英语语法——动词的形式与时态
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:345.50 KB
- 文档页数:23

闽教版小学英语语法知识英语动词4种时态:1、一般现在时:常与表示程度或频度的词连用,如:often(经常), usually(通常,一般), sometimes(有时), always(总是,一直), never(从不),表示经常性或习惯性的动作,表示现在的特征或状态,表示普遍真理。
用动词原形表示,第三人称单数后,动词要在词尾加s(或es,或变y为i再加es)。
如:I often get up at 7:00.He often gets up at 7:30.2、现在进行时:表示现在或现在这一阶段正在进行的动作。
用am / is / are 加动词ing形式表示,如: What are you doing? I am reading a book. What is he doing? He is singing.3、一般将来时:常与表示将来的时间连用,如:tomorrow , next week , next year 等,表示将要发生的动作或情况。
用am/ is/ are 加going to 形式表示,如:What are you going to do tomorrow? I’m g oing to ride a horse. 用will 加动词原形表示,如:What will you do next Sunday? I will go shopping. 用am/ is/ are 加动词ing 形式表示,如:What are you doing tomorrow? I’m going bowling.4、一般过去时:经常与表示过去的时间连用, 如: yesterday, last night 等, 表示过去某时发生的动作或情况。
动词要用动词的过去式。
如:Who was first? Ken was first.Where were you yesterday? I was at home.What did you do yesterday? I went to school.形容词的比较级和最高级:1、单音节词:比较级加er, 最高级加est. 如:tall—taller—the tallest, He is taller than his brother. Tom is the tallest in his class.2、多音节词和部分双音节词:比较级加more, 最高级加the most. 如:interesting---------more interesting---------the most interesting,Music is interesting subject. P.E. is more interesting than music.. Science is the most interesting subject.形容词变为比较级的变化规则:(1)一般情况下,在形容词的词尾直接加er。


⾼中英语语法必备之谓语动词的时态和语态详解⾼中英语动词的时态语态详解在英语中,句⼦不仅有时间状语说明动作发⽣的时间,其谓语动词本⾝也有形式的变化来指⽰时间,这种表明谓语动词发⽣时间的动词形式称为时态。
语态是表现主语和谓语关系的另⼀种动词形式。
⼀动词的时态⼀般说来,发⽣在现在的事情⽤现在的时态进⾏描述;发⽣在过去的事情⽤过去的时态进⾏描述;将要发⽣的事情⽤将来的时态进⾏描述。
英语中的时态共计16种,但常⽤的有11种。
(以动词do 为例)1.⼀般现在时(do/does);2.⼀般过去时(did);3.⼀般将来时( will do/ shall do);4.⼀般过去将来时( would do/should do);5.现在进⾏时( am/is/are doing);6.过去进⾏时(was/were doing);7.将来进⾏时( will/shall be doing);8.现在完成时(have/has done);9.过去完成时( had done);10.将来完成时( will/shall have done);11.现在完成进⾏时( have/has been doing);1.⼀般现在时(1)⼀般现在时是描述现在或经常性的性质、动作或状态的时态常⽤时间状语:sometimes, often, always, usually, seldom,every day / night / week / month / year, in the morning, in the afternoon, in the evening, at night(2)表⽰经常发⽣的动作,习惯性的动作或存在的状态I usually get up at four every morning when it’s still dark.He always goes to work late,which makes his boss angry and disappointed.(3)客观真理,客观存在,科学事实及⾃然现象The sun rises in the east and sets in the west every day.The man who has never been to the Great Wall is not a real man.Trees turn green in spring. Liquid turns into gas when it is hot enough.(4)表⽰格⾔或警句中Pride goes before a fall.Knowledge is power.Practice makes perfect.(5)⼀般现在时表将来表⽰已经计划、安排好了或时间表上所安排,并且⼀定要做的事情。

动词1)表示动作中状态的词叫做动词。
2)根据其在句中的功能,动词可分为四类,分别是:实义动词(Notional Verb)、系动词(Link Verb)、助动词(Auxiliary Verb)、情态动词(Modal Verb)。
说明:有些情况下,有些动词是兼类词,例如:We are having a meeting.我们正在开会。
(having是实义动词。
)He has gone to New York.他已去纽约。
(has是助动词。
)3)动词根据其后是否带有宾语,可分为两类,分别是:及物动词(Transitive Verb)、不及物动词(Intransitive Verb),缩写形式分别为vt. 和vi.。
说明:同一动词有时可用作及物动词,有时可用作不及物动词。
例如:She can dance and sing.她能唱歌又能跳舞。
(sing在此用作不及物动词。
)She can sing many English songs.她能唱好多首英文歌曲。
(sing用作及物动词。
)4)根据是否受主语的人称和数的限制,可分两类,分别是:限定动词(Finite Verb)、非限定动词(Non-finite Verb)例如:She sings very well.她唱得很好。
(sing受主语she的限制,故用第三人称单数形式sings。
)She wants to learn English well.她想学好英语。
(to learn不受主语she的限制,没有词形变化,是非限定动词。
说明:英语中共有三种非限定动词,分别是:动词不定式(Infinitive)、动名词(Gerund)、分词(Participle)。
5)根据动词的组成形式,可分为三类,分别是:单字词(One-Word Verb)、短语动词(Phrasal Verb)、动词短语(Verbal Phrase)例如:The English language contains many phrasal verbs and verbal phrases.英语里有许多短语动词和动词短语。
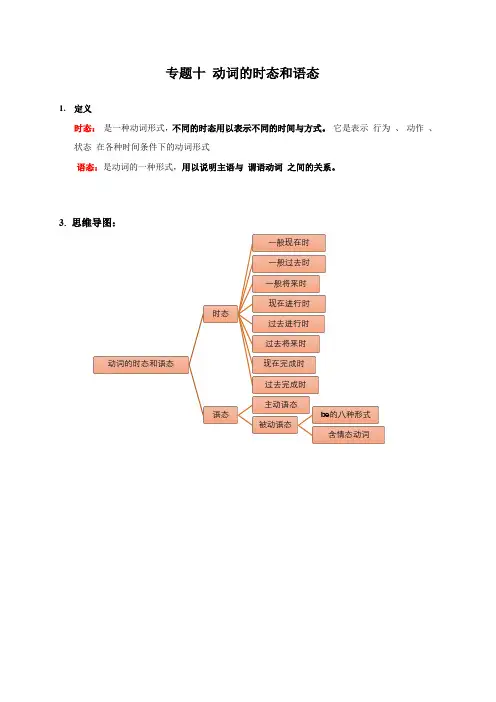
专题十动词的时态和语态1.定义时态:是一种动词形式,不同的时态用以表示不同的时间与方式。
它是表示行为、动作、状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式语态:是动词的一种形式,用以说明主语与谓语动词之间的关系。
3. 思维导图:动词的时态和语态时态一般现在时一般过去时一般将来时现在进行时过去进行时过去将来时现在完成时过去完成时语态主动语态被动语态be 的八种形式含情态动词1.动词的时态1.常考的时态构成及用法a.一般现在时d.现在进行时e.过去进行时f.过去将来时g.现在完成时h.过去完成时2. 动词的语态a. 分类:主动语态:表示主语是动作的执行者被动语态:表示并语是动作的执行者c.主动语态和被动语态的转换规则典型例题总分:50分姓名:得分:1.单选题(每小题1分,共50分)( ) 1. Jenny, together with the Greens the White Tower Park if it tomorrow.A.are going to; isn't rainyB.is going to; doesn't rainC.are going to; won't rainD.is going to; isn't rain( ) 2. The old man for quite some time.A.has diedB.dieC.has deadD.has been dead( ) 3. It is reported that a tall building in the city next year.A.will be builtB.were buildC.have builtD.will build( ) 4. My sister for 2 years.A.has marriedB.have got marriedC.has been marriedD.married( ) 5. Chinese ________in many schools around the world and many people love to learn it.A.teachesB.is teachingC.has taughtD.is taught( ) 6. When Tom was in primary school, he ________the piano every day.A.playsB.playedC.was playingD.has played( ) 7. A baby's first month birthday is a special event in China and _____with a special Party.A.celebratesB.is celebratedC.was celebratedD.will celebrate( ) 8. -Were you at home at 9 o'clock last night?-Yes, I a shower at that time.A.tookB.was takingC.was takenD.am taking( ) 9. National Day celebrations for China's seventieth birthday in about three months.A.will be heldB.will holdC.is heldD.was held( ) 10. We don't know if he tomorrow. If he, I will call youA.will come, will comeB.will come, comeses, will comees, comes( ) 11. He told me that he ______ his uncle in Thailand the next day.A.will visitB.has visitedC.is going to visitD.would visit( ) 12. -Tom, do you know ________? -In Beijing.A.where will the 24th Winter Olympics be heldB.where the 24th Winter Olympics will holdC.where the 24th Winter Olympics will be heldD.where will the 24th Winter Olympics hold( ) 13. Peter with his classmates ________ for the bus when the earthquake happened.A.is waitingB.was waitingC.are waitingD.were waiting( ) 14. his museum ________ here for over 80 years. It ________ one of the oldest buildings in this city.A.is; wasB.had been; isC.was; has beenD.has been; is( ) 15. -Mrs. Brown, how long can books from the school library ?-At most two weeks.A.borrowB.keepC.be borrowedD.be kept( ) 16.-An AI robot _____in our school dining hall next term.-I'm looking forward to it.A.will useB.will be usedC.is usedD.was used( ) 17. Usually a baby's face ____ smooth.A.is feelingB.feltC.feels likeD.feels( ) 18. She _____ an English magazine when I came in.A.readsB.has readC.will readD.was reading( ) 19. I will call you as soon as he______ here.A.arriveB.will arriveC.arrivesD.arrived( ) 20. Boys and girl, ______ learning and have fun!A.keepB.to keepC.keepingD.kept( ) 21. There ______a basketball game between these two grades in the gym this afternoon.A.willB.is going to haveC.is going to beD.will have( ) 22. We ______TV from seven to nine last night.A.were watchingB.will watchC.watchedD.watch( ) 23. Jack's mother taught me how ________ Yunnan rice noodles last weekend.A.to makeB.makingC.makeD.to making( ) 24. Mrs. Green said the plates ________ right away,or they would become difficult to wash.A.will be washedB.should washC.will washD.should be washed( ) 25. The documentary Under the Dome (《苍穹之下》)which ________ by Chai Jing showed us that the air pollution in China was very serious.A.producesB.producedC.is producedD.was produced( ) 26. -What did you do last night?- I ________ my homework and watched TV.A.didB.doC.am doingD.will do( ) 27.The hospital is very famous. It _______ in 2001.A.buildsB.builtC.was builtD.is built( ) 28.These rules are made the disabled.A.protectB.protectedC.to protectD.protecting( ) 29. -How much does the TV ?-Not too much. It's just a second-handed one.A.costB.spendC.takeD.pay for( ) 30. -Have you ever ________ an amusement park?- Yes, I have ________ Fun Times Amusement Park last year.A.been to, have gone toB.gone to, have been toC.go to, went toD.been to, went to( ) 31.We are glad to hear that the terrorists ________ by the brave policemen several days ago.A.are caughtB.were caughtC.have been caughtD.are going to be caught ( ) 32. -Why didn't you go to the party last night? - Because I _____.A.wasn't invitedB.didn't invitedC.haven't invitedD.don't invited ( ) 33. -What _____ you supposed ____ when you are in China?- You should shake hands.A.are, to doB.do, to doC.are, doingD.have, to do( ) 34. So far, we ________ English for three years.A.have learntB.learnC.learntD.had learnt( ) 35.The boy was made ______ the words again and again.A.copyB.copyingC.copiesD.to copy( ) 36. The sports meeting in our school now.A.being heldB.is havingC.is holdingD.is being held( ) 37. The window ____ ten minutes ago, and the room is bright now.A.can be cleanedB.is cleanedC.was cleanedD.will be cleaned( ) 38. -Oh, Mrs. King, your necklace looks nice. Is it new?-No, I _______ it for 2 years.A.hadB.have hadC.boughtD.have bought( ) 39. He has ordered a watch on line for his father and it _______ to him before Father's Day.A.sendB.will be sentC.was sentD.sent( ) 40. There ______ a funny cartoon on CCTV 6 this evening.A.willB.will haveC.is going to beD.is going to have( ) 41. -________ did your uncle leave his home town? -He ___________ for nearly twenty years.A.When, has leftB.When, has been awayC.How long, has leftD.How long, has been away ( ) 42. My uncle ________ Germany on business many times.A.has been onB.has gone toC.has been toD.has been in( ) 43. Her life ________ a lot during the last three years.A.changedB.changingC.has changedD.will change( ) 44. -Lisa was seen ______ an old man go across the street this morning. -What a kind girl she is!A.helpingB.helpedC.to helpD.helps( ) 45. My computer has broken down. I'll get it _______ this afternoon.A.repairsB.repairedC.to repairD.repairing。


1.动词时态(tense )时态---就是一种表示时间和状态的主动词形式。
1.1 现在进行时(present continuous/present progressive )1.1.1 时间:现在(present )--:动作发生的时间是现在而非过去,一般也就是说话时的时间。
1.1.2 状态:正在进行(continuous/progressive )。
指该动作在过去某个时间点开始,直到现在(说话时)仍然继续,在一定的时间范围内, 还将继续下去。
1.只有具有持续性概念的动作动词(action verb ), 才可能有进行时态, 而表示状态或瞬间动作的动词, 不能使用进行时态。
它们是不可持续的,往往具有状态动词的特征, 而不强调动作, 此类词一般常见的如下: 表感情意识状态:like/dislike/love/hate/prefer/want/need/know/realize/suppose/mean/understand/believe/remember感官意识状态:see/ hear/ smell/ taste表所属关系: 有…,包含:belong / contain/consist/depend/seem/have当think 表示“认为”的意思时,同样也不用进行时态2. 即使是动作动词,同样也有动作持续时间长短的问题。
有的动作持续时间短,所以动作一般就发生在说话时由于这种动作只是从宏观上看具有持续性,但其间一定是有间断的,说话时,该动作不一定发生,只是说话的时间点包含在该动作的持续时间内。
1.1.3 构造: 助动词be , 主动词verb+ ing ,参见“词类概述2.3.4”.陈述句: subject + be + verb-ing否定句:subject + be+ not+ verb-ing一般疑问句:be + subject + verb-ing :?复杂(特殊)疑问句:question word+ subject + verb-ing :1.1.4 用途:1.用于表述正在发生的短动作,即说话时正在发生。

高中英语语法(时态和语态)一.动词的时态时态是谓语动词所表示的动作或情况发生时间的各种形式。
英语动词有16种时态,但是常见的只有九种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、过去将来时、现在完成进行时。
(一)一般现在时(do / does)1.具体用法1) 表示经常性或习惯性动作We always care for each other and help each other. 我们总是互相关心互相帮助。
He goes to school every day.2)表示现在的特征或状态He is very happy.Do you sing? ----A little.3)表示普遍真理Light travels faster than sound. 光速比声速快。
Actions speak louder than words. 行动胜过言语。
* 常与一般现在时态连用的词或短语主要有:often, usually, sometimes, every day,every morning/afternoon, on Sundays/weekends等等。
I often go to the cinema on Sundays. 我经常星期天去看电影。
He goes to work early every day. 他每天上班很早。
(二)一般过去时( did )(1)表示过去某一特定时间所发生的、可完成的动作或状态,常与表示确切过去时间的词、短语或从句连用。
例如:We went to the pictures last night and saw a very interesting film.(2)表示过去习惯性动作。
例如:He always went to class last.I used to do my homework in the library.(三)一般将来时( will / shall do)1)表示将来打算进行或期待发生的动作或状态。


1.动词时态(tense )时态---就是一种表示时间和状态的主动词形式。
1.1 现在进行时(present continuous/present progressive )1.1.1 时间:现在(present )--:动作发生的时间是现在而非过去,一般也就是说话时的时间。
1.1.2 状态:正在进行(continuous/progressive )。
指该动作在过去某个时间点开始,直到现在(说话时)仍然继续,在一定的时间范围内, 还将继续下去。
1.只有具有持续性概念的动作动词(action verb ), 才可能有进行时态, 而表示状态或瞬间动作的动词, 不能使用进行时态。
它们是不可持续的,往往具有状态动词的特征, 而不强调动作, 此类词一般常见的如下:表感情意识状态:like/dislike/love/hate/prefer/want/need/know/realize/suppose/mean/understand/believe/remember感官意识状态:see/ hear/ smell/ taste表所属关系: 有…,包含:belong / contain/consist/depend/seem/have当think 表示“认为”的意思时,同样也不用进行时态2. 即使是动作动词,同样也有动作持续时间长短的问题。
有的动作持续时间短,所以动作一般就发生在说话时由于这种动作只是从宏观上看具有持续性,但其间一定是有间断的,说话时,该动作不一定发生,只是说话的时间点包含在该动作的持续时间内。
1.1.3 构造: 助动词be , 主动词verb+ ing ,参见“词类概述2.3.4”.陈述句: subject + be + verb-ing否定句:subject + be+ not+ verb-ing一般疑问句:be + subject + verb-ing :?复杂(特殊)疑问句:question word+ subject + verb-ing :1.1.4 用途:1.用于表述正在发生的短动作,即说话时正在发生。
英语语法:动词的时态和语态英语语法:动词的时态和语态一般现在时一般过去时一般将来时过去将来时现在进行时主动do/does did will/shalldowould/shoulddoam/is/aredoing被动am/is/aredonewas/weredonewill/shallbe donewould/shouldbe doneam/is/arebeingdone过去进行时将来进行时现在完成时现在完成进行时过去完成时主动was/weredoingwill/shallbe doinghave/hasdonehave/has beendoinghad done被动was/werebeingdone----------have/hasbeen done----------had beendone一、一般现在时1、表示经常发生的习惯性的、现在反复出现的动作或状态,常用的时间状语有:always,usually,seldom, sometimes, every day, now and then, once a week等。
2、表示眼下或目前等现在时间所发生的动作或存在的状态,这种状态带有一定的持续性。
3、表示客观事实或普遍真理。
4、书报的标题,故事的叙述,小说、戏剧、电影等情节介绍,图片的说明等。
5、时间表、时刻表、日程表、节目单、课程表等按规定将要发生的动作,只限于go, arrive, leave, start, stay, return, begin, e等动词。
6、在时间、条件、方式、让步状语从句中,表示将来的动作。
注意:一般现在时可以用于定语从句或宾语从句中表示将来。
7、用在某些表达中,表示现在正在发生的动作或存在的状态。
Here es the bus!How it rains!二、一般过去时1、表示在过去某一时间点发生的动作或所处的状态,与现在没有关系。
常用的时间状语有:yesterday, last night, at that time等。
2015考研英语语法:16个动词时态的形式和用法动词作为句子主干的核心部分之一,其时态和语态一直都是考查的重点和难点。
本文旨在对考研英语中的16种语法进行梳理,用一种更加巧妙的方法帮助广大考生理解并记忆知识点。
(一)总述所谓“时态”,可以被理解为“时间”+“动词状态”。
佛家称“过去、现在、将来”,这就是所谓“三世诸佛”。
这三者也是大部分人能够想到的时间,但是大家还忘记了一种可能,那就是站在过去的某个点去预测将来。
比如狄马克上周预言中国A股即将反弹,再比如我昨天预计明天早上我一定会去上班,这些都是过去谈论将来的例子,也决定了我们的语言当中必然要多出一种时间,那就是“过去将来时”。
至于动词状态,大家联想一下我们已经很熟悉的英语时态,再回到生活中对比一下,就会发现三个比较明显的状态:一般时态、进行时态和完成时态。
但在这里,我们又忽略了一种可能性,有的事件是现在已经完成,并且还将一直进行下去,比如说我从现在起,将会在这里和大家分享复习备考的知识,随着这篇文章的刊登,眼下的分享工作已经完成,但以后还会有别的文章陆续跟大家见面,所以这件事还将继续下去,这就是一个典型的完成进行的动作。
所以我们的状态也变成了四种:一般、进行、完成和完成进行时。
综上所述,我们有4种“时间”和4种“动作状态”,而时态就是这两者的排列组合,所以我们就很好理解,英语中总共有16种时态,总结为下表:至此,我们已经清楚英语中所包含的全部16个时态是如何来的,接下来,我们从形式和用法两个方面,来对这16个时态进行梳理。
(二)形式时态的用法比较多,但形式相对固定,因此,我们先从形式开始考查。
刚才说过,将时态理解为“时间”+“动作状态”,这种方法不仅可以用在对时态的理解上,也可以运用在对于时态形式的记忆上。
“时间”包括过去、现在、将来以及过去将来,是影响动词形式的一个因素。
比如发生在“现在”的动作,当主语为第一、第二人称和第三人称复数时,动词均为do,当主语是第三人称单数时,动词为does。
语法互动(七)动词的时态与语态1动词时态中考考点1.动词的第三人称的单数形式、过去式、过去分词和现在分词的构成。
2.动词的八种时态的基本结构及用法。
考点----- 般现在时1.一般现在时的基本结构及用法(1)结构:当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词用第三人称单数形式。
⑵动词的第三人称单数形式变化规则如下:(3)用法:①表示事实、现状、性质或经常性、习惯性的动作。
常与seldom, often, usually, always, sometimes, today, every day, once a week, every five minutes, on Sundays等时间状语连用。
I go to school at seven every day.我每天七点去上学。
②表示普遍真理和客观事实。
The earth goes around the sun.地球绕着太阳转。
③表示在现在时间里所发生的一个动作。
Here comes the bus.公共汽车来了。
④在时间和条件状语从句中代替一般将来时。
I'll go shopping with my mother if she is free tomorrow.如果明天我妈妈有空的话,我将和她去购物。
2.一般现在时的疑问句、否定句_般疑主语4■动词原形他?问句以咬+单数第三人称主语+I动词原形慎他? __________Be+主语+其他?疑问词(作主语或主语的定语)+特殊疑动词谟他?__回包T疑问词(非主语)+一般疑问句?主语' t+动词原形4■其他.单三人称+dDesn' H■动词原形他* 主语他.Do you see the bird in the tree?He doesn’ t go to school by bus.考点二一般过去时1.一般过去时的用法及标志词一般过去时表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态。
句中的谓语动词要变为过去式。
考研英语十二大基础语法体系一.英语动词的时态(一)英语动词的形式:英语的时态是通过动词的变化来体现的。
因此,了解动词的形式及其变化规律非常重要。
英语的实义动词有以下五种形式:(1)动词原形:动词原形在句子中形式不变。
主要用于主语为非第三人称单数的一般现在时,情态动词之后,或根据语法规定必须用动词原形的其他情况。
(2) 一般现在时:第三人称单数形式(简称现单三)主要用于主语为第三人称单数的一般现在时。
(3) 过去式:主要用于一般过去时。
(4) 现在分词:主要用于进行时态,或语法规定的其他情况。
(5) 过去分词:主要用于完成时态,或语法规定的其他情况。
动词一般现在时第三人称单数(现单三)的构成,见下表:与名词变复数形式相同,读音也相同。
动词过去式和过去分词,大多数是动词原形+ ed 构成,这是规则动词。
规则动词的拼写和读音规则如下表:不规则动词的过去式和过去分词有其特殊变化形式,需要个别记忆,同时也要善于发现不规则中的规则,即某些字母组合的不规则动词有一定的规律。
如:weep → wept, sleep → slept, sweep → swept. 现在分词一律由动词原形加-ing构成,规则如下表:为了学习的方便,人们把时间分为四个阶段:“现在、过去、将来、过去将来”。
英语动词所表示的动作在以上每个时间段中分别有四种状态:一般、进行、完成和完成进行。
因此我们便有了四四一十六个时态。
不同的时态有不同的变化形式。
以do 为例,列表如下:“时态”就是通过动词的形态变化,来表达动作发生的时间(现在、过去、将来、过去将来)及所处的状态(一般、进行、完成、完成进行)。
16个时态中,常用的有12个:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、过去将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、将来进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、将来完成时、现在完成进行时和过去完成进行时。
其他时态很少单独使用。
二.被动语态(一)被动语态的构成被动语态由“be+及物动词的过去分词”构成。
英语语法:初中英语动词时态和语态讲解(一)动词是谓语动所表示的动作或情况发生时间的各种形式。
英语动词有16种时态,但是常用的只有9种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、过去将来时、现在完成进行时。
下面分别介绍。
1、一般现在时的用法1)表示经常性、习惯性的动作;表示现在的状态、特征和真理。
句中常用often, usually, every day 等时间状语。
例如:a. He goes to school every day.b. He is very happy.c.The earth moves around the sun.2) 在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,用一般现在时表示将来。
例如:a. If you come this afternoon, we’ll have a meeting.b. When I graduate, I’ll go to countryside.3) 有时这个时态表示按计划、规定要发生的动作(句中都带有时间状语),但限于少数动词,如:begin, come, leave, go ,arrive, start , stop, return, open, close等。
例如:a. The meeting begins at seven.b. The rain starts at nine in the morning.4) 表示状态和感觉的动词(be, like, hate, think, remember, find, sound 等)常用一般现在进行时。
a. I like English very much.b. The story sound very interesting.5) 书报的标题、小说等情节介绍常用一般现在时。
2.一般现在时的用法1)表示过去某时间发生的事、存在的状态或过反复发生的动作。
a. He saw Mr. Wang yesterday.b. He worked in a factory in 1986.2)表示过去经常发生的动作,也可用“used to “ 和“would + 动词原形”。
初中英语八种时态归纳复习(一)一般现在时(一)定义表示经常性或习惯性的动作,或存在的状态,还表示主语具备的性格和能力及客观真理。
例:I get up at 6:30 in the morning . She is at home .(二)构成主要用动词原形表示,当主语是第三人称单数时,在动词词尾加s/es。
(三)句型1、肯定句:主语+谓语+其他。
She reads English everyday.2、否定句:主语+don’t/doesn’t+谓语+其他。
He doesn’t get up at 6:30 in the morning.3、一般疑问句:Do/Does+主语+V原+其他?Do you like English? Yes, I do. /No, I don’t.4、特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+do/does+主语+V原+其他?What time do you get up every morning?Where does your father work?(三)用法1、表示经常性或习惯性的动作,或存在的状态,带与表示频率的时间状语如:often , sometimes , usually,always , everyday year,month...), once/twice a week (month, year, etc.), seldom, on Sundays等连用。
I leave home for school at seven every morning.2、表示客观真理,科学事实、格言警句。
The sun rises in the east .日出东方。
The earth goes around the sun .地球绕着太阳转。
Ten minus two is eight.十减二等于八。
Light travels faster than sound .光的速度比声音的速度快。