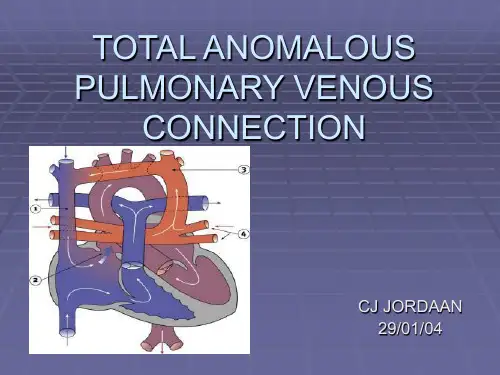
▪ Accounts for 25% of TAPVC ▪ The common pulmonary vein drains through the
diaphragm to the portal vein, ductus venosus or seldom to the IVC. ▪ Has the greatest propensity for STENOSIS:
▪ RV: Varies in size, depends on magnitude of pulmonary
blood flow, pulmonary venous stenosis, point of PV connection. (Infra cardiac connection- RV not dilated or hypertrophied)
the right atrium
▪ Infra cardiac: includes connections below the diaphragm to the
portal vein, hepatic veins, ductus venosus or IVC.
▪ Mixed: involves connections of two or more of these types; at least
one of the main lobar pulmonary veins is draining differently from the others
Each category can be further classified as obstructive or nonobstructive.
▪ This results in return of pulmonary venous blood