教案layoutofabusinessletter
- 格式:doc
- 大小:98.50 KB
- 文档页数:14


外贸函电课程教案课题:Basis of Business Correspondence课时:周次:授课日期:地点:授课方式及手段:Lecturing, Task-based approach, Questioning, Discussion …教学目标:After studying this part, the students are able to:A. Learn the structure and the format of business letters, envelopes and s;B. Learn basic principles of effective business letter-writing;C. Know the designing of a standardized letter and an ;D. Master the correct arrangement of various parts of a business letter and ;E. Practice writing business letters, s and envelopes.教学重难点:A. the Layout of Business LettersB. the Structures of Business Letters教学过程与容:Part 1 The Structure of Business LettersStep One warm-up1)Have you written a letter in Chinese? Who do you write to? How do you write?2) Have you written a let ter in English? What’s the differences between Chinese letter writing and English letter-writing?3)Do you think letter writing is very important in business? Why?Come to the introduction:The letter is a common communication medium. There are several reasons:1) A letter establishes a record that can be used for later reference2) Distance can be spanned at relatively small cost3) Routine matters can be completed efficiently with the help of letter forms.Step Two PresentationA. The layout of a business letter (商业信函的布局)Business letters will involve the following parts:(1) Letter Head /Heading Section (信头)(2)Reference Number and date Line(案号和日期)(3)Inside Address/the inside name and address (封地址)(4)Attention Line (注意事项)(5)Salutation /The Greeting (称呼)(6)the Subject Line /Subject-matter/the Subject Heading (事由)(7)the Body of the Letter (正文)(8)complimentary close/ the Closing (结束礼词/结尾敬语)(9)signature section / the signature (签署)(10)The identification Initials /the Reference Notation (经办人代号/主办人代号)(11)The Postscript—P.S. (再启)(12)The Enclosure (附件)(13)The Carbon Copy/ Carbon Copy Notation (抄送说明)Business letters usually consist of :seven standard parts (标准/规部分)six optional parts (任选部分)B.Explanation of letter parts (信的各部分的解释)Step Three consolidationAsk them to recognize all parts in a business letter. Using the given letter, find out each part of a business letter:Step Four HomeworkLearn the Chinese version of all parts in a business letter and its explanation.Part IIStep One RevisionAsk the students to say out the Chinese version of all parts in a business letter and its explanation.Step Two Presentation1.Ask the students the following questions:1)If you want to write a Chinese letter, what style do you usually follow?2)If you want to write a business letter in English, what style do you usually use?2. Formats of business letters (商业信函的版式/开本)(vide P3—5)Give the students three forms of letters, ask them to try to find out the differences of them:a. the indented form (缩进式)b. full blocked form (完全平头式)c. modified blocked form (改良平头式)Step Three Envelope addressing(信封的写法)注意:1) The three important requirements of envelope addressing are accuracy, clearness and good appearance. Here are two examples, which show, respectively, the indented form of address and the blocked form of address.2) Generally speaking, sender’s name and address are written at the left-hand top of the envelope, while receiver’s name and address are centered on the cover of the envelope so as to leave ample space for stamps and postmark. If sender’s name and address do not appear on the cover, it can be written on the back of the envelope.3) Mode of sending letter on lower left-hand side: 在信封左下角上的的类别registered (挂号信) Par Avion (法语)= By Airmail (航空信) confidential (绝密信, 信) Not bend (勿折) Express Mail (快件) Secret (秘信) Book Post (读书) Private (亲收) Printed Matter (印刷品) Personal (个人)4)If a letter is to be taken from you by someone to the addressee, put his name below the addressee’s with the following words in front of it:Politeness of / Kindness of/ Through the Courtesy of /Per Kindness of/ Forwarded by/ Per Favor of/ ByFavor of/ With Favor of/ Favored byDr. William Brown (收信人)Kindness of Prof. Water Snow (带信人)如果这封信是由他人代交的话,代交人的名字写在实际的收信人名字的下面,并在代交人名字前面加Kindness of/ Politeness of, 不需写地址。




Chapter One Business Letter Writing第1章商务书信写作●Time AllotmentIntroduction (15 mins)Outline (10 mins)Main Points ( 45 mins)Supplements ( 15 mins)Afterclass Exercise ( 5 mins)●Outline:第1节商务书信的结构和格式Structure结构:1、The Heading 信头2、The Inside Address 封内地址3、The Salutation 称呼4、The Subject Heading or Caption 事由5、The Opening Sentences 开头语6、The Body of the Letter 信的正文7、The Closing Sentences 结束语8、The Complimentary Close 结尾礼词9、The Signature 签名10、The Enclosure 附件11、Postscripts 再启Layout格式:1、Indended Style 缩行式2、Block Style 齐头式/平头式3、Modified Block Style 改良的齐头式/平头式4、Semi-block Style with Indended Paragraphs 混合式Section Two Superscription第2节角标Section Three Dissimilarities in Letter Writing第3节英美书信的不同写法Supplyment 补充:Some Useful Sentences on Opening Sentences and Closing Sentences. 开头语和结束语常用例句。
●Main PointsSection One The Structure and Layout of a Business Letter第1节商务书信的结构和格式Structure 结构1.The Heading 信头2.The Inside Address 封内地址3.The Salutation 称呼4.The Subject Heading or Caption 事由5.The Opening Sentences 开头语6.The Body of the Letter 信的正文7.The Closing Sentences 结束语8.The Complimentary Close 结尾礼词9.The Signature 签名10.The Enclosure 附件11.Postscripts 再启Layout 格式1.Indended Style 缩行式2.Block Style 齐头式/平头式3.Modified Block Style 改良的齐头式/平头式4.emi-block Style with Indended Paragraphs 混合式Section Three Dissimilarities in Letter Writing第3节英美书信的不同写法1. 英式的书信格式是缩行式或混合式,而美式则是绝对平头式或改良平头。

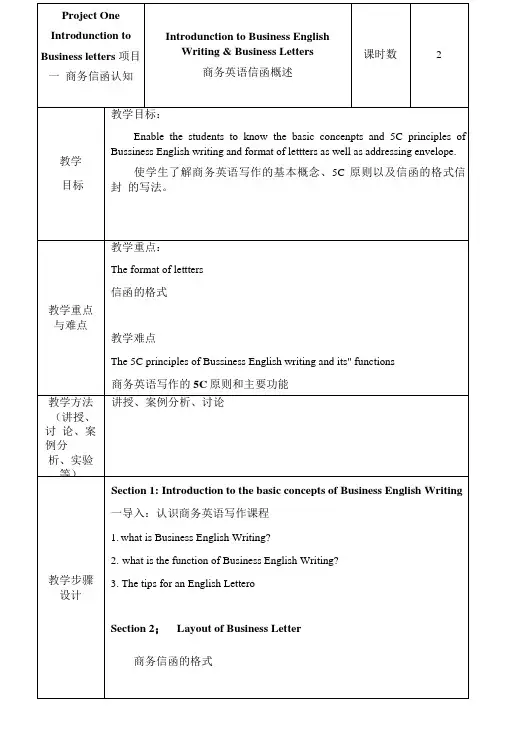
项目一交易磋商一、教学目标1.了解外贸函电的目的及作用。
2.了解“询盘”相关的基本商务知识、写作要求和内容要点3.分析信例总结并掌握函电格式的构成。
4.了解“发盘”相关的基本商务知识、写作要求和内容要点。
5.了解“还盘”相关的基本商务知识、写作要求和内容要点6.了解“建立业务关系”相关的基本商务知识、写作要求和内容要点。
7.了解“包装”相关的基本商务知识、写作要求和内容要点。
二、课时分配本项目共6个任务,安排12课时。
三、教学重点在本项目中,我们通过我国一家外贸公司与国外公司在业务磋商方面的信件往来,来掌握该项目的基本知识;会用学到的相关格式和内容表达,独立完成该环节的信件书写,并学会相关的词组句子、重要表达、实践知识等。
理解“建立业务关系”函电书写的内容、格式、步骤以及典型的表达。
理解“询盘”函电书写的内容、格式、步骤以及典型的表达,理解“发盘”函电书写的内容、格式、步骤,以及典型的表达, 理解“还盘”函电书写的内容、格式、步骤,以及典型的表达。
四、教学难点熟悉函电写作的7C原则。
掌握“还盘”的信件书写,结合格式、步骤、内容等方面,完成信件书写。
掌握“包装”的信件书写,结合格式、步骤、内容等方面,完成信件书写。
掌握“建立业务关系”的信件书写,结合格式、步骤、内容等方面,完成信件书写。
掌握“发盘”的信件书写,结合格式、步骤、内容等方面,完成信件书写。
掌握“询盘”的信件书写,结合格式、步骤、内容等方面,完成信件书写;五、教学内容任务一建立业务关系任务描述:在该任务中,练习者要从一名外贸公司出口部门业务员的身份出发,以“建立业务关系”为主题,运用下文中所学到的相关格式和内容表达,独立完成一份写给对方公司的信件。
知识储备I. The Purpose and Functions of Business LettersThe purposes of communication are to obtain complete understanding between the parties involved,and elicit the responses required. Generally speaking, the functions of a business letter are to ask for or to convey business information, to make or to accept an offer, to deal with matters concerning various businesses.Usually, there are certain essential requirements for a good business letter, which can be summed up in the Seven Cs, i.e. Completeness,Concreteness,Clearness/Clarity,Conciseness,Courtesy,Consideration, Correctness. These Cs often go hand-in-hand.II. The Basic Parts of Business LettersSee the letter first and find out how many parts are included in this letter:Guangdong Foreign Trade Development Corp.779 East Dongfeng Road,Guangzhou, ChinaCable Address: 5527 GFTDC Telex: 44388 GFTDC CNSeptember 15, 2010H. J. Wilkinson & Co. Ltd.245 Lombart Street,Lagos, NigeriaDear Sirs,We learned the name of your company from the Bank of China, Guangzhou /Guangzhou Branch of Bank of China.We are specialized in exporting the Chinese light industrial products, which enjoy good reputation in the world market for a long time.Enclosed please find a catalogue for your reference, and we look forward to entering into business relationship with you.Anticipate your early reply.Yours Sincerely,Liu MingLiu MingSales Manager of Export DepartmentIn sequential order of completion, a business letter basically consists of the following 13 parts.(7 of the 13 parts are basic and necessary.)(1) Letterhead(信头)As the first and most obvious part of a business letter,the letterhead expresses a company’s personality. It helps to form one’s impression of the writer’s firm. Styles vary considerably, but they all give similar information and include the essential particulars about the writer — name, address, zip-code, telephone number, telegram fax number and e-mail address of the company. It is usually designed and printed in the center or on the left margin at the top of the page. (2) Reference Number(参考号/发文编号)The reference number is generally used as a useful indication for filing and consulting for both sides, so it must be easily seen. It mayinclude a file number, a contract number, an L/C number or the initials of the signer and the typist’s initials. If you find the reference number in the incoming letter you need to take the form as “your ref.” and “our ref.” in your reply. The position of the reference number is often one or two lines below the letterhead.(3) Date(日期)Every letter should be dated. Never send out a letter without a date. If you are giving information, such as shipping or delivery or appointment dates, it is vital that the date should be correct. The position of the date is often one or two lines below the reference number or letterhead (if there is no reference number).September 8, 2007 — American form8th September, 2007 — British form(4) Inside Name and Address(信内地址)It consists of the name and address of the receiver. It appears exactly the same way as on the envelope. Inside name and address are always put at the left margin at least two lines below the date.Ms. Sarah Davis姓名The Sales Manager职务The Space Engineering Co.,Ltd. 公司名830 W. Lauridsen Boulevard 小地址Port Angeles, WA 98363大地址USA国家名(5) Salutation(称呼)The salutation is the polite greeting with which a letter begins. It should be placed two lines below the inside address. There are many forms of salutation in a business letter. The customary greeting in a business letter is “Dear Mr./Mrs./Ms./Miss ...(姓)”,“Dear Sirs”or “Dear Madam or Sir”.(6) Subject Line(事由标题)The subject line is often inserted between the salutation and the body of the letter. The subject line helps to attract attention to the topic of the letter. It is especially useful if two companies have a lot of correspondence with each other on a variety of subjects, as it immediately tells what the letter is about. It is also useful as a guide for filing. It can begin with or without “Re:” or “Subject:”. Sometimes, you can see the subject line is underlined. e.g.Re: Sewing MachinesSubject: Sewing MachinesSewing Machines(7) Body of the Letter(正文)This part contains the actual message of the letter. It should begin two lines below the subject line or two lines below the salutation if there is no subject line. Usually, it is divided into three parts: opening,actual message and closing. The body of the letter should be carefully planned and paragraphed. The opening is to give the reason of writing and often refers to previous correspondence. The actual message is to specify the writer’s concrete purposes, requirements and wishes. The closing is to express thanks and anticipations for future actions or plans. Sometimes the closing may be used to sum up the message and to suggest the writer’s requirements to the receiver.(8) Complimentary Close(结尾敬语/套语)The complimentary close is merely a polite way of bringing a letter to a close. It is usually placed two or four lines below the last line of the body of the letter. There are many different complementary closes that show respect, but it should match the salutation. The most common sets of salutation and the complimentary close are as follows:Yours faithfully,Yours sincerely,(9) Signature(落款签字)The signature is the signed name or mark of the person writing the letter or that of the firm he or she represents. All letters must be signed and a letter should be signed by hand, and in ink. Unsigned letters have no authority and a letter “signed” with a rubber stamp is a form of discourtesy. Usually, the name of the signer is typed below the signature because many handwritten signatures are illegible, and then followed by his or her job title or position. If the writer represents a certain institute, the name of the institute will be printed above the signature.e.g.The Overseas Co., Ltd. institute(Signature)signatureJohn Bellname of the signerGeneral Manager, Sales Department position(10) Reference Notation(经办人代号)Sometimes, the reference notation, which is also understood as identification mark,can also be placed two lines below the typed signature. The reference notation usually shows only the initials of the typist, but it can also be made up of the initials of the person who dictated the letter. The initials of the dictator are usually in capital letters. The two sets are separated by a colon or a slant, such as for Bill Clinton (manager) and Nancy Brown (secretary). The following examples are acceptable forms of the reference notation:BC: nbBC/nb(11) Enclosure Notation(附件)If any documents such as catalogues, price lists, order, copies of fax are sent with a letter, it is necessary to add enclosure notationto remind the receiver. The enclosure notation is usually placed two lines below the signature at the left margin. The marking may be in any of the following ways:Enclosure: 3 copies of ...Encl. 3 cataloguesEnc. 1 invoice Encls: as stated(12) Carbon Copy Notation(抄送)When copies of the letter are sent to others, you need to use the carbon copy notation below any enclosure notation at the left margin. It is used to show that the letter has been sent to someone relevant. The marking may be in any of the following ways, c.c./cc/bcc—blind carbon copy. e.g.c.c. Mr. J. Cooper(13) Postscript(附言/注)A postscript is used to emphasize a point to which the writer wants to draw the reader’s attention. Sometimes, the postscript can be added by some executives in pen and ink for the purpose of adding a personal touch to their typewritten letter. The marking word of postscript is P.S. and should be placed at least two lines below any other notation and flushed with the left margin.Of all the 13 parts, seven are standard, principal and necessary. The seven parts include the letterhead, the inside name and address,the date, the salutation, the body of the letter, the complimentary close and the signature. The others are optional parts which may be unnecessary for some letters and chosen as the writer wishes. Some letters may contain one or more of the optional parts, depending on the different situation of each writing requirement.注: The Basic Layout of Business Letters1. Letterhead(信头)*2. Reference Number(参考号/发文编号)3. Date(日期)*4. Inside Name and Address(信内地址)*5. Salutation(称呼)*6. Subject Line(事由标题)7. Body of the Letter(正文)*8. Complimentary Close(结尾敬语/套语) *9. Signature(落款签字)*10. Reference Notation(经办人代号)11. Enclosure Notation(附件)12. Carbon Copy Notation(抄送)13. Postscript(附言/注)注:带“*”号为信件必备部分。


Unit one The Layout of Business Letters商务信函的格式一、Introduction本课程是国际贸易专业高年级的核心业务课程之一,是一门将英语与外贸业务相结合的课程。
通过介绍外贸实务中各种英文业务函件、电传和传真以及其它方式的写作格式、商业术语和各种不同的表达方法,并通过介绍对外贸易各环节的具体做法,使学生在提高英语水平的同时,熟练掌握对外贸易业务中常用的基本术语及表达技能,培养和提高学生的外贸业务工作能力。
1、学习内容2、学习方法二、Essentials of Business Letter-writing三、The Layout of Business Letter首先,请大家看样例信,一封标准的商业书信有哪些部分组成,归纳一下有两大部分:一是必需部分;二是可供选择部分。
(一)Standard PartsStandard Parts就是一封商业书信必不可少的组成部分,一封商业书信缺了其中任何一项,就不能称其为一封格式完整的信;同时,这些项目也是普通英文社交书信的组成部分。
A standard business letter consists of seven parts: (1) the letterhead,(2) the inside address,(3) the date,(4) the salutation,(5) the body of the letter,(6) the complimentary close, and (7) the signature.1、The Letterhead信头It includes the essential particulars about the writer’s name, posta l address and zip-code, telephone and facsimile numbers.顾名思义,信头就是位于一封信开头的那部分,即位于信纸顶端的那部分。

商务英语写作教案Business English WritingChapter 1 Business English Writing: Classifications and Principles●Business Communication●Writing Principles——8C PrinciplesI.Business Communication●What is Communication?●What is Business Communication?●Objectives of Business Communication●Classification of Business Communication1. Definition of CommunicationCommunication is the sending and receiving of information, ideas, attitudes and emotions―either verbal or nonverbal―that produce a response between people. 2. Business communication is the communication which takes place in the business field.3. Objectives of Business Communication1) To be understood exactly as we intended;2) To secure a desired response to what we communicate;3) To build up and develop goodwill between the sender and receiver of the message.4.Classification of Communication1) Downward Communication is from superiors to subordinates, from bosses to employees, from decision-makers to operating personnel.2) Upward Communication is the opposite flow of downward communication. Messages from the bottom move up through many stages until they reach the top.3) Horizontal Communication is the exchange flows between or among organizational units on the same hierarchical level.internal horizontal communication external horizontal communicationII. Writing Principles——8C Principles●Completeness●Concreteness●Conciseness●Clarity●Correctness●Consideration●Courtesy●Creditability1. CompletenessA complete letter should include whatever details are needed to produce the response you want.To achieve the Completeness, you should consider the following suggestions:1) Try to list all essential points in your letter;2) V olunteer something extra which, you think, may be of some use to your reader now or in the future;3) Offer alternatives you are able to give. Maybe you will get a new transaction.4) Check for the five Ws (who, what, where, when and why) and the H (how).2. Concreteness1) Use specific rather than general language to give specific information.Compare:This copier saves you both money and time.BH200 Copier makes 60 copies a minute at a cost of one fen a copy.But sometimes generalizing is necessary or preferable for being diplomatic.Compare:Our firm sells clothes for women weighing over 200 pounds.Our firm sells fashions for women with generous figures.2) Use concrete rather than abstract words when possible.Compare:I am interested in your vehicle.I am interested in your brown 1997 Ford Sedan.3. ConcisenessConciseness is saying what you want to say in the fewest words possible without sacrificing the other C qualities.1) Avoid wordy expressions and statementse.g. “I wish to take this opportunity to thank you for your sincere cooperation.”“Thank you for your sincere cooperation.”2) Avoid triteness.3) Eliminate redundancy (repetition of language elements)Mr. Li will be here at 8 A.M. in the morning.4) Leave out irrelevant materialCompare:If you had not informed us of damage so promptly, we should/would be unable to do anything for you. However, in your case, we are glad to tell you…Because you were so prompt in informing us of the damage, we are glad to tell you…4. Clarity1) Write on the level of the reader’s u nderstanding.2) Avoid ambiguityAn ambiguous word is one that has more than one meaning in the same context. Compare:The L/C must reach us for arranging shipment not later than 8 October.The L/C must reach us not later than 8 October for arranging shipment3) Avoid needless jargon (special language in one field of business)If possible, try to include examples, illustrations or other visual aids for clarity, such as pictures, diagrams, simple tables, samples and printed materials.5. CorrectnessCorrectness means a message must be united (grammatically and mechanically correct) and coherent (logically organized).To achieve this aim, the writer should:1) Use the right level of language (formal, informal, substandard).2) Include accurate facts, figures and words.3) Maintain acceptable writing mechanics or structure.6. ConsiderationConsideration means to think of the reader first and write from the “you-attitude”. “You-attitude” is a style of writing that looks at things from the reader’s poi nt of view, emphasizing what the reader wants to know, respecting the reader’s intelligence and protecting the reader’s ego (self-esteem).1) To emphasize the “you” and “your” and deemphasize the “I” and ”my” in positive situations and to avoid the word “you” in negative situations and use passive words/verbs and impersonal expressions to avoid assigning blame.Compare:We provide health insurance to all employees.You receive health insurance as a full-time P&G employee.Compare:You made no allowance for inflation in your estimate.No allowance for inflation has been made in this estimate.This estimate makes no allowance for inflation.2) To emphasize the reader’s interests rather than your own concerns.Compare:The large scale of sales of our products will make our company more profitable.You will find that our product will sell rapidly and afford you a profit margin.3) To emphasize what you can do, not what you cannot do .Compare:We won’t be able to send you the brochure this month.We will send you the brochure next month.Try to use positive words to replace negative words.Improve:We hope you won’t be dissatisfied with the new range of our electric products.4) To express your sincere desire to be of help.7. CourtesyA courteous message, like a courteous person, is polite, considerate and emphathic. Courtesy is a major contributor to goodwill. By courtesy we mean treating people with respect and friendly human concern. It can be a key factor influencing our success in the business world.1) Be polite.2) Be equal to each otherCompare:How can anyone question our ability to repay the loan when we are such a large, reputable firm?Our qualification for the loan is a well established credit rating.3) Avoid mistrustCompare:We have received your letter in which you claimed that ten tea sets were damaged in shipment.We have noticed in your letter that a damage to ten tea sets in shipment was found.4) Avoid angerCompare:You obviously made a mistake by sending me the wrong goods.Thank you for your prompt delivery. However, the goods reached us were not the ones we ordered.8. CreditabilityCreditability means being honest and fair in all our business dealings.The observation of the 7Cs will ensure the achievement of last C– Creditability. Before doing business with others, one businessman should learn how to be a man. HomeworkRead the text and answer the question:How do you analyze the 8Cs from the pragmatic perspective?Chapter 2 The Structure and Layout of a Business LetterI. StructureII. LayoutIII. HomeworkI. Structure1. Standard Parts of Business Letters2. Optional Parts of Business LettersI. Structure1. Standard Parts of the Business Letter(1) Letter-head 信头It is the heading at the top of a letter and shows where the letter comes from. It usually consists of the name, address, telephone number and fax number and also the company logo, web site, e-mail address, etc.The letter-head is usually printed on the company’s stationery.e.g. OMNICORP INTERNATIONAL17 Bunder Hill RoadShrewsbury MA 01545Tel 03-345 6788 Fax 34567(2) Date 日期The format of date differs from country to country.e.g.①Friday, 10th, March 2006;②10th (or 10) March, 2006(U.S. military, Europe, Latin America);③March 10th(or 10), 2006(American business);④10, 3, 2006 or 10/3/2006(causing confusion).(3) Inside name and address 封内姓名和地址It should duplicate the address on the envelope. It should also include the reader’sname, title and address and is placed at the left margin about 2 or 3 spaces below the date and above the salutation.(4) Salutation 称呼It is your friendly greeting to the reader and agrees with the inside address.*Gentlemen (American) / Dear Sirs (British)/ Ladies and Gentlemen (Customary Salutations to a firm)*Dear Mr. /Mrs./ Miss / Ms (marital status unknown)*Dear +first nameIt is addressed to an individual you know well.*Dear Sir & Dear MadamThey are used in formal and impersonal situations or when you do not know the reader’s name.*Dear Director (Manager, Supervisor, Owner, Department Head)Neutral titles are preferred by many office managers.*Dear CustomerIt is used for messages that omit an inside address as in sales letters or announcements to more than one person.(5) Body 主体The body is the message and the most important part. It is difficult to discuss how to write in a few words because there are many purposes of letter writing. But do remember 7C Principles.(6) Complimentary close 礼貌结束语It is a polite way of closing the letter. It must agree with the salutation in the degree of formality.*Formal 正式Dear Sir / Gentlemen ——— Faithfully yours /Yours faithfullyLadies & Gentlemen ———Yours very truly (very truly yours, your truly)—no longer popular*Semi-formal 半正式Sincerely yours or yours sincerely(very popular between businessmen who have already established a business contact with each other)Cordially yours or Very cordially yours (used when you may or may not know the reader well, but wish him to feel the relationship is friendly).*Informal 非正式Dear David ——→sincerely, cordially, best regards, take care, thanks(7) Signature 签名Every business letter must be signed. It usually includes three or four parts:①the name of the company,②the signature of the writer,③the typed name④the business title.Page 37 Examples2) Optional Parts of the Business Letter(1) Reference 参考号The reference may include a file number or departmental code or the initials of the signer of the letter to be followed by the typist’s initials.e.g. Our ref: Dep. B/4LW/PB 524;KLM: tr orTR;KL Morning—tr;K.L Morning: trK.L. Morning: TR/tr (Identification Marks) 识别标记(2) Attention Line 经办It is used to direct the letter to a specific person or department when the company name is used in the addressee line. It is usually placed between inside address and the salutation.e.g. Attention: Purchasing Manager.(3) Subject Line 事由It helps both the writer and the reader identify the subject matter,e.g. Subject: Order No. 123;Re: Invoice No. 123;(4) Enclosure Notation 附件It tells the receiver that something is included in the envelope along with the letter. It also reminds the sender and the reader of checking for enclosures.(4) Enclosure Notation 附件e.g. Enclosure: Sales Contract;Enc. 3: Sales Contract;Commercial Invoice;Bill of LadingEncl. 3Enclosures 33 Enclosures:(5) Copy Notation 抄送It indicates a copy of the letter is being used to some other business people.It is placed below the signature at the left margin.●cc: (carbon copy) xc: (Xerox copy)●pc: (photo copy) c: (copy)e.g. cc: Mr. Taylor(6) Postscript 附言When you finish the letter and happen to think of something else, you may add it at the end of the letter.P.S. (p.s.; PS): ***If there are two things, use P.P.S. But this is a poor/bad habit and should be avoided.II. Letter style (Layout)1. Indented style (缩格式/ 传统格式)Page 422. Full block form齐头式This form begins each line at the left. This is the fastest to type because typists do not have to set and use tab stops for indenting. Page 433. Modified block style改良齐头式It is currently one of the most popular styles. To most readers, this style isappealing because it achieves the best visual balance on the page.The letterhead, date, complimentary close and signature are just to the right of the center. Page 444. Modified block style with indented paragraphs 混合式(Semi-block style)Many business letters use this style. Although the full block style is widely used, the indented style is also popular, probably because its paragraphs are indented in the same way of books, newspapers and magazines. Page 45Homework1. Give the names of the parts in the letter on Page 43.2. Study the forms of envelope addressing by yourself.3. Translate the sentences into English on Page 54.Chapter 4 Credit Inquiry and Establishing Business Relations●Letters of credit inquiry●Letters of establishing business relationsI. Credit inquiry——a kind of consultancy letter●Consultancy is the business of offering specialist professional advice including market research, credit standing investigation, market trend research and other services providing business information.●Consultancy service is usually provided by banks or professional consulting companies or individuals. As a business person, you should learn to write a consultancy letter to seek needed information.●In international business, an exporter may ask his new customer to give the name of his bank(er) or the name of firms which the customer has previously dealt as a reference.●Reference:1) a piece of written information about sb’s character, ability, etc. 证明书,证明材料2) a person who provides such information. 资信证明人●There are two kinds of reference: ba nks’ (bankers’) reference—banks银行证明人and trade reference—companies商业证明人.How to Write a Consultancy Letter for Credit Standing1. The name of the company to be investigated and why you are writing to the receiver.e.g. 玛丽兰公司提出要当我公司的代理,销售我们的缝纫机,并介绍我公司向贵行了解该公司的信用、业务能力和声誉的详细情况。
Layout of A Business LetterClearness 清楚Conciseness 简洁Courtesy 礼貌1.Letter Head 信头信头一般是事先印就的,它表示发信人的公司行号名称和地址。
此外还包括电话号码、电报挂号、专用电码(Code)、电传和传真号码以及经营的业务范围。
信头下面还可印有编号(Reference No),编号又可分为你方编号和我方编号。
假如信头中未印有你方编号,可把编号作为信的标题,或在信的开头引用对方来信的编号。
这样可使对方易于查对,并确保信件能送至你所要送达的人。
2.Date 日期日期应在距信头三至六行处。
缩行式的信,日期一般打在信头下的右上角;顶行式的信则打在左上角。
日期可按“日、月、年”的次序排,也可按“月、日、年”的次序排;数字可用基数字或序数字,如:3ed November, 2006 或3 November, 2006或November 3ed, 2006 或November 3, 2006注意不要缩写月份,需全部写出。
并且避免用数字表示,如3/11/2006,这样很容易造成误解。
因为英国习惯按日、月、年次序打印日期,因此3/11/2006被认为是11月3日;而美国习惯是按月、日、年打印日期,因此这一日期被认为是3月11日。
3.Inside Name and Address 封内行名和地址这是指收信人的行名和地址,一般应距日期两行,打在左边。
但有时政府机构所发的信则在信末的左下端。
英文信函的地址一般包含下列四部分:(a)门牌号码和街(路)名。
(b)城市。
(c)县、州(省)名和邮政编码(Post Code 或Zip Code)。
(d)国名。
“Messrs”是“Mr.”的复数形式。
在商业信函中,“Messrs”一字作为对公司的尊称,应用很普遍,但应注意只有在该公司的名称由人的姓名所组成时,才能使用,如:Messrs. John Smith & Co.Messrs. Black & White Co.但在下列情况下,即使公司名称是由人的姓名所组成,也不应加”Messrs”:(a)写个公司中某一个人的信 e. g. Mr. Charles Snow(b)非人称的公司名称 e. g. China Chemicals Co.(c)公司名称中已包括其职衔 e. g. Dr. Haris & Co.(d)公司名称前有定冠词”The” e. g. The Wells Machinery Co.4. Salutation 称呼每封业务信函开头必有称呼。
第1课商业书信的撰写Business Letter Writing教学目的要求:了解业务信函的撰写原则;掌握业务信函的布局(结构),七个部分7C 原则;掌握信封的写法。
教学重点与难点:商业信函时应注意的要点,商业信函书信的组成部分及格式教学时数:共计2学时(其中理论课2学时,实验课学时,习题课学时,讨论课学时)教学内容与方法:(要求内容充实;方法与手段合适,包括举例讲解、多媒体讲解、模型讲解、实物讲解、挂图讲解、音像讲解或板书内容及内容时间分配等。
)1.1Writing Principles of business Letters商业书信的撰写原则要写好业务信函,应掌握7个“C”原则1.1.1 Clearness (Clarity)清楚意思表达明确,要注意:(一)避免用词错误:(二)注意词语所放的位置:(三)注意句子的结构:a.explain yourself clearly;b.avoiding ambiguous sentences and needless jargon;c.statements in well-constructed sentences and paragraphs;1.1.2 Conciseness 简洁(一)避免废话连篇(二)避免不必要的重复(三)短句、单词的运用a.in the fewest possible words;b.briefly but completely;Example1(answers):Thank you for your information in your letter dated 5th August 1999.We are very interested in your tape recorders, It will be highly appreciated if you could send us photographs and a price list of the same.Looking forward to hearing from you soon.sincerely yours,1.1.3 Courtesy 礼貌语言要有礼且谦虚,及时地回信也是礼貌的表现。
外贸函电课程教案课题:Basis of Business Correspondence课时:周次:授课日期:地点:授课方式及手段:Lecturing, Task-based approach, Questioning, Discussion …教学目标:After studying this part, the students are able to:A. Learn the structure and the format of business letters, envelopes and e-mails;B. Learn basic principles of effective business letter-writing;C. Know the designing of a standardized letter and an e-mail;D. Master the correct arrangement of various parts of a business letter and e-mail;E. Practice writing business letters, e-mails and envelopes.教学重难点:A. the Layout of Business LettersB. the Structures of Business Letters教学过程与内容:Part 1 The Structure of Business LettersStep One warm-up1)Have you written a letter in Chinese Who do you write to How do you write2) Have you written a letter in English What’s the differences between Chinese letter writing and English letter-writing3)Do you think letter writing is very important in business WhyCome to the introduction:The letter is a common communication medium. There are several reasons:1) A letter establishes a record that can be used for later reference2) Distance can be spanned at relatively small cost3) Routine matters can be completed efficiently with the help of letter forms.Step Two PresentationA. The layout of a business letter (商业信函的布局)Business letters will involve the following parts:(1) Letter Head /Heading Section (信头)(2)Reference Number and date Line(案号和日期)(3)Inside Address/the inside name and address (封内地址)(4)Attention Line (注意事项)(5)Salutation /The Greeting (称呼)(6)the Subject Line /Subject-matter/the Subject Heading (事由)(7)the Body of the Letter (正文)(8)complimentary close/ the Closing (结束礼词/结尾敬语)(9)signature section / the signature (签署)(10)The identification Initials /the Reference Notation (经办人代号/主办人代号)(11)The Postscript—. (再启)(12)The Enclosure (附件)(13)The Carbon Copy/ Carbon Copy Notation (抄送说明)Business letters usually consist of :seven standard parts (标准/规范部分)six optional parts (任选部分)B.Explanation of letter parts (信的各部分的解释)Step Three consolidationAsk them to recognize all parts in a business letter. Using the given letter, find out each part of a business letter:Step Four HomeworkLearn the Chinese version of all parts in a business letter and its explanation.Part IIStep One RevisionAsk the students to say out the Chinese version of all parts in a business letter and its explanation.Step Two Presentationthe students the following questions:1)If you want to write a Chinese letter, what style do you usually follow2)If you want to write a business letter in English, what style do you usually use2. Formats of business letters (商业信函的版式/开本)(vide P3—5)Give the students three forms of letters, ask them to try to find out the differences of them:a. the indented form (缩进式)b. full blocked form (完全平头式)c. modified blocked form (改良平头式)Step Three Envelope addressing(信封的写法)注意:1) The three important requirements of envelope addressing are accuracy, clearness and good appearance. Here are two examples, which show, respectively, the indented form of address and the blocked form of address.2) Generally speaking, sender’s name and address are written at the le ft-hand top of the envelope, while receiver’s name and address are centered on the cover of the envelope so as to leave ample space for stamps and postmark. If sender’s name and address do not appear on the cover, it can be written on the back of the envelope.3) Mode of sending letter on lower left-hand side: 在信封左下角上的邮件的类别registered (挂号信) Par Avion (法语)= By Airmail (航空信) confidential (绝密信, 机密信) Not bend (勿折) Express Mail (快件) Secret (秘信) Book Post (读书邮件) Private (亲收) Printed Matter (印刷品) Personal (个人)4)If a letter is to be taken from you by someone to the addressee, put his name below the addressee’s with the following words in front of it:Politeness of / Kindness of/ Through the Courtesy of /Per Kindness of/ Forwarded by/ PerFavor of/ By Favor of/ With Favor of/ Favored byDr. William Brown (收信人)Kindness of Prof. Water Snow (带信人)如果这封信是由他人代交的话,代交人的名字写在实际的收信人名字的下面,并在代交人名字前面加Kindness of/ Politeness of, 不需写地址。
5)When a letter is mailed to a third person who is bound (必须)to pass it onto the addressee, write the third person’s name down below the addressee’s with the words “care of”(由…转交) (c/o) in front of it.Mr. Park Davis (收信人)c/o Mr. Harold Wood (转信人)318 Doswell AvenuePort Atkinson, WisconsinThe United States of America如果这封信是转交的话,转交人的名字写在实际收信人名字的下面,并在前面加 care of / 或c/o ,并写转交人的地址。