EN71-1玩具机械物理性能要求
- 格式:doc
- 大小:324.50 KB
- 文档页数:25


玩具安全——第一部分:机械和物理性能本标准为欧洲标准EN 71-1:2005 英文版ISC 97.200.50EN71 -12005年10月包含2006年2月勘误表 代替 EN 71-1:1998英文版本欧洲标准于 2005年9月19日由欧洲标准化委员会批准。
欧洲标准化委员会的成员必须遵守欧洲标准化委员会/欧洲电工标准化委员会的内部规章,这些规章规定了使本欧洲标准不加任何改动而具备国家标准同等效力的条件。
需要上述国家标准 最新目录及参考书目者可向欧洲标准化委员会中央秘书处或其任何一个成员组织申请索取。
本欧洲标准有三种正式文本(英文、法文、德文) 。
欧洲标准化委员会成员如将本标准翻译成除上述三种语言外的任何一种本国语言文本并通知中央秘书处,这一文本就具备与正式文本相 同的效力。
欧洲标准化委员会成员为下列国家的标准机构:奥地利、比利时、塞浦路斯、捷克共和国、 丹麦、爱沙尼亚、芬兰、法国、德国、希腊、匈牙利、冰岛、爱尔兰、意大利、拉脱维亚、立陶 宛、卢森堡、马耳他、荷兰、挪威、波兰、葡萄牙、斯洛伐克、斯洛文尼亚、西班牙、瑞典、瑞 士和英国。
畐欧洲标准化委员会中央管理处:rue de stassart , 36 B-1050布鲁塞尔玩具安全 第一部分:机械和物理性能欧洲标准ICS 97.200.50本英文版标准为EN 71-1:2005的英文译本。
它将代替单独的英文版EN 71-1:2001 。
在本标准的英国参与部分是委托技术委员会CW/15,玩具安全的,涉及的指责如下:--帮助读者理解本版本;--针对翻译部分提出相关建议于国际/欧洲委员会,或者修改的建议,保证英文版的影响力;--监控本标准在国际和欧洲的发展及传播。
机构在委员会提出的目录基于秘书处的要求得到。
相关参考国际上的执行或欧洲出版的本英文版标准涉及的文献为英国标准协会目录的相关部分“国际标准一致索引”,或者由英国标准协会电子目录或者在线英文版标准使用。



物理和机械性能该部分主要包括跌落检测、小零件检测、锐利边缘检测、拉力检测、压力检测、线缝检测、耳鼻眼拉力、扭力检测等。
物理测试部分一般要求:
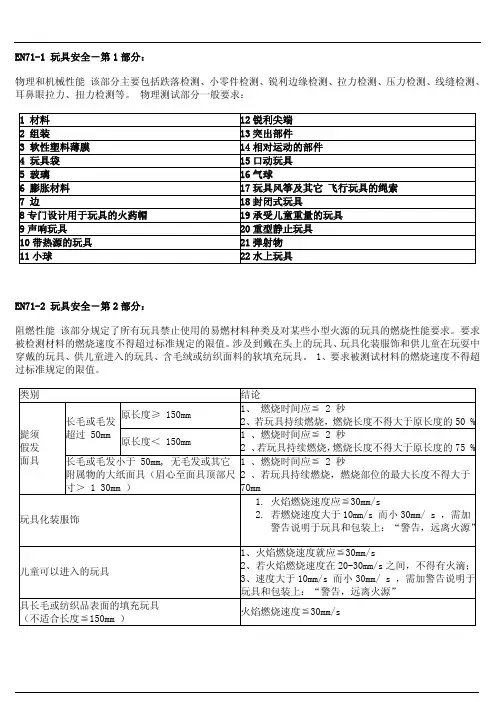
EN71-2 玩具安全-第2部分:
阻燃性能该部分规定了所有玩具禁止使用的易燃材料种类及对某些小型火源的玩具的燃烧性能要求。
要求被检测材料的燃烧速度不得超过标准规定的限值。
涉及到戴在头上的玩具、玩具化装服饰和供儿童在玩耍中穿戴的玩具、供儿童进入的玩具、含毛绒或纺织面料的软填充玩具。
1、要求被测试材料的燃烧速度不得超过标准规定的限值。
某些元素的转移该部分规定了玩具的可触及部件或材料中可迁移元素(锑、砷、钡、镉、铬、铅、汞、锡)的最大限值。
其检测原理是:可溶性元素是模拟材料在吞咽后与胃酸持续接触一段时间的条件下,从玩具材料中提取出的溶出物。
采用检出限适当的方法定量测定可溶性元素的含量。
限值要求:。

EN71认证玩具测试标准EN71是欧盟市场玩具类产品的规范标准。
儿童是全社会最关心和爱护的群体,儿童普遍喜爱的玩具市场发展迅猛,同时各类玩具由于各方面质量问题给儿童带来的伤害也时有发生,因此世界各国对本国市场上的玩具的要求正日益变得严格。
许多国家都就这些产品建立了自己的安全规章,生产公司必须保证其产品在该地区销售前符合相关标准。
制造商必须对因生产缺陷、不良设计或不适当材料的使用而导致的事故负责。
由此在欧洲推出玩具EN71认证法令,其意义是通过EN71标准对进入欧洲市场的玩具产品进行技术规范,从而减少或避免玩具对儿童的伤害。
EN-71玩具测试标准EN 71 Part 11、EN 71 Part 1:2005+A9:2009-physical &mechanical Test 物理和机械性测试(a)Without Sound module 不发声玩具(b)With Sound module 发声玩具(c)Earphone with Sound 耳机发声玩具(d)7000 Cycles Switch Test for Chest 玩具柜的7000次开关测试(e)Ride-on Toys 乘骑玩具(f)Mouth-actuated Toys口动玩具物理和机械性能该部分主要包括跌落检测、小零件检测、锐利边缘检测、拉力检测、压力检测、线缝检测、耳鼻眼拉力、扭力检测等。
物理测试部分一般要求:1 材料;2 组装;3 软性塑料薄膜;4 玩具袋;5 玻璃;6 膨胀材料;7 边;8专门设计用于玩具的火药帽;9 声响玩具;10 带热源的玩具;11 小球;12 锐利尖端;13 突出部件;14 相对运动的部件;15 口动玩具;16 气球;17 玩具风筝及其它飞行玩具的绳索;18 封闭式玩具;19 承受儿童重量的玩具;20 重型静止玩具;21 弹射物;22水上玩具EN 71 Part 22、EN 71 Part 2:1993-flammability Test 易燃性测试(a)Finished Product 成品(b)Pile fabric or material 绒毛织物或绒毛材料EN 71 Part 33、EN 71 Part 3:1994-Toxic Elements Test (8 Toxic Elements Results)有毒金属溶出测试(8种有毒金属元素测试结果)铅汞镉铬砷硒钡锑EN 71 Part 44、EN 71 Part 4:Experimental Set for Chemistry 化学实验玩具EN 71 Part 55、EN 71 Part 5:Chemisty Toys(Sets) Other than Experimental Sets 非实验用化学玩具EN 71 Part 66、EN 71 Part 6:Graphical Symbol for Age Warning Labelling 年龄警示标签图。

欧盟玩具安全标准EN 71-1:2014+A1:2018及启示■ 贾义涵 翁云云(浙江师范大学杭州幼儿师范学院)摘 要:EN 71-1:2014+A1:2018是欧盟现行的玩具机械物理性能的安全标准,标准主要阐释了机械物理安全性能的要求和与之对应的测试方法。
通过对标准文本的分析和解读,总结出其关键要点,这对于我们玩具的安全设计、选择、使用以及我国玩具安全相关法规的制定、实施具有一定的启示意义。
关键词:欧盟玩具安全标准,玩具安全,安全指令DOI编码:10.3969/j.issn.1002-5944.2021.02.029Introduction to European Standard EN 71-1:2014 + a1:2018 andReflectionsJIA Yi-han WENG Yun-yun(Hangzhou Kindergarten Teachers’ College, Zhejiang Normal University)Abstract: European Standard EN 71-1:2014 + A1:2018 specifies requirements and test methods for mechanical and physical properties of toys. This paper interpreted the content of the standard and summarized its key points, which may provide reference for the safe toy design, selection and toy play as well as the development and implementation of laws and regulations on toy safety in China.Keywords: European standard, toys safety, EU Toy Safety Directive标准评析产品伤害是全球最为关注的市场风险和公共安全问题之一[1]。

en71玩具测试标准
EN71标准是欧盟的玩具安全标准,主要针对玩具产品进行了一系列的测试和要求,以确保其安全性和符合相关法规。
以下是EN71标准中一些主要的测试项目和要求:
1. 机械和物理性能测试:测试玩具的尺寸、结构、耐久性、边缘和尖锐部分等,以确保它们在使用过程中不会对儿童造成伤害。
2. 可燃性测试:评估玩具材料的燃烧性能,包括燃烧速度、火焰蔓延性和剩余燃烧等,以防止火灾等安全事故的发生。
3. 有害物质测试:检测玩具中的重金属、有机化合物和其他有害物质的含量,例如铅、镉、汞等,以确保它们不会对儿童的健康造成危害。
4. 化学性能测试:评估玩具材料的化学性能,包括溶解性、PH值和酸碱性等,以确保它们不会对儿童的皮肤和口腔造成刺激和危害。
5. 安全性测试:针对特定类别的玩具,如弹簧玩具、玩具填充物等,进行安全性能评估,以确保它们在使用过程中不会对儿童造成伤害。
6. 标签和说明:要求制造商提供正确的标签和使用说明,以确保玩具的正确使用和警告信息,以避免因误用玩具而造成的伤害。
此外,EN71标准还针对不同年龄段的儿童制定了不同的安全要求和测试方法,以确保所有年龄段的儿童都能使用安全的玩具。
同时,EN71标准也不断更新和完善,以适应新的安全问题和法规要求。


EN71玩具测试标准简介及测试指令和测试项目
玩具指令适用于设计用于或预定于14岁以下儿童玩耍的任何产品或材料,若带电,电源不能超过24V.
玩具产品若在欧盟合法销售,则必须符合玩具指令88/378/EEC要求,并标注CE标志。
根据玩具产品
玩具通用标准-EN71
――EN71Part1Physical and Mechanical test机械及物理性能测试
包括跌落测试,小零件测试,锐利边缘测试,拉力测试,压力测试,线缝测试,部件测试,耳鼻眼拉力,扭力测试等,此测试只需万能试验机就可完成。
1.扭力——拉力测试(orque&tension)
2.跌落测试(Drop Test)
3.冲击测试(mpact Test)
4.压力测试(Compression Test)
――EN71Part2Flammalility test易燃性测试
包括对可燃性材料进行燃烧测试:毛发,衣物等
―EN71Part3Chemical test化学测试,即测试8种毒性元素(8kinds of toxic elements)之含量是否达到标准要求,这8种有毒元素包括:锑(限值60PPM),钡(限值1000PPM),镉(限值75PPM),铬(60PPM),铅(90PPM),汞(限值60PPM),硒(限值500PPM),砷(限值25PPM).
我司技术人员表示,对于上述元素检测最常用仪器为能量色散型X射线荧光光谱仪,而目前市场上较好的为岛津仪器的EDX-LE和EDX-GP这两种型号X 射线荧光光谱仪,检测过程快速,结果准确。
也可选择使用原子吸叫(AAS)或等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP),可精准检测以上有害物质。
咨询热线:134-2890-5334Q246639-6154艾先生。
欧洲en71标准
EN71是欧洲玩具安全标准的系列标准,主要由欧洲标准化委员会(CEN)发布。
这一系列标准旨在确保玩具的安全性,以防止儿童因使用玩具而受到伤害。
EN71标准分为多个部分,每个部分涵盖了不同方面的安全性要求。
以下是EN71标准的一些主要部分:
1.EN71-1:定义了机械和物理性质的要求,以确保玩具在正常
使用过程中不会引起危险。
2.EN71-2:涵盖了有关玩具可燃性的要求,以确保玩具在火灾
中不会造成不必要的危险。
3.EN71-3:关注玩具中有毒物质的要求,包括重金属、染料等。
4.EN71-4:针对实验室玩具和化学实验玩具的安全性要求。
5.EN71-5:关注活动材料的安全性,例如涂料、油漆、颜料等。
6.EN71-6:适用于图画和颜料方面的玩具,涵盖了关于玩具颜
料的特殊要求。
7.EN71-7:关注于泡泡剂的安全性要求。
8.EN71-8:针对弹射玩具的安全性要求。
9.EN71-9:适用于气体操作玩具的安全性要求。
10.E N71-10:针对液体流动玩具的安全性要求。
11.E N71-11:适用于玩具充气结构的安全性要求。
这只是EN71标准系列的一部分,每个部分都专注于特定类型的玩具或特定的安全性方面。
制造商和出口商通常需要确保其生产的玩具
符合EN71标准的适用部分,并通过相关的测试和认证程序,以确保玩具的安全性和合规性。
EN71拉力测试标准是指欧盟玩具安全指令2009/48/EC的协调标准,用于评估玩具的物理、机械、化学和电气性能,以确保其安全性。
EN71标准共包括13个部分,涵盖了玩具的安全要求。
其中,与拉力测试相关的主要是EN71-1和EN71-3两个部分。
1. EN71-1:物理和机械性能测试,主要包括锐利边缘、拉力、压力测试等。
这一部分针对玩具的物理和机械性能进行评估,确保玩具在使用过程中不会对儿童造成伤害。
拉力测试是其中的一项重要内容,主要测试玩具在受到拉力时的抗拉强度和稳定性。
2. EN71-3:八大重金属溶出。
这一部分主要测试玩具在接触到儿童口腔或皮肤时,八大重金属(锑、砷、钡、镉、铬、铅、汞、锡)的溶出量。
重金属溶出量超标可能会对儿童的健康造成威胁。
2Normative Reference The following standards are included:IEC 60126:1973IEC 60318:1970IEC 60651:1979IEC 60804:1985prEN ISO 868:1997EN ISO 3744:1994EN ISO 3746:1995ISO 4287-2:1984ISO 4593:1993ISO 6508:1986ISO 7619:1986EN ISO 11201:1995EN ISO 11202:1995EN ISO 11204:1995The following standards are included:EN 71-6EN 71-8EN 60318-1 (IEC 60318-1:1998)EN ISO 868 (ISO 868:2003)EN ISO 3746:1995 (ISO 3746:1995)EN ISO 4287 (ISO 4287:1997)EN ISO 6508-1 (ISO 6508-1:1999)EN ISO 11201 (ISO 11201:1995)EN ISO 11202 (ISO 11202:1995)EN ISO 11204 (ISO 11204:1995)ISO 4593ISO 7619-2IEC 60126--WordingsChildren over 36 months Children of 36 months and over3 Definitions 3.41 Ball Added Note 3 in the definition of ball:3.4 BallNote 3 The amendment EN 71-1:1998/A8:2003 (regarding small balls)was published in the OJEC (C 297 of 9 December 2003). However, in acorrigendum to this (30.3.2004, C 79/15), the following notice waspublished:“The standard EN 71-1:1998/A8:2003 only addresses the risks caused by‘small balls’ (as defined in the standard as “spherical, ovoid, or ellipsoidalobject”) that are designed to be thrown, hit, kicked, rolled, dropped orbounced. Toys containing small balls which are not covered by thestandard shall undergo an EC type-examination certificate before placedon the market”4General requirements 4.6 Expanding materialsToys and components of toys made of expanding materials, which fitentirely in the cylinder specified in 8.2, shall not expand more than 50 %in any dimension when tested according to 8.14 (expanding materials).4.6 Expanding materialsToys and components of toys made of expanding materials, which fitentirely in the cylinder specified in 8.2 (small part cylinder) before orafter being tested according to 8.3 (torque test), 8.4.2.1 (tension test,general), 8.5 (drop test), 8.7 (impact test) and 8.8 (compression test)shall not expand more than 50 % in any dimension when tested accordingto 8.14 (expanding materials).4.7 Edgesd) Where it is essential for the functioning of the toy (cover slips), sharp edges may be used in toy intended for children over 36 months. 4.7 Edgesd) Where it is essential for the functioning of the toy, hazardous sharp functional edges may be used in toys intended for children of 36 months and over.4.8 Points and wiresb) Where it is essential for the functioning of the toy, sharp points may be used in toys intended for children over 36 months. 4.8 Points and wiresb) Where it is essential for the functioning of the toy, hazardous sharp functioning points may be used in toys intended for children of 36 months and over.4.13 Cords of toy kites and other flying toysCords of toy kites and other flying toys, materially linking the toy to the child and which a length exceeding 2 m… 4.13 Cords of toy kites and other flying toysCords of toy kites and other flying toys linking the toy to the child and which a length of more than 2 m…4.15 Toys intended to bear the mass of a child 4.15.1.1 Warnings and instruction for use-- 4.15 Toys intended to bear the mass of a child4.15.1.2 Warnings and instruction for useAdded:Roller skates, inline skates and skateboards for children offered for sale as toys shall carry a warning (see 7.10).4.15 Toys intended to bear the mass of a child 4.15.1.4 BrakingThe requirement of 4.15.1.4 does not apply to: - roller skates, toy skateboards and scooters; 4.15 Toys intended to bear the mass of a child 4.15.1.5 BrakingThe requirement of 4.15.1.5 does not apply to: - roller skates, toy skateboards;4.15 Toys intended to bear the mass of a child4.15.1.4 BrakingFT2 is the maximum pull force in newtons for a toy intended for children over 36 months.4.15 Toys intended to bear the mass of a child4.15.1.5 BrakingFT2 is the maximum pull force in newtons for a toy intended for children of 36 months and over.4.15.3 Swings and similar toys Deleted4.15.4 Rocking horses and similar toys -- 4.15.3 Rocking horses and similar toysAdded:d) Toys that due to their construction, strength, design or other factors are not suitable for use by children of 36 months and over shall carry a warning (see 7.16).4General requirements4.15.5 Toys not propelled by a childToys not propelled by a child but designed to bear the mass of a child (e.g. garden slides, climbing frames, see-saws) shall conform to the following requirements:… 4.15.4 Toys not propelled by a childToys not propelled by a child but designed to bear the mass of a child (but not toys covered by EN 71-8) shall conform to the following requirements:…4.15.5 Toys not propelled by a childThe requirement in b) does not apply to toys with a device for fixing them to the ground and to toys which for evident reasons cannot be considered as being stable… 4.15.4 Toys not propelled by a childThis requirement does not apply to toys which for evident reasons cannot be considered as being stable…4.15.5 Toys not propelled by a childc) Any opening in the frame, situated 600 mm or more above the ground or above any other surface which is of such size that it will always support a child…d) The need to carry out checks and maintenance of the main parts from time to time shall be drawn to the attention of the user. 4.15.4 Toys not propelled by a childChanged to:c) Toys intended to bear the mass of a child shall, when appropriate, be accompanied by instructions for use, assembly and maintenance instructions.d) Toys that due to their construction, strength, design or other factors are suitable for use by children of 36 months and over shall carry a warning (see 7.16)4.15.6 Toy scooters4.15.6.2 Warnings and instructions for useToy scooters shall carry an indication as to which weight group they are intended for. They shall also be accompanied by a warning, instructions for use and precautions to be taken… 4.15.5 Toy scooters4.15.5.2 Warnings and instructions for useToys scooters shall carry a warning and an indication about the intended weight group. They shall also be accompanied by instructions for use and precautions to be taken…4.17 Projectiles -- 4.17 ProjectilesAdded:c) Helicopter rotors and single propellers intended to be powered into vertical or nearly vertical free flight by a spring mechanism or similar device, shall have a ring around the perimeter in order to reduce the risk of injuries.4.17.2 Projectile toys without stored energyb) Helicopter rotors and single propellers intended to be powered into vertical or nearly vertical free flight by a spring mechanism or similar device, shall have a ring around the perimeter in order to reduce the risk of injuries. 4.17.2 Projectile toys without stored energy Deleted4General requirements4.17.4 Bows and arrowsc) Arrows whose maximum kinetic energy exceeds 0,08J shall comply with 4.17.3b). 4.17.4 Bows and arrowsd) Arrows whose maximum kinetic energy exceeds 0,08J, shall conform to 4.17.3 b). The potential danger of discharging such arrows shall be drawn to the attention of the user (see 7.7).4.19 Percussion caps specifically designed for use in toysRequirements for percussion caps specified for use in toys shall be as given in Annex A and 7.14.Annex AA.1 Percussion capsAssuming reasonably foreseeable use, percussion caps specifically designed for use in toys shall not produce debris which could cause eye injuries, flames, glowing residues. A.2 Packaging of percussion capsThe packaging of percussion caps shall carry a warning (see 7.14). 4.19 Percussion caps specifically designed for use in toys Assuming reasonably foreseeable use, percussion caps specificallydesigned for use in toys shall not produce debris which could cause eye injuries, flames, glowing residues. The packaging of percussion caps shall carry a warning (see 7.13). 4General requirements4.21 Toys containing a heat source The following requirements do not cover burners in chemistry sets or related experimental kits and light bulb of 2,5W maximum and similar items. 4.21 Toys containing a heat sourceThe following requirements do not cover burners in chemistry sets or related experimental kits, light bulb with 2,5W or more , and similar items.5.3 Adhesion of plastic sheeting 5.3 Plastic sheeting 5.6 Swings Deleted 5 Toys intended for children under 36 months 5.9 Shape and size of certain toys The requirements in 5.9a) and b) do not apply to soft filled toys or soft filled parts of toys or parts of fabric. 5.8 Shape and size of certain toysThe requirements in 5.8 a) and b) do not apply to soft-filled toys, soft-filled parts of toys or parts of fabric. They do not apply to rigid elementshaving a major dimension equal to 30 mm or less.7.4 Toys intended to bear the mass of a child Deleted 7.7Functional sharp edges and points 7.6 Hazardous sharp functional edges and points 7 Warnings and instructions for use 7.11 Roller skates and toy skateboards 7.10 Roller skates, inline skates and toy skateboards 8.4.2.3 Protective components Subject the part to be tested to a tensile force of 60N ±2N. 8.4.2.3 Protective components Gradually apply a force of (60 ± 2) within 5 s. Maintain the force for 10 s.8.5 Drop test Prior to release, orientate the toy in a position that allows the most onerous impact. 8.5 Drop testPrior to release, orientate the toy in a position that allows the most onerous impact onto the coated surface of the steel plate . 8.14 Expanding materials Allow excess water to drain for 1 min and remeasure the item. 8.14 Expanding materials Allow water adhering to the toy or component to drain for 1 min and re-measure the item. 8.24 Strength of swings and similar toys Deleted 8.27 Borosilicate glass Deleted 8 Test methods 8.28 Openings in climbing frames and similar toys Deleted8.29 Diameter of ropes and chains for swings Deleted8.30 Brake performanceIf the brake is operated by a pedal, apply the force of 50 N to the pedal in the operating direction to produce the effect of the brake. 8.26 Brake performanceIf the brake is operated by a pedal, apply the force to the pedal in the operating direction to produce the effect of the brake.8.31 Determination of emission sound pressure levels8.31.1.4 Operating conditions- operate a squeeze toy by grasping the toy with both hands and holding it where it is meant to be held or, if in doubt, where the highest sound level can be achieved. Squeeze with both thumbs to achieve the highest possible sound level. Repeat 10 times at a low pace… 8.28 Determination of emission sound pressure levels8.28.1.4 Operating conditions- operate a squeeze toy by grasping the toy with both hands and holding it where it is meant to be held or, if in doubt, where the highest sound level can be achieved. Squeeze with both thumbs to achieve the highest possible sound level. Repeat 10 times in a manner which maximized the sound emission…8.31 Determination of emission sound pressure levels 8.31.1.4 Operating conditions-- 8.28 Determination of emission sound pressure levels8.28.1.4 Operating conditionsAdded:NOTE Further work is needed to obtain standardized recordings. In the interim, the following recordings may be used; Recorded tape created by BASF and TEAC for IEC in March 1981, called TEAC test tape – Level 1 kHz – 0dB.8.31 Determination of emission sound pressure levels8.31.2.2 InstrumentationThe instrumentation system, including the microphone and cable, shall meet the requirements of a type 1 or type 2 instrument specified in IEC 60651 or, in the case of integrating averaging sound level meters, in IEC 60684. When measuring high peak mission sound pressure levels, e.g. from toys using percussion caps, the microphone and the entire instrumentation system shall have the capability of handling linear peak levels exceeding the C-weighted peak levels by at least 10 dB. 8.28 Determination of emission sound pressure levels8.28.2.2 InstrumentationThe instrumentation system, including the microphone and cable, shall meet the requirements of a type 1 or type 2 instrument specified in IEC 61672-1 and IEC 61672-2 or, in the case of integrating-averaging sound level meters, in IEC 61672-1 and IEC 61672-2. When measuring high peak emission sound pressure levels, e.g. from toys using percussion caps, the microphone and the entire instrumentation system shall have the capability of handling linear peak levels exceeding the C-weighted peak levels by at least 10 dB. When EN ISO 11201 is used, a type 1 instrument is required.8Test methods8.34 Durability test for vertically opening hinged lids on toy chests 8.31 Toy chests lidsAnnex A Percussion caps specifically designed for use in toys -RequirementsDeletedAnnex B Requirements guide by toy categories Deleted AnnexAnnex C Background and rationale for this documentC.5 Glass…The test method in 8.27 for borosilicate glass is taken for EN 71-4.C.6 Expanding materials…The requirement in EN 71-1:1998 that seeds used in toys may not expand more than 5 % has been considered to be superfluous.C.11 Driving mechanisms…Toys that are intended for children under 36 months are subjected to more extensive testing under 5.1…C.17 Toys which a child can enterThe purpose of these requirements is to reduce the possible risk of entrapment of children in toys that form enclosures, such as tents and toy chests, and to avoid possible suffocation in head-enclosing toys such as space helmets.C.18 Masks and helmetsThese requirements are intended to ensure proper ventilation when wearing a mask or helmet and to reduce the risk whereby visors on toy motorcycle helmets and similar articles can break and damage the eyes. C.20 SwingsC.22 Toys not propelled by a childC.29 Adhesion of plastic sheeting Annex A Background and rationale for this documentA.6 GlassDeletedA.7 Expanding materialsDeletedA.12 Driving mechanismsDeletedA.18 Toys which a child can enterThese requirements are intended to reduce the risk of entrapment of children in toys that form enclosures (e.g. tents and toy chests).A.19 Masks and helmetsThese requirements are intended to ensure proper ventilation when wearing a mask or helmet, to avoid possible suffocation in head-enclosing toys (e.g. space helmets), and to reduce the risk whereby visors on toy motorcycle helmets and similar articles can break and damage the eyes.DeletedDeletedA.28 Plastic sheetingAnnex C.32 Shape and size of certain toys--C.45 Durability of mouth-actuated toysThe previous standard had a requirement solely dependent on pressurewhich could not always be applied…C.47 Static strengthThe standard requires only one specified height for the test masses,deleting the need for a mass with a center of gravity at 400 mm asindicated in previous standard…C.50 Toy scooters…It has not been considered necessary to require brakes for toy scootersfor the very young as they normally do not travel with great speed and arenot able to operate a brake. A higher force than 50 N applied to the rearwheel could cause the rider to eject over the steering of the scooter whenthe scooter comes to an abrupt stop. Reference is made to Annex II,Part II h) of the Toys Directive. A.31 Shape and size of certain toysAdded:…The intention of the requirement that toys need to be tested “as supplied” is that prior to being tested according to 8.16 (geometric shape of certain toys), the toy will not be subjected to any other test…A.44 Durability of mouth-actuated toysDeletedA.46 Static strengthDeletedA.49 Toy scooters…It has not been considered necessary to require brakes for toy scooters for the very young as they normally do not travel with great speed and are not able to operate a brake.。
en71测试标准玩具EN71检测有哪些标准?1.EN71测试就是欧盟玩具类,工艺品类,装饰品类的测试。
2.出口欧盟的玩具礼品婴幼儿产品应该满足EN71标准的要求才能出口。
3.EN71测试共11部分,一般做前三部分:1.1EN71,物理和机械性能测试,主要包括锐利边缘、拉力、压力测试等。
1.2EN71,阻燃测试,主要包括玩具的燃烧速度,涉及到毛绒玩具、丝织品玩具和戴在头上的玩具等。
1.3EN71,八大重金属溶出,八大重金属包括锑、砷、钡、镉、铬、铅、汞、锡。
EN71共11个部分:EN71-1机械性物理性测试EN71-2易燃性测试EN71-3某些元素的转移EN71-4化学和有关活动用的试验装置EN71-5化学玩具(试验装置除外)EN71-6年龄标志的图形表示EN71-7指画颜料的要EN71-7指画颜料的要EN71-8供户内和户外家庭娱乐用的摇摆、滑动和类似玩具EN71-9玩具中有机化合物通用要求EN71-10有机化合物的样品制备和提取EN71-11有机化合物的分析方法EN71认证检测需要的时间:通常情况下,普通玩具产品申请EN71认证时间为1-2周,具体产品复杂程度不同有相应变化。
EN71认证的流程:1、认证申请表2、相关样品及资料3、实验室测试4、出检测报告和证书.所需资料:1、2-3个测试样品2、产品使用说明书3、产品物料清单EN71认证证书的有效期是多久?在产品结构、指令要求没有变更的情况下,EN71其实是可以一直有效的,但有的买家也会要求一年或者半年检测一次.EN71认证需提供哪些资料?1.准备1-3套测试样品2.产品说明书3.申请表哪些产品需申请EN71认证检测?婴儿玩具:液体填充玩具,牙胶和奶嘴;磁性玩具:玩具箱,电动玩具;宠物玩具:电池玩具,工艺品;玩具枪和玩具弹,玩具化妆品;填充玩具和纺织品玩具,木制及塑胶玩具;自行车和滑板车玩具,摇马和乘骑玩具;游戏、拼图玩具和书籍等。
EN71认证检测包括哪些内容?利边测试尖锐点测试小物件测试;啮咬测试压力测试弯曲测试;缝线拉力测试拉力测试扭力测试;易燃性测试化学元素测试冲击测试。
EN71-1玩具机械物理性能要求详解EN71-1玩具机械物理性能要求涉及到玩具的机械物理安全性能,主要在EN71-1:2005+A4:2007《玩具安全--机械和物理性能》标准中规定。
这部标准是欧洲标准化委员会发布的与88/378/EEC《玩具安全指令》相协调的玩具安全标准。
EN71-1标准对出口到欧盟市场的玩具进行指导生产、安全质量控制起到重要作用。
该标准的适用范围是:供14岁及以下儿童玩耍而设计生产的玩具,此类的特点大多数是体积较小、重量轻。
下面介绍EN71-1标准的技术要求:1、材料要求玩具本身和用于制造玩具的所有材料目视检查应清洁干净,无污染;材料的检查应凭正常视力检查,而不是放大检查。
2、组装玩具成套玩具是由儿童进行组装的,应对于可供儿童使用的每一部件和组装完成的玩具进行测试。
组装玩具的要求不适用于组装活动本身具有特殊娱乐价值的玩具。
如果玩具由于成人组装后再交儿童玩耍的,则对组装后的完整玩具进行检测,而不需要对单个部件进行检测。
用于组装的玩具必须附有详细组装指南,指南中须指出是否有必要由成人组装或在使用前由成人检查组装是否正确。
3、柔韧塑料薄膜带有柔韧塑料薄膜的玩具须遵从以下要求:(1)无衬底的薄膜如面积大于100mm×100mm,则该薄膜的平均厚度必须大于0.038mm。
(2)薄膜厚度小于0.038mm且面积大于100mm×100mm, 必须在任意30mm×30mm面积内的薄膜上打孔,孔的总面积最小应占薄膜总面积的1%。
(3)对于塑料气球,不需要充气或损坏后测量其厚度,直接对双层塑料薄膜测量其厚度。
4、玩具袋玩具袋开口周长大于380mm,并用束带作收口,应符合以下要求:(1)用渗透(透气)材料制成,或(2)在玩具袋上有两个650mm2的通气孔,这两个通气孔相距至少150mm。
5、玻璃可触及玻璃可用于制造36个月以上儿童玩具,只要:(1)其使用对玩具功能是必须的;(如:光学玩具,玻璃灯泡,试验设备玻璃)(2)用于起加强作用的玻璃纤维;(3)实心玻璃弹子或娃娃玩具的实心玻璃眼睛。
6、膨胀物质本技术要求不适用于种植箱中的种子。
能够完全容入小零件筒的,由膨胀材料制成的玩具或玩具部件,在20℃的纯净水中浸泡24h±0.5h后,其各方向尺寸膨胀不能超过50%。
7、边缘可触及边缘不能有任何不合理的伤害危险;(1)根据边缘测试方法,测试玩具上的金属或玻璃边缘,不能通过锐利边缘,则被视作为存在潜在性危险的边缘。
如边缘未通过试验,则应评估玩具在预期使用中是否会产生不合理伤害危险。
不管该边缘是否修整过,都要根据边缘测试方法进行测试。
注:边缘可折叠,卷曲或成螺旋状,使其不可触及,也可用塑料或其它类似材料覆盖。
(2)搭接如果最大厚度为0.5mm的金属片与下垫面之间的间隙大于0.7mm, 则金属片的边缘必须符合a)。
(3)金属边缘包括紧固件,(如螺钉帽)和刚性的聚合材料边缘,不能有引起刺伤或擦伤的毛刺。
柔韧的聚合物质上溢料(如:聚烯烃)不视作毛刺。
(4)如为玩具的功能所必需,则锐利功能性边缘可用于供36个月以上儿童使用的玩具。
应加贴警告标志,提醒使用者注意锐利边缘的潜在危险。
然而,电导体,显微镜的载玻片和盖玻片的边缘无需警告。
8、尖端和金属丝金属丝和可触及尖端不能有造成任何不合理伤害的危险。
(1)玩具上的可触边缘按照尖端测试方法测试不能通过的,则判定为存在潜在危害的锐利尖端。
如尖端未通过测试,则应考虑玩具的可预见性使用,判定是否存在不合理的伤害危险,例如铅笔尖和类似的书写绘画工具的尖端不能视为锐利尖端。
(2)玩具功能必须的锐利尖端,可用于供超过36个月以上儿童使用的玩具。
应加贴警告标志,提醒使用者注意锐利尖端的潜在危险。
用于电导体的尖端视为功能性尖端,不要求警告。
(3)设计预定用于弯曲的金属丝或金属部件,例如用于改变玩具或玩具部件的造型(如:软体填充玩具)的金属丝,按照金属丝挠曲性测试时,不能断裂并产生危险锐利尖端或刺破玩具表面。
(4)设计不是用于弯曲的金属丝,但在玩耍过程中可能被弯曲,按照金属丝挠曲性测试时,不能断裂并产生危险锐利尖端或刺破玩具表面。
9、突出物突起状的管子和刚性元件,如构成对儿童的伤害则应进行保护。
保护性元件,按60±2N拉力测试时,保护元件不能失效。
玩具伞伞骨的末端应予以保护,若保护性元件按60±2N拉力测试时,保护失效,那么该末端通过边缘测试方法和尖端测试方法的测试,伞骨末端不能有锐利的边缘和尖端。
另外,如保护如前所述失效,则伞骨直径最小应为2mm,末端无毛刺,且修整光滑,大致成半球型。
10、相互运动的部件10.1折叠和滑动机构本要求不适用于潜在座位表面宽度小于140mm的玩具。
具有折叠和滑动机构的玩具应符合如下要求:(1)玩具推车和手推婴儿车,如果含有手柄或其它结构部件会折叠倒塌在儿童身上,则必须有一个主锁定装置及至少一个付锁定装置, 二者应直接作用于折叠机构上。
当玩具安装好后,至少其中一个锁定装置能自动工作。
按照玩具推车和手推车测试方法的要求测试,玩具不能倒塌,所有锁定装置都不能失效或解锁。
同一机构上的两个装置(如锁环),分别在玩具的左右侧,视为一个锁定装置。
玩具推车或手推车如可能在其中一个安全锁定装置未锁紧的情况下部分安装,则在此种状态下按玩具推车和手推车测试方法进行测试。
注:(1)项涵盖的玩具推车或手推车例子如图2-1所示。
部分安装指使用者可能误以为玩具已全部安装好的情况。
图2-1 玩具推车和手推婴儿车例子1-把杆移动 2-车架移动(2)玩具推车或手推车如不存在能折叠倒塌在儿童身上的手柄或其它机构,则至少有一个锁定装置或安全停止装置,这些装置可以是手动操作的。
按照玩具推车和手推车测试方法测试时,玩具不能倒塌,锁定装置和安全停止装置不能失效或解锁。
玩具推车或手推车如可能在没有安全锁定的情况下部分安装,则要在此种状态下进行测试。
注:(2)项涵盖的玩具推车或手推车例子如图2-2所示。
图2-2 玩具推椅例子1-车架移动(3)其它可折叠玩具上的折叠机构(如熨衣板、折叠椅、折叠桌子),如有剪切的运动,必须具有:①一个安全停止或锁定装置。
当按照其它折叠玩具测试方法测试时,玩具不能倒塌或锁定装置失效或解锁;并且②作剪切运动的移动件之间的间隙最小为12mm。
(4)除了上面(1)、(2)、(3)所述的玩具,其他带有折叠或滑动机构,承载或能够承载儿童体重,并且会伤害儿童手指的玩具;其移动元件间的间隙如能插入5mm的塞规,则12mm的塞规也能插入。
10.2驱动机构本要求不适用于不足以伤害手指或身体其它部分的驱动机构。
驱动机构和发条钥匙必须符合如下要求:(1)驱动机构应该封装,当进行跌落试验和冲击试验进行测试时,不能有可触及锐利边缘或锐利尖端或其它压伤手指或身体其它部分的部件暴露出来。
(2)大型重型玩具的驱动装置必须封装,按照倾翻试验进行测试时,不能有可触及锐利边缘或锐利尖端或其它压伤手指或身体其它部分的部件暴露出来。
(3)发条的钥匙或起动手柄的形状和尺寸必须使钥匙或手柄与玩具主体之间的间隙不能插入5mm的塞规,或能插入12mm的塞规。
任何钥匙或手柄上的孔洞都不能插入5 mm的塞规。
10.3铰链如果铰链连接的任一部件重量小于250克,则本要求不适用。
玩具如有两个部件是通过一个或多个铰链连接,并且在组装以后沿铰链线上边缘之间有空隙,若该间隙能插入5mm的塞规,则也应该能插入12mm的塞规。
10.4弹簧弹簧必须符合以下要求:(1)如果螺线弹簧的两个相邻螺线之间的间隙在任何使用位置大于3mm,螺线弹簧必须不可触及。
(2)如果拉伸螺旋弹簧在受到40N的拉力时,两个相邻的弹簧圈之间的距离大于3mm,必须不可触及。
撤力后不能复原的弹簧不适用于本项要求。
弹簧在受到40N的压力撤力后不能复原,或弹簧缠绕于玩具的另一元件(如导棒),以致可触探头A在相邻弹簧圈之间插入深度不超过5mm,那么该弹簧不适用于(3)项的要求。
(3)如果在压簧处于静止时,相邻两个弹簧圈之间距离大于3mm,并且玩具使用时,该弹簧能承受大于等于40N的力,则应不可触及。
11、口动玩具(1)按照小零件测试,口动玩具和口动玩具可拆卸吹嘴不能完全容入小零件筒。
(2)不可拆卸的口动玩具的吹嘴,如果首先根据浸泡试验进行测试,再根据扭矩试验和拉力试验进行测试后,能被拆卸脱落,则不能完全容入小零件筒。
(3)用嘴吹吸的玩具内,如有松散件,如口哨中的小球,或响哨中的簧片,当按照口动玩具的耐久性试验进行测试后,不能掉出能完全容入小零件筒内的物件。
(4)安装在气球上的可拆卸或不可拆卸的吹嘴,必须符合(1)、(2)项的要求。
12、气球乳胶气球的包装应附有警告。
“警告!八岁以下儿童可能被未充气或破裂的气球阻梗或窒息。
需要成人监护。
未充气气球远离儿童。
破裂气球立即扔掉。
”天然乳胶气球包装必须注明“由天然橡胶制成”。
13、玩具风筝和其它飞行玩具的绳线风筝和其它飞行玩具的绳线如与儿童直接联接,并且其长度超过2m,则按绳线电阻的测试方法测试,绳线电阻率必须超过每厘米100兆欧。
要提醒用户注意放风筝的潜在危险、不要靠近架空电线和有雷闪时放风筝。
14、封闭式玩具14.1儿童可进入的玩具(1)有门、盖或类似装置的任何玩具,如果内含连续体积大于0.03m3,其内部所有尺寸大于或等于150mm,则至少应有两个畅通的通气孔,每个孔的面积至少为650mm2,相距至少150mm,当玩具以任意位置放在地板上,相近的两个坚直平面模拟房间的角落成90°角,整个通气孔也要畅通。
如果连续空间被一个永久性间隔或隔板(两个或更多)分成内部最大尺寸小于150mm的空间,则不需要有通气孔。
(2)对于有门、盖或类似装置的玩具,从内部最大施加50N的力,则门、盖或类似装置应能打开。
注:这一条款显然要求不能在门、盖或其它装置上使用扣子,拉链和其它紧固件。
(3)具有垂直开启的铰链盖的玩具箱必须有盖支撑装置,以防止盖的突然倒塌或落下。
盖支承装置必须能支撑住盖,使在距离闭合处50mm到距离闭合处不超过60°弧形行程中任何一个位置上,盖在自身重量作用下落下的行程都不能大于12mm,但最后50mm的行程除外。
按玩具箱垂直开启的铰链盖耐久性测试进行7000周期打开和闭合试验前后,盖支撑装置必须符合本要求。
盖支撑装置必须不需消费者调节就能保证盖足够支撑力,按玩具箱垂直开启的铰链盖耐久性测试进行周期试验后,盖支撑装置也无需调节就能满足上述要求。
盖和盖支撑装置必须符合铰链条款的相关要求。
具有垂直开启铰链盖的玩具箱必须附有合适的安装和维护说明书。
14.2面具和头盔(1)全部包裹住头、不透气材料制成的面具和头盔,必须至少有1300mm2透气面积,可以是两个最少间隔150mm的通气孔或任意等效面积单个透气面。