最新英语(教)专业语言与应用语言学试题、答案及评分标准
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:17.56 KB
- 文档页数:12

英语新课标教师考试试题一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 英语新课标中提倡的课堂教学模式是:A. 教师主导B. 学生中心C. 传统讲授D. 自主学习答案:B2. 新课标要求教师在教学中应注重培养学生的:A. 应试技巧B. 语言知识C. 跨文化交际能力D. 语法运用能力答案:C3. 英语新课标中,学生应达到的最低语言技能水平是:A. 基础水平B. 初级水平C. 中级水平D. 高级水平答案:A4. 教师在设计教学活动时,应考虑的首要因素是:A. 教学内容B. 教学目标C. 学生兴趣D. 教学资源答案:B5. 英语新课标中,教师应如何对待学生的错误?A. 立即纠正B. 忽略不计C. 鼓励学生自我纠正D. 严厉批评答案:C6. 新课标鼓励教师使用的教学方法是:A. 传统讲授法B. 任务型教学法C. 翻译法D. 语法翻译法答案:B7. 英语新课标中,教师应如何评估学生的语言能力?A. 通过单一的笔试B. 通过口试和笔试C. 通过学生自我评价D. 通过教师主观判断答案:B8. 新课标中,教师应如何促进学生的自主学习?A. 提供充足的学习资源B. 制定严格的学习计划C. 限制学生的课外活动D. 要求学生完成大量作业答案:A9. 英语新课标提倡的课堂氛围是:A. 竞争性的B. 合作性的C. 压抑性的D. 随意性的答案:B10. 新课标中,教师应如何对待学生的个体差异?A. 忽视差异B. 强调统一标准C. 因材施教D. 惩罚落后学生答案:C二、填空题(每题1分,共10分)1. 英语新课标强调学生应具备的四个基本语言技能是听、说、读、__________。
答案:写2. 新课标中,教师应鼓励学生通过__________来提高语言实际运用能力。
答案:实践3. 英语新课标提倡的课堂教学活动应以__________为基础。
答案:学生经验4. 新课标中,教师应通过__________来激发学生的学习兴趣。
答案:多样化教学方法5. 英语新课标中,教师应培养学生的__________意识。

语言学考试题及答案英语一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 语言学是研究语言的科学,其主要研究对象是:A. 语言的起源B. 语言的结构C. 语言的演变D. 语言的运用答案:B2. 语音学是语言学的一个分支,它主要研究:A. 语言的社会功能B. 语言的物理属性C. 语言的语法结构D. 语言的语义内容答案:B3. 下列哪项是语义学的研究范畴?A. 语音的产生B. 词汇的意义C. 句子的构造D. 语言的演变答案:B4. 语言的语法规则包括:A. 词汇的选择B. 句子的构造C. 语调的运用D. 语言的起源答案:B5. 社会语言学主要关注语言与:A. 个人心理B. 社会结构C. 语言的演变D. 文化传承答案:B6. 心理语言学研究的是:A. 语言与社会的关系B. 语言与心理的关系C. 语言与文化的关系D. 语言与物理的关系答案:B7. 语言的产生和发展与人类的哪项能力密切相关?A. 逻辑思维B. 语言模仿C. 抽象思维D. 社会交往答案:D8. 语言的方言是指:A. 同一语言的不同变体B. 不同语言之间的相似性C. 语言的起源D. 语言的演变答案:A9. 语言的标准化是指:A. 语言的简化B. 语言的统一C. 语言的规范化D. 语言的创新答案:C10. 语言的借词是指:A. 从其他语言借用的词汇B. 同一语言内部的词汇C. 语言的起源D. 语言的演变答案:A二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. 语言学的分支包括语音学、语法学、语义学、__________和心理语言学。
答案:社会语言学2. 语言的最小意义单位是__________。
答案:语素3. 语言的音位是__________的最小单位。
答案:语音4. 语言的词汇包括基本词汇和__________。
答案:派生词汇5. 语言的句法结构包括词法和__________。
答案:句法6. 语言的语用学研究的是语言的__________。
答案:使用7. 语言的方言差异可能导致__________。

语言学真题及答案解析是一门探究语言的科学,它研究语言的结构、功能、历史、变化以及与社会、心理等诸多领域的关系。
本文将通过真题及答案解析的形式,探讨的一些重要方面。
1. 语音学语音学是的基础分支,研究语音的发音、音素、音节等。
下面是一道真题:“在英语中,/congratulations/这个词的音节数为几个?”答案解析:根据英语的发音规则,/cong/为第一个音节,/rat/为第二个音节,/u/为第三个音节,/la/为第四个音节,/ti/为第五个音节,/ons/为第六个音节,总共为六个音节。
2. 语言分类学语言分类学研究各种语言之间的共性和差异。
以下是一道真题:“下面哪个语言家族具有最多的使用者?”答案解析:根据最新的统计数据,汉语族是使用人口最多的语言家族,全球有将近14亿人使用汉语,超过其他任何语言家族。
3. 语义学语义学研究语言单位的意义,包括词义、短语义以及句义。
以下是一道真题:“以下哪个词语属于反义词?”答案解析:反义词是指意义上相对相反的词语。
根据选项,只有“上升”和“下降”是反义词关系,因此答案为“下降”。
4. 语用学语用学研究语言在实际交流中的使用和功能。
以下是一道真题:“在‘你能帮我一个忙吗?’这句话中,‘能’是表示请求还是表示能力?”答案解析:从句子的语境来看,“能”在这里是表示请求的意思,请求对方帮助。
因此,答案为“表示请求”。
5. 句法学句法学研究语言单位之间的组合和句子的结构。
以下是一道真题:“以下哪个是并列句?”答案解析:并列句是由并列连词连接的两个或多个主谓完整的句子,选项中只有D项“我喜欢音乐,我也喜欢电影。
”符合这个定义。
6. 语言变化语言是动态变化的,随着时间的推移,语言会发生变化。
以下是一道真题:“以下哪种语音变化是通过声调产生的?”答案解析:声调是语音的一种音高变化,在某些语言中,声调的变化可以改变词义。
因此,声调是一种通过声调产生的语音变化。
通过以上的真题及答案解析,我们可以看到的多个方面。

语⾔与应⽤语⾔学考试样卷及参考答案《语⾔与应⽤语⾔学》考试样卷及参考答案xam for Language and Linguistics: A Workbook《语⾔与语⾔学:实⽤⼿册》试卷You have 120 minutes to finish this exam.The exam consists of four sections:Section 1 Checking content awareness of the course (15 items, 30%)Section 2 Checking understanding of some general principles of language and linguistics (8 items, 24%)Section 3 Checking understanding of some specific aspects of language and linguistics (8 items, 24%)Section 4 Checking analytic application (2 items, 22%)This is a close exam. You are not allowed to consult any reference books or with other examinees.Always read the instructions very carefully before you do the exam items.Section 1 Checking content awareness of the course (15 items, 30%) (这部分正式考试时只选择其中的三种题型来⽤,每种题型有5个⼩题,共计15 个⼩题。
样题中每部分只提供了两个⼩题作为参考。
)Complete the following items by providing the information based on the course book.1. Activity 2 of Unit 3 is entitled “An Anatomy of the Word”. The keyissue dealt with is.2. According to the author, the best way to study linguistics is.There is one error in each of the following statements. Identify it and correct it.1. The course book discusses altogether six general functions of language.2. People seldom perform illocutionary acts in their daily activities.Choose those words or phrases that best complete the missing items. Note that there are more words or phrases than necessary.1. Language is as old as .2. It is wrong to assume that are the persons so named.3. is only one of the ways that represent language.4. Most of speech sounds are produced by . Only afew are uttered by ingressive airflow.5. Words do not stand for things through consciously madeby man.Match a proper definition from Column B with the term in ColumnA.1 politeness a) related to the thing it stands for by resemblance2 speech acts b) the study of the relationship between a person’s hand writing and his character3 an icon c) the strategies employed by language users to protect their own and their addressees’ face4 graphology d) related to the thing it stands by agreement and convention5 sign e) the positive image or impression of oneself that one shows or intends to show to the other participantsf) the ‘things one does withwords’ at the structural level of the sentenceClassify the following words into the appropriate groups to which they belong.1 a material world -2 a subjective world -3 a symbolic world -Decide whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Writea T if the statement istrue and an F if it is false.1. Child language acquisition is only mentioned in Unit 9.2. Different cultures have different views on language, e.g. onword magic, on language power,and so on.Chose the most appropriate word or phrase to complete each of the following statements.1. Unit 8 Language in Society discusses the relation between identity,including all of the following EXCEPT .a) national b) gender c) status d) culture2. Which of the following is used as a hedge in the sentence, “Sayingsomething will often, or even normally, produce certain consequential effects upon the feelings, thoughts, or actions of the audience, or of the speaker or of other person s.”a) saying b) certain c) consequential d) effectsSection 2 Checking understanding of some general principles oflanguage and linguistics (8 items, 24%)Give short answers to the following questions. You can answer them in your own words, or by using the exact expressions from the course book. Use examples to illustrate your point where necessary.1. What is the difference between a local dialect and Putonghua?2. What are the two general components that saying something has? Give an example to illustrate your pointSection 3 Checking understanding of some specific aspects of language and linguistics (8 items, 24%)Provide brief analysis to the questions below, using the linguistic knowledge you have learned in the course.1 The diagram shows the part of speech organ. Replace the letters (A, B,C and D) with technical terms given below. Note that there are moreterms than necessary.alphabet, alveolar ridge, uvula, hard palate, soft meat, soft palateABCD2. The diagram is an analysis of the word eat. The letters (A and B) indicate the missing analytic elements. Complete the analysis.Note that the letters (A, B, …I) indicate the slots that you have to fill in. Ignore the slots without any letters.4. Identify the illocutionary acts in the following talk exchanges.Situation:甲’s car hit⼄’s car at the rear. 警(i.e. traffic warden, 交通警) was talking to the two drivers.警:还要给你画现场吗?甲:你们看吧。

英语新课标教师考试答案一、选择题(每题2分,共10题,满分20分)1. 根据英语新课标,教师在教学过程中应该注重培养学生的哪种能力?A. 应试能力B. 语言运用能力C. 文化适应能力D. 记忆能力答案:B2. 新课标中提到的“四维目标”包括哪些方面?A. 知识与技能、过程与方法、情感态度与价值观B. 知识与技能、过程与方法、情感态度与文化意识C. 知识与技能、过程与方法、情感态度与价值观、文化意识D. 知识与技能、过程与方法、情感态度与价值观、思维品质答案:C3. 英语新课标强调的“核心素养”包括哪些内容?A. 语言能力、文化意识、思维品质、学习能力B. 语言能力、文化意识、思维品质、情感态度C. 语言能力、文化意识、思维品质、学习策略D. 语言能力、文化意识、思维品质、情感态度与价值观答案:A4. 教师在设计教学活动时,应该遵循什么原则?A. 以教师为中心B. 以学生为中心C. 以教材为中心D. 以考试为中心答案:B5. 根据新课标,教师在教学中应该如何处理语言知识与语言技能的关系?A. 只重视语言知识,忽略语言技能B. 只重视语言技能,忽略语言知识C. 语言知识与语言技能同等重要,相互促进D. 根据学生情况,灵活处理答案:C二、填空题(每题2分,共5题,满分10分)1. 英语新课标要求教师在教学中要注重培养学生的______意识。
答案:跨文化2. 新课标提倡的“任务型教学”是指教师设计具有______的教学活动,让学生在完成任务的过程中学习语言。
答案:实际意义3. 教师在教学中应该根据学生的______和______,合理选择和使用教学资源。
答案:认知水平;学习风格4. 英语新课标强调教师要培养学生的______能力,以适应未来社会的发展。
答案:自主学习5. 教师在教学中应该鼓励学生进行______和______,以提高他们的语言运用能力。
答案:合作学习;探究学习三、简答题(每题10分,共2题,满分20分)1. 请简述英语新课标中提到的“以学生为中心”的教学理念。
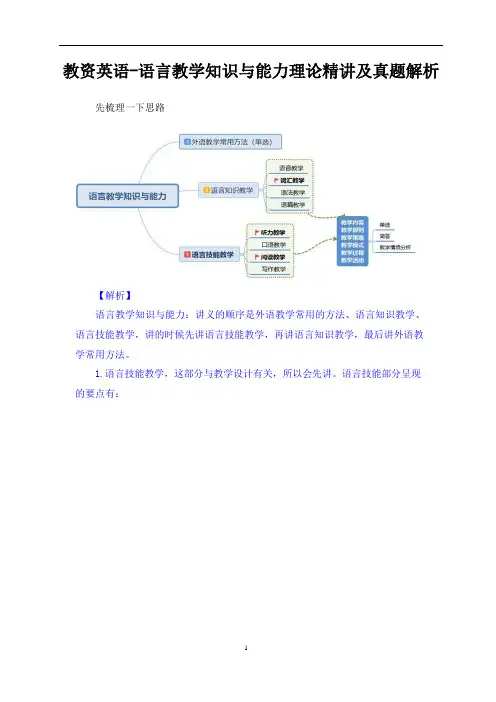
教资英语-语言教学知识与能力理论精讲及真题解析先梳理一下思路【解析】语言教学知识与能力:讲义的顺序是外语教学常用的方法、语言知识教学、语言技能教学,讲的时候先讲语言技能教学,再讲语言知识教学,最后讲外语教学常用方法。
1.语言技能教学,这部分与教学设计有关,所以会先讲。
语言技能部分呈现的要点有:(1)教学内容:对应的就是知识目标或者技能目标,大家比较熟悉。
(2)教学原则:比如“我是一个有原则的人”,说明这个人知道该做什么,不该做什么。
对于教学原则,就是注意事项,应该做什么,不应该做什么,更多的强调应该做什么。
(3)教学策略:方法、方案,有哪些方法可以实施。
(4)教学模式:有PPP 模式和PWP 模式,还有一些课型有另外的模式,主要以阅读课和听说课为主要的考查方向,这里会详细的讲解。
(5)教学过程和教学活动:对应的就是已经讲解过的教学设计部分的内容。
2.语言知识教学:之前讲PPP 和PWP 已经铺垫过,知识型涉及到语音、词汇、语法教学,这个部分初高中没有考过对应的课型,但是单选和简答、教学情境分析考查过。
3.外语教学常用的教学方法:单选题备考,也可以考主观答题,比如案例分析题。
4.首先学习第一个部分,语言技能教学:听力教学考查重点Part 1听力技能教学P146一、教学内容二、教学原则三、教学模式四、教学过程五、教学策略六、听力基本技能及教学活动【解析】听力技能教学:讲义 146 页。
呈现六个方面,老师在课件上用不同的颜色标注清楚了,绿色代表已经学习过的知识,比如教学过程听力如何安排已经讲过了;黑色部分虽然没有明确讲,但是没有那么重要;标红色的是讲解过程的重点,听力教学中重点讲教学原则和教学模式。
一、听力--教学内容了解P146听力技能教学的内容主要包括听力知识和听力技能。
(一)听力知识听力知识包括语音、听力策略、语言的使用等。
(二)听力技能听力技能包括辨别、识别交流的指示、听大意、听细节等。
【解析】听力教学内容:主要包括听力知识和听力技能。

英语语言学试卷精粹及答案(10套题)有答案的第一部分选择题41、Explain how the inventory of sounds can change, giving some examples inEnglish for illustration.42、Briefly discuss the individual factors which affect the acquisition ofa second language.英语语言学试题(2)五、论述题(每小题10分,共20分)36.Paraphrase each of the following sentences in two different ways to show the syntactic rules account for the ambiguity of sentences.(1)The shooting of the hunters might be terrible.(2)He saw young men and women present.(3)They were surprised at the president's appointment.37.Decide the meaning of the following affixes and give each affix two examples.re-un-anti-super--wise-itis-ize-age英语语言学试题(3)Ⅴ.Answer the following questions.(10%×2=20%)41.Explain with examples the three notions of phone, phoneme and allophone, and also how they are related.英语语言学试题(5)五、论述题(第41、42小题各7分,第43小题6分,共20分)41. Under what conditions will two sounds be assigned to the same phoneme?42. For the following sentence, draw a tree diagram to reveal its underlying structure.The girl ate the orange.43. Study the passage taken from Shakespeare’s HAMLET below carefully and identify every difference in expression between Elizabethan and Modern English that is evident.King: Where is Polonius?Hamlet: In heaven, Send thither to see.If your messenger find him not there,seek him i’ the other place yourself.But indeed, if you find him not withinthis month, you shall nose him as yougo up the stairs into the lobby.Act IV, Scene iii英语语言学试题(6)41. The phonological features that occur above the level of individual sounds are called suprasegmental features.Discuss the main suprasegmental features, illustrating with examples how they function in the distinction of meaning.42. Explain and give examples to show in what way componential analysis is similar to the analysis of phonemes into distinctive features.英语语言学试题(7)五、论述题(每小题10分,共20分)1. Comment on the following conversation in terms of Grice’s Cooperative Principle:A: Where’ve you been?B: Out.2. Analyse the following words and show how many morphemes each of them contains:specialize , indisputable, individualistic, downfall, unexceptionableness, ungentlemanliness(每个语素0. 5分)英语语言学试题(8)语言学试题)41.Why do we say tree diagrams are more advantageous and informative than linear structure in analyzing the constituent relationship among linguistic elements? Support your statement with examples.42.Describe the process of language perception, comprehension and production英语语言学试题(9)语言学试题及参考答案41. Explain sociological triggers for language change by giving a typical example in the history of English.42. Explain briefly the four main individual learnerfactors that affect a learner's acquisition of a second language.语言学试题参考答案一、单项选择题(本大题共10小题,每小题2分,共20分)1、C2、C3、D4、D5、D6、B7、B8、C9、A 10、D二、填空题(本大题共10小题,每小题1分,共10分)11、knowledge12、bilabial13、morphology14、sentence15、complete16、representatives17、coinage18、delete19、critical20、interlanguage三、判断改错题(本大题共10小题,每小题2分,共20分)21、FActually modern linguistics lays more emphasis on the spoken form of language than the written form for a number of reasons.22、FVoicing distinguishes meaning in English but not in Chinese.23、FThe meaning of some compound words has nothing to do with the sum total of the meanings of their components, such as the compound "redcoat".24、FApart from S and C, they also refer to a word, or a phrase that performs a particular grammatical function.25、FDialectal synonyms can often be found not only in different regional dialects such as British English and American English but also within the variety itself. For example, within British English, "girl" is called "lassie" in Scottish dialect, and "liquor" is called "whishey" in Irish dialect.26、T27、T28、FThey have a fairly clear fairly clear functional differentiation, i.e. one language may be used in some domains, other language in other domains.29、FThe true statement is "According to the strong version of the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis, language determines speakers' perceptions and patterns their way of life"30、T四、名词解释题(本大题共10小题,每小题3分,共30分)31、One of the major defining features of human language. Human language consists of two levels. At the lower level, there are a limited number of sounds which are meaningless while at the higher level there are an unlimited number of combinations of these sounds. It is also known as double articulation.32、Linguistics that studies language over a period of time, also known as historical linguistics, e.g.the study of the Chinese language since the end of the Qing dynasty up to the present.33、A way to transcribe speech sounds. The basicprinciple is to use one letter to indicate one sound. It isgenerally used in dictionaries and language teaching textbooks.34、The rules that govern which affix can be added to what type of stem to form a new word, e.g.-ly can be added to a noun to form an adjective.35、a rewrite rule that allows for the possible combinations of words to form phrases and sentences36、Relational opposites, a kind of antonyms, refer to pairs of words that exhibit the reversal of a relationship between the two items. For example, "husband" and "wife", "father" and "son" etc.37、Componential analysis is a way proposed by the structural semanticists to analyze word meaning. The approach is based upon the belief that the meaning of a word can be dissected into meaning components, called semantic features. For example, the word "man" is analyzed as comprising of +HUMAN,+ADULT,+ANIMATE,+MALE.38、Context is regarded as constituted by all kinds of knowledge assumed to be shared by the speaker and the hearer, For example, the knowledge of the language used and the knowledge of the world, including the general knowledge about the world and the specific knowledge about the situation in which linguistic communication is taking place.39、A euphemism is a mild, indirect or less offensive word or expression that replaces a taboo word or serves to avoid more direct wording that might be harsh, unpleasantly direct, or offensive, e.g. "pass away" for "die".40、Brain lateralization refers to the localization of cognitive and perceptual functions in a particular hemisphere of the brain. For example, the right hemisphere processes stimuli more holistically and the left hemisphere more analytically. In mostpeople, the left hemisphere has primary responsibility for language,while the right hemisphere controls visual and spatial skills.五、论述题(本大题共2小题,每小题10分,共20分)41、The inventory of sounds can change, and sound changes include changes in vowel sounds, sound loss, sound addition, and sound movement.1) Vowel sound change: English has undergone the systematic and regular change in the vowel sounds, known as the Great Vowel shift which occurred at the end of the Middle English period and which involved seven long, or tense vowels. These changes led to one of the major discrepancies between the phonemic representations of words and morphemes, i.e. between pronunciation and the spelling system of Modern English, e.g.five→/fi:v/(Middle English)→/faiv/(Modern English)2) Sound loss: Sounds can change by the loss of phonemes. In the history of English the velar fricative /x/ was lost. This sound existed in Old English, so "night" was pronounced as /nixt/, but in Modern English,its pronunciation is /nait/.3) Sound addition: Sound addition includes the gain or insertion of a sound. For example, the word leisure was borrowed from French, so the phoneme /3/ was added to the inventory of English sounds. A change that involves the insertion of a consonant or vowel sound to the middle of a word is known as epenthesis,e.g.spinle--spindle.4) Sound movement: Sound change as a result of sound movement known as metathesis involves a reversal in position of two adjoining sound segments. Metathesis is less common, butit does exist. In some dialects of English, for example, the word ask is pronounced /? ks/. Also, bridd ("bird") is an Old English word. When metathesis occurred to this word, the movement of /r/ sound to the right of the vowel sound resulted in its Modern English counterpart "bird".评分标准:满分为10分,总论及四小点各占2分。

语言学试题及答案英文1. 语言学是一门研究什么领域的学科?A. 人类语言B. 人类行为C. 人类文化D. 人类心理答案:A2. 请列举至少三种语言的类型。
答案:分析语言、综合语言、多词根语言。
3. 什么是音位学?A. 研究语言中意义的学科B. 研究语言中语法结构的学科C. 研究语言中声音系统的学科D. 研究语言中词汇的学科答案:C4. 下列哪项是语言学研究的主要分支?A. 社会语言学B. 物理化学C. 植物学D. 经济学答案:A5. 请解释“语言变异”的含义。
答案:语言变异指的是在不同地区、社会群体或个人之间,语言的发音、词汇、语法等方面存在的差异。
6. 什么是语用学?A. 研究语言如何被使用的学科B. 研究语言如何被创造的学科C. 研究语言如何被理解的学科D. 研究语言如何被翻译的学科答案:A7. 请列举两种语言的书写系统。
答案:表音文字(如英文)、表意文字(如汉字)。
8. 什么是语言的同化?A. 一种语言逐渐被另一种语言所替代B. 一种语言的词汇被另一种语言的词汇所替代C. 一种语言的语法结构被另一种语言的语法结构所替代D. 一种语言的发音系统被另一种语言的发音系统所替代答案:A9. 语言学中的“语料库”是什么?A. 语言学家收集的大量语言数据B. 语言学家进行实验的实验室C. 语言学家进行教学的教室D. 语言学家进行研究的图书馆答案:A10. 下列哪个术语与语言的演变无关?A. 语言演化B. 语言变迁C. 语言接触D. 语言创造答案:D。

应用语言学试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 应用语言学主要研究的领域是什么?A. 语言理论B. 语言教学C. 语言翻译D. 语言习得答案:B2. 下列哪项不是应用语言学的研究内容?A. 语言规划B. 语言测试C. 语言变异D. 语言哲学答案:D3. 应用语言学中的“应用”一词指的是什么?A. 理论的应用B. 实践的应用C. 两者都是D. 两者都不是答案:C4. 应用语言学的发展历程中,哪个时期被认为是现代应用语言学的开端?A. 20世纪初B. 20世纪50年代C. 20世纪70年代D. 20世纪90年代答案:B5. 在语言教学中,应用语言学关注的核心问题是什么?A. 语言形式B. 语言内容C. 学习者需求D. 教学方法答案:C6. 语言规划通常包括哪些方面?A. 语言选择B. 语言标准化C. 语言现代化D. 所有以上答案:D7. 语言测试的主要目的是什么?A. 评估语言能力B. 选拔人才C. 促进语言学习D. 所有以上答案:D8. 语言习得研究在应用语言学中的作用是什么?A. 提供教学理论基础B. 指导语言教学实践C. 两者都是D. 两者都不是答案:C9. 语言变异研究在应用语言学中的应用是什么?A. 了解语言多样性B. 促进语言理解C. 两者都是D. 两者都不是答案:C10. 语言翻译在应用语言学中的重要性体现在哪些方面?A. 文化交流B. 信息传递C. 两者都是D. 两者都不是答案:C二、简答题(每题10分,共30分)1. 简述应用语言学在语言教学中的应用。
答案:应用语言学在语言教学中的应用主要体现在教学方法的选择、教材的编写、教学评估以及学习者需求的分析等方面。
它关注如何将语言学理论应用于实际教学中,以提高教学效果和学习者的语言能力。
2. 描述语言规划的主要内容。
答案:语言规划的主要内容通常包括语言选择、语言标准化、语言现代化、语言保护和语言复兴等方面。
其目的是通过规划和政策制定,促进语言的统一、稳定和发展,以满足社会、经济和文化的需求。

英语语言学linian试题及答案英语语言学试题及答案1. 语言学的主要分支有哪些?答案:语言学的主要分支包括语音学、音系学、形态学、句法学、语义学、语用学、社会语言学、心理语言学、神经语言学、计算语言学等。
2. 请解释“语言习得”和“语言学习”的区别。
答案:语言习得是指儿童在成长过程中自然掌握母语的能力,而语言学习则是指在学校或其他正式环境中有意识地学习第二语言或外语。
3. 什么是语言的“深层结构”和“表层结构”?答案:深层结构是指句子的内在意义和逻辑关系,而表层结构则是指句子的外在形式,即我们实际听到或说出的句子。
4. 请列举至少三种不同的语言变异现象。
答案:语言变异现象包括地域变异(方言)、社会变异(社会方言)、时间变异(历史方言)等。
5. 什么是转换生成语法?答案:转换生成语法是由诺姆·乔姆斯基提出的语言学理论,它认为所有人类语言都遵循一套普遍的语法规则,而这些规则可以通过转换规则从深层结构转换到表层结构。
6. 请解释“语码转换”和“语码混合”的概念。
答案:语码转换是指在不同语言或方言之间切换使用,而语码混合则是指在同一句话中混合使用两种或两种以上的语言或方言。
7. 语言学中“语料库”的作用是什么?答案:语料库是语言学研究中用来收集和分析自然语言数据的大型数据库,它可以帮助研究者进行语言模式、语言变化和语言使用等方面的研究。
8. 请简述“语言相对性假设”。
答案:语言相对性假设,也称为萨丕尔-沃尔夫假设,认为一个人的思维方式受到其母语的影响,即语言的结构决定了思维的结构。
9. 什么是“语言的普遍语法”?答案:语言的普遍语法是指所有人类语言共有的一套基本语法规则,这些规则是语言能力的基础,由诺姆·乔姆斯基提出。
10. 请解释“语境”在语言交际中的作用。
答案:语境是指语言交际发生的环境,包括物理环境、社会环境和心理环境等。
语境对语言的理解和使用有重要影响,它可以帮助解释语言的模糊性,提供语言交流的背景信息。

二、概念辨析:1.本体语言学与应用语言学的异同:本体语言学主要研究语言本身,包括对语言事实的静态的和动态的描写,对语言规律的揭示和说明,以及在此基础上所总结的各种语言理论。
应用语言学是研究语言本体和本体语言学同有关方面发生关系的学科。
应用语言学不仅有利于语言应用本身,而且也有利于加深对语言本身的认识。
同时,应用语言学研究的是语言本体和本体语言学同应用方面交叉的部分。
理论语言学:一般把研究某种具体语言的语言学称为汉语语言学或英语语言学等等,把侧重理论探讨的称为理论语言学。
2.语言的兼并和转用:语言借用是指在文化接触和语言接触的过程中从其他语言中借入自己语言所需要的成分,包括语音、词汇和语法的借用。
语音的借用表现为增加新的音位和增加新的音位组合方式。
语言转用是一个民族或民族的部分人放弃使用本民族语言而转用另一民族语言的现象。
语言兼用:双语或多语是指某一语言社团(民族或国家)或个人同时使用两种或两种以上的语言。
包括社会双语和个人双语。
双语就是语言接触中的语言兼用现象,包括双语和多语。
对一个民族发展来讲,语言兼用是进步的表现。
3 ,洋泾浜和混合语:两者都属于语言接触的特殊形式,同时,在语言传播过程中势必与当地语言发生密切关系,放弃自身的特点,吸收其他语言的特点。
洋泾浜也叫皮钦语,是临时混合语,常常只是用于在不同的族群之间的临时交际,如经商所需要的彼此之间的沟通,只使用于有限的范围,使用时间通常也不长。
语汇比较贫乏,语音和语法都不太规范,如旧上海的洋泾浜语把“我不能”说成My no can,用英语的词和汉语的语法;将number one说得像“拿摩温”。
由于“先天不足”,它通常的存活时间都不长,有的可能只存在几年。
克里奥尔语(Creoles)是正式混合语,一般是从洋泾浜发展而来的。
如果洋泾浜因为种种原因得到了发展,语言混合的程度较深,时间较长,语汇不断增加,语法规则不断完善,被有的族群作为母语来学习和使用,或者获得官方语言的地位,就成为克里奥尔语。
对于外国语言学及应用语言学(英语教育方向)的入学考试,一般会考察以下几个方面的内容:
1. 英语语言能力:这是入学考试的重点部分,会考察学生的英语听、说、读、写、译等能力,包括对英语语法、词汇、句型、表达方式的掌握。
2. 语言学基础知识:入学考试会考察学生对语言学基础知识的掌握,如语音学、音系学、句法学、语义学、语用学等方面的知识。
3. 教育学基础知识:由于该专业属于教育学领域,入学考试也会考察学生对教育学基础知识的掌握,如教育心理学、课程与教学论、教育技术等方面的知识。
4. 综合素质:除了以上几个方面,入学考试还会考察学生的综合素质,如逻辑思维能力、分析问题能力、解决问题能力、团队协作能力等。
具体的考试形式和内容可能会因学校和专业的不同而有所差异,建议查看具体招生简章或咨询相关招生部门,获取更详细的信息。
英语语言学教程参考答案在英语语言学教程中,我们深入探讨了语言学的多个方面,包括语音学、语法学、语义学、语用学、社会语言学和心理语言学等。
以下是一些常见问题及其参考答案的概述。
一、语音学1. 问题:什么是音素?答案:音素是语言中最小的音位单位,能够区分词义。
例如,在英语中,/p/和/b/是两个不同的音素,因为它们可以改变词义,如“pat”和“bat”。
2. 问题:什么是元音和辅音?答案:元音是气流在口腔中不受阻碍时发出的声音,如英语中的/i:/(长音“ee”)。
辅音则是气流在口腔或喉部受到部分或完全阻碍时发出的声音,如/p/、/t/、/k/。
二、语法学1. 问题:什么是句子成分?答案:句子成分包括主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、补语等,它们共同构成句子的基本结构。
2. 问题:什么是时态和语态?答案:时态表示动作发生的时间,如过去时、现在时和将来时。
语态则表示动作的执行者和承受者之间的关系,如主动语态和被动语态。
三、语义学1. 问题:什么是词义?答案:词义是词在特定语境中所表达的意义。
它可以是直接的(字面意义)或隐喻的(比喻意义)。
2. 问题:什么是多义词和同形异义词?答案:多义词是一个词具有多个相关意义,如“bank”可以指银行或河岸。
同形异义词则是不同的词具有相同的拼写形式,但意义不同,如“bat”可以指球棒或蝙蝠。
四、语用学1. 问题:什么是言语行为?答案:言语行为是说话者通过语言实现的交际行为,如陈述、询问、请求、命令等。
2. 问题:什么是隐喻和转喻?答案:隐喻是一种将一个概念的属性应用到另一个概念上的修辞手法,如“时间是金钱”。
转喻则是用一个事物来代表与之相关的事物,如用“白宫”来指代美国政府。
五、社会语言学1. 问题:什么是方言和社会方言?答案:方言是某一地区或社会群体特有的语言变体。
社会方言是特定社会群体使用的语言形式,如青少年群体的俚语。
2. 问题:什么是语言变体和语言接触?答案:语言变体是语言在不同地区或社会群体中的不同表现形式。
英语语言应用试题及答案一、选择题(每题1分,共10分)1. The word "phenomenon" can be most closely associated with which of the following?A. EventB. FactC. IdeaD. Concept2. Which sentence is grammatically correct?A. She don't like to eat vegetables.B. She doesn't like eating vegetables.C. She don't likes eating vegetables.D. She doesn't likes to eat vegetables.3. Fill in the blank with the appropriate word to complete the sentence:"I have never seen such a beautiful _______."A. sceneryB. sceneC. viewD. sight4. What is the past tense of the verb "to lead"?A. LeadB. LedC. LeadsD. Leading5. Choose the correct option to complete the dialogue:- Where is the nearest subway station?- It's _______ the left of the library.A. onB. toC. atD. in6. Which of the following is a compound word?A. ClassroomB. FootballC. ComputerD. Bicycle7. The phrase "break a leg" is commonly used to:A. Encourage someone before a performance.B. Wish someone to have a broken leg.C. Ask someone to take a break.D. Warn someone to be careful.8. What is the comparative form of the adjective "big"?A. BiggerB. BigC. BigestD. More big9. In the sentence "He is the tallest boy in the class," the word "tallest" is:A. An adjectiveB. An adverbC. A nounD. A verb10. The word "unique" is best described as:A. UncommonB. UnusualC. One of a kindD. Rare二、填空题(每空1分,共10分)11. The _______ of the building is very impressive.(appearance)12. She _______ (was born) in 1995.13. The _______ (opposite) of "hot" is "cold."14. They _______ (agreed) to meet at the cafe tomorrow.15. The teacher asked the students to _______ (write) an essay on environmental protection.16. He _______ (not finish) his homework yet.17. The _______ (number) of the pages in this book is 300.18. She _______ (be) to Paris twice.19. The _______ (main) reason for his success is his hard work.20. The _______ (final) decision will be made by the committee.三、阅读理解(每题2分,共20分)Read the following passage and answer the questions.Passage:In recent years, the popularity of cycling as a form of exercise and transportation has increased significantly. Many cities have developed bike lanes to accommodate the growing number of cyclists. The benefits of cycling are numerous, including improved health, reduced traffic congestion, and lower carbon emissions. However, there are also challenges, such as safety concerns and the need for proper infrastructure.21. What has the popularity of cycling increased for?A. Exercise and transportationB. Health and environmentC. Traffic congestionD. Carbon emissions22. What have many cities done to accommodate cyclists?A. Reduced traffic congestionB. Lowered carbon emissionsC. Developed bike lanesD. Improved health23. Which of the following is NOT a benefit of cycling mentioned in the passage?A. Improved healthB. Reduced traffic congestionC. Lower carbon emissionsD. Increased safety24. What is one of the challenges mentioned in the passage?A. Lack of interest in cyclingB. Safety concernsC. Too many cyclistsD. High cost of bikes25. What does the passage suggest about the need for proper infrastructure?A. It is not necessary for cycling.B. It is important for the growth of cycling.C. It is a benefit of cycling.D. It is a challenge for non-cyclists.四、翻译题(每题3分,共15分)26. 请将下列句子翻译成英文:“这个城市的交通状况正在改善。
英语语言学试题3及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 在语言学中,研究语言结构的学科被称为:A. 社会语言学B. 心理语言学C. 结构语言学D. 应用语言学答案:C2. 语言中最小的意义单位是:A. 音素B. 词C. 语素D. 句子答案:C3. 下列哪项是语言的任意性特征?A. 语言的规则性B. 语言的创造性C. 语言的任意性D. 语言的稳定性答案:C4. 英语中,单词“cat”的词根是:A. catB. -catC. -cattD. ca-答案:A5. 语言的“经济性原则”指的是:A. 用最少的音位表达最多的意义B. 用最少的词汇表达最多的意义C. 用最少的句型表达最多的意义D. 用最少的语法规则表达最多的意义答案:A6. “Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for communication.” 这句话中,“arbitrary”一词的意思是:A. 任意的B. 必然的C. 相关的D. 必要的答案:A7. 语言学家乔姆斯基认为,人类天生具有:A. 语言能力B. 语言知识C. 语言习惯D. 语言技巧答案:A8. 语言的“双重艺术性”指的是:A. 语言的创造性和规范性B. 语言的任意性和规约性C. 语言的表达性和接收性D. 语言的描述性和规定性答案:B9. 下列哪个选项不是语言的功能?A. 信息传递B. 情感表达C. 社会控制D. 艺术创作答案:D10. 在英语中,单词“university”的词缀“uni-”表示:A. 一B. 多C. 不D. 再答案:A二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. 语言学的三个主要分支是语音学、__________和句法学。
答案:语法学2. 根据语言的起源,语言学可以分为历史语言学和__________语言学。
答案:比较3. 语言的“规约性”指的是语言符号的__________。
答案:约定性4. 在语言学中,研究语言在社会中的功能和影响的学科被称为__________语言学。
语言与应用试题及答案一、单项选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 语言是人类最重要的交际工具,以下哪项不是语言的功能?A. 表达思想B. 传递信息C. 娱乐消遣D. 记录历史答案:C2. 在语言学中,以下哪个术语指的是语言的音位系统?A. 语法B. 语义C. 语音D. 词汇答案:C3. 根据乔姆斯基的生成语法理论,语言的深层结构是指什么?A. 句子的表面形式B. 句子的深层意义C. 句子的生成规则D. 句子的语用功能答案:B4. 在翻译过程中,以下哪个原则强调的是忠实于原文?A. 信B. 达C. 雅D. 准答案:A5. 以下哪种语言现象不属于语言的变异?A. 方言B. 俚语C. 标准语D. 术语答案:C6. 语言的语用功能主要研究的是语言在实际使用中的什么?A. 语法结构B. 语音变化C. 交际效果D. 词汇选择答案:C7. 以下哪个选项是语言学研究的分支?A. 社会学B. 心理学C. 计算机科学D. 语音学答案:D8. 语言的词汇量增长最快的阶段通常是在哪个时期?A. 婴儿期B. 学龄前C. 青少年期D. 成年期答案:B9. 在语言教学中,以下哪种方法强调通过实践和使用语言来学习?A. 语法翻译法B. 直接法C. 听说法D. 交际法答案:D10. 以下哪种语言现象是语言的创新?A. 借用B. 混合C. 创造新词D. 语言退化答案:C二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. 语言的______功能是指语言能够表达情感和态度。
答案:表达2. 语言的______功能是指语言能够影响和改变现实。
答案:操作3. 在语言学中,______是指语言的最小意义单位。
答案:语素4. 语言的______是指语言的使用者对语言的理解和使用能力。
答案:能力5. 语言的______是指语言的使用者对语言的理解和使用习惯。
答案:习惯6. 在翻译中,______是指翻译者对原文的忠实度。
答案:信度7. 语言的______是指语言在不同社会群体中的不同形式。
英语语言学试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. The term "phoneme" refers to:A. A single speech soundB. A unit of meaningC. A unit of writingD. A unit of grammar答案:A2. Which of the following is NOT a branch of linguistics?A. PhoneticsB. PhonologyC. PsychologyD. Syntax答案:C3. The process of changing the form of a word to express different grammatical relationships is called:A. MorphologyB. SyntaxC. SemanticsD. Pragmatics答案:A4. In English, the word "mouse" is an example of:A. A countable nounB. An uncountable nounC. A proper nounD. An article答案:A5. The study of meaning in language is known as:A. SemanticsB. PragmaticsC. SyntaxD. Phonology答案:A6. The smallest unit of sound that can distinguish meaning ina language is called:A. PhonemeB. MorphemeC. SyllableD. Word答案:A7. The branch of linguistics that studies the social aspects of language is:A. SociolinguisticsB. PsycholinguisticsC. NeurolinguisticsD. Computational linguistics答案:A8. The use of language in context is studied in:A. SemanticsB. PragmaticsC. SyntaxD. Phonology答案:B9. The process of acquiring a first language is known as:A. Second language acquisitionB. Foreign language learningC. Language learningD. First language acquisition答案:D10. The systematic arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences is the study of:A. PhonologyB. SyntaxC. SemanticsD. Pragmatics答案:B二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. The study of speech sounds is called ____________.答案:Phonetics2. The smallest meaningful unit of language is known as a____________.答案:Morpheme3. The branch of linguistics that deals with the structure of words is ____________.答案:Morphology4. The study of how language is used in social contexts is called ____________.答案:Sociolinguistics5. The process by which children acquire their first language is known as ____________.答案:Language acquisition6. The study of the rules governing the formation of sentences in a language is ____________.答案:Syntax7. The branch of linguistics that examines the psychological aspects of language is ____________.答案:Psycholinguistics8. The study of the meanings of words, phrases, and sentences is known as ____________.答案:Semantics9. The branch of linguistics concerned with the relationship between language and culture is ____________.答案:Anthropological linguistics10. The study of how language is processed in the brain is called ____________.答案:Neurolinguistics三、简答题(每题10分,共30分)1. Explain the difference between a phoneme and an allophone. 答案:A phoneme is the smallest unit of sound that can distinguish meaning in a language, while an allophone is a variant of a phoneme that does not change the meaning of aword.2. What is the role of syntax in language?答案:Syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a language,including how words and phrases are arranged to create well-formed sentences.3. How does sociolinguistics contribute to our understandingof language?答案:Sociolinguistics helps us understand how languagevaries according to social factors such as class, gender, age, and ethnicity, and how these variations affect communication and social interaction.四、论述题(每题15分,共30分)1. Discuss the importance of pragmatics in language communication.答案:Pragmatics is crucial in language communication as it deals with the way context influences the interpretation of meaning. It helps us understand how speakers convey intended meanings beyond the literal interpretation of words and sentences, taking into account factors such as tone, body language, and shared knowledge.2. Explain the concept of language universals and give examples.答案:Language universals refer to the structural and functional features that are common to all human languages. Examples include the presence of nouns and verbs, the use ofword order to convey meaning, and the ability to form questions and negations.。
语言与应用语言学试题期末考试英语(教)专业语言与应用语言学试题注意事项一、将你的学号、姓名及分校(工作站)名称填写在答题纸的规定栏内。
考试结束后,把试卷和答题纸放在桌上。
试卷和答题纸均不得带出考场。
二、仔细阅读题目的说明,并按题目要求答题。
答案一定要写在答题纸指定的位置上?写在试卷上的答案无效。
三、用蓝、黑圆珠笔或钢笔答题,使用铅笔答题无效。
Information for the examinees:This examination consists of Four sections. They are:Section I: Content Awareness of the Course (30 points, 20 minutes)Section II: General Principles of Language and Linguistics (30 points, 25 minutes)Section III: Some Specific Aspects of Language and Linguistics (20 points, 35 minutes)Section IV: Analysis and Application (20 points, 40 minutes)The total marks for this examination are 100 points. Time allowed for completing thisexamination is 2 hours.You must write all your answers on the Answer Sheet.Section I: Content Awareness of the Course 30 pointsI. Choose the best answer to complete the following statements. Write your answers on theAnswer Sheet. (10 points, 1 point for each item)1. "Historical linguistics" seeks to provide scientific evidence __A. of the reasons for human speechB. of human habitation in AfricaC. why there are many world languagesD. concerning the origins of speech2. Which of the following does NOT have something to do with the production of speech sounds?A. Organic analysisB. Linguistic analysisC. Acoustic analysisD. Phonetic analysis3. In determining the symbolic nature of language humansA. examine Braille and signsB. examine the media and signsC. examine the language of the mediaD. examine the language itself4. The aims of Unit 4 are to understand that language functions in the worldA. through the use of naming devices and educationB. by people experiencing abstractions in educationC. based on experience, abstraction and symbolismD. through symbolic and abstract experiences5. The aim of Unit 5 is for students to understand that speech actsA. need to be defined precisely through oral actionsB. need to be terminated under appropriate circumstancesC. need to be defined, analysed and comprehendedD. need to be analysed by definition and example:6. Generally speaking, 脸 and 面子 is:A. more important for teenage girls than boysB. something teenagers don"t worry aboutC. not the same for adults as for teenagersD. the same for adults as for teenagers7. In face to face talk people"s interactive behaviour is based uponA. Principles of Desire and DecisionsB. The Principle of Mutual DesirabilityC. Principles of Decision MakingD. The Principle of Mutuality8. If an 9verseas Chinese is called monolingual this meansA. the person speaks primarily English but also speaks Chinese at homeB. the person has had to choose between speaking another language or ChineseC. the choice of speaking a language has been limited to one of two languagesD. the person has chosen to speak Chinese in public and at home9. According to the course our brain is divided into two hemispheres. Language functionsaremainly located in theA. left hemisphereB. lower hemisphereC. right hemisphereD. upper hemisphere10. The story of Genie in Unit 9 seems to highlight the language hypothesis of~A. Eric LennehergB. Antonio FrancsC. Jean-Marc-Gaspard ItarD. Sigmund Freud11. Choose those words or phrases that best complete the following sentences. Write youranswers on the Answer Sheet. Note that there are more words or phrases than necessary.(20 points, 2 points for each item)A. syntagmaticB. BrailleC. self-orientedD. languageE. homo sapiensF. homo habilisG. cognitiveH. ideographicI. other-orientedJ. paradigmaticK. classificationL. pictographicA. Professor Guide (in Unit 1) makes the major point that the possession of 11 ~ by12 bas contributed to civilized and meaningful living.B. The British manual alphabet and 13 are mediums of language representation .C. Chinese writing is 14 , rather than 15D. When we name things it involves an act of 16 . This act is not neutral thereforethere are social as well as 17 repercussions.E. When asking the names of people, Chinese people appear to be more 18compared to British people who seem to be very 19F. When words enter into sequential relation, it is called 20 relation.Section II: General Principles of Language and Linguistics 30 pointsIII. Decide if the following statements are True or False according to what you"ve learned from the course book. (10 points, 1 point for each item)21. The linguistic theory called " transformational-generative grammar" focuses on therelationship between the language and the brain.22. The lips are a part of the vocal tract.23. Signs and icons are, in reality, the same thing.24. Humans are not good at abstraction.25. Ill0cutionary acts can be performed both directly and indirectly.26. Some dialects or accents are related to social or economic status in China.27. The Chinese characters 1--~-,:~ and i are examples of written norms.28. Non-verbal signals are, generally, easily interpreted.29. Status and regional identity can be linked to dialect.30. The "classical" view of the terms ,~,~, and .1~,~, was that because the radical ,I~"was usedit connected the heart to the concept of thinking.IV. Read the questions in Column A and choose the right one from Column B to answer eachof them. Write the corresponding letter on the Answer Sheet. There is ONLY one answer foreach question. (20 points, 2 points for each item)Column AColumn B31. "Hi! I"m Irene."What speech act is the speaker performing?32. In Chinese, instead of saying "拉屎", we use "方便一下" or "去一号". What are these expressions known as?33. The word "rose" is related to the thing it stands for by the mind that understands it.What is the name given to this relationship?34. When words take place in sequence, what is this called?35. [A] "You must come and have dinner with us. "[B] "Sorry, I"ve got something to do."In the above exchange; What maxim of English politeness does the speaker observe or violate?36. What name do we give to the process -- from an immediate experience of a real thingto naming it and categorizing it?37. What is the term used hy Hayakawa that denies or ignores the existence of any middleground between two opposing forces?38. "Coo-..coo.."could ""you "" you "" te...tell me the--, way to the p--.p ."-post of{ice p ." p[ "" please?": What type of program me might be able to correct this person" s language problem?39. (A Chinese student at a bus stop in London for the first time--"Do you mind! Please join the queue like the rest of us."-- "Must I?"The student did not know he has to queue for the bus. tie did not have any prior knowledge. Linguistically, what is this sort of knowledge called?40. A visiting Chinese scholar at Nottingham University in the U.K. remarked: 请我到office 来找我。