2007版 武汉天河机场航图
- 格式:doc
- 大小:4.00 MB
- 文档页数:10

在孵化中进化一个航站区的设计必须具有前瞻性,预测是重要环节,所有的设计都是根据一个预测的数据来作为设计依据,一个普通建筑可能只需要满足现在时的需求,而航站区则是要满足未来5年、10年的未来时的需求。
与其他“中国制造”不同,它的诞生有一个相当长的孵化期。
而在这个过程中,它要不断吸收新需求,调整甚至颠覆原有的雏形。
这就是航站区规划设计,一个历时长久的设计过程。
1.1 项目背景及区位广州白云机场原址位于广州市白云区白云山西侧,于1933年夏季建成竣工。
由于位于市区中心,随着航空业务量的迅猛发展,老机场无法满足需求,新白云机场的选址工作从1992年开始进行,距广州市中心直线距离约28公里。
2000年8月正式破土动工,2004年8月2日落成竣工,并于同年8月5日零时正式启用。
广州白云国际机场一期工程占地面积约为15平方公里,航站楼总面积37.5万m²,总投资接近200亿元人民币,设计年旅客吞吐量为2500人次。
随着8月5日新机场的启用,同年年底旅客吞吐量到达2000万人次左右,货邮吞吐量为68万吨左右。
基于航空业务发展的需求2005年后又扩建东三、西三指廊及相关连接楼约14.8万m²,设计年旅客吞吐量为1000万人次。
目前现有航站楼总面积52.3万m²,总设计年旅客吐量为3500人次。
随着这几年航空业务的高速发展,今年广州白云国际机场预计年旅客吞吐量接近5000万人次,远远超出了现有航站楼的设计能力,二号航站楼的建设迫在眉睫。
1.2 广州白云国际机场的定位民航“十一五”规划确定广州白云国际机场是国家三大枢纽机场之一。
为满足中南地区经济社会发展需要,促进东南亚经济合作、泛珠区域经济一体化和对外开放,中国民用航空局在二OO七年十二月《全国民用机场布局规划》中明确中南机场群由广东、广西、海南、河南、湖北、湖南6省(自治区)内各机场构成,《规划》同时也明确将广州白云国际机场列为中南机场群的主要机场,重点培育广州白云国际机场为国际枢纽,增强其国际竞争力。

General InfoHong Kong, HKGN 22?18.5' E113?54.9' Mag Var: 1.9訖Elevation: 28'Public, IFR, Control Tower, Low Level Wind Shear Alert System, Customs Fuel: Jet A-1Repairs: Major Airframe, Major EngineTime Zone Info: GMT+8:00 no DSTRunway InfoRunway 07L-25R 12467' x 197' asphaltRunway 07R-25L 12467' x 197' asphaltRunway 07L (73.0衽) TDZE 22'Lights: Edge, ALS, Centerline, TDZDisplaced Threshold Distance 568'Runway 07R (73.0衽) TDZE 27'Lights: Edge, ALS, Centerline, TDZDisplaced Threshold Distance 525'Runway 25L (253.0衽) TDZE 27'Lights: Edge, ALS, Centerline, TDZRunway 25R (253.0衽) TDZE 22'Lights: Edge, ALS, Centerline, TDZDisplaced Threshold Distance 571'Communications InfoATIS 128.2 Arrival ServiceATIS 127.05 Departure ServiceHong Kong Tower South Tower 118.4Hong Kong Tower North Tower 118.7 SecondaryHong Kong Tower North Tower 118.2Hong Kong Ground South Ground Control 122.55Hong Kong Ground North Ground Control 121.6Hong Kong Delivery Clearance Delivery 129.9Hong Kong Delivery Clearance Delivery 124.65 SecondaryHong Kong Precision Approach Control 133.7Hong Kong Director Approach Control 119.5Hong Kong Director Approach Control 119.35Hong Kong Director Approach Control 120.1 SecondaryHong Kong Approach Control 119.1Hong Kong Departure Control 122.0Hong Kong Departure Control 124.05 SecondaryHong Kong Departure Control 123.8Hong Kong Departure Radar 122.0Zone Control 120.6Notebook Info1.1.ATISD-ATIS Arrival128.2D-ATIS Departure127.051.2.NOISE ABATEMENT PROCEDURES1.2.1NOISE MITIGATING MEASURESThe following procedures are implemented daily to reduce ACFT noise levels, whenoperating conditions permit. Noise mitigating procedures are not applicable tocalibration flights.1.2.1.1.PREFERENTIAL USE OF RWYS 07L/RAs a noise mitigating measure between 0001-0700LT, RWYs 07L/R will be nominated as the RWY direction-in-use whenever the tailwind component (including gusts) is10 KT or less when the RWY is dry, or 5 KT or less when the RWY is not dry. Duringthis period RWYs 25L/R may be used if operationally required, e.g. unserviceability of navigation aids, adverse weather conditions, ACFT performance, trafficsituations etc.1.2.2.RUN-UP TESTSEngine run-ups are subject to the following conditions:-An engine ground run is defined as any engine start-up not associated with aplanned ACFT departure.-Engine ground runs at ground idle power of not more than two engines at a time and for a duration not exceeding ten minutes may be carried out on the Passenger Apron or Cargo Apron.-Engine runs above ground idle power shall be carried out in the run-up facility andengine ground runs at idle power for a duration in excess of ten minutes shall onlybe carried out in approved locations.-All engine ground runs must be fully supervised by ground staff.-Maintenance or test running of jet engines not mounted on an ACFT is prohibitedunless performed in a test cell of adequate design.ENGINE GROUND RUN PROCEDURESInitial request for a ground engine run should be made to the APT Authority ApronControl Centre (Tel No: 2910 1112). The airline, ACFT maintenance agent engineer or mechanic in charge of the engine test is responsible for ensuring that all safetyprecautions against injury to persons or damage to properties, aircraft, vehicles and equipment in the vicinity are adopted.When ready to conduct the engine run, the pilot or authorized engineer shall obtain start-up clearance from Apron Control on 121.77 and a listening watch shall bemaintained on the frequency throughout the engine run. The ACFT anti-collisionbeacons must be activated for the entire duration of the ground engine run and Apron Control should be advised on its completion. The ground crew in charge mustmaintain communication with cockpit personnel and be able to stop the engine runimmediately if directed.1.3.LOW VISIBILITY PROCEDURES (LVP)1.3.1.GENERALLow Visibility Procedures are established for operations in a visibility of less than RVR 550m or a cloudbase of less than 200ft.ACFT operators must obtain approval from the Director-General of Civil Aviationprior to conducting any low visibility operations.Special procedures and safeguards will be applied during CAT II/III operations toprotect ACFT operating in low visibility and to avoid interference to the ILS signals.Pilots shall be informed when:-meteorological reports preclude ILS CAT I operations;-Low Visibility Procedures are in operation;-there is any unserviceability in a promulgated facility so that they may amendtheir minima.Pilots who wish to carry out an ILS CAT II/III approach shall inform ApproachControl on initial contact. Pilots may carry out a practice ILS CAT II/III approach at any time, but the full safeguarding procedures will not be applied and pilots should anticipate the possibility of ILS signal interference.1.3.2.ARRIVALACFT shall only vacate:-RWY 07L via TWYs A9 or A12;-RWY 07R via TWYs J7, J10, K6 or K7;-RWY 25L via TWYs H1, J3, K1 or K2;-RWY 25R via TWYs A1, A4 or A6.All RWY exits have TWY centre-line lead-off lights that are colour coded (green/yellow) to indicate that portion of the TWY that is within the ILS sensitive area.Pilots are to delay the 'RWY vacated' call until the ACFT has completely vacated the ILS sensitive area and passed the end of the colour coded TWY centre-line lights. 1.3.3.DEPARTUREACFT shall normally only enter:-RWY 07L via TWYs A1 or A2;-RWY 07R via TWYs H1, J1 or K1;-RWY 25L via TWYs J9, J10 or K7;-RWY 25R via TWYs A11 or A12.Holding positions on TWYs A1, A2, H1, J1, J9 and J10 are CAT I/II holding positions.Separate CAT II holding positions are provided on TWYs K1, K7 and K.Holding positions on TWYs A11 and A12 are CAT I/II/III holding positions.1.4.SURFACE MOVEMENT GUIDANCE AND CONTROL SYSTEMAPT is equipped with an Advanced Surface Movement Guidance and Control System (A-SMGCS) operating on a trial basis. The system is a Multistatic DependentSurveillance (MDS) multilateration system that utilises Mode S transponderstransmissions.To facilitate a full evaluation of the trial, pilots of ACFT equipped with 'weight-on-wheel' switch must ensure that the transponder is operating (select AUTO or XPNDR, do not switch to STAND-BY or OFF) and the assigned Mode A code is selected inaccordance with the following:-for a departing flight, from the request for push-back or taxi, whichever is earlier, -for an arriving flight, continuously until the ACFT is fully parked at the stand.For ACFT NOT equipped with 'weight-on-wheel' switch, follow existing transponder operating procedures.For ACFT that are capable of reporting ACFT Identification, (i.e. callsigns used inflight), the ACFT Identification should also be entered via FMS or Control Panel.1.5.TAXI PROCEDURESTaxi with extreme CAUTION and MIM engines power only.1.6.PARKING INFORMATION1.6.1.GENERALAll parking stands on the passenger apron are equipped with an automated docking guidance system for the centerline parking position.1.6.2.FRONTAL PARKING BAYSFrontal parking bays are those bays which are served by airbridges with directaccess to the passenger terminal building. All frontal parking bays can accommodate all current wide-body types of ACFT and have continuous yellow nosewheel guidance lines to indicate the correct parking centerline.Some frontal parking bays can also accommodate narrow-body types of ACFT at aseparate parking bay location displaced 30'/9m to the RIGHT of the wide-bodycenterline and indicated by a dashed yellow guidance line. The narrow-body parking bay is referred to by a "R" suffix, e.g. S23R. The following parking bays canaccommodate narrow-body types of ACFT:-South Apron E1R, E2R, E3R, S23R, S25R, S27R, S29R, S31R, S33R, S35R, S41R,S43R, S45R, S47R and S49R.-North Apron E16R, E17R, N22R, N24R, N26R, N28R, N30R, N32R, N34R, N60R,N62R, N64R, N66R, N68R and N70R.-West Apron W40R, W42R, W44R, W46R, W48R, W61R, W63R, W65R, W67R,W69R and W71R.1.6.3.REMOTE PARKING BAYS1.6.3.1.NORTH/SOUTH APRONAll remote parking bays on the North and South aprons have continuous yellownosewheel guidance lines.1.6.3.2.WEST APRONThe remote parking bays on the West apron are configured to accommodate up to5 wide-body type ACFT or up to 7 narrow-body type ACFT, or a combination of wideand narrow-body type ACFT.The wide-body parking locations have continuous yellow nosewheel guidance lines to indicate the correct parking centerline.The narrow-body parking locations are displaced to the LEFT and the RIGHT of thewide-body centerline and are indicated by dashed yellow nosewheel guidance lines.These narrow-body parking bays are referred to by a "L" or "R" suffix, e.g. W121L or W123R.1.7.OTHER INFORMATION1.7.1.GENERALBirds in vicinity of APT.1.7.2.LOCAL WIND EFFECTS1.7.2.1.GENERAL WARNINGDue to the proximity of the hilly terrain of Lantau Island to the South and East ofAPT, significant low-level windshear and moderate to severe turbulence can beexpected along the approaches to and departures from both RWYs when winds blowoff these hills, i.e. from East through Southwest at about 15 KT or more. As the hills to the North are further away, they play a less significant role, but none the less can create local wind effects when strong winds blow off these hills , i.e. fromNorthwest through Northeast, at about 20 KT or more.The terrain induced wind disturbances from nearby hills can be very small scale,sporadic and transient in nature. Whilst these wind disturbances may be small inphysical dimension and correspond to only several seconds of flight time, significant headwind changes (i.e. RWY orientated wind speed losses and/or gains being 15 KT or greater), can be expected as the ACFT flies through them. The sporadic andtransient nature of the terrain-induced wind disturbances results in some ACFTexperiencing windshear and/or turbulence, whilst others do not, even though thebroad meteorological conditions are the same. Successive ACFT which experiencewindshear and/or turbulence may also encounter a different sequence of events.Surface winds at the APT are generally not good indicators of the wind that may be experienced during the final phase of the approach. Winds at approximately 2000 ft may be a better representation of the prevailing wind conditions in the region.Generally, mean wind speed should decease towards lower altitudes but isolatedstrong gusts may be expected. Wind direction would also change with altitude due to blocking of the general wind flow by nearby hills or in the presence of low-leveltemperature inversion which occurs mostly in the cool season (about half of the time or more from November to April). It is possible for the magnitude of windshear and turbulence to increase towards final approach, resulting in deteriorating rather than improving conditions prior to touchdown.1.7.2.2.EASTERLY THROUGH SOUTHWESTERLY WINDSWhen prevailing winds are from the East through Southwest and with a speed inexcess of 15 KT, significant windshear and moderate turbulence can be expected on the approaches to or on departure from both RWYs. Larger magnitude of windshearand turbulence is possible when the wind speed is in excess of 30 KT. Because of the closeness to the hills of Lantau, the windshear and turbulence are more significantover the southern RWY (RWY 07R/25L).Low-level windshear and turbulence are expected to be more significant when thewind is from the direction 130^ - 210^ , especially in the presence of low-leveltemperature inversion or when the wind speed is more than 30 KT.1.7.2.3.NORTHWESTERLY THROUGH NORTHEASTERLY WINDSSignificant low-level windshear and moderate turbulence can be expected when wind speeds exceed 20 KT, especially for approaches to RWY 25L/R and along thedeparture and missed approach corridors from RWY 07L/R as these approach/departure corridors are closer to the hills to the North as compared with approaches to RWY 07L/R. Larger magnitude of windshear and turbulence over these approachand departure corridors is possible if the wind speed exceeds 30 KT, especially in the vicinity of "LOTUS".1.7.ND-SEA BREEZELand-sea breeze is not a strong wind phenomena but it can create a complex windfield in the vicinity of the APT and it can cause a significant change in winddirection within a distance of a few kilometers along the approach/departure areas.If the sea breeze opposes the prevailing wind flow it can result in significantwindshear even if fine weather conditions.1.7.2.5.LOW-LEVEL JET IN COOL SEASONDuring a surge of the winter monsoon, strong low-level jets of northeasterly windwith speeds up to 50 KT occasionally affect the APT. Under such circumstancessignificant windshear along the departure corridors of RWY 07L/R can be expected. 1.7.2.6.LOW-LEVEL WIND EFFECTSPilots should be aware of building-induced turbulence and windshear effects whenlanding at following conditions:- RWY 07R at strong northwesterly/northerly winds with a background speed ofabout 15 KT or more- RWY 25L at strong northwesterly/northerly winds- RWY 25R at strong southwesterly/southerly/southeasterly winds1.7.3.WINDSHEAR AND TURBULENCE WARNING SYSTEM (WTWS)1.7.3.1.MICROBURST/WINDSHEAR ALERTSThe Microburst or Windshear alert passed by ATC includes the type of alert (i.e.microburst or windshear), the magnitude of the RWY orientated wind speeddifference and the location (final approach or departure area as appropriate).When more than one occurence of wind shear is detected for a particular RWYcorridor, WTWS provided a consolidated Microburst or Wind Shear Alert for thatparticular RWY corridor based on a priority system wich takes into consideration the severity of the alerts and the confidence level of the different data sources whichgenerate the alerts.E.g. If a microburst with an intensity of minus 30 KT and a wind shear with anintensity of plus 15 KT are detected, only a Microburst Alert will be issued.Gain and loss events can co-exist within the same RWY corridor, particularly forterrain-induced wind shear. The WTWS is designed to assign a higher priority to aWind Shear Alert of wind loss compared to a Wind Shear Alert of wind gain. If the former is issued pilots are reminded that they may still encounter wind gain events.1.7.3.2.TURBULENCE ALERTSThe Turbulence Alert passed by ATC includes the intensity and type of alert (i.e.moderate or severe turbulence), and the location (final approach or departure areaas appropriate). The alert intensity (i.e. moderate or severe) follows ICAO'sstandard definition for reporting of turbulence .1.7.3.3.MICROBURST/WINDSHEAR ALERT COMBINED WITH TURBULENCE ALERTWhen a "Microburst Alert" or a "Windshear Alert" is given for a particular RWYand turbulence is also detected for that particular RWY, a "Turbulence Alert" willbe passed by ATC together with the "Microburst Alert" or "Windshear Alert". 1.7.4.LIGHTNING WARNING SYSTEMWhen the system predicts a strong probability of a lightning strike on the APTplatform, APT authority will issue a Red Lightning Warning. When airlines andhandling agents receive a Red Lightning Warning through SITA they should adviseinbound flights of the warning.If the period of the Red Lightning Warning is forecast to be prolonged, a messagewill be included on the ATIS broadcast advising of delays to parking and/or push-back.Because ground crew operations are suspended the wheels will not be chocked. APU should remain in operation. In the event of an inoperative APU, pilot shall keep one starboard engine running. ACFT unable to comply with this procedure should notifyGround Movement Control on initial contact.Ground crews will not commence a push-back when a Red Lightning Warning is inforce.1.8.LOW LEVEL TCAS ALERTS WITH HONG KONG CONTROL ZONEIFR flights sometimes experience TCAS alerts, these may be caused by transponder-equipped VFR or Special VFR flights operating on low-level routes in the vicinity of APT.Even though separation is provided, ATC will, under such circumstances, issuetraffic information to the ACFT concerned whenever practicable so that pilots will be aware of the possible TCAS alerts.2. ARRIVAL2.1.NOISE ABATEMENT PROCEDURES2.1.1NOISE MITIGATING MEASURESThe following procedures are implemented daily to reduce ACFT noise levels, when operating conditions permit. Noise mitigating procedures are not applicable tocalibration flights.2.1.1.1.CONTINUOUS DESCENT APPROACH (CDA) FOR RWYS 25L/RAs a noise mitigating measure between 2301-0700LT arrivals to RWYs 25L/R mayexpect an ILS/DME approach with a CDA procedure subject to the prevailing traffic situation.-ACFT on the CDA procedure are expected to achieve a continuous descent profileapproximating a 3^ vertical profile from 8000' to intercept the GS at or above4500'.During a CDA pilots should maintain a low thrust setting and should not haverecourse to level flight.-ACFT will be given radar vectors from about 27 NM from touchdown (12 NM toFAF), to intercept the LLZ outside of the FAF (LOTUS D15 IFL - RWY 25L, RIVER D15 ITFR - RWY 25R). The estimated track miles to touchdown will be passed withdescent clearance and further distance information may be given as required.-The recommended speed for the CDA intermediate approach segment is 210-225 KT, this should permit a relatively clean configuration for as long as practicable. Thepublished speed restrictions for the final approach segment are applicable for theCDA procedure, 180 KT at FAF and between 150-160 KT at 4 NM from touchdown.-If ACFT cannot comply with the CDA procedures or speed limitations, the pilotshould advise ATC in good time so that alternative arrangements can be made.2.2.CAT II/III OPERATIONSRWYs 07L, 07R and 25L approved for CAT II, RWY 25R for CAT II/III operations,special aircrew and ACFT certification required.2.3.RWY OPERATIONS2.3.1.RWY UTILISATIONVacate RWY as quickly as practicable.To facilitate minimum RWY occupancy time, each RWY has multiple rapid exit TWYs.Vacate via the first available rapid exit TWY commensurate with operationalconditions, or as instructed.ACFT vacating the RWY should not stop on the exit TWY until the entire ACFT haspassed the RWY holding point.2.3.2.REDUCED RWY SEPARATION MINIMUMS (RRSM)RRSM may be applied between a departing ACFT and a succeeding landing ACFT orbetween two successive landing ACFT on the same RWY provided the followingconditions exist:-visibility of at least 5 km;-ceiling in the departure/missed approach area 3000' or more;-during daylight hours from 30 minutes after local sunrise to 30 minutes before local sunset;-the second ACFT will be able to see the first ACFT clearly and continuously untilthe first is clear of the RWY;-no unfavorable surface wind conditions (including significant tailwind/turbulenceor windshear, etc);-braking action not adversely affected by water or other contaminants (i.e. RRSMwill be suspended whenever the RWY is wet or there is pilot report of poor braking action).Pilots shall inform ATC in good time in the event that ACFT may not vacate the RWY expeditiously due technical or OPR reason.When RRSM is applied, the successive landing ACFT may be given clearance to landbefore the first ACFT has cleared the RWY-in-use after landing or crossed the RWYend on departure provided there is reasonable assurance that the followingseparation distances will exist when the landing ACFT crosses the THR:RWY 07L/25R-Landing following departure:The departing ACFT is/will be airborne and has passed a point at least 2400m fromTHR (ABEAM TWY A8 for RWY 07L or TWY A5 for RWY 25R).-Landing following landing:The preceding ACFT has landed and has passed a point at least 2400m from THR(ABEAM TWY A8 for RWY 07L or TWY A5 for RWY 25R), is in motion and willvacate the RWY without backtracking.RWY 07R/25L-Landing following departure:The departing ACFT is/will be airborne and has passed a point at least 2900m fromTHR (ABEAM TWY K6 for RWY 07R or TWY K2 for RWY 25L).-Landing following landing:The preceding ACFT has landed and has passed a point at least 2900m from THR(ABEAM TWY K6 for RWY 07R or TWY K2 for RWY 25L), is in motion and will vacate the RWY without backtracking.ATC will provide warning to the second ACFT when issuing the landing clearance in line with ICAO standard phraseology, eg:-(Callsign....), preceding B737 landing about to vacate the RWY, surface wind 090 degrees/ 11 KT, cleared to land.-(Callsign....), departing A320 ahead about to rotate, surface wind 230 degrees/ 6 KT, cleared to land.Pilots must notify ATC in advance if they anticipate not being able to comply with any of the above requirements.2.4.OTHER INFORMATION 2.4.1.DISTANCE FROM TOUCHDOWN INFO In the event of airborne DME receiver failure or ground equipment failure,equivalent DME ranges will be provided by PRM controller for ILS CAT I approach at Final Approach Point and Outer Marker fix on frequency 133.7 MHz, as outlined in the following table:In the event of airborne DME receiver failure, pilots must advise ATC prior to commencing the approach.3.1.START-UP & PUSH-BACK PROCEDURES All ACFT other than helicopters and locally light ACFT shall obtain an ATC clearanceprior to engine start. Pilots are to inform HONG KONG Ground/Delivery, asappropriate, of callsign, parking stand number/location, identifier of the latestATIS received unless it has been included in the RCD (request for departure clearance down link) message via datalink, proposed flight level if it is different from thefiled flight plan and when applicable, special requirements (e.g. request for another departure RWY or inability to comply with SID climb profile).Additionally, departures for destinations in China routeing via BEKOL (A461) shall contact Hong Kong Delivery 15 minutes before estimated off-block time (EOBT) to obtain advance notification of any flow control restriction that may affect the flight.A 2-way Pre-Departure Clearance (PDC) data link service is available to approved operators from HONG KONG Delivery between 0730-0030LT daily. Pilots should send a RCD to ATC not more than 20min prior to EOBT. If the CLD message is not received within 5 min or there is any problem with date link exchange, pilot shall inform HONG KONG Delivery.Pilots not participating in the PDC service shall contact HONG KONG Deliverybetween 0730-0030LT. All pilots shall contact HONG KONG Ground (South) between 0030-0730LT 5 minutes prior to start to put their ATC clearance on request. Upon receipt of the ATC clearance the pilot shall read back the following information:-Callsign, - Destination, - Route, - SID, - SSR code.3. DEPARTUREPilots shall comply with instructions issued by HONG KONG Delivery regarding when to contact the relevant HONG KONG Ground frequency.Once an ATC clearance has been received, unless there is a specific time restriction included in the clearance, any delay in being ready to push-back, start engines ortaxi may result in the clearance being cancelled.Pilots shall contact HONG KONG Ground (South) except when notified it is sectorised, in which case pilots shall contact:-HONG KONG Ground (North) for North and West Aprons.-HONG KONG Ground (South) for South, Cargo and Business Aviation Aprons.Prior to requesting for push-back or taxi from a parking stand, pilots of ACFT equipped with a "weight-on-wheel" switch must ensure the transponder is operating (on "AUTO" or "XPNDR", and not "STDBY" or "OFF") and the assigned Mode A code is selected. ACFT with Mode S transponder capable of reporting ACFT Identification should have its identification in the ICAO flight plan format entered via FMS or Control Panel.The majority of parking bays have two standard push-back procedures, push-back BLUE and push-back RED. The normal push-back procedure is to the taxilane ABEAM the adjacent parking bay, but where this would result in the ACFT entering a critical area the push-back is extended to a Tug Stop Point clear of the critical area.Stands E2, E17, N24, N30, N60, N142, N143, S25, S31, S43, S102 thru S104, S108,S110 and W65 have a push-back/tow-forward procedure, push-back GREEN.If this push-back procedure is not acceptable due to operational restrictions, pilot should inform ATC immediately and alternative push-back arrangements will be given.ACFT making a push-back GREEN should be ready for taxi as soon as the push-back and tow-forward procedure and engine start process has been completed.Under certain traffic conditions it may be necessary for Hong Kong Ground to issue non-standard push-back instructions to expedite to flow of traffic. Pilots will be issued a "non-standard push-back" to a defined location and direction.Pilots shall ensure that the push-back colour code or non-standard push-back instructions issued by HONG KONG Ground are accurately relayed to their ground crew before push-back or engine start commences.There is a restriction to the starting of engines for ACFT in parking bays S103, S108 and W123. If ACFT in these bays are required to push-back through 180^, only one engine shall be started during the push-back, other engines shall only be started when the push-back manoeuvre has been completed.When known conditions exist which necessitate that engine start-up is carried out in the parking bay prior to the commencement of push-back, or greater than idle engine thrust will be required during engine start (e.g. cross-bleed start procedure), the pilot shall advise HONG KONG Ground of the fact when engine start or push-back clearance is requested.Whilst push-back procedure is being conducted, it is essential for safety reasonsthat communication contact is maintained between pilot and ground engineer in charge. ATC clearance will not normally be issued to ACFT whilst being pushed back, unless the pilot so requests.To avoid delay to other traffic using the apron ACFT should be ready to taxi as soon as the push-back manoeuvre and engine start procedure are completed. The standard push-back for stands N68 and N70 is into TWY B, therefore to avoid delays to other traffic it is essential that the ACFT should be ready to taxi as soon as the push-back manoeuvre is complete. If ACFT are unable to comply with this procedure, pilotsshall immediately inform HONG KONG Ground in order that alternative taxi instructions may be issued to other traffic.Pilots are reminded that they should always use minimum power when starting engines or manoeuvring within the apron area. It is especially important when commencing to taxi that break-away thrust is kept to an absolute minimum and then reduced to idle thrust as soon as practicable.。

国内机场简易航图册编著 冷 锋本图册包含国内46个机场,航图由Jeppesen FliteStar 8.51 导出,每页一个机场,包含绝大部分跑道的ILS 频率和机场通信信息,可作为VFR 进离场参照使用,仅个别机场因手头缺少资料未能补全。
所有航图只作为模拟飞行的参考,不可用于真实飞行使用。
在航图中点击机场内的星型标志可显示该机场相关的通讯频率。
版权所有飞行者俱乐部/bbs微软模拟飞行家http://59.33.37.77:8080/msfsbbs500500500500500500500500HONG KONGLANTAU ISLANDERZHOU DAOZHIWAN DAO BaoanChiu-Lung-Hsin-KuanFan LingNantouShekouYuen LongWAILINDING DAO69123691215182124273033369121503691215182124273033369121518212427303336912151821242730339121518212427CASTLE PEAK RANGE12000GNDATIS 128.2HONG KONG-IntlVHHH 19-124Hong Kong Sek Kong VHSK 50-41ATIS 127.45SHENZHEN Baoan ZGSZ 13-111UNL GND90GNDUNL 808020118GNDW 18A 461B330 2A02 L 642M 7710 P 91A 150VORBAILYCD07LCD34CI07LCI07RCL16CQ33D040CD040GD065FD065LD065RD126UD153ID155ZD157UD157VD202XD210XD224VD233M D245DD253C D259ED274KD300RFD07LFD25RFD33FI07LFI07R FI25LFI33FQ33LARCHLIMESLOTUSMALINMD07LNLG28PRAWNRAZORRENNYRIVER ROACHSOKOEBEKOLMCU09PAPAShenzhenTaipoTuanmunShiongshuiTinshuiweiXianggangziN 22?10.00'E 113?45.00'N 22?25.00'E 113?55.00'E 114?05.00'香港国际机场(VHHH)07L/111.1 07R/109.3 25L/108.9 25R/110.9跑道/仪表着陆频率:500HENGQIN DAOLANTAU ISLANDSANZAO DAOMacauXiazhaDAWANSHAN DAOWAILINDING DAO3691215182124273033369121518212427303336912151821242730332124273033242151821ATIS 126.4MACAU-IntlVMMC 20-110ZHUHAI Sanzao ZGSD 21-131UNL GND90GNDUNL 808020118GNDR 473 R 200-473 W 23W 18W 6W7B330 0R 20 2A02 BAILYCD07LCD34CI07LCI07RCL16D038HD040GD055JD147HD155JD155ZD157UD157VD202XD210XD219ND224VD228VD233M D245DD245R D245V D259ED274KD292XD344MD344NFD07LFI07LFI07RLIMESMALIN ML16NLG28PRAWNRENNYROMEOSMT30SOKOEMCU09PAPASIERAAomenN 22?00.00'E 113?25.00'N 22?15.00'E 113?35.00'E 113?45.00'澳门国际机场(VMMC)跑道/仪表着陆频率: 16/无 34/109.7HuairouNiubaotun369122731518213327ATIS 127.6BEIJING -Capital ZBAA 115-1241CD36RCF36LCF36RD196RD232CFD36RHUR34BeijingShunyiTongzhouE 116?40.00'315182133ABHETBayan Tohoi3518213ZBLA 2169-8591 15CD33CI33FD33LianzhouJunliangchengXianshuigu Xiaozhan391CF34CN34D149ID167IXianshuigu0Dongyang912FD31FQ31OM31Yuci250500100050100050500500500500BayiashanHuanghuashi LanglishiLongtoupuQingshanshiShashijieWumeishan3691215182124273033ATIS 128.8CHANGSHA Huanghua ZGHA 217-85UNL GND UNL GNDCD18CD36CF18CF36CN18CN36D002GD007ND026RD035QD151YD174LD174MD179J D194KD339HFD18FD36FI18FQ18OM18OM36ChangshaN 28?00.00'E 113?05.00'N 28?15.00'E 113?15.00'N 28?30.00'E 113?25.00'长沙黄花国际机场(ZGHA)跑道/仪表着陆频率: 18/110.3 36/109.900100010009133W 2D119GD120FD158HD165RD186DMAMSI50001821243033500500HENGQIN DAOSANZAO DAOGAOLAN DAOHEBAO DAOGujingMacauQianwuDAMANG36912151821242730333691215182124273033315182124273033ATIS 126.4MACAU -IntlVMMC 20-110ZHUHAI Sanzao ZGSD 21-131UNL GNDUNL808020118GNDR 473 R 200-473 W 23W 6W7R 200 2 A02 CD34D038HD055JD147HD155JD219ND245V D249NKILO ML16ROMEOSMT30FOXTTPAPASIERAZhuhaiN 21?50.00'E 113?15.00'N 22?05.00'E 113?25.00'N 22?20.00'E 113?35.00'珠海三灶机场(ZGSD)跑道/仪表着陆频率: 05/110.1 23/108.3500500500HONG KONG BaoanGuanlanHoujieNantouShekouSonggangXiazha3691215212427303336912151821242730333691215182124273033369121518213336912151821242730333691215182124273033CASTLE PEAK RANGE12000GNDATIS 128.2HONG KONG -IntlVHHH 19-124Hong Kong Sek Kong VHSK 50-41ATIS 127.45SHENZHEN Baoan ZGSZ 13-111UNL GND UNL GND118GND 18711890GNDUNL 808020118GNDW 23W 18W 6W 6A 461 B330 W 1850VOR CQ33D038HD040CD040GD055JD065DD065FD065LD166ND208FD224VD245DD245R D245VD251BD253CD259E D274KD292XD300MD311KD349JFD15FD33FI07LFI15FI25LFI33FQ33RITCHROACHSAKODSOSMAXK32TuanmunTinshuiweiN 22?30.00'E 113?40.00'N 22?45.00'E 113?50.00'E 114?00.00'深圳宝安国际机场(ZGSZ)跑道/仪表着陆频率: 15/111.3 33/110.791FI30FQ3039ATIS 126.6WUHANTianheZHHH 112-111WuhanZhifang915D168M691 G D122DD141C D148CD154EOM23200003000315182133D071D0?55.00'327A 581CI03CQ03D152ED194NFF03FQ03Haikou10002502510002501000250252525025025025025025010002502000250250250250250500250100250250250200500250250AotouChin-MenDatongDianqianGulangyuHaicheng JiaomeiLianheXindian3691215182124273033ATIS 127.2CHIN MEN Shang Yi RCBS 93-98ATIS 126.25XIAMEN Gaoqi ZSAM 59-111801230GND 8012 AGL 30GNDUNK GND7A 40 W1039DMECCD05CD23CF06CI05CI23CN05CQ05DD027FD027ND032QD048ND051ND055FD059ND232G D235SD246PFD05FD23FF06FQ05HEYENMA06MA308OM05TAMAUZUSANXiamenN 24?20.00'N 24?35.00'N 24?50.00'厦门高崎国际机场(ZSAM)跑道/仪表着陆频率: 05/110.3 23/109.79 1250250Langqi 691291273033912D037TD037YTantou250Maan3691215279D282SD282ZShaoxing225010005002501005001000250HongjiaiouJiuzhangqiuMingshui3691215182124273033Yaoqiang JINAN ZSJN 75-118UNK 276276GND3 A 59CF01CF19CN01CQ19D186MD186PD197ID198I D241MD343JD343QD360LD360QFD01FF19OM01ABARJinanMingshui N 36?40.00'N 36?55.00'N 37?10.00'济南遥墙国际机场(ZSJN)跑道/仪表着陆频率: 01/108.9 19/无91FD31 052502502502502502502502502502525252525025025025025025025250250250250DongshanMolingguanXiaodanyangZaicheng36912151821242730333691215182124273033ATIS 126.25NANJING Lukou ZSNJ 49-118UNL 276UNK GNDUNK GNDR 343R 343A 470 4 A 7CD06CD24CI24CN24D251MD261PD262KD266KD310FD349ID349KFD06FD24FI24OM06OM24Nanjing N 31?35.00'N 31?50.00'32?0500N 32?05.00南京禄口国际机场(ZSNJ)跑道/仪表着陆频率: 06/110.3 24/110.9250250250250250250250250250250250250250250250250CuozhenDianbuLiangyuanSanhezhenShangpaiheWushan03691215182124273033HEFEILuogang ZSOF 95-98UNL 276276GNDUNK GNDR 343 3 R34 CD14CD32CI14CI32CQ14CQ32D092H D099HD099ID099MD128KD133LD134E D139G D146LD158DD186LD190ED252KD252L D252MD262KD319CFD14FD32FQ14FQ32N 31?35.00'N 31?50.00'N 32?05.00'合肥骆岗机场(ZSOF)跑道/仪表着陆频率: 18/109.1 32/108.3CHANGXING DAOHENG SHAChuanshaFengchengHuinanMinhangNichengZhou Pu036912151821242730333691215182124273033036912151821242730333691215182124273033ATIS 127.85SHANGHAI ZSPD 10-131Pudong UNK GNDUNKGND4G 55G 455G 327A 593CF17CF35D009ED015LD050ID050KD068CD068ED069MD070LD109DD121ND139MD152LD167HD167KD167TD203FD208ED227ED232FD321FD338JD347DD352KFD17FI17OM35D081JD082LN 31?00.00'N 31?15.00'上海浦东机场(ZSPD)16/108.7 17/110.7 34/108.3 35/111.9跑道/仪表着陆频率:250250100025025025025025025000010002502505002502250500250AoshanweiCangkouLancunNancunNiuqibu36303303691215182124273033QINGDAO Liuting ZSQD 33-111UNK GNDCF17CF35D012LD025OD051FD070ED070ID176P D261DD272KD333HD353GD356GFD17FI17FQ35MM35OM35QingdaoJimoLicungN 36?05.00'N 36?20.00'N 36?35.00'青岛流亭国际机场(ZSQD)跑道/仪表着陆频率: 17/110.7 35/111.7CHANGXING DAOFengchengLiuheLuodianMinhangNanbuNanqiaoNanxiangSijingSongjiangTaicangZhou PuZhujing36912151821242730333691215182124273033ATIS 132.25SHANGHAIHongqiao ZSSS 10-111UNK GNDUNKGNDA 5935G 45A 599 G 204A 593G 330 CD18CD36CF18CF36D006OD015LD060ED070LD136ID160ED176PD188SD196FD202ED218GD232FD235LD263ED277D D282C D322H D331JD342ED355J SX39D081JD082LD235LD313OPOMOKMinhangSongjiang JiadingN 31?00.00'E 121?10.00'N 31?15.00'E 121?20.00'N 31?30.00'E 121?30.00'上海虹桥机场(ZSSS)跑道/仪表着陆频率: 18/109.1 36/110.350010005002525252505005002502505002502505005002502502502502502502505005002501000FushanMuping3691215182124273033YANTAI Laishan ZSYT 59-85UNK GNDW 4CD22CF04CI22D044L D060TD068OFD22OM04OM22YantaiFushanNinghai N 37?15.00'E 121?10.00'N 37?30.00'E 121?20.00'E 121?30.00'烟台莱山机场(ZSYT)跑道/仪表着陆频率: 04/111.7 22/110.92000927ATIS 126.4CHONGQING Jiangbei ZUCK 1365-91CD02D199LChongqing951821797 AGLW 90?25.00'200027391D156QD156T7000212733CI36D180PShule31518212733D171ED172E Kashi3151821333ZWWW 2126-118UrumqiDongshan7?35.00'273 A 588Wuija12Shuangcheng5005006912Mudanjiang1250250250500250250250500250250250250SanshilipuDASHAN DAOXIMAYI DAO3691215182124273033ATIS 126.65Zhoushuizi DALIAN ZYTL 108-108280GND UNL 280A 588W8W 5CD10CD28CF10CF28CQ10D084FD103ND217ED283ED309FFD28JinzhouDalianwanLushunkouN 38?45.00'E 121?20.00'N 39?00.00'E 121?35.00'N 39?15.00'E 121?50.00'大连周水子机场(ZYTL)跑道/仪表着陆频率: 10/109.1 28/111.16912200010005002000500200020001000200020001000100010005002000100010001000300010001000100050010002000200100010002000KOREA, NORTHBajiaziChaoyangchuanChongsongLaotougouSandaoYilan3691215182124273033UNK GNDZYYJ 623-85YANJI W 42W 39CF09LongjingN 42?40.00'E 129?15.00'N 42?55.00'E 129?30.00'N 43?10.00'E 129?45.00'延吉朝阳川机场(ZYYJ)跑道/仪表着陆频率: 09/108.7 27/无。


(完整版)航图介绍第⼀章航图概述图幅尺⼨:最佳尺⼨210*148mm,即国际标准组织规定的A5尺⼨负载量:指图⾯上各种划线、符号和注记所占⾯积的⽐例。
颜⾊:航图尽量减少所⽤⾊彩的数量或直接使⽤单⾊制作与印刷。
如⽤彩⾊,⼀般只采⽤⿊、灰和蓝⾊航图的定位⽅法:航图中的所有地物和符号都采⽤真北定位,⽽所需要注明⽅向的数据,都以磁北进⾏注记,同时,在图上注明磁差,并加注年变率。
航图的分类:国际民航组织在附件四《航图》中规定了17种航图的制图规范和要求。
必须提供的航图(六种)机场障碍物图—ICAO、A型(运航限制),机场图—ICAO,世界航图—ICAO 1:1000000精密进近地形图—ICAO ,仪表进近图—ICAO,航路图—ICAO⾮强制性制作的航图机场障碍物图—ICAO、B型,机场地⾯运⾏图—ICAO,航空器停放/停靠图—ICAO航空地图—ICAO 1:500 000 ,航空领航图—ICAO,⼩⽐例尺,作业图—ICAO机场图从航空器停机位到跑道;从跑道到航空器停机位;在该机场运⾏的基本资料停机位置图侯机楼设施复杂的机场提供停机位置图,便于航空器在滑⾏道和停机位之间以及航空器的停放/停靠等地⾯活动。
图中包含停机位置、停机位编号、滑⾏路线和通信频率的资料。
标准仪表进场图STAR已经设⽴标准仪表进场航线,但在区域图中不能详细表⽰的机场,提供标准仪表进场图。
本图提供航路飞⾏阶段到进近阶段按指定的标准仪表进场航线飞⾏所需的资料. 仪表进近图已制定仪表进近程序的机场提供仪表进近图。
通常每⼀种进近程序都有单独的仪表进近图。
本图提供执⾏飞向预定降落跑道的仪表进近程序所需的资料,包括复飞程序及相应的等待程序(适⽤时)。
图中包含机场、禁区、限制区、危险区、⽆线电通信设施、导航设施、最低扇区⾼度、以平⾯图和剖⾯图表⽰的程序的飞⾏航迹、机场运⾏标准、地形障碍物等资料和补充资料。
标准仪表离场图SID已经设⽴标准仪表离场航线,但在区域图中不能详细表⽰的机场,提供标准仪表离场图。


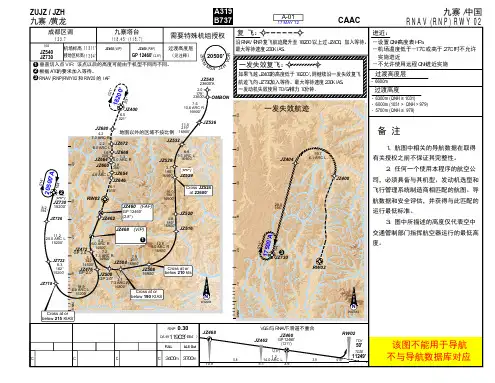
《武汉天河机场航行服务程序净空保护区域一体化图》使用管理办法(征求意见稿)第一条为加强机场净空保护工作,建立长效管理机制,保证民用航空安全与城市建设相协调,根据《中华人民共和国民用航空法》、《民用机场管理条例》、《民用机场飞行程序和运行最低标准管理规定》(CCAR-97)、《民用机场运行安全管理规定》、《湖北省民用机场净空安全保护条例》等有关法律、规定,结合武汉市实际,制定本办法。
第二条本办法适用于《武汉天河机场航行服务程序净空保护区域一体化图》(以下简称《净空一体化图》)武汉市范围内新建、改建、扩建工程项目及附属设施的规划设计及建设高度控制与管理。
第三条《净空一体化图》是依据相关法律规定及天河机场的机场障碍物限制面、飞行各保护区技术标准、管制运行控高等各项要求编制的净空保护控制图,是我市净空安全高度管理的法定图则。
第四条市相关行政(行业)管理部门在办理建(构)筑物及附属设施的审批工作时,应严格依照《净空一体化图》及相关法律限制高度进行审核。
全市涉及省级及以上行政(行业)管理部门立项审批的建设项目,依照行政(行业)管理职责分工,由对应的市行政(行业)管理部门负责衔接,按照《净空一体化图》和本办法规定,做好净空管控工作。
各区人民政府、各功能区管委会负责本辖区《净空一体化图》使用管理工作。
第五条建(构)筑物及其附属设施应按下列程序办理高度控制审批(审查)手续。
(一)位于机场障碍物限制面及东西湖、黄陂、蔡甸等地面导航台保护区域内的建(构)筑物及其附属设施,应严格遵守《净空一体化图》规定的限制高度、不得突破。
该区域内建(构)筑物及其附属设施的建筑高度应征求武汉天河机场有限责任公司意见,并报民航湖北监管局备案。
(二)位于机场障碍物限制面及地面导航台保护区域外,不高出机场地面标高150米(黄海高程180米)的建(构)筑物及其附属设施,由相关行政(行业)管理部门按照职责分工、依据《净空一体化图》及相关法律进行审批。

以武汉天河国际机场泛光照明为例谈机场泛光灯照明保障湖北机场集团有限公司动力能源保障部罗煌泛光灯是一种可以向四面八方均匀照射的点光源,它的照射范围可以任意调整,在场景中表现为一个正八面体的图标。
泛光灯不是聚光灯、投射灯、射灯。
泛光灯制造出的是高度漫射的、无方向的光而非轮廓清晰的光束,因而产生的阴影柔和而透明,用于物体照明时,照明减弱的速度比用聚光灯照明时慢得多,甚至有些照明减弱非常慢的泛光灯,看上去像是一个不产生阴影的光源。
而聚光灯投射出定向的、边界清楚的光束,照亮一个特定的区域。
对于处于扩建期的武汉天河国际机场来说,T2航站楼泛光灯主要采用高杆灯为主,移动照明为辅的交差互补组合型运营模式,严格按照民航泛光照明技术规范及技术要求实施运行及维护管理。
1《机坪泛光照明标准》简介机坪高杆灯为机坪泛光照明的主要设施,动力能源保障部负责高杆灯的及供电电缆等设施的日常管理和检查维护。
1.1总则为保证航空器夜间及低能见度条件下在机坪工作区内安全有效地运行,使机坪泛光照明做到安全适用、技术先进、经济合理,特制定本标准。
1.1.1机坪泛光灯必须对机坪工作区提供足够的照明,必须使得有关飞机标志、地面标志和障碍物标志的图形和颜色能够正确地加以辩认。
1.1.2机坪泛光灯的布置和朝向应使得每一机位能从两个方向以上受光,以尽量减少阴影1.1.3机坪泛光灯照明应不产生妨碍飞机驾驶员、塔台管制员、地面工作人员的眩光。
1.1.4机坪泛光灯的完好率应不低于80%,不允许整组灯不亮。
1.2术语和定义1.2.1机坪工作区Operation area机坪上供飞机停泊、进行地面作业的区域及其邻近的区域。
1.2.2飞机机位Aircraft Stand机坪上用以停放飞机的一块特定场地。
1.2.3机场净空Aerodrome obstaclefree space为保障飞机起降安全而规定的障碍物面以上的空间,用以限制机场及其周围地区碍物的高度。
1.2.4照度Illuminance表面上一点处的照度是入射在包含该点面元上的光通量dФ除以该面元面积dA之商。

航路3.1.2 B 系列航路航线B 系列航路航线航路、航线代号、导航点名称、坐标 磁航迹 距离(千米/海里)最低 飞行高度(米)宽度 (千米)巡航高度层方向管制单位B206▲阜康VOR (FKG) N44° 10.3′ E087° 58.9′358°/178° 3000↓ 乌鲁木齐ACC▲OMDAXN44° 34.5′ E087° 59.5′ 45(24)358°/178°▲RUROKN44° 47.4′ E087° 59.9′ 24(13)358°/178° ▲阿勒泰VOR (TAI) N47° 44.9′ E088° 05.1′ 328(177)339°/159°4500▲GOPTON49° 05.5′ E087° 28.0′156(84)↑B208(B208航线NIXAL-呼和浩特段为飞越航线,飞行高度限制为8400米含以上) ▲NIXALN43° 12.7′ E110° 53.0′168°/348° 2816↓ 呼和浩特ACC 7800(含)以下 北京ACC 7800(不含)以上▲呼和浩特VOR (HET) N40° 43.6′ E111° 53.9′ 289(156)174°/354°▲DOTOSN40° 31.7′ E111° 56.9′ 22(12)174°/354°3205ATPOK △N40° 06.8′ E112° 02.9′ 47(25)174°/354° ▲LIPRIN39° 58.2′ E112° 05.1′ 16(9)174°/354° ▲TODAMN39° 29.5′ E112° 12.1′ 54 (29)174°/354° ▲EKETAN37° 52.5′ E112° 35.4′ 183(99)174°/354° 太原ACC 7800(含)以下 北京ACC 7800(不含)以上▲太原VOR (TYN) N37° 45.0′ E112° 37.1′14(8)170°/350°B系列航路航线航路、航线代号、导航点名称、坐标磁航迹距离(千米/海里)最低飞行高度(米)宽度(千米)巡航高度层方向管制单位XIVEP△N37° 37.9′ E112° 39.5′13(7)170°/350°2623 太原ACC7800(含)以下北京ACC7800(不含)以上▲ANPIGN37° 03.3′ E112° 51.0′66(36) 170°/350°▲EGEBIN36° 47.6′ E112° 56.2′30(16) 170°/350°▲长治NDB (SQ)N36° 14.3′ E113° 07.1′64(34)165°/345°2391▲PADNON35° 50.8′ E113° 17.6′46(25) 165°/345°▲TAMIXN35° 36.7′ E113° 23.9′28(15)165°/345°郑州ACC9800(含)以下北京ACC9800(不含)以上▲NOPINN35° 26.8′ E113° 28.3′20(11) 165°/345°▲DUBAGN34° 51.8′ E113° 43.8′69(37)169°/349°9138▲新郑VOR (CGO)N34° 31.0′ E113° 50.5′40(21)146°/326°713▲周口VOR (ZHO)N33° 39.8′ E114° 39.2′121(65)135°/315°65220▲阜阳VOR (FYG)N32° 52.9′ E115° 43.9′133(72)134°/314°合肥ACC7800(含)以下上海ACC7800(不含)以上989▲BIPIMN32° 33.9′ E116° 11.0′55(30) 134°/314°P343△N32° 21.8′ E116° 28.2′35(19) 134°/314°▲PEDNUN32° 11.3′ E116° 43.7′31(17) 134°/314°▲合肥VOR (HFE)N31° 46.6′ E117° 18.0′71(38)↑B 系列航路航线航路、航线代号、导航点名称、坐标磁航迹距离(千米/海里)最低 飞行高度(米) 宽度 (千米) 巡航高度层方向管制单位 B213 (天河VOR-崇州VOR 段实施RNA V5运行,崇州VOR-拉萨VOR 段实施RNP4运行,申请使用时,已完成相关PBN 适航和运行合格审定的航空器,需严格按规定填写飞行计划报编组10和编组18内容,空管部门会在起飞前的协同决策阶段给予优先放行;对不符合PBN 适航和运行合格审定要求的航空器,空管部门将配备适当间隔以确保区域飞行的安全和秩序。
武汉天河国际机场使用手册总经理声明武汉天河国际机场为4E级民用机场,本场各项设施与管理工作均符合“民航总局第156号令”的相关要求。
《武汉天河国际机场使用手册》(以下简称《手册》)是按照中国民用航空规章《民用机场使用许可规定》(CAAC—139CA-R1)的要求,结合武汉天河国际机场的实际编制而成。
编制《手册》的目的,是为了建立一套适合武汉天河国际机场运行管理的政策、程序、方法,以及对运行保障实施科学管理的规章制度,认真履行机场管理机构的运行安全职责。
《手册》作为武汉天河国际机场的基础性法规文件,于2006年月日获得民航总局批准(民航机函号),自发布之日起施行。
在此,我要求武汉天河机场有限责任公司各单位、各部门及《手册》中涉及的相关人员,必须认真学习和掌握《手册》中关于机场运行的基本程序和方法,在运行保障工作中,不折不扣地贯彻执行,并随时接受中国民航管理当局的监督检查。
我授权,武汉天河机场有限责任公司飞行区管理部负责《手册》的修订、报批和动态管理工作,使之与实际相符合,以确保机场运行安全。
总经理(签名)日期:手册修改记录目录第一章总则 ............................................................................... 1-11.1 依据........................................... 1-11.2 变更、公告...................................... 1-21.3 适用范围....................................... 1-31.4 解释........................................... 1-31.5 企业基本情况................................... 1-31.6 总平面规则及管理............................... 1-61.7 机场土地使用管理............................... 1-91.8 城市建设发展规划对机场的要求.................. 1-10第二章机场安全管理系统 .......................................................... 2-12.1 机场安全管理方针政策........................... 2-12.2 机场安全管理组织............................... 2-12.3 机场安全信息管理和报告制度..................... 2-32.4 事故、差错的处理............................... 2-92.5 安全隐患(问题)处理.......................... 2-102.6 航空安全检查.................................. 2-112.7 员工安全培训.................................. 2-142.8 员工持证上岗.................................. 2-162.9 对驻场单位及外部人员管理原则.................. 2-18第三章机场使用细则与飞行程序................................................ 3-13.1 机场概况....................................... 3-13.2 无线电、导航设备................................ 3-33.3 灯光设备....................................... 3-53.4 航站区域及地形特征和主要障碍物................. 3-53.5 气象特征和运行最低标准......................... 3-63.6 机场临时关闭与恢复运行程序.................... 3-113.7 起落航线规定.................................. 3-183.8 仪表进近、过度高、过渡高渡层、等待和优先着陆..... 3-183.9 空域、走廊、放油区............................. 3-183.10 进、离场规定及航行管制规定.................... 3-193.11 飞机滑行规定和车辆人员在场内通行的规定 ....... 3-193.12 主要邻近机场................................. 3-213.13 特殊规定和注意事项........................... 3-23第四章飞行区场地管理.............................................................. 4-1概述................................................ 4-14.1 组织结构及职能分配............................. 4-34.2 跑道技术标准及检查维护......................... 4-34.3 滑行道技术标准及检查维护....................... 4-64.4 机坪技术标准及检查维护......................... 4-84.5 草地(升降带)技术标准及检查维护................. 4-94.6 排水系统技术标准及检查维护.................... 4-104.7 飞行区环场道、围界技术标准及检查维护........... 4-114.8 场务机具、车辆及其他检查维护措施............... 4-144.9 安全运行程序及措施............................ 4-164.10 赔偿损失..................................... 4-17第五章目视助航设施管理 .......................................................... 5-1概述................................................ 5-15.1 组织机构与职责................................. 5-35.2 进近灯光系统的组成、技术标准及检查维护.......... 5-45.3 目视进近坡度指示系统的组成、技术标准及检查维护.. 5-75.4 跑道和滑行道灯光系统技术标准及检查维护 ......... 5-85.5 机坪泛光照明技术标准及检查维护................ 5-125.6 助航灯光站及主要设备技术标准及检查维护 ........ 5-135.7 助航灯光安全运行程序及措施.................... 5-165.8 地面标志线技术标准及检查维护.................. 5-205.9 标记牌技术标准及检查维护...................... 5-225.10 标志物技术标准及检查维护..................... 5-255.11 航空器目视停靠引导系统技术标准及检查维护 ..... 5-265.12 损坏的赔偿................................... 5-26第六章供水、供电设施管理....................................................... 6-1概述................................................ 6-16.1 组织结构与职责分配............................. 6-26.2 航站区的供电设施及技术标准..................... 6-36.3 航站区的供电设施维护标准....................... 6-66.4 供电设备安全运行管理规定....................... 6-76.5 变电站消防设备及有关规定...................... 6-116.6 应急电源(备用发电机组)的技术标准、检查维护及应急供电处理............................................... 6-136.7 供水系统设施及技术标准........................ 6-16第七章机坪运行管理 ................................................................. 7-1概述................................................ 7-17.1 管理机构与职责................................. 7-27.2 进场控制....................................... 7-37.3 航空器地面运行管理............................. 7-37.4 车辆地面运行管理............................... 7-87.5 车辆停靠航空器................................ 7-127.6 车辆避让航空器的规定.......................... 7-137.7 货物的运送.................................... 7-147.8 航空垃圾、废弃物的运输......................... 7-157.9 人员地面运行的管理............................ 7-157.10 机坪施工..................................... 7-167.11 机坪运行管理权力............................. 7-167.12 罚则......................................... 7-16第八章机场控制区内车辆及驾驶人员的管理.............................. 8-1概述................................................ 8-18.1 管理机构及职责................................. 8-28.2 机场控制区道口管理............................. 8-38.3 车辆管理....................................... 8-38.4 车辆行驶....................................... 8-58.5 速度限制....................................... 8-68.6 车辆、设备的停放................................ 8-68.7 驾驶员的管理................................... 8-78.8 权力........................................... 8-8第九章施工管理 ........................................................................ 9-1概述................................................ 9-19.1 管理机构和职责................................. 9-29.2 工程项目管理的程序及相关要求................... 9-49.3 施工安全管理................................... 9-99.4 不停航施工管理................................ 9-109.5 不停航施工管理的相关规定...................... 9-13第十章空中交通管制设施的运行维护管理 ............................... 10-1概述............................................... 10-110.1 本场的主要通信导航及监视设备................. 10-210.2 运行维护管理................................. 10-310.3 本场主要的气象设施.......................... 10-23第十一章供油设施管理与安全运行.......................................... 11-1概述............................................... 11-111.1 储油设施(使用油库)的运行及安全管理 ......... 11-111.2 油罐及附件................................... 11-211.3 储油设施的防雷击设施设备技术标准及检查维护 ... 11-611.4 供油设施的运行安全管理及检查维护 ............. 11-711.5 航空燃油的种类、规格及主要技术指标 .......... 11-1111.6 航空燃油的质量控制.......................... 11-1111.7 航空器加油作业与处理........................ 11-1311.8 航空器抽卸燃料的作业与处理.................. 11-1711.9 F类航空器的加/抽油作业与处理............... 11-2011.10 加油车的行驶及停位......................... 11-2011.11 加油作业的安全规范......................... 11-2211.12 加/抽油作业对辅助设备的安全要求 ........... 11-2411.13 供油系统的应急保障......................... 11-25第十二章危险品管理 ............................................................... 12-1概述............................................... 12-112.1 管理机构和职责............................... 12-212.2 危险品运输的基本原则......................... 12-212.3 危险品航空运输的申请和许可................... 12-412.4 危险物品的运输准备要求....................... 12-612.5 危险物品运输的管理........................... 12-712.6 危险物品的安全检查.......................... 12-1312.7 危险品管理的信息报告程序.................... 12-1412.8 危险品管理的培训............................ 12-1512.9 防止隐含危险品的预防措施及危险品事件应急处置方案.................................................. 12-16第十三章公共安全管理............................................................ 13-1概述............................................... 13-113.1 管理机构及职责............................... 13-213.2 航站区公共安全............................... 13-213.3 候机楼公共设施安全........................... 13-313.4 航站区以外公共安全........................... 13-413.5 突发公共事件应急预案......................... 13-613.6 权力......................................... 13-613.7 罚则......................................... 13-7第十四章机场航空安全保卫(空防)管理.............................. 14-1概述............................................... 14-114.1 机场区域划分................................. 14-314.2 民航公安机关................................. 14-314.3 空防安全..................................... 14-514.4 隔离区通行证管理............................. 14-914.5 闭路电视监控................................ 14-1114.6 安全检查.................................... 14-1114.7 应急指挥中心................................ 14-2414.8 航空安全意外的调查.......................... 14-2714.9 损坏的赔偿.................................. 14-2814.10 新闻发布................................... 14-29第十五章机场净空及电磁环境保护区管理.............................. 15-1概述............................................... 15-115.1 组织机构及职责分配........................... 15-215.2 净空保护区技术标准及检查维修................. 15-415.3 障碍物位置及技术标准......................... 15-615.4 电磁环境保护管理............................ 15-1015.5 机场环境保护管理............................ 15-2915.6 噪音防治.................................... 15-3015.7 污水处理.................................... 15-30第十六章鸟害及野生动物危害防治 ........................................ 16-1概述............................................... 16-116.1 管理机构和职责............................... 16-216.2 机场鸟害防治方案的制定....................... 16-316.3 机场周边环境治理措施......................... 16-516.4 机场鸟害防治的措施........................... 16-516.5 机场鸟害防治的设备设施及检查维护 ............. 16-616.6 野生动物危害的防治........................... 16-9第十七章救援及消防设施管理 ............................................... 17-1概述............................................... 17-117.1 机场消防站................................... 17-317.2 消防业务车辆的技术标准....................... 17-417.3 消防装备、设备/器材配置....................... 17-617.4 消防车辆的检查维护........................... 17-617.5 消防应急通迅器材技术标准..................... 17-717.6 消防通讯器材检查维护......................... 17-817.7 消防业务车辆主要灭火剂的技术标准与检查维护 ... 17-817.8 航楼固定式消防设施的技术标准与检查维护 ....... 17-917.9 航站楼移动式消防设施的技术标准与检查维护 .... 17-1417.10 航站楼消防安全管理......................... 17-1517.11 机坪固定式消防设施技术标准及检查维护 ....... 17-1917.12 机坪移动式消防设备技术标准及检查维护 ....... 17-2017.13 残损飞机搬移设备技术及检查维护............. 17-2117.14 应急救援常规设备的配置及检查维护 ........... 17-2117.15 医疗救护机构与急救/救护设施设备的配置 ...... 17-23第十八章应急救援计划.......................................................... 18-1概述............................................... 18-118.1 组织机构图与相关职责......................... 18-218.2 应急救援的基本原则与规定..................... 18-718.3 应急信息流程................................ 18-1318.4 机场内航空器失事............................ 18-1418.5 机场外航空器失事............................ 18-2018.6 航空器空中故障.............................. 18-2118.7 非法干扰/劫持航空器......................... 18-2218.8 非法干扰/航空器的爆炸物威胁................. 18-2518.9 非法干扰/飞行活动区的爆炸物威胁............. 18-2818.10 燃油溢漏................................... 18-3018.11 航空器地面事故............................. 18-3218.12 残损航空器的搬移........................... 18-3418.13 道面的紧急抢修............................. 18-35第十九章应急预案计划(非航空器救援预案) ........................... 19-1概述............................................... 19-119.1 职责、基本原则、规定及信息通报流程............. 19-219.2 航站楼失火................................... 19-719.3 非法干扰/航站楼的爆炸物威胁................. 19-1019.4 非法干扰/冲击机场........................... 19-1219.5 危险品污染.................................. 19-1319.6 疫情........................................ 19-1419.7 医学紧急情况................................ 19-1419.8 自然灾害/强风、强降水、雷暴、台风、地震......... 19-18第二十章应急演练................................................................. 20-120.1 演练目的..................................... 20-120.2 演练类型..................................... 20-120.3 基本要求..................................... 20-120.4 演练的基本步骤............................... 20-3第二十一章机场资料 ............................................................. 21-121.1 机场业务职责和基本情况....................... 21-121.2 跑道与升降带................................. 21-721.3 滑行道....................................... 21-921.4 机坪........................................ 21-1021.5 机场管理范围内要求加装照明或制作标志的每一个障碍物的位置............................................ 21-1421.6 通信、导航、航管、气象等空中交通管制设施....... 21-1721.7 灯光、标志牌、标记物等目视助航设施............ 21-1821.8 旅客航站、货物航站及其他建筑(含地下工程)的说明21-2021.9 救援与消防、安全防护和安全检查设施及设备的说明21-2721.10 公用设施、供油设施、供电设施、机务维修设施的说明.................................................. 21-3321.11 电磁环境保护、噪声防治、污水治理和排放、冰雪控制、航空固体垃圾处理等环境保护设施及鸟害情况的说明 ...... 21-4021.12 机场建设史................................. 21-4121.13 城市总体规划对本机场的要求................. 21-46第一章总则1.1 依据1.1.1 《武汉天河国际机场使用手册》根据《中华人民共和国民用航空法》、《民用机场使用许可规定》(CCAR-139CA-R1)、《民用机场使用手册编制与管理基本要求》(AP-81-CA-7)、《民用机场使用手册机场资料编制要求》(AC-CA-2000-5)、《机场使用手册附图绘制基本要求》(AC-CA-2000-4)的标准和建议措施编制,符合民航总局有关机场使用许可的标准和规定,符合中国现行的法律法规及国际民航组织的建议和标准,是规范武汉天河国际机场安全运行和指导机场公司各部门工作的基本文件。