大词类和八大句子成分
- 格式:doc
- 大小:42.00 KB
- 文档页数:5

英语基础语法知识第一节十大词类一、词类能够自由运用的最小语言单位叫词。
根据词的形式、意义及其在句中的作用所作的分类叫词类(parts of speech)。
英语的词通常分为十大类,即名词、冠词、代词、数词、形容词、副词、动词、介词、连词和感叹词。
现分别叙述如下:(一)名词名词(noun)是表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。
例如:foreigner外国人soap 肥皂Newton牛顿law 法律freedom自由peace和平英语名词可分为两大类:1.普通名词(mon noun)是某一类人、事物、某种物质或抽象概念的名称。
例如:teacher教师market市场rice大米magazine杂志sound声音production生产2.专有名词(proper noun)是特定的某人、地方或机构的名称。
专有名词的第一个字母必须大写。
例如:Hemingway海明威Russia 俄罗斯New York 纽约United Nations联合国名词又可分为可数名词(countable noun)与不可数名词(uncountable noun)两种。
可数名词有单、复数之分。
绝大多数名词的复数形式的构成是在单数名词的后面加-s或-es。
例如:shop→shops商店bus→buses 公共汽车library→libraries图书馆toy→toys玩具leaf→leaves树叶英语中有一些名词的复数形式是不规则的。
例如:man→men男人tooth→teeth牙齿datum→data数据有关名词复数形式构成的具体规则,请参阅有关的英语语法书。
(二)冠词冠词(article)放在名词之前,帮助说明该名词所指的对象。
冠词分为不定冠词(indefinite article)和定冠词(definite article)两种。
不定冠词为a/an,用在单数名词之前,表示某一类人或事物的“一个”。
a用在以辅音开头的名词之前,an用在以元音开头的名词之前。


初高中衔接——英语语法一、十大词类1.名词:表示人或事物的名称。
2.动词:表示动作或状态。
3.形容词:表示人或事物的性质或状态。
4.数词:表示数目或顺序。
5.代词:代替名词或数词等。
6.副词:表示动作特征或性状特征。
7.冠词:表示名词的泛指或特指。
8.介词:表示名词或代词与其他词的关系。
9.连词:表示连接并列成分的词。
10.感叹词:表示说话时的感情或口气。
二、八大句子成分要弄清楚英语句子的结构,我们先要弄清楚组成一个句子的各个组成部分,即句子的成分:句子的主干成分:主语、谓语、宾语、表语、补语 句子的次要成分:定语、状语、插入语、同位语1、主语:(1)是一个句子所要说明的人和事物,(2)表示句子说的是什么人或什么事,(3)是一句的主体;(4)一般位于句首,但在there be 、疑问句(主语不是疑问词)、倒装句中,主语在谓语动词、助动词、情态动词之后。
主语可以用以下这些表示: 1. 名词;2. 代词; 3. 数词;4. 动名词;5. 不定式; 6. 词组或复合结构;7. 从句;8. 名词化的其他词类。
eg:1) A foreign language is a weapon in the struggle of life. 2) Who is speaking, please? This is Jack speaking. 3) Two will be enough.4) Smoking is very dangerous. 5) To see is to believe.6) Whether we’ll go depends on the weather. 7) “A” is an article.2、谓语:①它是说明主语的动作或状态的,说明主语做什么、怎么做;②作谓语的常有:及物动词或及物动词短语; 简单谓语:由一个动词(短语)构成 ③ A.情动/助动+动原 复合谓语:B.系动词+表语1) The soup tastes good 2) The boy is interested in playing PC games. 3) The boss made the workers work long hours.4) He practises playing the piano every day. 5) They had finished the job when the boss came 6) Record every word you hear. 7) He didn’t turn to me for help.*在英语简单句中,只能有而且(一般情况下)必须有一个谓语部分!3、宾语:(1)它是表示及物动词或及物动词短语所作用的对象的(动宾),如 I studyEnglish 中的English 和He makes full use of his spare time to study 中的his动词的分类情态动词 助动词 系动词实义动词及物动词不及物动词spare time.(2)介词后的名词或代词,叫做介词的宾语(介宾),如He went away with no words中的no words. (3)一般位于及物动词或介词之后。
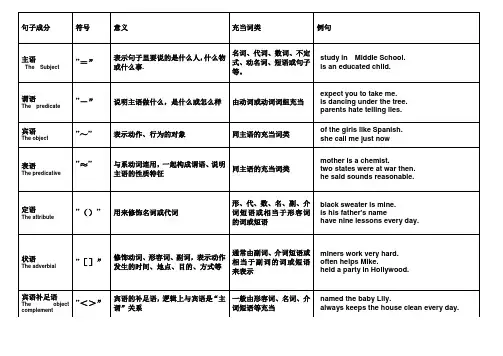
一.句子成分详解一览表二.专题练习I.指出下列句子划线部分是什么句子成分:1. The students got on the school bus.2. He handed me the newspaper.3. I shall answer your question after class.4. What a beautiful Chinese painting!5. They went hunting together early in the morning.6. His job is to train swimmers.7. He took many photos of the palaces in Beijing.8. There is going to be an American film tonight.9. He is to leave for Shanghai tomorrow.10. His wish is to become a scientist.11. He managed to finish the work in time.12. Tom came to ask me for advice.13. He found it important to master English.14. Do you have anything else to say15. To be honest; your pronunciation is not so good.16. Would you please tell me your address17. He sat there, reading a newspaper.18. It is our duty to keep our classroom clean and tidy.19. He noticed a man enter the room.20. The apples tasted sweet.II分析下列1. Our school is not far from my home.2. It is a great pleasure to talk with you3. All of us considered him honest.4. My grandfather bought me a pair of sports shoes.5. He broke a piece of glass.6. He made it clear that he would leave the city.7. ---I than her,child .8. Tees turn green when comes.9. They pushed the door open. 10. Grandma told me an interesting story last night.11. He wrote carefully some letters to his . the students think highly of his teaching13. We need a place twice larger than this one. 14. He asked us to sing an English song.15. Don't get nervous,help yourself to what you like.will make our school more beautiful.17. He didn't come.That is why he didn't know.18. She showed us her many of her pictures. 19. The old man lives a lonely life.20. Luckily the 1989 earthquake did not happen in the center of town.21. The cars made in Japan are better than those in Germany.22. There are so many people in the hall that it's hard for me to find him.23. No matter how difficult the task may be, we must fulfil it this month.24. Go back where you came from. 25. We must do whatever the people want us to do.26. At last he got home, tired and hungry. 27. Would you please pass me the cup28 Mary handed her homework to the teacher. 29. Do you know the latest news about him?’llget my hair cut tomorrow.III用符号划出下列短文各句中的主语”=”、谓语”-”、宾语”~”定语”()”、状语”[]”、补语”<>”:表语”≈”I hope you are very well. I'm fine, but tired. Right now it is the summer vacation and I'm helping my Dad on the farm. August is the hottest month here. It is the time of year for the rice harvest, so every day I work from dawn until dark. Sometimes we go on working after dark by the lights of our tractors. We grow rice in the south of the States, but in the north where it is colder they grow wheat. We have a lot of machines on the farm. Although the farm is large, my Dad has only two men working for him. But he employs more men for the harvest. My brother takes care of the vegetable garden. It doesn't often rain in the summer here. As a result, we have to water the vegetable garden. Every evening we pump water from a well. It then runs along channels to different parts of the garden.。

精心整理英语基础语法知识第一节 十大词类一、词类能够自由运用的最小语言单位叫词。
根据词的形式、意义及其在句中的作用所作的分类叫词类( 1. 2. Hemingway 海明威 Russia 俄罗斯New York 纽约 United Nations 联合国名词又可分为可数名词(countable noun )与不可数名词(uncountable noun )两种。
可数名词有单、复数之分。
绝大多数名词的复数形式的构成是在单数名词的后面加-s 或-es 。
例如: shop →shops 商店 bus →buses 公共汽车 library →libraries 图书馆toy→toys玩具leaf→leaves树叶英语中有一些名词的复数形式是不规则的。
例如:man→men男人tooth→teeth牙齿datum→data数据有关名词复数形式构成的具体规则,请参阅有关的英语语法书。
(二)冠词(三)1.人称代词,如:I, you, they, it等;2.物主代词,如:my, his, their, our, mine, hers等;3.反身代词,如:myself, yourself, itself, ourselves, oneself等;4.相互代词,如:each other, one another等;5.指示代词,如:this, that, these, those, such, same等;6.疑问代词,如:who, whom, whose, which, what等;7.关系代词,如:who, whom, whose, which, that等;8.不定代词,如some, any, no, all, one, every, many, a little, someone, anything等;(四)数词数词(numeral)是表示“数量”和“顺序”的词。
前者称为基数词,例如:one(一),twenty (二十)(五)例如:(六)12.疑问副词,例如:when(何时),where(何地),how(如何),why(为什么)等;3.连接副词,例如:therefor(因此),then(然后),however(然而),otherwise(否则)等;4.关系副词,例如:where, when, why等。
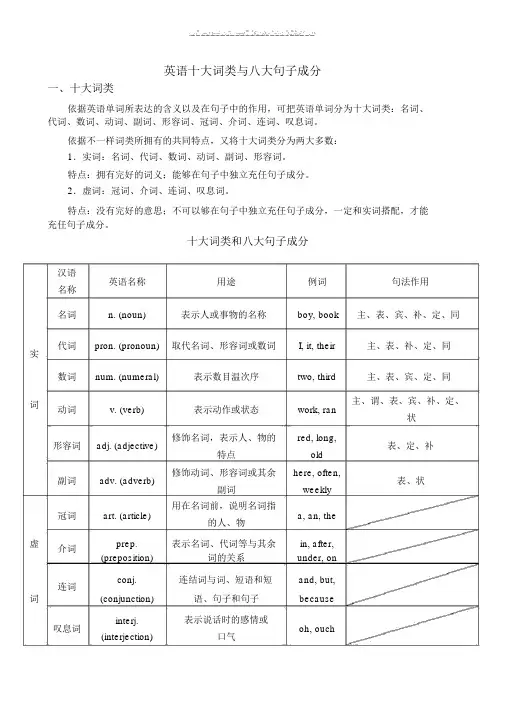
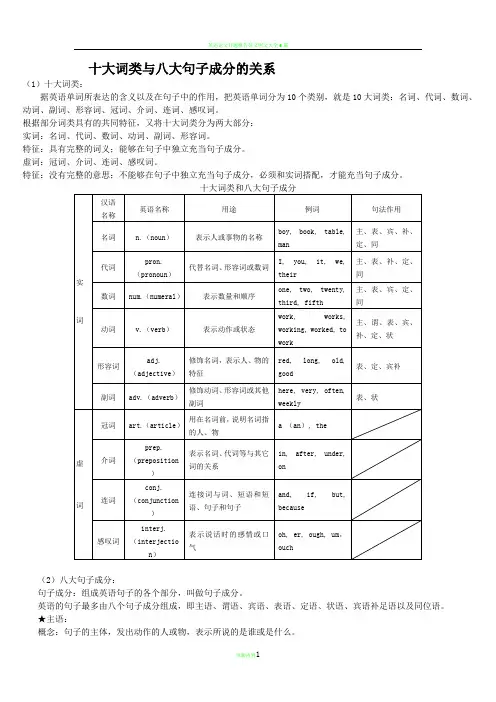
英语十大词类与八大句子成分一、十大词类依据英语单词所表达的含义以及在句子中的作用,可把英语单词分为十大词类:名词、代词、数词、动词、副词、形容词、冠词、介词、连词、叹息词。
依据不一样词类所拥有的共同特点,又将十大词类分为两大多数:1.实词:名词、代词、数词、动词、副词、形容词。
特点:拥有完好的词义;能够在句子中独立充任句子成分。
2.虚词:冠词、介词、连词、叹息词。
特点:没有完好的意思;不可以够在句子中独立充任句子成分,一定和实词搭配,才能充任句子成分。
十大词类和八大句子成分汉语英语名称用途例词句法作用名称名词n. (noun) 表示人或事物的名称boy, book 主、表、宾、补、定、同实代词pron. (pronoun) 取代名词、形容词或数词I, it, their 主、表、补、定、同数词num. (numeral) 表示数目温次序two, third 主、表、宾、定、同词动词v. (verb) 表示动作或状态work, ran 主、谓、表、宾、补、定、状形容词adj. (adjective) 修饰名词,表示人、物的red, long,表、定、补特点old副词adv. (adverb) 修饰动词、形容词或其余here, often,表、状副词weekly冠词art. (article) 用在名词前,说明名词指a, an, the 的人、物虚介词prep. 表示名词、代词等与其余in, after, (preposition) 词的关系under, on连词conj. 连结词与词、短语和短and, but, (conjunction) 语、句子和句子because 词叹息词interj. 表示说话时的感情或oh, ouch (interjection) 口气二、八大句子成分组成句子的各个部分叫做句子成分。
句子成分有主要成分和次要成分;主要成分有主语和谓语;次要成分有表语、宾语、定语、状语、补足语和同位语。

现代汉语词类和句法成分一一对应现代汉语词类和句法成分一一对应的关系是指,在现代汉语中,每个词类都对应着一种或多种句法成分。
下面列举了10个常见的词类和它们对应的句法成分。
1. 名词(N):名词在句子中可以作为主语、宾语、定语、补语等句法成分。
例如:“小明是一名学生。
”(主语)“我喜欢读书。
”(宾语)“这是一本有趣的书。
”(定语)“他当选为班长。
”(补语)2. 动词(V):动词在句子中可以作为谓语、宾语、补语等句法成分。
例如:“他在跑步。
”(谓语)“我喜欢看电影。
”(宾语)“他变得很强壮。
”(补语)3. 形容词(Adj):形容词在句子中可以作为定语、补语等句法成分。
例如:“这个苹果很红。
”(定语)“她吃得很饱。
”(补语)4. 副词(Adv):副词在句子中可以修饰动词、形容词、副词等句法成分。
例如:“他快速地跑过去。
”(修饰动词)“这个问题很难。
”(修饰形容词)“他非常努力地学习。
”(修饰副词)5. 介词(P):介词在句子中可以引导名词短语作为定语、状语、补语等句法成分。
例如:“他在桌子上放了一本书。
”(定语)“他每天都去图书馆学习。
”(状语)“她对他充满了爱。
”(补语)6. 代词(Pron):代词在句子中可以作为主语、宾语、定语、补语等句法成分。
例如:“他是我的朋友。
”(主语)“我喜欢她。
”(宾语)“这是你的书。
”(定语)“我认为他是对的。
”(补语)7. 连词(Conj):连词在句子中可以连接并列句子、从句等句法成分。
例如:“我喜欢唱歌,也喜欢跳舞。
”(连接并列句子)“他说他会来。
”(连接主句和从句)8. 助词(Aux):助词在句子中可以用来表示时态、语气、态度等句法成分。
例如:“我正在吃饭。
”(表示进行时态)“他可能会来。
”(表示可能性)“请你帮我一个忙。
”(表示请求)9. 叹词(Int):叹词在句子中可以用来表示感叹、问候等句法成分。
例如:“哇,好漂亮的花!”(表示感叹)“嗨,你好!”(表示问候)10. 量词(Cl):量词在句子中可以用来修饰名词短语,表示数量。

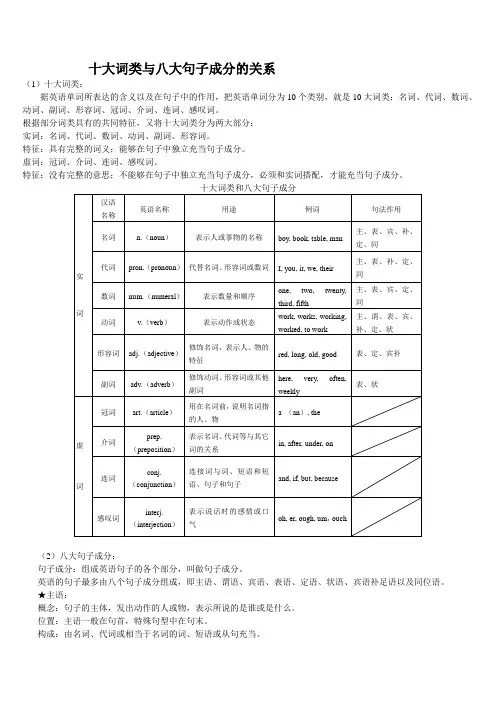
十大词类与八大句子成分的关系(1)十大词类:据英语单词所表达的含义以及在句子中的作用,把英语单词分为10个类别,就是10大词类:名词、代词、数词、动词、副词、形容词、冠词、介词、连词、感叹词。
根据部分词类具有的共同特征,又将十大词类分为两大部分:实词:名词、代词、数词、动词、副词、形容词。
特征:具有完整的词义;能够在句子中独立充当句子成分。
虚词:冠词、介词、连词、感叹词。
特征:没有完整的意思;不能够在句子中独立充当句子成分,必须和实词搭配,才能充当句子成分。
(2)八大句子成分:句子成分:组成英语句子的各个部分,叫做句子成分。
英语的句子最多由八个句子成分组成,即主语、谓语、宾语、表语、定语、状语、宾语补足语以及同位语。
★主语:概念:句子的主体,发出动作的人或物,表示所说的是谁或是什么。
位置:主语一般在句首,特殊句型中在句末。
构成:由名词、代词或相当于名词的词、短语或从句充当。
例:Henry is a good boy.亨利是个好孩子。
He ran away.他跑掉了。
To learn a foreign language is not easy.学习一门外语不容易。
Driving to Beijing is not difficult.开车去北京不难。
What has happened proves that our policy is right. 发生的一切证明我们的政策是对的。
Whether we’ll go depends on the weather. 我们是否去要看天气。
★谓语:概念:说明主语的动作、特征、状态等的句子成分,叫做谓语。
位置:谓语动词通常位于主语之后,特殊句型位于主语之前。
构成:由动词或动词短语充当。
例如:We go to school from Monday to Friday. 我们周一至周五上学。
I went to the zoo yesterday.昨天我去了动物园。
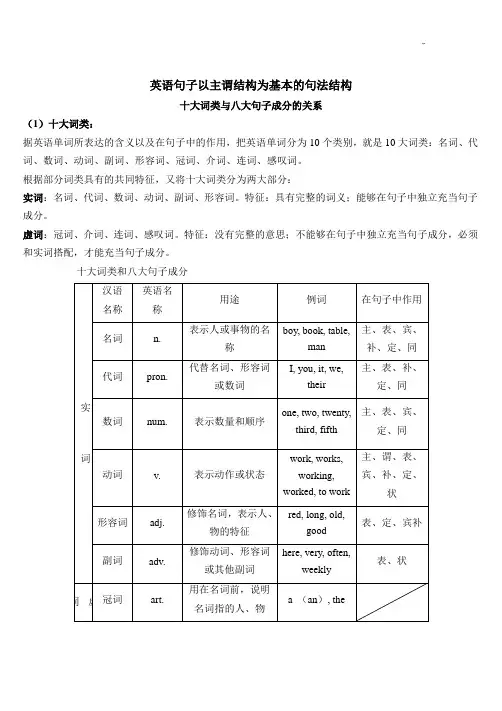
英语句子以主谓结构为基本的句法结构十大词类与八大句子成分的关系(1)十大词类:据英语单词所表达的含义以及在句子中的作用,把英语单词分为10个类别,就是10大词类:名词、代词、数词、动词、副词、形容词、冠词、介词、连词、感叹词。
根据部分词类具有的共同特征,又将十大词类分为两大部分:实词:名词、代词、数词、动词、副词、形容词。
特征:具有完整的词义;能够在句子中独立充当句子成分。
虚词:冠词、介词、连词、感叹词。
特征:没有完整的意思;不能够在句子中独立充当句子成分,必须和实词搭配,才能充当句子成分。
十大词类和八大句子成分(2)八大句子成分:句子成分:组成英语句子的各个部分,叫做句子成分。
英语的句子最多由八个句子成分组成,即主语、谓语、宾语、表语、定语、状语、宾语补足语以及同位语。
★主语:概念:句子的主体,发出动作的人或物,表示所说的是谁或是什么。
位置:主语一般在句首,特殊句型中在句末(如用it充当形式宾语,把真正的主语放在后面)。
构成:由名词(短语)、代词、动名词、动词不定式或从句充当。
例:Henry is a good boy.亨利是个好孩子。
To learn a foreign language is not easy.学习一门外语不容易。
Driving to Beijing is not difficult.开车去北京不难。
What has happened proves that our policy is right. 发生的一切证明我们的政策是对的。
★谓语:概念:说明主语的动作、特征、状态等的句子成分,叫做谓语。
位置:谓语动词通常位于主语之后,特殊句型(倒装句)位于主语之前。
构成:由动词或动词短语充当。
动词分为:实义动词、连系动词、情态动词和助动词。
(情态动词和助动词不能单独使用,必须和实义动词或系动词连用)实义动词分为及物动词(vt.)和不及物动词(vi.), 及物动词直接接宾语,不及物动词需加介词才能接宾语。
十大词类与八大句子成分的关系(1)十大词类:据英语单词所表达的含义以及在句子中的作用,把英语单词分为10个类别,就是10大词类:名词、代词、数词、动词、副词、形容词、冠词、介词、连词、感叹词。
根据部分词类具有的共同特征,又将十大词类分为两大部分:实词:名词、代词、数词、动词、副词、形容词。
特征:具有完整的词义;能够在句子中独立充当句子成分。
虚词:冠词、介词、连词、感叹词。
特征:没有完整的意思;不能够在句子中独立充当句子成分,必须和实词搭配,才能充当句子成分。
(2)八大句子成分:句子成分:组成英语句子的各个部分,叫做句子成分。
英语的句子最多由八个句子成分组成,即主语、谓语、宾语、表语、定语、状语、宾语补足语以及同位语。
★主语:概念:句子的主体,发出动作的人或物,表示所说的是谁或是什么。
位置:主语一般在句首,特殊句型中在句末。
构成:由名词、代词或相当于名词的词、短语或从句充当。
例:Henry is a good boy.亨利是个好孩子。
He ran away.他跑掉了。
To learn a foreign language is not easy.学习一门外语不容易。
Driving to Beijing is not difficult.开车去北京不难。
What has happened proves that our policy is right. 发生的一切证明我们的政策是对的。
Whether we’ll go depends on the weather. 我们是否去要看天气。
★谓语:概念:说明主语的动作、特征、状态等的句子成分,叫做谓语。
位置:谓语动词通常位于主语之后,特殊句型位于主语之前。
构成:由动词或动词短语充当。
例如:We go to school from Monday to Friday. 我们周一至周五上学。
I went to the zoo yesterday.昨天我去了动物园。
十大词类与八大句子成分的关系(1)十大词类:据英语单词所表达的含义以及在句子中的作用,把英语单词分为十个类别,就是十大词类:名词、代词、数词、动词、副词、形容词、冠词、介词、连词、感叹词。
根据部分词类具有的共同特征,又将十大词类分为两大部分:实词:名词、代词、数词、动词、副词、形容词。
特征:具有完整的词义;能够在句子中独立充当句子成分。
虚词:冠词、介词、连词、感叹词。
特征:没有完整的意思;不能够在句子中独立充当句子成分,必须和实词搭配,才能充当句子成分。
注:1.介词为虚词,不能单独充当句子成分,必须同名词、代词、短语、句子构成介词短语才能充当句子成分。
介词短语在句中常作表语、定语、状语和补足语2.动词分为系动词、助动词、情态动词和实义动词。
其中实义动词又可分为谓语动词:时态、语态、语气和非谓语动词:To do :可以充当主、表、宾、补、定、状Doing: 可以充当主、表、宾、补、定、状Done: 可以充当表、补、定、状(2)八大句子成分:句子成分:组成英语句子的各个部分,叫做句子成分。
英语的句子最多由八个句子成分组成,即主语、谓语、宾语、表语、定语、状语、补足语以及同位语。
★主语:概念:句子的主体,发出动作的人或物,表示所说的是谁或是什么。
位置:主语一般在句首,特殊句型中在句末。
构成:由名词、代词或相当于名词的词、短语或从句充当。
例:Henry is a good boy.亨利是个好孩子。
He ran away.他跑掉了。
The second is yours.To learn a foreign language is not easy.学习一门外语不容易。
Driving to Beijing is not difficult.开车去北京不难。
What has happened proves that our policy is right. 发生的一切证明我们的政策是对的。
Whether we’ll go depends on t he weather. 我们是否去要看天气。
英语句子以主谓结构为基本的句法结构。
十大词类与八大句子成分的关系(1)十大词类:据英语单词所表达的含义以及在句子中的作用,把英语单词分为10个类别,就是10大词类:名词、代词、数词、动词、副词、形容词、冠词、介词、连词、感叹词。
根据部分词类具有的共同特征,又将十大词类分为两大部分:实词:名词、代词、数词、动词、副词、形容词。
特征:具有完整的词义;能够在句子中独立充当句子成分。
虚词:冠词、介词、连词、感叹词。
特征:没有完整的意思;不能够在句子中独立充当句子成分,必须和实词搭配,才能充当句子成分。
(2)八大句子成分:句子成分:组成英语句子的各个部分,叫做句子成分。
英语的句子最多由八个句子成分组成,即主语、谓语、宾语、表语、定语、状语、宾语补足语以及同位语。
★主语:概念:句子的主体,发出动作的人或物,表示所说的是谁或是什么。
位置:主语一般在句首,特殊句型中在句末(如用it充当形式宾语,把真正的主语放在后面)。
构成:由名词(短语)、代词、动名词、动词不定式或从句充当。
例:Henry is a good boy.亨利是个好孩子。
He ran away.他跑掉了。
To learn a foreign language is not easy.学习一门外语不容易。
Driving to Beijing is not difficult.开车去北京不难。
What has happened proves that our policy is right. 发生的一切证明我们的政策是对的。
Whether we’ll go depends on the weather. 我们是否去要看天气。
★谓语:概念:说明主语的动作、特征、状态等的句子成分,叫做谓语。
位置:谓语动词通常位于主语之后,特殊句型(倒装句)位于主语之前。
构成:由动词或动词短语充当。
动词分为:实义动词、连系动词、情态动词和助动词。
(情态动词和助动词不能单独使用,必须和实义动词或系动词连用)实义动词分为及物动词(vt.)和不及物动词(vi.), 及物动词直接接宾语,不及物动词需加介词才能接宾语。
英语基础语法知识第一节十大词类一、词类能够自由运用的最小语言单位叫词。
根据词的形式、意义及其在句中的作用所作的分类叫词类(parts of speech)。
英语的词通常分为十大类,即名词、冠词、代词、数词、形容词、副词、动词、介词、连词和感叹词。
现分别叙述如下:(一)名词名词(noun)是表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。
例如:foreigner外国人 soap 肥皂Newton牛顿law 法律freedom自由peace和平英语名词可分为两大类:1.普通名词(common noun)是某一类人、事物、某种物质或抽象概念的名称。
例如:teacher教师 market市场rice大米magazine杂志sound声音production生产2.专有名词(proper noun)是特定的某人、地方或机构的名称。
专有名词的第一个字母必须大写。
例如:Hemingway海明威 Russia 俄罗斯New York 纽约 United Nations联合国名词又可分为可数名词(countable noun)与不可数名词(uncountable noun)两种。
可数名词有单、复数之分。
绝大多数名词的复数形式的构成是在单数名词的后面加-s或-es。
例如:shop→shops商店 bus→buses 公共汽车 library→libraries图书馆toy→toys玩具leaf→leaves树叶英语中有一些名词的复数形式是不规则的。
例如:man→men男人tooth→teeth牙齿datum→data数据有关名词复数形式构成的具体规则,请参阅有关的英语语法书。
(二)冠词冠词(article)放在名词之前,帮助说明该名词所指的对象。
冠词分为不定冠词(indefinite article)和定冠词(definite article)两种。
不定冠词为a/an,用在单数名词之前,表示某一类人或事物的“一个”。
a用在以辅音开头的名词之前,an用在以元音开头的名词之前。
高中英语语法—句法结构及句子成分知识点讲解十大词类与八大句子成分的关系(1)十大词类:据英语单词所表达的含义以及在句子中的作用,把英语单词分为10个类别,就是10大词类:名词、代词、数词、动词、副词、形容词、冠词、介词、连词、感叹词。
根据部分词类具有的共同特征,又将十大词类分为两大部分:实词:名词、代词、数词、动词、副词、形容词。
特征:具有完整的词义;能够在句子中独立充当句子成分。
虚词:冠词、介词、连词、感叹词。
特征:没有完整的意思;不能够在句子中独立充当句子成分,必须和实词搭配,才能充当句子成分。
十大词类和八大句子成分(2)八大句子成分:句子成分:组成英语句子的各个部分,叫做句子成分。
英语的句子最多由八个句子成分组成,即主语、谓语、宾语、表语、定语、状语、宾语补足语以及同位语。
★主语:概念:句子的主体,发出动作的人或物,表示所说的是谁或是什么。
位置:主语一般在句首,特殊句型中在句末(如用it充当形式宾语,把真正的主语放在后面)。
构成:由名词(短语)、代词、动名词、动词不定式或从句充当。
例:Henry is a good boy.亨利是个好孩子。
He ran away.他跑掉了。
To learn a foreign language is not easy.学习一门外语不容易。
Driving to Beijing is not difficult.开车去北京不难。
What has happened proves that our policy is right. 发生的一切证明我们的政策是对的。
Whether we’ll go depends on the weather. 我们是否去要看天气。
★谓语:概念:说明主语的动作、特征、状态等的句子成分,叫做谓语。
位置:谓语动词通常位于主语之后,特殊句型(倒装句)位于主语之前。
构成:由动词或动词短语充当。
动词分为:实义动词、连系动词、情态动词和助动词。
英语基础语法知识第一节十大词类一、词类能够自由运用的最小语言单位叫词。
根据词的形式、意义及其在句中的作用所作的分类叫词类(parts of speech)。
英语的词通常分为十大类,即名词、冠词、代词、数词、形容词、副词、动词、介词、连词和感叹词。
现分别叙述如下:(一)名词名词(noun)是表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。
例如:foreigner外国人 soap 肥皂Newton牛顿law 法律freedom自由peace和平英语名词可分为两大类:1.普通名词(common noun)是某一类人、事物、某种物质或抽象概念的名称。
例如:teacher教师 market市场rice大米magazine杂志sound声音production生产2.专有名词(proper noun)是特定的某人、地方或机构的名称。
专有名词的第一个字母必须大写。
例如:Hemingway海明威 Russia 俄罗斯New York 纽约 United Nations联合国名词又可分为可数名词(countable noun)与不可数名词(uncountable noun)两种。
可数名词有单、复数之分。
绝大多数名词的复数形式的构成是在单数名词的后面加-s或-es。
例如:shop→shops商店 bus→buses 公共汽车 library→libraries图书馆toy→toys玩具leaf→leaves树叶英语中有一些名词的复数形式是不规则的。
例如:man→men男人tooth→teeth牙齿datum→data数据有关名词复数形式构成的具体规则,请参阅有关的英语语法书。
(二)冠词冠词(article)放在名词之前,帮助说明该名词所指的对象。
冠词分为不定冠词(indefinite article)和定冠词(definite article)两种。
不定冠词为a/an,用在单数名词之前,表示某一类人或事物的“一个”。
a用在以辅音开头的名词之前,an用在以元音开头的名词之前。
一.句子成分详解一览表
二.专题练习
I.指出下列句子划线部分是什么句子成分:
1. The students got on the school bus.
2. He handed me the newspaper.
3. I shall answer your question after class.
4. What a beautiful Chinese painting!
5. They went hunting together early in the morning.
6. His job is to train swimmers.
7. He took many photos of the palaces in Beijing.
8. There is going to be an American film tonight.
9. He is to leave for Shanghai tomorrow.
10. His wish is to become a scientist.
11. He managed to finish the work in time.
12. Tom came to ask me for advice.
13. He found it important to master English.
14. Do you have anything else to say?
15. To be honest; your pronunciation is not so good.
16. Would you please tell me your address?
17. He sat there, reading a newspaper.
18. It is our duty to keep our classroom clean and tidy.
19. He noticed a man enter the room.
20. The apples tasted sweet.
II分析下列句子成分
1. Our school is not far from my home.
2. It is a great pleasure to talk with you
3. All of us considered him honest.
4. My grandfather bought me a pair of sports shoes.
5. He broke a piece of glass.
6. He made it clear that he would leave the city.
7. ---I love you more than her,child . 8. Tees turn green when spring comes.
9. They pushed the door open. 10. Grandma told me an interesting story last night.
11. He wrote carefully some letters to his friends. the students think highly of his teaching
13. We need a place twice larger than this one. 14. He asked us to sing an English song.
15. Don't get nervous,help yourself to what you like. will make our school more beautiful.
17. He didn't come.That is why he didn't know. 18. She showed us her many of her pictures. 19. The old man lives
a lonely life.
20. Luckily the 1989 earthquake did not happen in the center of town.
21. The cars made in Japan are better than those in Germany.
22. There are so many people in the hall that it's hard for me to find him.
23. No matter how difficult the task may be, we must fulfil it this month.
24. Go back where you came from. 25. We must do whatever the people want us to do.
26. At last he got home, tired and hungry. 27. Would you please pass me the cup?
28 Mary handed her homework to the teacher. 29. Do you know the latest news about him?
’llget my hair cut tomorrow.III用符号划出下列短文各句中的主语”=”、谓语”-”、宾语”~”定语”()”、状语”[]”、补语”<>”:表语”≈”
I hope you are very well. I'm fine, but tired. Right now it is the summer vacation and I'm helping my Dad on the farm. August is the hottest month here. It is the time of year for the rice harvest, so every day I work from dawn until dark. Sometimes we go on working after dark by the lights of our tractors. We grow rice in the south of the States, but in the north where it is colder they grow wheat. We have a lot of machines on the farm. Although the farm is large, my Dad has only two men working for him. But he employs more men for the harvest. My brother takes care of the vegetable garden. It doesn't often rain in the summer here. As a result, we have to water the vegetable
garden. Every evening we pump water from a well. It then runs along channels to different parts of the garden.。