英语语法 动词时态和语态 详解
- 格式:doc
- 大小:285.00 KB
- 文档页数:22

掌握英语语法中的时态和语态时态和语态是英语语法中两个非常重要的概念。
掌握好时态和语态的用法,对于英语学习者来说至关重要。
本文将详细介绍英语语法中的时态和语态,并提供一些例子以帮助读者更好地理解和掌握。
一、时态时态主要表示动作或状态发生的时间。
英语中常用的时态包括一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时等。
下面将逐一介绍各个时态的用法和例子。
1. 一般现在时:表达经常、习惯性的动作或状态。
例句:I brush my teeth every morning.(我每天早上刷牙。
)2. 一般过去时:表达过去发生的动作或状态。
例句:He watched a movie last night.(他昨晚看了一部电影。
)3. 一般将来时:表达将来要发生的动作或状态。
例句:She will visit her grandparents next week.(下周她将去看望她的祖父母。
)除了以上的三个基本时态,英语还有一些其他时态,如进行时态、完成时态等。
这些时态用于表达不同的语境和含义,在实际运用中需要根据具体情况进行选择。
二、语态语态表示主语与动作或状态之间的关系。
英语语态主要分为主动语态和被动语态。
下面将介绍主动语态和被动语态的定义和用法。
1. 主动语态:主动语态表示主语是动作的执行者。
例句:She writes a letter.(她写信。
)2. 被动语态:被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者,而不是执行者。
例句:The letter is written by her.(这封信是她写的。
)被动语态通常由助动词be加动词的过去分词构成,而主动语态则直接使用动词的原形。
三、时态和语态的综合运用在实际语言交流中,时态和语态经常会结合起来使用。
下面将给出一些综合运用的例子,以帮助读者更好地理解和掌握。
1. The book was written by him last year.(去年这本书是他写的。
)这个句子使用了过去时态的被动语态,表示过去某个时间点的动作。

给大家推荐一个英语微信群-Empty Your Cup
英语微信群是目前学习英语最有效的方法,群里都是说英语,没有半个中文,而且规则非常严格,是一个超级不错的英语学习环境,群里有好多英语超好的超牛逼的人,还有鬼佬和外国美眉。
其实坦白说,如果自己一个人学习英语太孤独,太寂寞,没有办法坚持,好几次都会半途而废。
只要你加入到那个群里以后,自己就会每天都能在群里坚持学,坚持不停地说和练,由于是付费群,群里的成员学习氛围非常强,每天的训练度都非常猛,本来很懒惰的你一下子就被感染了,不由自主地被带动起来参与操练,不好意思偷懒,别人的刻苦学习精神会不知不觉影响你,Empty Your Cup英语微信群(进群加喂新 601332975)可以彻底治好你的拖延症,里面学员都非常友好,总是给你不断的帮助和鼓励,让你在学英语的路上重新燃起了斗志,因为每天都在运用,你的英语口语就能得到了迅猛的提升,现在可以随便给一个话题,都能用英文滔滔不绝的发表5分钟以上对这个话题的看法和观点,想提高英语口语的 可以加入进来,It really works very well.。

英语语法:动词的时态和语态语态和时态学习英语的两大基础,是构成英语句型的关键,掌握了它们就为学好英语打下了坚实的基础。
所以用时必须熟练而准确。
小编在这里整理了相关知识,快来学习学习吧!英语语法:动词的时态和语态一、一般现在时1、表示经常发生的习惯性的、现在反复出现的动作或状态,常用的时间状语有:always,usually,seldom, sometimes, every day, now and then, once a week等。
2、表示眼下或目前等现在时间所发生的动作或存在的状态,这种状态带有一定的持续性。
3、表示客观事实或普遍真理。
4、书报的标题,故事的叙述,小说、戏剧、电影等情节介绍,图片的说明等。
5、时间表、时刻表、日程表、节目单、课程表等按规定将要发生的动作,只限于go, arrive, leave, start, stay, return, begin, come等动词。
6、在时间、条件、方式、让步状语从句中,表示将来的动作。
注意:一般现在时可以用于定语从句或宾语从句中表示将来。
7、用在某些表达中,表示现在正在发生的动作或存在的状态。
Here comes the bus!How it rains!二、一般过去时1、表示在过去某一时间点发生的动作或所处的状态,与现在没有关系。
常用的时间状语有:yesterday, last night, at that time等。
2、表示在过去某一段时间里反复出现的动作或状态,与现在没有关系。
3、用used to do或would do表示过去经常或反复发生的动作。
4、有些情况发生的时间没清楚表明,但实际上是“刚才,刚刚”发生的,属于过去时间,应使用过去时态。
常见的有I didn’t know…或I forgot…等。
5、一般过去时可与today, this week, this month等时间状语连用。
三、一般将来时1、will/shall do(1)表示将来会出现的动作或状态。

⾼中英语语法必备之谓语动词的时态和语态详解⾼中英语动词的时态语态详解在英语中,句⼦不仅有时间状语说明动作发⽣的时间,其谓语动词本⾝也有形式的变化来指⽰时间,这种表明谓语动词发⽣时间的动词形式称为时态。
语态是表现主语和谓语关系的另⼀种动词形式。
⼀动词的时态⼀般说来,发⽣在现在的事情⽤现在的时态进⾏描述;发⽣在过去的事情⽤过去的时态进⾏描述;将要发⽣的事情⽤将来的时态进⾏描述。
英语中的时态共计16种,但常⽤的有11种。
(以动词do 为例)1.⼀般现在时(do/does);2.⼀般过去时(did);3.⼀般将来时( will do/ shall do);4.⼀般过去将来时( would do/should do);5.现在进⾏时( am/is/are doing);6.过去进⾏时(was/were doing);7.将来进⾏时( will/shall be doing);8.现在完成时(have/has done);9.过去完成时( had done);10.将来完成时( will/shall have done);11.现在完成进⾏时( have/has been doing);1.⼀般现在时(1)⼀般现在时是描述现在或经常性的性质、动作或状态的时态常⽤时间状语:sometimes, often, always, usually, seldom,every day / night / week / month / year, in the morning, in the afternoon, in the evening, at night(2)表⽰经常发⽣的动作,习惯性的动作或存在的状态I usually get up at four every morning when it’s still dark.He always goes to work late,which makes his boss angry and disappointed.(3)客观真理,客观存在,科学事实及⾃然现象The sun rises in the east and sets in the west every day.The man who has never been to the Great Wall is not a real man.Trees turn green in spring. Liquid turns into gas when it is hot enough.(4)表⽰格⾔或警句中Pride goes before a fall.Knowledge is power.Practice makes perfect.(5)⼀般现在时表将来表⽰已经计划、安排好了或时间表上所安排,并且⼀定要做的事情。

中考英语必考语法详解一、动词时态1. 一般现在时 (Simple Present Tense)- 表示经常或惯性的动作:They often go to the park on weekends.- 表示客观事实和普遍真理:The earth revolves around the sun.2. 一般过去时 (Simple Past Tense)- 表示过去某个时间发生的动作:She studied English last night.- 表示过去的经常性动作:We used to live in that house.- 表示过去的状态:I was happy when I saw the gift.3. 现在进行时 (Present Continuous Tense)- 表示正在进行的动作:She is watching TV now.- 表示计划或安排的未来动作:I am meeting my friend tomorrow.4. 过去进行时 (Past Continuous Tense)- 表示过去某个时间段内正在进行的动作:He was playing football yesterday at this time.5. 现在完成时 (Present Perfect Tense)- 表示过去发生的与现在有联系的动作或状态:He has already finished his homework.6. 过去完成时 (Past Perfect Tense)- 表示过去某个时间点之前已经发生的动作或状态:She had already left when I arrived.7. 将来时 (Future Tense)- 表示将来要发生的动作或存在的状态:I will go to Beijing next week.二、被动语态1. 被动语态的构成:be + 过去分词- 主动语态:Tom eats an apple.- 被动语态:An apple is eaten by Tom.2. 被动语态的使用:- 强调动作的承受者:The book is written by a famous author.- 不知道或没有必要知道动作的执行者:The door was broken yesterday.三、情态动词1. can / could- 表示能力或许可:I can swim very well.- 表示请求或建议:Could you open the window, please?2. may / might- 表示允许或可能:You may go home now.3. must- 表示必须或肯定:She must finish her assignment by tomorrow.4. shall / should- 表示将要或应该:We should keep the classroom clean.四、倒装句1. 把助动词或情态动词提前,主语放在动词之后:- Never have I seen such a beautiful sunset.- Only after he left did I realize my mistake.2. 用于表示地点、方向、时间等状语提前:- At the top of the mountain stands a little cottage.- In front of the house is a beautiful garden.五、定语从句1. 定语从句用来修饰一个名词或代词,用以给出更多的信息。
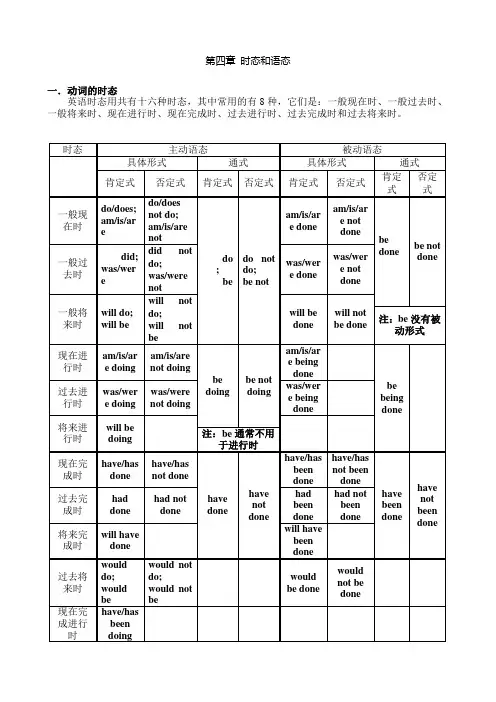
第四章时态和语态一.动词的时态英语时态用共有十六种时态,其中常用的有8种,它们是:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、现在完成时、过去进行时、过去完成时和过去将来时。
一. 一般现在时.1.构成. be动词:am is are ; 其他动词用动词原形,当主语是第三人称单数时要在谓语动词后加“s”,其变化规则与名词变复数一致。
2.用法. 1). 经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。
如usually, always, often, seldom, never, every...,eg. I leave home for school at 7 every morning.I don’t leave home for school at 7 every morning.Do I leave home for school at 7 every morning?He usually gets up early.He doesn’t usually get up early.Does he usually get up early?2) 客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。
eg. The earth moves around the sun.The earth doesn’t move around the sun 否定句Does the earth move around the sun? 疑问句Shanghai lies in the east of China.Shanghai doesn’t lie in the east of China 否定句Does Shanghai lie in the east of China? 疑问句Water boils at 100 centigrade degrees.3) 表示格言或警句中eg. Pride goes before a fall.注意. 此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。

英语语法动词的时态和语态如何表达兴趣和态度动词的时态和语态在表达兴趣和态度方面扮演着重要的角色。
时态用于表示动作发生的时间,而语态则涉及动作的执行者和承受者之间的关系。
下面我将详细解释时态和语态在表达兴趣和态度方面的应用。
1. 时态的表达:-现在时态(Present Tense):用于表达对现在情况的兴趣和态度。
例如:- I love playing the piano.(我喜欢弹钢琴。
)- She enjoys reading books.(她喜欢阅读书籍。
)-过去时态(Past Tense):用于表达对过去事件的兴趣和态度。
例如:- He was excited about the trip.(他对这次旅行感到兴奋。
)- They were disappointed with the result.(他们对结果感到失望。
)-将来时态(Future Tense):用于表达对将来事件的兴趣和态度。
例如:- We are looking forward to the party.(我们期待着这次聚会。
)- She will be thrilled to meet her favorite singer.(她将会很激动地见到她最喜欢的歌手。
)2. 语态的表达:-主动语态(Active Voice):用于表达主体对动作的积极态度和兴趣。
例如:- They enjoy playing soccer.(他们喜欢踢足球。
)- He loves cooking.(他喜欢做饭。
)-被动语态(Passive Voice):用于表达对动作的被动态度和兴趣。
例如:- The book was written by a famous author.(这本书是由一位著名作家写的。
)- The cake was made by my mom.(这个蛋糕是我妈妈做的。
)需要注意的是,时态和语态的选择不仅仅取决于兴趣和态度,还受到句子的语境和意义的影响。

高中英语语法(时态和语态)一.动词的时态时态是谓语动词所表示的动作或情况发生时间的各种形式。
英语动词有16种时态,但是常见的只有九种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、过去将来时、现在完成进行时。
(一)一般现在时(do / does)1. 具体用法1)表示经常性或习惯性动作We always care for each other and help each other. 我们总是互相关心互相帮助。
He goes to school every day.2)表示现在的特征或状态He is very happy.Do you si ng? ----A little.3)表示普遍真理Light travels faster than sound. 光速比声速快。
Actions speak louder tha n words. 行动胜过言语。
*常与一般现在时态连用的词或短语主要有:often, usually, sometimes, every day,every morning/afternoon, on Sundays/weekends 等等。
I ofte n go to the cin ema on Sun days. 我经常星期天去看电影。
He goes to work early every day. 他每天上班很早。
(二)一般过去时(did )(1)表示过去某一特定时间所发生的、可完成的动作或状态,常与表示确切过去时间的词、短语或从句连用。
例如:We went to the pictures last ni ght and saw a very in teresti ng film.(2)表示过去习惯性动作。
例如:He always went to class last.I used to do my homework in the library.(三)一般将来时(will / shall do)1)表示将来打算进行或期待发生的动作或状态。

英语语法动词的时态和语态如何表达原因和结果动词的时态和语态在表达原因和结果方面也扮演着重要的角色。
时态用于表示动作的时间,而语态则涉及动作的执行者和承受者之间的关系。
下面我将详细解释时态和语态在表达原因和结果方面的应用。
1. 时态的表达:-现在时态(Present Tense):用于表达原因和结果的现实性和普遍性。
例如:- The road is wet because it rained.(路面潮湿是因为下雨了。
)(原因)- He is tired because he worked all day.(他很累是因为整天工作。
)(结果)-过去时态(Past Tense):用于表达过去事件的原因和结果。
例如:- She missed the bus because she woke up late.(她错过了公交车是因为起床晚了。
)(原因)- They were happy because they won the game.(他们很高兴是因为赢了比赛。
)(结果)-将来时态(Future Tense):用于表达将来事件的原因和结果。
例如:- We will cancel the picnic if it rains.(如果下雨,我们将取消野餐。
)(原因)- She will be late for the meeting if she doesn't leave now.(如果她现在不走,她将会迟到会议。
)(结果)2. 语态的表达:-主动语态(Active Voice):用于表达动作的原因和结果。
例如:- He ate too much, so he feels sick now.(他吃得太多,所以现在他感觉不舒服。
)(原因)- They practiced a lot, and as a result, they won the competition.(他们练习了很多,结果他们赢得了比赛。

英语中的动词时态和语态的变化动词时态和语态是英语语法中的重要概念,它们用于表达动作的时间和动作的主体。
正确运用动词时态和语态可以使语言更加准确和流畅。
本文将探讨英语中动词时态和语态的变化。
一、动词时态的变化1.一般现在时(Simple Present Tense)一般现在时用于表示经常性的动作、习惯或真理等。
它的基本结构是主语 + 动词原形。
例如:- I eat breakfast every morning.(我每天早上吃早餐。
)- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.(水在100摄氏度时沸腾。
)2.一般过去时(Simple Past Tense)一般过去时用于表示过去发生的动作或状态。
它的基本结构是主语 + 动词过去式。
例如:- She studied English last night.(她昨晚学习了英语。
)- They went to the park yesterday.(他们昨天去了公园。
)3.一般将来时(Simple Future Tense)一般将来时用于表示将来发生的动作或状态。
它的基本结构是主语 + will + 动词原形。
例如:- I will visit my grandparents next week.(下周我将去看望我的祖父母。
)- They will have a party on Saturday.(他们将在星期六举办一个派对。
)4.现在进行时(Present Continuous Tense)现在进行时用于表示现在正在进行的动作。
它的基本结构是主语 + am/is/are + 动词-ing形式。
例如:- She is studying for the exam.(她正在为考试而学习。
)- They are playing soccer in the park.(他们正在公园里踢足球。
)5.过去进行时(Past Continuous Tense)过去进行时用于表示过去某个时间正在进行的动作。

英语语法中的动词时态和语态动词时态和语态是英语语法中非常重要的概念。
时态表示动作发生的时间,而语态则表示动作的主动与被动关系。
掌握好动词时态和语态的使用,可以帮助我们更准确地表达自己的意思,提高英语写作和口语表达的能力。
一、动词时态1. 现在时态现在时态用来表示现在正在进行的动作或状态。
例如:I am writing an article.(我正在写一篇文章。
)2. 过去时态过去时态用来表示过去发生的动作或状态。
例如:She studied English last night.(昨晚她学习了英语。
)3. 将来时态将来时态用来表示将来要发生的动作或状态。
例如:We will go to the beach tomorrow.(我们明天要去海滩。
)4. 现在完成时态现在完成时态用来表示过去发生的动作对现在产生的影响或结果。
例如:I have finished my homework.(我已经完成了作业。
)5. 过去完成时态过去完成时态用来表示过去某一时间点之前已经完成的动作。
例如:She had already left when I arrived.(当我到达时,她已经离开了。
)6. 将来完成时态将来完成时态用来表示将来某一时间点之前将会完成的动作。
例如:By theend of this month, I will have graduated from university.(到本月底,我将已经从大学毕业了。
)二、动词语态1. 主动语态主动语态表示主语是动作的执行者。
例如:He wrote a letter.(他写了一封信。
)2. 被动语态被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者。
例如:The letter was written by him.(这封信是他写的。
)动词的时态和语态的正确使用对于表达准确的意思至关重要。
下面是一些使用动词时态和语态的注意事项:1. 时态的一致性在一篇文章或一句话中,时态应该保持一致,不要随意变换时态,以免造成混淆。
第 12 章动词时态和语态【基础知识·归纳】一、动词的时态动词主要表示动作,其次表示状态。
动 作和状态的发生有一定的时间和表现方式, 一 般 现在 过去 将来 一般现在时 do 一般过去时 did 一般将来时 will do 过去将来时 would do 进 行 现在进行时 is doing 过去进行时 was doing 将来进行时 will be doing 过去将来进行时 would be doing 这就是英语中动词的时态。
英语动词的时态 主要由动词的不同形式来表示。
英语动词的 时态有十六种,现在以 do 为例展示如下: 完 成 现在完成时 have done 过去完成时 had done 将来完成时 will have done 过去将来完成时 would have done 完成进行 现在完成进行时 have been doing 过去完成进行时 had been doing 将来完成进行时 will have been doing 过去将来完成进行时 would have been doing过去将来在这 16 种时态中,其中有 8 种时态是 最重要的,也是用得最多的,它们是一般现 在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、过去将来 时、 现在进行时、 过去进行时、 现在完成时、 过去完成时、 ,其余的时态相对用得较少。
本章重点介绍 8 种基本时态的用法, 同时也 简单介绍另外 8 种时态的用法。
1. 一般现在时 一般现在时除主语是第三人称单数时 谓语动词要加 s 或 es 外,一律用动词原形。
其疑问句和否定句要借助助动词 do 或 does 来实现(be 和 have 除外) 。
(1) 一般现在时表现在 ① 表示现在经常性或习惯性的动作, 常与表 示频度的时间状语 every day, usually, always, often, sometimes, on Sunday 等连用。
高中英语语法:动词的时态与语态知识点We have meals three times a day.我们一日吃三餐。
(现在的习惯)He is always ready to help others.他总是乐于助人。
(现在的状态)When I was a boy, I often went to play in that park.我小时候常去那个公园玩。
(过去的习惯)1.一般现在时(1)一般现在时的构成一般现在时主要用动词的原形表示,如果主语为第三人称单数,则一般在动词原形后加s或一般现在时除了可以表示现在的经常性、习惯性动作或存在的状态外,还可表示:①客观真理、科学事实及自然现象。
此用法即使出现在过去语境中,也用一般现在时。
The sun rises in the east.太阳从东方升起。
②用于here, there开头的倒装句中,一般现在时表示现在正在发生的动作或存在的状态。
There goes the bell.铃响了。
Here comes the bus.公共汽车来了。
2.一般过去时(1)一般过去时的构成(2)一般过去时的用法一般过去时除了可以表示过去经常性、习惯性的动作或存在的状态外,还有以下用法:①want, hope, think, intend等动词的一般过去时往往表示“过去原……”之意。
I thought he was an honest man.我原以为他是个老实人。
He didn't intend to hurt you.他本来没打算伤害你。
②wonder的一般过去时有时也可表示现在的行为,但口气要比用一般现在时更加委婉、客气。
I wondered if you could do me a favour.我不知道你能否帮我一个忙。
③used to+动词原形,表示过去的习惯性动作而现在已经不再发生了。
We used to spend our vacation in the mountains.我们以前常常在山里度假。
1.动词时态(tense )时态---就是一种表示时间和状态的主动词形式。
1.1 现在进行时(present continuous/present progressive )1.1.1 时间:现在(present )--:动作发生的时间是现在而非过去,一般也就是说话时的时间。
1.1.2 状态:正在进行(continuous/progressive )。
指该动作在过去某个时间点开始,直到现在(说话时)仍然继续,在一定的时间范围内, 还将继续下去。
1.只有具有持续性概念的动作动词(action verb ), 才可能有进行时态, 而表示状态或瞬间动作的动词, 不能使用进行时态。
它们是不可持续的,往往具有状态动词的特征, 而不强调动作, 此类词一般常见的如下:表感情意识状态:like/dislike/love/hate/prefer/want/need/know/realize/suppose/mean/understand/believe/remember感官意识状态:see/ hear/ smell/ taste表所属关系: 有…,包含:belong / contain/consist/depend/seem/have当think 表示“认为”的意思时,同样也不用进行时态2. 即使是动作动词,同样也有动作持续时间长短的问题。
有的动作持续时间短,所以动作一般就发生在说话时由于这种动作只是从宏观上看具有持续性,但其间一定是有间断的,说话时,该动作不一定发生,只是说话的时间点包含在该动作的持续时间内。
1.1.3 构造: 助动词be , 主动词verb+ ing ,参见“词类概述2.3.4”.陈述句: subject + be + verb-ing否定句:subject + be+ not+ verb-ing一般疑问句:be + subject + verb-ing :?复杂(特殊)疑问句:question word+ subject + verb-ing :1.1.4 用途:1.用于表述正在发生的短动作,即说话时正在发生。
英语语法动词时态和语态的用法一、动词时态的用法动词时态是用来表示动作或状态发生的时间的形式。
英语中常用的动词时态有以下几种:1. 现在时态(Present Tense)现在时态表示现在的动作或状态。
它分为简单现在时、进行现在时和完成现在时三种形式。
简单现在时:用于表示经常性或普遍性的动作或状态。
e.g. She sings beautifully.她唱歌得很好听。
进行现在时:用于表示现在正在进行的动作或状态。
e.g. They are watching TV.他们正在看电视。
完成现在时:用于表示发生在过去并与现在有关的动作或状态。
e.g. I have finished my homework.我已经完成了作业。
2. 过去时态(Past Tense)过去时态表示过去的动作或状态,它同样分为简单过去时、进行过去时和完成过去时三种形式。
简单过去时:用于表示过去某个具体时间发生的动作或状态。
e.g. He went to the park yesterday.他昨天去了公园。
进行过去时:用于表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作。
e.g. They were playing soccer at that time.他们那时正在踢足球。
完成过去时:用于表示在过去某一时间之前已经完成的动作或状态。
e.g. She had already left when I arrived.我到达时她已经离开了。
3. 将来时态(Future Tense)将来时态表示将来的动作或状态,它同样分为简单将来时、进行将来时和完成将来时三种形式。
简单将来时:用于表示将来某个具体时间将要发生的动作或状态。
e.g. We will go shopping tomorrow.我们明天将去购物。
进行将来时:用于表示将来某一时刻将正在进行的动作。
e.g. They will be eating dinner at 7 o'clock tomorrow.他们明天7点将在吃晚餐。
动词时态语态用法解析→ 动词时态语态解释动词时态语态解释动词时态和语态是英语中非常重要的语法概念,它们决定了一个动作或状态在时间和主语角度上的表达方式。
本文将对动词时态和语态的用法进行解析,并提供一些重要的注意事项。
时态(Tense)英语中的动词时态用来表示一个动作或状态发生的时间。
最常用的时态包括以下几种:1. 现在时(Simple Present Tense):用于表示经常性的动作、客观事实或一般真理。
例如:"I eat dinner every day."2. 过去时(Simple Past Tense):用于表示过去发生的动作或状态。
例如:"She studied hard for the exam."3. 将来时(Simple Future Tense):用于表示将来发生的动作或状态。
例如:"They will go on a trip next week."4. 现在进行时(Present Continuous Tense):用于表示现在正在进行的动作或状态。
例如:"He is reading a book right now."5. 过去进行时(Past Continuous Tense):用于表示过去某个时间点正在进行的动作或状态。
例如:"We were playing soccer yesterday afternoon."6. 将来进行时(Future Continuous Tense):用于表示将来某个时间点正在进行的动作或状态。
例如:"I will be studying all night tomorrow."7. 现在完成时(Present Perfect Tense):用于表示过去某个时间点开始并一直延续到现在的动作或状态。
例如:"She has lived in this city for ten years."8. 过去完成时(Past Perfect Tense):用于表示过去某个时间点之前的动作或状态。
第 12 章动词时态和语态【基础知识·归纳】一、动词的时态动词主要表示动作,其次表示状态。
动 作和状态的发生有一定的时间和表现方式, 一 般 现在 过去 将来 一般现在时 do 一般过去时 did 一般将来时 will do 过去将来时 would do 进 行 现在进行时 is doing 过去进行时 was doing 将来进行时 will be doing 过去将来进行时 would be doing 这就是英语中动词的时态。
英语动词的时态 主要由动词的不同形式来表示。
英语动词的 时态有十六种,现在以 do 为例展示如下: 完 成 现在完成时 have done 过去完成时 had done 将来完成时 will have done 过去将来完成时 would have done 完成进行 现在完成进行时 have been doing 过去完成进行时 had been doing 将来完成进行时 will have been doing 过去将来完成进行时 would have been doing过去将来在这 16 种时态中,其中有 8 种时态是 最重要的,也是用得最多的,它们是一般现 在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、过去将来 时、 现在进行时、 过去进行时、 现在完成时、 过去完成时、 ,其余的时态相对用得较少。
本章重点介绍 8 种基本时态的用法, 同时也 简单介绍另外 8 种时态的用法。
1. 一般现在时 一般现在时除主语是第三人称单数时 谓语动词要加 s 或 es 外,一律用动词原形。
其疑问句和否定句要借助助动词 do 或 does 来实现(be 和 have 除外) 。
(1) 一般现在时表现在 ① 表示现在经常性或习惯性的动作, 常与表 示频度的时间状语 every day, usually, always, often, sometimes, on Sunday 等连用。
I go to school at 6 every morning. 每天早上我七点去上学。
He often goes to the cinema. 他经常去看电影。
② 表示现在(或经常性)的情况或状态 Mother is ill. 母亲病了。
We need a lot of money. 我们需要一大笔钱。
③ 表示现在的能力、特征、职业等 He sings well. 他唱歌唱得好。
Mr. Smith teaches French. 史密斯先生教法语。
④ 表示客观真理、 科学事实、 格言以及不受 时间限制的客观存在。
Summer follows spring. 春去夏来。
Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。
The earth turns around the sun. 地球绕着太阳转。
【特别提示】 此种用法即使出现在过去的语境中, 仍用一般现在时。
I learned that the earth goes around the sun when I was in primary school. 我在小学就学过地球是围绕太阳转的。
⑤ 表示现在正在发生的动作或存在的状态 Here comes the bus! 公共汽车来了! There goes the bell. 铃响了。
How hard it snows! 雪下得真大! (2) 一般现在时表将来 ① 当主句为将来时态或表示将来意义时, 时 间、条件、方式及让步状语从句必须用一般 现在时表将来。
I’ll write to her when I have time. 我有空会给她写信。
Turn off the lights before you leave. 走前关灯。
If we hurry, we may catch the bus. 如果我们赶紧走我们可能赶得上公共汽车。
Tell me in case you get into difficulty. 遇到困难请告诉我。
② 在 the more…the more …( 越 „„ 越„„) 句型中,前者通常用一般现在时代 替一般将来时, 因为前者相当于条件状语从 句。
The harder you study, the better results you will get. 你学习越努力,成绩就会越好。
③ 在 make sure(弄清楚),make certain(弄清 楚), take care(注意, 当心), be careful(注意, 当心),mind(注意),watch(注意)后的宾语从 句的谓语动词用一般现在时代替一般将来 时。
Make certain what time the train goes. 务必弄清火车发车时间。
Take care that it does not occur again. 注意别再发生这样的事。
Watch that the baby doesn’t go near the heater. 注意别让宝宝接近加热器。
【特别提示】 在 it doesn’t matter, I don’t care, I don’t mind 等结构(以及类似结构)后的名词性从 句也通常用一般现在表示将来意义。
It doesn’t matter where we go on holiday. 我们去哪儿度假都行。
Does it matter who goes first? 谁先去这有关系吗? I don’t care whether we win or lose. 我不在乎我们是赢还是输。
④ 表示按计划或时间表将要发生的动作, 通 常有表示将来的时间状语。
The plane takes off at 11:30 and arrives in Shanghai at l:20. 飞机十一点半起飞, 一点二 十分抵达上海。
【特别提示】 只限于少数动词能这样用,如 begin, start, end, finish, stop, go, come, leave, sail, arrive, return, close, open 等。
3. 一般现在时表过去 (1) 故事性读物中戏剧性的描绘(用一般现 在时可给人以历历在目的印象) 。
They threatened to shoot, but the marchers could not be stopped. The unarmed workerspress on and on. 他们威胁着要开枪,却没法挡住游行者,手 无寸铁的工人们不断向前逼进。
The crowd swarms around the gateway, excitement grows as the pop star appears. 人群聚集在大门口,当那位通俗歌星出现 时,众人情绪高涨。
(2) 用在报纸标题或小说章节的标题中 Earthquake kills over 100,000 people 地震使 10 万人丧生 PEACE TALKS FAIL 和谈失败 Ⅶ Go to Bristol 第七章 去布里斯托尔途中 【特别提示】 情节已经发生而用一般现在时,可 使标题生动。
2. 一般过去时 一般过去时用动词的过去式构成, 即一 般是在动词原形后加 ed。
(1) 一般过去时表示过去 ① 表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态, 常与 yesterday, last week, in 1989, just now, a moment ago, the other day 等连用。
He bought the computer five years ago. 这电脑是他五年前买的。
It was then a small fishing village. 那时它只是一个小渔村。
② 表示过去经常性或习惯性的动作 We often played together when we were children. 我们小时候常在一起玩。
【特别提示】 表过去习惯性的动词,也可用 used to 或 would。
He used to go to work by bus. 他过去常乘公共汽车去上班。
(2) 一般过去时表示现在 ① 在宾语从句中, 由于时态呼应的关系, 可 用一般过去时表示现在。
I didn’t know you were here. 我不知道你在 这儿。
(were 实际上指现在) I didn’t know you were so busy.我没想到你 这么忙。
(were 实际上指现在) ② 用于某些特殊结构中表示现在It’s time we started. 我们该动身了。
I wish I knew his name. 要是我知道他的名字就好了。
I’d rather you lived closer to us. 我希望你能住得离我们近点。
If I had the money now I’d buy a car. 假若我现在有钱,我就买辆小汽车。
【特别提示】 有些动词的过去时,如:expect, hope, intend, plan, wanted 等一般过去时,后接 不定式的完成时;或它们的过去完成时接 不定式的一般式,都可表示过去未曾实现 的意图、打算或希望。
I hoped to have been invited to his wedding party. /I had hoped to be invited to his wedding ceremony. 我本希望他来邀请我参加他的婚礼。
I intended to have joined their games./I had intended to join their games. 我本打算参加他们的比赛。
3. 一般将来时 (1) 一般将来时的基本用法 一般将来时的基本用法是表示单纯的 将来事实,由“will / shall + 动词原形”构成 (英语英语中第一人称可用 shall,美国英语 中一律都用 will)。
常用时间副词 tomorrow, soon 或短语 next year / week / month, in a few days, in the future, sometime 等做状语。
I think she will pass the exam. 我想他考试会及格的。
We shall have a lot of rain next month. 下个月将下很多雨。
(2) 表示将来时间的常见方法 英语中除了“will /shall+动词原形”表示 将来时态外,还可以有以下多种方法: ① be going to+动词原形 主要表示已经计划或安排好了的事情, 也可表示有迹象表明肯定要发生的事情。