锁相技术译文翻译
- 格式:doc
- 大小:43.00 KB
- 文档页数:6

锁相技术译文翻译英文原名:High Speed Digital Hybrid PLL Frequency Synthesizer 译文:高速数字混合锁相环频率合成器年纪专业:08级通信工程班姓名:学号:2011年 5月2日prepare the precise synchronization of the complicated design.In 2001, H. G. Ryu proposed a simplified structure of the DDFS (direct digital frequency synthesizer)-driven PLL for the high switching speed [2].However, there is a problem that the speed of the whole system is limited by PLL.Y. Fouzar proposed a PLL frequency synthesizer of dual loop configuration using frequency-to-voltage converter (FVC) [3].It has a fast switching speed by the PD (phase detector), FVC using output signal of VCO and the proposed coarse tuning controller.However, H/W complexity is increased for the high switching speed.Also, it shows the fast switching characteristic only when the FVC works well.Another method is pre-tuning one which is called DH-PLL in this study [4].It has very high speed switching property, but H/W complexity and power consumption are increased due to digital look-up table (DLT) which is usually implemented by the ROM including the transfer characteristic ofVCO(voltage controlled oscillator).For this reason, this paper proposes a timing synchronization circuit for the rapid frequency synthesis and a very simple DLT replacement digital logic block instead of the complex ROM type DLT for high speed switching and low power consumption. Also, the requisite condition is solved in the proposed method. The fast switching operation at every the frequency synthesis process is verified by the computer circuit simulation.II.DH-PLL synthesizerAs shown in Fig.1, the open-loop synthesizer is a direct frequency synthesis type that VCO generates the desired output by the FCW (frequency control word) input from the D/A 压转换器(FVC)具有双重回路结构的锁相环频率合成器【3】。

2000门课程名称翻译大全(十五)色彩 Color色谱 Color Spectrum摄影技巧 Techniques for Photography涉外企业管理 Enterprise Administration Concerning Foreign Natio社会调查的理论与方法 Theories & Methods for Social Investigation社会调查方法 Methods for Social Investigation社会工作 Social Work社会统计分析与SYSTAT应用 Social Statistics Analysis & SYSTAT Application社会统计学 Social Statistics社会问题研究 Research on Social Problems社会心理学 Social Psychology社会学概论 Introduction to Sociololgy社会学简论 Brief Introduction to Sociology社会学理论专题 Current Issues in Theories of Socilolgy 社会学问题研究 Research on Problems of Sociology社会学研究方法 Research Methods of Sociology社会主义财政学 Finance of Socialism社会主义各国政,经体制讨论 Discussion on Political & Economic Systems in Socialism审计学 Science of Auditing生产管理 Administration of Manufacturing生产过程计算机控制 Computer Control in Manufacturing Process生产过程自动化 Water-Turbine Engine生理学 Physiology生命科学与无机化学 Life Science and Inorganic Chemistry 生物工程产品 Bio-engineering Products生物工程导论 Introduction to Bio-engineering生物化学 Biochemistry生物化学工程 Biochemical Engineering生物化学及实验 Biochemistry Experiment生物检测技术 Measurement for Biotechnique生物控制论 Biocybernetics生物流变学 Biorheology生物物理 Biophysics生物学专题 Currents Issues in Biology生物医学超声学 Biomedical Supersonics失效分析 Invalidation Analysis诗歌美学 Aesthetics of Poetry时间序列 Time Sequence实变函数 Functions of Real Variable实验分析 Experimental Analysis实验力学 Experimental Mechanics实验力学基础 Basis of Experimental Mechanics实验流体 Experimental Flowing Object实验应力分析 Analysis of Experimental Stress世界近现代经济史 Modern History of World Economy世界近现代史 Modern History of the World世界文化史 History of World Culture世界政治经济与国际关系 World Politic Ecomony&International Relationship适应控制系统 Adaption Control System市场学 Science of Market市场研究 Research on Market市场预测 Market Predicting输入输出设计原理 Principle of Input and Output Designing 书法 Handwriting数据结构 Data Structure数据库概论 Introduction to Database数据库基础 Basis of Database数据库技术 Technique of Database数据库设计与分析 Design & Analysis of Database数据库系统原理 Principles of Database System数据库应用 Application of Database数据库原理及应用 Principle & Application of Database数控机床 Digit Control Machine Tool数控技术 Digit Control Technique数理方程 Mathematical Equations数理方程积分变换 Integral Transmission of Mathematical Equation数理方程与特殊函数 Equations of Mathmatical Physics & Special Functions数理逻辑 Mathematical Logic数理统计 Mathematical statistics数量经济 Quantity Economics数学分析 Mathematical Analysis数学规划 Mathematical Planning数学模型 Mathematical Modening数学物理方法 Method of Mathematical Physics数值电路 Digital Circuit数值分析 Numerical Analysis数值计算 Digital Computation数字测量技术 Digital Measuring Technique数字测量实验技术 Experimental Technique of Digital Measuring数字测试实验技术 Experimental Technique of Digital Testing数字电路 Digital Circuit数字电路及微机原理 Digital Circuit & Computer Principles 数字电视 Digital Television数字电子基础 Fundamental Digital Electionics数字电子技术 Digital Electronic Technique数字电子技术基础 Fundamental Digital Electronic Technique数字电子技术设计与实验 Experiment & Design of Digital Electron Technique数字电子线路 Digital Electrical Circuitry数字电子与微机原理 Digital Electronics & Principle of Microcomputer数字仿真 Digital Simulation数字化测量技术 Digital Measuring Technique数字控制及微机控制技术 Digital Control & Microcomputer Control Technique数字逻辑 Digital Logic数字图象处理 Digital Image Processing数字系统逻辑设计 Logical Design of Digital System数字系统设计 Design of Digital System数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing双曲线方程 Hyperbolic Equation水电能源学 Science of HydrOelectric Enelgy水电站过渡过程的特殊问题 Special Problems in the Transition of a Hydropower Station水电站计算机控制 Computer Control in Hydropower Station 水电站经济运行 Economic Operation in Hydropower Station 水电站控制系统分析 Analysis of Control System in Hydropower Station水电站自动化 Automation of Hydropower Station水动力学 Water Dynamics水机工艺结构分析 Technics Structure Analysis of Hydraulic Machinery水力机械测试技术 Test Technique of Hydraulic Machinery 水力机械的汽蚀 Gas Etching of Hydraulic Machinery水力机械调节 Adjustment of Hydraulic Machinery水力机械强度计算 Intensity Calculation of Hydraulic Machinery水力机械原理 Principles of Hydraulic Machinery水力机械制造工艺及结构分析 Manufacturing Technique &Structure Analysis of Hydraulic Machinery水力机械制造工艺学 Manufacturing Technique for Hydraulic Machinery水力学 Hydraulics水轮机 Water-Turbine Engine水轮机调节 Water-Turbine Engine Adaption水轮机调节系统 Adaptive System of Water-Turbine Engine 水轮机水力设计 Hydraulic Design of Water Engine水轮机原理及水力设计 Principles of Water-Turbine Engine & Design of Water Engine水轮机原理与CAD Principle of Water-Turbine Engine & CAD 水轮水力设计 Hydraulic Design of Water Engine水现代控制理论 Modern Theory of Water Controling水质稳定技术 Stability Technique of Water Quality思想教育 Virtue Education素描 Pencil Sketch速冻技术 Technique of Speed Freezing塑性力学 Plastic Machanics算法语言 Algorithmic Language随机过程 Stochastic Process & Time Series Analysis随机运筹学 Randomized Operational Research锁相技术 Phase Lock Technique---来源网络整理,仅供参考。


1、锁具结构mechanisms of lock1.1 弹子结构Pin tumbler mechanism 一组基本形状为圆柱形的零件,起销住或释放锁芯运动作用的结构称弹子结构。
1.2 叶片结构flat tumbler mechanism 一组形状为片状形的零件,起卡住或释放锁芯运动作用的结构称叶片结构。
1.3 磁性结构magnetic mechanism 应用磁性材料制成的零件,起锁住作用,其结构称为磁性结构。
1.4 密码结构combination mechanism 以数字编码组成的结构称密码结构。
1.5 电子编码结构electronic coding mechanism 应用电子原理编码组成的结构电子结构。
2、锁具分类classification of Locks2.1 挂锁padlock 以挂的形式锁住物件(体)的锁。
2.1.1 直开挂锁bottom opening padlock 钥匙从锁头底面插入后,旋转开启的锁。
2.1.2 横开挂锁lateral opening padlock 钥匙从锁头侧面插入后,旋转开启的锁。
2.1.3 顶开挂锁pushing opening padlock 钥匙插入后,向前顶开的锁2.1.4 双开挂锁double key padlock 用两把不同钥匙才能开启的锁。
2.2 建筑门锁door lock in building 适用于建筑楼房门上的锁。
2.2.1 外装门锁rim lock 锁体安装在门挺表面上的锁。
2.2.1.1 单舌单保险门锁single bolt single security door lock 单舌结构具有单保险功能的锁。
2.2.1.2 单舌双保险门锁single bolt double security door lock 单舌结构具有双保险的锁。
2.2.1.3 单舌三保险门锁single bolt triple security door lock 单舌结构具有三保险功能的锁。

锁相技术译文翻译英文原名:High Speed Digital Hybrid PLL Frequency Synthesizer译文:高速数字混合锁相环频率合成器年纪专业:08级通信工程班姓名:学号:2011年 5月2日To get the high-speed, it is necessary to prepare the precise synchronization of the complicated design.In 2001, H. G. Ryu proposed a simplified structure of the DDFS (direct digital frequency synthesizer)-driven PLL for the high switching speed [2].However, there is a problem that the speed of the whole system is limited by PLL.Y. Fouzar proposed a PLL frequency synthesizer of dual loop configuration using frequency-to-voltage converter (FVC) [3].It has a fast switching speed by the PD (phase detector), FVC using output signal of VCO and the proposed coarse tuning controller.However, H/W complexity is increased for the high switching speed.Also, it shows the fast switching characteristic only when the FVC works well.Another method is pre-tuning one which is called DH-PLL in this study [4].It has very high speed switching property, but H/W complexity and power consumption are increased due to digital look-up table (DLT) which is usually implemented by the ROM including the transfer characteristic ofVCO(voltage controlled oscillator).For this reason, this paper proposes a timing synchronization circuit for the rapid frequency synthesis and a very simple DLT replacement digital logic block instead of the complex ROM type DLT for high speed switching and low power consumption. Also, the requisite condition is solved in the proposed method. The fast switching operation at every the frequency synthesis process is verified by the computer circuit simulation.II.DH-PLL synthesizerAs shown in Fig.1, the open-loop synthesizer is a direct frequency synthesis type that VCO 要得到高运行速度,事先做好复杂设计的精确同步是必要的。

锁相技术译文翻译英文原名:An On-Chip All-Digital Measurement Circuit to Characterize Phase-Locked Loop Response in 45-nm SOI译文:45纳米SOI全数字片上测量电路表征锁相环响应特性English中文 An On-Chip All-Digital Measurement Circuit to Characterize Phase-Locked Loop Response in 45-nm SOI Dennis Fischette, Richard DeSantis, and John Haeseon LeeAdvanced Micro Devices, Inc., Sunnyvale, CA 94085-3905 USAAbstract —An all-digital measurement circuit, built in 45-nm SOI-CMOS enables on-chip characterization of phase-locked loop (PLL) response to a self-induced phase step. This technique allows estimation of PLL closed-loop bandwidth and jitter peaking. The circuit can be used to plot step-response vs. time, measure static phase error, and observe phase-lock status.INTRODUCTIONMany applications such as PCI Express ™require a PLL to produce a low-jitter clockat a given frequency while meeting stringentbandwidth and jitter peaking requirements.Process, voltage, and temperature (PVT) variations as well as random device mismatchmake it difficult to guarantee a narrow rangefor PLL response. For example, loopparameters such as VCO gain could vary by more than 2X over PVT corners. In Fig. 1, we see the closed-loop jitter transfer functions of two PLLs with identical reference clock and output frequencies. One PLL exhibits large peaking and low bandwidth while the other shows little peaking but high bandwidth. Although differences in this example are more extreme than usual, similar but smaller differences often result from PVT variations.45纳米SOI 全数字片上测量电路表征锁相环响应特性作者信息摘要——全数字化测量电路,45纳米SOI-CMOS 工艺使其能够片上表征锁相环(PLL )对自诱导相步进的响应。

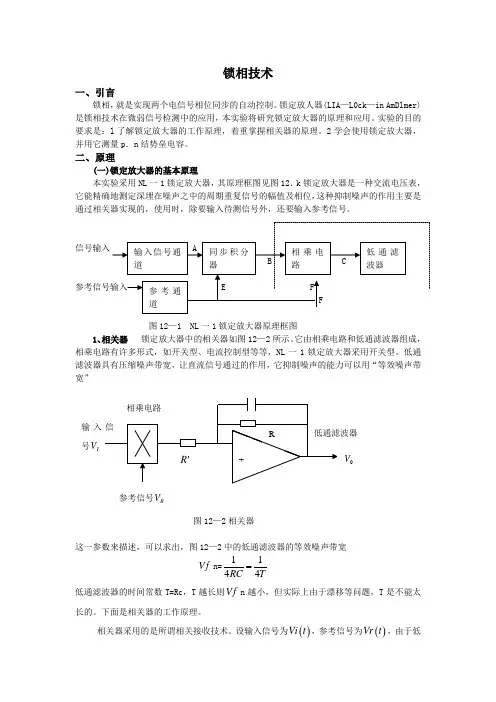
锁相技术一、引言锁相,就是实现两个电信号相位同步的自动控制。
锁定放人器(LIA —L0ck —in AmDlmer)是锁相技术在微弱信号检测中的应用,本实验将研究锁定放大器的原理和应用。
实验的目的要求是:l 了解锁定放大器的工作原理,着重掌握相关器的原理。
2学会使用锁定放大器,并用它测量p .n 结势垒电容。
二、原理(一)锁定放大器的基本原理本实验采用NL 一1锁定放大器,其原理框图见图12.k 锁定放大器是一种交流电压表,它能精确地测定深埋在噪声之中的周期重复信号的幅值及相位,这种抑制噪声的作用主要是通过相关器实现的,使用时,除要输入待测信号外,还要输入参考信号。
图12—1 NL 一1锁定放大器原理框图1、相关器 锁定放大器中的相关器如图12—2所示。
它由相乘电路和低通滤波器组成,相乘电路有许多形式,如开关型、电流控制型等等,NL 一1锁定放大器采用开关型。
低通滤波器具有压缩噪声带宽,让直流信号通过的作用,它抑制噪声的能力可以用“等效噪声带宽”图12—2相关器这一参数来描述,可以求出,图12—2中的低通滤波器的等效噪声带宽f n=1144RC T= 低通滤波器的时间常数T=Rc ,T 越长则f n 越小,但实际上由于漂移等问题,T 是不能太长的。
下面是相关器的工作原理。
相关器采用的是所谓相关接收技术。
设输入信号为()Vi t ,参考信号为()Vr t ,由于低通滤波器实际上是一个积分器,因此相关器的输出0V 是()Vi t 和()Vr t 乘积,再对时间积分,并取平均值有0V = ()1lim ()2T i t T V t Vr t dt T τ→∞--⎰ (12-1)式中t 是参考信号相对于输入信号的延迟时间,积分时间上限T 即低通滤波器的时间常数,通常把式(12.1)所表示的0V 称为()Vi t 和()Vr t 的相关函数,实现求相关函数的电子线路称为相关器或相关接收器。
下面的讨论会更清楚相关器的作用。


外文资料Phase-locked loop Technology :A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates a signal that has a fixed relation to the phase of a "reference" signal. A phase-locked loop circuit responds to both the frequency and the phase of the input signals, automatically raising or lowering the frequency of a controlled oscillator until it is matched to the reference in both frequency and phase. A phase-locked loop is an example of a control system using negative feedback. In the order of the PLL is the way of made the frequency stability in the send up wireless,include VCO and PLL integrated circuits,VCO send up a signal,some of the signal is output,and the other through the frequency division with PLL integrated circuits generate the local signal making compared.In the order to remain the same,it’s must be remain the phase displacement same.If the phase displacement have some changes,the output of the PLL integrated circuits have some changes too,to controlle VCO until phase diffe rence to restore,make both cotrolled oscillator’s frequency and phase with input signal which is close-loop electronic circuit keep firm relationship.Phase-locked loops are widely used in radio, telecommunications, computers and other electronic applications. They may generate stable frequencies, recover a signal from a noisy communication channel, or distribute clock timing pulses in digital logic designs such as microprocessors. Since a single integrated circuit can provide a complete phase-locked-loop building block, the technique is widely used in modern electronic devices, with output frequencies from a fraction of a cycle per second up to many gigahertz.Earliest research towards what became known as the phase-locked loop goes back to 1932, when British researchers developed an alternative to Edwin Armstrong's superheterodyne receiver, the Homodyne. In the homodyne or synchrodyne system, a local oscillator was tuned to the desired input frequency and multiplied with the input signal. The resulting output signal included the original audio modulation information.The intent was to develop an alternative receiver circuit that required fewer tuned circuits than the superheterodyne receiver. Since the local oscillator would rapidly drift in frequency, an automatic correction signal was applied to the oscillator, maintaining it in the same phase and frequency as the desired signal. The technique was described in 1932, in a paper by H.de Bellescise, in the French journal Onde Electrique.In analog television receivers since at least the late 1930s, phase-locked-loop horizontal and vertical sweep circuits are locked to synchronization pulses in the broadcast signal. When Signetics introduced a line of monolithic integrated circuits that were complete phase-locked loop systems on a chip in 1969, applications for the technique multiplied. A few years later RCA introduced the "CD4046" CMOS Micropower Phase-Locked Loop, which became a popular integrated circuit. Applications:Phase-locked loops are widely used for synchronization purposes; in space communications for coherent carrier tracking and threshold extension, bit synchronization, and symbol synchronization. Phase-locked loops can also be used to demodulate frequency-modulated signals. In radio transmitters, a PLL is used to synthesize new frequencies which are a multiple of a reference frequency, with the same stability as the reference frequency.Clock recovery :Some data streams, especially high-speed serial data streams (such as the raw stream of data from the magnetic head of a disk drive), are sent without an accompanying clock. The receiver generates a clock from an approximate frequency reference, and then phase-aligns to the transitions in the data stream with a PLL. This process is referred to as clock recovery. In order for this scheme to work, the data stream must have a transition frequently enough to correct any drift in the PLL's oscillator. Typically, some sort of redundant encoding is used; 8B10B is very common.Deskewing :If a clock is sent in parallel with data, that clock can be used to sample the data.Because the clock must be received and amplified before it can drive the flip-flops which sample the data, there will be a finite, and process-, temperature-, and voltage-dependent delay between the detected clock edge and the received data window. This delay limits the frequency at which data can be sent. One way of eliminating this delay is to include a deskew PLL on the receive side, so that the clock at each data flip-flop is phase-matched to the received clock. In that type of application, a special form of a PLL called a Delay-Locked Loop (DLL) is frequently used.Clock generation:Many electronic systems include processors of various sorts that operate at hundreds of megahertz. Typically, the clocks supplied to these processors come from clock generator PLLs, which multiply a lower-frequency reference clock (usually 50 or 100 MHz) up to the operating frequency of the processor. The multiplication factor can be quite large in cases where the operating frequency is multiple gigahertz and the reference crystal is just tens or hundreds of megahertz.Spread spectrum:All electronic systems emit some unwanted radio frequency energy. Various regulatory agencies (such as the FCC in the United States) put limits on the emitted energy and any interference caused by it. The emitted noise generally appears at sharp spectral peaks (usually at the operating frequency of the device, and a few harmonics).A system designer can use a spread-spectrum PLL to reduce interference with high-Q receivers by spreading the energy over a larger portion of the spectrum. For example, by changing the operating frequency up and down by a small amount (about 1%), a device running at hundreds of megahertz can spread its interference evenly over a few megahertz of spectrum, which drastically reduces the amount of noise seen by FM receivers which have a bandwidth of tens of kilohertz.中文翻译锁相环技术:锁相环或锁相回路(PLL)是一个信号控制系统,即用来锁定一系列的“参考”信号。

名词解释和简答题整理第一章锁相环路的基本工作原理:1.锁相环(PLL)---锁相环是一个能够跟踪输入信号相位的闭环自动控制系统。
2.捕获带:环路能通过捕获过程而进入同步状态所允许的最大固有频差|Δωo|max。
3.同步带:锁相环路能够保持锁定状态所允许的最大固有频差|Δωo|max。
4.快捕带:保证环路只有相位捕获一个过程的最大固有频差值|Δωo|max。
5.输入信号频率与环路自由振荡频率之差,称为环路的固有频率环路固有角频差:输入信号角频率ωi与环路自由振荡角频率ωo之差。
瞬时角频差:输入信号频率ωi与受控压控振荡器的频率ωv之差。
控制角频差:受控压控振荡器的频率ωv与自由振荡频率ωo之差。
三者之间的关系:瞬时频差=固有频差-控制频差。
6.鉴相器是一个相位比较装置,用来检测输入信号相位θ1(t)与反馈信号相位θ2(t)之间的相位差θe(t)。
输出的误差信号u d(t)是相差θe(t)的函数。
7.锁相环路由鉴相器、环路滤波器和压控振荡器三个主要部件构成;其独特的性能有载波跟踪特性、调制跟踪特性和低门限特性。
8.环路滤波器---即低通滤波器,滤除鉴相器输出电压中的高频分量,起平滑滤波的作用,提高环路的稳定性。
9.压控振荡器---压控振荡器是一个电压-频率变换装置,它的振荡频率应随输入控制电压u c(t)线性地变化。
10.环路的动态方程:pθe(t)= pθ1(t)-K o U d F(p)sin θ1(t)11.相平面:将瞬时频差与瞬时相差的关系在平面直角坐标系中所做的图。
相点:是相平面上相轨迹上的一个点,表示环路在某一时刻的状态。
12.如果锁相环路的起始状态处于不稳定平衡点时,环路自身没有能力摆脱这种状态,只有依靠外力(噪声或人为扰动)才能使环路偏离这个状态而进行捕获;所以一旦遇到这种情况就可能出现在不稳定平衡状态的滞留,致使捕获过程延长。
这种现象称为锁相环路的延滞现象。
13.环路固有频差Δωo大于环路增益K,锁相环路处于失锁差拍状态,被控振荡器未被输入信号锁定;但是由于锁相环路的控制作用,使锁相环路的平均频率向输入信号频率方向牵引。
锁相技术期末总结一、引言锁相技术是一种广泛应用于现代电子技术中的信号处理方法,主要用于提取信号中的相位信息。
它通过对输入信号与本地参考信号进行比较和修正,实现对信号相位的精确测量和调整。
锁相技术的应用领域非常广泛,包括无线通信、激光测距、声纳系统、医学影像等。
在本次课程学习中,我们深入了解了锁相技术的原理、应用和实现方法,并通过实践操作进一步巩固了对锁相技术的理解。
二、锁相技术的原理和基本概念锁相技术的原理是基于反馈控制和频率调制的,通过频率调制输入信号和本地参考信号,实现对信号相位的精确测量和调整。
1. 相位差测量原理通过将输入信号与本地参考信号进行乘法运算,并通过低通滤波器和放大器对乘积信号进行处理,最终得到与相位差成正比的直流电压。
根据这个原理,我们可以通过测量这个直流电压来得到输入信号与参考信号之间的相位差。
2. 锁相循环原理锁相循环是指通过反馈控制将输入信号的相位差调整到指定值的过程。
锁相循环由相位比较器、环路滤波器、VCO(Voltage Controlled Oscillator)和反馈网络等组成。
相位比较器用于比较输入信号的相位差和参考信号的相位差,输出误差信号;环路滤波器用于对误差信号进行滤波;VCO用于将滤波后的误差信号转换成频率信号,并与参考信号进行混频;反馈网络将VCO的输出作为参考信号送回相位比较器,形成一个闭环控制系统。
三、锁相技术的应用锁相技术在各个领域中都有广泛的应用,下面主要介绍其中几个典型的应用。
1. 通信领域锁相技术在通信领域中的应用主要包括载波恢复、时钟恢复和时钟同步。
在接收端,通过锁相环的频率跟踪功能可以自适应地追踪和调整接收信号的频率,从而实现载波恢复。
而由于通信系统中的时钟信号也是通过调制到信号中进行传输的,因此通过锁相循环也可以实现对时钟信号的恢复和同步。
2. 激光测距锁相技术在激光测距领域中被广泛应用。
激光测距的原理是利用激光光束射到目标上并接收反射光,通过测量光传播的时间来计算目标的距离。
摘要随着现代通信、雷达、电子侦察和对抗技术的飞速的发展,对作为核心部件的频率合成器的性能指标提出了越来越高的要求,宽频带、高频率分辨、低捷变时间、高频率稳定度、低相位噪声、低杂散、能程控等。
这些技术要求用普通的模拟电路技术是很难达到的,频率合成技术是产生大量高精度、高稳定度频率信号的主要技术。
小数分频频率合成器则是近年来出现的一种新技术,它与传统的整数分频频率合成器相比具有频率分辨率高、相位噪声低等优点。
本文介绍了锁相环和频率合成技术的基础理论,并对小数分频锁相环频率合成器及其实现技术进行了探讨。
ABSTRACTToday, as the electronic technology is developing fantastically fast, the request for higher performance of synthesizers is put forward, wide frequency range, high frequency resolution, low jump time, low phase noise, high spurious restraining and controlled by program. These requirements are too hard to be reached by using normal analog circuit. Frequency synthesizer is the key technology to produce a great deal of high resolution, high stabilization frequency signal.Fraction-N phase locked loop (FNPLL) frequency synthesizer has been appeared in recent years. It has the advantage of high frequency resolution and low phase noise when compared with traditional Integer-N phase locked loop (NPLL) frequency synthesizer.In this paper the basic theory of phase locked loop (PLL) and frequency synthesizer technology were introduced, the theory and implement of FNPLL frequency synthesizer were discussed too.目录一、锁相环基本原理 (4)1.1锁相环原理及组成 (4)1.2 锁相环路的相位模型及其基本方程 (4)二、频率合成基本原理 (5)2.1频率合成概念 (5)2.2频率合成器及其技术指标 (5)2.2.1频率范围 (5)2.2.2频率间隔(频率分辨率) (6)2.2.3频率转换时间 (6)2.2.4准确度与频率稳定度 (6)2.3频率合成器的类型 (6)2.3.1直接式频率合成器(DS) (6)2.3.2间接式频率合成器(IS) (6)2.3.3直接数字式频率合成器(DDS) (7)三、Σ-△小数分频锁相环频率合成器 (7)3.1锁相环频率合成器的发展 (7)3.2 Σ-△小数分频锁相环频率合成器工作原理 (7)四、结束语 (9)一锁相环基本原理1.1 锁相环原理及组成PLL是一种反馈控制电路,其特点是:利用外部输入的参考信号控制环路内部振荡信号的频率和相位。