DIGSI中文调试软件介绍
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:2.35 MB
- 文档页数:20

dig 解析类型-回复Dig 解析类型,是一种用于互联网域名系统(DNS)查询的工具和命令。
它允许用户向DNS服务器发送查询请求,并接收服务器返回的响应。
本文将详细介绍dig解析类型的定义、用途、工作原理以及常见的解析类型。
第一部分:定义和用途(200字)Dig(Domain Information Groper)是一个常用的DNS工具,可用于查询域名相关的DNS信息。
它是域名系统(DNS)协议的一部分,主要用于诊断网络和DNS相关问题。
用户可以使用dig查询DNS记录、验证域名配置、调试DNS服务器以及获取特定域名的详细信息。
由于dig是一个命令行工具,因此可以在各种操作系统上运行。
第二部分:工作原理(400字)Dig使用DNS协议来与域名服务器进行通信。
它采用了客户端/服务器模型,用户作为客户端发送查询到DNS服务器,服务器接收查询并返回结果。
当用户在终端上输入dig命令后,dig客户端将解析命令并构建DNS 查询报文,并将其发送到指定的DNS服务器(通常是用户所在网络的默认DNS服务器)。
DNS查询报文由多个部分组成,其中最重要的是查询部分。
查询部分包含了用户要查询的域名以及查询类型。
查询类型决定了要获取的DNS信息的类别。
常见的DNS查询类型包括:1. A记录:查询一个域名对应的IP地址;2. CNAME记录:查询一个域名的别名;3. MX记录:查询一个域名的邮件服务器信息;4. NS记录:查询一个域名的权威DNS服务器信息;5. SOA记录:查询一个域名的起始授权记录;6. PTR记录:查询一个IP地址对应的域名。
当DNS服务器接收到查询报文后,它会检查查询类型,并查找相应的DNS 记录。
如果找到了匹配的记录,它会将结果封装成DNS响应报文,并发送回用户的终端。
用户可以从响应报文中提取所需的DNS信息。
第三部分:常见的解析类型(800字)1. A记录是最常见的解析类型之一。
它将域名转换为IPv4地址。

版本: 23.06.05 概述1安装DIGSI4 2设置配电结构3修改保护功能的设置4设置信息项5创建逻辑函数6编辑默认及控制显示画面7在线工作8评估故障记录9DIGSI4入门指南综述10DIGSI 4入门i免责声明:我们已经核查过本指南的所有内容,确保其中关于硬件和软件的所有说明尽可能正确。
但是,其中的偏差不可能完全避免,所以对于本指南中所给信息中出现的错误和疏漏我方不负任何责任。
指南中的数据已经过检查,必要的修正会包含在后续版本中。
希望您对我们提出宝贵意见。
如有变更,恕不另行通知。
1.00.00 版权©西门子股份公司2003年版权所有未经本公司明确许可,不得分发、复制此文档或对其中内容进行传播和交流。
违者将赔偿所造成的损失。
西门子股份公司保留所有权利,尤其是专利使用和商标注册权。
注册商标DIGSI®是西门子股份公司的注册商标。
本指南中的其它标志也可能是注册商标,任何第三方为其本身的目的使用这些标志可能会造成对所有权的侵犯。
西门子股份公司指南编号E50417-G115D-C152-A1DIGSI 4入门ii目录1、概述. . . . . . ... . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . (1)2、安装DIGSI4. . .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (3)3、设置配电结构 (5)4、修改保护功能的设置 (12)5、设置信息项 (17)6、创建逻辑函数 (23)7、编辑默认及控制显示画面 (31)8、在线工作 (36)9、评估故障记录 (45)10、综述 (51)DIGSI 4入门iii概述1欢迎阅读DIGSI 4入门指南,在这本指南里我们将介绍许多您一直期待的东西:一个紧凑的DIGSI 4基本功能的概述,包括可选的软件模块。




dig的命令调试dig - 发送域名查询信息包到域名服务器Dig (domain information groper 域名信息搜索)是一个灵活的命令行工具, 它可以用来从域名系统服务器中收集信息. Dig 有两种模式:简单交互模式用于简单的查询,而批处理模式则可以对包含多个查询条目的列表执行查询. 所有查询选项都可以从命令行输入.通常简单的dig 用法为下列格式:dig @ server domain query-type query-class这里:server可为域名或者以点分隔的Internet地址. 如果省略该可选字段, dig 会尝试使用你机器的默认域名服务器.注意: 如果指定了一个域名,那么将使用域名系统解析程序(即BIND)来进行解析. 如果你的系统不支持DNS,那么可能必须指定一个以点分隔的地址.另外一种选择是, 如果在你配置的某个地方有一台这样的服务器, 那么你所要做的就是建立/etc/resolv.conf 并在其中指明默认域名服务器的位置,这样server 自身就可以解析了.参看resolver(5) 以获得/etc/resolv.conf 相关的信息. 警告: 修改/etc/resolv.conf 同样会对标准的解析程序库产生影响,而(潜在地) 某些程序会要用到它. 作为一种选择,用户可设置环境变量LOCALRES 为指定的文件,这将用来取代/etc/resolv.conf Po Ns Ev LOCALRES 是特定针对dig 解析程序的,并不会牵涉到标准解析程序Pc . 如果LOCALRES 变量未设置或者指定的文件不能读,那么就使用/etc/resolf.conf .domain是指一个你请求信息的域名. 参看-x 选项(在该部分的Sx OTHER OPTIONS 节中有介绍)以获知指定反向地址查询的便捷方法.query-type是指你所请求的信息类型(DNS查询类型). 如果省略,默认为``a '' (T_A = address . ) 以下类型是可识别的:。
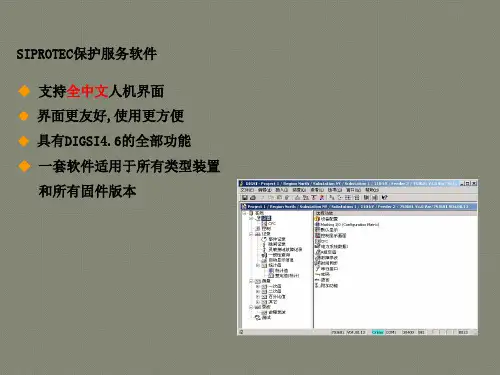


天津石化炼油部电气车间技术论文西门子继电保护软件DIGSI 4的使用及CFC简单编程姓名:张*2010年4月20日摘要本文主要描述西门子综保的调试设置软件DIGIS 4的功能及设置方法编写的。
从建立工程设置配电结构,到工程参数的设定和信息配置,最后到CFC逻辑编程,讲述了DIGIS 4软件的各个关键功能。
DIGIS 4软件的工程参数的设定和信息配置是软件的最基本的功能,CFC编程是DIGIS 4软件的精华部分。
工程参数的设定和信息配置可以实现对西门子继电保护装置进行定值的设定、跳闸出口及LED灯的定义等工作,而CFC逻辑函数可以实现我们需要的特殊功能。
论文中还结合1#区域变的电机反时限过流保护有延时闭锁的问题,给出合理建议,并使用CFC编出逻辑函数,确保电机启动过程中仍有速断、过流两套保护,提高保护的可靠性。
DIGIS 4软件中参数的设定是技术人员需要掌握的技能,同时掌握信息配置和CFC编程对今后的工作也是有很大的帮助。
关键词:DIGIS 4软件,建立工程,设置配电结构,参数设定,信息配置,CFC编程,切换定值组,限定电流值第一章建立工程及设置配电结构天津石化炼油部所使用的继电保护装置多为西门子厂家的7SJ--系列综保,这就要求我们对西门子继电保护软件DIGSI 4有一定的了解并能够轻松地使用此软件。
在此,我将对DIGSI4软件的应用进行详细介绍。
要使用DIGSI4软件进行保护定值参数的设定及CFC逻辑编程,首先要建立一个工程并设置其配电结构,这就需要解决以下三个问题:如何创建一个新工程如何在该工程中添加文件夹如何添加SIPROTEC 4 装置至该工程下面就让我来解决这三个问题。
打开DIGISI 4软件后,点击文件→新建。
在新建对话框中输入工程名称LX。
然后点击确定。
DIGSI4管理器会打开一个新工程窗口。
列表视图中已经包含了一个文件夹,且直接命名为文件夹。
既然其它要插入的文件夹都要相应地命名,不如给它一个和工程相关的名字。


Package‘DIGSS’October12,2022Title Determination of Intervals Using Georeferenced Survey SimulationVersion1.0.2Date2021-08-03Imports viridis,ggplot2,stats,grDevices,graphics,utilsDescription Simulation tool to estimate the rate of success that surveys possessing user-specific char-acteristics have in identifying archaeological sites(or any groups of clouds of ob-jects),given specific parameters of survey area,survey methods,and site properties.The sur-vey approach used is largely based on the work of Kintigh(1988)<doi:10.2307/281113>. Maintainer Mark Hubbe<***************>BugReports https:///markhubbe/DIGSS/issuesURL https:///markhubbe/DIGSSLicense MIT+file LICENSEDepends R(>=3.5)Encoding UTF-8RoxygenNote7.1.1Suggests knitr,rmarkdownVignetteBuilder knitrNeedsCompilation noAuthor Mark Hubbe[aut,cre],Cara Hubbell[aut],William Pestle[aut]Repository CRANDate/Publication2021-08-0414:30:05UTCR topics documented:areaEstimator (2)cloudGenerator (3)fieldMap (4)12areaEstimator parametersExample (6)plotSurveySumm (7)surveyLoops (8)surveySim (10)Index12 areaEstimator Area EstimatorDescriptionEstimate the area of multiple overlapping ellipsesUsageareaEstimator(sitemap,fieldarea,precision=1000)Argumentssitemap a matrix with sites per row and columns:site_number,site_area,eccentricity, angle,center.x,center.y,ellipse.a,ellipse.bfieldarea vector with dimensions offield surveyed in km:c(x_size,y_size)precision how many dots will be projected offield.Total dots equal precision*precision.Default value=1000(1million dots projected)DetailsThis function will estimate the area occupied by sites(ellipses)in a rectangularfield,taking into consideration the fact that sites can overlap.It is formatted to be used inside fieldMap().This function is a cookie-cutter area estimator,given the complexities of calculating the real areas of overlapping ellipses.It projects N x N equally spaced dots in the surveyfield and calculates the ratio of how many of them fall inside at least one site(ellipse).Using a precision of1000x1000 dots,it approximates area to within0.1%of real area.ValueThe rate of points that are inside at least one ellipse divided by all points projected in the area.Examples#create a matrix with2sites randomly located using fieldMap()site.example<-fieldMap(c(1,1),2,250000,plot=TRUE)#define size of fieldfield.area<-c(1,1)#calculate areaareaEstimator(site.example$site.frame,field.area)cloudGenerator3 cloudGenerator Cloud GeneratorDescriptionCreates a cloud of dots inside ellipsoid sitesUsagecloudGenerator(density,a,b,angle,center.x,center.y,type="uniform",precision=30,plot=FALSE)Argumentsdensity dots(artifacts)per m2a ellipse(site)long axis in kmb ellipse(site)short axis in kmangle ellipse(site)angle of rotation in radianscenter.x center of ellipse in x axiscenter.y center of ellipse in y axistype type of density distribution.Choose from:•uniform:dots are uniformly distributed within ellipse•linear:density of dots decreases linearly from center•spherical:density of dots decreases following elliptical function(abruptdrop near margins)•sinusoidal:density of dots decreases following sinusoidal equation precision how many slices of the distribution will be made(more=much slower run times).Default=30plot if function should plot results.function does not work outside surveySim()DetailscloudGenerator()creates a cloud of point inside an ellipsoid site of predefined size and shape,torepresent the locations of artifacts in a site.The function can build artifact scatters with differentdensities profiles.The function uses an"onion-layer"approach to approximate the density of pointsfrom the center.In practice,it means that each site is composed of N ellipse slices surrounding theprevious slice,with each slice having a different artifact density depending on the density functionselected.This approach also makes the surveySim function more efficient,since it will search forartifact hits only on the slices that intersect the survey pits.ValueA list with two objects:coords A list of the bands(N=precision)that represent the site,each populated with the X and Y coordinates for all artifac info A list with the number of pieces created($total.pieces),area of the site($total.area),and artifact density in the Examples#create a small site with low density uniform distributionuni.site<-cloudGenerator(0.1,0.1,0.05,pi/4,0.5,0.5,type="u")#plot a site with uniform artifact distribution through surveySimSiteParameters<-parametersExampleSiteParameters$simulations=1SiteParameters$site.density=1SiteParameters$obj.density=0.1SiteParameters$obj.distribution="u"surveySim(SiteParameters,plot.artifacts=TRUE)#plot a site with sinusoidal artifact distribution through surveySimSiteParameters$obj.distribution="si"surveySim(SiteParameters,plot.artifacts=TRUE)fieldMap Field MapDescriptionCreates randomly placed ellipsoid sites in a rectangularfield.UsagefieldMap(area,site.density,site.area,overlap=0.5,plot=FALSE,areaprecision=1000)Argumentsarea vector with horizontal and vertical size(hor,ver)of area surveyed in km.site.density number of sites/km2.Can be one constant value or vector with two values (min,max)to create a range of densities between simulations.site.area either:•One values with uniform area for all sites,or•Vector with4values(min,max,mean,st dev),to create variable areas.areas in this case are normally distributed based on mean and stdev,butwithin the range of min and max.overlap proportion of overlap possible between sites:from(0=no overlap allowed to1 =sites can occupy same space)plot whether site ellipses should should be plotted.areaprecision value passed to areaEstimator.Defines precision of area calculation.Default value(1000),returns area within0.1%of real area occupied by sitesDetailsfieldMap()creates and plots randomly placed ellipses representing archaeological sites.The sites are created inside a user-defined rectangle,with random positions and random rotations.It allows also to control the percentage of overlap between sites.ValueA list with three objects:site.frame A matrix with the properties of each site generated.totalArea The sum of areas of all site ellipses.actualArea The area occupied by the site ellipses taking into account their overlap)Examples#example of map with8sites or variable areas and partial overlapfield.example<-fieldMap(area=c(1,1),site.density=8,site.area=c(50000,250000,150000,50000),overlap=0.5,plot=TRUE)6parametersExampleparametersExample Parameters ExampleDescriptionA test list of parameters for surveySim()UsageparametersExampleFormatAn object of class surveySim of length10.DetailsThis is just a test list of parameters to be used as an example in surveySim().The values of this parameters are:Width between survey lines(col.width)=50mType of survey grid(grid.type)=hexagonalNumber of simulations=10Survey area=0.5km x0.5kmDensity of sites(site.density)=20Area of sites(site.area)=10,000m2Maximum site overlap=0.5Density of artifacts(obj.density)=1/m2Artifact distribution(obj.distribution)=sphericalSurvey radius(survey.radius)=0.5mplotSurveySumm7 plotSurveySumm Plot Survey SummariesDescriptionPlots the different results from surveySim()UsageplotSurveySumm(summaryList,plot="sites.found",labels=NULL)ArgumentssummaryList a list of survey summaries,the output of surveySim()plot what variable to plot.Options are:•sites.found-plots frequency of sites found•survey.hits-plots frequency of surveys that hit a site•success.rate.index-plots the success rate of surveys,i.e.the ratio ofsuccessful surveys over total surveys•sites.found.arti-plots frequency of sites found based on artifactspresent in sites•survey.hits.arti-plots frequency of surveys that found at least oneartifactlabels vector with name of each item in list,to be added to the legend.If NULL,names will be taken from listDetailsThis function will plot the results of the surveySim()simulations using Kernel Density plots.All the grids that are to be compared should be grouped into1list(list(a,b,c,etc...))The plot function allows you to choose different parts of the survey summaries produced by surveySim()you want to plot.Examples#create3Simulations with sites of different sizes:small.sites<-parametersExamplesmall.sites$site.area=500medium.sites<-parametersExamplemedium.sites$site.area=1000large.sites<-parametersExamplelarge.sites$site.area=2000#run the3simulationssmall.survey<-surveySim(small.sites)medium.survey<-surveySim(medium.sites)large.survey<-surveySim(large.sites)#create the comparative plot.#note that the results go into a list.If labels are not given,legend is built on list names plotSurveySumm(list(small.survey,medium.survey,large.survey),plot="sites.found",labels=c("Small sites","Medium sites","Large sites"))surveyLoops Survey LoopsDescriptionPerform multiple survey simulations changing values on one variable and plot the resultsUsagesurveyLoops(surveyParameters,loopVariable,loopSequence,plotResult) ArgumentssurveyParameterslist of parameters(object class surveySim)loopVariable variable to be looped.Can be any of the variables that exist in surveyParameters•col.width-vector of numbers with distances between STP rows•grid.type-vector of strings with names of grid types•simulations-vector of numbers with numbers of simulations•area-list with2vectors,one for x and one for y of area(vectors MUSTbe same length)•site.density-vector with numbers of site density OR list with2vectors,one with minimum site densities,one with maximum(vectors MUST besame length)•site.area-vector with numbers of site areas OR list with4vectors,onewith minimums,one with maximums,one with means,one with st.devs(vectors MUST be same length)•overlap-vector of numbers with varying overlaps•obj.density-vector with varying artifact density OR list with2vectors,one with minimum artifact densities,one with maximum(vectors MUSTbe same length)•obj.distribution-vector of names of artifact distribution•survey.radius vector with varying survey radiiloopSequence object with varying values,as defined aboveplotResult which results from the summary table will be plotted:•surveysPerSim-plots the total number of surveys created in each simula-tion•sitesFound-plots the frequency of sites found•sitesFoundOnArtifacts-plots the frequency of sites found based on sur-veysfinding at least one artifact•artifactsPerSurvey-plots the average number of artifacts found per sur-vey in each simulation•successRateIndex-plots the success rate index(ratio of survey pits thatfound a site over total number of survey pits made)DetailssurveyLoops()will run a series of simulations along one variable with values provided by user.Through this function,the user can simulate and evaluate the changes in efficiency and efficacy ofspecific variables,while holding every other value constant.The function runs multiple instancesof surveySim()using values of surveyParameters and replacing one of them with a sequence ofvalues offered by the user.ValueA list withfive objects:surveysPerSim A matrix with the number of survey pits done in each simulation.sitesFound A matrix with the summary statistics about frequency of sites found in each simulation. sitesFoundOnArtifacts A matrix with the summary statistics about frequency of sites detected based on artifacts found in artifactsPerSurver A matrix with the summary statistics about artifacts found per survey pit in each simulation. succesRateIndex A matrix with the summary statistics about success rate(number of succesful survey pits/total sur Examples#Loop the impact of increasing distances between survey rowswidth.loop<-surveyLoops(parametersExample,"col.width",c(50,75,100,125,150),"sitesFound")#Loop the impact of different artifact distributions on surveysdistr.loop<-surveyLoops(parametersExample,"obj.distribution",c("uniform","linear","spherical","sinusoidal"),"sitesFoundOnArtifacts")10surveySim surveySim Survey SimulationsDescriptionMaster function that runs survey simulationsUsagesurveySim(survey.parameters,artifact.analysis=TRUE,plot=TRUE,plot.artifacts=FALSE,areaprecision=1000)Argumentssurvey.parametersList of class surveySim.See package’s vignette or the help of parametersExamplefor details.The following items must be included in list of class surveySim•col.width the space between columns in the grid IN METERS•grid.type options are:"square","rectangle","staggered","hexagonal","arbitrary.staggered",following Kintigh1988•simulations number of random maps to be created and contrasted withthe grids•area vector with horizontal and vertical size of area surveyed in km OBS:Sites will all be ellipses with radii not too different and random angles•site.density measured as number of sites/km2.Can be either one valueor a vector with2values(min and max)to create a range of densities•site.area can be one of two options:1.one value indicating the area ofall sites,in m2;or2.a vector with4values:min,max,mean(or median),and standard deviation in m2•overlap maximum overlap of site area,ranging from0=no overlap al-lowed to1=complete overlap possible•obj.density artifacts per m2.Can be a single value(uniform for all sites)or a range of values defined as min and max•obj.distribution type of cloud distribution for artifacts inside sites.Choosefrom:’uniform’,’linear’,’spherical’,’sinusoidal’•survey.radius the radius of the survey pit(assumed to be a circle) artifact.analysisIncludes the analysis of artifacts in sites.Can be very time-consuming for mid-high artifact densities.Default=TRUEplot If TRUE the last iteration of the simulations will be plotted.surveySim11 plot.artifacts If TRUE the artifacts in each site will be plotted.Default=FALSE because it isresource intensive for mid-high densities.areaprecision Area covered by sites is approximated by a cookie-cutter approach.Defaultprecision=1000gives approximate area within1%error.Higher values reduceerror but are more resource intensive.DetailssurveySim()is the main function that will conduct the simulations of survey grids based on theSurvey Parameters created by user.ValueA list with four objects:Summary A matrix with summary statistics about number of surveys,frequency of site founds,artifacts presence,and suc BySite A matrix with results of the analyses by site from each of the survey areas created in the simulation. ByArtifact A matrix with results of the analyses by artifact presence in survey pits from each of the survey areas created in Parameters A list with the parameters used to run the simulation.#’@references Kintigh(1988)The Effectiveness of Subsurface Testing:A Simulation Approach.American Antiquity,53:686-707.doi:10.2307/281113Examples#Runs simulations based on parametersExamplesurveyExample<-surveySim(parametersExample)#Edit parametersExample to have50simulations and then run simulationstmp_parameters<-parametersExampletmp_parameters$simulations<-50survey50<-surveySim(tmp_parameters)Index∗datasetsparametersExample,6 areaEstimator,2cloudGenerator,3fieldMap,4parametersExample,6 plotSurveySumm,7surveyLoops,8surveySim,1012。
电力系统仿真软件DIgSI L ENT介绍吕 涛,韩祯祥(浙江大学电气工程学院,浙江 杭州 310027)摘 要:介绍了德国DIgSI LE NT公司的大型集成化电力系统仿真软件的主要功能、特点和应用。
提供了电力系统各个方面的分析功能。
高度图形化的操作模式和全新的数据管理理念使它区别于众多的电力系统分析软件,具有独特的优点。
关键词:电力系统;仿真软件;DIgSI LE NT中图分类号:TP391.9 文献标识码:B 文章编号:100129529(2004)1220037205I ntroduction of pow er system simulation softw are DIgSI LENTL¨U Tao,H AN Zhen2xiang(School of E lectrical Engineering,Zhejiang Univ.,Hangzhou310027,China)Abstract:The major functions,features and application of the large integrated power system simulation s oftware designed by DIgSI LE NT C om pany of G ermany were introduced.The s oftware has analytical functions for every aspects of power system and is distinctive from other power system analysis s oftware for its high degree graphic operation m ode and new data manage2 ment concept.K ey w ords:power system;simulation s oftware;DIgSI LE NT 电力系统仿真软件DIgSI LE NT的名称来源于数字仿真和电网计算程序(DIgital SImu Lation and E lectrical NeT w ok),最早的开发始于1976年。