数据库英文课件
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:82.00 KB
- 文档页数:45









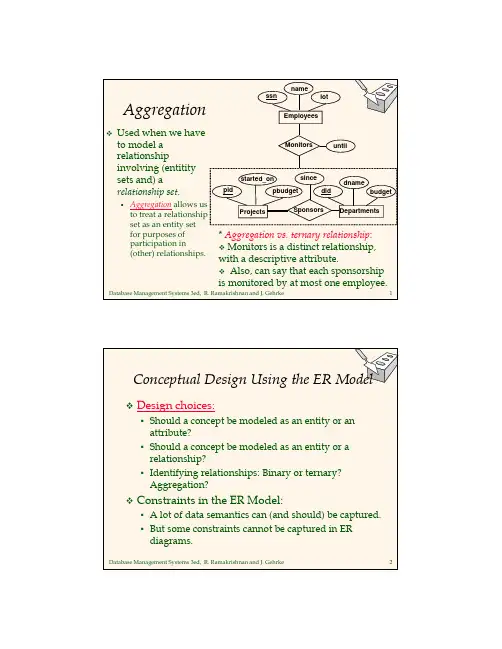

Database Principles and Applications IntroductionThe purpose of this document is to provide an overview of database principles and their applications. The document will discuss the fundamental concepts of databases, including data models, relational databases, and various database management systems. It will also explore the practical applications of databases in different industries and highlight their significance in modern data-driven environments.Table of Contents1.Data Models2.Relational Databases3.Database Management Systems4.Database Applications5.Conclusion1. Data ModelsData models serve as the foundation for organizing and representing data in a structured manner. They define the structure, relationships, and constraints of the data. There are several types of data models, including:•Hierarchical Model: Represents data in a tree-like structure with parent-child relationships.•Network Model: Represents data using a graph structure, allowing more complex relationships.•Relational Model: Represents data as tables or relations, with rows and columns.•Object-Oriented Model: Represents data as objects, with attributes and methods.•Entity-Relationship Model: Represents data using entities, attributes, and relationships.2. Relational DatabasesRelational databases are based on the relational model, which organizes data into tables, each with its own columns and rows. The relationships between tables are defined using primary and foreign keys. Key concepts in relational databases include:•Tables: Organized collections of data, with each column representinga specific attribute and each row representing a record.•Primary Key: A unique identifier for each record in a table.•Foreign Key: A field in one table that refers to the primary key in another table, establishing a relationship between the two.•Normalization: The process of organizing data to eliminate redundancy and improve data integrity.•SQL: Structured Query Language used for managing and querying relational databases.3. Database Management SystemsA Database Management System (DBMS) is software that allows users to create, manage, and manipulate databases. It provides an interface to interact with the underlying database and includes features such as:•Data Definition Language (DDL): Allows users to create, modify, and delete database structures, tables, and constraints.•Data Manipulation Language (DML): Enables users to insert, update, delete, and retrieve data from a database.•Transaction Management: Ensures the integrity and consistency of database operations.•Security: Provides mechanisms for authentication, authorization, and access control.•Query Optimization: Automatically optimizes queries for better performance.Some popular DBMSs include Oracle, MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, and PostgreSQL.4. Database ApplicationsDatabases have various applications across industries, playing a crucial role in managing and analyzing large amounts of data. Here are a few examples of database applications:•E-commerce: Databases are used to store product information, customer data, and manage orders.•Healthcare: Databases store patient records, medical history, and facilitate efficient healthcare management.•Finance: Databases are used for storing financial transactions, managing accounts, and processing payments.•Education: Databases manage student records, course information, and enable online learning platforms.•Logistics: Databases help in tracking inventory, managing supply chains, and optimizing logistics operations.The applications of databases are diverse and extend to almost every industry that deals with data management and analysis.ConclusionDatabase principles and applications are essential in modern data-driven environments. Understanding data models, relational databases, and database management systems is crucial for effective data organization and retrieval. The practical applications of databases span across industries and demonstrate their significance in today’s digital world. By leveraging databases, organizations can efficiently manage and analyze vast amounts of data, enabling informed decision-making and improving overall efficiency.。