最简单单的日语基础入门(The simplest single Japanese Basics)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:72.00 KB
- 文档页数:25


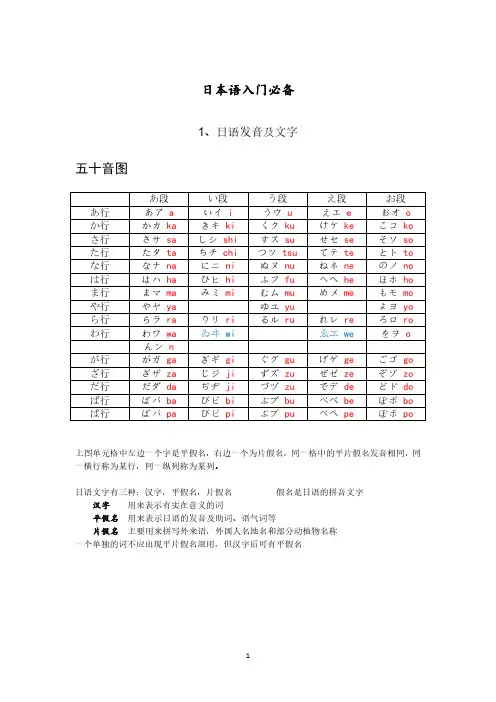




yi di kei ma si 我出门了yi da la xia yi 走好ta da yi ma 我回来了o gai li na sai 欢迎回来 a li ya duo 谢谢ma sa ga 难道是……(有怎么可能的意思)mo xi ga xi dei 难道是……(对事情的猜测)sou lei dei mo 即使如此fu sa ken len na you 别开玩笑了!jiao dang jiao nai you 开什么玩笑?na ji ga you 真的假的?na ni 什么kou kou dou gou 这是哪里?da lei ga 是谁?da lei da 什么na ni mou nou da 你是什么人? ang da da lei 你是谁?gou ki gen you 一切安好o ha you 早上好dou mou 你好(熟人间)kou ni qi wa 你好(不熟)sa you na la 再见jia nei (熟人)ji ji wei 父亲o dou sang 爸爸ha ha wai 母亲o ga sang 妈妈ao fu kou lao 老妈ao ya ji 老爸o ni jiang 哥哥a ni weio nei jiang 姐姐o dou dou 弟弟yi mou dou 妹妹o ji jiang 爷爷o ba jiang奶奶na li huo duo 原来如此ha ya kou 快点yi kou you 要出发了yi kou zou 我们走sa dei 接下来bei zi ni 没什么meng dai nai 没问题xing bai nai 别担心jiao dou 稍微ma dei 等等ya ba li 果然如此ya ha li 果然是ka wa yi 可爱kou wa you 可怕a nou 那个kou nou 这个dou kou da 在哪里?o dou kou 男人ong na 女人kong bang wa 晚上好o ya si mi ma sei 晚安(好好休息)nei mou lei 沉睡ou xi gou dou 工作ou mai mou xi ga xi dei 你,莫非是?wa la da 笑了kou dou mo 小孩mou si mei 女孩/女儿mou si gou 儿子si kei 喜欢dai si kei 最喜欢nou mei 喝ma xi long 纯白you lou xi kou ou nei gai yi xi ma si 请多指教(/照顾)gou mei na sai 对不起si ma nai 真对不起si mi ma sai 对不起ya da 不要dei mou 但是you kei 雪ha na 花dou xi dei 为什么nang dei dou you yi mi 什么意思dai jiu bu 没关系dai jiu bu dai si ga 没关系吧?sou da 是的gou gai 误会ou nou lei 可恶(含咒骂)qi ke xiu 可恶ba gei mou nou 怪物ke da zou 来了哦jia ma da 碍事hei da ./hei na 奇怪(人) miao na (抽象)sa ga lai 闪开da ka lai 所以ha ya kei ni gei long 快逃ha na sei 放开ya mei long 住手wo ga da 我知道xiu lou ga 我怎么知道xing ji 相信xing ji la nai 真不敢相信mou jia e si lou 鲁莽/乱来hong dou ga 真的吗?hong dou 真的ji zi wa 其实……gan ba lei 努力/加油ta si gei dei 救出ta si ga da 得救了you ga da 太好了mei xi 吃饭ou yi xi 好吃ha la hei dou 肚子饿了ma mou lou 保护ma gou 孙子hei na jiao gou 笨蛋(非贬义)you na 不要叫我…… kei ye da 消失kou lou xi 痛苦mou mou 桃si zi mei 雀ya you mei菖蒲sa ku la 樱ka zei 风ka kou gou 觉悟tai sai zi 最重要/珍贵mou da da 没用的dan ma lei 住口/闭嘴si gai 厉害(称赞)you mei 梦a ke mou 噩梦/恶魔xi dei yi lou 知道某种情况ma zei 糟了xi ma da hou hou 方法ou you bi 以及ma ta ge 真是的(感叹)zeb bei dei si ga 可惜了zi duo 一直ka la na zi一定sa lou 猴子dou xi dei 怎么了?o ma ji gou na sai 请等等fou da li dou mou 两个na ni you xi dei dang da 做了什么?yi nai 消失了/不见了kei you zi gei dei 请小心(保重)you lou si mou dei si ga 不可原谅you lou can zou 不能原谅o ji zi yi dei 冷静点mou ga xi 过去kai yi dei kui lai 要回来啊xi ya wa sai 幸福ka na xi 悲伤ya kou sou kou 约定o wa li 结束了o wa da o mou xi lei 有趣ha ji mei ma xi dei 初次见面xi zi ka ni xi lou 安静mei zi la xi na 真难得yi la xia yi ma sai 欢迎光临mai ni ji 每天sou xi dei 还有ha ji mei dei 开始da mei 不行zi ma nai ya zi 无聊的家伙ku da la nai 无聊/荒谬ki mu ji 舒服wa gou ma ma 任性zi lui 狡猾a mai 天真mo duo mo duo 更多更多ka ma wang 无所谓ka kou yi 好酷/帅bei zi ni 没什么/无所谓o sai yi dei 别生气xiu ga nai 没办法xi ga da nai na 没办法了啊(很无奈的)kou tou wa lou 我拒绝ta ben 大概/说不定yi king ga ni xi lou 适可而止o lou ga na 愚蠢 a seu na lai 不要着急ta nou mu 拜托kei lai 讨厌kei lei美丽kang bing xi te ke lei 你饶了我吧!ming na bu ji dei 大家没事吧?wa si lei dei 忘记o yi sa xi bu li si 好久不见hei mi zi 秘密nai xiu sa si ga 真不愧是……(名不虚传)mi zi gei da 找到了ta ma xi 灵魂kou kou da 就是这里了yi zi no ma ni (状况是)什么时候(发生的)ma da a xi da 明天见ying dei si ga 可以这样吗?sou lei da gei 只是如此而已mou li 不可能cou ya xi 不甘心ku da la nai 真无聊men dou si lou 真麻烦1:i chi (发音相当于我们的“i qi”——实际上大多数日本人念的1听起来最接近我们这边“i ji”的发音)2:ni 3:san 4:yon shi(我们应当念成“yong”或者“xi”)5:go 6:roku(……lo ku)7:nana shichi(后面的shichi相当于我们的“xi qi”的发音)(两种念法)8:hachi(……ha qi……大多数日本人念的很像“ha ji”)9:ku kyuu (两种念法)10:juu(相当于“jiu”)。

自学日语的方法 -------------日语入门技巧开始之前,先告诉朋友们日语自学是没有问题的。
很多人都是自学日语,如果您打算开始学习日语,但几乎还没什么基础的朋友,那您如果有兴趣可以看看这篇文章。
在自己学习之前,先用百度或搜狗、Google之类的搜索软件搜索“日语”这两个字,看一看日语的百度百科,对日语的来龙去脉有一个大致的了解。
日语的构成、敬语、简语等相关的知识有所了解。
不要因为日语有敬语等这些问题而害怕。
敬语无非是从中国古代学过去的。
就像在中国称呼别人的孩子称:贵公子,自己叫自己的小孩:犬子 ,称呼别人的太太称:贵夫人,自己的太太叫:贱内是一个样的。
首先是要明确自己学习日语的目的,哪怕只是为了兴趣也没关系,并制定自己的阶段计划,比如大约学半年去考4级,学1年考3级,学两年后考2级,有目标方向才能有动力,以后学习中请经常提醒自己的目标尚未实现,仍需努力。
(注:本人学日语是公司在我一点都不会日语的情况下,经常派本人去日本工作和出差所以才自学日语)第二是选择教材,一般可以选择“标准日本语”,该教材的特点是难度适中,适合自学,并有配套自学辅导教材,还有配套vcd教材。
网上也有一些学日语的电子书,及书附的视频及MP3,需要各位自己去找了。
我用的办法将这一堆里的学日语的书,都搞下来试一试,不好用就删掉。
因为好书需要适合你自己才行,用这样的办法不能在一种法上吊死。
毕竟我们是自学的。
《超好笑!我是日语学习书》和《别笑!我是日语XX书》这类书比较适我自己。
当然,日语学习的书本人从网上下了一大堆,一本不适合自己的就换另一本。
找到合适自己的日语书后,也可以网上买纸质书。
买书之前注意看一下别人是怎么评价自己要买的书的。
买一本配有光盘的日语书. 然后,跟着光盘学习日语平假名和片假名的发音和书写,同时还要按行和段分别背诵假名. 还要学会日语中的促音长音拗音拗长音等.第三就是选择一本好的字典。
这里就不推荐了。
不过,建议不用急着去买。

日常生活①単語(一)一. 果物水果(shu 1 gu o)0人芒:苹果(p ng gu o) (2+3) 扌^:梨(I ) (2):西瓜(x i gu® (1+1) /(1+0):香蕉(xi m g ji ®o)(1+1):芒果(mdng gu。
(2+3):荔枝(I zh i) (4+1)Pty :柠檬(nng m缶g) (2+2):菠萝(b o lu 0 (1+2):桃子(t (Ozi) (2+0):葡萄(p utao) (2+0)^<5^^ :樱桃(y ing tao) (1+0)柿:柿子(sh izi ) (4+0)二. 野菜蔬菜(sh u c d) 八夕廿彳:白菜(b d c i d (2+4)草:菠菜(b o c d) (1+4)七口】丿:芹菜(qn c d (2+4) U夕灭:生菜(sh引g c d (1+4) 二:韭菜(ji u c®(3+4)11^9^ :黄瓜(hu d ng gu耳(2+1)bvb :西红柿(x 1 hcng sh)i (1+2+4) / 番茄(f m qi )&1+2)肚丁:茄子(qi ezi) (2+0)声卡力、彳壬:土豆(t u d/3+2)Eld :萝卜(lu C o) (2+0):胡萝卜(h ulu C o) (2+2+0)乏 d :蘑菇(m o gu) (2+0)力U7v7-:菜花(c a i hu a (4+1)力壬:南瓜(n a n gu (2+1)卍一PA :青椒(q 1 ng ji(a+)1):豆芽(d <u y a) (4+1)二A二夕: 蒜(su a) (4)三.飲族物□ 一匕一:咖啡(k a f 百)(1+1){儿夕:牛奶(ni U①(2+3)日一夕、儿卜:酸奶(sum n d) (1+3)炭酸飲料:碳酸饮料(t a n suai y in li c o) (4+1+3+4)/汽水(q i shu i r)(4+3)声二一灭:果汁(gu6 zhi) (3+1)⑹酉:酒(ji U (3)已一儿:啤酒(p ^i U (2+3)才一夕一:矿泉水(ku nng qu Q shui) (4+2+3)白开水(ba k cishu ]) (2+1+3):葡萄酒(p ut商⑪(2+2+3)三.祭日春節:春节(ch m ji e) (1+2)除夜:除夕(ch u x i) (2+1)指年玉:压岁钱(y c su iqi间(1+4+2)乂一〒、一:劳动节(l(Od dng ji )e (2+4+2)国慶節:国庆节(gu O q ing ji e) (2+4+2)母①日:母亲节(m u qin ji e (3+0+2)父①日:父亲节(f u qin ji e) (4+0+2)四.郵便局力夕一:柜台(gu i i员(4+2)書留郵便:挂号信(gu d h CD x in) (4+4+4)郵便番号:邮政编码(y du zh E g bi c n m ©(2+4+1+3)切手:邮票(ycu pi co) (2+4)航空便:航空信(h dng keg x i n) (2+1+4)小包:包裹(b c o guc) (1+3)株:股票(g u pi d o) (3+4)年賀状:贺年卡(h e ni cn k©(4+2+3)差出人:发件人(f a ji cn r缶)(1+4+2) 受取人:收件人(shau ji c r 印)(1+4+2) 振◎込住:汇款(hu ku O n) (4+3)。


快速学习简单常用的日语对不起一一死米马散! or 狗埋!10、这是什么? 一一口来挖囊打卡?11、妈妈一一欧卡桑爸爸一一欧多桑姐姐——欧内桑妹妹 ---- 依毛偷爷爷辈 ---- 欧吉依桑奶奶辈一一欧巴阿桑 阿姨辈一一欧巴桑叔叔辈——欧吉桑13、太贵了! 塔卡依内!14、这个多少钱? 一一口来依哭拉跌( de )死卡? 15、我也不好意思——口七啦口扫 16、好吃——袄依洗衣 17、我要开动啦一一依塔大ki 马死 18、我吃饱啦一一锅七锁撒马跌洗他 19、为什么? 多无洗帖? or 囊跌? or 哪在?20、小心 ---- 阿布那依1、 你好一一口你七哇 (白天)、袄哈有(早上)、空帮哇(晚上)2、 谢谢一一阿里嘎脱3、 再见一一撒腰那拉 (这个不常用)4、 再见——八一八一 or 甲or 甲阿内or 甲马塔or 马塔内or 扫屋甲5、 没关系 卡马依马散 多依塔洗马洗帖(te )(对方说谢谢时用)6、是! 不是! ---- 害!依 ----- 挨! 7、 行!不行!——依——内!打咩!9、不知道一一希腊那依 哥哥欧尼桑弟弟欧偷偷12、一到十 起、你、桑、有、锅、楼哭、娜娜、哈气、哭、九精品文库 21、生日快乐一一烫叫比偶咩跌偷 最近忙吗? ――依马锅楼一扫嘎洗衣跌死卡?你多大了? 阿纳塔哇囊撒依跌死卡?我回来啦 -他大姨妈你回来啦一 —欧卡挨里我走啦一一 -依帖 ki 马死你走好 -依帖拉瞎依好久不见了 ■――偶嘿撒洗不利你身体还好吗?一一欧赶 ki 跌死卡?你要去哪? ――多口挨(e )依哭诺卡?您是哪位? ――多奇拉撒马别吵!一一 -萨瓦古纳不要放在心上一一ki 你洗那哭帖毛依依没怎么样一 —囊跌毛那依不,没事- —依呀,打依叫不不必担心- —新拜洗那哭帖毛依依有明白了一一 -哇卡他你说谎一- -五锁刺 ki去哪?一一 -多口挨?别过来一一 -口那依跌是个什么样的人?一一多那嘿( hi )头跌死卡? 原来如此 —那炉火多(阿笠博士和原田常用语好可怕一一 -口哇依那这样可以吗? 一一口累跌打依叫不去死吧一― -哭他巴累真有趣 -欧毛洗楼依内很郁闷一一 -武器空跌依鲁糟透了一— -咱咱打咩怎么样?一 -多无?真厉害 -死锅依!死给(男用)该死一一哭扫好漂亮一一 -ki 来(re )依打内22、 23、24、25、26、27、2& 29、30、31、32、 33、34、35、36、37、38 39、40、—卩呵卩呵—) 42、43、44、45、46、47、48 49、50、51、52、圣诞快乐一一库里斯马死欧咩跌偷(按英语那样读就行)精品文库精品文库阿霍(修次和服部常用~~嘻嘻~~) or 阿霍哭撒依 巴卡雅洛真的吗? ——混偷? or 马吉?果然如此一一哑怕里扫屋打(柯南常用语~~嘿嘿~~) 吹牛一一活啦不 ki 真可怜 •—卡瓦伊扫真可爱 ―卡瓦伊依内别哭了一 ―那卡那依跌我请客一 •—欧锅炉腰胡说一一 •五锁不!一一 •依呀游戏结束 ――给母欧巴太好了一 •—腰卡他冉来一遍 毛五一起烦人一一 •无路撒依。
日本语最简单基础入门教程相对于汉语而言,日语的主要特点有:文字方面,日语同时使用汉字、平假名、片假名和罗马字;词汇方面,日语当中的外来语范围很广、数量也非常大;语法方面,日语的修饰语前置性、过去时词素后置性与汉语相似,置词后置性、否定词素后置性等与汉语相反,动词、形容词等词尾变化丰富;语言变体方面,日语由于区域因素而产生的方言差异不如汉语那么严重,但是因为性别和社会心理因素而形成的男性用语、女性用语以及敬语等表现活跃。
第一节文字的多元性********************************************************** 本节要回答的问题有3个:** 1) 什么是文字的多元性? ** 2) 什么是五十音图? ** 3) 如何在假名与罗马字之间相互转换? **********************************************************多元性(Pluralism)是指来自不同种族的,有着不同宗教和政治信仰的人们在同一社会和平共处的原则。
在这里,日语文字的多元性是指日语中有着不同起源的、在文字的划分上分属表意文字、音节文字和拼音文字的汉字、假名(包括平假名和片假名)以及罗马字在日语这一语言中和平共处,共同服务于日语这一语言的状态。
古代日本人民只有自己的语言,没有自己的文字。
公元3世纪前后,中国的汉字(Chinese character)传入日本,日本人民开始利用汉字来记载本民族的语言。
汉字的传入对于日本整个国家和民族来说具有划时代的意义。
汉字刚刚传入日本的时候,所有的日语均用汉字来书写,当时的日语文字系统和今天的汉语文字系统一样是单一的。
不过,日语的文字系统并没有停留在这一状态。
大约在公元5世纪,日本人民以汉字为基础创造了一种崭新的音节文字——假名(Kana)。
假名到了日本的平安时代(公元10世纪)已基本定型。
从那以后,日语中同时采用汉字和假名两种文字的书写方式便固定下来,直到日本近代的明治维新时期。
全文的例句都是中、英、日外加罗马音四语对照确实是很难得的日语入门资料精通此文还怕神马坑日本语最简单基础入门教程(只讲书面用语,发音日常口语无视,花20分钟看下,游戏的话理解应该可到70%以上)相对于汉语而言,日语的主要特点有:文字方面,日语同时使用汉字、平假名、片假名和罗马字;词汇方面,日语当中的外来语范围很广、数量也非常大;语法方面,日语的修饰语前置性、过去时词素后置性与汉语相似,置词后置性、否定词素后置性等与汉语相反,动词、形容词等词尾变化丰富;语言变体方面,日语由于区域因素而产生的方言差异不如汉语那么严重,但是因为性别和社会心理因素而形成的男性用语、女性用语以及敬语等表现活跃。
第一节********************************************************** 本节要回答的问题有3个:** 1) 什么是文字的多元性?** 2) 什么是五十音图?** 3) 如何在假名与罗马字之间相互转换?**********************************************************多元性(Pluralism)是指来自不同种族的,有着不同宗教和政治信仰的人们在同一社会和平共处的原则。
在这里,日语文字的多元性是指日语中有着不同起源的、在文字的划分上分属表意文字、音节文字和拼音文字的汉字、假名(包括平假名和片假名)以及罗马字在日语这一语言中和平共处,共同服务于日语这一语言的状态。
古代日本人民只有自己的语言,没有自己的文字。
公元3世纪前后,中国的汉字(Chinese character)传入日本,日本人民开始利用汉字来记载本民族的语言。
汉字的传入对于日本整个国家和民族来说具有划时代的意义。
汉字刚刚传入日本的时候,所有的日语均用汉字来书写,当时的日语文字系统和今天的汉语文字系统一样是单一的。
不过,日语的文字系统并没有停留在这一状态。
大约在公元5世纪,日本人民以汉字为基础创造了一种崭新的音节文字——假名(Kana)。
最简单单的日语基础入门(The simplest single Japanese Basics)The easiest basic Japanese introduction ~!Japanese to Tokyo tone as the standard pronunciation, the tone can be divided into the following several types: Type 0, 1, 2, 3 type type, the type, the type, the type and the type etc.. High pitched accent, tone said softly.Type 0: means only the first shot is low and the other shots are high.Type 1: means that only the first shot is high and the following shots are low.2: that only the second high, the first and third beat the following pictures are low.The type that the second, third shot, the first beat and the fourth the following pictures are low.The second type: said to the fourth, the first and fifth beat the following pictures are low.The second type: take high to fifth, the first and sixth beat the following pictures are low.The second type: take high to sixth, the first and seventh beat the following pictures are low.The type and the following type of tone and so on.The auxiliary word of the 0 type word is followed by a loud tone. In addition to the 0 types of words, all the auxiliary words are followed by a low tone.Some words have two or more different tone types, namely, the word has different pronunciations in different situations.Some words have two or more connected accents (i.e., tone type symbols) within a word, indicating that the word has two or more stresses. Such as: "Hai Wa's estate period complete (positive and negative)" - 1 - 1 tone type 1, said this word has three stresses, namely "estate", "WA" and "period" three beat are high pitched (i.e. accent).The high pitch of Japanese cannot be divided into two. That is a word (including follow-up, auxiliary) only in a "low" and "low level", and "low high" tone configurations, and may not appear similar to the "low high" and "low high" or "high low high low" tone configuration. No matter how long the word is, its tone configuration must conform to this rule.Commonly used Japanese surname pronunciationChinese, Japanese, Chinese, JapaneseYamada, Yamada ~ Toyota and published by TOYOTA for nursingTanaka Tanaka: Honda Honda's importance to Na KaSaito Saitou and Yamamoto, national live longer Yamamoto ~ and MooMisaki Sato Misaki Sato national and complete this gloomy MooWood village with better forest, wood village woman is kindKinoshita Ki with Kobayashi Kobayashi, was in the hyperplastic speech.Sichuan Sichuan, Fujiwara Fujiwara officer examples: guys ra Hideo Sasaki served with national national Yezuo wild National. SUZUKI: I bear Yexiong wood with wild on the ~ ofHaruki Haruki, better kind of bamboo bamboo for students to construct the hyperplasticGrammatical nomenclatureJapanese ChineseThe subject period subject.Analysis period predicate predicateHakka with Chan on the period.Period complement complementConjoined modifiers for cancer. Terms last longer. J on the period of conjoined modifiers (body repair)Adverbial modifier terms by u. U's. J on period adverbial modifier (repair)Prompt the last period extraposed (prompt)With longer period, language on the appositive (with language)Automatic word. Complete automatic word (intransitive)He for longer. He verb verb (transitive verb)Easy language for the word's periodThe immediate on sentenceWen? Analysis on immediate estate (the festival)Lian Wen? Terms on immediate analysis (even the phrase's estate section)The need for immediate cancer's sentenceExamples on the sentence's immediate repliesChongwen's immediate complete compound sentencePing Che: preface J's immediate statementThe question on immediate questions on MooThe last command will last on immediate terms imperative (command)This paper, on moved longer on immediate ExclamativesCommonly used Chinese surname pronunciationChinese, Japanese, Chinese, JapaneseZhao Zhao j u u was yellowZhang j u king Wang ZetaChapter. J u once,Jiang Jiang j u Song song.Xiao Xiao j u, u Cao CaoLi, Li, sun, sun, SunLili terms last kind of LoloIn this cancer, cancer of Han HanZhu Zhu Wu Wu.Week. U j u this beamQi Hai Jiang national fountain was completeYo u Yang Yang Liu Liu this UXu Xu with J Liu much longerSlowly J Lv LvQin Qin's Chen.U Hu Hu bagSquare Maomao moo u uThe money, Wei Wei's estateFeng j u / better, Pan, harmed to justJapanese vocabulary classificationClassification according to the meaning, shape, or function of Japanese words can be divided into the following 12 categories (12 words):Words have independent words inflected words can be used as predicate verbAdjectiveAdjective verbUnflected words can serve as subject body nounsNumeralPronounCan not be subject modifier, modifier body language - conjoined wordsModifiers -- adverbsDo not act as modifiers in conjunction - conjunctionsThere is no continuity - exclamationsThe affiliated words inflected verbsUnflected wordsExplanation: independent words have independent concepts in sentences and have independent abilities in sentences. The subordinate word has no independent concept, and can not exist alone in the sentence. It can only be attached to the back of the independent word, and has a certain grammatical function.Reading of place namesThe following is a Japanese vocabulary for geographical names.Word pronunciation, tone, part of speech, definitionAki is the kind of speech (Qiu Yeyuan) typeEnglish alphabet, Japanese pronunciationEnglish alphabet, Japanese pronunciation, English alphabet, Japanese pronunciationA a, N or N, or staircase, orB B, O o, the.C, C, P, P topicsD, Q Q and D data - a fierceE e, R R,,, andF, S, or s or FG g, T T, and Department of TokyoH h and U u, unit or organizationI I and V V, andJ J W W, Tokyo her fierceK K, X X or fries in election,L L, Y y and orM m and Z Z or miraj fries do notNumeralThe last 00 terms of type0 types of miraj as1 Sweet UTI 2Two 2 two types:Three 3 three 0 SanFour / four. 4 / 1 type on yo yo Five 5 five period modelSix 6 six on 2Seven 7 seven / - 1 - type zeta. Eight 8 eight types: UTINine / nine on the 9 types of with u Ten 100 U 1 typeEleven 11 eleven u live UTITwelve 12 twelve u inThirteen 13 thirteen u SanFourteen 14 fourteen U /. Yo u'sFifteen 15 fifteen longer periodSixteen 16 sixteen on uSeventeen 17 seventeen u. U - - / UTI Eighteen 18 Eighteen: UTI uNineteen 19 nineteen complete with U / u on Twenty 20 twenty in UTwenty-one 21 twenty-one in u live UTI Thirty 30 thirty San uForty 40 forty 10 on uFifty 50 fifty longer periodSixty 60 sixty on uSeventy - seventy - 70 U / u UTI.Eighty 80 eighty ha UTI uNinety 90 ninety with u u(1) 100 100 hundredOne hundred and one hundred one hyakuichi 101 zero oneOne hundred and one hundred nineteen hundred Article 119 through olfactoryTwo hundred and two hundred 200Three hundred and three hundred is 300 ms.Four hundred and four hundred 400Five hundred and five hundred.Six hundred to six hundred and I ぴゃ 600.Article 700 seven hundred a hundredYao Yao ぴゃ repellent to 800.Article 900 article olfactory displayThousand thousand (1000) glandOne thousand and one thousand 1001 Sen IchiTwo thousand twenty two thousand 2000Two thousand four hundred 二千零四十 2040 I tell you all about Three thousand and three thousand and thousand trainingA three 千六百九十七 3697 all morning and I ぴゃ千六百九十七 third molarFour thousand and four thousand 4000 called meFive thousand and fifty five thousandSix thousand and six thousand and ろくせん 6000.Seven thousand, seven thousand and a printingEight thousand eight thousand, was endowedNine thousand nine thousand, you leadIt is ten thousand ten thousand ten thousand ichimaArticle 10 million million million man allArticle 63 63 million million million which is all I saury Hundred million million million manIt is one of the ten million million million manKeep one's 一亿亿一亿A trillion trillion trillion market swings百位数与千位数有音变,读法: retained his position as below One hundred hundredTwo hundred thousand two hundred d d hundred thousand meAre three thousand and three thousand and three hundred, three hundred @ @Four hundred and four thousand and four hundred and four thousand and one morningPlug your five hundred and five thousand and five hundred thousandArticle I ぴゃ one hundred six thousand and six thousand and ろくせんSeven hundred and seven hundred thousand, seven thousand and seven hundred such a printingYao Yao, sir ぴゃ eight thousand eight thousand was endowed withEarth's nine hundred and nine thousand nine hundred and nine thousand olfactory leadTen thousand, thousand, ten thousand, thousand Sen no ichimaThe amount of lyricsOne to one type 2Two and two make 二个两个 type三个 three three type IIIOne by four 四个 type IIIWhen one of the five 五个 type II六个 six むっつ type IIISeven 七个 nanatsu type IIDo one 八个 eight type IIIHere is one of nine 九个 [2].Article 1 十个 and typeThe 顺序词汇读法 physical quantityThe following quantity is displayed on the 顺序语词汇. 单词读音调词性释义 voice(2) one type name lyrics (GE).Name two type (0) 两个 Prince of two people.Sannin (III) type name lyrics (GE).I would like to (4) 2 type name lyrics (GE).In the period (five) on 2 five (a person) noun.On the in cancer (six) 2 (a person) six noun.In the field of oncology. UTI (seven) 2 (a person) seven noun.Is there on zeta (eight) 2 (a person) eight noun.With u in cancer (nine), nine (a person) type noun.(10): complete on the type ten (a noun) people.Have a cancer in cancer (He Ren) the type of noun several people; how many people.Week meansHe Yaori (aka yo u's for a few weeks):Monday (analysis by u:): Monday(to complete: Ka Kiyoshi): TuesdayWater Day (I live by: U): WednesdayThursday (MOO yo u: on Thursday):Jin Yaori (with yo u: on Friday)Earth Day (yo u:): SaturdaySunday (in yo u: UTI: Sunday)Date expression1 (1) (Zu ICDRG: UTI)One day (live in zeta zeta)The two day (for examples, analysis) The three day (after construct KA) The four day (after 10 KA)The five day (Che Zu KA)The six day (better, live)The seven day (aka of KA)The eight day (yo u KA)The nine day (as in language language) The ten day (and,,)The eleven day (u live in zeta zeta)The twelve day (in u in UTI)The thirteen day (U San in UTI)The fourteen day (yo u after KA)The fifteen day (longer period in UTI)The sixteen day (U on the in UTI)The seventeen day (. U in zeta zeta)The eighteen day (U: UTI in UTI)The nineteen day (complete with u in UTI)The twenty day (WA Zu KA)The twenty-one day (in u live in zeta zeta)The twenty-two day (in in u in UTI)The twenty-three day (in U San in UTI)The twenty-four day (in complete by cancer in UTI) / (in, after yo u)The twenty-five day (in longer period in UTI)The twenty-six day (in U on the in UTI)The twenty-seven day (in U - - in UTI)The twenty-eight day (in U: UTI in UTI)The twenty-nine day (in complete with u in UTI)The thirty day (San in U / ka construct for UTI)The thirty-one day (San u live in zeta zeta)I (aka cancer in UTI) / number of daysMonthly expressionsJanuary (sweet feeling, a UTI) month (after KA Che Zu)(in February, second month (analysis) in Zu KA)March (San Zu,) three months (San Zu,)(by April, four month's analysis) (cancer, published by analysis)May (five month period, (feeling) period, analysis)June (, on the analysis of six month (after), Zu)(July., seven months Zu UTI) (Na Na Ka Zu)(August: eight months Zu, UTI) (after KA wa Zu)(on September, nine months (feeling) with u, Zu)October (, complete analysis of ten month (after), Zu)November (last longer, eleven months Zu UTI) (u live after KA analysis)December (U, in ten second month (feeling) u in Ka Zu)He Yue (aka cancer, He Yue (Zu) / month - on KA Zu) / months Other time related expressionsCentury - Century (Hai ki estate)Year - year (NE cancer)(U ne light-years - light-years was on)The year before, the previous year (on last year's NE) / (and and and.)Last year, last year (with J cancer last year (NE) / NE on the national cancer)This year, this year (Language and woman)Next year, next year (j u ne's construct) / year (RA's Che NE)The year after year - (U / NE was on the coming years (National) Che ne RA's)Last month, the first month (estate's estate's analysis)Last month, the first month (Zu's estate)This month (this month) - this month (was on Zu)Next month - to month (RA Che Zu)The month after next month -- again (National Che RA Zu)Last week (last week) - the first week (on cancer. Estate estate complete)Last week (last week) - first week (on u estate.)This week (this week) - this week (on was complete.)Next week (next week) - week (RA u live.)Next week (next week) - another week (national environmental u RA Che)The day before yesterday (and and and live)Yesterday, yesterday (with the U)Today, today (with j u)Tomorrow, tomorrow (thou hyperplastic / j u to construct the zeta)The day after tomorrow, after tomorrow (actually after the national)In the morning, (thou national)Morning, noon (period cancer)Noon - day ()Afternoon, afternoon (period period)In the evening, evening party (name, u TA)Night - night (yo.)Day -- day ()The weekend weekend (. U Ma Zu)At the end of the month, at the end of the month (Ma Zu Zu)At the end of the year - end (NE's Ma Zu)To live in, the verb Aru, ()] as predicate sentences called existential sentence. There is the verb form is to this, thou [~ masu Che ~ masu]1. the meaning of existential verbsExistential verbs have two meanings, namely "being" and "being". The division of meaning depends mainly on the auxiliary verb before the verb:... Actually, this ~ masu (and sweet ~ masu) /... There...... In this thou ~ masu (, sweet ~ masu) /... In...Example: the court, actually this ~ masu. There is (a) yard.The court in this thou ~ masu. In the yard.2. the division of verbs in existenceThere thou this verb [] and [~ masu (and this sweet ~ masu ~ masu)] were used in different occasions, the specific division of labor are as follows:This thou ~ masu for said thingsLive for the ~ masu people, animalAnd this is used to represent the first person ~ masu - and related situations, including self deprecating toneExample: with this film, thou j u ~ masu. There's a film today.Dogs and cats, sweet ~ masu. There are dogs and cats.Have a kind of home in soil Thursday, and this ~ masu. / if it'sSaturday, I'll be at home.3. existential sentences"3.1." means the basic sentence pattern with "yes"... In (a)... Actually, this ~ masu (or sweet ~ masu) / in... There...... In... This is actually on (or live ~ ~ estate estate on / in)... No... (used for strengthening the negative tone)Example: in court with terms - sweet flower, wood, thou this ~ masu. There are beautiful flowers and trees in the yard.Te,, the fruit is actually is in on this Ma's estate. There is no fruit on the table.3.2. stands for the basic sentence pattern of "yes"... (or a)... In this thou ~ masu (or sweet ~ masu) /... In...... Wa... There is actually much ~'s estate (or Ma Che's estate) /... Not in... (used for strengthening the negative tone)Example: the cat, as sweet ~ masu intermediary. The cat is in the living room.Tanaka San wa moviola in Wa Hai Ma's estate. Mr. Tanaka is not at the cinema.Sentence pattern of desireDesire sentence usually consists of the auxiliary verb "or" sweet desire, pushing volume plus amount of verb verb "U? Yo u "and" Ta Hai "and" U? Yo u "after the verb" and "constitute a complete thought. There are three kinds of desire sentences in modern japanese.1. (first person + HA)... And / or... I live in a case. / (first person) think...For example: hyperplastic UTI: Japanese guys or Mian? Juan raft County Hai Geng skewer? Nbsp / / we want to learn japanese.(guys for woman wa te, see:) the last Noyes was still. I want to watch tv.2. (first person + HA)... And / or... For sweet and sweet ~ masu si. / (first person) think...Example: Japan: in line with international and at last after thinking for Che ~ masu. I want to study in japan.Hai Hai Dictionary (. J) or buy ICDRG: sweet and sweet ~ masu si. I want to buy a good dictionary.3. (first person + HA)... O... Yo u / u and Si Hai ~ masu. (first person) want to...Example: the doctor (woman graduate, Che Chan.) in and Si Hai - u ~ masu. I want to be a doctor after graduation.The new (for thou RA). Live or buy and complete the Department of Noyes and Che Si ~ masu. I'd like to have a new TV set.。