交感神经与副交感神经PPT课件
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:5.55 MB
- 文档页数:11

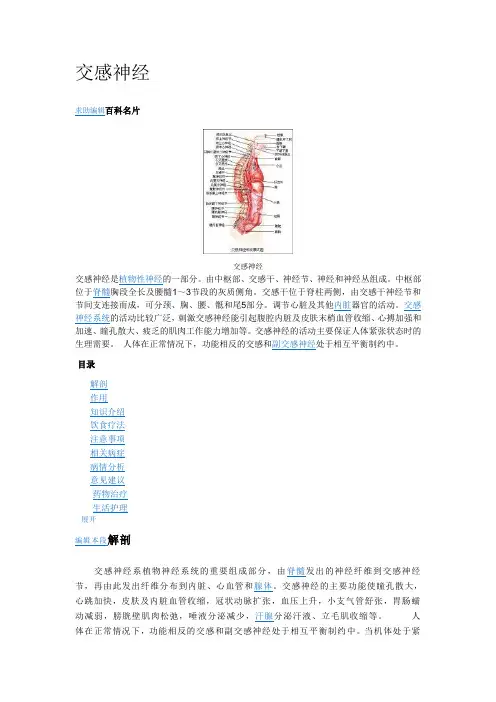
交感神经求助编辑百科名片交感神经交感神经是植物性神经的一部分。
由中枢部、交感干、神经节、神经和神经丛组成。
中枢部位于脊髓胸段全长及腰髓1~3节段的灰质侧角。
交感干位于脊柱两侧,由交感干神经节和节间支连接而成,可分颈、胸、腰、骶和尾5部分。
调节心脏及其他内脏器官的活动。
交感神经系统的活动比较广泛,刺激交感神经能引起腹腔内脏及皮肤末梢血管收缩、心搏加强和加速、瞳孔散大、疲乏的肌肉工作能力增加等。
交感神经的活动主要保证人体紧张状态时的生理需要。
人体在正常情况下,功能相反的交感和副交感神经处于相互平衡制约中。
目录解剖作用知识介绍饮食疗法注意事项相关病症病情分析意见建议药物治疗生活护理展开编辑本段解剖交感神经系植物神经系统的重要组成部分,由脊髓发出的神经纤维到交感神经节,再由此发出纤维分布到内脏、心血管和腺体。
交感神经的主要功能使瞳孔散大,心跳加快,皮肤及内脏血管收缩,冠状动脉扩张,血压上升,小支气管舒张,胃肠蠕动减弱,膀胱壁肌肉松弛,唾液分泌减少,汗腺分泌汗液、立毛肌收缩等。
人体在正常情况下,功能相反的交感和副交感神经处于相互平衡制约中。
当机体处于紧编辑本段作用1.对循环器官交感神经对心脏活动具有兴奋作用,能加速心搏频率和加速心搏力量。
对血管,主要是促进微动脉收缩,从而增加血流外周阻力,提高动脉血压。
但实际情况比较复杂,必须区别对待。
人体多数器官的血管只接受交感神经支配,交感神经对腹腔脏器的血管和皮肤的血管均具有显著的收缩作用;对骨骼肌的血管,既有缩血管的交感神经支配,又有舒血管的交感神经支配,对冠状循环的血管,交感神经的直接作用是使血管收缩,但其间接作用则是使血管舒张。
对外生殖器官血管则起收缩作用。
脑和肺的血管,虽也接受交感神经支配,但作用很弱。
2.对消化器官交感神经对胃肠运动主要具有抑制作用,即降低胃肠平滑肌的紧张性及胃肠蠕动的频率,并减弱其蠕动的力量;但当胃肠平滑肌紧张性太低或活动很弱时,交感神经也可使其活动增强。


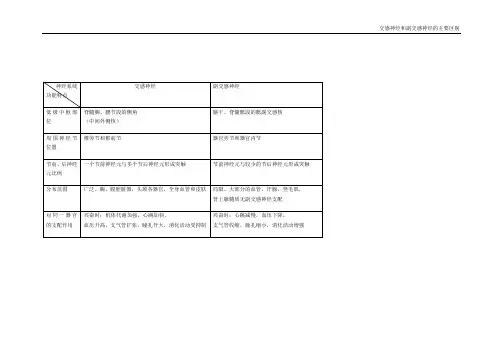
一、交感神经交感神经:其和副交感神经共同组成自主神经系统。
大部分的器官受到两者的共同支配,大部分情况下,两者相互拮抗(例外:唾液分泌),因而可以实现对该器官的精细调节,实现内环境的稳态。
中文名称:交感神经可分:颈、胸、腰、骶位于:脊柱两侧组成:中枢部、交感干、神经节、神经基本简介:交感神经:是植物神经系统的重要组成部分,由脊髓发出的神经纤维到交感神经节,再由此发出纤维分布到内脏、心血管和腺体。
交感神经的主要功能使瞳孔散大,心跳加快,皮肤及内脏血管收缩,冠状动脉扩张,血压上升,小支气管舒张,胃肠蠕动减弱,膀胱壁肌肉松弛,唾液分泌减少,汗腺分泌汗液、立毛肌收缩等。
人体在正常情况下,功能相反的交感和副交感神经处于相互平衡制约中。
当机体处于紧张活动状态时,交感神经活动起着主要作用。
交感神经的初级节前神经元位于脊髓的胸腰部。
部分的交感神经功能由高级中枢,如下丘脑,脑干和网状结构调节,这些部位会向交感神经的节前神经元发送神经冲动。
初级神经元会到脊柱旁的神经节、椎旁神经节换元,其使用的神经递质为(和副交感神经一样)乙酰胆碱。
这些神经节互连成干,被称为“交感神经干”。
节后神经元继续传递信号到目标器官,并使用神经递质去甲肾上腺素。
但一些交感神经纤维没有换元就离开交感神经干,到达主动脉的椎前神经节,或者到达受支配器官的器官旁神经节。
主要特性植物性神经(交感神经和副交感神经)植物性神经是能够自动调整与个人意志无关的脏器的作用和功能的神经,在植物性神经中,可分为交感神经和副交感神经。
交感神经系植物神经系统的重要组成部分,由脊髓发出的神经纤维到交感神经节,再由此发出纤维分布到内脏、心血管和腺体。
交感神经的主要功能使瞳孔散大,心跳加快,皮肤及内脏血管收缩,冠状动脉扩张,血压上升,小支气管舒张,胃肠蠕动减弱,膀胱壁肌肉松弛,唾液分泌减少,汗腺分泌汗液、立毛肌收缩等。
当机体处于紧张活动状态时,交感神经活动起着主要作用。
副交感神经系统的作用与交感神经作用相反,它虽不如交感神经系统具有明显的一致性,但也有相当关系。

交感神经和副交感神经发表时间:2004-11-6 16:31:43 点击 740 次一、交感神经系统的功能交感神经系统所支配的器官非常广泛,包括循环器官、呼吸器官、消化器官、内分泌器官、泌尿器官、生殖器官和眼球等,此外,对糖代谢和骨骼肌也有作用。
1.对循环器官交感神经对心脏活动具有兴奋作用,能加速心搏频率和加速心搏力量。
对血管,主要是促进微动脉收缩,从而增加血流外周阻力,提高动脉血压。
但实际情况比较复杂,必须区别对待。
人体多数器官的血管只接受交感神经支配,交感神经对腹腔脏器的血管和皮肤的血管均具有显著的收缩作用;对骨骼肌的血管,既有缩血管的交感神经支配,又有舒血管的交感神经支配,对冠状循环的血管,交感神经的直接作用是使血管收缩,但其间接作用则是使血管舒张。
对外生殖器官血管则起收缩作用。
脑和肺的血管,虽也接受交感神经支配,但作用很弱。
2.对消化器官交感神经对胃肠运动主要具有抑制作用,即降低胃肠平滑肌的紧张性及胃肠蠕动的频率,并减弱其蠕动的力量;但当胃肠平滑肌紧张性太低或活动很弱时,交感神经也可使其活动增强。
对唾液腺能促进其分必粘稠的唾液。
3.对呼吸器官和汗腺交感神经对细支气管平滑肌具有抑制作用,可使细支气管扩张,有利于通气。
汗腺只接受交感神经支配,交感神经兴奋引起汗腺分泌。
4.对眼球平滑肌交感神经使虹膜辐射肌收缩,引起瞳孔扩大。
5.对内分泌腺肾上腺髓质受交感神经节前纤维支配。
当交感神经兴奋时,肾上腺素与去甲肾上腺素的分泌增加。
由于肾上腺髓质激素的作用大部分与交感神经系统的作用是一致的,因此,在生理学上称之为交感肾上腺髓质系统。
6.对泌尿生殖器官交感神经的作用是抑制膀胱壁逼尿肌的活动和促进内括约肌的收缩,因而阻止排尿。
对生殖器官,交感神经能促进怀孕子宫的收缩,但使未孕子宫舒张。
交感神经还能促进男性精囊腺和射精管平滑肌收缩,从而引起射精动作。
7.对糖代谢交感神经能直接作用于肝细胞,促进肝糖原分解,从而使血糖升高。

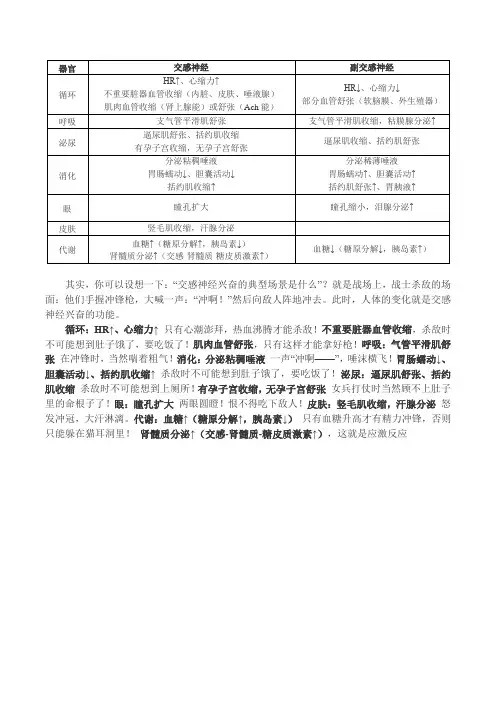
其实,你可以设想一下:“交感神经兴奋的典型场景是什么”?就是战场上,战士杀敌的场面:他们手握冲锋枪,大喊一声:“冲啊!”然后向敌人阵地冲去。
此时,人体的变化就是交感神经兴奋的功能。
循环:HR↑、心缩力↑只有心潮澎拜,热血沸腾才能杀敌!不重要脏器血管收缩,杀敌时不可能想到肚子饿了,要吃饭了!肌肉血管舒张,只有这样才能拿好枪!呼吸:气管平滑肌舒张在冲锋时,当然喘着粗气!消化:分泌粘稠唾液一声“冲啊——”,唾沫横飞!胃肠蠕动↓、胆囊活动↓、括约肌收缩↑杀敌时不可能想到肚子饿了,要吃饭了!泌尿:逼尿肌舒张、括约肌收缩杀敌时不可能想到上厕所!有孕子宫收缩,无孕子宫舒张女兵打仗时当然顾不上肚子里的命根子了!眼:瞳孔扩大两眼圆瞪!恨不得吃下敌人!皮肤:竖毛肌收缩,汗腺分泌怒发冲冠,大汗淋漓。
代谢:血糖↑(糖原分解↑,胰岛素↓)只有血糖升高才有精力冲锋,否则只能躲在猫耳洞里!肾髓质分泌↑(交感-肾髓质-糖皮质激素↑),这就是应激反应。

神经节-交感与副交感神经系统神经节神经节是功能相同的神经元细胞体在中枢以外的周围部位集合而成的结节状构造。
表面包有一层结缔组织膜,其中含血管、神经和脂肪细胞。
被膜和周围神经的外膜、神经束膜连在一起,并深入神经节内形成神经节中的网状支架。
由节内神经细胞发出的纤维分布到身体有关部分,称节后纤维。
按生理和形态的不同,神经节可分为脑脊神经节(感觉性神经节)和植物性神经节两类。
脑脊神经节在功能上属于感觉神经元,在形态上属于假单极或双极神经元。
植物性神经节包括交感和副交感神经节。
交感神经节位于脊柱两旁。
副交感神经节位于所支配器官的附近或器官壁内。
在神经节内,节前神经元的轴突与节后神经元组成突触。
神经节通过神经纤维与脑、脊髓相联系。
交感神经系统的作用主要有如下几方面:(1)对循环系统的作用:皮肤和横纹肌以及腹腔脏器的血管只接受交感神经的支配,冠状循环以及脑循环的血管都同时接受交感和副交感两种神经纤维,因此,刺激交感神经一般可使周围动脉收缩,而在去除交感神经后可使周围动脉扩张。
治疗周围血管疾患,施行交感神经切除术,即以此为依据。
(2)对消化系统的作用:交感神经对胃肠道的作用主要是抑制,使蠕动减慢,但当胃肠紧张性太低或不活动时,交感神经冲动则可以提高并兴奋之。
对消化腺的分泌功能,交感神经的作用甚不一致,对胰和唾液腺虽可促进其分泌,但因此部的血管收缩而分泌不明显,对胃液则阻止其分泌。
(3)对呼吸系统的作用:交感神经兴奋时,对小支气管主要为抑制其平滑肌的活动,因而使小支气管扩大,空气出入畅通。
气喘患者在注射麻黄素等制剂后得到暂时缓解,即因此故。
(4)对泌尿系统的作用:交感神经的作用能使膀胱壁松弛,内括约肌收缩,因而阻止小便排出。
此外,在生殖系统中对女性子宫平滑肌,对男性射精管和精囊的平滑肌等都有调节作用。
副交感神经系植物性神经系统的一部分。
由脑干和脊髓发出神经纤维到器官旁或器官内的副交感神经节,再由此发出纤维分布到平滑肌、心肌和腺体,调节内脏器官的活动。

交感神经和副交感神经(Sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves)Sympathetic nervous system1., the sympathetic nervous system of the circulatory organ can stimulate the heart activity, accelerate the heartbeat frequency and accelerate the heartbeat strength. To the blood vessel, it mainly promotes the contraction of the arteriole, thus increasing the peripheral resistance of the blood flow and increasing the arterial blood pressure. But the actual situation is quite complex and must be treated differently. Most human organs only accept vascular sympathetic innervation of sympathetic nerve on the abdominal viscera, blood vessels and skin blood vessels have significant effect on contraction; skeletal muscle blood vessels, both sympathetic vasoconstrictor, and sympathetic vasodilator, on the coronary circulation of the blood vessels, the direct effect of sympathetic nerve is vasoconstriction, but its indirect effect is vasodilatation. The vessels of external genital organs take the action of contraction. The blood vessels of the brain and lungs, although sympathetic, are weak.2. of the digestive organs of sympathetic nerve has inhibitory effect on gastrointestinal motility, which reduce the tension and the frequency of gastrointestinal motility of gastrointestinal smooth muscle, and weaken the creep strength; but when gastrointestinal smooth muscle tension is too low or the activity is very weak, sympathetic nerve activity can also cause the increase. Yes, the salivary glands promote the secretion of sticky saliva.3., the respiratory organs and sweat glands sympathetic nerve can inhibit the smooth muscle of bronchioles, which can dilatebronchioles and help ventilation. The sweat gland receives sympathetic innervation only, sympathetic nerve excitation causes sweat gland secretion.4., the sympathetic nerve of the eyeball smooth the iris radiation muscle and causes the pupil to expand.5. pairs of endocrine glands and adrenal medulla are innervated by sympathetic preganglionic fibers. When the sympathetic nerve is excited, the secretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine increases. Because the effect of the adrenal medulla hormone is largely consistent with the sympathetic nervous system, it is physiologically referred to as the sympathetic adrenal medulla system.6., the function of sympathetic nerve in urogenital organs is to inhibit the activity of detrusor and promote the contraction of internal sphincter, so as to prevent urination. To the genital organs, the sympathetic nerve can promote the contraction of the pregnant uterus, but make the nonpregnant uterus relax. Sympathetic nerve also can promote male seminal vesicle and ejaculation tube smooth muscle contractive, cause ejaculation motion thereby.7., the glucose metabolism and sympathetic nerve can directly act on the liver cells, and promote the decomposition of liver glycogen, thereby increasing blood sugar. But in whole, the effect of ascending blood glucose of sympathetic nerve is mainly realized by the increase of adrenaline secretion.Parasympathetic nervous systemThe main function of parasympathetic nerve is to reduce the pupil, slow heartbeat, skin and internal vascular relaxation, small bronchial contraction, gastrointestinal motility enhanced, sphincter relaxation, saliva secretion increased.The parasympathetic nervous system acts contrary to the sympathetic nervous system, although it is not as consistent as the sympathetic nervous system, but it is also related. Its fibers are not distributed in the limbs, while the sweat glands, vertical rectus, adrenal glands, thyroid, uterus and so on, have parasympathetic nerve distribution.Parasympathetic nervous system can keep the body in a quiet state of physiological balance, and its role in three aspects: first, to promote the activities of the gastrointestinal tract, digestive gland secretion, promote excretion of feces and urine, to maintain the body's energy. Reduce the pupil to reduce the stimulation and promote the production of liver glycogen, so as to save energy. Slow heartbeat, lower blood pressure, reduce the size of the bronchus, to save unnecessary consumption, and assist in reproductive activities, such as the expansion of the genital vessels and the increase of the secretion of sex organs.The difference between parasympathetic and sympathetic nervesThe difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves are: central position is different, the lower center of sympathetic nerve in the spinal cord to the first thoracic segment third lumbar section of the side angle, the lower center of parasympathetic nerve in the brainstem and spinal cord ofthe sacrum.The location of the surrounding ganglia is different, and the preganglionic fibers in the sympathetic nerve, along with the anterior root of the spinal nerve and the spinal nerve, emerge out of the spinal nerve,Sympathetic trunk ganglia. The part of neurons in the section, the sympathetic postganglionic fibers leave return spinal nerve and spinal nerve distribution with limbs and body wall of blood vessels, sweat and arrectores pilorum. Most preganglionic fibers change neurons in the sympathetic trunk, and the postganglionic fibers no longer join the spinal nerve, forming a nerve plexus around the arteries, with the arteries distributed to the head, neck and chest, and organs and glands of the abdominal cavity. The parasympathetic preganglionic fibers in a self central neurons in parasympathetic ganglia, postganglionic fibers distributed to smooth muscle, myocardium and glands, parasympathetic ganglia are generally in organs or organs near the wall, short postganglionic fiber.The effect of the two on the same organ is different. When the sympathetic nerve is excited, the abdominal visceral and peripheral vessels contract, the heart rate increases; the bronchial smooth muscle expands; the gastrointestinal movement and the stomach secretion are suppressed; the metabolism hyperfunction; the pupil disperses big and so on. Parasympathetic nervous stimulation, cardiac slowing down; bronchial smooth muscle contraction; gastrointestinal movement to strengthen the secretion of digestive juices; such as shrinking the pupil.The general visceral organs have both sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation, and the two nerves are antagonistic to the same organ, but in the whole, the activities of the two nerves are antagonistic, unified and coordinated. The sympathetic activity is relatively wide, relatively limited parasympathetic activity, when the body is in a state of calm, parasympathetic nerve excitement is dominant, is conducive to digestion and absorption of energy and nutrition, is conducive to the protection of the body. When strenuous exercise or adverse environment, sympathetic activities strengthen, mobilize the potential of many organs of the body, improve the ability to adapt to cope with the rapid changes in the environment, and maintain the relative stability of the internal environment.。