会计学--企业决策的基础 第二章作业答案
- 格式:doc
- 大小:54.00 KB
- 文档页数:4

Chapter 6Merchandising Activitie s Ex. 6.41PROBLEM 6.1AClaypool earned a gross profit rate of 32%, which is significantly higher than the industry average. Claypool’s sales were above the industry average, and it earned $77,968 more gross profit than the “average” store of its size. This higher gross profit was earned even though its cost of goods sold was $18,000 to $20,000 higher than the industry average because of the additional transportation charges.To have a higher-than-average cost of goods sold and still earn a much larger-than-average amount of gross profit, Claypool must be able to charge substantially higher sales prices than most hardware stores. Presumably, the company could not charge such prices in a highly competitive environment. Thus, the remote location appears to insulate it from competition and allow it to operate more profitably than hardware stores with nearby competitors.PROBLEM 6.5Ac. Yes. Sole Mates should take advantage of 1/10, n/30 purchase discounts, even if itmust borrow money for a short period of time at an annual rate of 11%. Bytaking advantage of the discount, the company saves 1% by making payment 20 days early. At an interest rate of 11% per year, the bank charges only 0.6%interest over a 20-day period (11% X 20/365 = 0.6%). Thus, the cost of passing up the discount is greater than the cost of short-term borrowing.Chapter 7 Financial assetsChapter 8 Inventories and the cost of goods soldSupplementary ProblemChapter 91617。

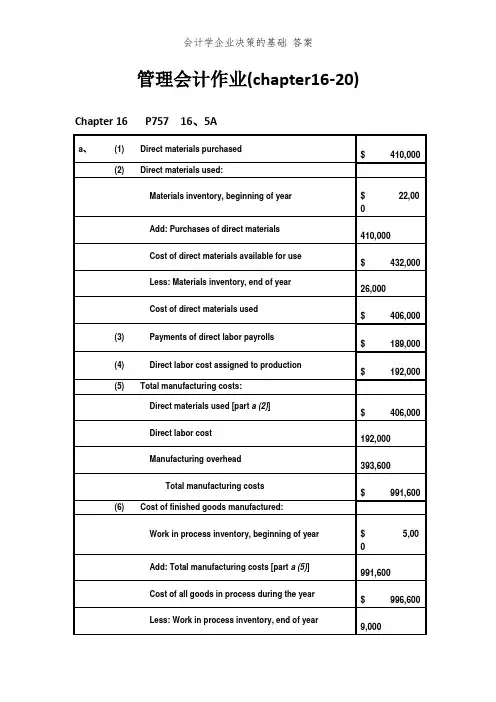
管理会计作业(chapter16-20) Chapter 16 P757 16、5AChapter 16 P761 16、4BChapter 17 P802 17、3Aa、Department One overhead application rate based onmachine-hours:ManufacturingOverhead = $420,000 = $35 per machine-hour Machine-Hours 12,000Department Two overhead application rate based on direct labor hours:ManufacturingOverhead = $337,500 = $22、50 per direct labor hourDirect Labor Hours 15,000Chapter 17 P805 17、8Ad、The Custom Cuts product line is very labor intensive in comparison to the Basic Chunksproduct line、Thus, the company’s current practice of using direct labor hours toallocate overhead results in the assignment of a disproportionate amount of total overhead to the Custom Cuts product line、If pricing decisions are set as a fixed percentage above the manufacturing costs assigned to each product, the Custom Cuts product line isoverpriced in the marketplace whereas the Basic Chunks product line is currently priced at an artificially low price in the marketplace、This probably explains why sales of Basic Chunks remain strong while sales of Custom Cuts are on the decline、e、The benefits the company would achieve by implementing an activity-based costing systeminclude: (1) a better identification of its operating inefficiencies, (2) a better understanding of its overhead cost structure, (3) a better understanding of the resource requirements of each product line, (4) the potential to increase the selling price of Basic Chunks to make it more comparable to competitive brands and possibly do so without having to sacrificesignificant market share, and (5) the ability to decrease the selling price of Custom Cuts without having to sacrifice product quality、Chapter 18 P835 18、1B、Ex、a、job costing (each project of a construction company is unique)18、1b、both job and process costing (institutional clients may representunique jobs)c、job costing (each set of equipment is uniquely designed andmanufactured)d、process costing (the dog houses are uniformly manufactured inhigh volumes)e、process costing (the vitamins and supplements are uniformlymanufactured in high volumes)Chapter 18 P841 18、3A4,000 EU @ $61、50 = $246,000b4,000 EU @ $13、50 = $54,000Chapter 18 P845 18、2Ba、(1) $49 [($192,000 + $48,000 + $54,000) ÷ 6,000 units](2) $109 [($480,000 + $108,000 + $66,000) ÷ 6,000 units](3) $158 ($49 + $109)(4) $32 ($192,000 ÷ 6,000 units)(5) $18 ($108,000 ÷ 6,000 units)b、In evaluating the overall efficiency of the Engine Department, management wouldlook at the monthly per-unit cost incurred by that department, which is the cost of assembling and installing an engine ($109 in part a)、Chapter 20 P918 20、1Ad、No、With a unit sales price of $94, the break-even sales volume in units is 54,000 units:Unit contribution margin = $94 - $84 variable costs = $10Break-even sales volume (in units) = $540,000$10= 54,000 unitsUnless Thermal Tent has the ability to manufacture 54,000 units (or lower fixed and/or variable costs), setting the unit sales price at $94 will not enable Thermal Tent to break even、Chapter 20 P918 20、2AChapter 20 P920 20、6ASales volume required to maintain current operating income:Sales Volume = Fixed Costs + Target OperatingIncomeUnit Contribution Margin= $390,000 + $350,000= $20,000 units $37。

会计学-企业决策的基础答案管理会计作业(chapter16-20)Chapter 16 P757 16.5AChapter 16 P761 16.4BChapter 17 P802 17.3Aa. Department One overhead application rate based on machine-hours:Manufacturing Overhead= $420,000= $35 per machine-hourMachine-Hours 12,000Department Two overhead application rate based on direct labor hours:Manufacturing Overhead= $337,500= $22.50 per direct labor hourDirect Labor Hours 15,000Chapter 17 P805 17.8Ad. The Custom Cuts product line is very labor intensive in comparison to the BasicChunks product line. Thus, the company’s current practice of using direct laborhours to allocate overhead results in the assignment of a disproportionate amount of total overhead to the Custom Cuts product line. If pricing decisions are set as a fixed percentage above the manufacturing costs assigned to each product, the Custom Cuts product line is overpriced in the marketplace whereas the Basic Chunks product line is currently priced at an artificially low price in the marketplace. This probablyexplains why sales of Basic Chunks remain strong while sales of Custom Cuts are on the decline.e. The benefits the company would achieve by implementing an activity-based costingsystem include: (1) a better identification of its operating inefficiencies, (2) a betterunderstanding of its overhead cost structure, (3) a better understanding of theresource requirements of each product line, (4) the potential to increase the sellingprice of Basic Chunks to make it more comparable to competitive brands and possibly do so without having to sacrifice significant market share, and (5) the ability todecrease the selling price of Custom Cuts without having to sacrifice product quality.Chapter 18 P835 18.1a. job costing (each project of a construction company is unique)B. Ex.18.1b. both job and process costing (institutional clients may represent uniquejobs)c. job costing (each set of equipment is uniquely designed andmanufactured)d. process costing (the dog houses are uniformly manufactured in highvolumes)e. process costing (the vitamins and supplements are uniformlymanufactured in high volumes)Chapter 18 P841 18.3Ab4,000 EU @ $13.50 = $54,000Chapter 18 P845 18.2Ba. (1) $49 [($192,000 + $48,000 + $54,000) ÷ 6,000 units](2) $109 [($480,000 + $108,000 + $66,000) ÷ 6,000 units](3) $158 ($49 + $109)(4) $32 ($192,000 ÷ 6,000 units)(5) $18 ($108,000 ÷ 6,000 units)b. In evaluating the overall efficiency of the Engine Department, management wouldlook at the monthly per-unit cost incurred by that department, which is the cost of assembling and installing an engine ($109 in part a).Chapter 20 P918 20.1Ad. No. With a unit sales price of $94, the break-even sales volume in units is 54,000 units:Unit contribution margin = $94 - $84 variable costs = $10Break-even sales volume (in units) = $540,000$10= 54,000 unitsUnless Thermal Tent has the ability to manufacture 54,000 units (or lower fixed and/or variable costs), setting the unit sales price at $94 will not enable Thermal Tent to break even.Chapter 20 P918 20.2AChapter 20 P920 20.6ASales volume required to maintain current operating income:Sales Volume =Fixed Costs + Target Operating IncomeUnit Contribution Margin=$390,000 + $350,000= $20,000 units$37。

Ex. 1.7i. Financial accountingh. Management accountingb. Financial reportingf. Financial statementsg. General-purpose assumptionc. Integritye. Internal controld. Public accountinga. BookkeepingCASE 1.1FANNIE MAESeveral factors prevent a large publicly owned corporation such as Fannie Mae from issuing misleading financial statements, no matter how desperately the company needs investors’ capital. To begin with, there is the basic honesty and integrity of the company’s management and its accounting personnel. Many people participate in the preparation of the financial statements of a large corporation. For these statements to be prepared in a grossly misleading manner, all of these people would have to knowingly participate in an act of criminal fraud.Next, there is the audit of Fannie Mae's financial statements by a firm of independent CPAs. These CPAs, too, would have to participate in a criminal conspiracy if the company were to supply creditors and investors with grossly misleading financial statements.If personal integrity is not sufficient to deter such an act of fraud, the federal securities laws provide for criminal penalties as well as financial liability for all persons engaged in the preparation and distribution of fraudulent financial statements. All that would be necessary for the SEC to launch an investigation would be a “tip” from but one individual within the company’s organization or its auditing firm. An investigation also would be launched automatically if the company declared bankruptcy or became insolvent shortly after issuing financial statements that did not indicate a shaky financial position.Problem 2.1 AProblem 3.8AExercise 4.2Exercise 4.14Problem 4.5AProblem 5.2AProblem 5.5A。


(5)(6)(7)(8)(9)Owner’s equity is not valued at either the original amountinvested or at the estimated market value of the business. In fact, owner’s equity cannot be valued independently of the values assigned to assets and liabilities. Rather, it is a residual figure—the excess of total assets over totalliabilities. (If liabilities exceed assets, owners' equity would be a negative amount.) Thus the amount of Berkeley's capital should be determined by subtracting the corrected figure for total liabilities ($23,100) from the corrected amount of total assets ($51,500). This indicates owners'equity of $28,400.The $22,400 described as “Other assets” is not an asset,because there is no valid legal claim or any reasonable expectation of recovering the income taxes paid. Also, the payment of federal income taxes by Pippin was not abusiness transaction by Big Screen Scripts. If a refund were obtained from the government, it would come to Pippin personally, not to the business entity.The proper valuation for the land is its historical cost of$39,000, the amount established by the transaction in which the land was purchased. Although the land may have acurrent fair value in excess of its cost, the offer by the friend to buy the land if Pippin would move the building appears to be mere conversation rather than solid, verifiable evidence of the fair value of the land. The "cost principle," although less than perfect, produces far more reliable financial statements than would result if the owners could "pull figures out of the air" in recording asset values.The accounts payable should be limited to the debts of the business, $32,700, and should not include Pippin’s personal liabilities.The amount owed to stagehands for work done throughSeptember 30 is the result of completedtransactions and should be included among the liabilities of the business. Even if agreement hasbeen reached with Mario Dane for her to perform in a future play, he has not yet performedand therefore, is not yet owed any money. Thus, this $25,000 is not yet a liability of thebusiness.therefore cannot be included in the assets. To do so would cause an overstatement of both assets and owners’ equity.The “Office furniture” amount must be reduced by $2,525.invested or at the estimated market value of the business. In fact, owner’s equity cannot be valued independently of the values assigned to assets and liabilities. Rather, it is a residual figure—the excess of total assets over total liabilities. (If liabilities exceed assets, owners' equity would be a negative amount.) Thus the amount of Berkeley's capital should be determined by subtracting the corrected figure for total liabilities ($23,100) from the corrected amount of total assets ($51,500). This indicates owners' equity of $28,400.。


会计基础第1章练习一、单选题1.下列各项中属于流动资产的有()。
A、库存现金 B、运输设备 C、专利权 D、开办费2.一般说来会计主体与法律主体是()。
A、是有区别的 B、相互一致的 C、不相关的D、相互可替代的3.下列各项中适用于划分各会计期间收入和费用的原则是(。
A、配比原则B、权责发生制 C、可比性 D、谨慎性4.下列项目中,不属于资产要素的是()。
A、应收账款 B、预收账款 C、债权 D、专利权5.负债是指企业由于过去交易或事项形成的()。
A、过去义务 B、现时义务 C、将来义务 D、潜在义务6.下列项目中,不属于收入范围的是()。
A、商品销售收入 B、劳务收入 C、租金收入D、代收款项7.在会计信息质量要求中,要求合理核算可能发生的费用和损失的是(A、谨慎性 B、可比性C、可理解性 D、可靠性8.在会计核算过程中,会计处理方法前后各期()。
A、应当一致,不得随意变更B、可以变动,但须经过批准C、可以任意变动D、应当一致,不得变动9.下列项目中,不属于会计核算方法的是()。
A、复式记账 B、成本计算 C、财产清查 D、编制财务预算二、多选题10.下列有关会计的说法中,正确的包括()A、本质上是一种经济管理活动B、对经济活动进行核算和监督C、以货币为主要计量单位D、核算特定主体的经济活动11.会计信息的质量要求包括()A、谨慎性 B、可理解性 C、可靠性 D、权责发生制12.会计的基本职能包括()。
A、进行会计核算B、实施会计监督C、预测经济前景,参与经济决策D、评价经营业绩13.下列公式中,属于会计等式的是()。
A、资产负债=所有者权益B、收入费用=利润C、本期借方发生额=本期贷方发生额D、期末余额=期初余额+本期增加额本期减少额14.下列项目中,属于利润要素的内容有()。
A、营业利润 B、利润总额 C、净利润 D、代收款项15.在下列组织中,可以作为会计主体的是()。
A、企业的事业部 B、分公司 C、生产车间 D、销售部门16.我国《企业会计准则》规定,会计期间分为()。

基础会计第二章试题及答案一、选择题1.下列不属于企业所有权职能的是: A. 当年利润分配 B. 管理和控制 C.分散企业风险 D. 资本投资答案:A. 当年利润分配2.初期固定资产的会计处理一般包括: A. 余额结转 B. 计提折旧 C. 全额折旧 D. 新增资产计记答案:D. 新增资产计记3.会计中的成本是指: A. 发生的现金或货币等价物支出 B. 销售收入减去可变成本 C. 各种资源或权利所表示的经济利益的代价 D. 有形长期资产的原始账面金额答案:C. 各种资源或权利所表示的经济利益的代价二、填空题1.现金流量表反映企业在一个会计期间内的现金收入、支出和净额的情况,能够帮助分析企业的偿债能力和发展潜力。
2.财务会计的主要任务是向外部用户提供企业的财务信息。
三、简答题1.请简要介绍会计中的资产和负债。
–资产指的是企业拥有并能为企业带来经济利益的物资和资源,如现金、存货、固定资产等。
负债则是企业对外部实体所承担的经济责任或义务,包括应付账款、短期债务等。
资产和负债在资产负债表中有详细列示。
2.解释会计主体的概念及其特点。
–会计主体是指进行会计核算的独立经济实体,具有独立的财务决策、财产所有权和经营管理能力。
其特点包括主体独立性、资产责任独立性、会计核算独立性等。
四、案例分析某企业在一季度的财务报表中,资产总额为1000万元,负债总额为600万元,所有者权益为400万元。
请计算该企业的资产负债表中的资产负债率和所有者权益比率,并对其进行分析。
•资产负债率 = 负债总额 / 资产总额 = 600万元 / 1000万元 = 60%•所有者权益比率 = 所有者权益 / 资产总额 = 400万元 / 1000万元 = 40%该企业的资产负债率为60%,所有者权益比率为40%,说明该企业的债务占比较大,所有者权益相对较少,需关注其偿债能力和财务稳定性。
以上是基础会计第二章试题及答案的内容,希望对您有所帮助。
第一章练习题1.会计主体是〔〕A.企业单位B.企业法人C.法律主体D.独立核算的特定单位正确答案:D解析:D、会计主体是指企业会计确认、计量和报告的空间范围,即会计核算和监督的特定单位或组织。
2.企业会计分期假设是以〔〕假设为前提的。
A.会计主体B.持续经营C.历史本钱D.货币计量正确答案:B解析: B、会计分期是对企业持续经营的生产经营活动人为划分为一个个连续的、长短相同的期间。
3.〔〕假设明确了会计工作的空间范围A.会计主体B.持续经营C.会计客体D.会计分期正确答案:A解析:A、会计主体这一会计根本假设,对会计确认、计量和报告范围从空间上作了有效界定。
4.会计核算的内容是特定会计主体的〔〕A.经济资源B.经济活动C.资金运动D.劳动成果正确答案:C解析: C、会计的对象是指会计所核算和监督的内容。
但凡特定主体能够以货币表现的经济活动,都是会计对象。
以货币表现的经济活动通常又称为资金运动。
因此,会计核算和监督的内容即会计对象就是资金运动。
5.以下哪一项描述会计的含义是不正确的?A.商业语言B.是目的而不是到达目的的手段C.决策有用的D.信息系统正确答案:B解析: B、会计是一种商业语言,但它不是目的,它是一种工具,具有核算和监督两项根本职能,并且也具有预测经济前景、参与经济决策、评价经济业绩等拓展职能,因此它是决策有用的,并且是一个信息系统。
6.以下有关会计主体假设的表达中,正确的〔〕A.界定会计主体是开展会计确认,计量和报告工作的重要前提B.明确会计主体,才能划定会计所要处理的各项事项的空间范围C.会计主体也等同于法律主体D.法律主体通常也是会计主体正确答案:A、B、D解析: C、会计主体是指企业会计确认、计量和报告的空间范围,即会计核算和监督的特定单位或组织。
一般而言,法律主体必然是一个会计主体,但是会计主体不一定是法律主体。
会计主体既可以是法人,如股份或有限责任公司,也可以是不具备法人资格的实体,如独资企业或合伙企业、集团公司、事业部、分公司、工厂的分部等。
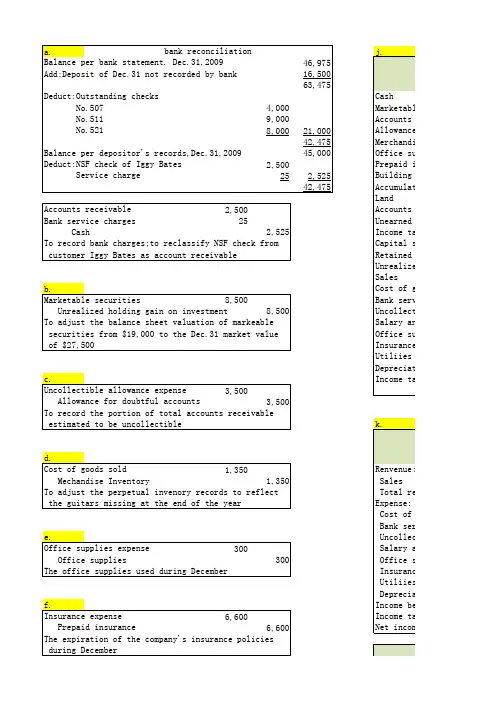
管理会计作业(chapter16-20)Chapter 16 P757 16.5AChapter 16 P761 16.4BChapter 17 P802 17.3Aa.Department One overhead application ratebased on machine-hours:Manufacturing Overhead$420,000=$35 per machine-hourMachine-Hours 12,00 0Department Two overhead application rate based on direct labor hours:Manufacturing Overhead$337,500=$22.50 per direct laborhourDirect Labor Hours 15,00 0Chapter 17 P805 17.8Ad .The Custom Cuts product line is very labor intensive in comparison to theBasic Chunks product line. Thus, the company’s current practice of using direct labor hours to allocate overhead results in the assignment of a disproportionate amount of total overhead to the Custom Cuts product line. If pricing decisions are set as a fixed percentage above the manufacturing costs assigned to each product, the Custom Cuts product line is overpriced in the marketplace whereas the Basic Chunks product line is currently priced at an artificially low price in the marketplace. This probably explains why sales of Basic Chunks remain strong while sales of Custom Cuts are on the decline.e .The benefits the company would achieve by implementing an activity-basedcosting system include: (1) a better identification of its operating inefficiencies, (2) a better understanding of its overhead cost structure, (3) a better understanding of the resource requirements of each product line, (4) the potential to increase the selling price of Basic Chunks to make it more comparable to competitive brands and possibly do so without having to sacrifice significant market share, and (5) the ability to decrease the selling price of Custom Cuts without having to sacrifice product quality.Chapter 18 P835 18.1B. Ex. 18.1a.job costing (each project of a construction company is unique)b.both job and process costing (institutional clients may represent unique jobs)c.job costing (each set of equipment is uniquely designed and manufactured)d.process costing (the dog houses are uniformly manufactured in high volumes)e.process costing (the vitamins and supplements are uniformly manufactured in high volumes)Chapter 18 P841 18.3AInputs:•Beginning WIP•StartedOutputs:•Units completed•Ending WIP•Beginning WIP•Units started•Units completed•Ending WIP•Cost of beginning WIP•Cost added during the period•Cost of goods transferredtransferred•Add ending WIP$246,000b4,000 EU @ $13.50 =$54,000Chapter 18 P845 18.2Ba .(1)$49 [($192,000 + $48,000 + $54,000) ÷ 6,000 units](2)$109 [($480,000 + $108,000 + $66,000) ÷6,000 units] (3)$158 ($49 + $109)(4)$32 ($192,000 ÷ 6,000 units)(5)$18 ($108,000 ÷ 6,000 units)b .In evaluating the overall efficiency of the Engine Department, managementwould look at the monthly per-unit cost incurred by that department, which is the cost of assembling and installing an engine ($109 in part a).Chapter 20 P918 20.1Ad .No. With a unit sales price of $94, the break-even sales volume in unitsis 54,000 units:Unit contribution margin = $94 - $84 variable costs = $10Break-even sales volume (in units)$540,000$1054,000 unitsUnless Thermal Tent has the ability to manufacture 54,000 units (or lower fixed and/or variable costs), setting the unit sales price at $94 will not enable Thermal Tent to break even.Chapter 20 P918 20.2AChapter 20 P920 20.6ASales volume required to maintain current operating income:Sales VolumeFixed Costs + TargetOperating IncomeUnit Contribution Margin$390,000 + $350,000= $20,000 units $37。
第二章 会计科目、账户和复式记账班级 _____________ 姓名 _________________ 学号 __________________一、单项选择题1. 会计科目是指对(B )的具体内容进行分类核算的项目。
A. 经济业务B.会计要素C.会计账户D.会计信息2.会计科目按其(B )不同,可分为资产类、负债类、所有者权益类、成本类和损益类 科目。
B. 反映的经济业务D.提供信息的详细程度及其统驭关系)不同,分为总分类科目和明细分类科目。
A. 反映的会计对象B. 反映的经济业务A. 合法性B.相关性C.谨慎性D.实用性 5.对会计要素具体内容进行总括分类、提供总括信息的会计科目称为( A.)。
A. 资产B.所有者权益C.成本D.损益 9.账户是根据( C )设置的,具有一定格式和结构,用于分类反映会计要素增减变动情 况及其结果的载体。
A.会计要素B.会计对象C.会计科目D.会计信息10. 根据明细分类科目设置的账户称为( B.)。
11. 下列账户中,属于所有者权益类账户的是( A )。
A. 本年利润 B.主营业务收入C.应付账款D.投资收益12. “制造费用”科目按其反映的经济内容,属于( D.)类科目。
A.资产 B.负债 C.所有者权益 D.成本13.关于会计科目与账户之间的关系,下列说法中不正确的是( D. )。
A. 两者核算内容一致B.两者性质相同C. 会计科目是设置账户的依据D.两者都有一定的结构和格式 14. 账户的余额按照表示的时间不同,分为( D.)。
A. 期初余额B.本期增加发生额和本期减少发生额C.期末余额 D.期初余额和期末余额15. 某账户的期初余额为 500元,期末余额为3000元,本期减少发生额为 800元,则本期增 加发生额为(D.)元。
C.反映的经济内容D.提供信息的详细程度及其统驭关系 4.应根据企业自身特点, 设置符合企业需要的会计科目, 是指会计科目设置的 (D )原则。
第一章练习题1.会计主体是()A.企业单位B.企业法人C.法律主体D.独立核算的特定单位正确答案:D解析:D、会计主体是指企业会计确认、计量和报告的空间范围,即会计核算和监督的特定单位或组织。
2.企业会计分期假设是以()假设为前提的。
A.会计主体B.持续经营C.历史成本D.货币计量正确答案:B解析: B、会计分期是对企业持续经营的生产经营活动人为划分为一个个连续的、长短相同的期间。
3.()假设明确了会计工作的空间范围A.会计主体B.持续经营C.会计客体D.会计分期正确答案:A解析:A、会计主体这一会计基本假设,对会计确认、计量和报告范围从空间上作了有效界定。
4.会计核算的内容是特定会计主体的()A.经济资源B.经济活动C.资金运动D.劳动成果正确答案:C解析: C、会计的对象是指会计所核算和监督的内容。
凡是特定主体能够以货币表现的经济活动,都是会计对象。
以货币表现的经济活动通常又称为资金运动。
因此,会计核算和监督的内容即会计对象就是资金运动。
5.下列哪一项描述会计的含义是不正确的?A.商业语言B.是目的而不是达到目的的手段C.决策有用的D.信息系统正确答案:B解析: B、会计是一种商业语言,但它不是目的,它是一种工具,具有核算和监督两项基本职能,并且也具有预测经济前景、参与经济决策、评价经济业绩等拓展职能,因此它是决策有用的,并且是一个信息系统。
6.下列有关会计主体假设的叙述中,正确的()A.界定会计主体是开展会计确认,计量和报告工作的重要前提B.明确会计主体,才能划定会计所要处理的各项事项的空间范围C.会计主体也等同于法律主体D.法律主体通常也是会计主体正确答案:A、B、D解析: C、会计主体是指企业会计确认、计量和报告的空间范围,即会计核算和监督的特定单位或组织。
一般而言,法律主体必然是一个会计主体,但是会计主体不一定是法律主体。
会计主体既可以是法人,如股份有限公司或有限责任公司,也可以是不具备法人资格的实体,如独资企业或合伙企业、集团公司、事业部、分公司、工厂的分部等。
B. Ex. 2.10
The burglary on January 7 is an event after reporting date (期后事项,资产负债表日后事项) which occur between the reporting date and the date on which the financial statements are authorised for issue by the board of directors.).
(1) The burglary on January 7 is a non-adjusting event which is indicative of conditions that arose after the reporting date and has no effect on items in the financial statements, but should be disclosed by notes if material.(2) If the burglary took place before December 31, it is an adjusting event which provides additional evidence of conditions existing at the reporting date and the amounts in the financial statements should be adjusted.
b.
Yes; the form of Fellingham’s organization is relevant to a lender. If the company is
not incorporated, the owner or owners are personally liable for the debts of the business organization. Thus, if the business is organized as a sole proprietorship, it is actually Small’s personal debt-paying ability that determines the collectibility of loans to the business. If the business is a partnership, all of the partners are personally liable for the company’s debts.
If Fellingham is organized as a corporation, however, a lender may look only to the corporate entity for payment. However, some lenders would not make sizable loans to a small corporation unless one or more of the stockholders personally guaranteed the loan. This is accomplished by having the stockholder(s) cosign the note.。