大学英语语法14——宾语从句和同位语从句共23页文档
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:3.39 MB
- 文档页数:23


名词性从句(宾语从句、表语从句、主语从句、同位语从句)讲解高考英语语法总复习复合句:主句+从句意思上来讲主句是主要的。
但是从句才是我们学习的重点。
从句有各种各样的变化,从句要作不同的成分的,主句与从句间要加不同的连接词,可能有时候还要倒置。
例句:America's new plan to buy up toxic assets will not work unless banks mark assets to levels which buyers find attractive.America's new plan to buy up toxic assets will not work(这一部分为主句)。
unless从句1前的连接词。
banks mark assets to levels 从句1。
表示条件的从句。
如果...which从句2前的连接词。
buyers find attractive 从句2。
修饰前面levels的定语从句。
(一)名词性从句(当成名词来用的句子)包括:1、宾语从句(最重要);2、表语从句(最不重要);3、主语从句(一般重要);4、同位语从句(一般重要)。
4种从句的写法一样,不一样的是位置不一样。
先看:1、宾语从句(最重要)1)含义:是一个作宾语的句子,位置是把它放到主句里作主句的宾语。
例句:The fossil record shows that many species have endured for millions of years.全句是一个主句,但是that many species have endured for millions of years作了该主句的宾语。
即that many species have endured for millions of years为宾语从句。
2)宾语从句的写法:先写两简单句,其中一个简单句作主句时省略掉宾语,然后将另一个简单句接到作主句的宾语位置当宾语即可,但是要注意连接词的使用。

大学英语语法知识点总结大学英语的学习中,语法是构建语言表达准确性和逻辑性的基石。
掌握好语法知识,不仅有助于我们在各类英语考试中取得好成绩,更能让我们在实际的交流和写作中准确清晰地表达自己的想法。
以下是对大学英语语法的一些重要知识点的总结。
一、动词时态动词时态是英语语法中的核心部分,它反映了动作发生的时间。
1、一般现在时表示经常发生的动作、习惯性的行为、客观事实或真理。
例如:“The earth revolves s around the sun”(地球绕着太阳转。
)其构成是主语+动词原形(当主语是第三人称单数时,动词要加“s”或“es”)2、一般过去时用于描述过去发生的动作或存在的状态。
比如:“I played basketball yesterday”(我昨天打篮球了。
)构成是主语+动词的过去式3、现在进行时表示正在进行的动作。
像:“He is reading a book now”(他正在读书。
)结构为:主语+ be 动词(am/is/are)+动词的现在分词4、过去进行时强调过去某个时刻正在进行的动作。
例如:“I was doing myho mework at 8 o'clock last night”(昨晚八点我正在做作业。
)其形式为:主语+ was/were +动词的现在分词5、现在完成时表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或者过去的动作一直持续到现在。
例如:“I have finished my work”(我已经完成了工作。
)由“主语+ have/has +动词的过去分词”构成6、过去完成时表示过去某一时间或动作之前已经发生或完成的动作。
例如:“By the end of last year, I had learned 5000 words”(到去年年底,我已经学了5000 个单词。
)结构为:主语+ had +动词的过去分词7、一般将来时用以表达将来要发生的动作或存在的状态。

宾语从句与同位语从句的区别宾语从句和同位语从句是英语语法中常见的两种从句结构,它们在使用和功能上有着一些区别。
本文将详细介绍宾语从句和同位语从句的定义、用法和区别,并通过实例加以说明。
一、宾语从句的定义和用法宾语从句是指在一个句子中作为主句的宾语部分的从句结构。
宾语从句通常由引导词如that, whether, if等引导,位于主句中的动词或介词后面,起到补充说明动作或状态的作用。
宾语从句一般有陈述句、一般疑问句、特殊疑问句等几种形式。
下面是一些宾语从句的例子:1. I know (that) he is a doctor.(陈述句)2. Do you know if/whether he is a doctor?(一般疑问句)3. Could you tell me where the library is?(特殊疑问句)从上面的例子中,我们可以看出宾语从句作为主句的宾语,对动词know和tell提供了具体的信息。
二、同位语从句的定义和用法同位语从句是在一个句子中作为主句的名词或代词的同位语部分的从句结构。
同位语从句一般由that引导,用来对先行词进行解释、说明或补充。
同位语从句位于主句中的名词或代词后面,用来进一步说明主句中的名词或代词。
下面是一些同位语从句的例子:1. The fact that he passed the exam pleased his parents.(同位语从句解释了fact这个名词)2. My belief is that everyone should be treated equally.(同位语从句解释了belief这个名词)3. Her idea is that we should travel together.(同位语从句解释了idea这个名词)从上面的例子中,我们可以看出同位语从句解释或说明了先行词所表示的名词或代词。
三、1. 位置不同:宾语从句位于主句的动词或介词后,作为主句的宾语部分。

同位语从句和宾语从句1.听到2008年在北京举行奥运会的消息时,人们欣喜若狂。
(news that)2.没人否认台湾自古以来就是中国的一部分是这个事实(fact)3.越来越多的人开始认识到这样一个事实:暴力电视节目对儿童的成长有不良影响。
(realize)4.毫无疑问这位士兵将因勇敢而被授予一枚金质奖章(award)5.新加坡政府实行居者有其屋的政策,而且非常成功6.有可能还会发生一场大地震。
(possibility)7.我们对这位作家一无所知,只晓得他出身贫苦。
(except)8.他向我保证他会把所有书都还给我的(assure)9.你应该就刚才的所作所为向在场的人道歉(apologize)10.学生们逐渐认识到友谊胜过金钱,患难中的朋友才是真正的朋友1.我们在医院一直照顾take care of的老太太死了.The old lady whom we had taken care of in the hospital last year died.2.你想娶marry的姑娘昨天偷了我的钱包。
The girl whom you want to marry stole your wallet yesterday.3.孙老师写的书是世界上最好的书。
The book that Mt. Sun wrote is the best book in the world.4.你喜欢女孩就是我喜欢的女孩。
The girl who you like is the girl who I like.5.昨天被我家的狗咬的人bite今天又被你家狗咬了。
The man who was bit by my dog was bit by my dog today again.6.你知道他打算娶reason你的原因吗?Do you know the reason for which he is going to marry you?Do you know the reason why he is going to marry you?7.我讨厌hate我住过的那个旅馆hotel。


同位语从句和宾语从句的区别同位语从句和宾语从句是英语语法中两个重要的句子结构。
虽然它们都可以用来承担从句的语法功能,但它们在句子结构上有一些区别。
本文将详细介绍同位语从句和宾语从句的区别。
一、同位语从句同位语从句是指在句子中作为同位语的从句。
同位语从句通常用来解释或补充前面的名词或代词。
同位语从句以及它所解释的名词或代词通常是同一个句子的成分,共同构成一个整体的句子结构。
首先,同位语从句通常由连词"that"引导。
"that"在同位语从句中往往可以省略。
同位语从句可以出现在名词的后面,对名词进行解释或者重新表达。
例如:1. 我的问题是,你去哪里了?2. 我听到的消息是,她考上了大学。
在这些例子中,同位语从句分别解释了"问题"和"消息"。
另外,同位语从句通常是不可改变的固定表达,不会改变句子的词序,并且它们一般不会出现感叹句或疑问句中。
接下来,我们将介绍宾语从句。
二、宾语从句宾语从句是指在句子中作为宾语的从句。
宾语从句通常用来承担动词或介词后的宾语,并完成宾语从句所陈述的内容。
宾语从句和主句之间存在着一种从属关系。
与同位语从句不同的是,宾语从句并不像同位语从句那样与名词或代词构成一个整体的句子结构。
宾语从句的结构可以相对独立,它本身就是一个完整的句子。
宾语从句一般由连词"that"引导,但在口语中通常可以省略。
此外,宾语从句的位置可以出现在及物动词或介词之后,并且动词的选择通常与宾语从句的内容和意义相对应。
例如:1. 她知道你在做什么。
2. 他们问我是否同意他们的计划。
在这些例子中,宾语从句分别作为动词"知道"和"问"的宾语,完成了相应的意思表达。
综上所述,同位语从句和宾语从句虽然在语法功能上有相似之处,但在句子结构上存在一些区别。
同位语从句通常用来解释或补充名词,其结构与名词相互依存;而宾语从句则作为动词或介词的宾语,其结构相对独立。

宾语从句与同位语从句的句子用法在英语语法中,宾语从句和同位语从句都是从句的一种形式。
它们在句子中担任不同的语法角色,分别为主句的宾语和同位语,具有不同的用法和结构。
本文将探讨宾语从句和同位语从句的句子用法,帮助读者更好地理解和运用。
一、宾语从句宾语从句是作为主句的宾语的从句,通常由连接词引导,连接词包括:whether/if(是否)、that、wh-词(如what、who、when、where、why、how)等。
下面是一些例句:1. I don't know whether/if he will come to the party.(我不知道他是否会来参加派对。
)2. She said that she was tired and wanted to go home.(她说她累了,想回家。
)3. The teacher asked the students what they had learned from the lesson.(老师问学生们从这节课上学到了什么。
)4. Can you tell me where the nearest bookstore is?(你能告诉我最近的书店在哪里吗?)在宾语从句中,连接词的选择要根据具体情况进行判断。
是否使用that通常没有含义上的差异,只是在口语中常省略。
在某些情况下,如表示选择、疑问或否定的宾语从句中,通常使用whether/if。
而引导词wh-词用于提问特定的信息。
二、同位语从句同位语从句是用于解释或说明名词或代词含义的从句。
它通常紧跟在名词或代词之后,具有进一步解释或限定的作用。
同位语从句常由that引导,但也可以由wh-词引导。
下面是一些例句:1. The fact that she passed the exam made her parents proud.(她通过考试的事实让她的父母感到骄傲。
)2. The question whether we should go on a vacation is still being discussed.(我们是否应该去度假的问题仍在讨论中。

从句小结从句总述:从句有主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句、同位语从句、定语从句和状语从句6类;由于主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句及同位语从句在句子的功用相当于名词,故而这4种从句又通称名词性从句;1.主语从句Subject Clause:用作主语的从句叫主语从句;引导主语从句的关联词有从属连词、疑问代词、疑问副词、缩合连接代词、缩合连接副词等;2.表语从句Predicative Clause:用作表语的从句叫表语从句;引导表语从句的关联词与引导主语从句的关联词大都一样;3.宾语从句Object Clause:在句子中起宾语作用的从句叫做宾语从句.宾语从句分为三类:动词的宾语从句,介词的宾语从句和形容词的宾语从句.4. 同位语从句Appositive Clause:在复合句中用作同位语的从句叫同位语从句;它一般跟在某些名词后面,用以说明该名词表示的具体内容;其关联词多为that;状语从句还可以分为条件状语从句、原因状语从句、方位状语从句和时间状语从句等;宾语从句学习宾语从句要抓住三要素:时态、语序、连接词;一:时态和语序1·主句用一般现在时,从句可用任意时态;2·主句用过去时,从句用过去某个时态;3·主句用过去时,从句是真理时,只用一般现在时;语序:宾语从句只能用陈述句语序,坚决不能用疑问句语序;二:连接词①从属连词连接宾语从句的从属连词主要有that,if,whether. that引导表示陈述句的宾语从句,而if和whether引导表示“是否”的宾语从句.例句:He told that he would go to the college the next year他告诉我他下一年上大学.I don’t know if there will be a bus any more.我不知道是否还会有公交车.②连接代词连接代词主要有who, whom ,whose ,what ,whoever ,whomever ,whosever, whatever, whichever等.连接代词一般指疑问,但what, whatever除了指疑问外,也可以指陈述.例句:Do you know who has won Red Alert game你知道谁赢了这一局红警游戏吗③连接副词连接副词主要有when,where,why,how,whenever,wherever,however等.例句:He didn’t tell me when we should meet again.他没有告诉我什么时候我们能再见面.三:动词的宾语从句We all expect that they will win , for members of their team are stronger.我们都预料他们会赢,因为他们的队员更强壮.I have found out that all the tickets for the concert have been sold out.我发现这场音乐会的所有票都卖光了.make sure确保make up one’s mind下决心keep in mind牢记例句:Make sure that there are no mistakes in your papers before you turn them in.在上交试卷前确保没有任何错误.四:可运用形式宾语it代替的宾语从句①动词find,feel,consider,make,believe等后面有宾语补足语的时候,则需要用it做形式宾语而将that宾语从句后置.例句:I think it necessary that we take plenty of hot water every day .我认为每天多喝开水是有必要的.I feel it a pity that I haven’t been to the get-together.我没去聚会,感觉非常遗憾.②有些动词带宾语从句时寻要在宾语与从句前加it这类动词主要有:hate, take , owe, have, see to.例句:I hate it when they with their mouths full of food.我讨厌他们满嘴食物时说话.五:介词的宾语从句用wh-类的介词宾语从句例句:We are talking about whether we admit students into our club.我们正在讨论是否让学生加入我们的俱乐部.I know nothing about my new neighbor except that he used to work with a company.对于我的新邻居我只知道他曾在一家公司上班,其他一无所知.六:形容词的宾语从句一般来说形容词不能带宾语,更不能带宾语从句;但以下形容词除外:sure,certain,glad,please,happy,sorry,afraid,satisfied,surprised例句:I am sure I will pass the exam.我确信我会通过考试.I am sorry that I have troubled you so long.很抱歉我这么长时间在打扰你.七:if,whether在宾语从句中的区别①if和whether在作“是否”解时,引导宾语从句常放在动词know,ask,care,wonder,find out等之后,介词后一般不用if②少数动词,如:leave,put,discuss,doubt后的宾语从句常用whether.③whether后可以加or not,但是if不可以.④在不定式前只能用whether.如:I can’t decide whether to stay. 我不能决定是否留下;⑤避免歧异时,我们常用whether而不用if.八:哪些宾语从句不可以省略引导词that①当一个动词带有两个或两个以上宾语从句时,此时第一个that可以省略,第二个that不可以省略;②当宾语从句有it做其先行词时;九:宾语从句的否定转移主句的谓语动词是think,believe,imagine,suppose,consider,espect,fancy,guess等,并且主句的主语是第一人称而且为一般现在时,从句的否定词一般要转移到主句上来,其反义疑问句一般与宾语从句一致.例句:I don’t think he will come to my party.而不能说成I think he won’t come to my party.我认为他不会来我的舞会.I don’t believe that man is killed by Jim,is he我认为那个人不是Jim所杀的,是不是★如果宾语从句中有某个含有否定意义的形容词或副词,其反义疑问句要用肯定形式.例句:We find that he never listens to the teacher carefully,does he我们发现他从来不仔细听老师讲课,是不是十:宾语从句的时态和语序当主句为现在时或将来时的时候,宾语从句的时态一般不受主句的时态所影响.当主句为过去时的时候,从句只能用和过去相关的时态;例句:The reporter asked if the government would take necessary measures to put down the to-do.记者问政府是否会采取必要的措施镇压骚乱.★如果从句是一个客观真理,那么从句的时候不根据主句的时态而变化例句:The teacher said that the moon goes around the earth yesterday.老师昨天说月亮绕着地球转.★宾语从句的插入语形式例句:Who do you think the public might choose as their favorite singer this year你认为今年公众会选谁为他们最喜欢的歌手.同位语从句Appositive Clause:在复合句中用作同位语的从句叫同位语从句;它一般跟在某些名词后面,用以说明该名词表示的具体内容;其关联词多为that;一、如:I heard the news that our team had won.我听到了我们队获胜的消息;I had no idea that you were here.我不知道你在这里;二、可以跟同位语从句的名词通常有news,idea,fact,promise,question,doubt,thought,hope,message,suggestion,wor ds消息,possibility等,可展开来的抽象名词;如:I’ve come from Mr wang with a message that he won’t be able to see you this afternoon.我从王先生那里来,他让我告诉你他今天下午不能来看你了;三、英语中引导同位语从句的词通有连词that,whether,连接副词how,when,where等;根据句意决定该用哪一个;l have no idea When he will be back.我不知道他什么时候回来;定语从句Attributive Clause:用作定语的从句叫定语从句;定语从句一般皆放在被它所修饰的名代词之后,这种名代词就叫作先行词Antecedent;引导定语从句的关联词为关系代词和关系副词;关系代词在定语从句中可用作主语、宾语、定语等;关系副词在定语从句中用作状语;①引导定语从句的关联词有who, whom, whose, that, when, where, why 和which. 在非限制定语从句中, 只可用which, who, whose, where , when., 如果指代前面整个句子, 多用which.例句:The dog that/which was lost has been found.失踪的狗已经找到了;Those who are in favor of the proposal are expected to discuss it in detail after the meeting.有人认为那些对这个提案有兴趣的人最好是在会后再具体讨论它;There are many organizations whose purpose is to help the homeless.存在着许多旨在帮助无家可归者的组织;②当引导定语从句的先行词前有all, any, no, little, much, very first 等词, 或先行词前为形容词最高级所修饰时,或先行词为all, anything, nothing, something, everything 时,从句的引导词只能用that.The only thing that matters to the children is how soon they can have their holiday.孩子们唯一关心的是他们什么时候放假;These are the very points that puzzle me.真正困扰我的是这些观点;Is there anything that bothers you有什么事烦着你吗This is the best film that was ever produced by the company.这部是那个公司有史以来拍摄得最好的电影;③as 可做引导词引导定语从句, 多和such, the same 连用. 或者用在“从句比主句先发生”的情况,有“像……一样”之意;As 引导的定语从句也可修饰整个句子, 既可放在先行词后,也可放在句子开头.例句:Such people as you describe are rare nowadays.你描述的那一类人现在很少了;The boy was run over by a motor-car, as often happened in pre-liberation Shanghai.那个男孩被一辆摩托轧过去了,这种事在解放前的上海是不少见的;As is often the case, the girl forgot to bring her dictionary.正如往常一样,这个女孩又忘了带上字典;④介词+which/whom/whose从句The driver is the man from whose room she had stolen the gold watch.她就是从那个司机的房间偷了金表的;Language is a tool by means of which people communicate ideas with each other.语言就是人们用来和其他人交流的一种工具;例题:Water dissolves a part of nearly everything _______ it comes in contact.a. whereb. that c with which d as soon as⑤代/名+介词+which 从句He is needing a book, the name of which I don't know.他需要一本书,但是我不知道书名;In factories and in our daily life, there are many waste materials, all of which can he turned into useful things under certain condition.在工厂里,在我们的日常生活中都有很多垃圾,其实这些垃圾在某种情况下是可以转变为有用的东西的;同位语从句与定语从句的区别;1、同位语从句与前面的名词是同位关系,即说明它前面名词的内容;而定语从句与前面的名词是修饰与被修饰关系,即限定它前面的名词范围,或补充一些情况;如:The news that l have passed the exam is true.我通过了考试这一消息是真的;同位语从句,即从句所表达的意思就是前面名词的内容;The news that he told me just now is true.他刚才告诉我的消息是真的;定语从句,从句对前面名词起修饰限制作用,即“他告诉我的”那个消息,而不是别的消息;2、引导同位语从句的that是连词,在从句中不充当任何成份,而引导定语从句的that是关系代词,除起连接作用外,还在从句中充当主语、宾语或表语等;如:The idea that computers can recognize human voices surprises many people.计算机能够识别人的声音的想法使许多人感到惊奇;that在从句中不充当任何成份;The idea that he gave surprises many people.他提出的观点令许多人感到吃惊;that在从句中作gave的宾语;状语从句Adverbial Clause:用作状语的从句叫作状语从句;其关联词是一些从属连词;修饰主句中的动词, 形容词和副词, 通常有从属连词引导, 按其意义和作用可分为时间, 地点, 条件, 原因, 让步, 目的, 结果, 方式, 比较.等分类1. 时间状语从句:1 常见连词有after,as,before,once,since,till,notuntil,when,wheneverno matter when,while, as long as…2 no sooner…than,hardlyscarcely, barely…when: 刚做…就….No sooner had I opened the door than the telephone rang.3 还有immediately, directly, instantly, the moment, the minute, the instant, the second, every time etcI’ll tell you about it the moment you come.I got in touch with him immediately I received his letter.2. 地点状语从句: 一般用where or wherever 引导I will stand where I can see the parade clearly.Wherever they went, they were warmly welcome.3. 条件状语从句:真实条件从句:if, unless, so long as, provided that, supposing that, on condition that, in the event that, in case that etcI will not go to her party if she doesn’t invite me.I will not go to her party unless she invites me.4. 原因状语从句: 从属连词有because, as ,since, for, now, that, in that, seeing that, considering that鉴于,由于As the school regulations are written quite clearly, there is nothing more to be explained.Considering that the sweater was hard made, it was not expensive.Seeing that they are inexperienced, they are doing quite a good job.5. 让步状语从句:1: even if, though, even though, while尽管no matter what/how/which, however, whatever, whichever, however etc.He will not give up smoking even though the doctor advises him to.Whatever the consequence may be, I will be on your side.However hard she tried to explain, nobody trusted her.It has been the same result, whichever way you do it.2 由as 引起的让步从句, 语气较强烈,被强调的词须放在句首.Simple as the question may seem, it is not at all common in nature.Cold as it is, the children play outdoors.Much as I respect him, I can’t agree with him.Object as you may, I will go on with my plan.3 whether…or,不管…或…whether you be a student or a teacher, you are required to obey the regulations of the school.6. 结果状语从句: so that, so…that, such…thatHe is so humorous that we’ll never forget him.She is such a nice girl that everybody likes to make friends with her.7. 目的状语从句: so that, in order that, for fear that, lest, in caseI checked all the results time and again for fear that there should be any mistakes.Telephone us in advance in order that we might make the necessary arragements.8.方式状语从句方式状语从句通常由as, just as…so…, as if, as though引导;1 as, just as…so…引导的方式状语从句通常位于主句后,但在just as…so…结构中位于句首,这时as从句带有比喻的含义,意思是"正如…","就像",多用于正式文体,例如:Always do to the others as you would be done by.你希望人家怎样待你,你就要怎样待人;As water is to fish, so air is to man.我们离不开空气,犹如鱼儿离不开水;Just as we sweep our rooms, so we should sweep backward ideas from our minds.正如打扫房屋一样,我们也要扫除我们头脑中落后的东西;2 as if, as though两者的意义和用法相同,引出的状语从句谓语多用虚拟语气,表示与事实相反,有时也用陈述语气,表示所说情况是事实或实现的可能性较大;汉译常作"仿佛……似的","好像……似的",例如:They completely ignore these facts as if as though they never existed.他们完全忽略了这些事实,就仿佛它不存在似的;与事实相反,谓语用虚拟语气;He looks as if as though he had been hit by lighting.他那样子就像被雷击了似的;与事实相反,谓语用虚拟语气;It looks as if the weather may pick up very soon.看来天气很快就会好起来;实现的可能性较大,谓语用陈述语气;说明:as if / as though也可以引导一个分词短语、不定式短语或无动词短语,例如:He stared at me as if seeing me for first time.他目不转睛地看着我,就像第一次看见我似的;He cleared his throat as if to say something.他清了清嗓子,像要说什么似的;The waves dashed on the rocks as if in anger.波涛冲击着岩石,好像很愤怒;9. 比较状语从句:1 as…as, not so/as…asthe film was not so exciting as we expected.这部电影没有我们期待的一样精彩The history of nursing is as old as the history of man.She likes them almost as much as Paul does.2 比较级+than, so much/a lot more thanShe looks much younger than she is.The universe is a lot more complicated than you think.3 no more…than, not more…than, less…thanJack is not more frightened than Mike is. 不像马克那么害怕Tom is no more rich than Black3 the more…the moreThe farther north you go, the severer the winter is.The more I see of him, the less I like him.。

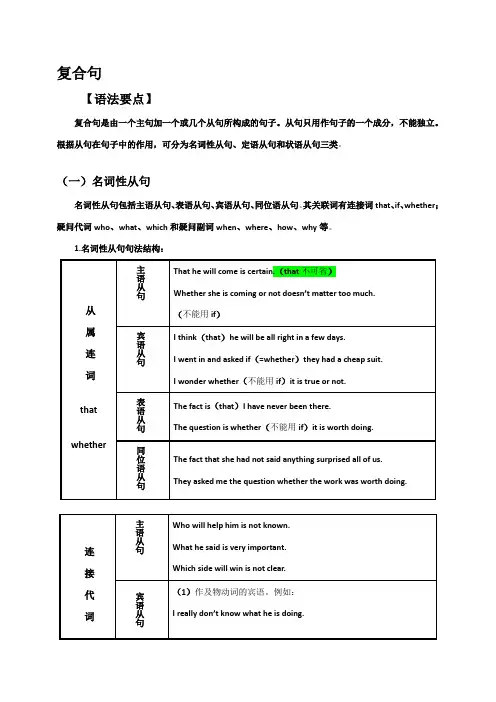
复合句【语法要点】复合句是由一个主句加一个或几个从句所构成的句子。
从句只用作句子的一个成分,不能独立。
根据从句在句子中的作用,可分为名词性从句、定语从句和状语从句三类。
(一)名词性从句名词性从句包括主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句、同位语从句。
其关联词有连接词that、if、whether;疑问代词who、what、which和疑问副词when、where、how、why等。
1.名词性从句句法结构:2.名词性从句的其它用法:1)if不能引导表语从句。
连接代词who、what、whose、which不能引导同位语从句。
2)有时as、as if/though、because也可以引导表语从句,能跟表语从句的谓语动词一般为系动词be、seem、look等。
例如:Things are not always as they seem to be.事情并不总是像表面上看来的那样。
It looks as if it were going to rain. It is because you eat too much.3)介词宾语不可以用which来引导,而要用what来引导。
例如:We can learn what we did not know. He will talk to us about what he saw in the .4)连词that引导的名词性从句除能用在except、but、in后之外很少作介词的宾语,。
其它一些介词的宾语从句如果由连词that引导,则需用it先行一步作形式宾语。
例如:He is a good student except that he is careless.You may depend on it that they will support you.5)若主句谓语动词是及物动词make、find、think、see、hear等,则把宾语从句置于宾语补足语之后,用it作形式宾语。
宾语从句英语知识点总结宾语从句的种类宾语从句可以分为名词性从句、宾语从句和同位语从句。
名词性从句包括主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句。
主语从句主语从句是指作为句子的主语的从句。
主语从句通常出现在it is/was + 从句的结构中。
如:It is important that we arrive on time.宾语从句宾语从句是指在句子中作为动词宾语的从句。
宾语从句通常出现在动词后面。
如:I know where she lives.表语从句表语从句是指在句子中作为表语的从句。
表语从句通常出现在系动词后面。
如:The important thing is that we try our best.同位语从句同位语从句是指与某个词或短语等同位的从句。
同位语从句通常出现在名词后面。
如:The fact that she passed the exam is good news.以上是名词性从句的种类。
宾语从句的引导词宾语从句的引导词有that, whether, if, why, where, when, how, who, whom, whose, what等。
不同的引导词对应着不同的宾语从句。
如:I don't know if he will come.She asked me where I was going.They wonder whether she can finish the work on time.引导宾语从句的不同引导词要根据具体情况来选用,不能随意替换使用。
宾语从句的时态宾语从句的时态要根据主句的时态来决定。
一般来说,当主句是现在时,宾语从句可以用任何时态。
如:I know that he is coming.(主句是现在时,宾语从句用进行时)I know that he has come.(主句是现在时,宾语从句用现在完成时)当主句是过去时,宾语从句的时态通常相应变化。
宾语从句与同位语从句的异同在英语语法中,宾语从句和同位语从句是两个常见的从句类型。
它们在句子结构和用法上有一些相似之处,但也存在一些明显的异同点。
本文将对宾语从句和同位语从句进行比较和总结,以便更好地理解和运用它们。
一、宾语从句宾语从句是作为主句的宾语出现的从句,通常用于表示动词后的宾语。
1. 句子结构:宾语从句一般由连接词引导,常见的连接词有:(1) 连接代词:that, whether, if等。
(2) 连接副词:how, when, where, why等。
宾语从句需要有主语和谓语,构成一个完整的句子。
2. 用法:宾语从句常用于以下情况:(1) 及物动词的宾语:例如,I know that he is a doctor.(2) 形容词的宾语:例如,I am happy that you passed the exam.(3) 名词的宾语:例如,She has no idea what to do.3. 语序:宾语从句的语序与陈述句或疑问句的语序相同,即主语在前,谓语在后。
特殊疑问句和一般疑问句在宾语从句中不需要变化。
二、同位语从句同位语从句是用来解释或补充说明先行词的从句,通常放在名词后面,起到同位语的作用。
1. 句子结构:同位语从句一般由连接词that引导,连接词that在同位语从句中没有实际的意义,仅起连接作用。
2. 用法:同位语从句常用于以下情况:(1) 说明名词的具体内容或含义:例如,The fact that he passed the exam surprised me.(2) 解释名词的性质或特点:例如,Her belief that everyone deserves equal opportunities is admirable.(3) 补充说明名词的身份或身份:例如,His claim that he is innocent is being investigated.3. 语序:同位语从句的语序通常保持与原句相同。
同位语从句和宾语从句的详细区分同位语从句和宾语从句是英语语法中两个重要的句法结构。
虽然它们都属于从句,但它们在语法功能和用法上有着明显的差异。
本文将详细区分同位语从句和宾语从句,并从语法结构、引导词、意义和用法等方面进行解析。
一、同位语从句的定义及特点同位语从句是指在名词或代词后面用以解释或说明该名词或代词的从句。
它的作用是对名词或代词进行进一步的解释、说明或补充。
同位语从句与主句之间往往存在着平行的关系。
同位语从句的引导词通常有“that”、“whether”、“if”等,它们在从句中起连接作用。
同位语从句常用于表示观点、证明、描写等方面,用以加强语气或补充信息。
例如:1. I have no idea whether he will come or not.(我不知道他是否会来。
)2. The fact that he passed the exam surprised me.(他通过了考试的事实让我吃惊。
)3. Our hope is that the new project will be successful.(我们的希望是新项目会成功。
)二、宾语从句的定义及特点宾语从句是指在句子中作动词的宾语,并且在结构上是一个完整的句子。
它的作用是接受动作的影响,表达说话人对一个事实、看法、意愿或建议等的陈述或询问。
宾语从句的引导词通常有“that”、“whether”、“if”、“what”、“who”等,根据不同的引导词,可以表达不同的含义和作用。
宾语从句常用于陈述性动词、描写性动词、感知性动词、思维性动词等后面,用以表达说话人的意向、观点、看法等。
例如:1. She didn't know what he was talking about.(她不知道他在说什么。
)2. I wonder if/whether he can come to the party.(我想知道他是否能来参加派对。
同位语从句和宾语从句的详细对比同位语从句和宾语从句是英语语法中常见的两种从句结构。
它们在句子中扮演不同的角色和功能,因此对它们进行详细的对比分析能够帮助我们更好地理解和运用。
一、同位语从句同位语从句是指在主句中作为名词的同位语的从句,用来进一步解释或说明名词的内容。
同位语从句通常使用连接词that引导,但在口语和非正式场合中常省略that。
1. 定义和功能:同位语从句用来对前面的名词进行解释、说明、或进一步补充信息。
例如:Our belief that hard work leads to success is widely accepted. (我们相信努力工作会导致成功的观念被广泛接受。
)2. 结构和特点:同位语从句常以that引导,但也可以省略。
它在句子中的位置通常紧跟在前面的名词后面。
例如:The fact that she passed the exam made us happy. (她通过了考试的事实让我们很高兴。
)3. 例句:a) My hope is that we can achieve world peace. (我希望我们能够实现世界和平。
)b) The announcement that the party is cancelled disappointed many people. (派对取消的通知让很多人感到失望。
)二、宾语从句宾语从句是指在主句中作为宾语的从句,用来充当动词或介词的宾语。
宾语从句通常使用连词that引导,但在口语和非正式场合中也可以省略。
1. 定义和功能:宾语从句用于替代主句中的宾语,起到进一步补充、说明或解释的作用。
例如:He asked me if I had finished my homework. (他问我是否完成了我的作业。
)2. 结构和特点:宾语从句以that引导时可以省略,但以其他连接词时通常不省略。
它在句子中的位置通常紧跟在主句中的动词或介词之后。
英语——名词性从句中的宾语从句和同位语从句有关知识点解说名词性从句指充当名词成分的从句,下分很多类型,是英语学习的重点,名词性从句在句子的功能相当于名词词组,能担任主语、宾语、表语、同位语、介词宾语等,因此根据它在句中不同的语法功能,名词性从句又可分别称为主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句,可以说搞懂了名词性从句,你的英语水平就极大的提升了一个level,现为大家带来关于名词性从句中的宾语从句和同位语从句有关知识点的讲解,建议家长为孩子收藏!一、宾语从句1. 引导词:宾语从句就是在复合句中用作宾语的从句。
一般说来,可用于引导主语从句的引导词也可用于引导宾语从句,如that, what, who, which, when, where, how, why, whether等。
如:We believe that he is honest. 我们相信他是诚实的。
She has got what she wanted. 她要的东西得到了。
I haven’t decided whether I should go. 我还没决定我是否会去。
I asked how he was getting on. 我问他情况怎样。
He asked when the train would get in. 他问火车什么时候进站。
He asked me where I was going. 他问我到哪儿去。
Please tell me which you like. 告诉我你喜欢哪一个。
He asked who lived next door. 他问谁住在隔壁。
She asked why he was silent. 她问他为什么一言不发。
2. if与whether:if通常不用于引导主语从句或表语从句,但可以用于引导宾语从句,与whether用法相同,常可互换。
如:I wonder if it’s large enough. 不知它是否够大。