中医药名词英文翻译04%28中医诊断学%29
- 格式:xls
- 大小:205.50 KB
- 文档页数:44
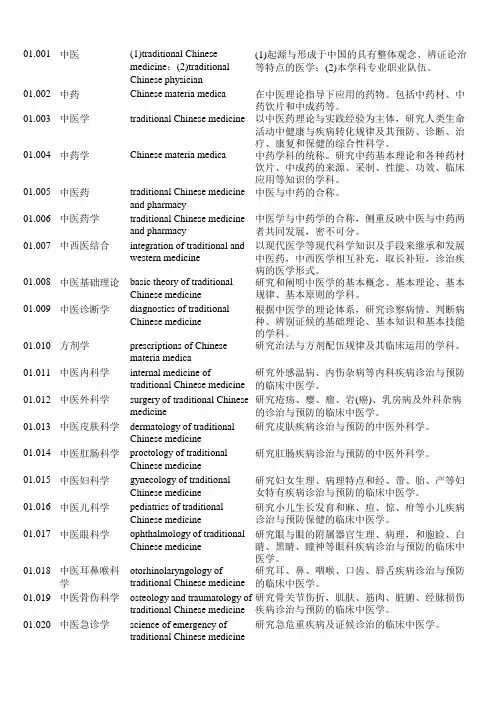
01.001中医(1)traditional Chinesemedicine;(2)traditionalChinese physician (1)起源与形成于中国的具有整体观念、辨证论治等特点的医学;(2)本学科专业职业队伍。
01.002中药Chinese materia medica在中医理论指导下应用的药物。
包括中药材、中药饮片和中成药等。
01.003中医学traditional Chinese medicine以中医药理论与实践经验为主体,研究人类生命活动中健康与疾病转化规律及其预防、诊断、治疗、康复和保健的综合性科学。
01.004中药学Chinese materia medica中药学科的统称。
研究中药基本理论和各种药材饮片、中成药的来源、采制、性能、功效、临床应用等知识的学科。
01.005中医药traditional Chinese medicineand pharmacy中医与中药的合称。
01.006中医药学traditional Chinese medicineand pharmacy 中医学与中药学的合称,侧重反映中医与中药两者共同发展,密不可分。
01.007中西医结合integration of traditional andwestern medicine 以现代医学等现代科学知识及手段来继承和发展中医药,中西医学相互补充,取长补短,诊治疾病的医学形式。
01.008中医基础理论basic theory of traditionalChinese medicine 研究和阐明中医学的基本概念、基本理论、基本规律、基本原则的学科。
01.009中医诊断学diagnostics of traditionalChinese medicine 根据中医学的理论体系,研究诊察病情、判断病种、辨别证候的基础理论、基本知识和基本技能的学科。
01.010方剂学prescriptions of Chinesemateria medica研究治法与方剂配伍规律及其临床运用的学科。

医学常用中医诊断术语英文翻译Medical Terminology in Traditional Chinese Medicine: English TranslationIntroduction:Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has a rich history and continues to play a significant role in healthcare practices around the world. As TCM gains more recognition and popularity, it becomes essential to have accurate translations of its diagnostic terms in English. This article aims to provide a comprehensive list of commonly used TCM diagnostic terms and their English translations to facilitate better communication and understanding between TCM practitioners and English-speaking patients.1. Zhen (诊) - DiagnosisThe process of identifying and determining the nature and cause of a patient's illness.2. Bing (病) - Disease/DisorderA pathological condition affecting the body, often associated with specific symptoms and signs.3. Zhen Duan (诊断) - DiagnosisThe act of diagnosing or identifying a disease based on various diagnostic methods.4. Bian Zheng (辨证) - Syndrome DifferentiationThe process of determining the specific syndrome or pattern underlying a patient's disease.5. Zhen Duan Zhi Shi (诊断指示) - Diagnostic IndicatorsThe symptoms, signs, and other clinical information used in making a diagnosis.6. Wen Bing (温病) - Febrile DiseasesA category of diseases characterized by fever, often caused by external pathogenic factors.7. Wei Qi (卫气) - Defensive QiA form of Qi that protects the body from external pathogenic factors.8. Zheng Qi (正气) - Righteous QiThe body's own vital energy or defensive energy that helps combat diseases.9. Yin-Yang (阴阳) - Yin and YangThe fundamental concepts of TCM, representing the opposing yet interconnected forces that govern the balance and functioning of the body.10. Qi (气) - QiThe vital energy or life force that flows through meridians, responsible for maintaining health and wellbeing.11. Xue (血) - BloodThe vital substance responsible for nourishing the body's organs and tissues.12. Jing Luo (经络) - Meridians and CollateralsThe pathways through which Qi and blood flow in the body, connecting various organs and systems.13. Zang-Fu (脏腑) - Organs and BowelsReferring to the internal organs and their associated functions in TCM.14. Jie (结) - SyndromeA combination of symptoms, signs, and patient history that characterizes a specific disease or condition.15. Bian Bing (辨病) - Disease DifferentiationThe process of identifying and differentiating various diseases based on their specific characteristics.16. Zheng (证) - Pattern/SyndromeA specific pattern or set of symptoms that reflect the nature and location of a disease in TCM.17. Tongue Diagnosis (舌诊) - Tongue ExaminationAssessing a patient's health condition and specific syndromes by observing the color, shape, coating, and moisture of the tongue.18. Pulse Diagnosis (脉诊) - Pulse ExaminationEvaluating a patient's overall health and specific syndromes by palpating the radial pulse for qualities such as rate, rhythm, and strength.Conclusion:Effective communication and understanding between TCM practitioners and English-speaking patients are crucial for optimal healthcare outcomes. This list of commonly used TCM diagnostic terms and their English translations serves as a valuable resource for bridging the language gap and facilitating better communication in the field of TCM. Emphasizing accurate and standardized translations of these terms will enhance the integration and acceptance of TCM within the global healthcare community.。

中医英文术语1. Acupuncture (针灸): A traditional Chinese medicine practice that involves inserting fine needles into specific points on the body to stimulate the flow of Qi (energy) and promote healing.2. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) (中医): An ancient Chinese medical system that includes various practices such as acupuncture, herbal medicine, dietary therapy, and mind-body exercises. TCM is based on the principle of balancing Yin and Yang and improving the flow of Qi.3. Qi (气): The vital energy or life force that flows through pathways in the body, known as meridians, according to TCM. Maintaining the balanced flow of Qi is believed to be crucial for good health.4. Yin and Yang (阴阳): In TCM, Yin and Yang are opposing forces that need to be balanced for optimal health. Yin represents darkness, cold, and passivity, while Yang represents light, heat, and activity.5. Meridians (经络): The pathways through which Qi flows in the body according to TCM. There are twelve main meridians and eight extra meridians, each associated with different organs or body functions.6. Herbal Medicine (草药): The use of plants, minerals, and animal products to treat illnesses and restore balance in TCM. Herbal remedies are often prescribed in the form of tea, pills, or powders.7. Cupping (拔罐): A therapy in which glass or plastic cups are placed on the skin to create a vacuum, stimulating blood flow and relieving muscle tension. Cupping is often used for pain relief and promoting healing.8. Moxibustion (艾灸): A technique that involves burning dried mugwort herb (moxa) near the skin or on acupuncture points to warm and stimulate the flow of Qi. Moxibustion is commonly used to treat cold-related conditions.9. Tui Na (推拿): A form of Chinese therapeutic massage that involves various techniques such as kneading, pressing, and stretching to stimulate the flow of Qi and relieve pain or tension.10. Gua Sha (刮痧): A technique in which a blunt instrument, such as a special spoon or coin, is used to scrape the skin in order to promote blood circulation and alleviate pain or inflammation.11. Five Elements (五行): The concept in TCM that categorizes phenomena into five elements - Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water. Each element corresponds to certain organs, emotional characteristics, seasons, and other aspects of health.12. Pattern Differentiation (辨证论治): The TCM diagnostic method that involves analyzing a patient's symptoms and signs to determine the underlying pattern of disharmony in the body. Treatment is then tailored based on the specific pattern identified.13. Herbal Formulas (方剂): Specific combinations of herbs prescribed by TCM practitioners to address the individual pattern of disharmony. These formulas are often customized for each patient's unique needs.14. Dampness (湿): An imbalance in TCM characterized by excessive moisture or fluid accumulation in the body, which can cause symptoms such as bloating, fatigue, and heavy sensation.15. Heat (热): An excess of Yang energy in the body, leading to symptoms such as fever, thirst, inflammation, and restlessness. Heat can be caused by external factors or internal imbalances.。
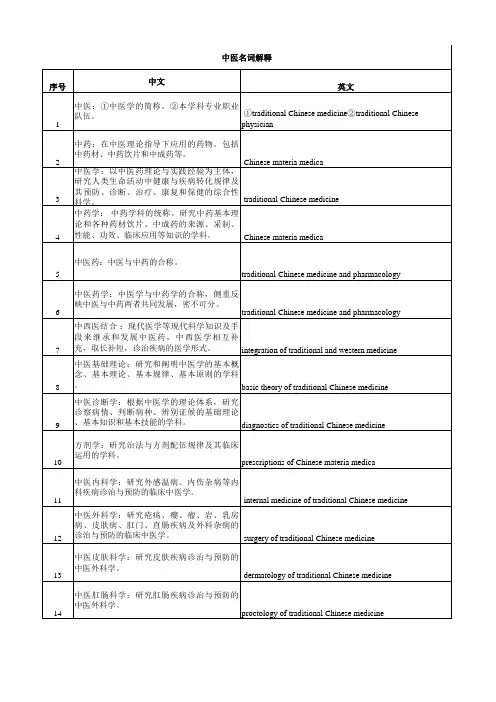

中医常用术语英文翻译[学科]中医①traditional Chinese medicine②traditional Chinesephysician ①中医学的简称。
②本学科专业职业队伍。
中药Chinesemateria medica 在中医理论指导下应用的药物。
包括中药材、中药饮片和中成药等。
中医学 traditionalChinese medicine 以中医药理论与实践经验为主体,研究人类生命活动中健康与疾病转化规律及其预防、诊断、治疗、康复和保健的综合性科学。
中药学Chinese materiamedica 中药学科的统称。
研究中药基本理论和各种药材饮片、中成药的来源、采制、性能、功效、临床应用等知识的学科。
中医药 traditionalChinese medicine and pharmacology本草:Materia medica中药:Chinese materiamedica,Chinese medicinals(包括植物药、动物药、矿物药等)中草药:Chinese HerbalMedicine,Chinese medicinal herbs中药学:Chinese pharmaceutics药材:Medicinalsubstance(material)中西医结合 integration of traditional and western medicine 中医基础理论 basictheory of traditional Chinese medicine 中医诊断学 diagnostics of traditional Chinese medicine 方剂学 prescriptions of Chinese materia medica,Traditional Chinese Medical Formulae/ prescriptions中医内科学 internal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine[阴阳]The Theory of Yinand Yang阴阳对立:Opposition of yin andyang阴阳制约:Restriction of/between yin and yang阴阳互根:Interdependence ofyin and yang阴阳消长:Waxing and waning ofyin and yang阴阳转化:Inter-transformationof yin and yang[五行学说]The Theory of FiveElements五行:water,fire,wood,metal,soil生:promote, generate,engender克: act, restrict,restrain乘:overact,over-restrict, over-restrain, subjugate, overwhelm侮:counteract,counter-restrict, counter-restrain, rebel[整体观念] concept of organicwholeness辩证法 dialectics生长化收藏 sprouting, growth,transformation,ripening,storage内外环境统一性 the unity betweenthe internal and external environments机体自身整体性 the integrity of thebody itself古代唯物论和辩证法 classic Chinesematerialism and dialectics 矛盾统一the contradictoryunity互相联系、相互影响related to each otherand influence each other标本 Biao (secondaryaspect) and Ben (primary aspect)本质与现象nature and phenomena矛盾的普遍性和特殊性universality andspeciality of contradictions寒者热之Cold disease shouldbe treated by warm therapy热者寒之warm disease shouldbe treated by cold therapy虚者补之deficiency syndromeshould be treated by tonifyingtherapy实者泻之excess syndromeshould be treated by purgation therapy治病必求其本 Treatment ofdiseases must concentrate on the root cause同病异治treatment ofthe same disease with different therapeutic methods异病同治treatment ofdifferent diseases with the same therapeutic method[精气神]清阳为天 The lucid Yangascends to form the heaven浊阴为地 The turbid Yindescends to constitute the earth气化 Qitransformation升降出入 ascending,descending, going out, coming in出入废则神机化灭,升降息则气立孤危。

中医诊断常用词汇的中英对照中医作为中国传统医学的重要组成部分,拥有悠久的历史和丰富的诊治经验。
在中医诊断过程中,医生会使用一系列特定的术语来描述症状和疾病。
本文将介绍一些中医诊断常用词汇的中英对照,以便更好地理解和学习中医理论。
一、症状描述1. 舌苔(Tongue Coating)中医诊断中,医生会仔细观察患者舌苔的颜色、质地和厚薄程度等。
常见的舌苔表现包括白色、黄色、薄白、薄黄等。
2. 脉象(Pulse)中医通过触摸患者脉搏来判断体内脏腑的功能和疾病情况。
常见的脉象包括弦脉、滑脉、实脉、虚脉等。
3. 咳嗽(Cough)咳嗽是中医常见的症状之一,可分为干咳、湿咳、痰多、痰黄等不同类型。
4. 发热(Fever)体温升高是常见的中医症状,可用于判断病证的性质及严重程度。
5. 头晕(Dizziness)中医将头晕分为眩晕、头昏、头眩等不同类型,以辅助诊断病因和辨证。
二、疾病诊断1. 冠心病(Coronary Heart Disease)冠心病是指冠状动脉血液供应不足引发的心脏病,常见症状包括胸痛、气短等。
2. 高血压(Hypertension)高血压是中医常见疾病,可引发头痛、头晕、眼花等症状。
3. 糖尿病(Diabetes)糖尿病是一种代谢性疾病,主要特征是血糖浓度增高。
中医将糖尿病分为三型,即上、中、下三焦糖尿病。
4. 高血脂(Hyperlipidemia)高血脂是指血液中脂质含量过高的病症,中医观点认为高血脂与体内湿气过盛有关。
5. 慢性胃炎(Chronic Gastritis)慢性胃炎是胃粘膜长期受损引起的一种炎症,中医常用‘胃气郁结’来描述其病因。
三、中医治疗方法1. 针灸(Acupuncture)针灸是中医常用的治疗方法之一,通过刺激人体穴位来调节气血,达到治疗疾病的目的。
2. 中药疗法(Chinese Herbal Medicine)中药疗法是中医的核心治疗方法,通过使用植物的根、茎、叶、花等部位制成的药材来疗效疾病。

中医①traditional Chinese medicine②traditional Chinese physician①中医学的简称。
②本学科专业职业队伍。
中药Chinese materia medica 在中医理论指导下应用的药物。
包括中药材、中药饮片和中成药等。
中医学traditional Chinese medicine 以中医药理论与实践经验为主体,研究人类生命活动中健康与疾病转化规律及其预防、诊断、治疗、康复和保健的综合性科学。
中药学Chinese materia medica 中药学科的统称。
研究中药基本理论和各种药材饮片、中成药的来源、采制、性能、功效、临床应用等知识的学科。
中医药traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医与中药的合称。
中医药学traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医学与中药学的合称,侧重反映中医与中药两者共同发展,密不可分。
中西医结合integration of traditional and western medicine 现代医学等现代科学知识及手段来继承和发展中医药,中西医学相互补充,取长补短,诊治疾病的医学形式。
中医基础理论basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine 研究和阐明中医学的基本概念、基本理论、基本规律、基本原则的学科。
中医诊断学diagnostics of traditional Chinese medicine 根据中医学的理论体系,研究诊察病情、判断病种、辨别证候的基础理论、基本知识和基本技能的学科。
方剂学prescriptions of Chinese materia medica 研究治法与方剂配伍规律及其临床运用的学科。
中医内科学internal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine 研究外感温病、内伤杂病等内科疾病诊治与预防的临床中医学。

中医临床常用英语词汇中医,一般指以中国汉族劳动人民创造的传统医学为主的医学,所以也称汉医。
是研究人体生理、病理以及疾病的诊断和防治等的一门学科。
中医①traditional Chinese medicine②traditional Chinese physician ①中医学的简称。
②本学科专业职业队伍。
中药 Chinese materia medica 在中医理论指导下应用的药物。
包括中药材、中药饮片和中成药等。
中医学 traditional Chinese medicine 以中医药理论与实践经历为主体,研究人类生命活动中安康与疾病转化规律及其预防、诊断、治疗、康复和保健的综合性科学。
中药学 Chinese materia medica 中药学科的统称。
研究中药根本理论和各种药材饮片、中成药的、采制、性能、成效、临床应用等知识的学科。
中医药 traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医与中药的合称。
中医药学 traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医学与中药学的合称,侧重反映中医与中药两者共同开展,密不可分。
中西医结合 integration of traditional and western medicine 现代医学等现代科学知识及手段来继承和开展中医药,中西医学相互补充,取长补短,诊治疾病的医学形式。
中医根底理论 basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine 研究和说明中医学的根本概念、根本理论、根本规律、根本原那么的学科。
中医诊断学 diagnostics of traditional Chinese medicine 根据中医学的理论体系,研究诊察病情、判断病种、区分证候的根底理论、根本知识和根本技能的学科。
方剂学 prescriptions of Chinese materia medica 研究治法与方剂配伍规律及其临床运用的学科。
![实用中医药英文辞典-Part[1].1](https://uimg.taocdn.com/7a981d7f1711cc7931b71691.webp)
中医, traditional Chinese medicine中药, Chinese materia medica中医学, traditional Chinese medicine中药学, Chinese materia medica中医药, traditional Chinese medicine; TCM 中医药学, traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacy中西医结合, integration of traditional and western medicine中医基础理论, basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine中医诊断学, diagnostics of traditional Chinese medicine方剂学, prescription of Chinese materia medica中医内科学, internal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine中医外科学, surgery of traditional Chinese medicine中医皮肤科学, dermatology of traditional Chinese medicine中医肛肠科学, ano-proctology of traditional Chinese medicine中医妇科学, gynecology of traditional Chinese medicine中医儿科学, pediatrics of traditional Chinese medicine中医眼科学, ophthalmology of traditional Chinese medicine中医耳鼻喉科学, oto-rhino-laryngology of traditional Chinese medicine中医骨伤科学, osteo-traumatology of traditional Chinese medicine中医急诊学, the art of first aid of traditional Chinese medicine针灸学, the art of acu-moxibustion of traditional Chinese medicine中医推拿学, the art of tuina of traditional Chinese medicine中医养生学, the art of healthcare of traditional Chinese medicine中医康复学, the art of rehabilitation of traditional Chinese medicine中医护理学, the art of nursery of traditional Chinese medicine温病学, the art of warm disease of traditional Chinese medicine药用植物学, pharmaceutical botany中药化学, chemistry of Chinese materia medica中药药理学, pharmacology of Chinese materia medica中药鉴别学, identification of Chinese materia medica中药炮制学, the art of processing of Chinese materia medica中药药剂学, pharmacy of Chinese materia medica中药制剂分析, analysis of drug form of Chinese materia medica中国医学史, Chinese medical history中医文献学, Chinese medical literature中医各家学说, theory of schools of traditional Chinese medicine医案, case histories国家中医药管理局, State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine中华中医药学会, China Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy 世界针灸学会联合会, The World Federation of Acupuncture-Moxibustion Societies中国针灸学会, China Association of Acupuncture and Moxibustion中国中西医结合学会, Chinese Association of the Integration of Traditional and Western Medicine中国民族医药学会, Chinese Association of Minority Medicine中医师, traditional Chinese physician中药师, traditional Chinese pharmacist汉文名, 英文名五十二病方, Wushier Bing Fang; Prescriptions for Fifty-two Diseases灵枢经, Lingshu Jing; Miraculous Pivot素问, Suwen; Plain Questions黄帝内经, Huangdi Nei Jing; Inner Canon of Huangdi神农本草经, Shennong Bencao Jing;Shennong's Classic of Materia Medica难经, Nan Jing; Classic of Questioning伤寒论, Shanghan Lun; Treatise on Cold Pathogenic Diseases金匮要略, Jingui Yao Lüe; Synopsis of Golden Chamber针灸甲乙经, Zhenjiu Jia Yi Jing; A-B Classic of Acu-moxibustion脉经, Mai Jing; Pulse Classic肘后备急方, Zhouhou Beiji Fang; Handbook of Prescriptions for Emergency刘涓子鬼遗方, Liu Juanzi Gui Yi Fang; Liu Juanzi's Remedies Bequeathed by Ghosts雷公炮炙论, Leigong Paozhi Lun; Master Lei's Discourse on Drug Processing神农本草经集注, Shennong Bencao Jing Jizhu; Variorum of Shennong's Classic of Materia Medica黄帝内经太素, Huangdi Nei Jing Tai Su; Grand Simplicity of Inner Canon of Huangdi 诸病源候论, Zhu Bing Yuan Hou Lun; General Treatise on Causes and Manifestations of All Diseases备急千金要方, Beiji Qianjin Yao Fang; Essential Recipes for Emergent Use Worth A Thousand Gold新修本草, Xin Xiu Bencao; Newly Revised Materia Medica千金翼方, Qianjin Yi Fang; A Supplement to Recipes Worth A Thousand Gold本草拾遗, Bencao Shiyi; A Supplement to Materia Medica食疗本草, Shiliao Bencao; Materia Medica for Dietotherapy外台秘要, Waitai Miyao; Arcane Essentials from the Imperial Library食医心鉴, Shi Yi Xin Jian; Heart Mirror of Dietotherapy海药本草, Haiyao Bencao; Oversea Materia Medica太平圣惠方, Taiping Sheng Hui Fang; Taiping Holy Prescriptions for Universal Relief经史证类备急本草, Jing Shi Zheng Lei Beiji Bencao; Classified Materia Medica from Historical Classics for Emergency太平惠民和剂局方, Taiping Huimin Hejiju Fang; Prescriptions of the Bureau of Taiping People’s Welfare Phar macy圣济总录, Shengji Zong Lu; General Records of Holy Universal Relief本草衍义, Bencao Yanyi; Augmented Materia Medica圣济经, Sheng Ji Jing; Classic of Holy Benevolence小儿药证直诀, Xiaoer Yao Zheng Zhi Jue; Key to Therapeutics of Children's Diseases伤寒明理论, Shanghan Mingli Lun; Concise Exposition on Cold Pathogenic Diseases幼幼新书, Youyou Xin Shu; New Book of Pediatrics宣明论方, Xuan Ming Lun Fang; Clear Synopsis on Recipes三因极一病证方论, Sanyin Ji Yi Bingzheng Fang Lun; Treatise on Three Categories of Pathogenic Factors儒门事亲, Rumen Shi Qin; Confucians' Duties for Parents妇人大全良方, Furen Da Quan Liang Fang; Complete Effective Prescriptions for Women's Diseases重修政和经史证类备急本草, Chong Xiu Zhenghe Jing Shi Zheng Lei Beiji Bencao; Revised Zhenghe Materia Medica for Emergency from Classics and History Documents脾胃论, Piwei Lun; Treatise on Spleen and Stomach仁斋直指方, Renzhai Zhi Zhi Fang; Effective Recipes from Renzhai House外科精要, Waike Jing Yao; Essence of External Diseases兰室秘藏, Lanshi Micang; Secret Book of Orchid Chamber秘传眼科龙木论, Michuan Yanke Longmu Lun; Nagajuna's Ophthalmology Secretly Handed Down汤液本草, Tangye Bencao; Materia Medicafor Decoctions瑞竹堂经验方, Ruizhutang Jingyan Fang; Empirical Recipes from Auspicious Bamboo Hall饮膳正要, Yin Shan Zheng Yao; Principles of Correct Diet世医得效方, Shi Yi De Xiao Fang; Effective Formulae Handed Down for Generations十四经发挥, Shisijing Fahui; Elucidation of Fourteen Channels格致余论, Gezhi Y u Lun; Further Discourses on the Properties of Things局方发挥, Jufang Fahui; Elaboration of Bureau Prescription回回药方, Huihui Yaofang; Huihui Formularies丹溪心法, Danxi Xinfa; Danxi's Mastery of Medicine普济方, Puji Fang; Prescriptions for Universal Relief救荒本草, Jiuhuang Bencao; Materia Medica for Famines本草品汇精要, Bencao Pinghui Jingyao; Collected Essential of Species of Materia Medica名医类案, Mingyi Leian; Classified Case Records of Celebrated Physicians古今医统大全, Gujin Yi Tong Daquan; Medical Complete Book, Ancient and Modern 医学纲目, Yixue Gangmu; Compendium of Medicine本草纲目, Bencao Gangmu; Compendium of Materia Medica万密斋医学全书, Wan Mizhai Yixue Quanshu; Wan Mizhai's Complete Medical Book赤水玄珠, Chishui Xuanzhu; Black Pearl from Red River万病回春, Wanbing Huichun; Curative Measures for All Diseases针灸大成, Zhenjiu Dacheng; Compendium of Acu-moxibustion证治准绳, Zhengzhi Zhunsheng; Standards for Diagnosis and Treatment 寿世保元, Shoushi Baoyuan; Longevity and Life Preservation外科正宗, Waike Zhengzong; Orthodox Manual of External Diseases医贯, Yi Guan; Key Link of Medicine济阴纲目, Ji Yin Gangmu; Outline for Women's Diseases景岳全书, Jingyue Quanshu; Jingyue's Complete Works类经, Lei Jing; Canon of Classification霉疮秘录, Meichuang Milu; Secret Record for Syphilis温疫论, Wenyi Lun; On Plague Diseases审视瑶函, Shen Shi Yao Han; Precious Book of Ophthalmology医方集解, Yifang Jijie; Collected Exegesisof Recipes洗冤录, Xi Yuan Lu; Records for Washing Away of Wrong Cases汤头歌诀, Tangtou Gejue; Recipes in Rhymes外科证治全生集, Waike Zhengzhi Quansheng Ji; Life-saving Manual of Diagnosis and Treatment of External Diseases 医宗金鉴, Yi Zong Jin Jian; Golden Mirrorof Medicine临证指南医案, Lin Zheng Zhinan Yi'an; Guide to Clinical Practice with Medical Records幼幼集成, Youyou Jicheng; Complete Work on Children's Diseases喉科指掌, Houke Zhizhang; Guide Book for Laryngology串雅内编, Chuanya Nei Bian; Internal Therapies of Folk Medicine串雅外编, Chuanya Wai Bian; External Therapies of Folk Medicine徐灵胎医学全书, Xu Lingtai Yixue Quanshu; Xu Lingtai's Complete Medical Book本草纲目拾遗, Bencao Gangmu Shiyi; Supplement to Compendium of Materia Medica续名医类案, Xu Mingyi Leian; Supplement to Classified Case Records of CelebratedPhysicians竹林寺女科, Zhulinsi Nüke; Bamboo Forest Temple’s Secret on Women’s Diseases温病条辨, Wenbing Tiaobian; Detailed Analysis of Epidemic Warm Diseases疡科心得集, Yangke Xinde Ji; Experience Gained in Treating External Diseases傅青主女科, Fu Qingzhu Nüke; Fu Qingzhu's Obstetrics and Gynecology医林改错, Yilin Gaicuo; Correction on Errors in Medical Classics验方新编, Yanfang Xin Bian; New Compilation of Effective Recipes植物名实图考, Zhiwu Mingshi Tukao; Textual Research on Reality and Titles of Plants理瀹骈文, Li Yue Pianwen; Rhymed Discourse for Topical Remedies血症论, Xuezheng Lun; On Blood Syndromes重楼玉钥, Chonglou Yuyao; Jade Key to the Secluded Chamber新针灸学, New Art of Acu-moxibustion黄帝, Huangdi; Yellow Emperor神农, Shennong岐伯, Qibo医和, Yihe扁鹊, Bianque淳于意, Chunyu Yi张仲景, Zhang Zhongjing华佗, Hua Tuo王叔和, Wang Shuhe皇甫谧, Huangfu Mi葛洪, Ge Hong雷斆, Lei Xiao陶弘景, Tao Hongjing徐之才, Xu Zhicai巢元方, Cao Yuanfang杨上善, Yang Shangshan孙思邈, Sun Simiao王焘, Wang Tao陈藏器, Chen Cangqi鉴真, Jianzhen王冰, Wang Bing 庞安时, Pang Anshi钱乙, Qian Yi唐慎微, Tang Shenwei 寇宗奭, Kou Zongshi 成无己, Cheng Wuji许叔微, Xu Shuwei刘昉, Liu Fang陈言, Chen Yan张元素, Zhang Yuansu 宋慈, Song Ci陈自明, Chen Ziming 李迅, Li Xun刘完素, Liu Wansu张子和, Zhang Zihe李杲, Li Gao杨士瀛, Yang Shiying 罗天益, Luo Tianyi齐德之, Qi Dezhi危亦林, Wei Yilin朱震亨, Zhu Zhenheng 忽思慧, Husihui王好古, Wang Haogu 倪维德, Ni Weide滑寿, Hua Shou汪机, Wang Ji薛己, Xue Ji万全, Wan Quan高武, Gao Wu徐春甫, Xu Chunfu李时珍, Li Shizhen杨继洲, Yang Jizhou 孙一奎, Sun Yikui方有执, Fang Youzhi 龚廷贤, Gong Tingxian 王肯堂, Wang Kentang 吴昆, Wu Kun陈实功, Chen Shigong 张景岳, Zhang Jingyue 喻昌, Y u Chang吴有性, Wu Youxing 傅仁宇, Fu Renyu赵献可, Zhao Xianke 傅山, Fu Shan汪昂, Wang Ang张璐, Zhang Lu叶桂, Ye Gui尤在泾, You Zaijing薛雪, Xue Xue王洪绪, Wang Hongxu吴谦, Wu Qian徐大椿, Xu Dachun赵学敏, Zhao Xuemin郑梅涧, Zheng Meijian陈修园, Chen Xiuyuan吴瑭, Wu Tang王清任, Wang Qingren费伯雄, Fei Boxiong王旭高, Wang Xugao吴尚先, Wu Shangxian王士雄, Wang Shixiong药王, King of Medicine ;Yao Wang医圣, medical sage疾医, general medicine疡医, royal surgeon食医, dietetician太医, palace physician医博士, erudite for general medicine针博士, erudite for acupuncture按摩博士, erudite for massage咒禁博士, erudite for exorcism太医署, Imperial Medical Academy太医局, Imperial Medical Service太医院, Imperial Academy of Medicine尚药局, Bureau of Administration of Royal Medicinal Affairs御药院, Royal Drug Museum和剂局, Bureau for Compounding惠民局, Medical Institute of Benevolence 十三科, thirteen branches of medicine大方脉, medical department for adult杂医科, department of miscellaneous diseases小方脉, medical department for children 风科, department of wind产科, department of obstetric眼科, department of ophthalmology口齿科, department of dentistry and stomatology 咽喉科, department of pharynx and larynx 正骨科, department of osteology金疮肿科, department of sores and wounds 针灸科, department of acu-moxibustion祝由科, department of incantation and psychology禁科, department of incantation金元四家, four scholastic sects of Jin-yuan Dynasties温病学派, sect of warm diseases砭石, stone needle刺禁, needling contraindications灸禁, moxibustion contraindications本草, materia medica医经, medical classic诊籍, case record明堂图, acu-moxibustion chart经方, classical formulae麻沸散, powder for anesthesia五石散, powder of five minerals寒食散, powder taken cold人痘接种术, pox inoculation厘, li分, fen钱, qian两, liang斤, jin合, ge升, sheng寸, cun尺, chi炮炙, processing修事, processing咀, cutting炼丹术, alchemy煮散, powder for boiling平旦服, take at dawn七方, seven kinds of prescriptions大方, major prescriptions小方, minor prescriptions缓方, gentle prescriptions急方, urgent prescriptions奇方, odd-ingredient prescriptions偶方, even-ingredient prescriptions重方, compound recipe十剂, ten functional types of formularies宣剂, diffusing formula通剂, obstruction-removing formula补剂, tonifying formula泄剂, purgative formula轻剂, light formula重剂, heavy formula滑剂, lubricating formula涩剂, astringent formula燥剂, dry formula湿剂, moist formula八阵, eight tactical arrays补阵, supplementing array和阵, harmonizing array攻阵, offensive array散阵, dissipating array寒阵, cold array热阵, heat array固阵, securing array因阵, adaptation array八法, eight methods汗法, diaphoresis吐法, emetic method下法, purgative method和法, harmonizing method温法, warming method清法, clearing method消法, resolving method补法, tonifying method汉文名, 英文名整体观念, holism天气, celetial qi地气, earth qi气立, establishment of general qi天人相应, adaptation of human body to natural environment辨证论治, treatment based on syndrome differentiation理法方药, principle-method-recipe-medicines 阴阳, yin-yang阴阳学说, yin-yang theory阳气, yang qi阴气, yin qi 生之本, root of life阴阳对立, opposition of yin-yang阴静阳躁, steady yin and vexed yang阳化气, yang transforming qi阴成形, yin shaping up body阴阳互根, mutual rooting of yin-yang阴阳消长, waxing and waning of yin-yang阴阳转化, mutual convertibility of yin-yang 重阳必阴, extreme yang changing into yin重阴必阳, extreme yin changing into yang阴平阳秘, relative equilibrium of yin-yang阴阳自和, natural harmony of yin-yang五行, five phases五行学说, five phases theory木, wood火, fire土, earth金, metal水, water木曰曲直, wood characterized by bending and straightening火曰炎上, fire characterized by flaring up土爰稼穑, earth characterized by sowing and reaping金曰从革, metal characterized by clearing and changing水曰润下, water characterized by moistening and descending五时, five seasons五方, five orientations五行相生, mutual generation of five phases母气, mother qi子气, child qi母病及子, illness of mother viscera affecting the child one子病及母, illness of child viscera affecting the mother one木生火, wood generating fire火生土, fire generating earth土生金, earth generating metal金生水, metal generating water水生木, water generating wood五行相克, mutual restriction of five phases所胜, being restrained所不胜, restraining木克土, wood restricting earth火克金, fire restricting metal土克水, earth restricting water水克火, water restricting fire金克木, metal restricting wood五行相乘, over-restriction of five phases五行相侮, counter-restriction of five phases 亢害承制, restraining excessiveness to acquire harmony制化, restriction and generation运气学说, doctrine of five evolutive phases and six climatic factors干支, heavenly stems and earthly branches甲子, sixty-year cycle运气, five evolutive phases and six climatic factors五运, five evolutive phases六气, six climatic factors主气, host climatic qi客气, guest climatic qi司天, celestial manager qi在泉, qi in the earth主运, host evolutive phase客运, guest evolutive phase客主加临, guest climatic qi adding to fixed host qi运气相合, combined analysis of five evolutive phases and six climatic factors运气盛衰, rise and fall of five evolutive phases and six climatic factors天符, coincidence of heavenly qi岁会, yearly weather平气, normal climatic factors运气太过, excess of five evolutive phases and six climatic factors运气不及, deficiency of five evolutive phases and six climatic factors标本中气, manifestation, root cause and medial qi脏腑, zang-fu viscera脏象, visceral manifestations五脏, five zang viscera藏精气而不泻, storing essence without leaking五神, five emotions五华, five lustre五体, five body constituents五志, five minds七情, seven emotions五液, five humors心, heart心包络, pericardium心气, heart qi心血, heart blood心阴, heart yin心阳, heart yang君火, sovereign fire心藏神, heart storing spirit心主血脉, heart governing blood and vessels 心开窍于舌, heart opening at the tongue心恶热, heart being averse to heat肺, lung肺气, lung qi肺阴, lung yin肺阳, lung yang肺主气, lung governing qi肺藏魄, lung storing inferior spirit肺朝百脉, lung connecting all vessels肺主治节, lung governing management and regulation肺主宣发, lung governing diffusion肺主肃降, lung governing purification and descending肺司呼吸, lung controlling breathing肺主通调水道, lung governing regulation of water passages肺主皮毛, lung governing skin and hair肺开窍于鼻, lung opening at the nose肺恶寒, lung being averse to cold脾, spleen脾气, spleen qi脾阴, spleen yin脾阳, spleen yang脾主运化, spleen governing movement and transformation脾为后天之本, spleen being acquired foundation脾主升清, spleen governing ascending clear 脾统血, spleen controlling blood脾主四肢, spleen governing limbs脾主肌肉, spleen governing muscles脾藏营, spleen storing nutrients脾藏意, spleen storing idea脾开窍于口, spleen opening at the mouth脾喜燥恶湿, spleen liking dryness and disliking dampness胰, pancreas肝, liver肝气, liver qi肝血, liver blood肝阴, liver yin肝阳, liver yang肝主疏泄, liver controlling conveyance and dispersion肝主升发, liver governing ascending and dredging肝为刚脏, liver being bold and firm viscera 肝体阴用阳, liver being substantial yin and functional yang肝主筋, liver governing tendons肝藏血, liver storing blood肝藏魂, liver storing soul肝开窍于目, liver opening at the eyes肝恶风, liver being averse to wind肾, kidney命门, vital gate命门之火, vital gate fire精室, essence chamber肾精, kidney essence肾气, kidney qi肾阴, kidney yin肾阳, kidney yang天癸, tian gui相火, ministerial fire肾为先天之本, kidney being congenital origin 肾主封藏, kidney governing storage肾主生殖, kidney governing reproduction肾主水液, kidney governing water metabolism肾主纳气, kidney governing inspiration肾藏精, kidney storing essence 肾藏志, kidney storing will肾主骨, kidney governing bones肾开窍于耳, kidney opening at ears肾恶燥, kidney being averse to dryness六腑, six fu viscera传化物而不藏, digesting andtransporting food anddrink without storing essence胆, gallbladder胆气, gallbladder qi胆汁, bile中清之腑, fu-viscera with clear juice中正之官, fu-viscera with decisive character 胃, stomach胃气, stomach qi胃阴, stomach yin胃阳, stomach yang胃津, stomach fluid水谷之海, reservoir of food and drink胃主受纳, stomach receiving food and drink 胃喜润恶燥, spleen liking moistness and disliking dryness小肠, small intestine回肠, ileum受盛化物, reservoir and transformation分清泌浊, separating clear and excreting turbid大肠, large intestine传导之官, official of transportation膀胱, bladder膀胱气化, functioning of bladder三焦, sanjiao上焦, upper jiao上焦如雾, upper jiao being organ of fogging 中焦, middle jiao中焦如沤, middle jiao being organ of soaking 下焦, lower jiao下焦如渎, lower jiao being organ of draining 奇恒之腑, extraordinary fu-viscera脑, brain脑髓, brain marrow脑户, door of brain囟门, fontanel元神之府, fu-viscera of mental activity髓, marrow骨, bone髓之府, fu-viscera of marrow骨度, bone-length measurement脉, vessel血之府, house of blood胞宫, uterus; womb胞脉, uterine vessels胞门, parturient canal阴道, vagina月经, menstruation胎衣, placenta脏腑相合, interconnection of zang-fu viscera 心合小肠, heart being connected with small intestine肺合大肠, lung being connected with large intestine脾合胃, spleen being connected with stomach 肝合胆, liver being connected with gallbladder肾合膀胱, kidney being connected with bladder心肾相交, intercourse between heart and kidney肝肾同源, homogeny of liver and kidney肺肾相生, mutually promotion of lung and kidney仓廪之本, root of granary; spleen and stomach经络, channel; meridian经络学说, channel theory经脉, channel经气, channel qi标本, manifestation and root cause根结, root and knot气街, pathway of qi四海, four seas十二经脉, twelve regular channels; twelve regular meridians手三阳经, three yang channels of hand; three yang meridians of hand手三阴经, three yin channels of hand; three yin meridians of hand足三阳经, three yang channels of foot; three yin meridians of foot足三阴经, three yin channels of foot; three yin meridians of foot手太阴肺经, Taiyin Lung Channel of Hand; Taiyin Lung Meridian of Hand手阳明大肠经, Yangming Large Intestine Channel of Hand; Yangming Large Intestine Meridian of Hand足阳明胃经, Yangming Stomach Channelof Foot; Yangming Stomach Meridianof Foot足太阴脾经, Taiyin Spleen Channel of Foot; Taiyin Spleen Meridian of Foot手少阴心经, Shaoyin Heart Channelof Hand; Shaoyin Heart Meridian of Hand 手太阳小肠经, Taiyang Small Intestine Channel of Hand; Taiyang Small Intestine Meridian of Hand足太阳膀胱经, Taiyang Bladder Channelof Foot; Taiyang Bladder Meridian of Foot 足少阴肾经, Shaoyin Kidney Channelof Foot; Shaoyin Kidney Meridian of Foot手厥阴心包经, Jueyin Pericardium Channel of Hand; Jueyin Pericardium Meridianof Hand手少阳三焦经, Shaoyang Sanjiao Channel of Hand; Shaoyang Sanjiao Meridian of Hand足少阳胆经, Shaoyang Gallbladder Channel of Foot; Shaoyang Gallbladder Meridian of Foot足厥阴肝经, Jueyin Liver Channel of Foot; Jueyin Liver Meridian of Foot奇经八脉, Eight Extraordinary Channels; Eight Extraordinary Meridians督脉, Governor Channel; Governor Vessel任脉, Conception Channel; Conception Vessel 冲脉, Chong Channel; Chong Vessel带脉, Belt Channel; Belt Vessel阴跷脉, Yin Heel Channel; Yin Heel Vessel阳跷脉, Yang Heel Channel; Yang Heel Vessel 阴维脉, Yin Link Channl; Yin Link Vessel阳维脉, Yang Link Channel; Yang Link Vessel 十四经, fourteen channels经别, branched channel经筋, aponeurotic channel皮部, dermal parts络脉, collaterals孙络, tertiary collaterals浮络, superficial collaterals别络, connecting collaterals形, shape皮毛, skin and hair腠理, striae and interstitial space玄府, invisible minute pores肌肉, muscle筋, ①soft tissue ②tendon膜, membrane; aponeurosis关节, joint百骸, bones完骨, mastoid process枕骨, occipital bone头颅骨, skull曲牙, mandibular angle眉棱骨, supra-orbital bone辅骨, ①fibula and radius ②condyle 高骨, protruding bones交骨, pubis bone颈骨, cervical vertebra髁骨, hip bone髋, hip上横骨, manubrium of sternum尾闾骨, coccyx腰骨, lumbar bone手骨, hand bone合骨, medial malleolus跖, plantar头, head精明之府, house of intelligence腰, waist肾之府, house of kidney膝, knee筋之府, house of tendons膜原, mo yuan; interpleuro-diaphramatic space膏肓, gao huang; inter心之下,膈之上的部位。

气随液脱depletion of fluidinvolving qi desertion 大汗、大吐、大泻,使津液大量丢失,气亦随津液大量外泄而脱失的危重病理变化。
气阴两虚deficiency of both qiand yin气虚和阴虚同时并见的病理变化。
内风endogenous wind又称“肝风内动”,“虚风内动”。
指由脏腑机能失调而引起具有动摇、震颤特点之各种症状的病理变化,与肝脏关系最为密切。
包括阴虚风动、肝阳化风、血虚生风、热极生风等。
风胜则动predominate wind causingmotion 风邪侵袭,或肝风内动,出现头目肢体动摇、震颤等的病理变化。
阴虚风动stirring wind due to yindeficiency 肝肾阴液枯竭,筋脉失养而风气内动的病理变化。
肝阳化风hyperactive liver yangcausing wind 肝肾阴亏,水不涵木,肝阳亢逆无制而动风的病理变化。
热极生风extreme heat causingwind 邪热炽盛,伤及营血,燔灼肝经,筋脉失养而挛急抽搐的病理变化。
血虚生风blood deficiency causingwind血液亏虚,筋脉失养,虚风内动的病理变化。
血燥生风blood dryness causingwind 血虚津亏,失润化燥,肌肤失于濡养而致干燥瘙痒及脱屑的病理变化。
痰瘀生风phlegm stasis causingwind 痰与瘀血壅阻经络,阻碍气血,使脏腑功能失常而引动内风的病理变化。
内寒endogenous cold与外寒相对,指脾肾阳虚,不能温煦机体脏腑,而使阴寒内生的病理变化。
内湿endogenous dampness与外湿相对,指脾肾阳虚,运化失职,导致体内水液停滞而湿浊内生的病理变化。
湿胜[则]濡泻predominant dampnesscausing diarrhea湿邪偏盛就容易导致大便湿软泄泻的病理变化。

中医①traditional Chinese medicine②traditional Chinese physician ①中医学的简称。
②本学科专业职业队伍。
中药 Chinese materia medica 在中医理论指导下应用的药物。
包括中药材、中药饮片和中成药等。
中医学 traditional Chinese medicine 以中医药理论与实践经验为主体,研究人类生命活动中健康与疾病转化规律及其预防、诊断、治疗、康复和保健的综合性科学。
中药学 Chinese materia medica 中药学科的统称。
研究中药基本理论和各种药材饮片、中成药的来源、采制、性能、功效、临床应用等知识的学科。
中医药 traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医与中药的合称。
中医药学 traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医学与中药学的合称,侧重反映中医与中药两者共同发展,密不可分。
中西医结合 integration of traditional and western medicine 现代医学等现代科学知识及手段来继承和发展中医药,中西医学相互补充,取长补短,诊治疾病的医学形式。
中医基础理论 basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine 研究和阐明中医学的基本概念、基本理论、基本规律、基本原则的学科。
中医诊断学 diagnostics of traditional Chinese medicine 根据中医学的理论体系,研究诊察病情、判断病种、辨别证候的基础理论、基本知识和基本技能的学科。
方剂学 prescriptions of Chinese materia medica 研究治法与方剂配伍规律及其临床运用的学科。
中医内科学 internal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine 研究外感温病、内伤杂病等内科疾病诊治与预防的临床中医学。
AAbdominal flatulence 中满Abdominal fullness and distention 腕痛胀满Abdominal retention 鼓胀Accompanied Symptoms 兼证Activating blood and dissolving stasis 活血化瘀Acuesthesia 得气Acupuncture points 腧穴Acupuncture therapies 针刺疗法Adjuvant drugs 佐药Afternoon fever 日哺发热Alternate chills and fever 寒热往来Anorexia 食欲不振Aphtha 口疮Apoplexy 中风Ashi point 阿是穴Associate drugs 臣药Association of combination of traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine 中西医结合研究会Association of traditional Chinese medicine 中医学会Asthenic cardioyang 心阳虚Asthenic cardioyin 心阴虚Asthma 哮证Otopuncture therapy 耳针疗法Auscultation-olfaction 闻诊Aversion to wind and cold 畏恶风寒BBasis of theory of traditional Chinese medicine 中医理论基础Belching 嗳气Blood deficiency 血虚Blood heat 血热Body fluid 津液CCalming liver wind 平肝熄风Canthus 目眦Carbuncle 痈Cathartic method 攻里法Cardiac and renal coordination 心肾相交Cardiac-splenic asthenia 心脾两虚Chest pain 胸痛Chest stuffiness 胸闷Chi pulse 尺脉Chinese materia medica and pre script ions 中药与方剂Chinese medical 中国医学史Chinese medicine anesthesia 中药麻醉Chinese patent drugs 中成药Clear abundant urine 小便清长Clearing damp 利水渗湿Clearing heat and expectoration 清热化痰Clearing wind-damp 祛风胜湿Clearing Ying heat and cooling blood 清营凉血Coating color 苔色Cold hands and feet 手足厥冷Cold-heat mixing 寒热交错Cold limbs 手足厥冷Cold stroke 中寒Coma 神昏Compendium of Materia Medica 本草纲目Complications 并病Constipation 大便不通Consumptive disease 虚劳Contrary treatment 反治DDefensive Qi instability 卫气不固Deficiency-excess mixing 虚实夹杂Delirium 谵语Diagnostic methods of traditional Chinese medicine 中医诊法Diaphoresis 汗法Diaphoresis, pungent cold 辛凉解表Diaphoresis, pungent warm 辛温解表Diarrhea 泄泻Different treatments for the same disease 同病异治Differentiation, eight principles 八纲辨证Differentiation of diseases 辨病Differentiation of symptoms and signs 辨证Differentiation, six meridians 六经辨证Differentiation, triple energizer 三焦辨证Differentiation, Wei-Qi-Ying-Xue 卫气营血辨证Differentiation, Zang-Fu 脏腑辨证Diphtheria 白喉Diseases of Qi-blood-fluid 气血津液病症Dispersing cold and freeing Bi 散寒通痹Doctrines of various historical schools 中医各家学说Dry heat 燥热Dry stool 大便干结Dysentery 痢疾Dyspepsia 食滞Dysphagia 噎膈Dyspnea 喘证Dysuria 癃闭EEdema 水肿Eight principles 八纲Electuary 冲服剂Elimination 消法Emesis 吐法Endogenous hygrosyndrome 内湿Endogenous cold 内寒Endogenous dryness 内燥Epilepsy 痫证Epitaxis 鼻衄Eruption 斑疹Etiology 病因Exterior syndrome 表证Exterior sthenia 表实Exterior asthenia 表虚Extremely cold limbs 手足厥逆FFacial distortion 口眼歪斜Feeling 按诊Fluid deficiency 津液不足Frequent micturition 小便频数Frequent vomiting 反胃GGastric asthenia 胃虚Gastric cavity 胃脘Gastro-Qi 胃气Generation-inhibition in five elements 五行相克Gingiva 牙龈Greyish fur 灰苔HHarmonizing liver-spleen 调和肝脾Heart fire hyperactivity 心火亢盛Heart-kidney Yang deficiency 心肾阳虚Heart Yang hypoactivity 心阳不振Healthy Qi 正气Hectic fever 潮热Hemorrhage Zheng 血证IInsomnia 失眠Inspection 望诊Intergeneration 相生Inter-restriction 相克Inter-subjuation 相乘Irregular pulse 结代脉KKidney Yang deficiency 肾阳虚Kidney Yin deficiency 肾阴虚LLarge intestine damp-heat 大肠湿热Large pulse 大脉Leukorrhea 白带Liver fire flaming 肝火上炎Liver-stomach disharmony 肝胃不和Liver wind agitation 肝风内动Liver Yang rising 肝阳上亢Liver Yin deficiency 肝阴虚Long pulse 长脉Longer menstrual interval 月经后期Loose stool 便溏Lung heart 肺热Lung Qi deficiency 肺气虚Lung Qi impairment 肺气失宣MMeasles 麻疹Menstrual irregularities 月经失调Merdian-collateral theory 经络学说Meridial distribution 归经Mutual promotion 相须NNight sweat 盗汗Nine orifices 九窍Normal pulse 平脉Nourishing blood and liver 养血柔肝PPale tongue 淡白舌Palpation 切诊Palpitation 心悸Pathogenesis 病机Peeled coating 剥脱苔Pestilence 疫疠Pharynx neurosis 梅核气Phlegm-damp obstructing lung 痰湿阻肺Pill 丸Pores 玄府Principal and subordinate 标本Pulse condition 脉象Pulse-taking 脉诊Purgation-tonifying 攻补兼施QQi-blood and fluid 气血津液Qi deficiency 气虚Qi depression 气滞Qi function 气机RRapid pulse 数脉Relaxing bowels 润肠通便Removing stasis to promote blood circulation 化瘀行血Resolving damp, aromatic 芳香化湿Resuscitation 开窍Retch 干呕Reverse restriction 相侮SSchool in favour of the doctrine of warm diseases 温病学派School of febrile diseases by cold injury 伤寒学派Scrofula 瘰疬Sighing 太息Smallpox 天花Somnolence 多寐Sore 疮Spleen Qi deficiency 脾气虚Spleen Yang deficiency 脾阳虚Spleen Yin deficiency 脾阴虚Spontaneous sweating 自汗Stranguria 小便涩痛Stomach cold 胃寒Stomach heat 胃热Strengthening healthy energy 扶正Striae 腠理Stringy pulse 弦脉Sunstroke 中暑TTenesmus 里急后重Tonifying deficiency 虚则补之Tonifying kidney and holding Qi 补肾纳气Tonifying Qi and spleen 益气健脾Treating excess with purgation 实则泻之Treatment with syndrome differentiation 辨证论治Twenty-eight pulses 二十八脉UUlcer 溃疡Urinal incontinence 小便失禁Uterus 女子胞VVitaport 命门WWhitish fur 白苔Whooping cough 百日咳YYellowish fur 黄苔Ying and Yang in balance 阴平阳秘ZZheng 证一阳"frist yang, Shaoyang Channel"一阴"frist yin, Jreyin Channel"一逆one mista ade in treatment一息respiration一侧的unilateral一日量daily dose一服药a dose of medicine一夫法finger breadth measurement一身痛重general pain and heaviness乙癸同源Yi(the live) and Gui)the Kidney) bejing the same source二阴"two lower orifices, ie, the external urethral orifice and the anus" 二浊reddish and whitish turbid urine二十八脉twenty-eight kinds of pulse condition二阳并病Shaoyang syndrome complicated by T aiyang syndrome二便不利difficulty in urination and defecation二便失禁urinary and fecal incontinence十问inquire about ten aspects of the patient十剂ten kinds of pre script ion十八反eighteen incompatible medicaments十二剂twelve kinds of pre script ion十二节twelve joints十二禁twelve contraindications十二经twelve regular channels十二时traditional twelve two-hour periods十二脏twelve internal organs十二怪脉"ten moribund pulses, ten kinds of paradoxical pulse condition" 十九畏nineteen nedicaments of nutual antagonism十三科the thirteen medical specialties十四经the fourteen channels十五络(脉)fifteen main collaterals十二节刺twelve methods of needling十二经别branches of the twelve regular channels十二经筋muscle along the twelve regular channels十二皮部twelve skin areas十六郄穴sixteen cleft points十四经穴"accupuncture points on the fourteen regular channels, acupoints on regular channels"十五络穴fifteen main collaterals points十二经动脉arteries of the twelve channels十二井穴twelve well-points十二经之海sea of the twelve channels丁痂scar丁奚疳infantile malnutrition due to excessive feeding丁躬势bowing丁字形骨折T-shaped fracturre七方"seven pre script ions, Seven formulae"七恶the symtoms and signs indicating poor prognosis of suppurative infections of the exterior part of the body七窍seven orifices七情seven emotions七疝seven kinds of hernia七伤 1.seven kinds of impairments 2.seven symptoms suggesting consumption of the kidney-qi七冲门seven important portals七怪脉"seven moribund pulses, seven paradoxical pulse conditions, seven fatal pulse conditions"七日风=脐风neonatal tetanus七星针=梅芬针seven star needle八纲the eight principal syndromes serving as guidelines in diagnosis八法eight therapeutic methods八廓the eight regions of the white of the eye八溪eight joints八会穴"eight hui-points, eight influential points"八片锦different pictures of superficial venules of index finger in children as a reference for diagnosis八纲辨证analyzing and differentiating pathological conditions in accordance with the eight principal syndromes八脉交会穴eight confluence points人中疔boi on philtrum人咬伤human bite; bite by man人迎脉Renying pulse人背复位back-carrying reduction人痘接种human variolation人工牛黄"artificial ox gallstone, Calculus Bovis Factitius"人事不省=神昏unconsciousness入臼joint reduction儿风eclampsia儿病=恶阻儿茶"catechu, blzck catechu, Catechu"儿枕痛after-pains儿捧母心breech presentation儿科四大要证four chief diseases in pediatrics九刺nine types of needling九气nine kinds of illness due to disturbance of qi九窍nine orifices九脏nine internal organs九虫病parasitic diseases九窍出血bleeding from the nine orifices九六补泻法nini-six reinforcing-reducing method刀伤incised wound刀晕traumatic syncope刀创伤drug for incised wound刀斧伤wound by knife or ax三宝"three exxentialsessence, qi and configurative force"三痹three types of arthralgiz三刺=齐刺three-stratum puncture三法"three therapeutic methods-diaphoresis, emesis, and purgation" 三伏"1.three periods of dog days, 2.the third period of dog days"三关the three passes三焦"tri-jiao, sanjiao, triple warmer, triple heater"三毛(丛,聚)clump hair三品three grades of medicines三消three types of diabetes三因three categories etiologic factors三虫病three intestinal parasitoses三春柳=柽柳三焦病disease of tri-jiao三焦经Tri-jiao Channel三焦咳tri-jiao cough三棱针"three-deged needle, tri-ensiform needle"三陷证three typesof inward penetration of pyogenic agent三阳病disease of the three yang channels三阳经three yang channels三阳络Sanyanglo三阴病diseases of the three yin channels三阴经three yin channels三阴痉convulsion with symptoms of three yin channels三阴疟three-yin malaria三板疗法"tri-tabular massage, massage with three Kinds of boards"三部九候three portions and nine pulse-takings7 三焦辨证differentiation of syndrome according to the pathological changes of trijiao 三焦实热heat in tri-jiao of excess type三焦虚寒cold syndromes of deficiency type三阳合病disease involving all three yang channels三点挤压法three-point pressure method三焦主决渎the triple warmer manages the dredging of water pathway干便dry stool干疽cellulitis at the anterolateral aspect of the shoulder干咳"dry cough, unproductive cough"干呕retching干陷dry type of inward penetation of pyogenic agent干癣1.chronic eczema 2.neurodermatitis干皮dried bark干血劳emaciation due to blood disorders干胁痛dry hypochondriac pain干脚气dry beriberi干霍乱dr cholera干眼症xerophthalmia干拔罐1.dry cupping 2.ordinary cupping土earth(in five elements)土方"folk recipe, local recipe"土疳=针眼hordeolum土栗infection of the heel土风疮popular urticaria土生甘sweet flavour is attributed to earth土生金earth generates metal土克水earth restricts water土脯子mantis cheeks土乘水earth subjugates water土不制水earth fails to control water土生万物earth produces myriads of things土喜温燥earth prefers warmth and dryness土郁夺之Dampness accumulated in the spleen(earth) should be removed8 下胞Lower eyelid下膊forearm下法"purgation, purgative therapy"下疳chancre下膈intake of food in the morning and vomiting in the evening下工"an inferior medical worker, an inexperienced healer"下骨sending down the fishbone下极1.anus 2.perineum 3.area between inner canthi 4.another name for Hengku下焦"lower-jiao, lower warmer, lower heater, lower burner"下利diarrgea下迫tenesmus下气"1.a therapeutic mithod to keep the adverse qi flowing downward 2.aerofluxus, breaking wind 3.qu of the lower part of the body"下窍lower orifices下泉urine下乳=催乳lactogenesis下脘1.phlorus 2.Hsiawan下陷=中气下陷descending disorders下消"diabetes of the kindney type, diabetes incolving the lower-jiao"下搭手lower back cellulitis下丹田lower elixir field下发背"lumbar carbuncle, deep-rooted ulcer in the lumbar region"下焦病lower-jiao syndrome下马痈acute pyogenic infection of right下石疽indurated mass of knee下牙床mandible下注疮eczema of shank下病上取treating diseases of the lower part of the body by needling points on the upper part of the body下腹胀气flatulence in the lower abdomen下汲肾阴consumption of the kidney-yin by the excessive heart fire下焦如渎lower-jiao resembling water passages下焦主出The Lower-jiao is in charge of excretory system下厥上竭exharstion of blood with cold limbs下厥上冒dizzeness caused by adverse flow of qi下利清谷diarrhea with undigested food in the stool下损及上dusease in the lower part affecting the upper下胎毒法dispelling toxic heat and meconium gathered at the fetus for the new born下者举之Sinking disorders should be treated with drugs of raising property; prolapse and ptosis must be treated with the lifting method to reinforce the vital function of the spleen 下焦湿热downward flow of damp and heat下利赤白dysenteric diarrhea下横骨伤fracture of public bone下行通路descending pathway 最新回复zzzxxx001 at 2007-7-06 22:45:43大夫"an official's title in the feudal age, now used for a doctor in northern China"大肠large intestine大毒extremely poisonous drugs大方heavy pre script ion大分distinct line between large muscles大风= 麻风大腹upper abdomen大谷large space between muscles大汗"profuse sweating, byperhidrosis, excessive perspiration"大经rge channels 2.the needling of points on a large channel exhibiting symptoms 大厥coma大络large collatereals大脉"large pluse, gigantic pulse"10 大衄profuse bleeding from the mouth and nose大气"atmosphere, air"大溲(解)"defecation, bowel movements"大泻vigorous reduction大医respected doctor大针large needle大眦=内眦great canthus大节large joints大产eutocia大便feces; stool;defecation大耳mycrotia大肉large muscles大嘴macrostomia大肠病disease of large intestine大肠经"Large Intestine Channel, LI"大肠虚asthenia of large intestine大肠痈acute appendictis大肠胀flatulence of large intestine大方科speciality of internal medicine大瘕泄dysentery大结胸large accumulation of phlegm-heat in the chest大头垫megacaput pad大头风=大头瘟infection with swollen head大腿疽=股疽大腿痈carbuncle of thigh大泻刺drainage needling大指间web of great toe大周天large cirde of vital energy大眦漏=漏睛dacryocystitis大方脉adult's pulse大出血"massive hemorrhage,hematorrhea"大肠气inguinal hernia大麻风"lepra, leprosy"大便溏loose stool大补元气invigorating primodial qi大肠寒结constipation due to retention of cold-pathogen in large intestine大肠滑脱prolapse of rectum大肠气滞qi stagnation of large intestine大肠热结large intestinal11 大肠湿热large intestinal damp-heat大肠虚寒asthenia-cold of large intestine大肠液亏deficiency of fluid in large intestine大方脉科internal medicine大风恶疫=麻风大肉陷下obvious emaciation and muscular atrophy大头伤寒=大头瘟大眦脓漏dacryocystitis with pyorrhea大气疗法aerotherapy大风荷毒most dangerous pathogenic factors大肠津亏fluid deficiency in the large intestine大便干结dry stool大便不通constipation大便色黑"black stool, melena"大便如漆tarry stools大便失禁incontinence of feces大便困难dyschesia大便频数frequency of bowel movement大汗淋漓profuse perspiration大骨枯槁bones become dry and brittle大渴引饮extreme thirst大肠主传导large intestine takes charge of transportation大实有羸状appearance of deficiency in extreme excess兀兀欲吐intense nausea万灵药panacea寸a length measurement corresponding to the middle segment of one's middle finger 寸脉cun pulse寸口脉cunkou pulse寸白虫proglottid of tapeworm寸白虫病taeniasis寸、关、尺"cun,guan,and chi,inch,bar,and cubit"上胞upper eye lid上膊upper arm上膈"postcibal vomiting,vomiting immediately after in gestion"12 上工"Shang-gong,superior medical worker"上火sufering from excessive internal heat上焦"upper-jiao,upper warmer,upper heater"上气1.abnormal rising of qi 2.the upper qi上窍upper orifices上脘1.shangwan 2.episgastrium上消diabetes involving the upper-jiao上搭手cellulitis near the scapular region上丹田upper elixir field上腭痈abscess on palate上耳背Shangerpei上发背suppurative inflammation of the uppermost part of the back上横骨sternal notch上马痈left buttock carbuncle上石疽upper stony mass behind the ear上水鱼abscess of the popliteal region上牙床upper dental bed上肢瘫paralysis of upper extremities上焦证upper warmer syndrome上胞下垂"ptosis,blepharoptosis"上病下取treating diseases in the upper part by managing the lower上膈下膈upper stenosis and lower stenosis上寒下热cold in the upper and heat in the lower上焦病症syndrome of the upper-jiao上焦如雾the upper-jiao resembling a sprayer上焦主纳The upper-jiao is in charge of receiving上骱手法reduction of dislocation上厥下竭syncope due to exhaustion below上气喘促shortness of breath上热下寒heat in the upper and cold in the lower上实下虚excess in the upper and deficiency in the lower上损及下the upper effecting the lower上吐下泻vomiting and diarrhea上下配穴"coordination of the acupionts of the upper with those of the lower, superior-inferior point association"上虚下实deficiency in the upper and excess in the lower上肢不遂moter impairment of the upper extremities上翘下钩势dorso-extension and ventro-flexion exercise口"mouth,oral cavity"口臭"foul breath, halitosis"口疮"aphthae,canker sore"口淡tastelessness口服"per oral,per os"口疳aphthae in children口紧=唇紧口噤"lockjaw, trismus"口苦bitter taste口软flaccidity of mouth in infants口水"saliva,spittle"口酸sour taste口{口呙} wry mouth口咸salty taste口吃"stutter,stammer"口糜erosion of mucous membrance of the oral carity口渴thirst口不仁numbness of mouth口齿科specialty of stomatology and dentistry口甘甜sweet taste口疳风=舌头泡blisters of the tongue口丫疮"ulcer on the angle of lips,perleche"口中和normal sense of mouth口臭口烂halitosis and aphthosis口唇发紫cyanotic lips口唇紧缩=唇紧口干唇裂dry mouth with cracked lips口噤唇青trismus with cyanotic lips口舌糜烂aphthous stomatitis14 口涎外溢"1.involuntary drooling 2.sialorrhea,ptyalism,sialism,excessive flow of saliva" 口眼{口呙}斜"1.facia hemiparalysis deviation of the eye and mouth, wry mouth with distorted eyes"口中无味=口淡flat feeling in mouth口干唇燥dry mouth and lips口不知谷味loss of appetite口齿咽喉科"1.Department of the Mouth, Teath and Throat 2.specialty of mouth tooth-throat" 口沃沫多唾excessive salivation with froth千日疮verruca vulgaris千岁疮=流注疮widespread scrofula久咳chronic cough久痢protracted drsentery久疟chronic malaria久痔=肛漏recto-analfistula久泻chronic diarrhea久热伤阴persistent fever injuring yin essence久不受孕fail to be impregnated for a long time久泻不止chromic diarrhea丸剂"pill,bolus"广肠sigmoidorectum广疮=杨梅疮syphilis广明anterosuperior part of the human body丫叉毒丫刺毒pustule in the web between the fiest and second metacarpals亡血"hemorrhage, bleading"亡阳"yang depletion,yang exhaustion"亡阴"yin depletion,yin exhaustion"亡血家patient with hemorrhagic diathesis尸厥corpse-like syncope尸体"corpse,cadaver"尸咽"ophthalmo-oro-genital syndrome,Behcet's syndrome"卫defensive function卫气defensive energy卫分证" weifen syndrome,febrile disease at wei phase,syndrom of wei system"卫生局"health bureau, sanitary bureau"卫生学sanitary science卫气不固=表气不固wei-energy fail to protect the body卫气同病"syndrome of both weifen and qufen,syndrome of both qi and wei systems"卫气管血辨证analysing and differentiating the development of an epidemic febrile disease by studying condition of the four systems女科"1.women's diseases,gynecology and obster\trics 2.medical department for women,department of gyhecology and obstetrics"女医1.woman physician 2.physician who attends to women's diseases女劳疸jaundice due to sexual intemperance女劳复relapse of disease due to intemperance in sexual life女子胞uterus女阴溃疡ulcerative vulvitiszzzxxx001 at 2007-7-06 22:46:39小产"abortion, miscarriage"小肠the small intestine小毒"d toxicity 2.drugs with a little toxicity,slightly poisonous drugs"小方"minor pre script ion,minor or mild pre script ion"小分small space between muscles小腹=少腹lower abdomen小逆minor mistake in treatment小溲urine小溪=溪谷小心=心包络=命门小眦"lateral canthus, external canthus"小耳microtia小眼microphthalmus小嘴microstomia小便"urine, urination, micturition"小肠病disorder of the small intestine16 小肠经=手太阳小肠经small intestine channel小肠咳"small intestine cough, cough accompanied by flatulence"小肠疝[气] hernia小肠痈small intestinal abscess小肠胀flatulence of the small intestine小方科specialty of pediatrics小腹满distension of lower addomen小夹板splintlet小结胸accumulation of phligm-heat in the chest小伤寒"common cold, common cold of wink-cold type"小舌头uvula小腿疽=胫疽leg cellulitis小中风faint小周天a small circle of the evolutive小眦漏fistula in the lateral canthus小方脉infantile pulse小腹疽(痈)carbuncle of lower abdomen小便短赤scanty dark urine小便短小oliguria小便黄赤dark urine小便辣痛ardor urine小便淋沥dribbling urination小便涩痛difficulty and pain in micturition小便灼热burning sensation during urination小肠实热excessive heat in the small intestine小肠虚寒hypofunction of the small intestine with cold manifestations小儿暴惊sudden fright in children小儿表热exterior-heat syndrome in children小儿虫吐parasite vomiting in children小儿喘急dyspnea in children小儿卒利acute infantile diarrhea in children17 小儿扎目incessant winking of eyes in children小儿发热fever in children小儿发痧eruptive disease in children小儿疳眼eye disorder due to malnutrition in children小儿寒吐vomiting in children due to cold小儿脚拳1.infantile pedal spasm 2.spasm of toes in children小儿惊吐vomiting in children induced by frightening小儿咳逆choking cough in children小儿客忤convulsive seizure in duced by terror in children小儿羸瘦emaciation in children小儿里热endopathic heat syndrowme in children小儿脉法pulse-taking in children小儿热吐vomiting in children due to heat小儿实热heat syndrome of excess type in children小儿食积infantile indigestion with food retention小儿手拳contracture of fingers in children小儿瘫痪infantile paralysis小儿痰鸣wheezing cough in children小儿通睛"esotropia in children, convergent strabismus in children"小儿吐泻vomiting and diarrhea in children小儿哮喘asthma in children小儿虚热heat syndrome of deficiency type in children小儿遗溺(尿)"1.incontinence of urine in children 2.bed-wetting, nocturnal enuresis in children"小儿脉科specialty of pediatrics小户嫁痛pain in vagina小溲热赤dark urine with burning sensation小腿转筋spasm of calf小儿夜啼nocturnal fretfulness infinfants小儿疳积mallnutrition and indigestion syndrome in children18 小儿浮肿edema in children小儿痢疾dysentery in children小儿感冒common cold in children小儿痢证epilepsy in children小儿淋证infection of urinary system in children小儿风水acute glomerular小儿血虚anemia in children小儿自汗"spontaneous perspiration in children, hyperhidrosis in children"小儿咳嗽cough in children小儿腹痛abdominal pain in children小儿无耳anotia小便不利"dysuria, difficulty in micturition"小便不禁=小便失禁"incontinence of urine, aconuresis"小便淋沥dripping discharge of urine小便频数frequency of micturition小儿暑热(渴)证summer fever of children小儿痰湿吐"vomiting in children, due to phlegmdampness"小肠主受盛small intestion has a function of reception小腹中痞块mass in the lower abdomen小儿涕液不收incessant running nose in children小儿推拿疗法infantile massage小儿囟门不合non-closure of fontanels in infants小儿时行痿poliomyelitis小儿遗毒烂斑congenital syphilis飞痘pustules from smallpox vaccination飞法flying method飞疡(扬)喉hematoma of uvulla飞腾八法=灵龟八法the eight magic turttle techniques飞蚊幻视muscae volitantes叉喉风acute laryngeal disorder with compressive feeling in the throat19 马牙1.gingival cyst of mucous gland in the newborn 2.yellowish eruptions on the gum of the newborn马桶癣contact dermatitis of buttock马脾风acute asthmatic attack in children马蹄针staple puncture马刀侠瘿sabre and beadstring scuofulae马蜞咬伤bite by leech子烦restlessness during pregnancy子户=气穴子淋stranguria during pregnancy子满gestational edema子门cervical orifice of uterus子气1.qi of the child organ 2.edema of legs in pregnancy子舌=重舌子嗽=妊娠咳嗽intractable cough during pregnancy子痫(冒)eclampsia gravidarum子悬"upward flow of fetusqi, feeling of distension in the thorax during pregnancy" 子喑"gestational aphonia, aphonia during pregnancy"子痈acute or chronic orchitis and epedidymitis子脏=女子胞医学翻译子肿edema during pregnancy子宫石womb stone子宫痛uterismus子母痔prolapsed internal hemorrhoids子病及母disorder of the child organ affecting the mother organ子肠不收=子宫脱(垂)出uterine prolapse子盗母气illness of the child organ may involve the mother organ子户肿胀swelling of vulva子死腹中=死胎不下dead foetus in the uterus子午捣臼zi wu dao jiu needli绪论introduction中医学traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)中医学理论体系theory system of TCM中医基础理论basic theory of TCM整体观念holism concept五脏一体观holism of five ogans形神一体观holism of body and spirit天人一体观holism of human beings and universe医学模式medical pattern辨证syndrome differentiation论治treatment variation疾病disease证候syndrome症状symptom体征physical sign辨病disease diagnosing同病异治different treament for the same disease异病同治the same treatment for the different disease第一章中医学的哲学基础Ancient philosophic basis of TCM精jing(as the world origin in ancient philosophy)气qi(as the world origin in the ancient philosophy)精气学说theory of jingqi生命life中介medium气机qi activity气化qi transformation感应induction水地说hypothesis of jing originating from water and earth云气说hypothesis of qi originating from cloud and air气一元论monism of qi元气一元论monism of qi阴阳yinyang; yin and yang阴阳学说theory of yinyang阴阳对立inter-opposition between yin and yang阴阳互根inter-dependence between yin and yang阴阳消长wane and wax between yin and yang阴阳交感inter-induction between yin and yang阴阳互藏inter-containing between yin and yang阴阳转化inter-transformation between yin and yang阴阳自和reestablishment to yin-yang equilibrium阴阳平衡both yin and yang in equilibrium五行five elements五行学说theory of five elements五行相生inter-promotion of five elements五行相克inter-inhibition of five elements五行制化relationship of promotion and restriction of five elements 五行相乘inter-invasion of five elements五行相侮reverse restriction in five elements五行胜复resistance of oppressed elements母病及子mother-organ diorder involving its child-organ子病及母child-organ disorder involving its mother-organ滋水涵木replenishing water to nourish wood培土生金reinforcing earth to generate metal益火补土tonifying fire to supplement earth金水相生mutual generation between metal and water抑木扶土inhibiting wood and strengthening earth培土治水cultivating earth to control water佐金平木assisting metal and calming wood泻南补北purging the south (fire) and nourishing the north (water) 宏观观察obsevation on macroscopic level中和golden mean类比analogy第二章藏象Viscera state藏象viscera state藏象学说doctrine of viscera state脏腑viscera; zangfu organs五脏five zang organs心heart肺lung脾spleen肝liver肾kidney六腑six fu organs胆gall baldder胃stomach小肠small intestin大肠large intestine三焦tri-jiao; sanjiao膀胱urinary blader奇恒之腑extraordinary fu organs脑brain髓marrow骨bone脉vessel女子胞uterus满而不实full of essence without foodstuff实而不满full of foodstuff without essence心主神明heart controlling mental activities心主血脉heart controlling blood circulation心藏神heart storing spirit肺主气lun governing qi肺主呼吸之气lung governing respiratory qi肺主一身之气lung governing physical qi肺朝百脉convergence of vessels in the lung肺主行水lung governing water metabolism肺主治节lung governing coordinative activities of viscera肺为华盖lung being the canopy肺为娇脏lung being the delicate organ肺主宣发肃降lung controlling dispersing outward and inwards 气门pore后天之本source of acquired constitution脾主运化spleen governing transportation and transformation 脾气主升spleen governing ascending脾主统血spleen governing blood脾喜燥恶湿spleen preferring dryness to dampness。
04.001诊法diagnostic method以中医学理论为指导,临床收集病变资料,探求病因、病位、病性及病势,辨别证候,判断疾病,从而指导临床治疗的方法。
04.002四诊four diagnostic methods望、闻、问、切4种中医诊察疾病基本方法的合称。
04.003症状symptom机体因发生疾病而表现出来的异常状态,包括患者自身的各种异常感觉与医者的感觉器官所感知的各种异常表现。
04.004内证interior syndrome患者身体内部的疾病征象。
04.005外证exterior syndrome表现于机体外部的疾病征象。
04.006四诊合参comprehensive analysisof data gained by fourdiagnostic methods 综合运用望、闻、问、切4种基本方法,对所获得的资料进行全面分析综合,为准确辨病辨证提供依据的中医诊断原则。
04.007司外揣内governing exterior toinfer interior 通过诊察机体外部的异常征象,推测与分析身体内部相关状态的中医诊断方法。
04.008审症求因differentiation ofsymptoms and signs toidentify etiology 通过审察病变的各种表现,来推求疾病的病因病机,进行辨证,并指导治疗的中医诊断原则。
04.009平人healthy person气血调和的健康人。
04.010望诊inspection用视觉观察病人的神、色、形、态、舌象、排泄物、小儿指纹等的异常变化,以了解病情的诊断方法。
04.011望神inspection of spirit用视觉观察人体生命活动的整体外在表现和精神状态的诊断方法。
04.012得神fullness of vitality人精神饱满,目光灵活,反应灵敏,语言清晰,面色润泽,呼吸平稳,脉象和缓有力等生命活动正常的表现。
中医术语英文大全以下是一些常见的中医术语及其对应的英文译名:1. 中医 (Traditional Chinese Medicine)2. 针灸 (Acupuncture and Moxibustion)3. 按摩 (Massage)4. 草药 (Herbal Medicine)5. 中药 (Traditional Chinese Medicine)6. 推拿 (Tuina)7. 食疗 (Diet Therapy)8. 气功 (Qigong)9. 气血 (Qi and Blood)10. 经络 (Meridians)11. 寒热 (Cold and Heat)12. 脉象 (Pulse Diagnosis)13. 五行 (Five Elements)14. 通脉散结 (Promoting Qi Circulation and Resolving Stagnation)15. 疏肝理气 (Soothing the Liver and Regulating Qi)16. 补肾固本 (Tonifying the Kidneys and Strengthening the Essence)17. 温阳散寒 (Warming Yang and Dispelling Cold)18. 疏风清热 (Dispelling Wind and Clearing Heat)19. 透疹退湿 (Promoting Eruption and Resolving Dampness)20. 润肺止咳 (Moistening the Lungs and Stopping Cough)这只是一小部分中医术语的英文译名,由于中医涉及的领域广泛且复杂,还有许多其他的中医术语没有在列表中列出。
序号汉文名英文名注释中医①traditional Chinese medicine②traditional Chinese physician ①中医学的简称。
②本学科专业职业队伍。
中药 Chinese materia medica 在中医理论指导下应用的药物。
包括中药材、中药饮片和中成药等。
中医学 traditional Chinese medicine 以中医药理论与实践经验为主体,研究人类生命活动中健康与疾病转化规律及其预防、诊断、治疗、康复和保健的综合性科学。
中药学 Chinese materia medica 中药学科的统称。
研究中药基本理论和各种药材饮片、中成药的来源、采制、性能、功效、临床应用等知识的学科。
中医药 traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医与中药的合称。
中医药学 traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医学与中药学的合称,侧重反映中医与中药两者共同发展,密不可分。
中西医结合 integration of traditional and western medicine 现代医学等现代科学知识及手段来继承和发展中医药,中西医学相互补充,取长补短,诊治疾病的医学形式。
中医基础理论 basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine 研究和阐明中医学的基本概念、基本理论、基本规律、基本原则的学科。
中医诊断学 diagnostics of traditional Chinese medicine 根据中医学的理论体系,研究诊察病情、判断病种、辨别证候的基础理论、基本知识和基本技能的学科。
方剂学 prescriptions of Chinese materia medica 研究治法与方剂配伍规律及其临床运用的学科。
中医内科学 internal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine 研究外感温病、内伤杂病等内科疾病诊治与预防的临床中医学。
中医①traditional Chinese medicine②traditional Chinese physician ①中医学的简称。
②本学科专业职业队伍。
中药 Chinese materia medica 在中医理论指导下应用的药物。
包括中药材、中药饮片和中成药等。
中医学 traditional Chinese medicine 以中医药理论与实践经验为主体,研究人类生命活动中健康与疾病转化规律及其预防、诊断、治疗、康复和保健的综合性科学。
中药学 Chinese materia medica 中药学科的统称。
研究中药基本理论和各种药材饮片、中成药的来源、采制、性能、功效、临床应用等知识的学科。
中医药 traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医与中药的合称。
中医药学 traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医学与中药学的合称,侧重反映中医与中药两者共同发展,密不可分。
中西医结合 integration of traditional and western medicine 现代医学等现代科学知识及手段来继承和发展中医药,中西医学相互补充,取长补短,诊治疾病的医学形式。
中医基础理论 basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine 研究和阐明中医学的基本概念、基本理论、基本规律、基本原则的学科。
中医诊断学 diagnostics of traditional Chinese medicine 根据中医学的理论体系,研究诊察病情、判断病种、辨别证候的基础理论、基本知识和基本技能的学科。
方剂学 prescriptions of Chinese materia medica 研究治法与方剂配伍规律及其临床运用的学科。
中医内科学 internal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine 研究外感温病、内伤杂病等内科疾病诊治与预防的临床中医学。
01.001中医(1)traditional Chinesemedicine;(2)traditionalChinese physician (1)起源与形成于中国的具有整体观念、辨证论治等特点的医学;(2)本学科专业职业队伍。
01.002中药Chinese materia medica在中医理论指导下应用的药物。
包括中药材、中药饮片和中成药等。
01.003中医学traditional Chinesemedicine 以中医药理论与实践经验为主体,研究人类生命活动中健康与疾病转化规律及其预防、诊断、治疗、康复和保健的综合性科学。
01.004中药学Chinese materia medica中药学科的统称。
研究中药基本理论和各种药材饮片、中成药的来源、采制、性能、功效、临床应用等知识的学科。
01.005中医药traditional Chinesemedicine and pharmacy中医与中药的合称。
01.006中医药学traditional Chinesemedicine and pharmacy 中医学与中药学的合称,侧重反映中医与中药两者共同发展,密不可分。
01.007中西医结合integration oftraditional and westernmedicine 以现代医学等现代科学知识及手段来继承和发展中医药,中西医学相互补充,取长补短,诊治疾病的医学形式。
01.008中医基础理论basic theory oftraditional Chinesemedicine 研究和阐明中医学的基本概念、基本理论、基本规律、基本原则的学科。
01.009中医诊断学diagnostics oftraditional Chinesemedicine 根据中医学的理论体系,研究诊察病情、判断病种、辨别证候的基础理论、基本知识和基本技能的学科。
01.010方剂学prescriptions of Chinesemateria medica研究治法与方剂配伍规律及其临床运用的学科。