Oracle分析函数与分组关键字的用法
- 格式:docx
- 大小:208.60 KB
- 文档页数:5

Oracle中分析函数用法小结一.分析函数适用场景:○1需要对同样的数据进行不同级别的聚合操作○2需要在表内将多条数据和同一条数据进行多次的比较○3需要在排序完的结果集上进行额外的过滤操作二.分析函数语法:FUNCTION_NAME(<argument>,<argument>...)OVER(<Partition-Clause><Order-by-Clause><Windowing Clause>)例:sum(sal) over (partition by deptno order by ename) new_aliassum就是函数名(sal)是分析函数的参数,每个函数有0~3个参数,参数可以是表达式,例如:sum(sal+comm) over 是一个关键字,用于标识分析函数,否则查询分析器不能区别sum()聚集函数和sum()分析函数partition by deptno 是可选的分区子句,如果不存在任何分区子句,则全部的结果集可看作一个单一的大区order by ename 是可选的order by 子句,有些函数需要它,有些则不需要.依靠已排序数据的那些函数,如:用于访问结果集中前一行和后一行的LAG和LEAD,必须使用,其它函数,如AVG,则不需要.在使用了任何排序的开窗函数时,该子句是强制性的,它指定了在计算分析函数时一组内的数据是如何排序的.1)FUNCTION子句ORACLE提供了26个分析函数,按功能分5类分析函数分类等级(ranking)函数:用于寻找前N种查询开窗(windowing)函数:用于计算不同的累计,如SUM,COUNT,AVG,MIN,MAX等,作用于数据的一个窗口上例:sum(t.sal) over (order by t.deptno,t.ename) running_total,sum(t.sal) over (partition by t.deptno order by t.ename) department_total制表(reporting)函数:与开窗函数同名,作用于一个分区或一组上的所有列例:sum(t.sal) over () running_total2,sum(t.sal) over (partition by t.deptno) department_total2制表函数与开窗函数的关键不同之处在于OVER语句上缺少一个ORDER BY子句!LAG,LEAD函数:这类函数允许在结果集中向前或向后检索值,为了避免数据的自连接,它们是非常有用的.VAR_POP,VAR_SAMP,STDEV_POPE及线性的衰减函数:计算任何未排序分区的统计值2)PARTITION子句按照表达式分区(就是分组),如果省略了分区子句,则全部的结果集被看作是一个单一的组3)ORDER BY子句分析函数中ORDER BY的存在将添加一个默认的开窗子句,这意味着计算中所使用的行的集合是当前分区中当前行和前面所有行,没有ORDER BY时,默认的窗口是全部的分区在Order by 子句后可以添加nulls last,如:order by comm desc nulls last 表示排序时忽略comm列为空的行.4)WINDOWING子句用于定义分析函数将在其上操作的行的集合Windowing子句给出了一个定义变化或固定的数据窗口的方法,分析函数将对这些数据进行操作默认的窗口是一个固定的窗口,仅仅在一组的第一行开始,一直继续到当前行,要使用窗口,必须使用ORDER BY子句根据2个标准可以建立窗口:数据值的范围(RANGES)或与当前行的行偏移量.5)Rang窗口Range 5 preceding:将产生一个滑动窗口,他在组中拥有当前行以前5行的集合ANGE窗口仅对NUMBERS和DATES起作用,因为不可能从VARCHAR2中增加或减去N个单元另外的限制是ORDER BY中只能有一列,因而范围实际上是一维的,不能在N维空间中例:avg(t.sal) over(order by t.hiredate asc range 100 preceding) 统计前100天平均工资6)Row窗口利用ROW分区,就没有RANGE分区那样的限制了,数据可以是任何类型,且ORDER BY 可以包括很多列7)Specifying窗口UNBOUNDED PRECEDING:这个窗口从当前分区的每一行开始,并结束于正在处理的当前行CURRENT ROW:该窗口从当前行开始(并结束)Numeric Expression PRECEDING:对该窗口从当前行之前的数字表达式(Numeric Expression)的行开始,对RANGE来说,从行序值小于数字表达式的当前行的值开始. Numeric Expression FOLLOWING:该窗口在当前行Numeric Expression行之后的行终止(或开始),且从行序值大于当前行Numeric Expression行的范围开始(或终止)range between 100 preceding and 100 following:当前行100前, 当前行100后注意:分析函数允许你对一个数据集进排序和筛选,这是SQL从来不能实现的.除了最后的Order by子句之外,分析函数是在查询中执行的最后的操作集,这样的话,就不能直接在谓词中使用分析函数,即不能在上面使用where或having子句!!!下面我们通过一个实际的例子:按区域查找上一年度订单总额占区域订单总额20%以上的客户,来看看分析函数的应用。

ORACLE_分析函数大全Oracle分析函数是一种高级SQL函数,它可以在查询中实现一系列复杂的分析操作。
这些函数可以帮助我们在数据库中执行各种数据分析和报表生成任务。
本文将介绍Oracle数据库中的一些常用分析函数。
1.ROW_NUMBER函数:该函数为查询结果中的每一行分配一个唯一的数字。
可以用它对结果进行排序或分组。
例如,可以使用ROW_NUMBER函数在结果集中为每个员工计算唯一的编号。
2.RANK和DENSE_RANK函数:这两个函数用于计算结果集中每个行的排名。
RANK函数返回相同值的行具有相同的排名,并且下一个排名值将被跳过。
DENSE_RANK函数类似,但是下一个排名值不会被跳过。
G和LEAD函数:LAG函数返回结果集中指定列的前一个(上一个)行的值,而LEAD函数返回后一个(下一个)行的值。
这些函数通常用于计算增长率或发现趋势。
4.FIRST和LAST函数:这两个函数用于返回结果集中分组的第一个和最后一个行的值。
可以与GROUPBY子句一起使用。
5.CUME_DIST函数:该函数用于计算给定值的累积分布。
它返回值的累积分布在结果集中的位置(百分比)。
6.PERCENT_RANK函数:该函数用于计算结果集中每个行的百分位数排名。
它返回值的百分位数排名(0到1之间的小数)。
7. NTILE函数:该函数用于将结果集分成指定数量的桶(Bucket),并为每个行分配一个桶号。
通常用于将数据分组为更小的块。
8.LISTAGG函数:该函数将指定列的值连接成一个字符串,并使用指定的分隔符分隔每个值。
可以用它将多个值合并在一起形成一个字符串。
9.AVG、SUM、COUNT和MAX/MIN函数:这些是常见的聚合函数,可以在分析函数中使用。
它们用于计算结果集中的平均值、总和、计数和最大/最小值。
以上只是Oracle数据库中的一些常用分析函数。
还有其他一些分析函数,如PERCENTILE_CONT、PERCENTILE_DISC等可以用于更高级的分析计算。
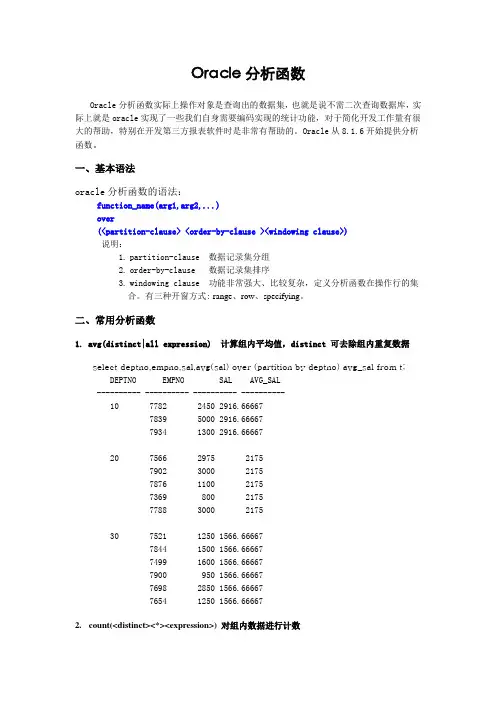
Oracle分析函数Oracle分析函数实际上操作对象是查询出的数据集,也就是说不需二次查询数据库,实际上就是oracle实现了一些我们自身需要编码实现的统计功能,对于简化开发工作量有很大的帮助,特别在开发第三方报表软件时是非常有帮助的。
Oracle从8.1.6开始提供分析函数。
一、基本语法oracle分析函数的语法:function_name(arg1,arg2,...)over(<partition-clause> <order-by-clause ><windowing clause>)说明:1.partition-clause 数据记录集分组2.order-by-clause 数据记录集排序3.windowing clause 功能非常强大、比较复杂,定义分析函数在操作行的集合。
有三种开窗方式: range、row、specifying。
二、常用分析函数1. avg(distinct|all expression) 计算组内平均值,distinct 可去除组内重复数据select deptno,empno,sal,avg(sal) over (partition by deptno) avg_sal from t;DEPTNO EMPNO SAL AVG_SAL---------- ---------- ---------- ----------10 7782 2450 2916.666677839 5000 2916.666677934 1300 2916.6666720 7566 2975 21757902 3000 21757876 1100 21757369 800 21757788 3000 217530 7521 1250 1566.666677844 1500 1566.666677499 1600 1566.666677900 950 1566.666677698 2850 1566.666677654 1250 1566.666672.count(<distinct><*><expression>) 对组内数据进行计数3.rank() 和dense_rank()dense_rank()根据 order by 子句表达式的值,从查询返回的每一行,计算和其他行的相对位置,序号从 1 开始,有重复值时序号不跳号。

oracle高级分析函数使用实例2014年11月26日10:26:55∙标签:∙oracle∙1744ORACLE的分析函数,发现大家写SQL的时候有些功能写的比较麻烦或者不知道复杂的功能怎么通过SQL实现,ORACLE自带的分析函数有很多相应的功能:它是Oracle分析函数专门针对类似于"经营总额"、"找出一组中的百分之多少" 或"计算排名前几位"等问题设计的。
分析函数运行效率高,使用方便。
分析函数是基于一组行来计算的。
这不同于聚集函数且广泛应用于OLAP环境中。
Oracle从8.1.6开始提供分析函数,分析函数用于计算基于组的某种聚合值,它和聚合函数的不同之处是对于每个组返回多行,而聚合函数对于每个组只返回一行。
语法:<analytic-function>(<argument>,<argument>,...)over(<query-partition-clause><order-by-clause><windowing-clause>)其中:1 over是关键字,用于标识分析函数。
2 <analytic-function>是指定的分析函数的名字。
Oracle分析函数很多。
3 <argument>为参数,分析函数可以选取0-3个参数。
4 分区子句<query-partition-clause>的格式为:partition by<value_exp>[,value_expr]...关键字partition by子句根据由分区表达式的条件逻辑地将单个结果集分成N组。
这里的"分区partition"和"组group"都是同义词。
5 排序子句order-by-clause指定数据是如何存在分区内的。

oracle max over partition by用法全文共四篇示例,供读者参考第一篇示例:Oracle数据库是一种关系数据库管理系统,提供了丰富的功能和语法来处理数据。
在处理数据的时候,我们经常需要使用分析函数来进行复杂的计算和分析,max over partition by是一种常用的功能之一。
本文将介绍max over partition by的用法以及它在实际应用中的作用。
在Oracle数据库中,max over partition by是一种分析函数,它可以在一组数据中查找指定列的最大值,并返回结果。
它的语法如下:```max(column) over (partition by column_name)```column是要查找最大值的列,而column_name则是根据哪个列进行分区。
通过在max后面加上over partition by关键字,我们可以在指定的分区内查找最大值。
举个例子来说明max over partition by的用法:假设有一个销售订单表orders,包含了订单号(order_id)、商品编号(product_id)和销售额(amount)三个字段,我们现在想要查找每个商品的销售额最大值。
我们可以使用max over partition by来实现:```select order_id, product_id, amount,max(amount) over (partition by product_id) asmax_amountfrom orders```在实际应用中,max over partition by有很多用途。
我们可以使用它来查找每个员工的最高工资、每个部门的最大利润等等。
通过对数据进行分区并利用分析函数,我们可以更方便地对数据进行深入分析和计算。
除了max over partition by之外,Oracle还提供了其他一些强大的分析函数,如min over partition by、sum over partition by等等,它们都可以帮助我们更加高效地处理复杂的数据分析任务。

Oracle之分析函数⼀、分析函数 1、分析函数 分析函数是Oracle专门⽤于解决复杂报表统计需求的功能强⼤的函数,它可以在数据中进⾏分组然后计算基于组的某种统计值,并且每⼀组的每⼀⾏都可以返回⼀个统计值。
2、分析函数和聚合函数的区别 普通的聚合函数⽤group by分组,每个分组返回⼀个统计值,⽽分析函数采⽤partition by分组,并且每组每⾏都可以返回⼀个统计值。
3、分析函数的形式 分析函数带有⼀个开窗函数over(),包含分析⼦句。
分析⼦句⼜由下⾯三部分组成: partition by :分组⼦句,表⽰分析函数的计算范围,不同的组互不相⼲; ORDER BY:排序⼦句,表⽰分组后,组内的排序⽅式; ROWS/RANGE:窗⼝⼦句,是在分组(PARTITION BY)后,组内的⼦分组(也称窗⼝),此时分析函数的计算范围窗⼝,⽽不是PARTITON。
窗⼝有两种,ROWS和RANGE; 使⽤形式如下:OVER(PARTITION BY xxx PORDER BY yyy ROWS BETWEEN rowStart AND rowEnd) 注:窗⼝⼦句在这⾥我只说rows⽅式的窗⼝,range⽅式和滑动窗⼝也不提。
⼆、OVER() 函数 1、sql 查询语句的 order by 和 OVER() 函数中的 ORDER BY 的执⾏顺序 分析函数是在整个sql查询结束后(sql语句中的order by的执⾏⽐较特殊)再进⾏的操作, 也就是说sql语句中的order by也会影响分析函数的执⾏结果: [1] 两者⼀致:如果sql语句中的order by满⾜分析函数分析时要求的排序,那么sql语句中的排序将先执⾏,分析函数在分析时就不必再排序; [2] 两者不⼀致:如果sql语句中的order by不满⾜分析函数分析时要求的排序,那么sql语句中的排序将最后在分析函数分析结束后执⾏排序。
2、分析函数中的分组/排序/窗⼝分析函数包含三个分析⼦句:分组(partition by),排序(order by),窗⼝(rows/range)窗⼝就是分析函数分析时要处理的数据范围,就拿sum来说,它是sum窗⼝中的记录⽽不是整个分组中的记录,因此我们在想得到某个栏位的累计值时,我们需要把窗⼝指定到该分组中的第⼀⾏数据到当前⾏, 如果你指定该窗⼝从该分组中的第⼀⾏到最后⼀⾏,那么该组中的每⼀个sum值都会⼀样,即整个组的总和。

oracle 统计/分析函数Oracle从8.1.6开始提供分析函数,分析函数用于计算基于组的某种聚合值,它和聚合函数的不同之处是对于每个组返回多行,而聚合函数对于每个组只返回一行。
语法:Sql代码1.<analytic-function>(<argument>,<argument>,...)2.over(3.<query-partition-clause>4.<order-by-clause>5.<windowing-clause>6.)说明:<1> over是关键字,用于标识分析函数。
<2> <analytic-function>是指定的分析函数的名字。
<3> <argument>为参数,分析函数可以选取0-3个参数。
<4> 分区子句<query-partition-clause>的格式为:partition by<value_exp>[,value_expr]...关键字partition by子句根据由分区表达式的条件逻辑地将单个结果集分成N组。
这里的"分区partition"和"组group" 都是同义词。
<5> 排序子句order-by-clause指定数据是如何存在分区内的。
其格式为:order[siblings]by{expr|position|c_alias}[asc|desc][nulls first|nulls last]其中:A.asc|desc:指定了排列顺序。
B.nulls first|nulls last:指定了包含空值的返回行应出现在有序序列中的第一个或最后一个位置。
<6>窗口子句windowing-clause给出一个固定的或变化的数据窗口方法,分析函数将对这些数据进行操作。

Oracle数据库分析函数⽤法⽬录1、什么是窗⼝函数?2、窗⼝函数——开窗3、⼀些分析函数的使⽤⽅法4、OVER()参数——分组函数5、OVER()参数——排序函数1、什么是窗⼝函数?窗⼝函数也属于分析函数。
Oracle从8.1.6开始提供窗⼝函数,窗⼝函数⽤于计算基于组的某种聚合值,窗⼝函数指定了分析函数⼯作的数据窗⼝⼤⼩,这个数据窗⼝⼤⼩可能会随着⾏的变化⽽变化。
与聚合函数的不同之处是:对于每个组返回多⾏,⽽聚合函数对于每个组只返回⼀⾏基本语法: ‹分析函数› over (partition by ‹⽤于分组的列名› order by ‹⽤于排序的列名›)。
语法中的‹分析函数›主要由序列函数(rank、dense_rank和row_number等组成)与聚合函数(sum、avg、count、max和min等)作为窗⼝函数组成。
从窗⼝函数组成上看,它是group by 和 order by的功能组合,group by分组汇总后改变了表的⾏数,⼀⾏只有⼀个类别,⽽partiition by则不会减少原表中的⾏数。
恰如窗⼝函数的组成,它同时具有分组和排序的功能,且不减少原表的⾏数。
OVER 关键字表⽰把函数当成窗⼝函数⽽不是聚合函数。
SQL 标准允许将所有聚合函数⽤做窗⼝函数,使⽤ OVER 关键字来区分这两种⽤法。
2、窗⼝函数——开窗OVER 关键字后的括号中经常添加选项⽤以改变进⾏聚合运算的窗⼝范围。
如果 OVER 关键字后的括号中的选项为空,则窗⼝函数会对结果集中的所有⾏进⾏聚合运算。
分析函数 over(partition by 列名 order by 列名 rows between 开始位置 and 结束位置)为什么叫开窗呢?因为在over()括号中的,partition() 函数可以将查询到的数据进⾏单独开⼀个窗⼝处理。
譬如,查询每个班级的学⽣的排名情况,查询每个国家的历年⼈⼝等,诸如此类,都是在查询到的每⼀个班级、每⼀个国家中都开⼀个窗⼝,单独去执⾏命令。

oracle常⽤关键字和函数数据库的增删改查:增:insert into ... values();例:insert into p_emp values(sq_emp.nextval,'⼩⽩','保洁',7902,sysdate,600,null,30,0);commit;注意,表⾥边有多少列,values()⾥边的内容就有多少,⼀⼀对应关系。
后边加分号结束语句,然后commit;提交。
⾃增长序列:右击Sequences,new⼀个新的⾃增序列,起⼀个name,然后有⼀个nextval属性,实现⾃增长。
查:select ... from ...例:select t.*,t.rowid from p_emp t(⽤t代表p_emp),加上t.rowid,可以直接在表⾥进⾏修改。
单⾏语句可以不加分号!删除:delete ... where ...例:delete p_emp e where e.empon = 1;commit;从⼀个表⾥边删除某-⾏,地址是当empon = 1的那⼀⾏。
改:update 表 set 表.属性 = ... where 表.属性 = ...;update p_emp e set e.ename = '李华' where e.empon = 1;commit;数据库的常⽤关键字:1.in---:在某个范围内例⼦:select * from p_emp e where e.sal in(400,300,5000);查表p_emp的⼯资分别为400,300,5000,的那⼀⾏。
2.like---:模糊查询 %表⽰任意字符,_表⽰单个字符。
例⼦:select * from p_emp e where e.ename like 'T%';查询名字以t开头的,注意like后⾯必须加 ‘ ’,查询的为字符串的话,开头要⼤写。

Oracle analysis function(Oracle分析函数)ORACLE advanced function application- grouping function1, ROLLUPTotal, subtotal -- statistical standards and the corresponding dimension of the packet- decrease from right to left: group by rollup (a, B, c): A, B, C; a, B (C; a (b total), C subtotal total);--1)CALL VPD_PKG.SET_CONTEXT_COMPID ('-1');SELECT, A.VPD_COMPID, TO_CHAR (A.TTIME,'MM'), COUNT (*)FROM XTBILL2011 AGROUP, BY, ROLLUP (A.VPD_COMPID, TO_CHAR (A.TTIME,'MM'));--2) partial rollup groupingFor after grouping, sum of a.typeidSELECT, A.DWDH, A.YEAR, A.TYPEID, COUNT (*)FROM XTYWBILL AGROUP, BY, A.DWDH, A.YEAR, ROLLUP (A.TYPEID);2, CUBE--rollup can only "right to left", such as the need for a full range of dimensions for statistics, you need to use the cube function--1)SELECT, A.VPD_COMPID, TO_CHAR (A.TTIME,'MM'), COUNT (*)FROM XTBILL2011 AGROUP, BY, CUBE (A.VPD_COMPID, TO_CHAR (A.TTIME,'MM'));--2) cube: can summaries and subtotals do not need to remove some.SELECT, A.VPD_COMPID, TO_CHAR (A.TTIME,'MM'), COUNT (*)FROM XTBILL2011 AGROUP, BY, A.VPD_COMPID, CUBE (TO_CHAR (A.TTIME,'MM'));3, GROUPING SETS- Description: focus only on some dimensions of the single packet, subtotal--group, by, grouping, sets (a, B, c) are equivalent to group,by, a, group, by, B, group, by, C- these three groups of union all results--1)SELECT, A.VPD_COMPID, TO_CHAR (A.TTIME,'MM'), COUNT (*) FROM XTBILL2011 AGROUP, BY, GROUPING, SETS (A.VPD_COMPID, TO_CHAR(A.TTIME,'MM'));--2) partial grouping sets grouping- sum based on group by, only pay attention to the subtotal SELECT, A.DWDH, A.YEAR, A.TYPEID, COUNT (*)FROM XTYWBILL AGROUP, BY, A.DWDH, GROUPING, SETS (A.YEAR, A.TYPEID); SELECT, A.VPD_COMPID, TO_CHAR (A.TTIME,'MM'), COUNT (*) FROM XTBILL2011 AGROUP, BY, A.VPD_COMPID, GROUPING, SETS (TO_CHAR(A.TTIME,'MM'));4, CUBE, ROLLUP as the parameters of GROUPING SETS--grouping sets operations are grouped only on single columns without providing aggregate functionality, and if grouping sets is required, aggregate functionality is provided,- then you can use rollup or cube as the parameters of the grouping sets, such as the following statement to provide aggregate functionality:SELECT, A.VPD_COMPID, TO_CHAR (A.TTIME,'MM'), AS, TTIME, COUNT (*)FROM XTBILL2011 AGROUP, BY, GROUPING, SETS (ROLLUP (A.VPD_COMPID), ROLLUP (TO_CHAR (A.TTIME,'MM'));This statement yields two total rows, because rollup or cube is the parameter of grouping sets, which is equivalent to eachUnion all for --rollup and cube operations. So the above statement is equivalent to:SELECT, A.VPD_COMPID, NULL, AS, TTIME, COUNT (*)FROM XTBILL2011 AGROUP BY ROLLUP (A.VPD_COMPID)UNION ALLSELECT, NULL, TO_CHAR (A.TTIME,'MM'), COUNT (*)FROM XTBILL2011 AGROUP, BY, ROLLUP (TO_CHAR (A.TTIME,'MM'));5, combination column grouping brief introduction:- grouping methods: rollup (a, B, c), <=>group, by, a, B, C, group, by, a, B, group, by, null- grouping methods: rollup (a, (B, c)), <=>group, by, a, B, C, group, by, a, group, by, null- grouping mode: rollup (a, B),汇总(C)< = >组,B、C组,B;;组,C组由;组;C组为空;——分组方式:汇总(A,B),(C)分组集< = >组,B、C组,C;C 组的;——分组方式:汇总(一),汇总(B),汇总(C)<= >组由;组B;C组;组的,B组,C;;组B、C;A,B,C组;组由空6、分组函数——为了区别哪些是小计,分组函数派上用场了!选择a.vpd_compid,to_char(a.ttime,'mm '),计数(*),分组(a.vpd_compid),分组(to_char(a.ttime,'mm ')),解码(分组(a.vpd_compid),1,“所有单位',a.vpd_compid)vpd_compid,解码(to_char(a.ttime,'mm '),1,“所有月份',to_char(a.ttime,'mm '))时间从xtbill2011一组汇总(a.vpd_compid,to_char(a.ttime,'mm '));——过滤某些分组结果选择a.vpd_compid,to_char(a.ttime,'mm '),计数(*),分组(a.vpd_compid),分组(to_char(a.ttime,'mm ')),解码(分组(a.vpd_compid),1,“所有单位',a.vpd_compid)vpd_compid,解码(to_char(a.ttime,'mm '),1,“所有月份',to_char(a.ttime,'mm '))时间从xtbill2011一组汇总(a.vpd_compid,to_char(a.ttime,'mm '))具有分组(a.vpd_compid)= 1或分组(to_char(a.ttime,'mm '))= 0;7、grouping_id函数——可用汇总或立方体与grouping_id组合运用,过滤出想要的分组统计信息选择a.vpd_compid,to_char(a.ttime,'mm”),grouping_id (a.vpd_compid,to_char(a.ttime,'mm ')),计数(*)从xtbill2011一集团通过立方体(a.vpd_compid,to_char(a.ttime,'mm '))有grouping_id(a.vpd_compid,to_char(a.ttime,'mm '))= 2;——1,2,3,0——grouping_id(A,B,C)过滤分组结果分组级别位向量grouping_id结果A,B,C 0 0 0 0A,B 0 0 1 10,1,1,3汇总1 1 1 78、group_id函数——判断重复的分组选择a.vpd_compid,to_char(a.ttime,'mm”)为时间,group_id() ID,计数(*)从xtbill2011一通过分组套组(汇总(a.vpd_compid),汇总(to_char(a.ttime,'mm ')))有group_id() = 0;9、实例应用说明:下拉表;创建表T(order_date日期--订购日期order_no号--订购号order_book VARCHAR2(10),--订购书籍order_fee号--订单总金额order_num数);插入T选择to_date('2010-05-01 ','yyyy-mm-dd ')+水平,trunc(dbms_random。

Oracle数据库 having grouping用法1. 什么是HAVING和GROUPING?在Oracle数据库中,HAVING和GROUP BY是用于对查询结果进行分组和过滤的两个重要关键字。
GROUP BY用于将行分组成多个集合,而HAVING用于对这些集合进行筛选。
•GROUP BY用于按照指定的列或表达式进行分组,返回每个分组的聚合值。
•HAVING用于在GROUP BY的结果上进行筛选,只返回满足特定条件的分组。
2. HAVING和GROUP BY的用法2.1 GROUP BY语句GROUP BY语句用于对查询结果进行分组,并对每个分组应用聚合函数,例如SUM、MAX、MIN等。
下面是GROUP BY的语法示例:SELECT列1, 列2, ..., 列n, 聚合函数FROM表名WHERE条件GROUP BY列1, 列2, ..., 列n;2.2 HAVING语句HAVING语句是在GROUP BY的基础上进行筛选的。
它可以用于对每个分组的聚合结果进行过滤或条件判断。
下面是HAVING的语法示例:SELECT列1, 列2, ..., 列n, 聚合函数FROM表名WHERE条件GROUP BY列1, 列2, ..., 列nHAVING条件;2.3 HAVING和WHERE的区别HAVING和WHERE都可以用于对记录进行筛选,但二者有一些区别:•WHERE用于在分组前对记录进行筛选,不管是否存在GROUP BY语句,都会生效。
•HAVING用于在分组后对分组结果进行筛选,仅在使用GROUP BY语句时才会生效。
3. HAVING和GROUP BY的案例分析3.1 示例数据为了更好地理解HAVING和GROUP BY的用法,我们先创建一个示例数据表,并插入一些数据。
CREATE TABLE employee (id INT,name VARCHAR(50),department VARCHAR(50),salary INT);INSERT INTO employee (id, name, department, salary) VALUES (1, 'John', 'HR', 5 000);INSERT INTO employee (id, name, department, salary) VALUES (2, 'Jane', 'IT', 6 000);INSERT INTO employee (id, name, department, salary) VALUES (3, 'Mike', 'HR', 4 000);INSERT INTO employee (id, name, department, salary) VALUES (4, 'Emily', 'IT', 5500);INSERT INTO employee (id, name, department, salary) VALUES (5, 'Chris', 'Finan ce', 7000);INSERT INTO employee (id, name, department, salary) VALUES (6, 'Sarah', 'Finan ce', 4500);3.2 分组计数假设我们需要根据部门统计每个部门的员工数量,并且只返回部门人数大于等于2的部门。
Oracle分析函数与分组关键字的用法以下是我以前工作中做报表常用的几个函数,在此分享一下,希望对大家有帮助。
(一)分析函数●row_numberPurposeROW_NUMBER is an analytic function. It assigns a unique number to each row to which it is applied (either each row in the partition or each row returned by the query), in the ordered sequence of rows specified in the order_by_clause, beginning with 1.You cannot use ROW_NUMBER or any other analytic function for expr. That is, you can use other built-in function expressions for expr, but you cannot nest analytic functions.按部门分组后根据工资排序,序号rn特征:连续、无并列select t.*, row_number() over(partitionby t.deptno orderby sal desc) rn from emp t;●rankPurposeRANK calculates the rank of a value in a group of values. Rows with equal values for the ranking criteria receive the same rank. Oracle then adds the number of tied rows to the tied rank to calculate the next rank. Therefore, the ranks may not be consecutive numbers.•As an aggregate function, RANK calculates the rank of a hypothetical row identified by the arguments of the function with respect to a given sort specification. The arguments of the function must all evaluate to constant expressions within each aggregate group, because they identify a single row within each group. The constant argument expressions and the expressions in the ORDER BY clause of the aggregate match by position. Therefore, the number of arguments must be the same and their types must be compatible.As an analytic function, RANK computes the rank of each row returned from a query with respect to the other rows returned by the query, based on the values of the value_exprs in the order_by_clause.按部门分组后根据工资排序,序号rn特征:不连续、有并列select t.*, rank() over(partitionby t.deptno orderby sal desc) rn from emp t;dense_rankPurposeDENSE_RANK computes the rank of a row in an ordered group of rows. The ranks are consecutive integers beginning with 1. The largest rank value is the number of unique values returned by the query. Rank values are not skipped in the event of ties. Rows with equal values for the ranking criteria receive the same rank.As an aggregate function, DENSE_RANK calculates the dense rank of a hypothetical row identified by the arguments of the function with respect to a given sort specification. The arguments of the function must all evaluate to constant expressions within each aggregate group, because they identify a single row within each group. The constant argument expressions and the expressions in the order_by_clause of the aggregate match by position. Therefore, the number of arguments must be the same and types must be compatible.As an analytic function, DENSE_RANK computes the rank of each row returned from a query with respect to the other rows, based on the values of the value_exprs in the order_by_clause.按部门分组后根据工资排序,序号rn特征:连续、有并列select t.*, dense_rank() over(partitionby t.deptno orderby sal desc) rn from emp t;(二)分组函数根据查询结果观察三者的区别,grouping sets用起来更灵活。
oracle数据库group by用法(一)Oracle数据库Group By用法详解在Oracle数据库中,GROUP BY是一种常用的查询语句,用于按照指定的列对查询结果进行分组。
通过GROUP BY语句,可以对分组后的数据进行聚合运算,如计算总和、平均值等。
本文将介绍一些常见的GROUP BY用法,并对其进行详细解释。
1. 基本用法下面是GROUP BY的基本语法:SELECT column_name(s)FROM table_nameWHERE conditionGROUP BY column_name(s)•column_name(s):指定要分组的列名,可以是一个或多个列名。
•table_name:指定要操作的表名。
•condition:查询条件,可选。
2. 分组查询通过GROUP BY可以实现对指定列的分组查询,例如:SELECT department, COUNT(*)FROM employeesGROUP BY department;上述示例中,我们通过GROUP BY将employees表中的数据按照department列进行分组,并计算每个部门的员工数量。
3. 加入聚合函数GROUP BY常常和聚合函数一起使用,以进行进一步的统计和计算。
下面是一个示例:SELECT department, AVG(salary)FROM employeesGROUP BY department;上述示例中,我们按照department列进行分组,并计算每个部门的平均工资。
4. 多个分组列GROUP BY语句支持多个分组列的定义,即可以按照多个列对查询结果进行分组。
示例如下:SELECT department, gender, AVG(salary)FROM employeesGROUP BY department, gender;上述示例中,我们按照department和gender两列进行分组,并计算每个部门和性别的平均工资。
Oracle分析函数RANK(),ROW_NUMBER(),LAG()等的使⽤⽅法ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY COL1 ORDER BY COL2)表⽰根据COL1分组,在分组内部根据 COL2排序⽽这个值就表⽰每组内部排序后的顺序编号(组内连续的唯⼀的)RANK() 类似,不过RANK 排序的时候跟派名次⼀样,可以并列2个第⼀名之后是第3名LAG 表⽰分组排序后,组内后⾯⼀条记录减前⾯⼀条记录的差,第⼀条可返回 NULLBTW: EXPERT ONE ON ONE 上讲的最详细,还有很多相关特性,⽂档看起来⽐较费劲row_number()和rownum差不多,功能更强⼀点(可以在各个分组内从1开时排序)rank()是跳跃排序,有两个第⼆名时接下来就是第四名(同样是在各个分组内)dense_rank()l是连续排序,有两个第⼆名时仍然跟着第三名。
相⽐之下row_number是没有重复值的lag(arg1,arg2,arg3):arg1是从其他⾏返回的表达式arg2是希望检索的当前⾏分区的偏移量。
是⼀个正的偏移量,时⼀个往回检索以前的⾏的数⽬。
arg3是在arg2表⽰的数⽬超出了分组的范围时返回的值。
SQL> set pagesize 100;SQL> select rownum from emp;ROWNUM----------1234567891011121314已选择14⾏。
已⽤时间: 00: 00: 00.10SQL> select deptno,row_number() over(partition by deptno order by sal) from emp order by deptno;DEPTNO ROW_NUMBER()OVER(PARTITIONBYDEPTNOORDERBYSAL)---------- ---------------------------------------------10 12320 1234530 123456已选择14⾏。
Oracle分析函数与分组关键字的用法
以下是我以前工作中做报表常用的几个函数,在此分享一下,希望对大家有帮助。
(一)分析函数
●row_number
Purpose
ROW_NUMBER is an analytic function. It assigns a unique number to each row to which it is applied (either each row in the partition or each row returned by the query), in the ordered sequence of rows specified in the order_by_clause, beginning with 1.
You cannot use ROW_NUMBER or any other analytic function for expr. That is, you can use other built-in function expressions for expr, but you cannot nest analytic functions.
按部门分组后根据工资排序,序号rn特征:连续、无并列
select t.*, row_number() over(partition
by t.deptno order
by sal desc) rn from emp t;
●rank
Purpose
RANK calculates the rank of a value in a group of values. Rows with equal values for the ranking criteria receive the same rank. Oracle then adds the number of tied rows to the tied rank to calculate the next rank. Therefore, the ranks may not be consecutive numbers.
•
As an aggregate function, RANK calculates the rank of a hypothetical row identified by the arguments of the function with respect to a given sort specification. The arguments of the function must all evaluate to constant expressions within each aggregate group, because they identify a single row within each group. The constant argument expressions and the expressions in the ORDER BY clause of the aggregate match by position. Therefore, the number of arguments must be the same and their types must be compatible.
As an analytic function, RANK computes the rank of each row returned from a query with respect to the other rows returned by the query, based on the values of the value_exprs in the order_by_clause.
按部门分组后根据工资排序,序号rn特征:不连续、有并列
select t.*, rank() over(partition
by t.deptno order
by sal desc) rn from emp t;
dense_rank
Purpose
DENSE_RANK computes the rank of a row in an ordered group of rows. The ranks are consecutive integers beginning with 1. The largest rank value is the number of unique values returned by the query. Rank values are not skipped in the event of ties. Rows with equal values for the ranking criteria receive the same rank.
As an aggregate function, DENSE_RANK calculates the dense rank of a hypothetical row identified by the arguments of the function with respect to a given sort specification. The arguments of the function must all evaluate to constant expressions within each aggregate group, because they identify a single row within each group. The constant argument expressions and the expressions in the order_by_clause of the aggregate match by position. Therefore, the number of arguments must be the same and types must be compatible.
As an analytic function, DENSE_RANK computes the rank of each row returned from a query with respect to the other rows, based on the values of the value_exprs in the order_by_clause.
按部门分组后根据工资排序,序号rn特征:连续、有并列
select t.*, dense_rank() over(partition
by t.deptno order
by sal desc) rn from emp t;
(二)分组函数
根据查询结果观察三者的区别,grouping sets用起来更灵活。
友情提示:grouping(expr)函数仅用于分组中,如果expr为null 返回1
●Rollup
select decode(grouping(dept.dname), 1, '总计', dept.dname) dname, decode(grouping(emp.job), 1, '小计', emp.job) job,
sum(sal),
avg(sal)
from emp, dept
where dept.deptno = emp.deptno
group by rollup(dept.dname, emp.job)
order by dname, job;
●Cube
select decode(grouping(dept.dname), 1, '所有部门', dept.dname) dname, nvl(emp.job, '小计') job,
sum(sal),
avg(sal)
from emp, dept
where dept.deptno = emp.deptno
group by cube(dept.dname, emp.job)
order by dname, job;
grouping sets
select dept.dname, emp. job, sum(sal), avg(sal)
from emp, dept
where dept.deptno = emp.deptno
group by grouping sets((dept.dname, emp.job), dept.dname, emp.job) order by dname, job;。