中国历史朝代的英文表达
- 格式:doc
- 大小:24.00 KB
- 文档页数:2

中国历史朝代的英语翻译说法一、夏朝(Xia Dynasty)夏朝是中国历史上第一个朝代,大约存在于公元前2070年至公元前1600年。
在英语中,夏朝通常被翻译为“Xia Dynasty”。
二、商朝(Shang Dynasty)商朝继夏朝之后,存在于公元前1600年至公元前1046年。
商朝的英语翻译为“Shang Dynasty”。
三、西周(Western Zhou Dynasty)西周时期从公元前1046年开始,持续到公元前771年。
在英语中,西周被称为“Western Zhou Dynasty”。
四、东周(Eastern Zhou Dynasty)东周分为春秋和战国两个时期,存在于公元前770年至公元前221年。
其英语翻译为“Eastern Zhou Dynasty”。
五、秦朝(Qin Dynasty)秦朝是中国历史上第一个统一的中央集权国家,存在于公元前221年至公元前206年。
在英语中,秦朝被称为“Qin Dynasty”。
六、汉朝(Han Dynasty)汉朝分为西汉和东汉两个时期,存在于公元前206年至公元220年。
其英语翻译为“Han Dynasty”。
七、三国时期(Three Kingdoms)三国时期是指魏、蜀、吴三国鼎立的时期,存在于公元220年至公元280年。
在英语中,这一时期被称为“Three Kingdoms”。
八、晋朝(Jin Dynasty)晋朝分为西晋和东晋两个时期,存在于公元265年至公元420年。
其英语翻译为“Jin Dynasty”。
九、南北朝(Southern and Northern Dynasties)南北朝时期,中国分裂为南北两部分,存在于公元420年至公元589年。
在英语中,这一时期被称为“Southern and Northern Dynasties”。
十、隋朝(Sui Dynasty)隋朝是中国历史上第二个统一的中央集权国家,存在于公元581年至公元618年。

朝代的英文单词单词:dynasty1.1 词性:名词1.2 中文释义:王朝,朝代1.3 英文释义:A succession of rulers from the same family or line.1.4 同义词:regime, monarchy---2 起源与背景2.1 词源:源于古希腊语“dynastēs”,意为“统治者”或“有权力的人”。
2.2 趣闻:中国历史上有许多著名的朝代,如唐朝、宋朝等,每个朝代都有其独特的政治、经济、文化特点。
在欧洲,也有一些著名的王朝,如哈布斯堡王朝等。
---3 常用搭配与短语3.1 短语:dynasty change(朝代更替)例句:The frequent dynasty changes in Chinese history reflect theplexity of social development.翻译:中国历史上频繁的朝代更替反映了社会发展的复杂性。
3.2 短语:found a dynasty(建立一个朝代)例句:The emperor managed to found a new dynasty.翻译:这位皇帝设法建立了一个新朝代。
---4 实用片段(1). "In ancient times, the change of dynasties often brought great changes to the country." The history teacher said in class. "Yes, for example, the establishment of the Tang Dynasty promoted the prosperity of culture." A student replied.翻译:“在古代,朝代的更替常常给国家带来巨大的变化。
”历史老师在课堂上说。
“是的,比如唐朝的建立就推动了文化的繁荣。

Song宋But in 960 a new power, Song (960-1279), reunified most of China Proper. The Song period divides into two phases: Northern Song (960-1127) and Southern Song (1127-1279). The division was caused by the forced abandonment of north China in 1127 by the Song court, which could not push back the nomadic invaders.公元960年,一个新兴势力,宋(公元960-1279),再次统一了中国大部分地区。
但在1127年宋朝廷因没能打退游牧民族的入侵而被迫放弃北方。
所以宋朝又被分成北宋(公元960-1127)和南宋(公元1127-1279)两个阶段。
The founders of the Song dynasty built an effective centralized bureaucracy staffed with civi lian scholar-officials. Regional military governors and their supporters were replaced by centrally appointed officials. This system of civilian rule led to a greater concentration of power in the emp eror and his palace bureaucracy than had been achieved in the previous dynasties.宋朝的统治者建立了有效的中央集权制;广泛任用民间的学术文人;地方的军事官员及其党羽都被中央任命的官员所替代。


中国史英语单词1. What are the major dynasties in Chinese history?The major dynasties in Chinese history include the Xia, Shang, Zhou, Qin, Han, Tang, Song, Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties.中国历史上的主要朝代包括夏、商、周、秦、汉、唐、宋、元、明和清朝。
2. Who was Confucius and what was his philosophy?Confucius was a Chinese philosopher and politician who lived during the Spring and Autumn period. His philosophy, known as Confucianism, emphasized the importance of morality, family values, and social harmony.孔子是一位生活在春秋时期的中国哲学家和政治家。
他的哲学思想被称为儒家思想,强调道德、家庭价值观和社会和谐的重要性。
3. What was the Silk Road and why was it important?The Silk Road was a network of trade routes that connected China with the Mediterranean world. It was important because it facilitated the exchange of goods,ideas, and technologies between different regions, and helped to promote cultural and economic exchange.丝绸之路是连接中国和地中海世界的贸易路线网络。

中国历史朝代英语作文Chinese History Dynasties。
China, one of the world's oldest civilizations, has a long and rich history that spans over 5,000 years. Throughout this time, China has been ruled by a series of dynasties, each with its own unique characteristics and contributions to Chinese culture and society. In this essay, we will take a closer look at some of the most influential dynasties in Chinese history.The Xia Dynasty (c. 2100-1600 BC) is considered thefirst dynasty in Chinese history. It is said to have been founded by Yu the Great, who is credited with controlling floods and bringing order to the region. The Xia Dynastywas known for its bronze work, as well as its use of oracle bones to communicate with the gods.The Shang Dynasty (c. 1600-1046 BC) followed the Xia Dynasty and was known for its advances in agriculture,bronze work, and writing. The Shang Dynasty was also the first dynasty to leave written records, which provide valuable insights into early Chinese culture and society.The Zhou Dynasty (1046-256 BC) is divided into two periods: the Western Zhou (1046-771 BC) and the Eastern Zhou (771-256 BC). The Western Zhou was a time of stability and prosperity, while the Eastern Zhou was marked by political instability and social unrest. The Zhou Dynastyis known for its contributions to Confucianism and Taoism, two of the most important philosophical traditions in Chinese history.The Qin Dynasty (221-206 BC) was founded by Qin Shi Huangdi, who is credited with unifying the various warring states of China into a single empire. The Qin Dynasty is known for its construction of the Great Wall of China, as well as its standardization of weights, measures, and currency.The Han Dynasty (206 BC-220 AD) followed the Qin Dynasty and is considered one of the most importantdynasties in Chinese history. The Han Dynasty is known for its advances in science, technology, and the arts. It was during this time that paper was invented, the Silk Road was established, and Confucianism became the dominant philosophy.The Tang Dynasty (618-907 AD) is considered a goldenage of Chinese culture and society. The Tang Dynasty is known for its advances in poetry, painting, and music, as well as its strong economy and military. The Tang Dynasty also had extensive trade and cultural exchanges with other civilizations, including the Arab world and Japan.The Song Dynasty (960-1279 AD) followed the TangDynasty and is known for its advances in science, technology, and the arts. The Song Dynasty is credited with inventing the compass, gunpowder, and movable type printing. The Song Dynasty was also a time of great cultural and intellectual achievement, with many important works of literature, philosophy, and art produced during this time.The Ming Dynasty (1368-1644 AD) followed the YuanDynasty and is known for its contributions to Chinese art and culture. The Ming Dynasty is credited with developing the blue-and-white porcelain that is still highly prized today, as well as the construction of the Forbidden City in Beijing.The Qing Dynasty (1644-1912 AD) followed the Ming Dynasty and is the last dynasty in Chinese history. TheQing Dynasty is known for its expansionist policies, aswell as its efforts to modernize and reform Chinese society. The Qing Dynasty also had extensive trade with European powers, which led to the Opium Wars and the eventual downfall of the dynasty.In conclusion, the dynasties of Chinese history havehad a profound impact on Chinese culture and society. Each dynasty has its own unique characteristics and contributions, and together they form a rich tapestry of Chinese history and civilization.。
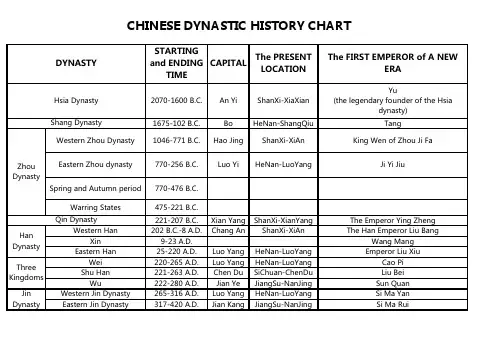
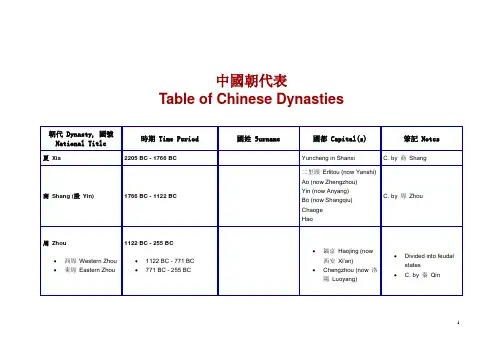
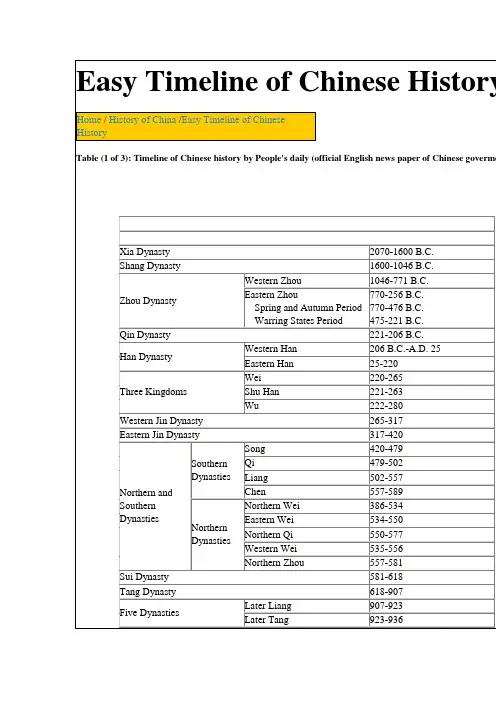
中國朝代表Table of Chinese Dynasties春秋時代Spring and Autumn Period 770 BC - 476 BCNumerous small statesunitedinto a few larger states戰國時代Warring States Period•韓Han•趙Zhao•魏Wei•楚Chu•燕Yan•齊Qi•秦Qin 475 BC - 221 BC•until 230 BC•< 403 BC - 228 BC•until 225 BC•until 223 BC•until 222 BC•until 221 BC•until 206 BC••••••••••Daliang (開封Kaifeng)••薊Ji (now 北京Beijing)••• C. by 秦Qin• C. by 秦Qin• C. by 秦Qin• C. by 秦Qin• C. by 秦Qin• C. by 秦Qin•O. by 漢Han秦Qin221 BC - 206 BC 嬴Ying 咸陽Xianyang O. by 漢Han漢Han•西漢Western Han•新Xin(interregnum)•東漢Eastern Han 206 BC - AD 220•206 BC - AD 9•AD 9 - AD 25•AD 25 - AD 220•劉Liu•王Wang•劉Liu•長安Chang'an(now 西安Xi'an)•長安Chang'an(now 西安Xi'an)•洛陽Luoyang許昌Xuchang•O. by 新Xin•O. by 東漢EasternHan•O. by 魏WeiDynasties Period inthe South(Two of which arethe 東晉EasternJinand 吳Wu, seeabove)o劉宋LiuSongo南齊Southern Qio南梁SouthernLiango南陳SouthernChen•北朝NorthernDynastieso北魏Northern(Later) Weio420 - 479o479 - 502o502 - 557o557 - 589•386 - 581o386 - 534o534 - 550o535 - 556o550 - 577o557 - 581•304 - 439o304 - 329o304 - 347o319 - 350o324 - 376o337 - 370oooo•ooooo•oooooo建康Jiankang(now 南京Nanjing)o建康Jiankang(now 南京Nanjing)o建康Jiankang(now 南京Nanjing)o建康Jiankang(now 南京Nanjing)•o平城Pingcheng(now 大同Datong),386 - 493oooo•oooo C. by 北周N. Zhouo O. by 隋Sui•oooo東魏Eastern Weio西魏WesternWeio北齊Northern Qio北周NorthernZhou•五胡十六國Sixteen Kingdoms byFive Clans ofBarbarianso前趙FormerZhaoo成漢ChengHano後趙LaterZhaoo前涼o351 - 394o384 - 417o384 - 409o385 - 431o386 - 403o397 - 414o398 - 410o400 - 420o401 - 439o407 - 431o409 - 436ooooooooooo洛陽Luoyang,493 -534/535o鄴Yeo長安Chang'an(now 西安Xi'an)o鄴Yeo長安Chang'an(now 西安Xi'an)•o長安Chang'an(now 西安Xi'an)oooooooooooooooFormerLiango前燕Former Yan o前秦Former Qin o後秦LaterQino後燕LaterYano西秦Western Qin o後涼LaterLiango南涼SouthernLiango南燕SouthernYano西涼WesternLiango北涼NorthernLiang o武威Wuwei o長安Chang'an(now 西安Xi'an)o長安Chang'an(now 西安Xi'an)oooo武威Wuwei o樂都Ledu oo敦煌Dunhuang o武威Wuwei ooo夏Xia o北燕NorthernYan隋Sui581 - 618 楊Yang 長安Chang'an (now 西安Xi'an)O. by 唐Tang唐Tang618 - 907 李Li 長安Chang'an (now 西安Xi'an)O. by 後梁Later Liang五代十國Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms•五代Five Dynastiesin the Northo後梁LaterLiango後唐LaterTango後晉LaterJino後漢LaterHano後周Later 907 - 960•907 - 960o907 - 923o923 - 936o936 - 946/947o947 - 950/951o951 - 960•902 - 978o902 - 937o937 - 975/976o924/925 - 963•ooooo•ooo•o汴京Bianjing(now 開封Kaifeng)o洛陽Luoyango汴京Bianjing(now 開封Kaifeng)o汴京Bianjing•o O. by 後唐Later Tango O. by 後晉Later Jino O. by 後漢Later Hano O. by 後周Later Zhouo O. by 宋SongZhou•十國Ten Kingdoms in the Southo吳Wuo南唐SouthernTango南平SouthernPing (荊南Jingnan)o楚Chuo前蜀Former Shuo後蜀LaterShuo閺Mino北漢NorthernHano南漢SouthernHan o927 - 951o907 - 925o934 - 965o909 - 945/946o951 - 979o917 - 971o907 - 978ooooooo(now 開封Kaifeng)o汴京Bianjing(now 開封Kaifeng)•o江都Jiangdu(now 揚州Yangzhou)o南昌Nanchango江陵Jiangling(now 荊州Jingzhou)o長沙Changshao成都Chengduo成都Chengdu•oo S. to 宋Songoooooooo S. to 宋Songo吳越WuYue o福州Fuzhouoo興王Xingwang(now 廣州Guangzhou) o杭州Hangzhou宋Song•北宋Northern Song •南宋SouthernSong•遼Liao (契丹Khitan)•西夏Western Xia(Tangut)•金Jin (女真Juchen) 960 - 1279•960 - 1127•1127 - 1279•916 - 1125•1038 - 1227•1115 - 1234•趙Zhao•趙Zhao•耶luu4 Yeluu•李Li•完顏Wanyan•汴京Bianjing (now開封Kaifeng)•臨安Lin'an (now 杭州Hangzhou)•燕京Yanjing (now北京Beijing)•Ningxia (nowYinchuan)•中都Zhongdu (now北京Beijing),11?? - 1214開封Kaifeng, 1214•Def. by 金Jin,moved south• C. by 蒙Mongols• C. by 金Jin• C. by 蒙Mongols• D. i. from 遼Liao,c. by 蒙Mongols中華民國Republic of China (ROC)•北京Beijinggovernment•Sun Yat-sen's 廣州Canton government •國民政府(大陸)Nationalistgovernment(mainland)•中華蘇維埃共和國Chinese SovietRepublic•汪精衛WangJingwei's puppetgovernment•滿州國Manchukuo •台灣Taiwan 1912 - present•1912 - 19??•1917? - 192?•1928 - 1949•1931 - 1934•1940 - 1945?•1931 - 1945•Dec 8, 1949 - presentN/A•北京Beijing•廣州Guangzhou•南京Nanjing, 1928- 1937重親Chongqing,1937 - 1945南京Nanjing, 1945- 1949•瑞金Ruijin•南京Nanjing•新京Xinjing (now長春Changchun)•台北Taipei, Dec 8,1949 - present(provisional)••rival govt•國民黨KMT,D. by 中共Communists,moved to 台灣Taiwan•Defeated by 國民黨KMT•日本Japanese-supported•日本Japanese-supported•R. by 日本Japan in1945中華人民共和國People's Republic of China (PRC) Oct 1, 1949 - present N/A 北京Beijing None中国历史朝代表中国历史朝代表夏:约前2071-约前1600 商:约前1600-约前1046 周:西周:前11世纪-前771 东周:前770-前771春秋:前770-前256战国:前475-前221秦:前221-前206汉:西汉:前206-公元23东汉:25-220三国:魏:220-265蜀:221-263吴:222-280晋:西晋:265-316东晋:317-420十六国:304-439南北朝:南朝:宋:420-479 齐:479-502梁:502-557陈:557-589北朝:北魏:386-534东魏:534-550北齐:550-557西魏:535-557北周:557-581隋:581-618唐:618-907五代十国:后梁:907-923 后唐:923-936后晋:936-946后汉:947-950后周:951-960十国:902-979宋:北宋:960-1127南宋:1127-1279辽:907-1125西夏:1038-1227金:1115-1234元:1279-1368明:1368-1644清:1644-1911中国历史朝代表。

中国历史朝代英语作文Chinese History Dynasties。
China, a country with a long history, has undergone numerous dynasties and empires throughout its history. Each dynasty has its unique characteristics and achievements, leaving a profound impact on Chinese culture and society.In this essay, we will briefly introduce the major Chinese dynasties.The first dynasty in Chinese history is the Xia Dynasty, which existed from 2100 BC to 1600 BC. The Xia Dynasty wasa primitive society, and its rulers were mainly tribal leaders. The Xia Dynasty was succeeded by the Shang Dynasty, which lasted from 1600 BC to 1046 BC. The Shang Dynasty was the first dynasty to have written records, and it is known for its bronze culture.After the Shang Dynasty, the Zhou Dynasty was established in 1046 BC. The Zhou Dynasty was divided intotwo periods, the Western Zhou Dynasty (1046 BC-771 BC) and the Eastern Zhou Dynasty (771 BC-256 BC). The Eastern Zhou Dynasty was further divided into the Spring and Autumn Period (770 BC-476 BC) and the Warring States Period (475 BC-221 BC). During the Warring States Period, the famous philosopher Confucius lived and taught, and his philosophy of Confucianism has had a profound impact on Chinese culture.In 221 BC, the Qin Dynasty was established, and thefirst emperor of China, Qin Shi Huang, unified China and standardized the writing system, weights and measures, and currency. The Qin Dynasty was followed by the Han Dynasty, which lasted from 206 BC to 220 AD. The Han Dynasty is known for its strong central government and the Silk Road, which connected China with the West.After the Han Dynasty, China was divided into the Three Kingdoms Period (220-280 AD), the Jin Dynasty (265-420 AD), the Southern and Northern Dynasties (420-589 AD), and the Sui Dynasty (581-618 AD). In 618 AD, the Tang Dynasty was established, which is considered a golden age in Chinesehistory. The Tang Dynasty was known for its prosperity, cultural achievements, and the spread of Buddhism in China.The Tang Dynasty was followed by the Song Dynasty (960-1279 AD), which was divided into the Northern Song Dynasty (960-1127 AD) and the Southern Song Dynasty (1127-1279 AD). The Song Dynasty is known for its achievements in science, technology, and literature.After the Song Dynasty, China was ruled by the Yuan Dynasty (1271-1368 AD), which was established by the Mongols, and the Ming Dynasty (1368-1644 AD), which was established by the Han Chinese. The Ming Dynasty is known for its achievements in art, literature, and architecture.Finally, in 1644 AD, the Qing Dynasty was established, which was the last dynasty in Chinese history. The Qing Dynasty was ruled by the Manchus, and it lasted until 1912 when the Republic of China was established.In conclusion, the Chinese dynasties have played a significant role in shaping Chinese history and culture.Each dynasty has its unique characteristics and achievements, leaving a profound impact on Chinese society.。

关于介绍朝代的英语作文The Qin Dynasty was the first imperial dynasty of China, known for its strict legalism and centralized rule. It was founded by Qin Shi Huang, who unified China andstandardized measurements, currency, and writing systems. The dynasty was short-lived but left a lasting impact on Chinese history.The Han Dynasty followed the Qin Dynasty and is considered a golden age in Chinese history. It was knownfor its advancements in art, literature, and technology, as well as its establishment of the Silk Road trade route. The Han Dynasty also saw the rise of Confucianism as the dominant philosophy in China.The Tang Dynasty is often referred to as the "goldenage of China," known for its flourishing economy, art, and culture. It was a time of great prosperity and innovation, with advancements in poetry, painting, and music. The Tang Dynasty also saw the expansion of China's territory andinfluence in Asia.The Song Dynasty followed the Tang Dynasty and is known for its achievements in science, technology, and commerce.It was a time of great intellectual and cultural growth,with advancements in printing, papermaking, and agriculture. The Song Dynasty also saw the development of Neo-Confucianism as the dominant ideology in China.The Ming Dynasty is known for its restoration of Chinese culture and traditions after years of foreign rule. It was a time of great artistic and architectural achievements, with the construction of the Forbidden City and the Great Wall of China. The Ming Dynasty also saw the voyages of Zheng He, which expanded China's influence inthe Indian Ocean.The Qing Dynasty was the last imperial dynasty of China, known for its expansion of territory and cultural exchange with the West. It was a time of great political and social change, with the introduction of Western ideas and technologies. The Qing Dynasty ended with the XinhaiRevolution in 1911, marking the end of imperial rule in China.。
王朝英语复数王朝英语复数(The Plural of Dynasty in English)王朝英语复数指的是在英语中表达“王朝”这一概念时,其复数形式的用法。
在英语中,复数形式的使用是根据单词的规则和语法来决定的。
对于“王朝”这一词汇,它通常是一个可数名词,因此可以有复数形式。
在英语中,表示“王朝”的词汇可以使用两种方式:一种是直接在“dynasty”的后面加上复数形式的“s”,即“dynasties”;另一种是将“dynasty”转化为复数形式的“dynasties”。
例如,在描述中国历史中的几个著名王朝时,我们可以使用这两种表达方式:1. The Ming and Qing dynasties ruled China for several centuries.(明朝和清朝统治了中国几个世纪。
)2. The Ming and Qing dynasty ruled China for several centuries.(明王朝和清王朝统治了中国几个世纪。
)这两种表达方式在语法上都是正确的,但在使用时要根据具体语境和口语风格来选择。
在学术写作或正式场合中,使用第一种表达方式更为常见,因为它更加简洁和直接。
然而,如果你希望在口语交流中更加详细地表达,第二种表达方式更为合适。
需要注意的是,虽然“dynasty”的复数形式是“dynasties”,但它并不意味着有多个“王朝”同时存在。
相反,它指的是不同的历史时期中的不同王朝。
每个王朝都是独立的,拥有自己的统治者和特定的历史背景。
总之,王朝英语复数是根据语法规则来决定的,可以使用“dynasties”或者将“dynasty”转化为复数形式的“dynasties”。
在具体应用中,要根据语境和口语风格来选择合适的表达方式。