible meaning of FTA?A. Foreign Trade AssociationB. Free Trade AgreementC. Foreign Trade AgreementD. Free Trade Association43. Why does China develop closer economic ties with such a small country as Switzerland?A. Because of its world-leading banking system.B. Because of its strong economy.C. Because of its geographical position in Europe.D. Because of its political position in Europe.44. What is China’s advantage in attracting free traders?A. Its political system.B. Its economic system.C. Its beautiful scenery.D. Its huge market.45. Which of the following statements is NOT true according to the passage?A. Joining WTO helped China become a major economic power in this world.B. The Sino-Swiss FTA won’t have influence on other European country’s economy.C. China can benefit a lot from Sino-Swiss FTA,especially in agriculture.D. Europe has opened FTA negotiations with some Asian and American countries.Ⅴ. Read the following passages and finish the exercises of each one(40%)Passage 1E-commerce Growing in China’s Small TownsE-commerce is becoming increasingly popular in China’s small towns,with local residents spending even more money than their urban peers.A resident of Tonglu County in east China’s Zhejiang province,23-year-old Liu Hua said he spends a lot of money on Taobao,China’s biggest online shopping website.He said he and his mother spend more than 10,000 yuan(1,632 U. S. dollars)each year on online shopping.I shop more online than in real stores. I mostly buy electronics and food,while my mom buys clothing and cosmetics,?Liu said.“Tonglu is small and high-tech electronics aren’t available here. In addition,such goods are usually more expensive in stores than online,” he said.According to a report released by Taobao in late July,people living in counties and townshipsspent an average of 5,628 yuan per person online,almost 1,000 yuan more than their urban counterparts. Major global brands like Estee Lauder,Nike and Vans have sold well in counties and townships,the report said.Small-town shoppers spent 765 yuan on average per person on Estee Lauder cosmetics,slightly more than 652 yuan by the first- and second-tier city dwellers,according to the report.Another report released in March by the McKinsey Global Institute showed that the online shopping habits of residents of small towns and counties are similar to those of urban residents,even though incomes in counties and townships tend to be smaller.According to the report,for every 100 yuan spent online,57 yuan is spent by people in third-and fourth-tier cities,greater than the nationai average of 39 yuan.However,the presence of counterfeit goods and a poorly-developed logistics industry have risen as challenges to the development of c-commerce.“I always concerned about fake products and the risk of my products being damaged while being delivered,” Liu said.Xu Zheng,a resident of Harbin,the capital of northeast China’s Heilongjiang Province,had complaints about the speed at which his online purchases are delivered.“I have to wait for three to four days or even longer for online goods,” Xu said.E-commerce giant Alibaba Group formed a consortium in May to build a nationwide intelligent logistics network that can ensure rapid delivery of online purchases.Wang Xiaozhang,a professor at Zhejiang University,said the enlarging role of online shopping is related to confined shopping choices in small towns and the convenience brought by technology.“Both sellers and buyers should develop credit and the government should create relevant regulations if and when poor delivery efficiency and damaged products become severe problems,” he said.A. Mark the following statements true(T)or false(F)according to the passage(10%)46. China’s small towns see great popularity of online shopping in recent years.47. Some products are not available in small downs,which is one factor for the increase of online shopping in small towns.48. Urban residents spend more on online shopping because they earn more money than small town residents do.49. People show some worries about fake products in online shopping.50. Delivery of online purchases is no problem for the well developed logistics in small towns.Passage 2(56)Seemingly unnoticed by the rest of the world are the extraordinary strides China has made to create and use various forms of alternative energy,particularly clean sources like hydropower,solar and nuclear power.Constantly we read of pollution caused by China’s use of coal for power,but the fact is that a considerable portion of the energy China uses every day comes not from fossil fuels but these three alternative sources.(57)China is the world’s largest producer of hydroelectricity,which supplies at least 17 percent of the country’s domestic power demands.The biggest hydropower producer in the world is the Three Gorges Dam project blocking the mighty Yangtze River at Yichang,Hubei province.One measure of its size and strength is the fact that in times of heavy rain and upland flooding,this remarkable facility contains a reservoir of water stretching up to 600 kilometers upriver.When floodwaters gushing into the dam approach its tolerance levels,the sluice gates are opened to relieve the pressure on the dam’s huge wall,and with an immense roar,water gushes out at the rate of 70,000 cubic meters per second.(58)Besides hydropower,China is also a global leader in solar energy. More than 400 Chinese photovoltaic companies produce energy-gulping solar panels that are sold across the globe,making a huge contribution to reducing the use of air-polluting fossil fuel.Equally important,solar power now contributes a significant 3. 5 gigawatts of power across China,a figure set to expand exponentially by 2020.The Golmud Solar Farm in Qinghai province is the world’s largest solar power facility,absorbing a yearly average of 3,300 hours of sunshine that bombards the Golmud Desert. This year it won an award for China’s Best-Quality Power Project. Altogether there are solar panels capable of producing 870 megawatts here,and its capacity is expected to reach 1,070 MW by year’s end.Many other solar power facilities are located across much of China,including such areas as Tianjin,Tibet,Shandong and Guangdong,with new ones being opened regularly.(59)With regard to nuclear power,China has always taken a cautious and conservative approach to this capricious alternative and has a relatively small total of 16 nuclear power stations in four different locations,which are mainly along its coastline so that seawater can be used for cooling.That is less than 3 percent of the world’s total of 443 nuclear power stations. Furthermore,these 16 nuclear power stations provide only 1 percent of the country’s power needs.(60)With runaway industrial development inevitably came the pollution problems that still blight some of China’s biggest cities,but considerable improvements to air quality have been achieved through a wide range of measures.According to the Beijing non-profit Institute of Public and Environmental Affairs,several cities are now being more open about their air quality information,including Beijing,Guangzhou and Shenzhen.“Some cities have moved forward,” said Institute Director Ma Jun. “But among all of China’s 113 cities,there are still many not making proper disclosures.”Beijing is now releasing details of air pollutants comprising tiny particulate matter about 2.5 micrometers in size,which is a much higher standard than the PM 10 measure previously used.The following statistics underscore the seemingly permanent pollution problem in Beijing:the population has now swelled to 17 million;the number of cars on its roads is now 5 million plus,or an additional 1. 5 million in the past four years;and 27 million tons of coal were burned by the capital in 2010.On the other side of the ledger,Beijing now has 35 new monitoring locations and has become the leading city in China in its monitoring of PM2. 5 data.B. Answer the following questions or complete the statements according to your。
湖北省高等教育自学考试实践(技能)课程大纲课程名称:听力课程代码:00593一、实践能力的培养目标。
《听力》是英语专科阶段开设的英语基本技能课程。
本课程通过多种形式的训练,帮助学生初步克服听力障碍,听懂英语国家人士在一般社交场合的交谈和相当于中等难度的听力材料,能理解大意、抓住主要论点或情节,能根据所听材料进行分析、领会说话人的态度、感情和真实意图,并用英语简要地做笔记。
在课程结束时,学生听懂英语国家人士所作的难度不超过所学语言知识的讲座,掌握中心大意,理解主要内容,并能辨别说话人的态度和语气。
听懂VOA慢速新闻广播和文化节目,抓住主要内容。
能在15分钟内听写根据已学知识编写而成或选用的录音材料(词数150个左右,念四遍,语速为每分钟100个单词),错误率不超过10%。
二、实践(技能)课程教学基本要求。
(含学时、学分要求)《听力》是英语专科阶段开设的英语基本技能课程。
本课程学分为8分,计划教学学时为144,同时要求应考生自主学习时间不低于144学时。
在本课程教学过程中,还应注意:①助学单位要把握正确的助学导向。
助学单位要鼓励辅导教师遵循自学考试大纲规定的考试内容和考核目标,认真研究指定教材,明确本课程的特点、学习范围和学习要求,对应考生进行切合需要的辅导,并从学习方法上给予指导,特别要注意引导应考生全面系统地掌握课程内容,不猜题、押题,防止把“助学”变成“助考”。
②助学单位要正确处理一般和重点的关系。
听力技能的提高涉及的问题是多方面多层次的,除了正常的语言能力还需要平日的知识积累,但由于条件所限,指定教材中所能够重点讨论的问题十分有限。
一般和重点是相互联系、密不可分的,把握不住全部不可能掌握重点,这也是质和量的关系。
因此,社会助学单位应知道应考生全面系统地学习教材,在全面学习的基础上,再进行重点指导。
要引导应考生把全面理解和重点深入探讨结合起来,切记孤立地抓重点。
③助学单位要鼓励应考生独立完成课上和课下作业,并按照前面所讲的学习方法对他们提出要求。
自考英语教学法知识点总结:中学英语教学指引思想:是对中学英语教学旳总体科学结识,涉及对教学目旳,教学路子旳结识以及科学观,学习观,教学观等。
智力因素重要涉及:思维力,记忆力,想象力,观测力,注意力等。
非智力因素涉及:动机,爱好,情感,意志,性格等。
语言是指语言系统,也就是语音,词汇,语法系统。
言语是指人们使用语言所进行旳体现和理解旳话语活动,也就是说听,说,读,写活动。
教学路子指旳是达到教学目旳基本途径或总路线,涉及成体系旳教学法。
语感是指学习者对语言信息旳敏锐感知和理解,是自动化旳意识活动。
教学基本原则是教学指引思想旳构成部分,是指引思想旳具体化,条理化,在中学英语教学法科学体系中占有重要旳地位。
语法是对语言旳一般描述,重要是对其组织原则旳理论描述, ______学,句法学,词汇学,语义学。
“双规”化简就是运用语音规则,把大量旳表面看起来相称复杂旳词旳读音和拼写化繁为简,化难为易。
句型也叫句式,是从口语和书面语旳无数实际句子中概括出来旳句子模型或模式,句型是有代表性旳,常用性旳。
分析性听:是指在听旳活动中有明显旳语言分析,此外是指把听旳材料分析为各个语言层次,让学生分步听,进行听旳基本功训练。
综合性听:是指在听旳活动中无明显旳语言分析而直接达到对内容旳理解,也指在听力基本功训练基本上所进行旳整篇成文旳听旳练习。
话语构造就是说话旳套路,说旳各句子之间旳联系规律。
泛读就是广泛地阅读,大量地阅读,迅速地阅读。
默读泛指一切不出声地读,默读既涉及不出声地“声读”,也涉及直接理解文字地“视读”。
实行纵式阅读:真正旳默读一般都是迅速阅读,在阅读过程中,人旳目光重要体现为上下移动,因而阅读有慢速旳横向或横式转变为纵向或纵式。
写旳含义:在教学中写有两个方面旳含义,一是书写或书法,涉及字母,单词,句子,标点符号,国际音标旳对旳写法;二是写作,即笔头体现,如作文,写信,写日记等。
心理控制法:即惊异,悬念,满足。
密度:指单位时间所授教学内容。
自考05439考核知识点
《新编商务英语泛读2》
Unit 1Definition of advertising,types of advertising,advertising media,considerations in choosing media.广告的定义、类型,广告媒体(媒介),对选择媒体的考虑。
Unit 2 The four functions of money;cashless ways of dealing with money.钱的四个功能,非现金处理钱的方式。
Unit 3 The five steps in entering business in China.在中国进入业务的五个步骤。
Unit 4 The reasons why Dell is so successful in China.戴尔在中国如此成功的原因。
Unit 5 Sources to investigate for information on employers;preparing the essential written materials,details about the resume and the cover letter.雇主的信息来源调查;准备必要的书面材料、详细的简历和求职信。
Unit 6 The definition of insurance,types of insurance.
保险的定义,保险的类型。
Unit 7 The concepts behind consumers’actions;the 3 steps for the purchase process.基于消费者行为背后的概念;购买过程的3个步骤。
Unit 8 The personnel policy in management;the building up of Microsoft Co.人事政策管理;微软公司的建立。
Unit 9 The definition of bonds,stocks,the features of bonds,types of stocks,how to buy and sell securities,the stock market,the bond market,considerations before investing in securities;the definition of mutual funds.债券的定义,股票、债券的特点,股票的类型,如何买卖证券,股票市场,债券市场,在投资证券之前的考虑,共同基金的定义。
Unit 10 types of products,the benefits of packaging.产品的类型,包装的好处。
《新编商务英语泛读3》
Unit 1 Why price is important;factors affecting pricing,supply and demand,goals of pricing.为什么价格是很重要的;影响定价、供给和需求的因素、目标定价。
Unit 2How can a marketer understand and appreciate the values,customs,symbols and language of other societies.营销人员如何理解和欣赏价值,海关、符号和其他国家的语言。
Unit 3The four PS of marking:Product,Price,Promotion and Placement.四个注意年代的标志:产品、价格、促销和位置。
Unit 4Types of promotional methods;how to better communicate with people.促销方法的类型,如何更好地与人沟通。
Unit 5The definition of physical distribution,the benefits of physical distribution.物流的定义,物流的好处。
Unit 6The meaning of customer relations,how to stress customer needs.客户关系的意义,如何应击客户需求。
Unit 7 The reason why overseas sales are important,global marketing strategy,multinational approach.海外销售重要的原因,全球营销战略,跨国的方法。
Unit 8Six methods of payment in foreign trade;understanding of the American Banking System.六种外贸付款的方法;对美国银行体系的理解。
Unit 9 The definition of a company,characteristics companies,different types of shares in a company;the definition of the income statement and the balance statement.企业公司的定义、特点,公司里不同类型的股票,损益表和余额明细表的定义。
Unit 10The six condition of a valid contracts;the exchange rate,the advantage of floating rate. 有效合同的六个条件,汇率,浮动利率的优势。
《新编商务英语泛读4》
Unit 1 The definition of “public relations”,the benefits of publicity.“公共关系”的定义,宣传的好处。
Unit 2 Understanding the meaning of “impulse buying” and “reflex buying”;the influence of advertising.理解“冲动消费”和“反射购买”的意义;广告的影响。
Unit 3 Mulchandani’s ways to cater the customers’ needs;the major concern of a salesperson. Mulchandani满足客户的需求的方法,销售人员主要关心的问题。
Unit 4 The eight steps to success in negotiating,types of funds.在谈判中获得成功的八个步骤,基金的类型。
Unit 5The benefits and risks of going downmarket.进入低端市场的益处和风险。
Unit 6 The reasons why Shanghai is so attractive to foreign investors;the result of labor cost.为什么上海对外国投资者很有吸引力的原因,劳动力成本的结果。
Unit 7 Technical terms for stock.股票术语
Unit 8 The benefits of home ownership;the benefits and risks of marking loans from the back for houses,cars,education,etc.房屋所有权的好处;从贷款回来的房子,汽车,教育等标记的益处和风险。
Unit 9 The risks that Western venture capitalists in China are faced with;the development of private companies in recent years.西方风险资本家在中国面临的风险,近年来民营企业的发展。
Unit 10The major factors that the Chinese government will consider in revaluation of RMB;what’s the right attitude for foreign investors to invest in China?中国政府会考虑人民币升值的主要因素,对外国投资者在中国投资的正确态度是什么?。