java程序设计方案基础第十章第一题
- 格式:doc
- 大小:14.00 KB
- 文档页数:2
习题十参考答案10.1什么是进程?什么是线程?二者有什么联系和区别?进程是程序的一次动态执行过程,它对应了从代码加载、执行到执行完毕的一个完整过程,这个过程也是进程从产生、发展到消亡的过程。
线程是比进程更小的执行单位。
一个进程在其执行过程中,可以产生多个线程,形成多条执行线索。
每条线索,即每个线程也有它自身的产生、存在和消亡的过程,是一个动态的概念。
在进程运行过程中,每个进程都有一段专用的内存区域,并以PCB作为它存在的标志;与进程不同的是,线程间可以共享相同的内存单元(包括代码与数据),并利用这些共享单位来实现数据交换、实时通信与必要的同步操作。
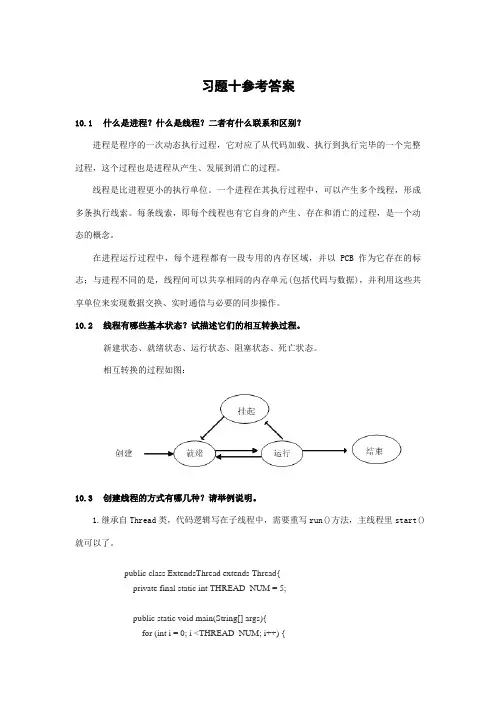
10.2线程有哪些基本状态?试描述它们的相互转换过程。
新建状态、就绪状态、运行状态、阻塞状态、死亡状态。
相互转换的过程如图:10.3创建线程的方式有哪几种?请举例说明。
1.继承自Thread类,代码逻辑写在子线程中,需要重写run()方法,主线程里start()就可以了。
public class ExtendsThread extends Thread{private final static int THREAD_NUM = 5;public static void main(String[] args){for (int i = 0; i <THREAD_NUM; i++) {new ExtendsThread("thread"+i).start();}}public ExtendsThread(String name){super(name);}@Overridepublic void run() {// TODO Auto-generated method stubfor (int i = 0; i < this.THREAD_NUM; i++) { System.out.println(this.getName()+i);}}}运行结果:thread00thread01thread02thread03thread04thread20thread21thread22thread23thread24thread40thread41thread42thread43thread44thread11thread12thread13thread14thread30thread31thread32thread33thread342.实现Runnable接口public class ImplRunnable implements Runnable {private static final int THREAD_NUM = 5;@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_NUM; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+i);}}public static void main(String[] args) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubfor (int j = 0; j < THREAD_NUM; j++) {ImplRunnable implRunnable= new ImplRunnable();new Thread(implRunnable,"thread"+j).start();}}}运行结果thread10thread12thread13thread14thread30thread31thread32thread33thread34thread00thread01thread02thread03thread04thread20thread21thread22thread23thread24thread40thread41thread42thread43thread4410.4试说明线程优先级及其调度的关系,并编写一个程序说明其关系。

第一章1.1public class Test{public static void main(String[]args){System.out.println("Welcome to Java!"); System.out.println("Welcome to Computer Science!");System.out.println("Progr amming is fun.");}}1.2public class Test{public static void main(String[]args){for(int i=0;i<=4;i++){System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");}}}1.3public class Test{public static void main(String[]args){System.out.println("]");System.out.printl n("]");System.out.println("]]");System.out.println("]]");}}public class Test{public static void main(String[]args){System.out.println("A"); System.out.println("A A");System.out.println("AAAAA");System.out.println("A A");}}public class Test{public static void main(String[]args){System.out.println("V V");System.out.println("V V");System.out.println("V V");System.out.println(" V");}}1.4public class Test{public static void main(String[]args){System.out.println("a a^2a^3");System.out.println("111");System.out.println("248");System.out.println("3 927");System.out.println("41664");}}1.5public class Test{public static void main(String[]args){System.out.println((9.5*4.5-2.5*3)/(45.5-3.5) );}}1.6public class Test{public static void main(String[]args){int i=1,sum=0;for(;i<=9;i++)sum+ =i;System.out.println(sum);}1.7public class Test{public static void main(String[]args){System.out.println(4*(1.0-1.0/3+1.0/5-1.0/7+1.0/9-1.0/11));System.out.println(4*(1.0-1.0/3+1.0/5-1.0/7+1.0/9-1.0/11+1.0/13));}}1.8public class Test{public static void main(String[]args){final double PI=3.14; double radius=5.5;System.out.println(2*radius*PI);System.out.println(PI*radius*radius);}}1.9public class Test{public static void main(String[]args){System.out.println(7.9*4.5);System.out.p rintln(2*(7.9+4.5));}}1.10public class Test{public static void main(String[]args){double S=14/1.6;double T=45*60+30;double speed=S/T;System.out.println(speed);}1.11public class Test{public static void main(String[]args){int BN=312032486; //original person numbers double EveryYS,EveryYBP,EveryYDP,EveryYMP;EveryY S=365*24*60*60;EveryYBP=EveryYS/7;EveryYDP=EveryYS/13;Every YMP=EveryYS/45;int FirstYP,SecondYP,ThirdYP,FourthYP,FivthYP;FirstYP=(int)(BN+EveryYBP+EveryYMP-EveryYDP);SecondYP=(int)(FirstYP +EveryYBP+EveryYMP-EveryYDP);ThirdYP=(int)(SecondYP+EveryYBP+Ev eryYMP-EveryYDP);FourthYP=(int)(ThirdYP+EveryYBP+EveryYMP-EveryYD P);FivthYP=(int)(FourthYP+EveryYBP+EveryYMP-EveryYDP);System.out.pri ntln(FirstYP);System.out.println(SecondYP);System.out.println(ThirdYP);Syste m.out.println(FourthYP);System.out.println(FivthYP);}}1.12public class Test{public static void main(String[]args){double S=24*1.6; double T=(1*60+40)*60+35;double speed=S/T;System.out.println(sp eed);}}1.13import java.util.Scanner;public class Test{public static void main(String[]args){Scanner input=new Scan ner(System.in);System.out.println("input a,b,c,d,e,f value please:");double a=input.nextDouble();double b=input.nextDouble();double c=input.nextDouble();double d=input. nextDouble();double e=input.nextDouble();第二章package cn.Testcx;import java.util.Scanner;public class lesson2{public static void main(String[]args){@SuppressWarnings("resource")Scanner in put=new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("请输入一个摄氏温度:");double Celsius=input.nextDouble();double Fahrenheit=(9.0/5)*Celsius+3 2;System.out.println("摄氏温度:"+Celsius+"度"+"转换成华氏温度为:"+Fahrenheit+"度");System.out.print("请输入圆柱的半径和高:");double radius=input.nextDouble();int higth=input.nextInt();double are as=radius*radius*Math.PI;double volume=areas*higth;System.out.println("圆柱体的面积为:"+areas);System.out.println("圆柱体的体积为:"+volume);System.out.print("输入英尺数:");double feet=input.nextDouble();double meters=feet*0.305;System.out.print ln(feet+"英尺转换成米:"+meters);System.out.print("输入一个磅数:");double pounds=input.nextDouble();double kilograms=pounds*0.454;Syste m.out.println(pounds+"磅转换成千克为:"+kilograms);System.out.println("输入分钟数:");long minutes=input.nextInt();long years=minutes/(24*60*365);long days=(minutes%(24*60*365))/(24*60);System.out.println(minutes+"分钟"+"有"+years+"年和"+days+"天");long totalCurrentTimeMillis=System.currentTimeMillis();long totalSeconds=t otalCurrentTimeMillis/1000;long currentSeconds=totalSeconds%60;long totalM inutes=totalSeconds/60;long currentMinutes=(totalSeconds%(60*60))/60;long currenthours=(totalMinutes/60)%24;System.out.print("输入时区偏移量:");byte zoneOffset=input.nextByte();long currentHour=(currenthours+(zoneOf fset*1))%24;System.out.println("当期时区的时间为:"+currentHour+"时"+currentMinutes+"分"+currentSeconds+"秒");System.out.print("请输入v0,v1,t:");double v0=input.nextDouble();double v1=input.nextDouble();doublet=input.nextDouble();float a=(float)((v1-v0)/t);System.out.println("平均加速度a="+a);System.out.println("输入水的重量、初始温度、最终温度:");double water=input.nextDouble();double initialTemperature=input.nextDou ble();double finalTemperature=input.nextDouble();double Q=water*(finalTemp erature-initialTemperature)*4184;System.out.println("所需热量为:"+Q);System.out.print("输入年数:");int numbers=input.nextInt();long oneYearsSecond=365*24*60*60;Longpop ulation=(long)((312032486+((oneYearsSecond/7.0)+(oneYearsSecond/45.0)-(oneYearsSecond/13.0))*numbers));System.out.println("第"+numbers+"年后人口总数为:"+population);System.out.print("输入速度单位m/s和加速度a单位m/s2:");double v=input.nextDouble();double a1=input.nextDouble();double l engthOfAirplane=(Math.pow(v,2))/(2*a1);System.out.println("最短长度为:"+lengthOfAirplane);System.out.print("输入存入的钱:");double money=input.nextInt();double monthRate=5.0/1200;for(int i=1;i<7; i++){double total=money*(Math.pow(1+monthRate,i));System.out.println("第"+i+"个月的钱为:"+total);//告诉我书上的银行在哪里,我要去存钱,半年本金直接翻6倍、、、}System.out.print("用户请输入身高(英寸)、体重(磅):");double height=input.nextDouble();double weight=input.nextDouble(); double BMI=(weight*0.45359237)/(Math.pow((height*0.0254),2));System.out.println("BMI的值为"+BMI);System.out.print("输入x1和y1:");System.out.print("输入x2和y2:");double x1=input.nextDouble();double y1=input.nextDouble();double x2 =input.nextDouble();double y2=input.nextDouble();double point1=Math.pow((x2-x1),2);double point2=Math.pow((y2-y1),2);double distance=Math.pow((point1+point2),(1.0/2));//也可以Math.pow((point1+point2),0.5)System.out.println("两点间的距离为:"+distance);System.out.print("输入六边形的边长:");double side=input.nextDouble();double area=(3*(Math.pow(3,0.5))*(Math.p ow(side,2)))/2;System.out.println("六边形的面积为:"+area);}}。

第10章作业参考答案1 .填空题(1)多线程(2)阻塞Runnable(4)并行(5)同步2 .选择3 .简答题(1)回答要点线程可以彼此独立的执行,它是一种实现并发机制的有效手段,可以同时使用多个线程来完成不同的任务,并且一般用户在使用多线程时并不考虑底层处理的细节。
进程(process)是程序的一次执行过程,或是正在运行的一个程序。
线程是比进程更小的程序执行单位,一个进程可以启动多个线程同时运行,不同线程之间可以共享相同的内存区域和数据。
(2)回答要点有三种方式,如下所示:①继承Thread类:编写简单,如果需要访问当前线程,那么无需使用Thread.currentThread() 方法,直接使用this即可获得当前线程。
但线程类已经继承了Thread类,所以不能再继承其他父类。
②实现Runnable接口:防止由于Java单继承带来的局限性。
但编程稍微复杂,如果要访问当前线程,那么必须使用Thread.currentThread()方法。
③使用Callable接口和Future接口创立多线程:防止由于Java单继承带来的局限性,有返回值,可以抛出异常。
但编程稍微复杂,如果要访问当前线程,那么必须使用Thread. currentThread。
方法。
(3)回答要点线程从新建到死亡称为线程的生命周期。
(4)回答要点启动一个线程是调用start。
方法,使线程所代表的虚拟处理机处于可运行状态,这意味着它可以由JVM调度并执行。
这并不意味着线程就会立即运行。
4 .编程题(1)源代码:参考本章资料文件夹下“作业1”。
(2)源代码:参考本章资料文件夹下“作业2”。


Java程序设计各章习题及其答案第一章习题及思考题1、Java程序是由什么组成的?一个程序中必须有public类吗?Java源文件的命名规则是怎样的?答:一个Java源程序是由若干个类组成。
一个Java程序不一定需要有public类:如果源文件中有多个类时,则只能有一个类是public 类;如果源文件中只有一个类,则不将该类写成public也将默认它为主类。
源文件命名时要求源文件主名应与主类(即用public修饰的类)的类名相同,扩展名为.java。
如果没有定义public类,则可以任何一个类名为主文件名,当然这是不主张的,因为它将无法进行被继承使用。
另外,对Applet小应用程序来说,其主类必须为public,否则虽然在一些编译编译平台下可以通过(在BlueJ下无法通过)但运行时无法显示结果。
2、怎样区分应用程序和小应用程序?应用程序的主类和小应用程序的主类必须用public修饰吗?答:Java Application是完整的程序,需要独立的解释器来解释运行;而Java Applet则是嵌在HTML编写的Web页面中的非独立运行程序,由Web浏览器内部包含的Java解释器来解释运行。
在源程序代码中两者的主要区别是:任何一个Java Application 应用程序必须有且只有一个main方法,它是整个程序的入口方法;任何一个Applet小应用程序要求程序中有且必须有一个类是系统类Applet的子类,即该类头部分以extends Applet结尾。
应用程序的主类当源文件中只有一个类时不必用public修饰,但当有多于一个类时则主类必须用public修饰。
小应用程序的主类在任何时候都需要用public来修饰。
3、开发与运行Java程序需要经过哪些主要步骤和过程?答:主要有三个步骤(1)、用文字编辑器notepad(或在Jcreator,Gel, BuleJ,Eclipse, Jbuilder等)编写源文件;(2)、使用Java编译器(如Javac.exe)将.java源文件编译成字节码文件.class;(3)、运行Java程序:对应用程序应通过Java解释器(如java.exe)来运行,而对小应用程序应通过支持Java标准的浏览器(如Microsoft Explorer)来解释运行。


j a v a语言程序设计基础篇第十版练习答案精编Document number:WTT-LKK-GBB-08921-EIGG-2298601import class Exercise14_01 extendsApplication {@Override Not needed for running from the command line.*/public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}02import class Exercise14_02 extends Application {@Override Not needed for running from the command line.*/public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}03import class Exercise14_03 extends Application {@Override One is to use the hint in the book.ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 1; i <= 52; i++) {(i);}HBox pane = new HBox(5);;().add(new ImageView("image/card/" + (0) +".png"));().add(new ImageView("image/card/" + (1) +".png"));().add(new ImageView("image/card/" + (2) +".png"));Not needed for running from the command line.*/public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}04import class Exercise14_04 extends Application {@Override dd(txt);}Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}05import class Exercise14_05 extends Application {@Override dd(txt);}Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}05import class Exercise14_05 extends Application {@Override dd(txt);}Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}06import class Exercise14_06 extends Application {@Override dd(rectangle);}}Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}07import class Exercise14_07 extends Application {@Override Not needed for running from the command line.*/public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}08import class Exercise14_08 extends Application {@Override ng"), j, i);}}Not needed for running from the command line.*/public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}09import class Exercise14_09 extends Application {@Override Not needed for running from the command line.*/public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}class FanPane extends Pane {double radius = 50;public FanPane() {Circle circle = new Circle(60, 60, radius);;;getChildren().add(circle);Arc arc1 = new Arc(60, 60, 40, 40, 30, 35);; ddAll(arc1, arc2, arc3, arc4);}}10import class Exercise14_10 extends Application {@Override ddAll, ;Arc arc2 = new Arc(100, 140, 50, 20, 180, 180); ;;().addAll(ellipse, arc1, arc2,new Line(50, 40, 50, 140), new Line(150, 40, 150, 140));Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}11import class Exercise14_11 extends Application {@Override ddAll(circle, ellipse1, ellipse2,circle1, circle2, line1, line2, line3, arc);Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}12import class Exercise14_12 extends Application {@Override ddAll(r1, text1, r2, text2, r3, text3, r4, text4);Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}13import class Exercise14_13 extends Application {@Override ddAll(arc1, text1, arc2, text2, arc3, text3, arc4, text4);Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}14import class Exercise14_14 extends Application {@Override ddAll(r1, r2, line1, line2, line3, line4);Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}15import class Exercise14_15 extends Application {@Override ddAll(polygon, text);Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}16import class Exercise14_16 extends Application {@Override ind().divide(3));().bind());().bind().divide(3));;Line line2 = new Line(0, 0, 0, 0);().bind().multiply(2).divide(3));().bind());().bind().multiply(2).divide(3));;Line line3 = new Line(0, 0, 0, 0);().bind().divide(3));().bind().divide(3));().bind());;Line line4 = new Line(0, 0, 0, 0);().bind().multiply(2).divide(3));().bind().multiply(2).divide(3));().bind());;().addAll(line1, line2, line3, line4);Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}17import class Exercise14_17 extends Application {@Override ddAll(arc, line1, line2, line3, circle, line4, line5, line6, line7, line8);Not needed for running from the command line.*/public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}18import class Exercise14_18 extends Application {@Override ddAll(polyline, line1, line2,line3, line4, line5, line6, text1, text2);Not needed for running from the command line.*/public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}19import class Exercise14_19 extends Application {@Override ddAll(polyline1, polyline2, line1,line2,line3, line4, line5, line6, text1, text2,text3,text4, text5, text6, text7);Not needed for running from the command line.*/public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}20import class Exercise14_20 extends Application {@Override dd(new Line(x1, y1, x2, y2));dd(new Line(x2, y2, (x2 + (arctan + set45) * arrlen)),((y2)) + (arctan + set45) * arrlen)));().add(new Line(x2, y2, (x2 + (arctan - set45) * arrlen)),((y2)) + (arctan - set45) * arrlen)));}/*** The main method is only needed for the IDE with limited* JavaFX support. Not needed for running from the command line.*/public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}21import class Exercise14_21 extends Application {@Override istance(x2, y2) + "");().addAll(circle1, circle2, line, text);Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}22import class Exercise14_22 extends Application {@Override ddAll(circle1, circle2, line, text1, text2);Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}23import class Exercise14_23 extends Application {@Override ddAll(r1, r2, text);Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}24import class Exercise14_24 extends Application {@Override ddAll(polygon, new Circle(x5, y5, 10), text);Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}25import class Exercise14_25 extends Application {@Override ddAll(circle, polygon);Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}26import class Exercise14_26 extends Application {@Override ddAll(clock1, clock2);Not needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}27import class Exercise14_27 extends Application {@OverrideNot needed for running from the command line. */public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}class DetailedClockPane extends Pane {private int hour;private int minute;private int second;lear();getChildren().addAll(circle, sLine, mLine, hLine);dd(new Line(xOuter, yOuter, xInner, yInner));}dd(text);}}}28import class Exercise14_28 extends Application {@OverrideNot needed for running from the command line.*/public static void main(String[] args) {launch(args);}}class ClockPaneWithBooleanProperties extends Pane { private int hour;private int minute;private int second;private boolean hourHandVisible = true;private boolean minuteHandVisible = true; private boolean secondHandVisible = true;public boolean isHourHandVisible() {return hourHandVisible;}public void setHourHandVisible(boolean hourHandVisible) {= hourHandVisible;paintClock();}public boolean isMinuteHandVisible() {return minuteHandVisible;}public void setMinuteHandVisible(boolean minuteHandVisible) {= minuteHandVisible;paintClock();}public boolean isSecondHandVisible() {return secondHandVisible;public void setSecondHandVisible(boolean secondHandVisible) {= secondHandVisible;paintClock();}lear();getChildren().addAll(circle, t1, t2, t3, t4);if (secondHandVisible) {getChildren().add(sLine);}if (minuteHandVisible) {getChildren().add(mLine);}if (hourHandVisible) {getChildren().add(hLine);}}}import class Exercise14_29 extends Application {final static double HGAP = 20;final static double VGAP = 20;final static double RADIUS = 5;final static double LENGTH_OF_SLOTS = 40;final static double LENGTH_OF_OPENNING = 15;final static double Y_FOR_FIRST_NAIL = 50;final static double NUMBER_OF_SLOTS = 9;final static double NUMBER_OF_ROWS =NUMBER_OF_SLOTS - 2;@Override dd(c);}}dd(new Line(x, y, x, y + LENGTH_OF_SLOTS)); }dd(new Line(centerX - (NUMBER_OF_ROWS - 1) * HGAP / 2 - HGAP,y + LENGTH_OF_SLOTS, centerX -(NUMBER_OF_ROWS - 1) * HGAP / 2 + NUMBER_OF_ROWS * HGAP,y + LENGTH_OF_SLOTS));dd(new Line(centerX + HGAP / 2,Y_FOR_FIRST_NAIL + RADIUS,centerX - (NUMBER_OF_ROWS - 1) * HGAP / 2 + NUMBER_OF_ROWS * HGAP, y));().add(new Line(centerX - HGAP / 2,Y_FOR_FIRST_NAIL + RADIUS,centerX - (NUMBER_OF_ROWS - 1) * HGAP / 2 - HGAP, y));dd(new Line(centerX - HGAP / 2,Y_FOR_FIRST_NAIL + RADIUS,centerX - HGAP / 2, Y_FOR_FIRST_NAIL - LENGTH_OF_OPENNING));().add(new Line(centerX + HGAP / 2,Y_FOR_FIRST_NAIL + RADIUS,centerX + HGAP / 2, Y_FOR_FIRST_NAIL - LENGTH_OF_OPENNING));Not needed for running from the command line.*/public static void main(String[] args) { launch(args);}}。


第10章多态性与虚函数一、单项选择题1.实现运行时的多态性要使用(D)。
A.重载函数B.构造函数C.析构函数D.虚函数2.通过运算符重载,可以改变运算符原有的(A)。
A.操作数类型B.操作数个数C.优先级D.结合性3.将运算符重载为类成员函数时,其参数表中没有参数,说明该运算符是(B)。
A.不合法的运算符B.一元运算符C.无操作数的运算符D.二元运算符4.在重载一个运算符时,其参数表中没有任何参数,说明该运算符是(B)。
A.作为友元函数重载的一元运算符B.作为成员函数重载的一元运算符C.作为友元函数重载的二元运算符D.作为成员函数重载的二元运算符5.如果表达式++a中的"++"是作为成员函数重载的运算符,若采用运算符函数调用格式,则可表示为(D)。
A.a.operator++(1)B.operator++(a)C.operator++(a,1)D.a.operator++()6.如果表达式a>=b中的">="是作为非成员函数重载的运算符,则可以等效地表示为(C)。
A.a.operator>=(b)B.b.operator>=(a)C.operator>=(a,b)D.perator>=(b,a)7.有如下程序:#include<iostream>using namespace std;class A{public:virtual void funl (){cout<<"A1";}void fun2 (){cout<<"A2";}};class B: public A{public:void funl (){cout<<"Bl";}void fun2 (){cout<<"B2";}};int main(){A*p=new B;p->funl ();p->fun2();return 0;}程序执行后,输出结果为(C)。


java程序设计基础课后习题答案Java程序设计基础课后习题答案Java程序设计是一门广泛应用于软件开发领域的编程语言。
在学习这门课程时,除了理论知识的学习外,课后习题也是非常重要的一部分。
通过课后习题的练习,可以帮助学生巩固所学的知识,并且提高编程能力。
下面将为大家提供一些Java程序设计基础课后习题的答案,希望对大家的学习有所帮助。
习题一:编写一个Java程序,输出从1到100之间所有的奇数。
```javapublic class OddNumbers {public static void main(String[] args) {for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {if (i % 2 != 0) {System.out.println(i);}}}}```习题二:编写一个Java程序,计算1到100之间所有偶数的和。
```javapublic class EvenSum {public static void main(String[] args) {for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {if (i % 2 == 0) {sum += i;}}System.out.println("1到100之间所有偶数的和为:" + sum); }}```习题三:编写一个Java程序,判断一个数是否为素数。
```javaimport java.util.Scanner;public class PrimeNumber {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("请输入一个整数:");int num = scanner.nextInt();boolean isPrime = true;for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(num); i++) {if (num % i == 0) {isPrime = false;}}if (isPrime) {System.out.println(num + "是素数");} else {System.out.println(num + "不是素数");}}}```习题四:编写一个Java程序,统计一个字符串中每个字符出现的次数。
第10章习题参考答案
一、简答题
1.什么是多态?类的多态是怎么实现的?
多态(Polymorphism)按字面的意思就是“多种状态”,在面向对象语言中,接口的多种不同的实现方式即为多态。
多态表示不同的对象可以执行相同的动作,但要通过它们自己的实现代码来执行。
多态通过重载和覆盖实现,重载发生在一个类中,覆盖发生在子类,子类重写父类相同名称的方法。
2.创建多态需要哪些条件?
在代码中实现Java的多态必须遵循的必要条件:存在子类继承父类关系(包括接口的实现)、子类覆盖父类中的方法,在实现多态,需有子类对父类方法的覆盖(重写)。
3.类是怎么向接口转型实现多态的?
定义一个父类类型的引用指向一个子类的对象既可以使用子类强大的功能,又可以抽取父类的共性。
所以,父类类型的引用可以调用父类中定义的所有属性和方法,而对于子类中定义而父类中没有的方法,它是无可奈何的;同时,父类中的一个方法只有在在父类中定义而在子类中没有重写的情况下,才可以被父类类型的引用调用;对于父类中定义的方法,如果子类中重写了该方法,那么父类类型的引用将会调用子类中的这个方法,这就是动态连接。
10.1 设计一个名为Time的类。
这个类包含:表示时间的数据域hour、minute和secon d。
一个以当前时间创建Time对象的无参构造方法(数据域的值表示当前时间)。
一个构造Time对象的构造方法,这个对象有一个特定的时间值,这个值是以毫秒表示的、从1970年1月1日午夜开始到现在流逝的时间段(数据域的值表示这个时间)。
一个构造带特定的小时、分钟和秒的Time对象的构造方法、
三个数据域hour、minute和second各自的get方法。
一个名为setTime(long elapseTime)的方法使用流逝的时间给对象设置一个新时间。
代码:
class Time{
long hour,minute,second。
long time。
public Time(){
time=System.currentTimeMillis()。
}
public Time(long time){
this.time=time。
}
public Time(long hour,long minute,long second){
time= (hour*3600+minute*60+second)*1000。
}
public long getHour() {
second = (time / 1000)。
minute = (second / 60)。
return hour = ( minute/ 60) % 24+8。
}
public long getMinute() {
second = (time / 1000)。
return minute = (second/ 60) % 60。
}
public long getSecond() {
return second = (time / 1000) % 60。
}
public void setTime(long elapseTime) {
time = elapseTime。
}
}
public class XiTi101 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Time t1=new Time()。
System.out.println("时间:"+t1.getHour()+":"+t1.getMinute()+":"+
t1.getSecond())。
Time t2=new Time(555550000-8*60*60*1000)。
System.out.println("时间:"+t2.getHour()+":"+t2.getMinute()+":"+t2.getSecond())。
}
}
/*未来获得北京时间,必须加上8小时,所以之后必须减去8小时,即减去8*60*60*1000毫秒*/。