空间信息并行处理方法与技术(黄方,王力哲,谭喜成著)思维导图
- 格式:xmin
- 大小:5.81 KB
- 文档页数:1

思维可视化:让教学看见思考的力量——以《抵抗弯曲》为例谈信息技术环境下小学科学高年级学生高阶思维可视化发布时间:2021-08-18T10:34:22.720Z 来源:《教学与研究》2021年4月11期作者:王思业[导读] 随着教育信息化的发展和基础教育新课程改革的不断深入,网络技术为学科课程提供了有效可行的教学平台,信息技术资源的开发和利用正深入到科学教学领域中。
王思业福建省泉州市第二实验小学 362000【摘要】随着教育信息化的发展和基础教育新课程改革的不断深入,网络技术为学科课程提供了有效可行的教学平台,信息技术资源的开发和利用正深入到科学教学领域中。
本文立足课题“基于信息技术环境的小学科学高年级学生高阶思维可视化的实践研究”,根据课题组两年多的探索实践,对在信息技术环境下小学科学高年级学生高阶思维可视化在具体教学实践中的教学策略进行了的试述。
【关键词】信息技术;高年级学生高阶思维;可视化根据科学的课程目标,教师应在以培养科学素养、创新精神和实践能力为宗旨的科学基础课程中,通过教学活动,培养小学生(尤其是高年级的小学生)的思维由具体形象思维过渡到抽象逻辑思维,让他们初步形成以抽象、分析、综合、评价、创造、比较、分类、判断、推理等为特征的高阶思维能力。
那么,在教育信息化的时代背景下,怎样才能在具体教学实践中让高年级学生的高阶思维可视化,让教学看得见思考的力量呢?一、几种典型的可视化形式(一)高阶思维“图化”一图胜千言,由于图像包含的信息量是较大的,人们在每1/10秒内获得一个视觉信息,这比通过阅读消化和理解一段文字要快捷的多,而利用信息技术能快速、轻松地将科学课堂上的数据分析、推理类比、分析创造等高阶思维图表化、图像化、图形化,甚至是透视化、动漫化。
图示化作为策略性工具贯穿于教、学、评、测全环节,研究实践表明,变隐形的思维路径为清晰可见的思维过程,是训练和培养高阶思维的最佳方法。
(二)高阶思维“物化”思维的物化过程是思维主体的一种存在形式,从观念的对象到实在的对象的转化过程就是思维的物化,这是思维发展的正向要求,也是验证思维发展的必然要求。


2007,43(5)ComputerEngineeringandApplications计算机工程与应用1引言空间光调制器(SLMs)是一种能对光波的空间分布进行调制的器件,广泛应用于全息系统中,是全息系统的核心部分。
美国德克萨斯仪器公司(TI)生产的新型反射式空间光调制器-数字微镜器件(DMD),是一种MEMS器件,由可偏转的铝镜阵列构成,工作原理为当二进制数据写入底部SRAM存储单元中时,以电寻址方式根据SRAM中内容确定铝镜沿对角线偏转的方向,由此确定二进制数据值。
与其它的调制器如液晶显示器(LCD)等相比,DMD具有更高的分辨率、更宽的响应范围和更快的响应速度、信噪比和光能利用率高、工作温度范围大、偏振无关等特点。
因此将DMD用于全息系统,比使用LCD有更大的优点。
目前的DMD全息系统大致可以分为两类,分别用于记录[1]和重构[2,3],二者的主要区别在于:在全息图记录系统中,DMD上记录的是待用于全息记录的二维透视图序列;在全息图重构系统中,DMD上记录待重构的全息图。
文中提出一种基于DMD投影系统的全息重构系统,鉴于目前全息重构系统对二值全息图进行重构[2,3],文中实现灰度级全息图的重构,避免了全息图在二值化过程中造成的信息丢失。
目前用于重构的全息图有夫琅和费全息图[2]和文献[3]中提出的算法生成的全息图,本文针对基于Lohmann单透镜系统的分数傅立叶变换快速算法生成全息图,通过DMD全息系统重构验证了算法的正确性和系统的可行性。
2DMD空间分辨率与分数傅立叶变换算法及其全息图DMD作为全息图结构,首先遇到的问题就是DMD的有限分辨率,DMD像素单元表明其可以分辨的最大空间频率。
全息图的最大空间频率取决于物光波和参考光波的方向夹角!max:fmax=1"*sin(!max/2)(1)式中"为光波波长。
因此只有当物体足够小并且参考光波和物光波夹角充分小时,DMD才可以分辨出全息图空间结构。





参考文献(人工智能)曹晖目的:对参考文献整理(包括摘要、读书笔记等),方便以后的使用。
分类:粗分为论文(paper)、教程(tutorial)和文摘(digest)。
0介绍 (1)1系统与综述 (1)2神经网络 (2)3机器学习 (2)3.1联合训练的有效性和可用性分析 (2)3.2文本学习工作的引导 (2)3.3★采用机器学习技术来构造受限领域搜索引擎 (3)3.4联合训练来合并标识数据与未标识数据 (5)3.5在超文本学习中应用统计和关系方法 (5)3.6在关系领域发现测试集合规律性 (6)3.7网页挖掘的一阶学习 (6)3.8从多语种文本数据库中学习单语种语言模型 (6)3.9从因特网中学习以构造知识库 (7)3.10未标识数据在有指导学习中的角色 (8)3.11使用增强学习来有效爬行网页 (8)3.12★文本学习和相关智能A GENTS:综述 (9)3.13★新事件检测和跟踪的学习方法 (15)3.14★信息检索中的机器学习——神经网络,符号学习和遗传算法 (15)3.15用NLP来对用户特征进行机器学习 (15)4模式识别 (16)4.1JA VA中的模式处理 (16)0介绍1系统与综述2神经网络3机器学习3.1 联合训练的有效性和可用性分析标题:Analyzing the Effectiveness and Applicability of Co-training链接:Papers 论文集\AI 人工智能\Machine Learning 机器学习\Analyzing the Effectiveness and Applicability of Co-training.ps作者:Kamal Nigam, Rayid Ghani备注:Kamal Nigam (School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 15213, knigam@)Rayid Ghani (School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 15213 rayid@)摘要:Recently there has been significant interest in supervised learning algorithms that combine labeled and unlabeled data for text learning tasks. The co-training setting [1] applies todatasets that have a natural separation of their features into two disjoint sets. We demonstrate that when learning from labeled and unlabeled data, algorithms explicitly leveraging a natural independent split of the features outperform algorithms that do not. When a natural split does not exist, co-training algorithms that manufacture a feature split may out-perform algorithms not using a split. These results help explain why co-training algorithms are both discriminativein nature and robust to the assumptions of their embedded classifiers.3.2 文本学习工作的引导标题:Bootstrapping for Text Learning Tasks链接:Papers 论文集\AI 人工智能\Machine Learning 机器学习\Bootstrap for Text Learning Tasks.ps作者:Rosie Jones, Andrew McCallum, Kamal Nigam, Ellen Riloff备注:Rosie Jones (rosie@, 1 School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 15213)Andrew McCallum (mccallum@, 2 Just Research, 4616 Henry Street, Pittsburgh, PA 15213)Kamal Nigam (knigam@)Ellen Riloff (riloff@, Department of Computer Science, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT 84112)摘要:When applying text learning algorithms to complex tasks, it is tedious and expensive to hand-label the large amounts of training data necessary for good performance. This paper presents bootstrapping as an alternative approach to learning from large sets of labeled data. Instead of a large quantity of labeled data, this paper advocates using a small amount of seed information and alarge collection of easily-obtained unlabeled data. Bootstrapping initializes a learner with the seed information; it then iterates, applying the learner to calculate labels for the unlabeled data, and incorporating some of these labels into the training input for the learner. Two case studies of this approach are presented. Bootstrapping for information extraction provides 76% precision for a 250-word dictionary for extracting locations from web pages, when starting with just a few seed locations. Bootstrapping a text classifier from a few keywords per class and a class hierarchy provides accuracy of 66%, a level close to human agreement, when placing computer science research papers into a topic hierarchy. The success of these two examples argues for the strength of the general bootstrapping approach for text learning tasks.3.3 ★采用机器学习技术来构造受限领域搜索引擎标题:Building Domain-specific Search Engines with Machine Learning Techniques链接:Papers 论文集\AI 人工智能\Machine Learning 机器学习\Building Domain-Specific Search Engines with Machine Learning Techniques.ps作者:Andrew McCallum, Kamal Nigam, Jason Rennie, Kristie Seymore备注:Andrew McCallum (mccallum@ , Just Research, 4616 Henry Street Pittsburgh, PA 15213)Kamal Nigam (knigam@ , School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213)Jason Rennie (jr6b@)Kristie Seymore (kseymore@)摘要:Domain-specific search engines are growing in popularity because they offer increased accuracy and extra functionality not possible with the general, Web-wide search engines. For example, allows complex queries by age-group, size, location and cost over summer camps. Unfortunately these domain-specific search engines are difficult and time-consuming to maintain. This paper proposes the use of machine learning techniques to greatly automate the creation and maintenance of domain-specific search engines. We describe new research in reinforcement learning, information extraction and text classification that enables efficient spidering, identifying informative text segments, and populating topic hierarchies. Using these techniques, we have built a demonstration system: a search engine forcomputer science research papers. It already contains over 50,000 papers and is publicly available at ....采用多项Naive Bayes 文本分类模型。

政学协同社区智慧图书馆建设的SIR演化博弈分析作者:万立军郭爽来源:《新世纪图书馆》2021年第07期摘要为满足社区居民多元化与复杂化的服务需求,可通过政府与高校合作完善社区图书馆建设、提高服务质量实现。
基于传染病理论与演化博弈理论,构建“政府—高校—社区居民”的SIR演化博弈模型,将政府与高校的策略演化过程引入到改进的SIR模型中,同时运用期望效用理论弥补感知收益的量化缺陷,探讨政府与高校不同的决策对完善社区图书馆服务建设的影响,并进行数值仿真验证。
研究表明:非量化损益的敏感度及社区居民的投诉率与认可度均在一定程度上影响政学主体的行为决策,建立三方协作机制、完善非物质性奖励制度以及增加惩罚力度對系统演化至平衡稳定状态起着关键作用。
关键词政学协同机制社区图书馆智慧图书馆建设演化博弈分类号 G250.76DOI 10.16810/ki.1672-514X.2021.07.013SIR Evolutionary Game Analysis of the Construction of Smart Library in the Community of Politics and ScienceWan Lijun, Guo ShuangAbstract In order to meet the diversified and complicated service needs of community residents, the cooperation between the government and universities can improve the construction of community libraries and improve the service quality. Based on the theory of infectious diseases and evolutionary game theory,construct an SIR evolutionary game model of “government-university-community residents”, introduce the strategic evolution process of government and colleges and universities into the improved SIR model, and use the expected utility theory to make up for thequantified shortcomings of perceived benefits, explore the influence of different decisions made by the government and universities on perfecting the service construction of community libraries, the impact of different decisions of the government and universities on improving the quality of community library service supply, and perform numerical simulation verification. The research shows that the sensitivity of non-quantified gains and losses and the complaint rate and recognition of community residents affect the behavioral decision-making of political subjects to a certain extent. Establishing a tripartite collaboration mechanism, improving the non-material reward system, and increasing penalty plays a key role in the evolution of the system to a balanced and stable state.Keywords Collaborative mechanism of politics. Community library. Construction of smart library. Evolutionary game.0 引言近年来,党中央全力推进社会主义文化强国建设工作,2018年1月1日正式实施的《中华人民共和国公共图书馆法》完善了我国法律体系在专业服务、信息交流等方面存在的不足[1],也促使我国社区图书馆得以长足进步。
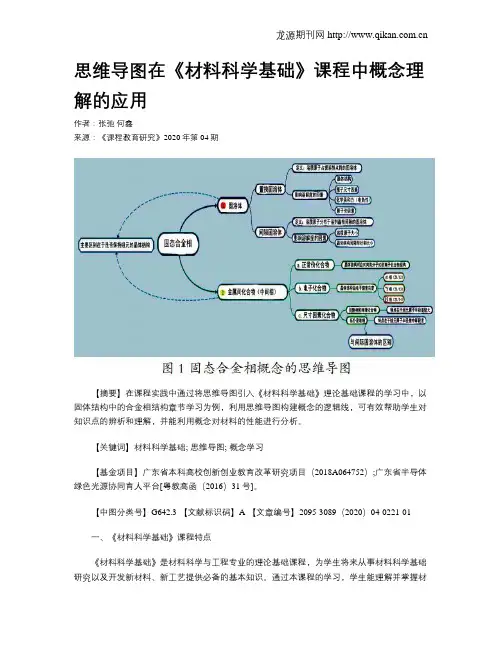
思维导图在《材料科学基础》课程中概念理解的应用作者:张弛何鑫来源:《课程教育研究》2020年第04期【摘要】在课程实践中通过将思维导图引入《材料科学基础》理论基础课程的学习中,以固体结构中的合金相结构章节学习为例,利用思维导图构建概念的逻辑线,可有效帮助学生对知识点的辨析和理解,并能利用概念对材料的性能进行分析。
【关键词】材料科学基础; 思维导图; 概念学习【基金项目】广东省本科高校创新创业教育改革研究项目(2018A064752);广东省半导体绿色光源协同育人平台[粤教高函(2016)31号]。
【中图分类号】G642.3 【文献标识码】A 【文章编号】2095-3089(2020)04-0221-01一、《材料科学基础》课程特点《材料科学基础》是材料科学与工程专业的理论基础课程,为学生将来从事材料科学基础研究以及开发新材料、新工艺提供必备的基本知识。
通过本课程的学习,学生能理解并掌握材料科学基础的基本概念和基本原理,并且能够运用其判别材料的结构和性能;将数学、物理、化学、工程基础知识和材料科学相关专业知识有机结合起来,分析材料与器件中的组织结构、性质、加工工艺和性能优化等复杂工程问题,并获得有效结论;能利用材料科学基本原理,对材料成分、结构、性能之间的关系进行合理的分析和解释。
为学生学习后续专业课程、从事材料科学研究和工程技术工作打下坚实的理论基础。
作为一门基础理论课程,《材料科学基础》具有概念多、内容延展性大等特点,对学生掌握知识的系统性与逻辑性要求较高。
在学习过程中容易存在概念混乱,逻辑线难以理清的问题。
基本概念是后续分析材料性能及理解材料成分、结构、性能之间关系的重要基础。
因此,有必要利用辅助学习工具来帮助学生在学习的过程中准确掌握基本概念。
二、思维导图的介绍思维导图(Mind Mapping)是英国著名心理学家托尼巴赞在20世纪60年代提出的一种新的思维模式,他对思维导图的定义是:图解的形式和网状的结构,加上关键词及关键图像,存储,组织和优化信息。