博士考试大纲
- 格式:doc
- 大小:41.00 KB
- 文档页数:2

2024年博士研究生入学考试英语考试大纲2024 Doctoral Graduate Entrance Examination English Exam OutlineI. Listening ComprehensionThis section of the exam will test the candidates' ability to understand spoken English in academic and professional settings. Candidates will listen to a series of recordings, including lectures, conversations, and presentations, and answer multiple-choice questions based on the content. The topics will cover a wide range of subjects relevant to doctoral studies, such as research methods, literature reviews, and academic discussions.II. Reading ComprehensionIn this section, candidates will read academic texts, including scholarly articles, research papers, and book excerpts, and answer questions to demonstrate their understanding of the content. The passages will be of varying lengths and complexity, requiring candidates to identify main ideas, supporting details, and logical relationships within the text.III. Writing SkillsCandidates will be required to demonstrate their ability to write coherent and well-structured essays on a variety of topics related to their field of study. This section will test candidates' proficiency in academic writing, including the ability to formulate clear arguments, provide evidence to support their claims, and organize their ideas in a logical manner. Candidates may be asked to analyze a case study, evaluate a research question, or propose a research methodology.IV. Vocabulary and GrammarThis section will assess candidates' knowledge of vocabulary and grammar in academic English. Candidates will be tested on their ability to use complex vocabulary and grammar structures accurately and appropriately in written and spoken English. This section may include exercises on word meaning, word usage, sentence structure, and grammatical rules.V. Speaking SkillsCandidates will be required to engage in conversations and discussions on academic topics with examiners. This section will test candidates' ability to express ideas clearly and coherently, respond to questions, and engage in academic discourse. Candidates will be evaluated on their fluency, pronunciation, vocabulary usage, and grammar accuracy.Overall, the 2024 Doctoral Graduate Entrance Examination English Exam is designed to assess candidates' readiness for doctoral studies by evaluating their listening, reading, writing, speaking, vocabulary, and grammar skills in academic English. Candidates are encouraged to prepare thoroughly for the exam by practicing listening and reading comprehension, academic writing, vocabulary building, and speaking skills in English. Good luck to all the candidates!。

2023年博士生入学考试初试科目考试大纲
科目名称:电网络理论
一、考试总体要求
《电网络理论》是介绍现代电路分析中一些较为成熟和先进的内容,是了解现代电路理论的“窗口”。
牢记基本概念,掌握基本方法,与大学电路原理的内容有机地联系在一起。
掌握与电气工程及电子工程相关的电路理论的一些新思想、新方法、新元件和新进展。
综合利用所学知识解决复杂电路分析计算问题。
二、考试内容
1.网络理论基础:网络元件的新体系,网络的互联规律性以及网络及元件的基本性质,如(1)线性与非线性、(2)无源性和有源性、(3)时变性与时不变性、(4)互易性与非互易性等。
2.简单非线性电路:非线性电阻电路的基本概念和常用分析方法以及一、二阶非
线性动态电路的分析方法。
重点掌握低阶自治电路的定性分析。
3.多口网络:含源及无源多口网络的常见矩阵表示法,重点掌握不定导纳矩阵的计算方法及其应用。
4.电路的代数方程:电路代数方程的矩阵形式,混合分析法,稀疏表格法和改进节点法,重点掌握混合分析法和改进节点法。
5.动态电路的时域方程:网络分析的状态变量法,状态方程的列写,线性状态方程的解析解法,重点掌握含有高阶元件、非线性元件或非常态电路的状态方程的列写。
6.网络的灵敏度分析:灵敏度分析的意义和在本专业分析计算中的主要应用,重点掌握伴随网络法。
三、考试题型
证明题、计算题、论述题
四、参考书目
1.梁贵书.高等电网络.讲义..2..高等电力网络分析. 2007。

博士考试大纲
一、材料力学部分
1、 弯曲变形
2、 扭转变形
3、 组合变形
4、 应力状态
5、 能量法
6、 动载荷
二、弹性力学部分
1、 应力函数
2、 梁的平面问题弹性解
3、 弹性力学空间问题的基本方程
4、 弹性力学接触问题
三、高等动力学部分
1、 刚体定点运动运动学
2、 刚体定点运动动力学
3、 分析力学基础:相关概念;完整系统动力学(以拉格朗日动力学为主),非完整系统的劳思方程
参考教材:
1、 材料力学(上、下册) 刘鸿文 高等教育出版社
2、 弹性力学(上册) 徐其纶 高等教育出版社
3、 高等动力学(上、下册)张延教 南理工内部教材。

博士入学数学(高等数学、数值分析)课考试大纲
高等数学部分(50分)
1. 极限与连续
数列的极限,函数及函数的极限,极限的性质及运算法则,无穷小的比较,函数的连续性。
2. 导数与微分
导数的概念,导数的基本公式,导数的四则运算及求导法则,高阶导数,微分,函数的极值。
3. 微分中值定理
微分中值定理,洛必达法则,泰勒公式。
4. 积分
原函数与不定积分,定积分的概念与性质,换元积分法,分部积分法,微积分学基本定理,定积分的应用。
5. 微分方程
微分方程的基本概念,一阶微分方程,几种可积的高阶微分方程,线性微分方程及其通解的结构,常系数齐次(非齐次)线性微分方程。
6. 多元函数微积分
多元函数,偏导数与高阶偏导数,全微分,复合函数及隐函数的求导法,多元函数的极值,二重积分。
7. 无穷级数
无穷级数的敛散性,正项级数敛散性的判别,任意项级数,绝对收敛,幂级数及幂级数的收敛半径和收敛域,函数的幂级数展开。
数值分析部分(50分)
1.非线性方程求根
简单迭代法、牛顿法、割线法及其计算效率。
2.线性代数方程组的数值解法
向量与矩阵范数,高斯列主元消去法,误差分析;雅可比迭代法、高斯—赛德尔迭代法、超松弛迭代法及其收敛性讨论。
3.插值与拟合逼近
函数的拉格朗日插值、牛顿插值、埃尔米特插值、样条插值;曲线拟合的最小二乘逼近方法;误差分析。
4.数值积分
代数精度,低阶牛顿—柯特斯求积公式及其复化,龙贝格算法;高斯积分公式;数值积分公式的稳定性。
5.常微分方程初值问题的数值解法
常用单步法和多步法及其稳定性讨论;预测—校正格式。

博士研究生入学考试《数值分析(机电院)》考试大纲第一部分考试形式和试卷结构一、考试方式:考试采用闭卷笔试方式,试卷满分为100分。
二、考试时间:180分钟。
三、试卷内容结构:约占 60%,主观题约占 40%。
四、试卷题型结构:试卷由三部分组成:选择/判断、填空、分析/计算。
其中:1、选择/判断题,约占20%。
测试考生对本课程基本概念、基本知识和数值计算常用算法设计与分析方法的掌握程度。
2、填空题,约占40%。
测试考生运用数值计算相关基础知识和基本方法,开展计算、简要分析以及求解实际问题的能力。
3、分析、计算题,约占40%。
测试考生综合运用数值计算理论、典型方法解决综合问题,并开展相关计算方法收敛性以及误差分析等能力。
第二部分考察的知识及范围1.误差度量与数值算法设计误差基本概念:误差来源与分类,截断误差、舍入误差、绝对误差、相对误差,有效数字以及数值稳定性。
函数计算误差分析:一元函数误差估计,四则运算误差估计。
数值算法设计原则:简化计算步骤以节省计算量(秦九韶算法)、减少有效数字损失,选择数值稳定的算法。
2.函数的插值方法以及误差估计插值问题的基本概念:插值问题的描述,插值多项式的存在和唯一性,差商、差分的概念以及性质。
拉格朗日插值:线性插值与抛物插值,n次拉格朗日插值,插值余项公式。
牛顿插值:均差的概念与性质,牛顿插值公式及其余项,差分的概念与性质。
埃尔米特插值:两点三次埃尔米特插值及其余项,n点埃尔米特插值,非标准埃尔米特插值及其余项。
分段低次插值:分段线性插值,分段三次埃尔米特插值。
三次样条插值:三次样条函数建立,三次样条插值方法。
3.函数逼近与曲线拟合正交多项式:函数内积、欧几里德范数,正交函数序列,正交多项式,勒德让多项式,切比雪夫多项式。
最佳平方逼近:最佳平方逼近问题及解法,基于正交函数、勒德让多项式、切比雪夫多项式的最佳平方逼近。
最小二乘法:最小二乘曲线拟合问题的提出和解法,最小二乘计算,最小二乘法的应用(算术平均、超定方程组)。

武汉理工大学管理类专业博士研究生入学考试《运筹学与管理经济学》考试大纲一、考试内容1、运筹学部分(1)模型论:经济管理数学模型的建立,包括线性规划模型及其他形式的数学模型(2)线性规划:单纯型法及其计算步骤(3)线性规划的扩展运用:数据包络分析(DEA模型)(4)线性规划的对偶理论与灵敏度分析:对偶问题及其本质、影子价格、对偶单纯型法、灵敏度分析(5)目标规划:目标规划的数学模型、目标规划的单纯型法与灵敏度分析(7)动态规划:动态规划基本原理与模型、动态规划模型求解(8)存储论:确定性存储模型(9)决策论:风险型决策方法、效用函数方法、层次分析法(AHP模型)2、管理经济学部分(1)企业的目标与环境:企业的目标、企业价值及NPV、企业的内部环境与外部环境、利益相关者理论、机会成本理论(2)管理经济学的分析方法:最优化方法、边际分析法(3)需求、供给与均衡:需求及影响需求的因素、供给及影响供给的因素、市场均衡(4)弹性理论:弹性的通用公式、点弹性与弧弹性、需求的价格弹性、需求的收入弹性、交叉弹性、弹性与决策(5)生产与成本理论:生产函数、技术进步、规模报酬、短期成本函数、长期成本函数、规模经济、范围经济(6)市场结构与决策:四种市场结构、完全竞争市场中企业的产量决策、完全垄断市场中企业的价格与产量决策、垄断竞争市场中企业的价格与产量决策、信息不对称与企业决策、寡头垄断企业的价格与产量决策、博弈论应用、古诺模型与斯塔科尔伯格模型二、参考书目1、胡运权主编,《运筹学教程(第三版)》,清华大学出版社,2007年2、运筹学教材编写组,《运筹学(第三版)》,清华大学出版社,2005年3、(美)克里斯托弗R. 托马斯,S. 查尔斯.莫瑞斯著,陈章武,葛凤玲译,《管理经济学(第8版)》,机械工业出版社,2005年4、王春香,《管理经济学》,中国人民大学出版社,2008年。

全国医学博士英语统一考试大纲The National Medical Doctoral English Unified Examination (NMDEUE) is a standardized test designed to evaluate the English language proficiency of medical doctoral candidates across China. This examination is a critical requirement in the process of obtaining a medical doctorate in China. The NMDEUE ensures that medical doctoral students have the linguistic skills necessary to understand and communicate with the global medical community.Section 1: Listening Comprehension (40 minutes)The Listening Comprehension section of the NMDEUE measures a candidate's ability to comprehend spoken English through a series of multiple-choice questions. The examination tests students' ability to identify specific information, extract the main ideas, and infer attitudinal and contextual meanings of audio clips, dialogues, and longer passages. This section tests listening proficiency in different contexts, including academic and everyday life situations, such as medical conferences, patient interviews, discussions with colleagues, and medical instructions.Section 2: Reading Comprehension (75 minutes)The Reading Comprehension section of the NMDEUE measures a candidate's ability to comprehend written English through a series of multiple-choice questions. This section of the exam tests the candidate's ability to identify specific information, extract the main ideas, and infer contextual meaning from articles and academic papers related to medical science. Candidates will be required to read and answer multiple-choice questions based on academic readings such as medical journal articles, pharmacology texts, andpatient histories.Section 3: Writing Skills (85 minutes)The Writing Skills section of the NMDEUE measures a candidate's ability to convey complex medical information in English. Candidates will be required to write a summary, a critique, and a response to a scientific article. This section of the exam tests students' ability to express medical language in a clear, concise, and accurate manner. This section evaluates the student's ability to use appropriate medical terminology, grammar, and syntax in written English. The writing tasks will be based on medical topics drawn from the core syllabus of the medical doctorate program. Section 4: Speaking Skills (20 minutes)The Speaking Skills section of the NMDEUE measures a candidate's ability to articulate complex medical concepts in spoken English. Candidates will be required to answer a series of open-ended questions related to medical science. This section of the exam will test the student's ability to use appropriate medical terminology, grammar, and syntax in spoken English while demonstrating appropriate pronunciation, intonation, and stress. The Speaking Skills section evaluates the student's ability to communicate effectively in academic and professional medical settings.ConclusionThe NMDEUE is an essential component of the medical doctoral program in China. It is a standardized test designed to evaluate a candidate's proficiency in English across the domains of listening comprehension, reading comprehension, writing skills, andspeaking skills. The examination ensures that medical doctoral students in China have the linguistic skills necessary to communicate effectively on a global level. By meeting the criteria set by the NMDEUE, medical doctoral candidates are equipped with the necessary tools to pursue a successful career in the highly competitive medical industry.The NMDEUE is a demanding examination that requires thorough preparation and a high degree of language proficiency. Candidates who intend to take this exam must have a strong foundation in English grammar, vocabulary, syntax, and pronunciation. They must also be familiar with the medical terminology that is used in English-speaking countries.The Listening Comprehension section of the NMDEUE requires candidates to have good listening skills and the ability to identify specific information in a variety of spoken contexts. To prepare for this section, candidates are advised to listen to English-language podcasts, watch English movies or TV shows, and practice taking notes while listening to lectures. It is also helpful to familiarize oneself with various accents and dialects used in English-speaking countries.The Reading Comprehension section of the NMDEUE demands extensive reading comprehension skills and the ability to extract main ideas and critical details from academic papers and articles. Candidates should practice reading medical journals and textbooks in English and learn to annotate and summarize what they have read. They should also study different types of texts, such as scientific articles, case studies, and patient histories.The Writing Skills section of the NMDEUE is a comprehensiveevaluation of a candidate's writing skills. Candidates must be able to write clear and concise sentences, use appropriate medical terminology and syntax, and structure their writing effectively. In preparation, candidates should study different types of writing, including summaries, critiques, and responses to scientific articles. They should also practice organizing their writing and using cohesive and coherent language.The Speaking Skills section of the NMDEUE requires candidates to express themselves clearly, confidently, and effectively in spoken English. To prepare, candidates should practice speaking in English in various contexts, such as medical conferences, patient interviews, and interactions with colleagues. They should also learn how to use appropriate intonation, stress, and pronunciation when communicating in English.In addition to language proficiency, the NMDEUE evaluates a candidate's ability to apply medical knowledge in English. Therefore, candidates must have a deep understanding of medical terminology and concepts. They must be familiar with the core syllabus of the medical doctoral program and have a good grasp of medical sciences, including anatomy, pharmacology, and pathology. They should also be familiar with current trends in medical research and be able to discuss key issues in medical ethics and practice.ConclusionThe NMDEUE is a rigorous examination that evaluates a candidate's language proficiency and knowledge of medicalsciences. It is an essential requirement in the medical doctoral program in China, and passing this examination is crucial for obtaining a medical doctoral degree and pursuing a successful career in the global medical industry.To achieve success in the NMDEUE, candidates must prepare thoroughly and systematically. They should study and practice all four sections of the exam, including listening comprehension, reading comprehension, writing skills, and speaking skills. They should also focus on improving their language proficiency by reading and listening to English-language materials, practicing writing and speaking in English, and building their medical knowledge through systematic study and research.Overall, the NMDEUE is a challenging but rewarding examination that tests a candidate's ability to communicate effectively in English and apply medical knowledge in a global context. By passing the NMDEUE, medical doctoral candidates in China can demonstrate their language proficiency and readiness to excel in the dynamic and competitive field of medicine.。
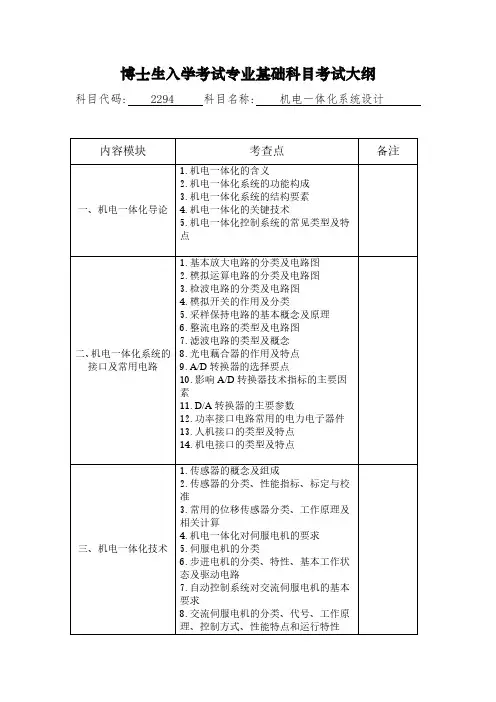
博士生入学考试专业基础科目考试大纲科目代码: 2294 科目名称: 机电一体化系统设计内容模块考查点备注一、机电一体化导论1.机电一体化的含义2.机电一体化系统的功能构成3.机电一体化系统的结构要素4.机电一体化的关键技术5.机电一体化控制系统的常见类型及特点二、机电一体化系统的接口及常用电路1.基本放大电路的分类及电路图2.模拟运算电路的分类及电路图3.检波电路的分类及电路图4.模拟开关的作用及分类5.采样保持电路的基本概念及原理6.整流电路的类型及电路图7.滤波电路的类型及概念8.光电藕合器的作用及特点9.A/D转换器的选择要点10.影响A/D转换器技术指标的主要因素11.D/A转换器的主要参数12.功率接口电路常用的电力电子器件13.人机接口的类型及特点14.机电接口的类型及特点三、机电一体化技术1.传感器的概念及组成2.传感器的分类、性能指标、标定与校准3.常用的位移传感器分类、工作原理及相关计算4.机电一体化对伺服电机的要求5.伺服电机的分类6.步进电机的分类、特性、基本工作状态及驱动电路7.自动控制系统对交流伺服电机的基本要求8.交流伺服电机的分类、代号、工作原理、控制方式、性能特点和运行特性9. 自动控制系统对直流伺服电机的要求10.直流伺服电机的分类、代号、工作原理、主要特性和优缺点11.PWM功率放大器的工作原理12.自动控制技术的发展阶段13.控制系统的基本要求及分析方法14.计算机控制系统的分类15.PLC的发展历程、特点及工作方式16.简单PLC语句表的描写及梯形图的绘制四、机电一体化系统设计1.机电一体化机械系统设计的相关理论及知识2.机电一体化系统原理方案设计的步骤3.机电一体化系统结构方案设计的步骤4.机电一体化系统控制系统的设计步骤5.优化设计的一般步骤6.干扰的含义、分类、传播及抑制7.提高控制系统可靠性的方法与措施试卷满分:100试题结构:1.问答类题型:4道,每道5分;2.论述类题型(论述题、材料分析题、案例分析题等):4道,每道20分。

2023年宁波大学普通招考博士研究生专业基础考核笔试科目考试大纲科目名称: 数学综合知识一、考试形式与试卷结构(一)试卷满分值及考试时间本试卷满分为100分,考试时间为120分钟。
(二)答题方式答题方式为闭卷、笔试。
试卷由试题和答题纸组成;答案必须写在答题纸相应的位置上。
(三)试卷内容结构考试内容主要包括泛函分析和抽象代数部分。
泛函分析部分包括线性泛函分析中的空间理论、线性算子、无穷维空间上的函数、谱理论、紧线性算子为主要内容,要求考生系统地掌握泛函分析的基本概念、理论和方法,并能应用这些理论和方法,具有较强的分析问题与解决问题的能力。
抽象代数部分包括基本代数结构如群、环、模和域的基本概念、基本理论,代数结构的一些基本思想和方法,要求考生具有抽象思维能力、逻辑推理能力、综合运用所学的知识分析问题和解决问题的能力。
(四)试卷题型结构1. 计算题2. 证明题二、考查目标主要考察学生对泛函分析和抽象代数部分的基本概念、基本原理和基本方法的掌握程度和利用其理论解决分析和代数等领域的问题,要求具有理论证明和计算能力。
三、考查范围或考试内容概要第一部分:泛函分析1.距离空间,内容包括:距离空间的概念,点列的收敛性,映射的连续性,内点,开集,领域等概念,距离的等价性,映射的连续性等;距离空间的闭集,集合的闭包,集合的稠密性和距离空间的可分性,列紧集和距离空间的列紧性;距离空间的完备性,包括Cauchy列,完备距离空间的定义,完备空间与不完备空间举例,距离空间的完备化;完备距离空间的性质,内容包括闭集套定理,Banach压缩映照原理及其应用。
2.赋范空间,内容包括:赋范空间的概念,Banach空间定义,范数连续性,范数与距离的关系,点列的收敛性;完备赋范空间,赋范空间的完备化,重要的完备空间p L空间和p l空间;赋范空间的的几何结构;有限维赋范空间。
3.内积空间和Hilbert空间,内容包括:内积空间的基本性质,内积和范数的关系、内积空间特征、Hilbert空间的定义,一些典型的内积空间、Hilbert空间例子;正交和正交分解,Hilbert空间正交分解定理;正交系和正交投影,Fourier级数,Bessel不等式与Fourier级数的收敛性;正交基和正交列的完备性;可分Hilbert空间的等距同构。

2023年宁波大学普通招考博士研究生专业基础考核笔试科目考试大纲科目名称: 水产资源综合利用基础一、考试形式与试卷结构(一)试卷满分值及考试时间本试卷满分为100分,考试时间为120分钟。
其中微生物学及食品化学各占50分。
(二)答题方式答题方式为闭卷、笔试。
试卷由试题和答题纸组成;答案必须写在答题纸相应位置上。
(三)试卷内容结构考试内容主要包含微生物学和食品化学。
微生物学结构参见三、考查范围或考试内容概要。
食品化学考试内容主要包括食品化学成分特点、在加工贮运过程中的变化以及这些变化对食品品质、安全性等影响,食品化学理论在水产品加工、贮藏及水产资源高值化利用中的应用。
(四)试卷题型结构1.名词解释2.问答题3.论述题二、考查目标课程考试的目的在于测试考生对于微生物学、食品化学的基本概念、基本理论、基础知识的掌握情况以及综合运用微生物学、食品化学知识与原理解决微生物学实际问题的能力。
三、考查范围或考试内容概要(一)微生物学1.微生物与人类要求:重点掌握微生物的五大共性。
2.微生物的形态结构和功能要求:重点掌握细菌、放线菌、霉菌、酵母菌细胞形态结构及其生理功能;掌握常见的细菌、霉菌和酵母菌的生物学特性及应用;了解真菌的无性孢子和有性孢子的形成及其特性。
3. 微生物的分类和鉴定要求:掌握微生物分类单位及鉴定依据,了解最新的鉴定方法及原理。
4.病毒要求:掌握病毒的一般特性;噬菌体的形态结构及繁殖方式;温和噬菌体与溶源性。
5.微生物的营养与代谢要求:掌握微生物的营养类型;微生物的营养机制;微生物的代谢类型及途径;微生物的代谢调控及应用。
6.微生物的生命活动与环境条件要求:重点掌握单细胞微生物的典型生长曲线;掌握微生物纯培养分离法;物化因素对微生物生长繁殖的影响、作用机制。
了解微生物的生长、生长的影响因素及生长控制方法;了解有害微生物的控制原理及方法。
7.微生物的遗传和育种及在发酵工业中的应用要求:掌握微生物的突变机制;诱变育种;了解生产菌种保存;了解微生物的基因重组;掌握基因工程育种操作的基本原理与方法。
复旦大学博士生入学考试大纲软件工程一、软件工程概论1. 计算机软件,特点,分类,语言2. 软件工程定义,软件工程框架,软件生存周期3. 软件过程:ISO/IEC 12207软件生存周期过程,能力成熟度模型CMM ,能力成熟度模型集成CMMI4. 软件过程模型5. 敏捷软件开发6. CASE工具与环境二、系统工程1. 基于计算机的系统2. 系统工程的任务3. 可行性分析:经济可行性、技术可行性、法律可行性、方案的选择和折衷三、需求工程1. 需求工程概述2. 需求获取3. 需求分析、协商与建模4. 需求规约与验证5. 需求管理四、设计工程1. 软件设计工程概述2. 软件设计原则3. 软件体系结构设计4. 部件级设计技术5. 设计规约与设计评审五、结构化分析与设计1. 结构化分析方法概述2. 数据流图3. 数据字典4. 描述基本加工的小说明5. 结构化设计概述6. 数据流图到软件体系结构的映射7. 初始结构图的改进六、面向对象的分析和设计1. 面向对象的基本概念2. 面向对象分析和设计过程3. UML,UML视图,UML图4. 用况建模5. 静态建模6. 动态建模7. 物理体系结构建模七、基于构件的软件开发1. 基于构件的软件开发概述2. 建造可复用构件3. 应用系统工程4. 构件的管理八、软件测试1. 软件测试基础2. 白盒测试3. 黑盒测试4. 测试策略5. 面向对象测试6. 测试完成标准7. 调试九、Web工程1. 基于Web系统和应用的属性2. Web 工程过程3. Web 分析4. Web设计5. Web测试6. 新型界面风格、特点,如:Apple I*的界面风格及Adriod的界面风格十、软件维护与再工程1. 软件维护2. 再工程技术十一、软件项目管理1. 软件项目管理概述2. 软件度量3. 软件项目估算4. 项目进度管理5. 风险管理6. 软件项目的组织7. 软件质量管理8. 软件配置管理参考书:《软件工程(第2版)》钱乐秋,赵文耘,牛军钰编著,清华大学出版社,2013年。
1.开场白Good morning. I am very glad to be here for this interview. 2.姓名,英文名,毕业院校,毕业专业,毕业学院First let me introduce myself. My name is LiShuai, and my English name is Jacky Lee. I've finished my undergraduate education in Xidian University, Majoring in Electronic Science and Technology in the college of Technical Physics.3.性格,爱好,实践经验I am open-minded, willing and have broad interests like basketball, reading and especially in engineering such as software programming, website design, hardware design. For example, during the past four years, I have accomplished two websites: one is the website of our school, and the other is the website of the doctor forum of china 2007. Furthermore, I am interested in C plus plus programming language and have written some application programs. In July in the last year,I finished my graduate project with flying colors,which was a software application about Image Process . In addition, I have also finished some projects about embedded system by using MCU when I was a junior.4.为什么想读研,将来愿意从事的方向,读研时的打算Although I have broad interests in many aspects and grasp the essential knowledge of the major, but I think at present, I can do many things in a superficial level, but not be competent to do things professionally owing to lack of ample knowledge and ability. So I think further study is still urgent for me to realize self-value.The major that I hope pursue for my further education is IC design. Because I find integrated circuits are playing a more and more important role in our modern society. And nowadays in China, with the recognition by the government, our domestic integrated circuits industry is growing rapidly and that may provide a lot of chances to us.I plan to concentrate on study and research in this field in my graduate time. And I hope I can form a systematic view of micro electronics and IC design technology and make a solid foundation for future profession after three years study here.5.结束语OK, that’s all. Thank you very much.第一段关于a的话题,早已引起了广泛的社会关注。
中国地质大学(北京)博士研究生《经济学》考试大纲
科目名称:经济学
代码:2025
一、考试性质
本门课程考试的主要内容是经济学的基本理论、现实经济问题的分析解释、政府经济政策的分析评价。
注重考察考生是否已经掌握经济学的基本理论知识与方法,能否运用经济学理论分析解释现实经济问题。
它的评价标准是使高校优秀硕士毕业生能达到及格或及格以上水平。
二、考试形式与试卷结构
1.答卷方式:闭卷、笔试
2.答卷时间:180分钟
3.题型比例:满分100分。
题型全为论述题,要求从5道题目中选择4道题目作答,
每题25分。
三、考查要点
1.经济学基本理论
微观经济理论、宏观经济理论。
2.现实经济问题的分析解释
运用经济学理论分析经济运行中所存在的失业、通货膨胀、经济衰退、经济周期、结构转型、地方债务、民间融资、产业发展等各类现实问题。
3.政府经济政策的分析评价
对政府解决各类现实经济问题的政策措施进行分析评价。
四、参考资料
高鸿业主编,西方经济学(第六版)(微观部分、宏观部分),北京:中国人民大学出版社,2014.
曼昆,经济学原理(第7版),北京:北京大学出版社,2015.
厉以宁主编,西方经济学(第三版),北京:高等教育出版社,2010.
报刊:《经济观察报》、《21世纪经济报道》、《中国经营报》等财经类报刊。
四川大学博士研究生招生入学考试英语考试大纲
一、考试时间:180分钟
二、考试内容、题型
1、阅读理解(30分)包括:一般性文章6篇,每篇约300词左右。
测试考
生在规定的时间内通过阅读获取相关信息的能力。
考生须完成1800-2000英语词的阅读量(6篇短文)并就所给题目从四个选项中选出正确答案。
要求考生能:1)掌握中心思想、主要内容和具体细节;2)进行相关的判断和推理;3)准确把握某些词和词组在上下文中的特定意义;4)领会作者观点和意图、判断作者的态度。
2、词汇(10分)包括:20个选择题,每题0.5分。
测试考生是否具备一定
的词汇量和根据上下文对词和词组意义判断的能力。
3、完型填空(10分)包括:一篇短文中20处空白形式的选择题,每题0.5
分。
测试考生在语篇层次上的理解能力和根据上下文对英语进行综合分析和应用的能力。
4、英汉互译(30分)包括:1)英译汉:短文一篇约250左右英语词,全部
译成汉语。
2)汉译英5句(复合句)。
测试考生是否能正确进行英汉互译的能力,要求译文达意、通顺、符合英语或汉语的表达习惯。
5、作文(20分)写出150词以上的短文一篇,给出题目和提纲,按提纲写
作。
注:英语以外的其它语种(包括日语、德语、法语和俄语),可参照此纲要酌情命题。
博士研究生招生考试《建筑学理论》科目考试大纲一、考查目标要求考生全面系统地掌握建筑学科领域中关于建筑设计、城市设计、建筑历史、建筑技术科学中的基本理论与相关哲学基础,掌握主要的建筑学研究方法,并能灵活运用。
具备较强的分析问题与解决问题的能力,具有较强综合研究能力。
二、考试形式与试卷结构(一)试卷满分及考试时间满分为100分,考试时间为3小时;(二)答题方式答题方式为闭卷、笔试;(三)试卷内容结构1、建筑设计及其理论(20分)2、建筑历史与遗产保护(20分)3、城市设计(20分)4、建筑技术科学(20分)5、区域建筑学(20分)6、综合应用(40分)前五个部分根据自己研究经历及未来研究方向选择三道题进行解答,最后综合应用为必答。
(四)试卷题型结构题型结构为论述题。
三、考查内容及要求1、建筑设计及其理论内容侧重从创作主体的建构、创作过程的解析和建筑本体意义等几个方面掌握建筑实践创作的相关理论;掌握从区域环境、建筑美学、建筑文化、建筑技术等多方面进行系统研究的建筑认识论;掌握建筑创作过程中思维表达;掌握传统的以及前沿的数字化技术等设计方法。
2、建筑历史与遗产保护内容侧重在人居史的视角下掌握不同地域、不同时期建筑形式与其社会结构、自然资源、宗教文化和技术的关系;多元学科背景下,城乡环境中不同时代和性质的建筑遗产保护的理论与方法。
3、城市设计内容侧重以现代城市设计理论为核心,融合建筑学、风景园林学等多学科基础理论,掌握城市外部空间和形体环境的设计理论与组织手法,掌握城市空间更新理论及设计方法,了解城市设计数据技术与应用。
4、建筑技术科学内容侧重以绿色与低碳为目标的建筑设计理论与策略,掌握建筑节能关键技术与适宜技术;掌握健康建筑设计评价标准以及建筑能耗模拟与量化分析等内容。
5、区域建筑学内容侧重掌握区域建筑学提出的时代背景,是一种基于建筑学本体的观念拓展;掌握理论包含的从本体论、方法论、操作模式,到自然、城市、文化的区域维度探索的理论框架。
2023年宁波大学普通招考博士研究生专业基础考核笔试科目考试大纲科目名称: 物理学综合一、考试形式与试卷结构(一)试卷满分值及考试时间本试卷满分为100分,考试时间为120分钟。
(二)答题方式答题方式为闭卷、笔试。
试卷由试题和答题纸组成;答案必须写在答题纸相应的位置上。
(三)试卷内容结构试卷内容包括了物理综合(力学、热学、光学、电磁学)的基本内容。
(四)试卷题型结构选择题、简答题、计算题等。
二、考查目标物理综合考试的目的在于测试申请人对于力学、热学、光学、电磁学基础课程的基本概念、基本理论、基础方法及其应用的掌握情况以及分析和解决问题的能力。
三、考试范围或考试内容概要(一)力学1.质点运动学掌握质点的位矢、速度、加速度概念,能够在直角坐标、自然坐标下求解变加速问题。
熟悉伽利略变换和相对运动。
2.牛顿运动定律掌握常见的力,能够运用牛顿定律求解质点和质点系力学问题,熟悉平动与转动非惯性系。
3.运动定理与守恒定律掌握质点和质点系的动量定理与动量守恒定律,动能定理、功能原理与机械能守恒定律,角动量定理与角动量守恒定律。
能够综合运用上述定理与守恒定律,求解力学问题。
4.万有引力掌握万有引力定律,理解引力场中的角动量、势能性质,能够综合运用万有引力定律、角动量守恒和机械能守恒求解引力场问题。
5.刚体力学掌握刚体绕定轴转动的惯量,能够运用转动定理、功与能,求解刚体定轴转动,了解刚体定点转动。
6.振动掌握简谐振动的运动学与动力学性质,熟悉简谐振动的能量转化、合成,了解阻尼振动、受迫振动。
7.机械波掌握平面简谐波方程,掌握波的干涉、驻波,和多普勒效应。
参考教材或主要参考书:力学(第三版),漆安慎、杜婵英,高等教育出版社,2012(二)热学1.热学的基本知识熟悉热学研究对象、掌握热力学第零定律、热力学第一定律、热力学第二定律和热力学第三定律、气体物体方程、气体分子动理论、能量均分定理、气体分子平均自由程和碰撞频率、系统状态函数(内能、焓、熵等)、做功和热量、以及熵增加原理等基本概念。
《复分析》考试大纲科目代码:2091 基本内容及基本要求:
一、最大模定理及其推广
1、最大模定理
1)最大模定理;
2)Schwarz引理;
3)Hadamard三圆定理;
4)Phragmen-Lindelof定理
2、有界函数
1)有界函数的性质;
2)Beurling定理
二、黎曼定理
1、正规族
1)等度连续与一致有界;
3)Ascoli-Arzela定理;
4)正规族
2、黎曼定理
1)单叶函数及其性质;
2)黎曼定理;
3)边界对应问题;
4)Schwarz-Christoffel公式;
5)模函数及其应用;
6)Landau定理
三、整函数的无穷乘积与因子分解理论
1、整函数
1)Poisson-Jensen公式;
2)整函数;
3)Weierstrass分解;
5)整函数的级与相关定理
2、 Hadamard分解定理
1)函数增长率与零点分布;
2)零点收敛定理;
3)典型乘积;
4)Hadamard因子分解定理
四、整函数与亚纯函数值分布论初步
1、整函数的值分布
1)Borel定理与Bloch定理
2)Picard小定理与Picard大定理
3)Schottky定理
4)Montel正规定则
2、亚纯函数值分布
1)第一基本定理
2)亚纯函数的级与型
3)第二基本定理
五、调和函数
1、调和函数
1)Poisson公式;
2)极值原理;
3)调和函数序列与Harnack定理;
2、次调和函数。