CCNA security笔记
- 格式:docx
- 大小:1.28 MB
- 文档页数:16

ccna读书笔记进行搜索troubleshooting ip address一些网络问题的排难:1.打开windows里的1个dos窗口,ping本地回环地址,如果反馈信息失败,说明ip协议栈有错,必须重新安装tcp/ip协议。
2.如果1成功,ping本机ip地址,如果反馈信息失败,说明你的网卡不能和ip协议栈进行通信。
(written by 红头发,chinaitlab bbs)第三篇:ccna培训读书笔记ccna培训笔记总结1、 ccna基础:熟悉一些常用的网络设备、熟悉常用的网络电缆、熟悉简单的lan技术和拓扑结构、熟悉简单的wan技术和拓扑结构、知道一些简单的宽带技术、精通osi参考模型、熟悉tcp/ip参考模型、会进行ip地址计算2、 ccna:routing and switching supportccnp:routing and switching support ccie:routing and switchingsecuritycommunications and services3、 ciscoios 执行模式: user exec(用户执行模式) privilege exec(特权模式)4、熟悉应用交换机命令行帮助工具:上下文提示帮助(提供命令列表和具体命令可供选择的参数)、历史命令缓存(重新回放原来输入的命令,对比较复杂的命令尤其有效)、控制台错误信息(如果输入命令错误,指出错误原因,并提示你修改)5、 configuration mode(配置模式):global configuration mode(全局配置模式)和 interface configuration mode(接口配置模式)6、为交换机命名hostname sw1、配置管理地址ip address 配置ip地址、配置缺省网关 ip default- 、使用show命令显示交换机的配置 show version、show running-configuration、show interfacetype/nummber(0/1)、show ip7、路由器启动后如果在nvram中发现配置文件,其就会进入用户模式提示符,如果没有发现,就会进入setup初始化状态8、 enable secret(安全使能密钥)和enable password(使能密钥)不能相同,如果设定安全使能密钥的话,使能密钥就没什么用了9、路由器基于上写文的帮助功能:对不识别的符号进行解析、命令提示、回放最后一次输入的命令以及历史命令方便路由器的配置节省时间10、快捷键诠释:ctrl+a(把光标快速移动到整行的最开始) ctrl+e (把光标快速移动到整行的最末尾)ctrl+b(后退一个字符) ctrl+f(前进一个字符) ctrl+d(删除单独一个字符)show history 显示历史缓冲区中的内容11、把ram中正在运行的配置保存在nvram中 copy running-configstartup-config12、配置路由器的密码:line console o/vty 04/—login—password cisco 或者是以前的老命令enable password/secret cisco取消密码命令 no login—no enable password 13、14、15、 interfacetype slot/port 配置接口命令适合于模块化的设备接口设定时钟速率(仅仅在dce接口上)router(con-if)#clock rate 6400 serial 口一般是连接在csu/dce等类型的提供时钟频率的设备上,但是,假如你的试验环境里采用了背对背的配置,那么需要将一端作为dce设备提供时钟频率。

●OSI与TCP/IP协议框架●OSI各层功能特点●封装与解封装(PDU)●IP包头结构●IP报文传输过程●常见IP相关协议(ARP,ICMP…)●传输层功能●TCP与UDP对比1.1OSI与TCP/IP协议框架OSI是网络界的法律,主要目的是实现各厂商设备的兼容操作,TCP/IP是互联网的主流协议。
图1是OSI与TCP/IP协议模型的对比。
图1OSI与TCP/IP协议模型1.2OSI每层功能及特点1、物理层:其作用是传输BIT信号,典型设备代表如HUB(集线器)。
2、数据链路层:包括LLC和MAC子层,LLC负责与网络层通讯,协商网络层的协议。
MAC负责对物理层的控制。
本层的典型设备是SWITCH(交换机)。
3、网络层:本层的作用是负责路由表的建立和维护,数据包的转发。
本层的典型设备是ROUTER(路由器)。
4、传输层:本层将应用数据分段,建立端到段的虚连接,提供可靠或者不可靠传输。
5、会话层:本层负责两个应用之间会话的管理和维护。
6、表示层:本层解决数据的表示、转换问题,是人机之间通讯的协调者,如进行二进制与ASCII码的转换。
7、应用层:本层是人机通讯的接口。
典型的应用程序如FTP、HTTP等。
1.3OSI封装,解封装以及PDU1.3.1封装所谓封装是指在发送方发生的自上而下的过程在每一层为应用数据添加上特定的头部/尾部信息(PDU,Protocol Data Unit,协议数据单元)Application(应用程序)→segment(数据段)→packet(数据包)→frame(数据帧)→bit (比特,二进制位)1.3.2解封装所谓解封装是指在接收方发生的自下而上的过程逐层的去掉头部以及尾部信息1.4IP包结构IP包结构的结构如图2所示。
图2IP包结构其中的重要字段包括:TTL(Time To Live,生存时间):每经过路由器一次,此值减一。
如果该值为0路由器就不会再转发此数据包。
Protocol(协议):网络层和传输层之间的通讯接口,用于识别传输层的传输协议。

1.网络的定义:一组使用介质(线缆)互连的中间系统(集线器、交换机和路由器等网络设备)以及终端系统(PC和服务器)。
2.工作组Network Group LAN为微软提出,没有中间系统的概念。
3.Physical Topology Categories:4.Bandwidth:单位时间可传输的数据量。
5.Delay:帧从网络的一端到另一端所花费的时间。
6.单工线缆:光缆;双工线缆:同轴电缆、双绞线。
7.所有的网络设备都会将收到的所有信号进行放大。
8.集线器工作在以太网下,其提供的为共享带宽,使用半双工模式,其端口的最大带宽为10Mbit/s。
9.集线器为物理层设备,无法识别任何控制信息,转发机制为放大信号+泛洪处理。
所有连接集线器的设备同处一个冲突域。
10.冲突域:冲突产生的时候能够接收到冲突碎片的设备的集合,就是冲突域(主要存在于半双工模式下)。
11.以太网采用CSMA/CD来防止产生冲突。
12.令牌环:使用令牌来避免冲突,带宽也只有10M,容错率较低(仅使用一个方向传送信息,当环状网络中一个节点down后,将无法传送数据)。
13.总线型和令牌环为局域网拓扑;星形拓扑既是局域网拓扑,也是广域网拓扑。
14.总线型拓扑为集线器式以太网,星形拓扑为交换机式以太网。
15.PC发送信息时,必须包含两个信息:信息的发送方和接收方以及信息所使用的应用程序。
16.以太网交换机的所有接口都支持全双工。
17.MAC地址表示方式:XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX(微软)和XXXX.XXXX.XXXX(cisco)。
18.MAC地址的前24bit为OUI,能确定一个生产厂商,后24bit为厂商自行分配。
19.MAC地址使用CAM表,MAC地址的学习分为static和dynamic两种。
20.交换机能学习源MAC,不能学习目的MAC。
21.Cisco设备的MAC地址表默认aging time为300秒。
22.交换机收到帧,先根据FCS进行校验,然后放大信号,最后根据源MAC和目的MAC来进行匹配,若不能匹配,则进行泛洪。

CCNA笔记1[图]分类: 思科 | 标签: ciscoCCNA笔记1[图] - -最高3层定义了端用户如何进行互相通信;底部4层定义了数据是如何端到端的传输.最高3层,也称之为上层(upper对数据的操作诸如加密,压缩等等3.Session层:建立会话,分隔不同应用程序的数据4.Transport层:提供可靠和不可靠的数据投递;在错误数据重新传输前对其进行更正work层:提供逻辑地址,用于routers的路径选择6.Data根据MAC地址提供对传输介质的访问;实行错误检测,但是不实行错误更正7.Physical层:在设备之间传输比特(bit);定义电压,线速,针脚等物理规范然后数据开始传输;数据传输完毕以后,终止虚电路连接(virtual于是发送方继续发送数据.这就是流控制的用途而bridges是基于软件性质的延时:1个帧从进去的端口到达出去的端口所耗费的时间透明桥接(transparent bridging):如果目标设备和帧是在同1个网段,那么层2设备将堵塞端口防止该帧被传送到其他网段;如果是和目标设备处于不同网段,则该帧将只会被传送到那个目标设备所在的网段每个和switches相连的网段必须是相同类型的设备,比如你不能把令牌环(Token Ring)上的主机和以太网上的主机用switches混合相连,这种方式叫做media translation,不过你可以用routers来连接这样不同类型的网络。
在LAN内使用switches比使用hubs的好处:1.插入switches的设备可以同时传输数据,而hubs不可以。
2.在switches中,每个端口处于1个单独的冲突域里,而hubs的所有端口处于1个大的冲突域里,可想而知,前者在LAN内可以有效的增加带宽.但是这2种设备的所有端口仍然处于1个大的广播域里。
再检查是否可以采用全双工模式,如果不行,则切换到半双工模式。
Ethernet当I/G位为1的时候,我们可以设想它为广播或多播.第46位叫做G/L位,也叫U/L位.当这个位为0的时候代表它是由IEEE分配的全局地址;当这个位为1的时候,代表本地管理地址(例如在DECnet 当中)UDP协议不2.TCP协议可靠;UDP协议不可靠3.TCP协议是面向连接;UDP协议采用无连接4.TCP协议负载较高;UDP协议低负载5.TCP协议的发送方要确认接受方是否收到数据段;UDP反之6.TCP协议采用窗口技术和流控制;UDP协议反之硬件地址也叫节点地址(nodeB类的为255.255.0.0;C类的为255.255.255.0C Address划分子网的几个捷径:1.你所选择的子网掩码将会产生多少个子网?:2的x次方-2(x代表掩码位,即2进制为1的部分)2.每个子网能有多少主机?: 2的y次方-2(y代表主机位,即2进制为0的部分)3.有效子网是?:有效子网号=256-10进制的子网掩码(结果叫做block size或base number)4.每个子网的广播地址是?:广播地址=下个子网号-15.每个子网的有效主机分别是?:忽略子网内全为0和全为1的地址剩下的就是有效主机地址.最后有效1个主机地址=下个子网号-2(即广播地址-1)子网掩码255.255.255.192(/26)1.子网数=2*2-2=22.主机数=2的6次方-2=623.有效子网?:block size=256-192=64;所以第一个子网为192.168.10.64,第二个为192.168.10.1284.广播地址:下个子网-1.所以2个子网的广播地址分别是192.168.10.127和192.168.10.1915.有效主机范围是:第一个子网的主机地址是192.168.10.65到192.168.10.126;第二个是192.168.10.129到192.168.10.190子网掩码255.255.192.0(/18)1.子网数=2*2-2=22.主机数=2的14次方-2=163823.有效子网?:block size=256-192=64;所以第一个子网为172.16.64.0,最后1个为172.16.128.04.广播地址:下个子网-1.所以2个子网的广播地址分别是172.16.127.255和172.16.191.2555.有效主机范围是:第一个子网的主机地址是172.16.64.1到172.16.127.254;第二个是172.16.128.1到172.16.191.254子网掩码255.255.255.224(/27)1.子网数=2的11次方-2=2046(因为B类地址默认掩码是255.255.0.0,所以网络位为8+3=11)2.主机数=2的5次方-2=303.有效子网?:block size=256-224=32;所以第一个子网为172.16.0.32,最后1个是172.16.255.193到172.16.255.223Variable减少路由表大小.使用VLSM时,所采用的路由协议必须能够支持它,这些路由协议包括RIPv2,OSPF,EIGRP和BGP. 关于更多的VLSM知识,可以去进行搜索Troubleshooting IP Address一些网络问题的排难:1.打开Windows里的1个DOS窗口,ping本地回环地址127.0.0.1,如果反馈信息失败,说明IP协议栈有错,必须重新安装TCP/IP协议。
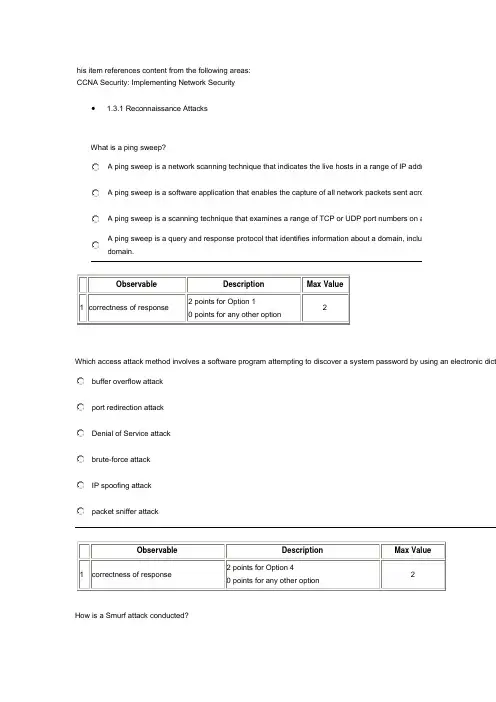
his item references content from the following areas:CCNA Security: Implementing Network Security• 1.3.1 Reconnaissance AttacksWhat is a ping sweep?A ping sweep is a network scanning technique that indicates the live hosts in a range of IP addresA ping sweep is a software application that enables the capture of all network packets sent acrossA ping sweep is a scanning technique that examines a range of TCP or UDP port numbers on a hA ping sweep is a query and response protocol that identifies information about a domain, includindomain.Observable Description Max Value1 correctness of response2 points for Option 10 points for any other option2Which access attack method involves a software program attempting to discover a system password by using an electronic dictbuffer overflow attackport redirection attackDenial of Service attackbrute-force attackIP spoofing attackpacket sniffer attackObservable Description Max Value1 correctness of response2 points for Option 40 points for any other option2How is a Smurf attack conducted?by sending a large number of packets, overflowing the allocated buffer memory of the target deviceby sending an echo request in an IP packet larger than the maximum packet size of 65,535 bytesby sending a large number of ICMP requests to directed broadcast addresses from a spoofed source address on the sameby sending a large number of TCP SYN packets to a target device from a spoofed source addressObservable Description Max Value1 correctness of response2 points for Option 30 points for any other option2A port scan is classified as what type of attack?access attackDenial of Service attackreconnaissance attackspoofing attackObservable Description Max Value1 correctness of response2 points for Option 30 points for any other option2What are the basic phases of attack that can be used by a virus or worm in sequential order?paralyze, probe, penetrate, persist, and propagateprobe, penetrate, persist, propagate, and paralyzepenetrate, persist, propagate, paralyze, and probepersist, propagate, paralyze, probe, and penetrateObservable Description Max Value1 correctness of response2 points for Option 20 points for any other option2What are the three major components of a worm attack? (Choose three.)enabling vulnerabilityinfecting vulnerabilitypayloadpenetration mechanismprobing mechanismpropagation mechanismObservable Description Max Value1 correctness of response Option 1, Option 3, and Option 6 are correct.1 point for each correct option.0 points if more options are selected than required.3Which type of software typically uses a network adapter card in promiscuous mode to capture all network packets that are sent aport scannerping sweeperpacket snifferInternet information queryObservable Description Max Value1 correctness of response2 points for Option 30 points for any other option2An attacker is using a laptop as a rogue access point to capture all network traffic from a targeted user. Which type of attack is ttrust exploitationbuffer overflowman in the middleport redirectionObservable DescriptionMax Value1 correctness of response2 points for Option 30 points for any other option2Which three options describe the phases of worm mitigation? (Choose three.)The containment phase requires the use of incoming and outgoing ACLs on routers and firewalls.The containment phase tracks down and identifies the infected machines within the contained areas.The inoculation phase disconnects, blocks, or removes infected machines.The inoculation phase patches uninfected systems with the appropriate vendor patch for the vulnerability.The quarantine phase terminates the worm process, removes modified files or system settings, and patches the vulnerabilit used to exploit the system.The treatment phase disinfects actively infected systems.ObservableDescriptionMaxValue1 correctness ofresponseOption 1, Option 4, and Option 6 are correct.1 point for each correct option.0 points if more options are selected thanrequired.3Which phase of worm mitigation requires compartmentalization and segmentation of the networdown or stop the worm and prevent currently infected hosts from targeting and infecting other scontainment phaseinoculation phasequarantine phasetreatment phaseObservable Description Max Value1 correctness of response2 points for Option 1 20 points for any other optionWhat is a characteristic of a Trojan Horse?A Trojan Horse can be carried in a virus or worm.A proxy Trojan Horse opens port 21 on the target system.An FTP Trojan Horse stops anti-virus programs or firewalls from functioning.A Trojan Horse can be hard to detect because it closes when the application that launched it closes.Observable Description Max Value1 correctness of response2 points for Option 10 points for any other option2Which two statements are characteristics of a virus? (Choose two.)A virus typically requires end-user activation.A virus has an enabling vulnerability, a propagation mechanism, and a payload.A virus replicates itself by independently exploiting vulnerabilities in networks.A virus provides the attacker with sensitive data, such as passwords.A virus can be dormant and then activate at a specific time or date.Observable Description Max Value1 correctness of response Option 1 and Option 5 are correct.1 point for each correct option.0 points if more options are selected than required.2Which two are characteristics of DoS attacks? (Choose two.)They always precede access attacks.They attempt to compromise the availability of a network, host, or application.They are difficult to conduct and are initiated only by very skilled attackers.They are commonly launched with a tool called L0phtCrack.Examples include smurf attacks and ping of death attacks.Observable DescriptionMaxValue1correctness ofresponseOption 2 and Option 5 are correct.1 point for each correct option.0 points if more options are selected thanrequired.2Which two statements describe access attacks? (Choose two.)Port redirection attacks use a network adapter card in promiscuous mode to capture all network packets that are sent acro Password attacks can be implemented using brute-force attack methods, Trojan Horses, or packet sniffers.Buffer overflow attacks write data beyond the allocated buffer memory to overwrite valid data or exploit systems to execute code.Port scanning attacks scan a range of TCP or UDP port numbers on a host to detect listening services.Trust exploitation attacks can use a laptop acting as a rogue access point to capture and copy all network traffic in a public wireless hotspot.Observable Description Max Value1 correctness of responseOption 2 and Option 3 are correct.1 point for each correct option.0 points if more options are selected than required.2A disgruntled employee is using Wireshark to discover administrative Telnet usernames and passwords. What type of network at describe?Denial of Serviceport redirectionreconnaissancetrust exploitationObservable Description Max Value1 correctness of response2 points for Option 30 points for any other option2Which two network security solutions can be used to mitigate DoS attacks? (Choose two.)virus scanningdata encryptionanti-spoofing technologiesintrusion protection systemsapplying user authenticationObservable Description Max Value1 correctness of response Option 3 and Option 4 are correct.1 point for each correct option.0 points if more options are selected than required.2Users report to the helpdesk that icons usually seen on the menu bar are randomly appearing on their computer screens. What c reason that computers are displaying these random graphics?An access attack has occurred.A virus has infected the computers.A DoS attack has been launched against the network.The computers are subject to a reconnaissance attack.Observable Description Max Value1 correctness of response2 points for Option 20 points for any other option2A network administrator detects unknown sessions involving port 21 on the network. What could be causing this security breachAn FTP Trojan Horse is executing.A reconnaissance attack is occurring.A denial of service attack is occurring.Cisco Security Agent is testing the network.Observable Description Max Value1 correctness of response2 points for Option 10 points for any other option2Which statement accurately characterizes the evolution of network security?Internal threats can cause even greater damage than external threats.Internet architects planned for network security from the beginning.Early Internet users often engaged in activities that would harm other users.Threats have become less sophisticated while the technical knowledge needed by an attacker has grown.Observable Description Max Value1 correctness of response2 points for Option 10 points for any other option2What is considered a valid method of securing the control plane in the Cisco NFP framework?authorization of actionsDHCP snoopingdynamic ARP inspectionlogin and password policyrouting protocol authenticationrole-based access controlObservable Description Max Value1 correctness of response2 points for Option 50 points for any other option2What are two reasons for securing the data plane in the Cisco NFP framework? (Choose two.)to protect against DoS attacksto provide bandwidth controlto force technicians to use SSH and HTTPS when managing devicesto provide a record of who accessed the device, what occurred, and when it occurredto allow users to control the flow of traffic that is managed by the route processor of their network devicesWhich type of security threat can be described as software that attaches to another program tospecific unwanted function?viruswormproxy Trojan HorseDenial of Service Trojan Horse。


第二章ISO七层模型七层功能介绍:应用层:提供用户接口表示层:数据表示过程(编码方式、加密方式)会话层:区分不同会话的数据流传输层:可靠或不可靠的数据传输、数据重传前的错误纠正网络层:提供路由器用来就定路径的逻辑寻址数据链路层:将比特流组合成帧、用MAC地址访问介质、发现错误(fcs)但不能纠正物理层:设备间接受或发送比特流(说明电压、线速和线缆、水晶头阵脚定义方式)物理层定义介质类型、连接器类型、信令类型,包含802.3、EIA/TIA.232、v3.5标准10base2——细缆以太网(base表示基带传输,10表示10M)10base5——粗缆以太网10baset——双绞线物理层设备:集线器、中继器(放大信号)、解码/编码器、传输介质连接器冲突(collision)冲突域(collision domain)广播域(broadcast domain):广播帧传输的网络范围,一般是有路由器来界定边界(router 不转发广播)数据链路层数据链路层:(网桥和交换机)MAC子层:负责MAC寻址和定义解释访问控制方法MAC子层访问控制模式:1.争用式:冲突不可避免:CMSA/CD;FCFS2.轮流式:访问时间可预见,不发生冲突:令牌环LLC子层:为上层协议提供SAP服务访问点,并为数据加上控制信息,就是为与上层通信的时候提供了一个接口。
LLC子层协议:802.2:该协议只在LLC子层,为以太网和令牌环网提供通信功能SAP(server access point服务访问点)LLC子层为了网络层的各种协议提供服务(相应的接口),上层可能运行不同的协议,为区分不同的协议数据,需要采用服务访问点交换机每个端口都是一个冲突域,所有端口都是一个广播域;集线器每个端口都是一个冲突域网络层网络层:提供逻辑寻址功能广播信息控制多点发送信息控制路径优化流量管制逻辑寻址提供W AN连接传输层区分不同的上层应用建立应用间的端到端的链接定义流量控制为数据传输提供可靠或者是不可靠的链接服务(tcp、udp)协议数据单元PDU协议数据单元:(PDU,protocol data unit)简单地说就是表示数据在每层的名字上层:message 数据Transport layer:segment数据段Network layer:packet数据包Data-link layer:frame帧Physical layer:bit比特封装/解封装Llc:逻辑链路控制Fcs:帧校验序列。

CCNE 方向:路由和交换,安全,负责运营商(通信和服务),语音,网络存储
(一般每三年升级一次)
在什么情况下使用集线器、交换机和路由器(集线器X1,交换器X多)
利用CISCO软件确认端口、协议、地址和可连接性
根据要求互连交换机和路由器
配置交换机和路由器以支持LAN和W AN服务
设置IP子网以便于有效的管理网络
通过配置访问列表来控制对网络段或网络资源的访问
确认交换机、路由器及其配置的网络服务是按我们的预定在运作
判断网络故障的原因并解决之
对一些实际工程案例有一定的分析和解决能力
ISO:国际标准化组织OSI:开放系统互连优点————层优点(2课4条) MAC媒体(媒介)访问控制
FCS:循环冗余校验(排错但无法纠正)
X1的设备:集线器【多端口中继器】,中继器(信号放大),编码--解码器,传输介质连接器
路由器分割广播域、
CSMA/CD:一种访问网络控制方法。

第三章了网划分、变长子网掩码(LVSM)和TCP/IP排错一、IP地址I P地址:就是给每个连接在Internet上的主机分配的一个32bit地址。
IP地址就好像电话号码:有了某人的电话号码,你就能与他通话了。
同样,有了某台主机的IP地址,你就能与这台主机通信了。
I P地址的表示方式:用二进制来表示,每个IP地址长32bit,即4个字节。
注:一台计算机只能有一个IP地址,这种观点是错误的。
IP地址是IP网络中数据传输的依据,它标识了IP网络中的一个连接。
一台主机可以有多个IP地址。
IP分组中的IP地址在网络传输中是保持不变的。
1、基本地址格式现在常用的IP网络使用32位地址,以点分十进制表示,如192.168.0.1。
地址格式为:IP地址=网络地址+主机地址或IP地址=网络地址+子网地址+主机地址。
2、保留地址的分配根据用途和安全性级别的不同,IP地址还可以大致分为两类:公共地址和私有地址。
公用地址在Internet中使用,可以在Internet中随意访问。
私有地址只能在内部网络中使用,只有通过代理服务器才能与Internet通信。
3、I P地址查询开始---运行,输入cmd---在弹出的对话框里输入ipconfig /all ,然后回车出现列表,其中有一项:ip address就是ip地址4、I P地址分类网络号:用于识别主机所在的网络;主机号:用于识别该网络中的主机。
I P地址的分类:共分五类,A类保留给政府机构,B类分配给中等规模的公司,C类分配给任何需要的人,D类用于组播,E类用于实验,各类可容纳的地址数目不同。
A、B、C三类I P地址的特征:当将IP地址写成二进制形式时,A类地址的第一位总是0,B类地址的前两位总是10,C类地址的前三位总是110。
A类地址:(1)A类地址第1字节为网络地址,其它3个字节为主机地址。
它的第1个字节的第一位固定为0.(2)A类地址范围:1.0.0.1---127.255.255.254(3)A类地址中的私有地址和保留地址:①10.X.X.X是私有地址(所谓的私有地址就是在互联网上不使用,而被用在局域网络中的地址)。

ccna读书笔记第一篇:红头发na读书笔记第二章第二篇:红头发na读书笔记第三章第三篇:na培训读书笔记第四篇:读书笔记第五篇:读书笔记更多相关范文na中文笔记第2章:(更多内容:)inter protocols 作者:红头发chapter2 inter protocolstcp/ip and the dod modeldod模型被认为是osi参考模型的浓缩品,分为4层,从上到下是:1.process/application layer2.host-to-host layer3.inter layer4.work aess layer其中,如果在功能上和osi参考模型互相对应的话,那么:1.dod模型的process/application层对应osi参考模型的最高3层2.dod模型的host-to-host层对应osi参考模型的transport层3.dod模型的inter层对应osi参考模型的work层4.dod模型的work aess层对应osi参考模型的最底2层the process/application layer protocolsprocess/application层包含的协议和应用程序有:tel,ftp,x windows,tftp,smtp,snmp,nfs和lpd等等dynamic host configuration protocol(dhcp)/bootp(bootstrap protocol)动态主机配置协议(dhcp)服务器可以提供的信息有:1.ip地址2.子网掩码(sub mask)3.域名(domain name)4.默认网关(default gateway)5.dns6.wins信息the host-to-host layer protocolshost-to-host层描述了2种协议:1.传输控制协议(transmission control protocol,tcp)2.用户数据报协议(user datagram protocol,udp)transmission control protocol(tcp)当1个主机开始发送数据段(segment)的时候,发送方的tcp协议要与接受方的tcp协议进行协商并连接,连接后即所谓的虚电路(virtual circuit),这样的通信方式就叫做面向连接(connection-oriented).面向连接的最大优点是可靠,但是它却增加了额外的网络负担(overhead)user datagram protocol(udp)udp协议的最他特点是无连接(connectionless),即不可靠,因为它不与对方进行协商并连接,它也不会给数据段标号,也不关心数据段是否到达接受方key concepts of host-to-host protocols现在把tcp协议和udp协议的一些特性做个比较:1.tcp.协议在传送数据段的时候要给段标号;udp协议不2.tcp协议可靠;udp协议不可靠3.tcp协议是面向连接;udp协议采用无连接4.tcp协议负载较高;udp协议低负载5.tcp协议的发送方要确认接受方是否收到数据段;udp反之6.tcp协议采用窗口技术和流控制;udp协议反之port numberstcp和udp协议必须使用端口号(port number)来与上层进行通信,因为不同的端口号代表了不同的服务或应用程序.1到1023号端口叫做知名端口号(well-known port numbers).源端口一般是1024号以上随机分配the inter layer protocols在dod模型中,inter层负责:路由,以及给上层提供单独的网络接口inter protocol(ip)ip协议查找每个数据包(packets)的地址,然后,根据路由表决定该数据包下1段路径该如何走,寻找最佳路径inter control message protocol(icmp)icmp协议一样是工作在dod模型的inter层,ip协议使用icmp协议来提供某些不同的服务,icmp协议是一种管理协议1.目标不可达(destination unreachable):假如1个routers不能把ip协议数据报发送到更远的地方去,于是router将发送icmp协议信息给数据报的发送方,告诉它说目标网络不可达2.缓冲区已满(buffer full):假如router的缓冲区已经存满发送方发来的ip协议数据报了,它将发送icmp协议信息给发送方并告诉它缓冲区已满,如果再继续接受的话将导致缓冲区溢出,造成数据丢失3.跳(hops):ip协议数据报经过1个router,称为经过1跳4.ping(packet inter groper):采用icmp协议信息来检查网络的物理连接和逻辑连接是否完好5.traceroute:根据icmp协议信息来跟踪数据在网络上的路径,经过哪些跳address resolution protocol(arp)地址解析协议(arp)用于根据1个已知的ip地址查找硬件地址.它把ip地址翻译成硬件地址reverse address resolution protocol(rarp)rarp协议用于把mac地址翻译成ip地址ip addressingip地址是软件地址,mac地址是硬件地址,mac地址是烧录在nic里的,mac地址用于在本地网络查找主机地址.ip地址是唯一的,也叫做网络地址(work address);硬件地址也叫节点地址(node address) work address网络地址分为5类:1.a类地址:4个8位位组(octets).第一个octet代表网络号,剩下的3个代表主机位.范围是0xxxxxxx,即0到1272.b类地址: 前2个octets代表网络号,剩下的2个代表主机位. 范围是10xxxxxx,即128到1913.c类地址: 前3个octets代表网络号,剩下的1个代表主机位. 范围是110xxxxx,即192到2234.d类地址:多播地址,范围是224到2395.e类地址:保留,实验用,范围是240到255work address:special purpose一些特殊的ip地址:1.ip地址127.0.0.1:本地回环(loopback)测试地址2.广播地址:255.255.255.2553.ip地址0.0.0.0:代表任何网络4.网络号全为0:代表本网络或本网段5.网络号全为1:代表所有的网络6.节点号全为0:代表某个网段的任何主机地址7.节点号全为1:代表该网段的所有主机广播地址tcp/ip协议规定,主机号部分各位全为1的ip地址用于广播.所谓广播地址指同时向网上所有的主机发送报文,也就是说,不管物理网络特性如何,inter网支持广播传输.如136.78.255.255就是b类地址中的一个广播地址,你将信息送到此地址,就是将信息送给网络号为136.78的所有主机.有时需要在本网内广播,但又不知道本网的网络号时,tcp/ip协议规定32比特全为1的ip地址用于本网广播,即255.255.255.255private ip address私有ip地址(private ip address):节约了ip地址是空间,增加了安全性.处于私有ip地址的网络称为内网,与外部进行通信就必须靠网络地址翻(work address translation,nat)一些私有地址的范围:1.a类地址中:10.0.0.0到10.255.255.255.2552.b类地址中:172.16.0.0到172.31.255.2553.c类地址中:192.168.0.0到192.168.255.255broadcast address广播地址:1.层2广播:ff.ff.ff.ff.ff.ff,发送给lan内所有节点2.层3广播:发送给网络上所有节点3.单播(unicast):发送给单独某个目标主机4.多播:由1台主机发出,发送给不同网络的许多节点introduction to work address translation(nat)nat一般都操作在cisco router上,用于连接2个网络,同时把私有地址翻译公有地址一些nat的种类以及特点:1.静态nat(static nat):本地地址和全局地址一一对应.这样的方式需要你拥有真正的inter上的ip地址2.动态nat(dynamic nat):把未注册的ip地址对应到已注册ip地址池中的某个ip地址上.你不必需要静态配置你的router使内外地址对应3.超载(overloading):采用的最广泛的nat配置类型.类似动态nat,但是它是把1组未注册的ip地址根据不同的端口(ports)对应到1个已注册的ip地址上.因此,它又叫做端口地址翻译(port address translation,pat)。

2011-4-18路由Bit比特Byte字节11110000 8BIT8Bit=1Byte1,000 微秒= 1毫秒1,000,000 微秒= 1秒tracertIP查看到目标经过了多少跳物理层粗缆1CM 细缆0.35CM非屏蔽双绞线UTP屏蔽双绞线STPtelnet tcp 23http tcp 80dns udp 53pop tcp 110smtp tcp 25ftp tcp 21syslog 514snmp 161数据链路层LLC 802.3MAC8前导码6源MAC 6目的MAC 2协议号IP包头4校验网络层4比特版本表示IP版本号4比特IHL 表示IP报头长度8比特服务类型QOS16比特总长度Packet的总长度最大65535Packet标识符与标志和分片偏移一起用于IP报文分片16比特标识给切片打标记3比特标识符13比特分段偏移区分顺序8比特生存期TTL8比特协议协议号6TCP 17UDP 89OSPF 88EIGRP区分上层数据16比特校验和校验IP包头32比特源地址源IP32比特目的地址目的IPios用户模式查看(范围有限)特权模式查看全部配置调试(有限)全局模式修改所有参数不允许查看12.3版本可以查看+参数do show 接口模式一般都不进入初始配置对话CTRL+C退出3500 12 10/100M口2 1000M光纤模块口3550 24 10/1000M口 2 1000M 光纤模块口支持路由功能OSI和TCP模型至TCP/IP协议服务:是网络中各层向其相邻上层提供的一组操作服务访问点SAP:N+1层实体是通过N层的SAP来使用N层所提供的服务SAP相当于相邻之间的接口CT-通信行业IT-计算机网络行业分层结构OSI七层和TCP/IP四层协议OSI:开放的通信系统互联参考模型服务:为上一层提供服务接口:上一层如何使用下一层的服务协议:如何使用本层的服务OSI七层:应用层表示层会话层传输层网络层数据链路层物理层(自下至上)TCP/IP 4层模型应用层应用层主机到主机层传输层互联网层互联网层网络接口层—数据链路层物理层标准模型常说的TCP/IP协议栈标示位:URG:表示在数据包中有紧急数据,和紧急指针配合使用。
CCNA 50小时完整版教程笔记一、服务器和客户机的概念1. 谁提供服务,谁是服务器;谁请求服务,谁是客户机2. 可以自己向自己请求服务,也可以自己向自己提供服务二、OSI参考模型1. 分层的好处i. 数据通讯每个环节的变化不影响其他环节ii. 有利于各厂商的设备标准化2. 各层概述i. 应用层(Application)——能够产生网络流量的网络应用程序。
例如:QQ,IE等,计算器之类则不属于应用层。
ii. 表示层(Presentation)——加密、压缩、二进制等。
IE编码选择错误导致轮吗就属于表示层错误。
iii. 会话层(Session)——网络会话进程,可用netstat –n –nb 查看iv. 传输层(Transport Layer)——可靠传输(TCP),不可靠传输(UDP),流量控制,滑动窗口技术v. 网络层(Network Layer)——选择路径vi. 链路层(Date Link)——定义了如何标识网络设备vii. 物理层(Physical)——电压,接口等3. 从排错角度看OSI参考模型i. 从底层往高层逐一排错ii. 物理层故障:连接错误iii. 链路层故障:ARP病毒,ADSL拨号,iv. 网络层故障:选择路径上出了问题,例如无网关,无路由等v. 传输层故障:vi. 会话层故障:vii. 表示层故障:例如IE编码错误等viii. 应用层故障:IE插件等4. 从安全角度看OSI参考模型i. 物理层安全:多余接口,机房门禁等。
ii. 链路层安全:交换机端口绑定MAC地址等iii. 网络层安全:IP访问控制列表等iv. 应用层(上三层)安全:杀毒软件,应用层防火墙等三、网络设计的三层模型1. 接入层交换机:直接连接终端的交换机,一般接口多,带宽相对较低2. 汇聚层交换机:连接接入层的交换机,带宽相对较高3. 核心层交换机:连接汇聚层的交换机,转发速度快四、网络设备1. 集线器(Hub):带冲突检测的载波侦听多路访问(CSMA/CD)i. 不安全,数据靠广播传输ii. 效率低,一个(多个)集线器是一个冲突域,共享带宽2. 网桥(Bridge)i. MAC地址学习ii. 隔离冲突域3. 交换机(Switch)i. 安全,数据根据Mac地址表转发ii. 效率高,一个端口是一个冲突域,每个端口带宽不受其他端口影响iii. 一个(多个)交换机是一个广播域4. 路由器(Routor)i. 基于IP地址转发ii. 广域网接口iii. 隔离广播域iv. ACL5. 网线i. 交叉线:连接同类设备ii. 直通线:连接不同设备iii. 全反线:连接Console口iv. 100M用4根,1000兆用8根(大多数设备,具体还要看规范)五、半双工和全双工以太网1. 半双工:不能同时收发,例如HUB网络2. 全双工:可以同时收发,例如交换机网络六、TCP/IP协议1. 应用层(Application Layer):对应OSI的应用层、表示层、会话层。
思科CCNA认证学习笔记(⼗五)思科ACL、NAT配置命令总结本⽂讲述了思科ACL、NAT配置命令。
分享给⼤家供⼤家参考,具体如下:ACL 访问控制列表ACL可以根据设定的条件对接⼝上的数据包进⾏过滤,允许其通过或丢弃。
被⼴泛地应⽤于路由器和三层交换机,借助于ACL,可以有效地控制⽤户对⽹络的访问,从⽽最⼤程度地保障⽹络安全。
ACL功能:1. 访问控制—在路由器上流量进或出的接⼝上规则流量;2. 定义感兴趣流量 —为其他的策略匹配流量,抓取流量访问控制:定义ACL列表后,将列表调⽤于路由器的接⼝上,当流量通过接⼝时,进⾏匹配,匹配成功后按照设定好的动作进⾏处理即可,动作——允许、拒绝匹配规则:⾄上⽽下逐⼀匹配,上条匹配按上条执⾏,不再查看下条;末尾隐含拒绝所有;ACL分类:1. 标准ACL–仅关注数据包中的源ip地址2. 扩展ACL–关注数据包中源、⽬标ip地址、⽬标端⼝号、协议号配置ACL有两种写法:编号写法 1-99 标准 100-199 扩展删除⼀条整表消失命名写法⼀个名字⼀张列表可以随意删除某条,配置:标准ACL—编号:由于标准ACL仅关注数据包中的源ip地址,调⽤时尽量的靠近⽬标,避免误删;编号写法:Router(config)#access-list 1 deny host 192.168.4.2 拒绝单⼀设备Router(config)#access-list 1 deny 192.168.4.2 0.0.0.0 拒绝单⼀设备Router(config)#access-list 1 deny 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 拒绝范围Router(config)#access-list 1 deny any 拒绝所有Router(config)#access-list 1 deny host 192.168.4.2 拒绝172.16.4.2Router(config)#access-list 1 permit any 允许所有Router(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0.1 进接⼝Router(config-subif)#ip access-group 1 out 调⽤命名写法:Router(config)#ip access-list standard aRouter(config-std-nacl)#deny host 192.168.4.2Router(config-std-nacl)#permit anyRouter(config-std-nacl)#exitRouter(config)# no ip access-list standard a 删除表扩展ACL配置:扩展ACL关注数据包中的源、⽬标ip地址,故调⽤时应该尽量的靠近源,当然不能在源上,因为ACL不能限制本地产⽣的流量;编号写法:r1(config)#access-list 100 deny ip host 192.168.4.2 host 192.168.1.2前⾯是源ip地址,后⾯是⽬标ip地址,也就是拒绝192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255—192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 这个范围r1(config)#access-list 100 permit ip any anyr1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0r1(config-if)#ip access-group 100 in命名写法Router(config)#ip access-list extended aRouter(config-ext-nacl)#deny host 192.168.4.2Router(config-ext nacl)#permit anyRouter(config-ext -nacl)#exitRouter(config)#no ip access-list extended a 删除表关注⽬标端⼝号:ICMP——ping 跨层封装协议,不存在端⼝号Telnet——远程登录基于TCP⽬标23号端⼝设备开启远程登录配置命令:r1(config)#username ccna privilege 15 secret 123456r1(config)#line vty 0 4 0 4 代表最多五个账户登录r1(config-line)#login local规则⼀个设备到另⼀个设备的⽬标端⼝远程登录被拒绝r1(config)#access-list 101 deny tcp host 1.1.1.1 host 2.2.2.2 eq 23r1(config)#access-list 101 permit ip any anyr1(config)#access-list 102 deny icmp host 1.1.1.1 host 2.2.2.2 拒绝pingr1(config)#access-list 102 permit ip any any 单向ping 后加echoNAT ⽹络地址转换配置了NAT的路由器⾄少有⼀个有效的外部全球IP地址,即公有IP地址,这样,所有使⽤本地地址的主机在和外界通信时,都要在NAT路由器上将其本地地址转换成全球IP地址,才能和因特⽹连接。
Key words:layer 2 switchingyer 2 switching provides the following:·Hardware-based bridging (ASIC)·Wire speed·Low latency·Low cost二层交换提供的性能:·基于硬件的桥接(ASIC)·线速·低延迟·低开销What makes layer 2 switching so efficient is that no modification to the data packet takes place. The device only reads the frame encapsulating the packet, which makes the switching process considerably faster and less error-prone than routing processes are.二层交换之所以这样有效,因为它对数据包不做任何修改!设备只是读取了封装了数据包的帧,与路由选择过程相比,交换就显得非常快,且不易出错。
It’s true—layer 2 switches really are pretty much just bridges that give us a lot more ports, but there are some important differences you should always keep in mind:·Bridges are software based, while switches are hardware based because they use ASIC chips to help make filtering decisions.·A switch can be viewed as a multiport bridge.·Bridges can have only one spanning-tree instance per bridge, while switches can have many. (I’m going to tell you all about spanning trees in a bit.)·Switches have a higher number of ports than most bridges.·Both bridges and switches forward layer 2 broadcasts.·Bridges and switches learn MAC addresses by examining the source address of each frame received.·Both bridges and switches make forwarding decisions based on layer 2 addresses.第二层交换机和网桥的对比:网桥是基于软件的,而交换机是基于硬件的,因为交换机是使用ASIC芯片来帮助做出过滤的决定;交换机可以看成是多端口的网桥;每个网桥只有一个生成树实例,而交换机可以有许多成树实例;交换机的端口数量比大多数网桥都多;]网桥和交换机都转发第2层广播;网桥和交换机可以通过检查接收到每个帧的源地址来学习到MAC地址;网桥和交换机都基于第2层地址做出转发的决定。
CCNA学习笔记(1-4章)封装:封装是在数据上加上包头和将数据中包在里面的过程。
OSI模型的七层协议以及每层的意义:从下往上:物理层:定义了实际的规范以及实际的bit流。
这其中包括电压大小,接口特性等码型编码(电压时序)、电气特性、机械、规程和功能。
常见的物理层接口:RS232(V.24)、v.35、DTE与DCE:DTE网络终端设备,DCE线路终端端接设备,接口,就是用于连接DTE与DCE的数据链路层:提供了物理链路上可靠的传输功能。
涉及到物理寻址和与其相应的逻辑寻址、网络拓扑、网络访问、错误检测、帧的顺序传送以及流量控制等问题。
常见的二层协议有:以太网,令牌环,ISDN,ppp帧中继,802.3的结构中数据帧的格式是:前导符,帧定界符,目的地址,源地址,长度,数据,FCS802.5中的令牌环网中,有两种数据帧,令牌(token)和数据帧(dataframe)MAC地址分由12个16进制数组成,其中前6位是由组织指定的,后面的6位是由厂家自行分配的。
网络层:网络层提供了两台主机之间的连接和路径选择。
常见的协议有:IP IPX appletalk传输层:传输层提供的是一条可靠的点到点的连接,向上屏蔽一切网络上传输的问题。
在发送段将将要发送的数据进行分段,在接收端完成数据段到数据流的重组。
常见的协议有:TCP ISDP SPX会话层:会话层的建立,管理和终止两个通信主机间的会话通信,常见的协议:NFS X-windows表示层:确保一个系统应用层发出的信息能北另一个系统的应用层读取,必要的时候翻译成一种通用的格式,一个标准的任务就是完成加密和解密,常见的的表示层的协议是:jepg TIFF应用层:为用户提供应用程序提供网络服务,如:HTTP TELNET广域网服务:(SLIP)串行线网际协议:是一个合法的物理层的协议,可以在网络之间建立一个串行的连接(RS232)ppp点到点协议:对SLIP进行了改进,以满足以太网的需要。
CCNA SECURITY笔记A)命令级别:a) . Privilege exec level 1 clear line *privilege configure all level 5 router”all”就是把全局配置模式下的router这个命令下面的所有命令给于5级别。
如果不加all,则只有router 后面的命令在5级别可以使用。
意思是把原来exec下面的【包括#和>下面的,不论是原来是什么级别的命令clear line *】移动到1级别去。
将高级别的命令放到级别的时候也要有先后顺序的:比如:你要把router 这个命令放到level 1下面去,但是你没有把configure terminal放过去,你是看不到router 命令的。
因为路由器觉得router是在全名模式下的命令,你必须要进入全局模式下才可以敲入router.如下图:R1(config)>routerR1(config)>router os 1R1(config-router)>network 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 a 0虽然进入到全名模式也是>这个符号,但是也要进入这种全局模式。
才有router命令。
b) .View 命令集:将命令做成一集合,然后授权给某个用户使用。
控制力度更强。
则此用户只能使用此命令集中的命令。
Root view 比15级别更强Aaa new-modeEablesecretwang/enble pass wang配置进入到root view下面的密码Root view 可以创建删除VIEW,但是15级别不可以。
Enable view (进入root view)Parser view y uan(创建一个view)Secret yeslabccies配置y uan这个子view下面的密码Commands exec include show version使用本地数据库绑定VIEW先去掉aaa new-model 只是为了演示,其实一般都是用AAA做VIEW的授权User yuan password yuanUser yuan view yuanB ) CISCO路由器的加密级别0,5,6,70 是不加密5 是MD56是在做VPN的时候加密的6: key config-key password-encrypt wang1245passwor encryption aescryptiskmap key 0 yuan add 192.168.1.1最后变成:cryptoisakmp key 6 ZFSN\VVKfdcf\cBKKBLZWDgVXGD address 192.168.1.17是开启了service password-encrytionC) chatper认证不能够使用enable secret 加密1.security passwords min-length2.no service password-recovery 【让你无法找回running-config】就是让用户在重启的时候无法进入ROMMON下面中破解密码。
3.privilige exec level 1 clear line在ISR路由器上面有效保护IOS和configure的安全。
secure boot-image [加密保护隐藏IOS]secure boot-config【加密备份配置】只有CONSOLE进入才可以no掉。
6.login block-for 10s attempt 10 within 10s(10S内联系登入10次,在10S内谁都不可以登入了)login on-failure log every 10 (log 和trap的区别,貌似有LOG就不可以有TRAP)login delay 2login quiet-mode access-class admin(由于第一句话在10S内谁都不可以登入了,将管理员IP地址例外)ip access-list standard adminpermit 192.1681.1permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.2558.rommon>boot IOSrouter# secure boot-config restore flash:/secure.cfgrouter#copy flash:/secure.cfg running-config9.console口默认是no login 的10.在做8O21.X和AUTH-PROXY只能使用AAA authentication default group radius , 不能使用命名的策略。
11.tcp 的小服务(service tcp-small),可以做TCP的PING,对方时间回显,字符回来等,客户端踢掉ctrl+shift+6 ,x.服务器端踢掉clear tcptcb回话号(show tcpbrife)。
12.主机算不算是有路由能力的设备。
route print 可以看见主机的路由表,但是不设置网关也可以上网。
对于主机,如果网关的代理ARP关闭了,而且又不配网关,那么主机去往任何的非同以网段的IP地址的时候,将不会发送任何ARP请求。
如果配置了网关那么将向网关请求ARP请求。
配置网关设备关闭代理ARP的时候上不了网。
如果网关设备开启了代理ARP的时候,那么配不配网关都无所谓,但是像家用的一些路由器是关闭了代理ARP功能的。
13.IP选项源站路由,路由器默认是打开的。
可以通过PING测试,可以自己填写下一条来指引数据包的流向。
而且源站路由如果你知道一个做了PAT的站点的外网地址,你可以穿越PAT到达这个站点的内网地址。
在你写了下一条任何路由器上面关闭的ip source-route那么目的地将无法到达。
14.service finger在开启的时候,可以远程telnet 192.168.1.1 finger等于在192.168.1.1上面show user.15.ICMP Ureachable只是在路由器发给一个地址,而下一条的地址不知道的情况下,发给自己的。
如果是下下一条不知道那么自己将收不到这个Ureachable的。
一般可以在边界的接口上面取消这种告警。
16.terminal monitor17.loggin buffered是将相关的告警信息保存一份到本地的内存中。
可以通过show logging查看出来。
18.sy slog服务器:logging trap 消息登记loggin host 192.168.1.1 logging buffered +日志缓存区大小。
19.snmp的三个组建:agenet:就是运行了agent的设备。
management:server:安装了SNMP软件的PC。
MIB:关于设备上面的信息数据库。
mangent\server 可以通过162端口get agent上面的信息。
mangentment\server可以通过162set agent上面的相关参数。
angent可以通过161端口在有信息的时候主动发送trap消息给server.配置:设置get/set的参数:snmp community yuanro/rw (get/set设置读和写时候的关键字信息)snmp-server host 192.168.1.1 GW(在V2中是关键信息和community一样,但是在V3就是用来加密的PASSWORD)snmp-server enable traps20.ssh 配置:ip domain name , crypto key genratersa , line vty 0 4, login local, transport input ssh ssh v2 的密钥长度必须大于768长度,crypto key genratersa modulus 1024sh21.NTP端口是UDP 123 ,NTP在SYSLOG和PKI中非常重要。
配置:clocktimezone GMT +8clock set 16:33:33 3 jun 2012ntp authentication-key 1 md5 120010161C 7ntp authenticatentp trusted-key 1ntp master(服务器的配置)ntp服务器有一个特性就是它必须先自己同步自己,然后给其他设备同步。
所有如果设置了NTP的ACL的话,要放开自己ntp access-group server 127.0.0.1 和其他向它同步的设备的IP 地址。
客户端配置:clocktimezone GMT +8ntp server 192.168.1.1 key 1ntp authentication-key 1 md5 120010161C 7ntp authenticatentp trusted-key 122.CAM表,就是交换机端口和本端口学习到的MAC地址的映射。
常见的MAC地址攻击,就是:MAC地址防洪,MAC地址欺骗。
解决方案:1.PORT-SECURITY:遵行的原则是:默认一个端口就只能有一个MAC地址存在,一个VLAN下的两个端口不能学习到同一个MAC地址。
23.STP保护:ROOT GUARD:在端口下面开启,这个端口还是可以连接交换机,接的交换机也可以参与STP的选举,但是你不能选取成为ROOT,如果你成为ROOT,那么这个接口将成为一种生成树不连续状态和SHUTDOWN差不多。
1.BPDU GUARD:接口下面只能接PC,如果收到BPDU的包端口将立刻SHUTDOWN。
2.BPDU FILETER:如果是在全局启用,那么只对开启了PORTFAST和AUTO AGE端口生效,并且不发送任何的BUDU给下联的设备。
如果从下联的设备接受了BPUD,那么PORTFAST和BPUD FILTER的特性将失效,端口将重新进入STP运算状态。
如果是在某一个接口下面启用BPUD FITLER和PORTFAST那么这几接口将不发也不收任何的BPUD。
但这可能会出现环路。
所以BPDU FILTER和PORTFAST连用的时候说明你的接口下面一定要接主机,如果接的是交换机那么发送的BPDU在开启了FILTER接口被干掉了可能出现环路哦。
比如:下图:在A,B口都启用了PORTFAST 和BPDUFILTER,那么这个肯定是有环路的。
3.在SPANNING-TREE PORTFAST口的接口收到任何的BUDU那么这个接口的这个一特性将丢失,重新进行STP 的运算,所以开启这个特征的设备一般和BPDU FILTER接口使用。