最新Meta分析的报告标准
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:90.72 KB
- 文档页数:2


诊断性试验Meta分析报告一、引言诊断性试验在医学领域中具有至关重要的作用,它们帮助医生确定患者是否患有某种疾病,以及评估疾病的严重程度和预后。
然而,单个诊断性试验往往受到样本量、研究人群、研究方法等因素的限制,其结果可能存在偏差。
Meta 分析作为一种系统评价方法,能够综合多个诊断性试验的结果,提供更全面、更准确的诊断信息。
二、目的本 Meta 分析的目的是综合评估某种诊断性试验在特定疾病中的诊断价值,为临床医生的诊断决策提供依据。
三、资料与方法(一)检索策略我们在多个数据库(如 PubMed、Embase、Cochrane Library 等)中进行了系统的检索,检索时间范围为_____至_____。
检索词包括疾病名称、诊断性试验名称以及相关的关键词。
(二)纳入与排除标准纳入标准:①研究对象为疑似患有特定疾病的患者;②使用了所关注的诊断性试验;③报告了诊断准确性的相关指标,如敏感度、特异度、阳性预测值、阴性预测值等。
排除标准:①重复发表的研究;②研究质量差,如样本量过小、方法学存在明显缺陷等;③无法获取全文或关键数据的研究。
(三)数据提取由两名研究者独立提取纳入研究的基本信息(如作者、发表年份、研究地点等)、研究对象的特征(如年龄、性别、疾病严重程度等)、诊断性试验的方法和参数、诊断准确性的指标等。
如有分歧,通过讨论或咨询第三方解决。
(四)质量评估采用 QUADAS-2(Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies 2)工具对纳入研究的质量进行评估,评估内容包括病例的选择、待评价试验、金标准、病例流程和进展情况等方面。
(五)数据分析使用 Review Manager 53 软件进行数据分析。
对于诊断准确性的指标,计算合并的敏感度、特异度、阳性似然比、阴性似然比和诊断比值比,并绘制森林图和受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线。
采用随机效应模型或固定效应模型进行合并分析,根据异质性检验的结果(I²值)选择合适的模型。



Meta分析系列之八_Meta分析的报告规范Meta分析是一种整合多个独立研究结果的统计方法,它通过对已有研究进行系统性的统合和分析,从而得出更具统计学意义的结论。
然而,随着Meta分析的日益流行,报告规范也变得尤为重要。
本文将介绍Meta分析报告的规范要求,以确保研究的科学性和可信度。
首先,Meta分析报告应该包含一个明确的研究问题和目标。
研究问题应该确切而具体,以便能够明确地指导Meta分析的进行。
研究目标则应该清晰地表明Meta分析的目的是什么,例如评估某一特定干预措施的效果或比较不同研究中的效果差异等。
其次,Meta分析报告应明确包含研究的筛选过程与结果。
研究的筛选过程应详细描述,包括检索文献的数据库、使用的关键词、筛选标准等。
并应该提供一个完整的流程图,展示文献筛选的过程。
同时,对于被纳入Meta分析的研究,应该列出其基本信息,比如作者、发表年份、样本量等,以便读者对研究的特征进行评估。
第三,Meta分析报告应说明统计方法的选择与使用。
在Meta分析中,常用的统计方法包括固定效应模型和随机效应模型。
研究者应当说明选择了哪种方法,并说明其合理性。
同时,还应该描述具体的数据分析过程,包括合并效应的计算公式、异质性检验的方法以及敏感性分析等。
这样可以让读者充分了解Meta分析的分析过程,以提高研究的可信度。
第四,Meta分析报告应提供合并效应的结果。
合并效应是Meta分析的关键结果之一,它能够总结出所研究的全部数据的效应大小和方向。
研究者应该明确报告合并效应的估计值和置信区间,这可以用来判断结果的显著性和可靠性。
此外,还可以根据研究的特点,对合并效应进行亚组分析或敏感性分析,以探索不同因素对效应的影响。
最后,Meta分析报告应慎重地进行结论的阐述与讨论。
结论应该准确、客观地总结Meta分析的结果,避免夸大或缩小效应的影响。
同时,讨论部分应该对结果进行解释,并与已有研究进行比较和讨论,以便更全面地理解和解释Meta分析的结果。

文献纳入标准和排除标准:纳入标准:1、各研究假设和研究方法相似;2、有研究开展或发表的年限;3、各研究对样本大小有明确规定;4、各研究中患者的选择和病例的诊断及其分期有明确标准,干预和对照的措施明确;5、如研究报告可提供OR(RR、率差、HR)及其95%可信区间,或可以转化为OR(RR、率差、HR)及其95%可信区间;如为计量资料应可提供均数,标准差和样本量等。
剔除标准:1、重复报告;2、存在研究设计缺陷,质量差;3、数据不完整、结局效应不明确;4、统计方法错误且无法修正,无法提供或可供转化为OR(RR、率差、HR)及其95%可信区间,计量资料无法提供均数和标准差。
我觉得还可以参考相关文献,看他们是怎样设定纳入和剔除标准的。
如何评断meta分析文献纳入排除标准的好坏纳入排除标准是每个Meta分析中必不可少的一部分。
纳入排除标准设置的好坏,直接关系到一个Meta分析研究纳入文献的质量。
首先,先看几个Meta分析中的纳入排除标准的设定。
1) Lancet Infect Dis 2014; “Treatment outcomes of childhood tuberculousmeningit is:a systematic review and meta-analysis”2) Anaesthesia 2008. “Dexmedetomidine and cardiac protection for non‐cardiac surg ery: a meta‐analysis of randomisedcontrolled trials”3) Cochrane 系统评价:Locomotor trainingfor walking after spinal cord injury我们发现,越是严谨的Meta分析,对纳入排除标准设定的越是细致,在文章表述过程中也越完整(参看cochrane系统评价)。
因此,我们可以总结到,Meta分析的纳入标准一般都包括五个方面,即PICOS,也就是对参与人群、干预措施、比较、结局指标、研究类型。


系统评价Meta分析详细介绍目录一、系统评价Meta分析的基本概念 (2)1.1 系统评价的定义 (3)1.2 Meta分析的定义 (4)二、系统评价Meta分析的目的和意义 (4)三、系统评价Meta分析的流程 (5)3.1 明确研究问题 (6)3.2 检索文献 (7)3.3 筛选文献 (8)3.4 数据提取 (9)3.5 整理数据 (10)3.6 进行Meta分析 (11)3.7 结果解释 (12)3.8 评估偏倚风险 (13)3.9 结果的综合评价 (14)四、系统评价Meta分析中的统计方法 (15)4.1 基本统计方法 (16)4.2 元分析统计方法 (17)五、系统评价Meta分析的质量评价 (19)5.1 文献质量评价 (20)5.2 结果的一致性评价 (21)5.3 可靠性评价 (22)六、系统评价Meta分析的结果解释和应用 (24)6.1 结果的解释 (25)6.2 结果的应用 (26)6.3 对未来研究的启示 (27)七、系统评价Meta分析的局限性 (28)7.1 样本选择偏差 (29)7.2 数据质量问题 (31)7.3 不同研究结果间的异质性 (32)八、系统评价Meta分析的伦理问题 (33)8.1 保护受试者隐私 (35)8.2 避免学术不端行为 (36)九、系统评价Meta分析的未来发展趋势 (37)9.1 技术的发展 (38)9.2 方法学的创新 (39)一、系统评价Meta分析的基本概念系统评价(Systematic Review,简称SR)是一种多学科研究方法,旨在通过收集、整理和分析大量关于某一主题的独立研究结果,以便得出全面、准确和可靠的结论。
Meta分析(Metaanalysis)是系统评价的一种扩展和深化,它通过对多个独立研究的统计分析,对原始研究结果进行加权汇总,以提高研究结果的可靠性和推广性。
系统评价的目的是对现有的研究进行全面、客观和公正的评估,从而为实践提供有价值的指导。

诊断性meta分析手把教你做临床Meta 分析——诊断试验性 Meta-Disc分析导读:诊断性meta分析,手把教你做临床 Meta 分析——诊断试验性 Meta-Disc 分析,诊断性meta分析stata,诊断性试验meta,推荐访问:诊断性meta分析stata诊断性试验meta手把教你做临床 Meta 分析——诊断试验性Meta-Disc 分析临床治疗的基础首先是需要准确的诊断,准确诊断性 Meta 分析是 Meta 分析的一个重要部分,本次想向大家推荐的是一款专用于诊断性试验的免费 Meta 分析软件,临床医学、临床检验、临床病理、临床科研人员、临床康复科及临床影像科等工作人员可用它写上一篇高大上的诊断准确性试验的 Meta 分析文章。
安装软件Meta-DiSc 是一个免费的下载软件,登录http://www.hrc.es/investigacion/metadisc_en.htm,下载安装软件,目前最新版本是 1.4 版。
运行软件在试行此软件之前,必须明确和熟悉准确诊断性 Meta 分析里结果计算的经典四格表(可能不会在您所纳入的文献中出现,需要研究人自己总结并准确的填写在四格表内,不易混淆而且方便分析)。
TP:True positive 表示真阳性的结果,用数字表示;FP:False positive 表示假阳性的结果,用数字表示;FN:False negative 表示假阴性的结果,用数字表示;TN:True negative 表示真阴性的结果,用数字表示。
1打开软件,可以看到如下界面Author:第一作者名 + 文章年限,如 Rachow 2013;StudyID:纳入文献的排序编号,亦可以按照自己理想的排名排序;2数据的输入有三种方法可以输入,我们掌握其中两种就足够运用,一种是当纳入的文献较多的时候,可以按照软件中表格的形式对应写在 Excel 表上,点击复制 Ctrl+c,并点击黏贴 Ctrl+v,便可以 copy 至软件中的表格内;另一种当纳入的文献数量较少时,则可以直接用手动输入到 Meta-disc 数据表内,如下图。
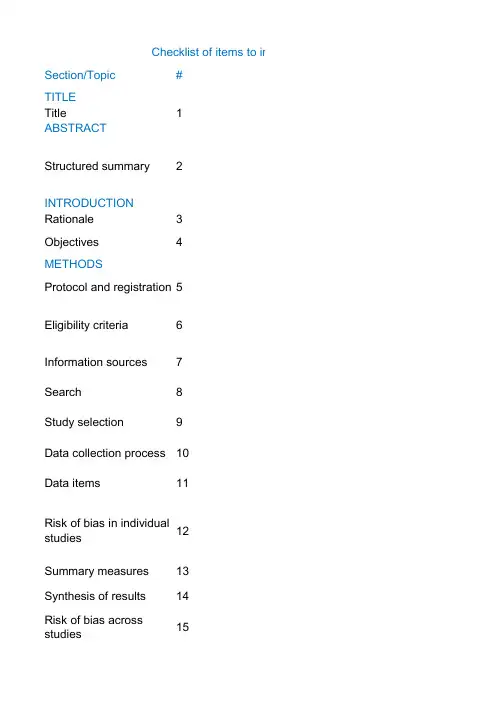
Section/Topic# Title1Structured summary2Rationale3 Objectives4Protocol and registration5 Eligibility criteria6 Information sources7 Search8 Study selection9 Data collection process10 Data items11 Risk of bias in individual studies12Summary measures13 Synthesis of results14Risk of bias across studies15Checklist of items to incTITLE ABSTRACTINTRODUCTION METHODSAdditional analyses16Study selection17Study characteristics18Risk of bias withinstudies19Results of individualstudies20Synthesis of results21Risk of bias acrossstudies22Additional analysis23Summary of evidence24Limitations25Conclusions26Funding 27FUNDINGRESULTSDISCUSSIONo include when reporting a systematic review or meta-analysis.(PRISMA) Checklist ItemIdentify the report as a systematic review, meta-analysis, or both.Provide a structured summary including, as applicable: background; objectives;data sources; study eligibility criteria, participants, and interventions; studyappraisal and synthesis methods; results; limitations; conclusions andimplications of key findings; systematic review registration number.Describe the rationale for the review in the context of what is already known.Provide an explicit statement of questions being addressed with reference to participants, interventions,comparisons, outcomes, and study design (PICOS).Indicate if a review protocol exists, if and where it can be accessed (e.g., Web address), and, if available, provide registration information including registration number.Specify study characteristics (e.g., PICOS, length of follow-up) and reportcharacteristics (e.g., years considered,language, publication status) used as criteria for eligibility, giving rationale.Describe all information sources (e.g., databases with dates of coverage,contact with study authors to identify additional studies) in the search and date last searched.Present full electronic search strategy for at least one database, including any limits used, such that it could be repeated.State the process for selecting studies (i.e., screening, eligibility, included in systematic review, and, if applicable,included in the meta-analysis).Describe method of data extraction from reports (e.g., piloted forms,independently, in duplicate) and any processes for obtaining and confirming data from investigators.List and define all variables for which data were sought (e.g., PICOS, funding sources) and any assumptions and simplifications made.Describe methods used for assessing risk of bias of individual studies (including specification of whether this was done at the study or outcome level), and how this information is to be used in any data synthesis.State the principal summary measures (e.g., risk ratio, difference in means).Describe the methods of handling data and combining results of studies, ifdone, including measures of consistency (e.g., I2) for each meta-analysis.Specify any assessment of risk of bias that may affect the cumulative evidence(e.g., publication bias, selective reporting within studies).Describe methods of additional analyses (e.g., sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression), if done,indicating which were pre-specified.Give numbers of studies screened, assessed for eligibility, and included in the review, with reasons for exclusions at each stage, ideally with a flow diagram. For each study, present characteristics for which data were extracted (e.g., study size, PICOS, follow-up period)and provide the citations.Present data on risk of bias of each study and, if available, any outcome-level assessment (see Item 12).For all outcomes considered (benefits or harms), present, for each study: (a) simple summary data for each intervention group and (b) effect estimates and confidence intervals, ideally with a forest plot.Present results of each meta-analysis done, including confidence intervals and measures of consistency.Present results of any assessment of risk of bias across studies (see Item 15). Give results of additional analyses, if done (e.g., sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression [see Item 16]).Summarize the main findings including the strength of evidence for each main outcome; consider their relevance to key groups (e.g., health care providers, users, and policy makers).Discuss limitations at study and outcome level (e.g., risk of bias), and at review level (e.g., incomplete retrieval of identified research, reporting bias).Provide a general interpretation of the results in the context of other evidence, and implications for future research.Describe sources of funding for the systematic review and other support (e.g., supply of data); role of funders for the systematic review.Reportedon PageReason√√√×本文纳入的是观察性研究,并非RCT ×本综述并未注册√√√√√√×对纳入的研究进行了质量评价,但质量评价结果并未在亚组分析时用到,因为没有找到完全适用于入选研究的质量评价标准,所以质量评价结果可信度不高√√√√√√×同12√√√√√√√√。

荟萃meta纳入和排除标准
荟萃分析(meta-analysis)的纳入和排除标准通常包括以下方面:
纳入标准:
1. 研究类型:通常包括随机对照试验(RCT)、观察性研究、队列研究、病例对照研究等。
2. 研究主题:研究主题应与荟萃分析的主题相关,且应具有明确的研究目的和假设。
3. 研究质量:研究应具有较高的质量,排除低质量的研究。
4. 样本量:研究应具有足够的样本量,以获得可靠的结论。
5. 结局指标:研究应具有与荟萃分析相关的结局指标,如死亡率、发病率、生活质量等。
排除标准:
1. 研究类型:非随机对照试验、个案报告、描述性研究等非前瞻性研究将被排除在外。
2. 研究质量:低质量的研究将被排除在外。
3. 样本量:样本量过小或无足够样本量的研究将被排除在外。
4. 数据不完整:数据不完整或无法获得所需数据的研究将被排除在外。
5. 重复发表:重复发表或内容高度相似的研究将被排除在外。
需要注意的是,纳入和排除标准并不是一成不变的,而是根据具体的研究问题和目的而定的。
因此,在进行荟萃分析时,应根据具体情况制定合适的纳入和排除标准,以确保研究的可靠性和有效性。
文献纳入标准和排除标准:纳入标准:1、各研究假设和研究方法相似;2、有研究开展或发表的年限;3、各研究对样本大小有明确规定;4、各研究中患者的选择和病例的诊断及其分期有明确标准,干预和对照的措施明确;5、如研究报告可提供OR(RR、率差、HR)及其95%可信区间,或可以转化为OR(RR、率差、HR)及其95%可信区间;如为计量资料应可提供均数,标准差和样本量等。
剔除标准:1、重复报告;2、存在研究设计缺陷,质量差;3、数据不完整、结局效应不明确;4、统计方法错误且无法修正,无法提供或可供转化为OR(RR、率差、HR)及其95%可信区间,计量资料无法提供均数和标准差。
我觉得还可以参考相关文献,看他们是怎样设定纳入和剔除标准的。
如何评断meta分析文献纳入排除标准的好坏纳入排除标准是每个Meta分析中必不可少的一部分。
纳入排除标准设置的好坏,直接关系到一个M eta分析研究纳入文献的质量。
首先,先看几个Meta分析中的纳入排除标准的设定。
1) Lanc et Infect Dis 2014; “Treatment outcomes of childhood tuberculousmening itis: a systematic review and meta-analysis”2) Anaesthesia 2008. “Dexmedetomidine and cardiac protection for non‐cardiac surgery: a meta‐analysis of randomisedcontrolled trials”3) Cochrane 系统评价:Locomotor trainingfor walking after spinal cord injury我们发现,越是严谨的Meta分析,对纳入排除标准设定的越是细致,在文章表述过程中也越完整(参看cochrane系统评价)。
met a分析总结篇一:m et a分析资源大总结经过一段时间对me ta的分析和了解,自己虽算不上精通m et a分析,但自己还是觉得自己对me ta分析产生了一定的兴趣!现在将我获得的各种资源汇总如下!与大家一起分享,一起进步!(一)m et a分析的选题原则首先,选定的题目要有争议性!如果关于某项研究,大家的结论都是一致的,那没有再做me ta分析的必要了!其次,选定的题目要有原始文献作支撑!俗话说,巧妇难为无米之脆!m et a分析质量的好坏,关键还是取决于有无高质量的原始研究作为强大的后盾力量!再者,所选题目要具有创新!创新是论文是否发表的很重要的决定性因素!me ta分析不像其他原始研究~我在美国做可能是A结果,我在中国做可能就是B结果!这两个研究是不同的因为研究的地域、人群等不同!但me ta分析是针对目前所有发表或者未发表的研究报告进行二次研究!我理解的创新就是要在前人的工作基础上,结合自己的体会和阅读文献的感悟,提出一个合理,科学的问题!最后,所选题目要有意义!所有科学研究的终极目标是促进人类更好的发展!对于m et a分析(无论是干预性研究的m et a或者是诊断性试验的me ta,e tc),必须明确你的研究目的是什么?!这样做有什么意义!!(二)me ta分析的经典之作~唐茂芝、董佳毅八篇S R(声明:这八篇SR著作权属原作者所有!这里仅仅是分享而已,不带有任何其他目的!)我刚开始学习me ta分析的时候,我导师就要求我们先看一下这八篇S R!最初看的有点吃力!但是后面慢慢就习惯了!下面是这八篇SR,与大家分享一下!(三)关于me ta分析理论入门的P PT(特别适用于刚入门的战友们!!)下面是我刚接触me ta是看的P P他,也一并传上来,给初学m et a的战友们打气加油!!(四)me ta分析的证据分级和检索策略众所周知,不同原始文献的证据级别是不一样的!小弟整理了目前有关分级的标准!传上来与大家一起学习!另外,我也把三大数据库的检索使用方法一并传上来!(这些资料均来自互联网!版权属原作者所有!发帖者仅为交流学习之用,无其他意图!)(五)m et a分析的圭臬毫无疑问,要做好m et a分析,Cc hr an eHa nb K是每个人必读的经典之作!下面我把5.0和5.1都上传上来!另外,还上创一个介绍m et a分析的英文文献!(六)关于me ta研究论文的写作指导一片好的me ta分析,无论是文章结构还是语言表达,都十分完美!!那有没有一个me ta分析写作的固定模版呢!?答案是肯定的!下面我上传SR写作的模版和报告规范!!呵呵,暂时就整理出这些啦!!本来是想把En dn te和S ta ta 一起传上来的,但是这两个文件有点大!所以各位战友如有需要,在园子里搜索一下吧!!谢谢大家了!!上面有什么不对的,请大家不吝赐教哈!!我们一起学习,一起进步!!祝大家国庆节快乐!!篇二:循证医学-me ta分析入门总结一、选题和立题(一)形成需要解决的临床问题:系统评价可以解决下列临床问题:1.病因学和危险因素研究;2.治疗手段的有效性研究;3.诊断方法评价;4.预后估计;5.病人费用和效益分析等。
系统综述(meta分析)格式与标准系统综述(Meta分析)格式与标准⼀、标题1 题⽬:点明主题。
题⽬⼀般可定为****Meta分析或****效果评价。
⼆、摘要2摘要:尽量简明扼要。
包含以下部分:⽬的、⽅法、结果、结论。
按照各⾃需求可适量加上背景、资料来源、纳⼊标准、研究⼈群、⼲预措施、质量评价⽅法和限制、对主要结果的分析等。
三、关键词3 关键词:为此⽂章的关键字,能点出⽂章的主题。
⼀般为3-4个词,不宜过多。
四、引⾔4引⾔:对此⽂章主题的简要介绍、发展近况、新颖性、有何意义等等。
五、资料与⽅法5 纳⼊标准:使⽤纳⼊研究的⽅法学特征(如试验⽅法,随访时间)和报告特征(如发表年份、语⾔、发表状态)作为可靠、合理的标准6 信息来源:在检索策略中列出所有的信息来源(如使⽤的数据库、与研究作者联系获得详细信息)和最后检索⽇期。
⼀般英⽂检索可⽤Pubmed数据库,中⽂检索可⽤我们学校的CNKI数据库及万⽅数据库等。
7 检索:⾄少提供⼀个数据库的完整检索⽅式,包括对检索的限制,检索词,这个策略是否能被重复使⽤。
8 研究筛选:表明研究筛选过程,提供检索、纳⼊标准、质量评价后的纳⼊研究的数⽬,每个阶段给出排除理由,最好提供流程图。
9 统计分析⽅法:所⽤的分析软件和分析⽅法,⼀般有Stata软件或Revman软件。
六、结果10 资料提取:从研究中提取资料,列出所有的⽂献的研究特征,如发表年份、来源地区、作者、实验数据、随访时间、质量评价等。
该部分⽤表格的⽅式给出。
11 单个研究的偏倚:描述⽤于评价每个研究的偏倚危险的⽅法(提供是在实施阶段或结局阶段),在数据合成过程中是如何使⽤这些⽅法的12 合成⽅法:描述主要的合成⽅法(如危险度、均差)13 合成结果:描述数据处理⽅法和合成的结果,在每个Meta分析中进⾏异质性检验(I2),不存在异质性则采⽤固定效应模型,否则⽤随机效应模型。
14 研究的结果:对于所有呈现的结局(危害、有益):①每个⼲预组的简单总结表;②估计效应值和置信区间。