初中英语语法句子种类(部分图片)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:21.51 KB
- 文档页数:5









初中英语常用语法结构图示一、词法:单数普通名词可数名词复数,复数变化规则名词不规则名词复数形式不可数名词及量的表示专有名词: 人名、地名、国家名。
大写,不加冠词名词的格’s 多用于有生命的事物of 多用于无生命的事物人称代词:主格与宾格:人称代词的排序;物主代词:形容词性物主代词;名词性物主代词反身代词:构成;Own 的用法that, this, these, those的用法;指示代词such, so 的用法,the same as.的用法;so+(助)动词+主语与so+主语+(助)动词的区别。
代词one, another, the other, others, other等词的用法;one与it的区别; both,与all的区别;some, any的用法区别.不定代词every与each的用法either,neither,none的用法-body,-one-thing-where与some, any, every,no的组合;any,many ,a few,few,much,a little,little等词的用法。
疑问代词:who, what, which, whose, whomIt的用法表示天气、气候、季节、时间、阴暗、距离、状况等做主语;作形式主语与形式宾语;定冠词的用法:特指冠词:(a, an, the)不定冠词的用法:不特指不用冠词的情况作用:定语和表语及其位置.The+形容词=复数名词用法单音节词形容词构成双音节词多音节词比较级与最高级不规则词as+原级+as ;not as(so)+原级+ as比较级+比较级The+比较级+范围The+比较级,the +比较级序数词+最高级副词与形容词的用法区别及相互转换级别方面用法与形容词相同already, yet; ago, before, since; now, just now;sometime. Some time, sometimes;频度副词;副词几个副词的用法so that, so…that; too…to;too, either,everyday, every day, every other day;enough;at, in on;above, below, over, under, up, down;along, across, through;around, about;表示地点among, between;in front of, in the front ofbehind, before, after;to , towards, for;out of, from, into, off;介词in; on; at;for; since; during;表示时间till, until;during, for, through;since, from;till, by;表示原因: at, from, if;表示方式: by, in动词+介词:形容词+介词: be good at, be good to, be good for;介词+名词: on, about基数词:序数词:分数数词倍数加减乘除百分数年月日的表达小时与分钟的表达实义动词(行为动词);分类联系动词;助动词;情态动词主谓一致;动词不定式作定语,作宾语补足语动名词:与动词不定式的区别一般现在时:主+V(原、单三)+其他动词一般将来时:主+will+V(原)+其他一般过去时:主+V(过去时)+其他时态过去将来时:主+would +V(原)+其他现在进行时:主+am/is/are+Ving+其他过去进行时:主+was/were+Ving+其他现在完成时:主+have/has+p.p+其他过去完成时: 主+had+p.p+其他be going to结构:主+am/is/are/was/were/will be…+v原+其他。
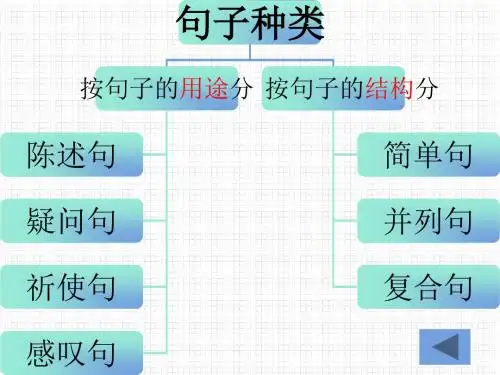
初中英语语法-句子的种类按照英语句子的使用目的和用途,句子可分为四类:陈述句(Declarative Sentence)、疑问句(Interrogative Sentence)、祈使句(Imperative Sentence)和感叹句(Exclamatory Sentence)。
陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句。
疑问句有一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
图解语法1. 陈述句说明一个事实或陈述一个人的看法,陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句特别提示:肯定陈述句改成否定句或一般疑问句时,如句中有already,some,something,somebody等词,须分别改成yet,any,anything,anybody等。
另外,也要注意,too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等。
2. 疑问句3. 常用的特殊疑问句4. 特殊的反意疑问句①主句是祈使句时,“will you?”意为“请求”,“won’t you?”表示提醒对方注意。
例句:Look at the blackboard, will you / won’t you?Don’t be late again, will you?②感叹句后的反意疑问,用一般现在时态的否定形式例句:What fine weather, isn’t it?How beautifully she sings, doesn’t she?③陈述部分是“I am …”时,用“aren’t I?”而不用“am not I?”例句:I'm working now, aren’t I?④陈述部分主语是everything,nothing,anything或something 时,疑问句主语用it例句:Something is wrong with my radio, isn’t it?Nothing is difficult, is it?⑤陈述部分的主语是somebody, nobody, everybody, anybody, no one,none, neither 时,疑问句的主语用they例句:Everyone is here, aren’t they?No one knows about it, do they?⑥陈述部分的主语是:1) this或that时,问句的主语用it2) these或those时,问句主语用they3) there be句时,反意疑问句中用there例句:This is a plane, isn’t it?These are grapes, aren’t they?There was a hospital here, wasn’t there?⑦陈述部分的主语是one时,问句的主语可用one,也可用you (美语用he)例句:One should be ready to help others, shouldn’t one?⑧陈述句中有few, seldom, never hardly,not,rarely,no,nobody,too…to等时,疑问句部分用肯定结构;如由前后缀构成否定词,疑问句部分仍用否定结构例句:He is never late for school, is he?You got nothing from him, did you?It is useless, isn’t it?⑨陈述部分主语是从句、不定式(短语)、动词-ing形式时,疑问句的主语用it例句:What you need is more important, isn’t it?⑩陈述部分由think, believe, suppose, imagine等引导的宾语从句:1) 主语是第一人称时,问句与从句的主谓语一致2) 主语是其他人称,问句与主句的主谓语一致例句:I think he will come, won’t he?I don’t think he can pass the exam, can he?He believed you had seen her before, didn’t he?? have是实义动词时,疑问句用助动词do,does,did;have 是助动词,则不然例如:They had a meeting just now, didn’t they?She’s been to many places of interest, hasn’t she?? 陈述部分有have /has /had to 时,疑问句要用助动词的否定形式例句:You have to water the vegetables now, don’t you?? 陈述部分有had better时,疑问句中用hadn’t刘局:We had better go to school at once, hadn’t we?? 陈述部分有must:1) 作“一定;必须”解释时,疑问句用mustn’t或needn’t;2) 表示推测,作“一定是;必定”解释时,疑问句需根据其后的动词原形选用相应的形式;3) 对过去动作推测时,问句的助动词用did或have;4) 对过去的状态推测时,问句的be用was例句:He must work hard at physics, mustn’t he?You must go to Guangzhou, needn’t you?You mustn’t smoke here, must you?Tom must be at home, isn’t he?She must have finished her work, hasn’t/didn’t she?He must have been a policeman, wasn’t he?? 陈述部分有ought to,used to,疑问句要用 shouldn’t,usedn’t / didn’t例句:Jill used to be a teacher, usedn’t / didn’t she?? 陈述句部分是复合句时,疑问句的主语和助动词要与主句一致例句:He was reading when the teacher came in, wasn’t he?特别提示:反意疑问句是“否定陈述句+肯定问句”时,如回答内容是肯定的,用“Yes+肯定结构”,反之,用“No+否定结构”。
初中英语语法汇总五种基本句型五种基本句型2 五种基本句型句子是由主语、谓语动词、表语、宾语、宾语补足语等组成的,依其组合方式可分为五种基本句型,如下表所示:注意句子成分的表示法S:Subject(主语)V:Verb(动词)O:Object(宾语)P:Predicative(表语)OC:Object Complement(宾语补足语)五种基本句型见下表种类句型主语谓语部分S. 谓语动词V. 表语P. 宾语O. 宾语补足语OC.第1种S+V We work.(不及物)第2种S+V+O He plays(及物) the piano第3种S+V+P WE are(系动词) students第4种S+V+ino(间接宾语) She gave(及物) me a pen+DO(直接宾语)第5种S+V+O+OC He made(及物) the boy laugh1 第1种句型:主语+不及物动词:S+VBirds fly.鸟飞.----- ---主语谓语(不及物动词)He runs in the park.他在公园里跑.------ --------------主语谓语地点状语(不及物动词)此句型是《主语+不及物动词》构成句子的主体部分。
因为是不及物动词,后面当然不能带宾语了,但是可以有状语来修饰。
例如上面例句中的in thepark,是地点状语。
Class begins.(begin在句中是不及物动词)开始上课。
比较we begin Our class at eight.我们八点钟开始上课。
该句属于第2种句型,begin在句中是及物动词,由此可见有些动词既可作及物动词也可以作不及物动词。
必背!只能当不及物动词的词walk 步行swim 游泳happen(take place)发生go去come来work 工作laugh 笑stay呆在……arrive 到达2 第2种句型:主语+及物动词+宾语:S+V+OMy father read the book.我父亲读过那本书.----------- ------ ----------主语谓语(及物动词) 宾语注意有些不及物动词后面加上介词就可把它看成一个及物动词,后面就可以加宾语了。
初中英语语法-句子的种类按照英语句子的使用目的和用途,句子可分为四类:陈述句(Declarative Sentence)、疑问句(Interrogative Sentence)、祈使句(Imperative Sentence)和感叹句(Exclamatory Sentence)。
陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句。
疑问句有一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
图解语法1. 陈述句说明一个事实或陈述一个人的看法,陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句特别提示:肯定陈述句改成否定句或一般疑问句时,如句中有already,some,something,somebody等词,须分别改成yet,any,anything,anybody等。
另外,也要注意,too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等。
2. 疑问句3. 常用的特殊疑问句4. 特殊的反意疑问句①主句是祈使句时,“will you?”意为“请求”,“won’t you?”表示提醒对方注意。
例句:Look at the blackboard, will you / won’t you?Don’t be late again, will you?②感叹句后的反意疑问,用一般现在时态的否定形式例句:What fine weather, isn’t it?How beautifully she sings, doesn’t she?③陈述部分是“I am …”时,用“aren’t I?”而不用“am not I?”例句:I'm working now, aren’t I?④陈述部分主语是everything,nothing,anything或something 时,疑问句主语用it例句:Something is wrong with my radio, isn’t it?Nothing is difficult, is it?⑤陈述部分的主语是somebody, nobody, everybody, anybody, no one,none, neither 时,疑问句的主语用theyEveryone is here, aren’t they?No one knows about it, do they?⑥陈述部分的主语是:1) this或that时,问句的主语用it2) these或those时,问句主语用they3) there be句时,反意疑问句中用there例句:This is a plane, isn’t it?These are grapes, aren’t they?There was a hospital here, wasn’t there?⑦陈述部分的主语是one时,问句的主语可用one,也可用you (美语用he)例句:One should be ready to help others, shouldn’t one?⑧陈述句中有few, seldom, never hardly,not,rarely,no,nobody,too…to等时,疑问句部分用肯定结构;如由前后缀构成否定词,疑问句部分仍用否定结构例句:He is never late for school, is he?You got nothing from him, did you?It is useless, isn’t it?⑨陈述部分主语是从句、不定式(短语)、动词-ing形式时,疑问句的主语用it例句:What you need is more important, isn’t it?⑩陈述部分由think, believe, suppose, imagine等引导的宾语从句:1) 主语是第一人称时,问句与从句的主谓语一致2) 主语是其他人称,问句与主句的主谓语一致例句:I think he will come, won’t he?I don’t think he can pass the exam, can he?He believed you had seen her before, didn’t he?? have是实义动词时,疑问句用助动词do,does,did;have 是助动词,则不然They had a meeting just now, didn’t they?She’s been to many places of interest, hasn’t she?? 陈述部分有have /has /had to 时,疑问句要用助动词的否定形式例句:You have to water the vegetables now, don’t you?? 陈述部分有had better时,疑问句中用hadn’t刘局:We had better go to school at once, hadn’t we?? 陈述部分有must:1) 作“一定;必须”解释时,疑问句用mustn’t或needn’t;2) 表示推测,作“一定是;必定”解释时,疑问句需根据其后的动词原形选用相应的形式;3) 对过去动作推测时,问句的助动词用did或have;4) 对过去的状态推测时,问句的be用was例句:He must work hard at physics, mustn’t he?You must go to Guangzhou, needn’t you?You mustn’t smoke here, must you?Tom must be at home, isn’t he?She must have finished her work, hasn’t/didn’t she?He must have been a policeman, wasn’t he?? 陈述部分有ought to,used to,疑问句要用 shouldn’t,usedn’t / didn’t例句:Jill used to be a teacher, usedn’t / didn’t she?? 陈述句部分是复合句时,疑问句的主语和助动词要与主句一致例句:He was reading when the teacher came in, wasn’t he?特别提示:反意疑问句是“否定陈述句+肯定问句”时,如回答内容是肯定的,用“Yes+肯定结构”,反之,用“No+否定结构”。
译成汉语时,要将“Yes”译成“不是”,“No”译成“是的”。
例如:— You won’t be away for long, will you? 你不会离开太久,是吗?— Yes, I will. 不,我会离开很久。
(事实是会离开很久)— No, I won’t. 是的,我不会离开很久。
(事实是不会离开很久)Let’s go home, shall we? 回家吧,好吗?(包括说话人)Let me have a try, will you? 让我试一试,行吗?(不包括说话人)注意判别:'s是has和is与主语的缩略形式,'d是would和had与主语的缩略形式。
例如:He’s going to play basketball, isn’t he?She’s been to Beijing many times, hasn’t she?You’d better tell him about it at once, hadn’t you?They’d like something delicious to eat, wouldn’t they?5. 祈使句表示请求、命令、劝告、建议、号召等的句子,常省略主语you,句首用动词原形。
①肯定祈使句:动词原形+其他成分,如:Listen to me carefully.②否定祈使句:Don’t (never)+动词原形+其他成分,如:Don’t be late for class next time.Don’t do that again.Never leave today’s work for tomorrow.③ Let引导的祈使句 Let +第一、三人称+(not)动词原形,表示建议做某事,如:Let me try again.Let Jack wait a minute.④祈使句的强调语气 Do+动词原形+其他成分,如:Do come back at once!Do be careful.⑤祈使句的特殊形式:1) No+名词/动名词+其他2) None+of介词短语3) 祈使句+and+简单句,表示“如果……就……”4) 祈使句+or+简单句,表示“……否则……”5) 在祈使句后面,加一个问句,使语气更加委婉例句:No smoking! 请勿吸烟!None of your nonsense!Go down the street, and you’ll see a cinema. 沿着这条街走,你就会看到一家电影院。
Be quick, or we’ll be late. 快点,否则我们要迟到了。
Don’t tell anyone, will you? 不要告诉任何人,好吗?6. 感叹句表达喜、怒、哀、乐等强烈感情的句子叫作感叹句。
感叹句的主谓语可以省略,句末用感叹号“!”,常用what或how来引导。
what 修饰名词,how 修饰形容词、副词。