第十二章静态友元
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:124.50 KB
- 文档页数:30


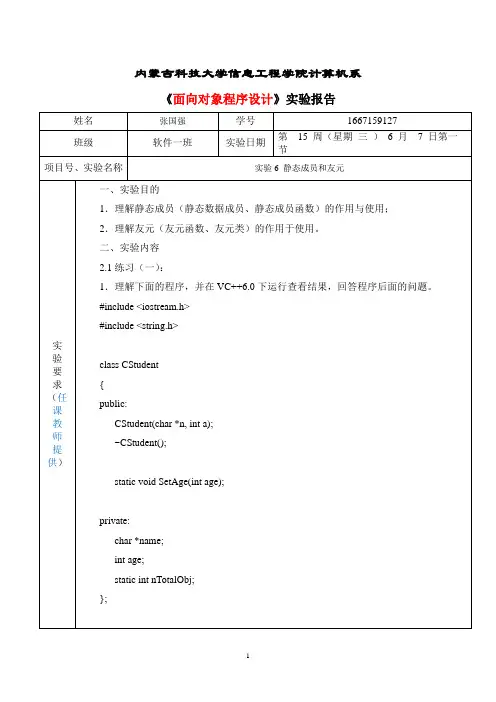
实验四静态成员与友元【实验目的】1.掌握友元函数的定义、使用方法以及特点。
2.握静态成员函数和静态数据成员的功能。
【实验内容】1.调试下列程序,写出输出结果,并分析输出结果。
#include "iostream.h"class My{public:My(int aa){A=aa;B-=aa;}static void fun(My m);private:int A;static int B;};void My::fun(My m){cout<<"A="<<m.A<<endl;cout<<"B="<<B<<endl;}int My::B=100;int main(){My P(6),Q(8);My::fun(P);Q.fun(Q);return 0;}分析:2.设计一个含有静态成员、静态成员函数的程序,分析程序结果,理解静态成员(函数)与类和对象的关系。
参考程序:#include<iostream.h>class A{friend class B;//友元类的声明public:void Set(int i){x=i;}friend int add(A & f1);// 友元函数的声明void Display(){cout<<"x="<<x<<",y="<<y<<endl;}private:int x;static int y;};int add(A & f1){return f1.x+1;}class B{public:B(int i,int j);void Display();private:A a;//A类的对象a作为类B的私有成员};int A::y=1;//静态成员必须先赋初值B::B(int i,int j){a.x=i;A::y=j;}void B::Display(){cout<<"x="<<a.x<<",y="<<A::y<<endl; }void main(){A b;b.Set(5);//友元函数的调用cout<<add(b)<<endl;b.Display();B c(6,9);//a.x=6,X::y=9;c.Display();b.Display();}问题:(1)分析友元函数add()的定义、调用与成员函数的区别。


实验四静态变量、友元1、阅读程序要阅读的程序中存在语法错误,请将其找出来,能用自己的话说清理由#include <iostream>#include <string>using namespace std;class Box{public:Box(int h,int w,int l):height(h),width(w),length(l){}int volume( ){return height*width*length;};private:static int height; //静态的数据成员int width;int length;};int main(){Box b(2,3,4);cout<<"volume is "<<b.volume()<<endl;return 0;}答: Box(int h,int w,int l):height(h),width(w),length(l){}出现错误,不能用参数初始化对静态数据成员初始化.2、书后第九题#include<iostream>using namespace std;class sell{public:sell(int qu):quantity(qu){}void input();static void display();static int average();void kix();private:int quantity;int num;float price;static float discount;static float sum;static int n;};float sell::discount=0.98;float sell::sum=1;int sell::n=3;void sell::kix(){if(n>10)sum=quantity*discount*price;elsesum=quantity*price;}int sell::average(){return (sum/n);}void sell::display(){cout<<"总销售价:"<<sum<<endl; }void sell::input(){ cout<<"销货员号:";cin>>num;cout<<"销货件数:";cin>>quantity;cout<<"销货单价";cin>>price;}int main(){ sell a[3]={sell(3),sell(1),sell(0)};for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ cout<<i+1<<endl;a[i].input();a[i].kix();a[i].display();a[i].kix();cout<<"平均售价:"<<a[i].average()<<endl;}return 0;}3、阅读下面的程序,仔细阅读注释。

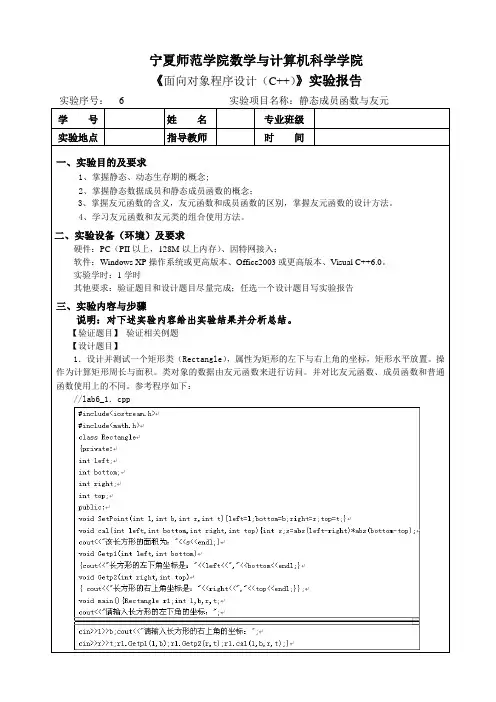
3.2 实验与实践任务3.2.1 实验名称静态成员和友元3.2.2 实验目的1.掌握静态成员的定义和使用。
2.掌握友元的定义和使用。
3.2.3 实验要求1.调试程序要记录调试过程中出现的问题及解决办法;2.编写程序要规范、正确,上机调试过程和结果要有记录,并注意调试程序集成环境的掌握及应用,不断积累编程及调试经验;3.在编写程序时,要按照多文件结构来组织程序。
4.做完实验后给出本实验的实验报告,实验报告的内容包括实验目的、实验内容和结果分析。
3.2.4 实验内容【P1】商店销售某一商品,商店每天公布统一的折扣(discount)。
同时允许销售人员在销售是灵活掌握售价(price),在此基础上,对一次购10件以上者,还可以享受9.8折优惠。
现在已知当天3名销售员的销售情况为:销售员货号(num)销货件数(quantity)销货单价(price)101 5 23.5102 12 24.56103 100 21.5请编程序,计算出当日此商品的总销售款sum,以及每件商品的平均售价。
要求用静态数据成员和静态成员函数【P2】创建一个SavingsAccount类:用static(静态)数据成员包含每个存款人的annualInterestRate(年利率)。
类的每个成员包含一个private数据成员savingsBalance,表示当前存款额。
提供一个calculateMonthlyInterest 成员函数,计算月利息,用savingsBalance乘以annualInterestRate除以12取得,并将当月月息加入savingsBalance。
提供一个静态成员函数modifyInterestRate,将静态annualInterestRate设置为新值。
实例化两个不同的SavingsAccount对象saver1和saver2,余额分别为$2 000.00和$3 000.00 将annualInterestRate设置为3%,计算每个存款人的月息并打印出新的结果。

南昌航空大学实验报告2011年11月9号课程名称:面向对象程序设计B 实验名称:静态成员与友元班级:姓名:同组人:无指导教师评定: 签名:一、实验目的(1)学习静态成员的使用,理解静态成员的特殊用途。
(2)学习友元函数及友元类,领会友元类的作用。
二、实验内容应用VC++6.0的编辑环境构造一个类Stack,设计一个整数链表类,实现栈操作。
类中需有记录结点个数的数据成员(静态成员),要有判空操作。
编制应用程序,取100次随机数(<1000),如果取到的随机数比前一个随机数大的话,入栈,然后逐个取出(即出栈过程)求其和。
用堆分配方法逐个产生满足条件(递增有序)的结点,插入栈中,每当出栈时,要及时将结点删除,求和工作放在类定义外(友元)。
注意:栈中最多会有100个元素,最少会有一个元素,这是由条件(递增有序)决定的。
三、概要设计要实现的功能:构造一个类Stack、设计一个整数链表类,实现栈操作、取100次随机数(<1000),如果取到的随机数比前一个随机数大的话,入栈,然后逐个取出(即出栈过程)求其和。
函数原型为:struct SNode{int data;SNode *next;};class Stack{public:Stack();~Stack();void Push(int e);//insert a data into stackint Pop();//delete a data from stackfriend int GetSum(Stack &);//get sum of stack,friend function//friend class getsum;// get sum of stack,friend class,you can try it using friend classstatic int num;//static numberprivate:SNode *head;};四、详细设计定义类Stack的函数:Stack::Stack(){Head=new SNode;Head->next=NULL;}设计一整数链表类,实现取100次随机数(<1000),如果取到的随机数比前一个随机数大的话,入栈,然后逐个取出的栈操作的函数:void Stack::Push(int e){SNode *p,*q;if(!(p=new SNode))exit(0);p->data=e;q=Head;while(q->next)q=q->next;q->next=p;p->next=NULL;num++;}int Stack::Empty(){return !num;}int Stack::Pop(){int e;if(Empty()){cout<<"The Stack is empty!"<<endl; exit(0);}SNode *p,*q;p=Head;q=p;while(p->next){q=p->next;if(!q->next)break;p=p->next;}p->next=NULL;e=q->data;delete q;num--;return e;}int Stack::GetTop(){int e;if(Empty()){cout<<"The Stack is empty!"<<endl; exit(0);}SNode *p;p=Head;while(p->next){p=p->next;}e=p->data;return e;}求和的函数为:int GetSum(Stack &a){int sum=0,m,tmp;m=a.num;cout<<endl<<"Pop Stack List is:"<<endl;for(int i=0;i<m;i++){tmp=a.Pop();cout<<" "<<tmp;sum+=tmp;}cout<<endl;return sum;}五、程序调试在函数调试的过程中,出现了以下错误提示信息:1、“Stack::Empty”: 函数调用缺少参数列表;请使用“&Stack::Empty”创建指向成员的指针原因为将语句if(Empty())中的括号()漏掉了。



c语言中友元的定义友元是C语言中的一种特殊的关系,它允许一个类或函数访问另一个类的私有成员。
在C++中,友元是通过关键字“friend”来实现的。
但在C语言中,由于没有类的概念,所以友元的定义略有不同。
一、友元的概念及作用1.1 友元的定义在C语言中,友元可以被理解为两个函数之间或者一个函数和一个变量之间建立起来的特殊关系。
这种关系允许其中一个函数或变量访问另一个函数或变量的私有成员。
1.2 友元的作用友元主要用于解决以下问题:(1)保护类成员:C语言中没有类这个概念,但是我们可以通过结构体来模拟。
结构体中可以包含公有成员和私有成员,私有成员只能在结构体内部访问。
如果我们想让另外一个函数或者变量也能够访问到这些私有成员,就需要使用友元。
(2)提高效率:如果两个函数需要频繁地进行数据交换,而这些数据又需要保护起来不被外界访问,那么我们就可以使用友元来提高效率。
二、友元的使用方法2.1 声明方式在C语言中,我们可以通过在函数或变量前面加上“extern”关键字来声明一个友元。
例如:extern void function1();extern int variable1;2.2 定义方式在C语言中,我们可以通过在函数或变量前面加上“static”关键字来定义一个友元。
例如:static void function2();static int variable2;2.3 访问方式当我们需要访问另一个函数或变量的私有成员时,可以使用以下方式:(1)将需要访问的私有成员设置为公有成员。
(2)将需要访问的函数或变量声明为友元。
三、友元的注意事项3.1 友元的使用应该谨慎虽然友元可以方便地访问私有成员,但是过度使用会破坏封装性和安全性。
因此,在使用友元时应该谨慎考虑。
3.2 友元不具备继承性如果一个类A是另一个类B的友元,那么类A并不会继承类B的私有成员。
因此,在使用友元时要注意这一点。
3.3 友元不能被继承如果一个类A是另一个类B的友元,那么子类C并不能继承这个特权。
实验三静态成员和友元函数实验名称:静态成员和友元函数学时安排:2实验类别:设计性实验实验要求:1人1组一、实验目的和任务1)熟练掌握友元函数设计的方法2)掌握友元函数的含义,友元函数和成员函数的区别。
二、实验原理介绍根据要求正确定义静态成员和友元函数。
将别的模块声明为友元,使类中本隐藏的信息如私有和保护成员就可以被友元访问。
三、实验设备介绍软件需求: Visual C++ 6.0硬件需求: 对于硬件方面的要求,建议配置是Pentium III 450以上的CPU处理器,64MB 以上的内存,200MB的自由硬盘空间、CD-ROM驱动器、能支持24位真彩色的显示卡、彩色显示器、打印机。
四、实验内容和步骤【实验3-1】静态成员为账户类ACCOUNT增加静态成员count和 InterestRate表示账户数量和利率,增加静态成员函数GetCount返回账户数目 GetInterestRate返回银行利率class ACCOUNT {public:ACCOUNT(string accno,string name,float balance);~ACCOUNT();void Deposit(float amount);void Withdraw(float amount);float GetBalance();void Show(void);static int GetCount();static float GetInterestRate();private:static int count;static float InterestRate;string _accno,_accname;float _balance;};【实验3-2】友元函数为账户类ACCOUNT增加一个友元函数,实现账户结息,要求输出结息后的余额(不计算利息税),并在main函数中调用进行测试。
friend void Update(ACCOUNT& a);【实验3-3】(加分题)在main函数中,设计一个ACCOUNT类型的数组,为数组中的10个对象初始化,并调用成员函数测试存款、取款、显示等函数,再调用友元函数测试进行结息。
淮海工学院计算机科学系实验报告书课程名:《C++程序设计》题目:静态成员和友元班级:学号:姓名:1、实验内容或题目(1)分析调试教材p310页第2题,并修改程序要求允许对日期对象作如下定义:Date d3(d1);//用已有的日期对构造一个新对象。
(2)设计一个点类,其中包括一对坐标数据成员、一个求两点之间距离的友元函数dist和显示坐标点成员函数,并用数据进行测试。
(3)p312页9-11题。
(4)调试分析教材例9.5的运行结果。
2、实验目的或要求(1)熟练掌握构造函数和析构函数的功能和使用方法;(2)掌握友元函数和友元类;(3)掌握成员函数的重载等特性;(4)掌握静态成员和静态成员函数的使用方法。
2、实验步骤与源程序源代码1、1#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Date{public:Date(int,int,int);Date(int,int);Date(int);Date();void display();private:int month;int day;int year;};Date::Date(int m,int d,int y):month(m),day(d),year(y){ }Date::Date(int m,int d):month(m),day(d){year=2005;}Date::Date(int m):month(m){day=1;year=2005;}Date::Date(){month=1;day=1;year=2005;}void Date::display(){cout<<month<<"/"<<day<<"/"<<year<<endl;}int main(){Date d1(10,13,2005);Date d2(12,30);Date d3(d1);Date d4;d1.display();d2.display();d3.display();d4.display();return 0;}1.2#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Date{public:Date(int,int,int);Date(int,int);Date(int);Date();void display();private:int month;int day;int year;};Date::Date(int m,int d,int y):month(m),day(d),year(y) {}Date::Date(int m,int d):month(m),day(d){year=2005;}Date::Date(int m):month(m){day=1;year=2005;}Date::Date(){month=1;day=1;year=2005;}void Date::display(){cout<<month<<"/"<<day<<"/"<<year<<endl;} int main(){Date d1(10,13,2005);Date d2(12,30);Date d3(10);Date d4;d1.display();d2.display();d3.display();d4.display();return 0;}2#include <iostream>#include <cmath>using namespace std;class Point{public:Point (double xx,double yy){X=xx;Y=yy;}int getX(){return X;}int getY(){return Y;}friend float Distance(Point &,Point &); private:int X,Y;};float Distance(Point &p1,Point &p2){double x=double(p1.X-p2.X);double y=double(p1.Y-p2.Y);return (sqrt(x*x+y*y));}int main(){Point p1(3,4),p2(4,5);cout<<"距离为"<<Distance(p1,p2)<<endl;return 0;}3#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Product{public:Product(int n,int q,float p):num(n),quantity(q),price(p){}; void total();static float average();static void display();private:int num;int quantity;float price;static float discount;static float sum;static int n;};void Product::total(){float rate=1.0;if(quantity>10) rate=0.98*rate;sum=sum+quantity*price*rate*(1-discount);n=n+quantity;}void Product::display(){cout<<sum<<endl;cout<<average()<<endl;}float Product::average(){return(sum/n);}float Product::discount=0.05;float Product::sum=0;int Product::n=0;int main(){Product Prod[3]={Product(101,5,23.5),Product(102,12,24.56),Product(103,100,21.5) };for(int i=0;i<3;i++)Prod[i].total();Product::display();return 0;}4using namespace std;class Date;class Time{public:Time(int,int,int);friend void display(const Date &,const Time &); private:int hour;int minute;int sec;};Time::Time(int h,int m,int s){hour=h;minute=m;sec=s;}class Date{public:Date(int,int,int);friend void display(const Date &,const Time &); private:int month;int day;int year;};Date::Date(int m,int d,int y){month=m;day=d;year=y;}void display(const Date &d,const Time &t){cout<<d.month<<"/"<<d.day<<"/"<<d.year<<endl;cout<<t.hour<<":"<<t.minute<<":"<<t.sec<<endl; }int main(){Time t1(10,13,56);Date d1(12,25,2004);display(d1,t1);return 0;}5using namespace std;class Time;class Date{public:Date(int,int,int);friend Time;private:int month;int day;int year;};Date::Date(int m,int d,int y):month(m),day(d),year(y){ } class Time{public:Time(int,int,int);void display(const Date &);private:int hour;int minute;int sec;};Time::Time(int h,int m,int s):hour(h),minute(m),sec(s){ } void Time::display(const Date &d){cout<<d.month<<"/"<<d.day<<"/"<<d.year<<endl;cout<<hour<<":"<<minute<<":"<<sec<<endl;}int main(){Time t1(10,13,56);Date d1(12,25,2004);t1.display(d1);return 0;}6#include <iostream>#include <string>using namespace std;class Student{private:int num;string name;char sex;public:Student(int n,string nam,char s){num=n;name=nam;sex=s;cout<<"Constructor called."<<endl;}~Student(){cout<<"Destructor called."<<endl;}void display(){cout<<"num"<<num<<endl;cout<<"name"<<name<<endl;cout<<"sex"<<sex<<endl;}};int main(){Student stu1(10010,"Wang_li",'f');stu1.display();Student stu2(10011,"Zhang_fun",'m');stu2.display();return 0;}3、测试数据与实验结果(可以抓图粘贴)1.11.22345C++程序设计实验报告64、结果分析与实验体会通过本次作业,在初步了解友元的同时,也发现了一些问题,对以前的一些知识有些遗忘了。
友元函数的声明和定义友元函数是一种特殊的函数,它可以访问类的私有成员和保护成员。
友元函数可以在类的外部定义,但是必须在类的内部进行声明。
下面我们来详细介绍友元函数的声明和定义。
友元函数的声明在类的定义中,我们可以使用关键字“friend”来声明一个友元函数。
语法如下:```class MyClass {friend void myFriendFunction();};```上面的代码声明了一个名为“myFriendFunction”的友元函数。
这个函数可以访问MyClass类的所有成员,包括私有成员和保护成员。
在声明友元函数时,我们并不需要指定类的作用域,因为友元函数并不属于类的成员函数。
但是,我们可以在类的内部使用类名限定友元函数的作用域。
例如:```class MyClass {public:friend void myFriendFunction() {// 可以访问MyClass的所有成员};```上面的代码定义了一个名为“myFriendFunction”的友元函数,并在该函数中通过类名访问了MyClass的成员。
友元函数的定义友元函数的定义与普通函数的定义类似。
我们可以在类的外部定义一个友元函数,并在函数前面加上类名和作用域解析符号“::”。
例如:```class MyClass {friend void myFriendFunction();};void MyClass::myFriendFunction() {// 可以访问MyClass的所有成员}```上面的代码定义了一个名为“myFriendFunction”的友元函数,并在函数前面加上了类名和作用域解析符号“::”。
需要注意的是,友元函数并不属于类的成员函数,因此它没有this指针。
因此,在友元函数中无法访问类的非静态成员。
但是,我们可以通过类名限定的方式访问静态成员。
例如:class MyClass {static int myStaticMember;friend void myFriendFunction();};void MyClass::myFriendFunction() {int value = MyClass::myStaticMember;}```上面的代码定义了一个名为“myFriendFunction”的友元函数,并在函数中通过类名访问了MyClass的静态成员myStaticMember。