希尔国际商务复习资料
- 格式:docx
- 大小:14.39 KB
- 文档页数:2
十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台全球资本市场12.1 复习笔记考点一:全球资本市场1.一般资本市场的功能资本市场将希望投资的群体和希望借款的群体连接在了一起。
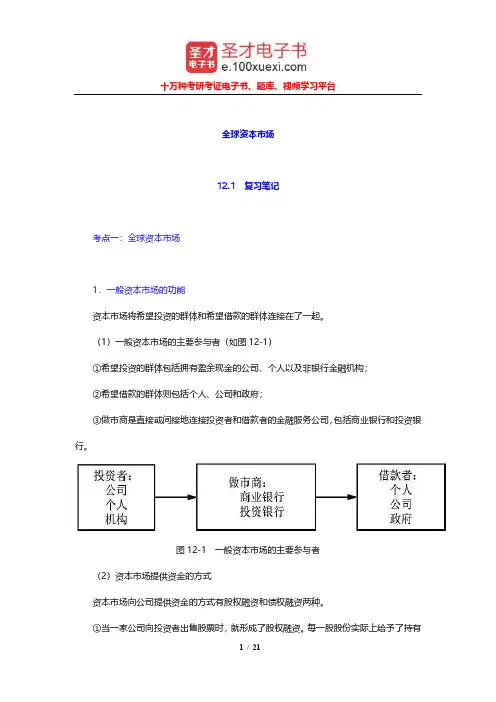
(1)一般资本市场的主要参与者(如图12-1)①希望投资的群体包括拥有盈余现金的公司、个人以及非银行金融机构;②希望借款的群体则包括个人、公司和政府;③做市商是直接或间接地连接投资者和借款者的金融服务公司,包括商业银行和投资银行。
图12-1 一般资本市场的主要参与者(2)资本市场提供资金的方式资本市场向公司提供资金的方式有股权融资和债权融资两种。
①当一家公司向投资者出售股票时,就形成了股权融资。
每一股股份实际上给予了持有十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台者对企业利润的一份要求权。
公司通过向股东支付股息承认这种权利。
②债权融资要求借款公司无论是否盈利都要按固定的时间间隔偿还事先确定的一部分贷款数额(本金加上规定的利息之和)。
债权融资包括来自银行的现金贷款和向投资者出售公司债券筹集的资金。
当一个投资者购买了一家公司的债券,他就得到了在规定的年份里从该公司按固定的数额获取收入的权利。
2.全球资本市场的吸引力(1)借款者的视角:较低的资金成本国内资本市场的流动性不足,而在全球市场中,更广泛的投资者群体意味着借款者可以付出较低的代价来获得资金。
资金成本是借入资金的价格,即借款者必须向投资者支付的收益率,也就是债权融资中的利率和股权融资中的股息收入与预期股票差价。
(2)投资者的视角:分散投资组合投资者可以在国际范围内分散投资组合,与纯粹的国内资本市场相比,可降低投资风险,因为各国之间股票市场价格的变动不是完全相关的。
不同国家股票市场变动之间相对较低的相关性反映了两个基本的情况:①由于各国推行不同的宏观经济政策以及面对不同的经济问题,因此它们的股票市场受不同的因素影响,并向不同的方向变动。
②由于受到资本管制,即限制跨国资本流动(尽管这种限制正在迅速减少),不同的股票市场之间仍然或多或少地存在分割现象,这有助于切断风险的传递。

十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台外汇市场10.1 复习笔记考点一:外汇市场1.外汇市场和汇率的定义(1)外汇市场是将一个国家的货币转换成另一个国家的货币的市场。
(2)汇率是一种货币转换成另一种货币的比率。
2.外汇市场的作用外汇市场主要有两个作用:一是货币转换;二是外汇风险的管理。
(1)货币转换①定义货币转换是指将一个国家的货币转换成另一个国家的货币。
②国际企业利用外汇市场进行货币转换的四种情形a.一家公司出口所收回的货款,对外投资所得的收益,或是从与国外公司签订的技术转让协议中获得的收益,都可能是外币。
公司在本国使用这些款项,就必须利用外汇市场将它们转换成本国货币。
b.当国际企业必须用外国货币支付外国公司的商品和服务时,要利用外汇市场。
十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台c.国际企业有多余款项想在货币市场做短期投资时,要利用外汇市场。
d.外汇投机要利用外汇市场。
外汇投机主要涉及资金的短期运作,期望从一种货币转换到另一种货币时通过汇率的变动获利。
(2)外汇风险的管理外汇风险的管理是指针对外汇风险提供一定的保障,外汇风险是指不可预见的未来汇率变化对企业产生不利影响的可能性。
公司规避外汇风险的行为称作套期保值。
①即期汇率a.定义即期汇率是外汇交易商在特定日期将一种货币转换成另一种货币时使用的汇率。
b.性质即期汇率会不断变化。
一种货币的汇率是由这种货币的供求与另一种货币供求的相互作用决定的。
②远期汇率▼a.定义远期汇率,又称期汇汇率,是买卖双方事先约定在未来日期进行外汇交割的汇率。
即期汇率与远期汇率的差价称为升水或贴水。
远期汇率适用于远期外汇交易。
b.远期外汇交易的作用从事国际贸易的企业可以通过远期外汇交易来对冲外汇风险,避免出现未来汇率变动使一笔业务在到期执行的时候变得无利可图的可能。
③掉期(货币互换)掉期(货币互换)是按两个不同的交割日期同时买进和卖出一定数量的外汇。
掉期交易十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台可在国际企业同银行之间、不同的银行之间,以及政府之间进行,以便在一个限定期限内把一种货币换成另一种货币而不必承担外汇风险。

目 录第Ⅰ篇 引言和概论第1章 全球化第Ⅱ篇 国家差异第2章 政治、经济和法律体系中的国家差异第3章 经济发展中的国家差异第4章 文化差异第5章 伦理、企业社会责任和可持续发展第Ⅲ篇 全球贸易与投资环境第6章 国际贸易理论第7章 政府政策与国际贸易第8章 国际直接投资第9章 区域经济一体化第Ⅳ篇 全球货币制度第10章 外汇市场第11章 国际货币体系第12章 全球资本市场第Ⅴ篇 国际企业的战略与组织结构第13章 国际企业的战略第14章 国际企业的组织第15章 进入战略和战略联盟第Ⅵ篇 国际商务运营第16章 出口、进口和对等贸易第17章 全球生产与供应链管理第18章 全球营销与研发第19章 全球人力资源管理第20章 国际企业的会计和财务第Ⅰ篇 引言和概论第1章 全球化1描述在过去30年中世界经济所发生的转变。
这些转变对总部设在英国、北美、中国香港的国际企业各意味着什么?答:(1)过去30年中世界经济所发生的转变在过去30年中,全球经济发生了巨大变化。
20世纪60年代,世界经济的格局可用四个事实来描述:第一是美国在世界经济和世界贸易中起主导作用;第二是美国支配了当时的世界对外直接投资;第三是在国际商务舞台上,美国的大型多国企业占统治地位;第四是地球上大约一半的计划经济国家对西方国际企业的排斥。
在过去30年中,这四个事实都已发生了变化或正在迅速地发生变化:①美国虽仍是世界上最强大的工业国,但在相对规模上较20世纪60年代下降了许多。
日本、泰国、马来西亚、中国台湾和韩国,它们的世界产出份额显著增加。
②各国在对外直接投资总存量中所占的份额的趋势是:发展中国家的份额在稳步增长,而发达国家的份额在逐渐下降。
③多国企业的性质也在变化。
多国企业的统计构成中出现了两个值得注意的趋势:一是非美国的多国公司的增加,尤其是日本的多国企业;二是小型多国公司的增长。
④许多东欧国家和拉美国家进行民主政治改革,实行自由市场经济,为国际企业提供了巨大的出口与投资机会。

国际商务希尔十一题引言概述:国际商务是指跨国界进行的商业活动,涉及到不同国家之间的贸易、投资、合作等方面。
在国际商务中,希尔十一题是一个重要的议题,它涉及到国际商务中的风险管理和决策制定。
本文将从五个大点阐述希尔十一题的相关内容。
正文内容:1. 希尔十一题的背景和概述1.1 希尔十一题的起源和定义1.2 希尔十一题在国际商务中的重要性1.3 希尔十一题的研究方法和工具2. 希尔十一题的风险管理2.1 希尔十一题的风险识别和评估2.2 希尔十一题的风险控制和防范2.3 希尔十一题的风险应对和处理3. 希尔十一题的决策制定3.1 希尔十一题对决策的影响3.2 希尔十一题的决策制定过程3.3 希尔十一题的决策实施和监控4. 希尔十一题的国际商务案例分析4.1 案例一:跨国公司在新兴市场的投资决策4.2 案例二:国际贸易中的汇率风险管理4.3 案例三:国际合作中的文化差异对决策的影响5. 希尔十一题的未来发展趋势5.1 希尔十一题在数字化时代的挑战和机遇5.2 希尔十一题在全球化背景下的发展趋势5.3 希尔十一题与可持续发展的关系总结:综上所述,希尔十一题在国际商务中具有重要的地位和作用。
在风险管理方面,希尔十一题帮助企业识别、评估和应对风险,保障商务活动的顺利进行。
在决策制定方面,希尔十一题影响着决策的全过程,从决策制定到实施和监控。
通过案例分析,我们可以更好地理解希尔十一题在实际商务中的应用。
未来,随着数字化和全球化的发展,希尔十一题将面临新的挑战和机遇,并与可持续发展紧密相连。
因此,对于从事国际商务的企业和从业者来说,深入研究和应用希尔十一题是至关重要的。

希尔《国际商务》(第11版)笔记和课后习题(含考研真题)详解第16章~第17章【圣才出品】第Ⅵ篇国际商务运营第16章出口、进口和对等贸易16.1复习笔记考点一:出口的前景和困难1.出口的前景对大多数行业的大多数企业来说,出口的最大前景就在于能在外国市场上发现巨大的赚钱和获利机会。
一个企业的国际市场通常要比其国内市场大得多。
因此,通过扩大市场规模,出口能使企业达到规模经济,从而降低它的单位成本,进而使得企业增加其收入和利润。
2.出口的困难许多中小企业对出口机会的反应十分被动,这由以下原因造成:(1)对国外市场的规模和分布不熟悉,难以抓住出口机会。
(2)被出口的复杂性与出口机制所吓倒,因为国外商务活动的习惯做法、语言、文化、法律制度以及货币都与国内市场大不相同。
(3)首次出口遇到的大麻烦使企业对以后的出口业务望而生畏。
考点二:提高出口业绩1.收集信息(1)概述出口的一大障碍是对可以得到的机会缺乏认识。
一个企业的产品通常会有许多市场,但这些市场所在国因为文化、语言、时间、空间的差异而与该企业的国内基地相隔离,所以企业很难发掘这些市场。
因此提高出口业绩首先就要收集信息。
(2)信息来源①在美国,商务部是最具综合性的信息来源。
在商务部内有两个机构——国际贸易管理局与美国和外国商业服务处,专门致力于为商业机构提供情报和援助。
此外,小企业管理局、贸易委员会、商业银行以及大的会计师事务所也可以帮助潜在的出口商。
②其他国家的机构如中国国际贸易促进委员会、德国的贸易协会和日本的综合商社等也都为出口商寻求出口机会。
2.利用出口管理公司(1)出口管理公司的概述出口管理公司由一些出口专家组成,为首次出口的商家提供全方位的服务,处理出口过程中所有的问题,它的作用相当于其客户企业的出口营销部或国际业务部。
(2)出口管理公司的作用对于首次出口的商家来说,聘请出口管理公司可以帮助商家发现出口机会并避免出口过程中出现太多的失误。
(3)出口委托的形式①出口管理公司帮助一个企业建立出口业务,当业务运转正常时,便完全移交给该公司,并由该公司独立经营。

十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台进入战略和战略联盟15.1 复习笔记考点一:基本进入决策1.进入哪个外国市场一个国家作为潜在市场对于国际企业的吸引力有赖于在该国家从事经营活动时的利润、成本和风险的平衡。
潜在市场吸引力的来源包括:(1)在一个国家从事经营活动的长期经济利润。
这取决于市场规模(从人口统计数据看)、该市场消费者的现有财富(购买力)以及未来可能财富(取决于经济增长率)等因素。
在其他条件相同的情况下,通货膨胀温和和私营部门债务较少的政治稳定的有着自由市场体制的发达国家与发展中国家对利润-成本-风险的平衡更有利。
(2)国际企业在外国市场所能创造的价值。
这取决于它能为那个市场提供的产品的适用性以及当地竞争的性质。
企业可以根据吸引力来为各个国家评级,级别高的市场可考虑作为进入的首选。
2.进入时机一旦企业找到了具有吸引力的市场,它必须考虑进入时机的问题。
早进入一个市场通常可能获得第一进入者(先入者)优势,也可能面临第一进入者(先入者)劣势。
十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台(1)先入者优势①定义当国际企业在其他外国企业之前进入一个外国市场,这种与早进入一个市场相关的优势通常称作第一进入者(先入者)优势。
②来源a.通过建立一个强大的品牌形象抢先阻止竞争对手和赢得需求;b.在目标国扩大销售量,并在经验曲线上领先于竞争对手,使先入者相对后来者拥有成本优势,这种优势能使先入者把价格降低到后入者之下,从而把后入者驱逐出市场;c.先入者通过把消费者牢牢地捆绑在它们所提供的产品和服务上来创造出转换成本,这样的转换成本使后来者很难赢得顾客。
(2)先入者劣势①定义在其他国际企业之前进入一个外国市场的做法也有其劣势,这通常称为第一进入者(先入者)劣势。
②开拓成本开拓成本是先入者必须承担而后来者可以避免的成本。
当东道国的经营体制与母国市场有很大不同时,企业必须花费巨大的努力、时间和开支以学习这些游戏规则,由此产生了开拓成本。

希尔《国际商务》(第9版)笔记和课后习题(含考研真题)详解(第6章国际贸易理论)【圣才出品】第6章国际贸易理论6.1 复习笔记⼀、贸易理论综述16~17世纪盛⾏的重商主义主张国家应当⿎励出⼝,同时限制进⼝。
亚当·斯密的绝对优势理论第⼀次解释了为什么不受限制的⾃由贸易(⼀国政府不打算通过配额或关税来影响它的公民从别国进⼝什么商品或⽣产什么产品出⼝给别国)对⼀个国家是有利的。
斯密认为应当由市场机制这只看不见的⼿来决定⼀国进⼝和出⼝什么商品。
他的论点还表明对贸易采取的这种⾃由放任态度符合⼀国的最⼤利益。
在斯密理论的基础上,19世纪英国经济学家⼤卫李嘉图提出相对优势学说,这是现代不受限制的⾃由贸易论点的理论基础。
20世纪,两位瑞典经济学家艾利·赫克歇尔和伯蒂尔·俄林改进了李嘉图的理论,创⽴了著名的赫克歇尔-俄林理论。
1.贸易利益斯密、李嘉图和赫克歇尔-俄林的理论精确地确认了国际贸易的特定利益。
⼀国⽣产不了的商品通过国际贸易可以得到,绝⼤多数国际贸易是有利的。
另外,斯密、李嘉图和赫克歇尔-俄林的理论还解释了为什么⼀个国家通过国际贸易来获取⾃⼰可以⽣产的产品仍能获得利益。
如果⼀国公民购买某些别国⽣产的产品,即使这些产品本国能⽣产,该国经济仍可获得利益。
这种利益产⽣的原因是国际贸易允许⼀国在制造业中实⾏专业化,专门出⼝该国能最有效率⽣产的产品,⽽进⼝在别国能更有效率⽣产的产品。
限制进⼝经常对国内⽣产者有利,⽽对国内消费者不利。
2.国际贸易模式斯密、李嘉图和赫克歇尔-俄林的理论也解释了在世界经济中观察到的国际贸易模式。
对于不能⽤赫克歇尔-俄林理论解释的国际贸易模式的⼀种早期反应是产品⽣命周期论。
由雷蒙德·弗农提出的这⼀理论认为,在产品⽣命周期的初期,⼤多数新产品由发明国⽣产和出⼝,当新产品在国际上被⼴泛接受后,就开始转到其他国家⽣产,该产品甚⾄最终可能被出⼝到原发明国。
沿着类似的思路,20世纪80年代⼀些经济学家如保罗·克鲁格曼提出了⼀种新贸易理论。

希尔《国际商务》(第7版)笔记和课后习题(含考研真题)详解(全球生产、外包与物流)第16章全球生产、外包与物流16.1 复习笔记一、战略、生产和物流生产(production)定义为“涉及产品创造的活动”,包括提供服务和制造产品的活动。
物流(logistics)是指控制原材料在价值链中转移的活动,包括从获得原材料到生产再到分配的过程。
因为公司有效地从事生产活动依赖于物流方面及时地提供高质量的原材料投入,所以生产和物流是紧密联系在一起的。
国际企业中生产和物流的职能有以下重要的战略目标:1.降低成本将生产活动分散到全球各地,每一项活动都得以有效开展,这样就能够降低成本。
有效地管理全球供应链以使供需更好地匹配,这样也能够降低成本。
2.通过消除供应链和制造过程中的次品,提高产品质量降低成本和提高质量这两个目标并不是彼此独立的。
加强质量控制将在三个方面降低成本:(1)因为时间没有被浪费在不适销的劣质产品上,所以生产率提高了。
这项节约直接导致单位成本的减少。
(2)降低了与次品相关的返工和报废成本。
(3)降低了与修理次品相关的保修成本和花费更少的时间。
大部分管理者用来增强产品可靠性的主要手段是六西格玛质量改进理念。
六西格玛理念是从全面质量管理(total quality management,TQM)体系直接演变而来的。
如今六西格玛(six sigma)理念取代全面质量管理体系,它是旨在全公司范围内减少次品、提高生产率、消除浪费和削减成本的统计上的理念。
除了降低成本和提高质量两个目标,还有两个目标在国际商务中尤其重要。
其一,生产和物流必须适应当地反应的需要。
其二,生产和物流必须能对客户需求的转变迅速作出反应。
二、选择生产地跨国公司面临的一个基本决策是在哪里从事生产活动,以最好地实现成本最小化和提高产品质量的双重目标。
考虑的因素按三个大标题可分为国家因素、技术因素和产品因素。
1.国家因素政治经济、文化和相对要素成本在国与国之间是不同的。

第4章国际商务伦理4.1 复习笔记一、国际商务中的伦理问题“伦理”一词是指支配一个人的行为、职业操守或一个组织的行为正确与否的约定俗成的法则。
商业伦理(business ethics)是指支配商人行为的一整套约定俗成的规则,而伦理策略(ethical strategy)则是指不违反这些规则的策略或行动纲领。
国际商务中会产生许多伦理问题,其根源在于国与国之间在政治制度、法律、经济发展和文化方面存在巨大的差异。
在国际商务中,最为常见的伦理问题是员工待遇、人权、环境污染、腐败以及跨国公司的道德义务等。
1.员工待遇当东道国的工作条件明显低于跨国公司母国的条件时,暂时还没有确定的标准供企业选择实施。
但无论如何,跨国公司绝不能对其在国外的企业或转包商们恶劣的工作环境听之任之或视而不见。
2.人权有观点认为,一个跨国公司在一个缺乏民主和人权的国家做生意是合乎伦理的。
长期的外国投资促进了经济,提高了当地的生活水平,这些发展最终将推动更多的人要求参与管理、政治多元化以及言论自由。
但这一观点是有局限性的。
有些国家非常落后,以至于很难合乎伦理地经商。
3.环境污染当东道国的环境保护制度不如母国时,也会发生伦理问题。
环境是公共产品,但又是任何人都可以破坏的。
这种情况被称为“公地悲剧”。
公地悲剧即一项大家共同拥有的资源,不属于任何个人,但每个人都能使用,而且在过度使用,结果便导致资源的逐渐消减。
4.腐败“加急费”或“通融费”并不是用来获取那种如果不支付就拿不到合同的费用,也不是用来获取排他性利益的费用,而是为保证一家企业能从外国政府得到它应有的公平待遇所支付的费用,如果不支付有可能因某个官员的拖延而得不到。
一些经济学家提出,在一个国家,已有的政治体制扭曲或限制了市场机制的正常运行,通过黑市、走私和向政府官员支付公关费等方式,“加速”政府批准商业投资,有可能促进福利。
相反,另一些经济学家认为,腐败降低了商业投资的回报,导致较低的经济增长。

第一章全球化2012、05、08——2012、05、181、什么是全球化(globalization)?全球化是指转向一个更为一体化与相互依存的世界经济。
全球化有不同的侧面,包括市场全球化和生产全球化。
市场全球化(globalization of markets)是指把历史上独特和分离的国家市场合并为一个巨大的全球市场。
生产全球化(globalization of production)指的是从全球各地去筹供商品和服务,以利用本国在生产要素(factors of production)上的成本和质量差异。
2、全球机构的出现(1)世界贸易组织(World Trade Organization)主要负责监管世界贸易秩序和确保各国遵守世界贸易组织各成员国签署的贸易协定中规定的规则。
(2)国际货币基金组织(International Monetary Fund)和世界银行(World Bank)是由44个国家于1944年在新罕布什尔州的布雷顿森林会议上所创建的。
国际货币基金组织的任务是维持国际货币系统的秩序‘而世界银行则是为了促进经济发展。
世界银行重点在于向一些资金短缺的穷国政府发放低息贷款,以资助它们希望从事的重大基础设施投资项目。
当一国的经济出现混乱和货币相对其他国家大幅贬值时,国际货币基金组织通常视为可求助的最后的贷款者。
但是,国际货币基金组织的贷款常常是附加条件的,作为贷款的代价,国际货币基金组织要求贷款国需采取特定的经济政策,以扭转混乱局面,使经济回归稳定和增长。
(3)联合国(United Nations)成立于1945年10月24日,由51个国家承诺通过国际合作和集体的安全防卫措施来维护和平。
根据宪章,联合国有四项宗旨:维护国际和平和安全;发展各国友好关系;共同解决国际问题和促进尊重人权;以及协调成为各国行动的中心。
3全球化的推动力一是自第二次世界大战结束后,商品、服务和资本的自由流动的障碍减少了;二是技术变革,特别是近年来通信、信息处理和运输技术的发展。

希尔《国际商务》(第11版)笔记和课后习题(含考研真题)详解完整版>精研学习网>免费在线试用20%资料全国547所院校视频及题库资料考研全套>视频资料>课后答案>往年真题>职称考试目录隐藏第Ⅰ篇引言和概论第1章全球化1.1复习笔记1.2课后习题详解1.3考研真题详解第Ⅱ篇国家差异第2章政治、经济和法律体系中的国家差异2.1复习笔记2.2课后习题详解2.3考研真题详解第3章经济发展中的国家差异3.1复习笔记3.2课后习题详解3.3考研真题详解第4章文化差异4.1复习笔记4.2课后习题详解4.3考研真题详解第5章伦理、企业社会责任和可持续发展5.1复习笔记5.2课后习题详解5.3考研真题详解第Ⅲ篇全球贸易与投资环境第6章国际贸易理论6.1复习笔记6.2课后习题详解6.3考研真题详解第7章政府政策与国际贸易7.1复习笔记7.2课后习题详解7.3考研真题详解第8章国际直接投资8.1复习笔记8.2课后习题详解8.3考研真题详解第9章区域经济一体化9.1复习笔记9.2课后习题详解9.3考研真题详解第Ⅳ篇全球货币制度第10章外汇市场10.1复习笔记10.2课后习题详解10.3考研真题详解第11章国际货币体系11.1复习笔记11.2课后习题详解11.3考研真题详解第12章全球资本市场12.1复习笔记12.2课后习题详解12.3考研真题详解第Ⅴ篇国际企业的战略与组织结构第13章国际企业的战略13.1复习笔记13.2课后习题详解13.3考研真题详解第14章国际企业的组织14.1复习笔记14.2课后习题详解14.3考研真题详解第15章进入战略和战略联盟15.1复习笔记15.2课后习题详解15.3考研真题详解第Ⅵ篇国际商务运营第16章出口、进口和对等贸易16.1复习笔记16.2课后习题详解16.3考研真题详解第17章全球生产与供应链管理17.1复习笔记17.2课后习题详解17.3考研真题详解第18章全球营销与研发18.1复习笔记18.2课后习题详解18.3考研真题详解第19章全球人力资源管理19.1复习笔记19.2课后习题详解19.3考研真题详解第20章国际企业的会计和财务20.1复习笔记20.2课后习题详解20.3考研真题详解内容简介隐藏本书是希尔《国际商务》教材的学习辅导书,主要包括以下内容:1.整理名校笔记,浓缩内容精华。
第一章全球化2012、05、08——2012、05、181、什么是全球化(globalization)?全球化是指转向一个更为一体化与相互依存的世界经济。
全球化有不同的侧面,包括市场全球化和生产全球化。
市场全球化(globalization of markets)是指把历史上独特和分离的国家市场合并为一个巨大的全球市场。
生产全球化(globalization of production)指的是从全球各地去筹供商品和服务,以利用本国在生产要素(factors of production)上的成本和质量差异。
2、全球机构的出现(1)世界贸易组织(World Trade Organization)主要负责监管世界贸易秩序和确保各国遵守世界贸易组织各成员国签署的贸易协定中规定的规则。
(2)国际货币基金组织(International Monetary Fund)和世界银行(World Bank)是由44个国家于1944年在新罕布什尔州的布雷顿森林会议上所创建的。
国际货币基金组织的任务是维持国际货币系统的秩序‘而世界银行则是为了促进经济发展。
世界银行重点在于向一些资金短缺的穷国政府发放低息贷款,以资助它们希望从事的重大基础设施投资项目。
当一国的经济出现混乱和货币相对其他国家大幅贬值时,国际货币基金组织通常视为可求助的最后的贷款者。
但是,国际货币基金组织的贷款常常是附加条件的,作为贷款的代价,国际货币基金组织要求贷款国需采取特定的经济政策,以扭转混乱局面,使经济回归稳定和增长。
(3)联合国(United Nations)成立于1945年10月24日,由51个国家承诺通过国际合作和集体的安全防卫措施来维护和平。
根据宪章,联合国有四项宗旨:维护国际和平和安全;发展各国友好关系;共同解决国际问题和促进尊重人权;以及协调成为各国行动的中心。
3全球化的推动力一是自第二次世界大战结束后,商品、服务和资本的自由流动的障碍减少了;二是技术变革,特别是近年来通信、信息处理和运输技术的发展。
十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台伦理、企业社会责任和可持续发展5.1 复习笔记考点一:国际商务中的伦理问题1.概述(1)伦理的定义“伦理”是指支配一个人的行为、职业操守或判断评估一个组织的行为正确与否的约定俗成的法则。
(2)商业伦理与伦理策略的定义商业伦理是指支配商人行为的一整套约定俗成的规则,而伦理策略则是指不违反这些规则的策略或行动纲领。
(3)国际商务中伦理问题产生的根源国际商务中会产生许多伦理问题,其根源在于国与国之间在政治制度、法律、经济制度和文化方面存在巨大的差异。
(4)国际商务中常见的伦理问题在国际商务中,最为常见的伦理问题是员工待遇、人权、环境污染、腐败以及道德义务等。
十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台2.员工待遇当东道国的工作标准明显低于跨国公司母国的标准时,会发生伦理问题,跨国公司应及时采取行动来解决问题。
3.人权有观点认为,一个跨国公司在一个缺乏民主和人权的国家做生意是合乎伦理的。
因为长期的外国投资促进了经济发展,提高了当地的生活水平,这些发展最终将推动更多的人要求参与管理、政治多元化以及言论自由等。
但这一观点是有局限性的,有些国家非常落后,以至于很难合乎伦理地经商。
4.环境污染当东道国的环境保护制度不如母国严格时,也会发生伦理问题。
环境是公共产品,每个人都可以从中获益,但每个人都可以破坏环境,并且没有人对环境负有明确责任,因此会导致“公地悲剧”的发生。
5.腐败有经济学家指出,通过黑市、走私和向政府官员支付公关费可能会促进福利。
因为一些国家已有的政治体制扭曲或限制了市场机制的正常运行,采用该方法会“加速”政府批准商业投资。
也有经济学家认为,腐败降低了商业投资的回报,导致较低的经济增长速度。
因此,加急费的合理性导致了一个伦理困境。
十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台6.道德义务(社会责任)社会责任指商人在作商务决策时应考虑其经济行为可能导致的社会后果,应该尽力做到经济和社会双赢。
第14章进入战略和战略联盟14.1 复习笔记一、基本进入决策1.进入哪个外国市场一个国家作为潜在市场对于国际企业的吸引力有赖于在那个国家从事经营活动时的收益、成本和风险的平衡。
一个国家从事经营活动的长期经济利润是市场规模(从人口统计数据看)、该市场消费者的现有财富(购买力)以及取决于经济增长率的消费者未来可能财富等因素作用的结果。
在其他条件相同的情况下,收益—成本—风险平衡对有着自由市场体制,同时没有急剧上升的通货膨胀率和私营部门债务的政治稳定的发达国家与发展中国家更有利。
另一个重要的因素是国际企业在外国市场所能创造的价值,这取决于它能为那个市场提供的产品的适用性以及当地竞争的性质。
通过思考这些因素,企业可以根据它们的吸引力和长期盈力潜力来为各个国家评级。
那些级别高的市场就可考虑作为进入的首选。
2.进入时机一旦企业找到了有吸引力的市场,它必须考虑进入时机(timing of entry)的问题。
当国际企业在其他外国企业之前进入一个外国市场,这种进入很早;而在其他国际企业已经建立了分支机构后再进入,就是晚。
与早进入一个市场相关的经常具有的优势通常被称作第一进入者(先入者)优势(first-mover advantages)。
第一进入者优势之一就是通过建立一个强大的品牌形象抢先阻止竞争对手和赢得需求的能力。
另一个优势是在那个国家扩大销售量,并在经验曲线上领先于竞争对手,使先入者对后来者拥有成本优势的能力。
这种成本优势能使先入者把价格降低到后来者之下,从而把后者驱逐出市场。
第三个优势是先入者创造出转换成本,从而把消费者牢牢地捆绑在它们所提供的产品和服务上的能力。
这样的转换成本使后来者很难赢得顾客。
在其他国际企业之前进入一个外国市场的做法也有其劣势。
这通常被称为第一进入者(先入者)劣势(first-mover disadvantages)。
先进入者主要的劣势可能包括开拓成本(pioneering costs)。
十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台政府政策与国际贸易7.1 复习笔记考点一:贸易政策措施1.综述贸易政策措施主要包括:关税、补贴、进口配额、自愿出口限制、国产化规定和行政管理政策以及反倾销政策。
近几十年来,关税壁垒下降,非关税贸易壁垒如补贴、配额、自愿出口限制和反倾销政策却呈现上升趋势。
2.关税(见表7-1)表7-1 关税十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台3.补贴(见表7-2)表7-2 补贴4.进口配额和自愿出口限制(见表7-3)十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台表7-3 进口配额和自愿出口限制5.国产化规定(见表7-4)表7-4 国产化规定6.行政管理政策行政管理的贸易政策是指通过烦琐的政府规章制度提高进口品进入一个国家的难度。
与十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台所有贸易政策措施一样,行政管理措施有利于生产者而有损于消费者,使消费者难以获得高品质的外国产品。
7.反倾销政策(见表7-5)表7-5 反倾销政策考点二:政府干预的情况1.干预的政治理由(1)保护就业和产业政府干预最常见的政治理由是保护就业和产业免遭外国不公平的竞争。
(2)保护国家安全有时候国家认为某些产业对国家安全极其重要,必须对其采取保护措施,一般与国防有关的产业,例如航空产业,会经常得到这种优待。
(3)报复有些人认为政府应该利用干预贸易政策的威胁作为讨价还价的工具,以此来打开外国市十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台场,迫使贸易伙伴“按照游戏规则”行事。
(4)保护消费者许多国家的政府出于保护消费者免受不安全产品危害的目的,颁布了相关法规,间接地限制或禁止了这些产品的进口。
(5)推动对外政策目标的实现各国政府有时利用贸易政策来支持它们的对外政策目标。
政府可以同意对一个国家的优惠贸易条件以加强两国关系。
贸易政策也可用作一种施压手段或用来惩罚不遵守国际法规或准则的“流氓国家”。
(6)保护人权保护和促进人权是许多民主国家对外政策的重要缘由,许多政府有时试图利用贸易政策去改进贸易伙伴的人权政策。
十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台政治、经济和法律体系中的国家差异2.1 复习笔记考点一:政治体制1.初识政治体制(1)含义政治体制指一个国家的政府体制。
(2)两个考察指标①对集体主义或个人主义的重视程度;②民主或极权的程度。
这两个考察指标是相互联系的,主张集体主义的体制通常会趋向于极权,主张个人主义的体制通常会趋向于民主。
(3)政治体制的重要性一国的经济体制和法律体系取决于该国的政治体制。
2.集体主义与个人主义(1)集体主义①集体主义的含义十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台集体主义是指集体目标优先于个人目标的一种政治体制。
在集体主义中,一个社会整体的需求一般要比个人自由更被看重。
②社会主义在当代,集体主义的思想由社会主义继承。
社会主义是根据马克思的理论提出的,其核心思想是建立国家所有制企业,使获益者是整个社会而不是少数资本家。
(2)个人主义①含义个人主义是指一个人应享有其经济和政治追求的自由。
相对于集体主义而言,个人主义强调个人的利益应优先于国家的利益。
②两个核心原则a.强调保障个人自由和个人表达的重要性;b.强调只有通过让人民追求自己的经济利益,才能实现社会福利最大化,而不是由某个集体机构(如政府)来规定什么是社会的最高利益。
③核心思想个人主义的核心思想就是强调个人的经济和政治自由乃是一个社会赖以存在的基础。
3.民主与极权(1)民主的含义民主是指政府是由人民直接选举或通过其所选代表间接选举出来的一种政治制度。
(2)极权的含义极权是指个人或一个政党对人们生活的各个方面都拥有绝对的控制权,并且禁止政治反十万种考研考证电子书、题库、视频学习平台对党派存在的一种政治制度。
(3)联系民主、极权和集体主义、个人主义是有相关性的,民主和个人主义往往如影随形,而极权通常与集体主义息息相关。
考点二:经济体制1.市场经济(1)特征①所有生产性活动都为私人所有,而非为国家所有;②消费者的购买模式通过价格机制传递给生产者,从而决定生产商品和服务的种类与数量;③不能对供给设置任何限制,否则可能导致整个社会福利下降。
第17章全球营销与研发17.1 复习笔记一、市场细分市场细分(market segmentation)就是根据消费者购买行为方面的一些重要差异,把整个市场划分成若干个消费者群体。
由于不同的细分市场呈现出不同的购买行为模式,因此不同的细分市场可以有不同的产品设计、定价策略、分销渠道和沟通策略的选择。
这样做的目的无非是使消费者的购买行为与营销组合之间能更好吻合,从而实现销售的最大化。
跨国公司管理者考虑在国外细分市场时需要认识到两个主要问题:各国细分市场在结构上有差异以及存在超越国界的细分市场。
前者限制了跨国公司在全球推行标准化营销战略的能力;后者大大提高了跨国公司把全球市场当作一个单一的统一体对待的能力,使它们能够实施全球化战略,在全球范围内销售标准化的产品,使用相同的基本营销组合帮助其在各个国家的市场对产品进行定位和销售。
二、产品特性一个产品可以被看作由一组特性组成。
1.文化差异在社会结构、语言、宗教、教育等方面,不同的国家有着不同的国情,这些差异对制定营销战略有着重大的影响。
然而,消费者的品位和偏好正在变得国际化,但离以标准化口味和偏好为特征的全球化文化尚有很长的一段距离。
2.经济发展消费者的消费行为受到一国经济发展水平的影响。
处于高度发达国家中的公司倾向于在产品中加入许多额外的特性,他们乐意多花钱购买那些按照他们的品位和偏好特别研发的具有附加功能的产品;欠发达国家中的消费者通常不需要这些产品特性,他们所需要的是具有基本特性的产品。
3.产品与技术标准各国政府强制执行的不尽相同的产品标准排除了大规模生产和销售标准化产品的可能。
技术标准的差异抑制了市场的全球化步伐。
有些差异是由很久以前所做的特别决定造成的,而非政府行为所致,但这些决定带来的长期影响是深远的。
三、分销策略公司营销组合的关键要素是它的分销策略:企业选择如何将产品送达顾客的方法。
图17-1是一个典型的、由一个渠道组成的分销系统。
图17-1 一个典型的分销系统这个渠道包括一个批发商和一个零售商。
Chapter1
1、What Is Globalization?
Globalization - the shift toward a more integrated and interdependent world economy
The world is moving away from self-contained national economies toward an interdependent, integrated global economic system
2、What Is The Globalization of Markets?
Historically distinct and separate national markets are merging
It no longer makes sense to talk about the “German market” or the “American market”Instead, there is the “global market”
falling trade barriers make it easier to sell globally
consumers’ tastes and preferences are converging on some global norm
firms promote the trend by offering the same basic products worldwide
Firms of all sizes benefit and contribute to the globalization of markets
97% of all U.S. exporters have less than 500 employees
98% of all small and mid-sized German companies participate in international markets
3、What Is The Globalization of Production
Firms source goods and services from locations around the globe to capitalize on national differences in the cost and quality of factors of production like land, labor, energy, and capital Companies can
lower their overall cost structure
improve the quality or functionality of their product offering
4、What Is Driving Globalization
Declining barriers to the free flow of goods, services, and capital
average tariffs are now at just 4%
more favorable environment for FDI
global stock of FDI was $15.5 trillion in 2009
facilitates global production
Technological change
microprocessors and telecommunications
the Internet and World Wide Web
transportation technology
5、Lower barriers to trade and investment mean firms can
view the world, rather than a single country, as their market
base production in the optimal location for that activity
But, firms may also find their home markets under attack by foreign firms
6、Technological change means
lower transportation costs
help create global markets and allow firms to disperse production to economical, geographically separate locations
low cost information processing and communication
firms can create and manage globally dispersed production
low cost global communications networks
help create an electronic global marketplace
global communication networks and global media
create a worldwide culture and a global consumer product market。