数学常用符号中英文
- 格式:docx
- 大小:12.75 KB
- 文档页数:1

常⽤数学符号读法⼤全以及主要数学符号含义常⽤数学符号读法⼤全以及主要数学符号含义⼤写⼩写英⽂注⾳国际⾳标注⾳中⽂注⾳Ααalpha alfa 阿⽿法Ββbeta beta 贝塔Γγgamma gamma 伽马Δδdeta delta 德⽿塔Εεepsilon epsilon 艾普西隆Ζζzeta zeta 截塔Ηηeta eta 艾塔Θθtheta θita 西塔Ιιiota iota 约塔Κκkappa kappa 卡帕∧λlambda lambda 兰姆达Μµmu miu 缪Ννnu niu 纽Ξξxi ksi 可塞Οοomicron omi kron 奥密可戎∏πpi pai 派Ρρrho rou 柔∑σsigma sigma 西格马Ττtau tau 套Υυupsilon jupsilon ⾐普西隆Φφphi fai 斐Χχchi khai 喜Ψψpsi psai 普西Ωωomega omiga 欧⽶伽数学符号:(1)数量符号:如:i,2+i,a,x,⾃然对数底e,圆周率π.(2)运算符号:如加号(+),减号(-),乘号(×或·),除号(÷或/),两个集合的并集(∪),交集(∩),根号(√),对数(log,lg,ln),⽐(:),微分(dx),积分(∫)等.(3)关系符号:如“=”是等号,“≈”是近似符号,“≠”是不等号,“>”是⼤于符号,“<”是⼩于符号,“→”表⽰变量变化的趋势,“∽”是相似符号,“≌”是全等号,“∥”是平⾏符号,“⊥”是垂直符号,“∝”是反⽐例符号,“∈”是属于符号,“C”或“C下⾯加⼀横”是“包含”符号等.(4)结合符号:如圆括号“()”⽅括号“[]”,花括号“{}”括线“—”(5)性质符号:如正号“+”,负号“-”,绝对值符号“‖”(6)省略符号:如三⾓形(△),正弦(sin),余弦(cos),x的函数(f(x)),极限(lim),因为(∵),所以(∴),总和(∑),连乘(∏),从n个元素中每次取出r个元素所有不同的组合数(C(r)(n) ),幂(A,Ac,Aq,x^n),阶乘(!)等.数学符号的意义符号意义∞⽆穷⼤π圆周率|x|绝对值∪并集∩交集≥⼤于等于≤⼩于等于≡恒等于或同余ln(x)以e为底的对数lg(x)以10为底的对数floor(x)上取整函数ceil(x)下取整函数x mod y求余数x - floor(x) ⼩数部分∫f(x)dx不定积分∫[a:b]f(x)dx a到b的定积分→等价于趋向于数学符号的应⽤P为真等于1否则等于0∑[1≤k≤n]f(k) 对n进⾏求和,可以拓⼴⾄很多情况如:∑[n is prime][n < 10]f(n)∑∑[1≤i≤j≤n]n^2lim f(x) (x->?) 求极限f(z) f关于z的m阶导函数C(n:m) 组合数,n中取mP(n:m) 排列数m|n m整除nm⊥n m与n互质a ∈A a属于集合A#A 集合A 中的元素个数“∑”数学⾥的连加符号,叫西格马,求和的意思要给出上下界限(⽐如k是⾃然数∑k(上界限⾄n,下界限从k=0开始) ∑k=0+1+2+……+n {⼤括号(bracket)是⽤来规定运算次序的符号。
数学符号及读法大全常用数学输入符号:≈≡≠=≤≥<>↉↊ↁ±+-× ÷/∫ⅽⅴ∞ⅸⅹ∑∏ⅻ∩ⅰⅿⅾ//‖ⅶↄↂ√()【】{}ⅠⅡ▝↋ⅷαβγδεδεζΓ符号含义i -1的平方根f(x) 函数f在自变量x处的值sin(x) 在自变量x处的正弦函数值exp(x) 在自变量x处的指数函数值,常被写作e x a^x a的x次方;有理数x由反函数定义ln x exp x 的反函数a x同 a^xlogb a 以b为底a的对数; b logba = acos x 在自变量x处余弦函数的值tan x 其值等于 sin x/cos xcot x 余切函数的值或 cos x/sin xsec x 正割含数的值,其值等于 1/cos xcsc x 余割函数的值,其值等于 1/sin xasin x y,正弦函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = sin y acos x y,余弦函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = cos y atan x y,正切函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = tan y acot x y,余切函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = cot y asec x y,正割函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = sec y acsc x y,余割函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = csc yζ角度的一个标准符号,不注明均指弧度,尤其用于表示atan x/y,当x、y、z用于表示空间中的点时i, j, k 分别表示x、y、z方向上的单位向量(a, b, c) 以a、b、c为元素的向量(a, b) 以a、b为元素的向量(a, b) a、b向量的点积a•b a、b向量的点积(a•b)a、b向量的点积|v| 向量v的模|x| 数x的绝对值表示求和,通常是某项指数。
下边界值写在其下部,上边界值写在其上部。
如j从1到100 的和可以表示成:。
这表示 1 + 2 + … + nM 表示一个矩阵或数列或其它|v> 列向量,即元素被写成列或可被看成k×1阶矩阵的向量<v| 被写成行或可被看成从1×k阶矩阵的向量dx 变量x的一个无穷小变化,dy, dz, dr等类似ds 长度的微小变化ξ变量 (x2 + y2 + z2)1/2或球面坐标系中到原点的距离r 变量 (x2 + y2)1/2或三维空间或极坐标中到z轴的距离|M| 矩阵M的行列式,其值是矩阵的行和列决定的平行区域的面积或体积||M|| 矩阵M的行列式的值,为一个面积、体积或超体积det M M的行列式M-1矩阵M的逆矩阵v×w向量v和w的向量积或叉积ζvw向量v和w之间的夹角A•B×C标量三重积,以A、B、C为列的矩阵的行列式uw在向量w方向上的单位向量,即 w/|w|df 函数f的微小变化,足够小以至适合于所有相关函数的线性近似df/dx f关于x的导数,同时也是f的线性近似斜率f ' 函数f关于相应自变量的导数,自变量通常为x∂f/∂x y、z固定时f关于x的偏导数。


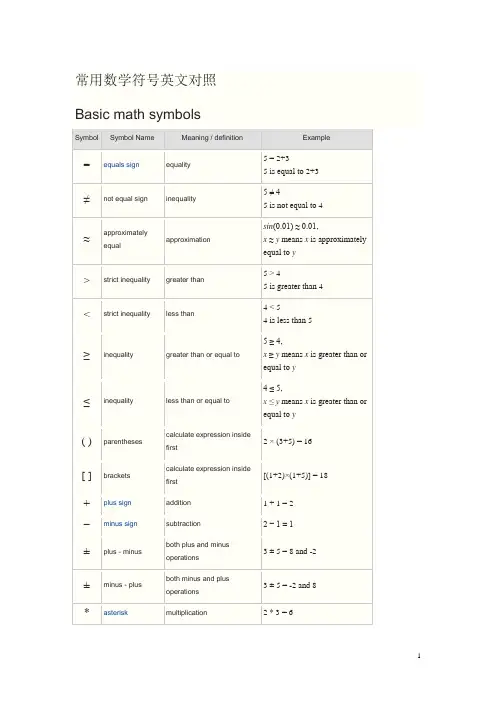
常⽤数学符号英⽂对照常⽤数学符号英⽂对照Basic math symbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example = equals sign equality 5 = 2+35 is equal to 2+3≠not equal sign inequality 5 ≠ 45 is not equal to 4≈approximatelyequal approximationsin(0.01) ≈ 0.01,x≈y means x isapproximately equal to y> strict inequality greater than 5 > 45 is greater than 4< strict inequality less than 4 < 54 is less than 5≥inequality greater than or equal to 5 ≥ 4,x≥y means x is greater than or equal to y≤inequality less than or equal to 4 ≤ 5,x ≤ y means x is greater than or equal to y( ) parentheses calculate expressioninside first2 × (3+5) = 16[ ] brackets calculate expressioninside first[(1+2)×(1+5)] = 18 + plus sign addition 1 + 1 = 2 minus sign subtraction 2 1 = 1±plus - minus both plus and minusoperations3 ± 5 = 8 and -2±minus - plus both minus and plusoperations3 ± 5 = -2 and 8* asterisk multiplication 2 * 3 = 6×times sign multiplication 2 × 3 = 6 ·multiplicationmultiplication 2 · 3 = 6dot÷division sign /division 6 ÷ 2 = 3 obelus/ division slash division 6 / 2 = 3–horizontal line division / fractionmod modulo remainder calculation 7 mod 2 = 1. period decimal point, decimal2.56 = 2+56/100separatora b power exponent 23= 8a^b caret exponent 2 ^ 3= 8√a square root √a ·√a= a√9= ±33√a cube root 3√a ·3√a ·3√a= a3√8= 24√a fourth root 4√a ·4√a ·4√a ·4√a= a4√16= ±2n√a n-th rootfor n=3,n√8= 2 (radical)% percent 1% = 1/100 10% × 30 = 3‰per-mille 1‰ = 1/1000 = 0.1% 10‰× 30 = 0.3 ppm per-million 1ppm = 1/1000000 10ppm × 30 = 0.0003 ppb per-billion 1ppb = 1/1000000000 10ppb × 30 = 3×10-7 ppt per-trillion 1ppt = 10-1210ppt × 30 = 3×10-10 Geometry symbols Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example∠angle formed by two rays ∠ABC = 30°measured angle ABC = 30°sphericalangle AOB = 30° ∟ right angle = 90°α = 90° °degree 1 turn = 360° α = 60° degdegree 1 turn = 360degα = 60deg ′ prime arcminute, 1° = 60′α = 60°59′″ double primearcsecond, 1′ = 60″α = 60°59′59″line infinite lineABline segment line from point A to point Bray line that start from point Aarc arc from point A to point B= 60° ⊥ perpendicular perpendicular lines (90° angle)AC ⊥ BC| | parallel parallel lines AB | | CDcongruent to equivalence of geometric shapes and size ABC XYZ ~ similarity same shapes, not same size ?ABC~ ?XYZ Δtriangle triangle shapeΔABC ? ΔBCD |x -y | distancedistance between points x and y| x -y | = 5πpi constantπ = 3.141592654...is the ratio between the circumference and diameter of a circlec = π·d = 2·π·rAlgebra symbolsSymbol Symbol NameMeaning /definitionExamplex x variable unknown value tofindwhen 2x= 4, then x= 2≡equivalence identical toequal by definition equal bydefinition:= equal by definition equal bydefinition~ approximately equal weakapproximation11 ~ 10≈approximately equal approximation sin(0.01) ≈ 0.01∝proportional to proportional to y∝x when y=kx, k constant ∞lemniscate infinity symbol much less than much less than 1 1000000much greater than much greater than 1000000 1( ) parentheses calculateexpressioninside first2 * (3+5) = 16[ ] brackets calculateexpressioninside first[(1+2)*(1+5)] = 18{ } braces setxfloor brackets rounds number tolower integer4.3 = 4xceiling brackets rounds number toupper integer4.3 = 5x! exclamation mark factorial 4! = 1*2*3*4 = 24 |x| single vertical bar absolute value | -5 | = 5 f(x) function of x maps values of xto f(x)f(x) = 3x+5(f°g) function composition (f°g) (x) =f(g(x))f(x)=3x,g(x)=x-1 ?(f°g)(x)=3(x-1)(a,b) open interval (a,b) ={x|ax∈ (2,6)[a,b] closed interval [a,b] ={x|a≤x≤b}x∈ [2,6]delta change /differencet=t1-t0discriminant Δ =b2- 4ac∑sigma summation - sumof all values inrange of series∑x i= x1+x2+...+x n∑∑sigma double summation∏capital pi product - productof all values inrange of series∏x i=x1?x2?...?x ne e constant/ Euler's number e=2.718281828...e= lim (1+1/x)x,x→∞γEuler-Mascheroni constant γ = 0.527721566...φgolden ratio golden ratio constantπpi constant π=3.141592654...is the ratioLinear Algebra SymbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example·dot scalar product a·b×cross vector product a×bA?B tensor product tensor product of A and B A?Binner product[ ] brackets matrix of numbers( ) parentheses matrix of numbers|A| determinant determinant of matrix Adet(A) determinant determinant of matrix A||x|| double vertical bars normA T transpose matrix transpose (A T)ij= (A)jiA?Hermitian matrix matrix conjugate transpose (A?)ij= (A)ji A*Hermitian matrix matrix conjugate transpose (A*)ij= (A)ji A-1inverse matrix A A-1=Irank(A) matrix rank rank of matrix A rank(A) = 3Probability and statistics symbols Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition ExampleP(A) probabilityfunction probability of eventAP(A) = 0.5P(A∩B) probability ofeventsintersectionprobability that ofevents A and BP(A∩B) = 0.5P(A∪B) probability ofevents union probability that ofevents A or BP(A|B) conditionalprobabilityfunctionprobability of eventA given event BoccuredP(A | B) = 0.3f(x) probabilitydensityfunction (pdf)P(a≤x≤b) =∫f(x)dxF(x) cumulativedistributionfunction (cdf)F(x) =P(X≤x)µpopulation mean mean of population valuesµ= 10E(X) expectationvalue expected value ofrandom variable XE(X) = 10E(X | Y) conditionalexpectation expected value of random variable Xgiven YE(X | Y=2) = 5var(X) variance variance of random variable Xvar(X) = 4σ2variance variance ofpopulation valuesσ2= 4deviation standard deviation ofrandom variable Xstd(X) = 2σXstandard deviationstandard deviation value of random variable X σX = 2 medianmiddle value of random variable xcov (X ,Y )covariancecovariance of random variables X and Y cov (X,Y ) = 4 corr (X ,Y ) correlationcorrelation of random variables X and Y corr (X,Y ) = 0.6ρX ,Y correlationcorrelation of random variables X and Y ρX ,Y = 0.6∑summation summation - sum of allvalues in range of series∑∑double summationdouble summationMo mode value that occursmost frequently in populationMR mid-rangeMR = (x max +x min )/2Mdsample median half the population is below this value Q 1lower / first quartile25% of population are below this valueQ 2median / second quartile50% of population are below this value = median of samples Q 3upper / third quartile75% of population are below this valuex sample meanaverage / arithmetic meanx = (2+5+9) / 3 = 5.333s 2sample variancepopulation samples variance estimators 2 = 4s sample standard deviationpopulation samples standard deviation estimators = 2z x standard scorez x = (x -x ) / s xX ~distributionof X distribution of random variable X X ~ N (0,3)N (µ,σ2)normal distribution gaussian distribution X ~ N (0,3)U (a ,b ) uniform distribution equal probability in range a,bX ~ U (0,3)exp (λ)exponential distribution f (x ) = λe -λx , x ≥0 gamma (c , λ) gamma distribution f (x ) = λ c x c-1e -λx /Γ(c ), x ≥0χ 2(k )chi-square distributionf (x ) = x k /2-1e -x /2 /( 2k/2Γ(k /2) )F (k 1, k 2)F distributionBin (n ,p ) binomial distribution f (k ) = n C k p k (1-p )n-k Poisson (λ)Poisson distribution f (k ) = λk e -λ / k !Geom (p )geometric distribution f (k ) = p (1-p ) kHG (N ,K ,n )hyper-geometric distributionBern (p )Bernoulli distributionSet theory symbolsSymbolSymbol NameMeaning / definitionExample{ }set a collection of elementsA = {3,7,9,14},B = {9,14,28} A ∩ B intersectionobjects that belong to set A and set BA ∩B = {9,14}A ∪B unionobjects that belong to set A or set BA ∪B = {3,7,9,14,28}A ?B subsetsubset has fewer elements or equal to the set{9,14,28} ? {9,14,28}A ? Bproper subset / strict subsetsubset has fewer elements than the set{9,14} ? {9,14,28} A ? B not subset left set not a subset of right set {9,66} ? {9,14,28}A ?B supersetset A has more elements or equal to the set B{9,14,28} ? {9,14,28} A ? B proper superset / strict supersetset A has more elements than set B{9,14,28} ? {9,14} A ? B not superset set A is not a superset of set B {9,14,28} ? {9,66}2Apower set all subsets of Apower set all subsets of AA =B equality both sets have the same membersA={3,9,14}, B={3,9,14},。

常用数学符号的汉英读法1. 逻辑:Logic∃存在:there exists∀任意:for allp q⇒由p推出q :p implies q / if p, then q⇔p、q相互推出:p if and only if q /p is equivalent to q / p and q are equivalentp q2.集合:Sets∈x 属于A:x belongs to A / x is an element (or a member) of Ax A∉x 不属于A:x does not belong to A / x is not an element (or a member) of Ax A⊂A真包含B:A is contained in B / A is a subset of BA B⊃A真包含于B:A contains B / B is a subset of AA BA B A 与B的交集:A cap B / A meet B / A intersection BA B A 与B的并集:A cup B / A join B / A union B3. 实数:Real numbersx+x加1:x plus one1x-x减1:x minus one1x±x加或减1:x plus or minus one1xy x乘y:xy / x multiplied by yxx除以y:x over yy=等于:the equals sign5x=x等于5 :x equals 5 / x is equal to 5≡x恒等于y:x is equivalent to (or identical with) yx y≠x不等于y :x is not equivalent to (or identical with) yx y>x 大于y:x is greater than yx y≥x 大于或等于y:x is greater than or equal to yx y<x 小于y:x is less than yx y≤x 小于或等于y;x is less than or equal to yx y<<0小于x小于1:zero is less than x is less than 1x01≤≤0小于或等于x小于或等于1:zero is less than or equal to x is less than or equal to 1 01x||x x的模(x的绝对值):mod x / modulus x2x x的2次方:x squared / x (raised) to the power 23x x的3次方:x cubed4x x的4次方:x to the fourth / x to the power fournx x的n次方:x to the nth / x to the power nnx-x的负n次方:x to the (power) minus nx的2次根式:(square) root x / the square root of xx的3次根式:cube root (of) xx的4次根式:fourth root (of) xx的n次根式:nth root (of) x2+x与y的和的平方:x plus y all squared()x y2()x yx 与y 的商的平方:x over y all squared !n n 的阶乘:n factorialx x 拔:x bari x i x :i x / x subscript i / x suffix i/ x sub i1n i i a =∑ i a 从1到n 求和:the sum from i equals one to n i a / the sum as i runs from 1 to n of the i a 4.线性代数:Linear algebra OA 向量OA :OA / vector OAOA 有向线段OA :OA / the length of the segment OA a b 向量a 与b 平行:vector a parallel to vector ba ⊥b 向量a 与b 垂直:vector a is perpendicular to vector b5. 函数:Functions()f x 函数()f x : fx / f of x / the function f of x:f S T → f 是从集合S 到T 的函数:a function f from S to Tx y → 从x 到y :x maps to y / x is sent (or mapped) to y'()f x ()f x 的导数:f prime x / f dash x / the (first) derivative of f with respect to x ''()f x ()f x 的二阶导数:f double-prime x / f double-dash x /the second derivative of f with respect to x'''()f x ()f x 的三阶导数:f triple-prime x / f triple-dash x /the third derivative of f with respect to x()()n f x ()f x 的四阶导数: the nth derivative of f with respect to x1f x ∂∂ f 关于1x 的偏导数:the partial (derivative) of f with respect to 1x 221f x ∂∂ f 关于1x 的二阶偏导数:the second partial (derivative) of f with respect to 1x 0∞⎰ 从0到∞求积分:the integral from zero to infinitylim x → x 趋于0求极限:the limit as x approaches zero 0lim x →+ x 右趋于0求极限:the limit as x approaches zero from above 0lim x →- x 左趋于0求极限:the limit as x approaches zero from belowlog e y 以e 为底数的y 的对数:log y to the base e / log to the base e of y / natural log (of) y ln y y 的自然对数:log y to the base e / log to the base e of y / natural log (of) y。
×times sign multiplication 2 × 3 = 6 ·multiplication dot multiplication 2 · 3 = 6÷division sign /division 6 ÷ 2 = 3obelus/ division slash division 6 / 2 = 3–horizontal line division / fractionmod modulo remainder calculation 7 mod 2 = 1. period decimal point, decimal2.56 = 2+56/100separatora b power exponent 23= 8a^b caret exponent 2 ^ 3= 8√a square root √a ·√a = a√9 = ±33√a cube root 3√a ·3√a ·3√a = a3√8 = 24√a fourth root 4√a ·4√a ·4√a ·4√a = a4√16 = ±2n√a n-th root (radical) for n=3, n√8 = 2% percent1% = 1/100 10% × 30 = 3‰per-mille1‰ = 1/1000 = 0.1%10‰ × 30 = 0.3ppm per-million1ppm = 1/1000000 10ppm × 30 = 0.0003ppb per-billion 1ppb = 1/1000000000 10ppb × 30 = 3×10-7ppt per-trillion 1ppt = 10-1210ppt × 30 = 3×10-10Geometry symbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example ∠angle formed by two rays ∠ABC = 30°measuredABC = 30°anglespherical angle AOB = 30°∟right angle = 90°α = 90°°degree 1 turn = 360°α = 60°deg degree 1 turn = 360deg α = 60deg′prime arcminute, 1° = 60′α = 60°59′″double prime arcsecond, 1′ = 60″α = 60°59′59″line infinite lineAB line segment line from point A to point Bray line that start from point Aarc arc from point A to point B= 60°⊥perpendicular perpendicular lines (90° angle) AC ⊥ BC| | parallel parallel lines AB | | CD≅congruent to equivalence of geometric shapes and size ∆ABC≅∆XYZ ~ similarity same shapes, not same size ∆ABC~ ∆XYZ Δtriangle triangle shape ΔABC≅ΔBCD |x-y| distance distance between points x and y | x-y | = 5πpi constant π = 3.141592654...is the ratio between the circumference and diameter of acirclec = π·d = 2·π·rrad radians radians angle unit 360° = 2π rad c radians radians angle unit 360° = 2πcgrad gradians / gons grads angle unit 360° = 400 gradg gradians / gons grads angle unit 360° = 400 g Algebra symbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning /definitionExample[a,b] closed interval [a,b] ={x | a≤x≤b}x∈[2,6]∆delta change /difference∆t = t1 - t0∆discriminant Δ =b2 - 4ac∑sigma summation -sum of allvalues in rangeof series∑ x i= x1+x2+...+x n∑∑sigma doublesummation∏capital pi product -product of allvalues in rangeof series∏ x i=x1∙x2∙...∙x ne e constant / Euler's number e =2.718281828...e = lim (1+1/x)x , x→∞γEuler-Mascheroni constantγ =0.527721566...φgolden ratio golden ratioconstantπpi constant π =3.141592654...is the ratiobetween thecircumference anddiameter of acirclec = π·d = 2·π·rLinear Algebra SymbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example ·dot scalar product a · b×cross vector product a × bA⊗B tensor product tensor product of A and B A⊗B inner product[ ] brackets matrix of numbers( ) parentheses matrix of numbers| A | determinant determinant of matrix Adet(A) determinant determinant of matrix A|| x || double vertical bars normA T transpose matrix transpose (A T)ij = (A)jiA†Hermitian matrix matrix conjugate transpose (A†)ij = (A)ji A*Hermitian matrix matrix conjugate transpose (A*)ij = (A)ji A-1inverse matrix A A-1 = Irank(A) matrix rank rank of matrix A rank(A) = 3 dim(U) dimension dimension of matrix A rank(U) = 3 Probability and statistics symbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition ExampleP(A) probabilityfunctionprobability of event A P(A) = 0.5P(A∩B) probability ofeventsintersectionprobability that ofevents A and BP(A∩B) = 0.5P(A∪B) probability ofevents union probability that ofevents A or BP(A∪B) = 0.5P(A | B) conditionalprobabilityfunctionprobability of event Agiven event BoccuredP(A | B) = 0.3f (x) probabilitydensity function(pdf)P(a ≤ x ≤ b) = ∫f (x) dxF(x) cumulative F(x) = P(X≤ x)distribution function (cdf)μpopulationmean mean of populationvaluesμ = 10E(X) expectationvalue expected value ofrandom variable XE(X) = 10E(X | Y) conditionalexpectation expected value ofrandom variable Xgiven YE(X | Y=2) = 5var(X) variance variance of randomvariable Xvar(X) = 4σ2variance variance ofpopulation valuesσ2 = 4std(X) standarddeviation standard deviation ofrandom variable Xstd(X) = 2σX standarddeviation standard deviationvalue of randomvariable XσX=2median middle value of random variable xcov(X,Y) covariance covariance ofrandom variables Xand Ycov(X,Y) = 4corr(X,Y) correlation correlation ofrandom variables Xand Ycorr(X,Y) = 0.6ρX,Y correlation correlation ofrandom variables Xand YρX,Y = 0.6∑summation summation - sum of all values in range of series∑∑doublesummationdouble summationBin(n,p) binomialdistributionf (k) = n C k p k(1-p)n-kPoisson(λ)Poissondistributionf (k)= λk e-λ / k!Geom(p) geometricdistributionf (k) = p(1-p) kHG(N,K,n) hyper-geometric distributionBern(p) Bernoulli distributionCombinatorics SymbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Examplen! factorial n! = 1·2·3·...·n5! = 1·2·3·4·5 = 120 n P k permutation 5P3 = 5! / (5-3)! = 60 n C kcombination 5C3 = 5!/[3!(5-3)!]=10Set theory symbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example{ } set a collection of elements A = {3,7,9,14},B = {9,14,28}A ∩B intersection objects that belong to set A and setBA ∩B = {9,14}A ∪B union objects that belong to set A or setBA ∪B ={3,7,9,14,28}A ⊆B subset subset has fewer elements orequal to the set{9,14,28} ⊆{9,14,28}A ⊂B proper subset / strict subset has fewer elements than {9,14} ⊂subset the set {9,14,28}A ⊄B not subset left set not a subset of right set {9,66} ⊄{9,14,28}A ⊇B superset set A has more elements or equalto the set B{9,14,28} ⊇{9,14,28}A ⊃B proper superset / strictsupersetset A has more elements than setB{9,14,28} ⊃{9,14}A ⊅B not superset set A is not a superset of set B {9,14,28} ⊅{9,66}2A power set all subsets of A power set all subsets of AA =B equality both sets have the same members A={3,9,14}, B={3,9,14}, A=BA c complement all the objects that do not belong to set AA \B relative complement objects that belong to A and not toBA = {3,9,14},B = {1,2,3},A-B = {9,14}A -B relative complement objects that belong to A and not toBA = {3,9,14},B = {1,2,3},A-B = {9,14}A ∆B symmetric difference objects that belong to A or B butnot to their intersectionA = {3,9,14},B = {1,2,3},A ∆B ={1,2,9,14}A ⊖B symmetric difference objects that belong to A or B butnot to their intersectionA = {3,9,14},B = {1,2,3},A ⊖B ={1,2,9,14}a∈A element of set membership A={3,9,14}, 3 ∈Ax∉A not element of no set membership A={3,9,14}, 1 ∉A(a,b) ordered pair collection of 2 elementsA×B cartesian product set of all ordered pairs from A andB|A| cardinality the number of elements of set A A={3,9,14},|A|=3#A cardinality the number of elements of set A A={3,9,14},#A=3aleph-null infinite cardinality of natural numbers setaleph-one cardinality of countable ordinal numbers setØ empty set Ø = { } C = {Ø} universal set set of all possible values0natural numbers / wholenumbers set (with zero) 0= {0,1,2,3,4,...} 0 ∈01natural numbers / wholenumbers set (withoutzero)1= {1,2,3,4,5,...} 6 ∈1 integer numbers set = {...-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,...} -6 ∈rational numbers set = {x | x=a/b, a,b∈} 2/6 ∈real numbers set = {x | -∞ < x <∞} 6.343434∈complex numbers set= {z | z=a+bi,-∞<a<∞,-∞<b<∞}6+2i∈Logic symbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example ·and and x·y^ caret / circumflex and x ^ y& ampersand and x & y+ plus or x + y∨reversed caret or x∨y | vertical line or x | yx' single quote not - negation x'x bar not - negation x¬not not - negation ¬x! exclamation mark not - negation ! x⊕circled plus / oplus exclusive or - xor x⊕y ~ tilde negation ~ x⇒implies⇔equivalent if and only if (iff)↔equivalent if and only if (iff)∀for all∃there exists∄there does not exists∴therefore∵because / sinceCalculus & analysis symbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example limit limit value of a functionεepsilon represents a very small number,ε→0near zeroe e constant / Euler'snumber e = 2.718281828...e = lim(1+1/x)x ,x→∞y ' derivative derivative - Lagrange's notation (3x3)' = 9x2y '' second derivative derivative of derivative (3x3)'' = 18xy(n)nth derivative n times derivation (3x3)(3) = 18 derivative derivative - Leibniz's notation d(3x3)/dx = 9x2second derivative derivative of derivative d2(3x3)/dx2 = 18xnth derivative n times derivationtime derivative derivative by time - Newton's notationtime secondderivativederivative of derivativeD x y derivative derivative - Euler's notationD x2y second derivative derivative of derivativepartial derivative ∂(x2+y2)/∂x = 2x ∫integral opposite to derivation ∫f(x)dx∫∫double integral integration of function of 2variables∫∫f(x,y)dxdy∫∫∫triple integral integration of function of 3variables∫∫∫f(x,y,z)dxdydz∮closed contour / lineintegral∯closed surfaceintegral∰closed volumeintegral[a,b] closed interval [a,b] = {x | a ≤ x ≤ b}(a,b) open interval (a,b) = {x | a < x < b}i imaginary unit i≡ √-1 z = 3 + 2i z* complex conjugate z = a+bi→z*=a-bi z* = 3 - 2i z complex conjugate z = a+bi→z = a-bi z = 3 - 2i ∇nabla / del gradient / divergence operator ∇f (x,y,z) vectorunit vectorx * y convolution y(t) = x(t) * h(t)Laplace transform F(s) = {f (t)}Fourier transform X(ω) = {f (t)}δdelta function∞lemniscate infinity symbol。

⼀、⼀般符号对应的英⽂单词 . period 句号 , comma 逗号 : colon 冒号 ; semicolon 分号 ! exclamation 惊叹号 ? question mark 问号 ─ hyphen 连字符 ’ apostrophe 省略号;所有格符号 — dash 破折号 ‘’single quotation marks 单引号 “”double quotation marks 双引号 ( ) parentheses 圆括号 [ ] square brackets ⽅括号 《》French quotes 法⽂引号;书名号 ... ellipsis 省略号 ¨ tandem colon 双点号 " ditto 同上 ‖ parallel 平⾏ / virgule 斜线号 & ampersand = and ~ swung dash 代字号 § section; division 分节号 → arrow 箭号;参见号 + plus 加号;正号 - minus 减号;负号 ± plus or minus 正负号 × is multiplied by or cross 叉乘 ÷ is divided by 除号 = is equal to 等于号 ≠ is not equal to 不等于号 ≡ is equivalent to 全等于号 ≌ is equal to or approximately equal to 等于或约等于号 ≈ is approximately equal to 约等于号 < is less than ⼩于号 > is more than (is greater than在数学中更常⽤)⼤于号 ≮ is not less than 不⼩于号 ≯ is not more than 不⼤于号 ≤ is less than or equal to ⼩于或等于号 ≥ is more than or equal to ⼤于或等于号 % per cent 百分之… ‰ per mill 千分之… ∞ infinity ⽆限⼤号 ∝ varies as 与…成⽐例 √ (square) root 平⽅根 ∵ since; because 因为 ∴ hence 所以 ∷ equals, as (proportion) 等于,成⽐例 ∠ angle ⾓ ⌒ semicircle 半圆 ⊙ circle 圆 ○ circumference 圆周 π pi 圆周率 △ triangle 三⾓形 ⊥ perpendicular to 垂直于;另外normal to,right to也都有垂直的意思。

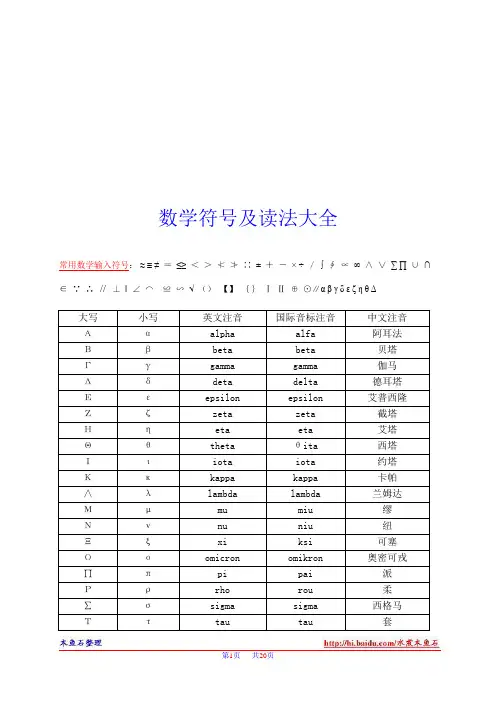
、希腊字母:α——阿尔法β——贝塔γ——伽马Δ——德尔塔ξ——可sei ψ——可赛ω——奥秘噶μ——米哟λ——南木打σ——西格玛τ——套φ——fai2、数学运算符:∑—连加号∏—连乘号∪—并∩—补∈—属于∵—因为∴—所以√—根号‖—平行⊥—垂直∠—角⌒—弧⊙—圆∝—正比于∞—无穷∫—积分≈—约等≡—恒等3、三角函数:sin—赛因cos—考赛因tan—叹近体cot—考叹近体sec—赛看近体csc —考赛看近体序号大写小写英文注音国际音标注音中文注音1 Α α alpha a:lf 阿尔法2 Β β beta bet 贝塔3 Γ γ gamma ga:m 伽马4 Δ δ delta delt 德尔塔5 Ε ε epsilon ep`silon 伊普西龙6 Ζ ζ zeta zat 截塔7 Η η eta eit 艾塔8 Θ θ thet θit 西塔9 Ι ι iot aiot 约塔10 Κ κ k appa kap 卡帕11 Λ λ lambda lambd 兰布达12 Μ μ mu mju 缪13 Ν ν nu nju 纽14 Ξ ξ xi ksi 克西15 Ο ο omicron omik`ron 奥密克戎16 Π π pi pai 派17 Ρ ρ rho rou 肉18 Σ σ sigma `sigma 西格马19 Τ τ tau tau 套20 Υ υ upsilon jup`silon 宇普西龙21 Φ φ phi fai 佛爱22 Χ χ c hi phai 西23 Ψ ψ psi psai 普西24 Ω ω omega o`miga 欧米伽希腊字母的正确读法是什么?1 Α α alpha a:lf 阿尔法2 Β β beta bet 贝塔3 Γ γ gamma ga:m 伽马4 Δ δ delta delt 德尔塔5 Ε ε epsilon ep`silon 伊普西龙6 Ζ ζ zeta zat 截塔7 Η η eta eit 艾塔8 Θ θ thet θit 西塔9 Ι ι iot aiot 约塔10 Κ κ kappa kap 卡帕11 ∧λ lambda lambd 兰布达12 Μ μ mu mju 缪13 Ν ν nu nju 纽磁阻系数14 Ξ ξ xi ksi 克西15 Ο ο omicron omik`ron 奥密克戎16 ∏ π pi pai 派17 Ρ ρ rho rou 肉18 ∑ σ sigma `sigma 西格马19 Τ τ tau tau 套20 Υ υ upsilon jup`silon 宇普西龙21 Φ φ phi f ai 佛爱22 Χ χ chi phai 西23 Ψ ψ psi psai 普西角速;24 Ω ω omega o`miga 欧米伽希腊字母读法Αα:阿尔法AlphaΒβ:贝塔BetaΓγ:伽玛GammaΔδ:德尔塔DelteΕε:艾普西龙Epsilonζ :捷塔ZetaΖη:依塔EtaΘθ:西塔ThetaΙι:艾欧塔IotaΚκ:喀帕Kappa∧λ:拉姆达LambdaΜμ:缪MuΝν:拗NuΞξ:克西XiΟο:欧麦克轮Omicron∏π:派PiΡρ:柔Rho∑σ:西格玛SigmaΤτ:套TauΥυ:宇普西龙UpsilonΦφ:fai PhiΧχ:器ChiΨψ:普赛PsiΩω:欧米伽Omega数学符号大全2008年01月29日星期二 15:25因为自然科学的讨论经常要用到数学,但用文本方式只能表达L!t d5w x r ^ |$s Y 左右结构的数学公式,上下结构、根式、指数等都很难表达。
常用数学符号读法大全数学中有很多运算用希腊字母来表示,这些字母通用性很强,往往用来表示分类标示、数学运算符,物理或化学中也经常应用。
但有些比较复杂,好多同学不会读,下面就是小编给大家带来的数学符号读法,希望能帮助到大家!下面就将常用列表如下:大写小写英文注音国际音标注音中文注音Αα alpha alfa 阿耳法Ββ beta beta 贝塔Γγ gamma gamma 伽马Δδ deta delta 德耳塔Εε epsilon epsilon 艾普西隆Ζζ zeta zeta 截塔Ηη eta eta 艾塔Θθ theta θita西塔Ιι iota iota 约塔Κκ kappa kappa 卡帕∧λ lambda lambda 兰姆达Μμ mu miu 缪Νν nu niu 纽Ξξ xi ksi 可塞Οο omicron omikron 奥密可戎∏π pi pai 派Ρρ rho rou 柔∑σ sigma sigma 西格马Ττ tau tau 套Υυ upsilon jupsilon 衣普西隆Φφ phi fai 斐Χχ chi khai 喜Ψψ psi psai 普西Ωω omega omiga 欧米伽· 数学符号:(1)数量符号:如:i,2+i,a,x,自然对数底e,圆周率π。
(2)运算符号:如加号(+),减号(-),乘号(×或·),除号(÷或/),两个集合的并集(∪),交集(∩),根号(√),对数(log,lg,ln),比(:),微分(dx),积分(∫)等。
(3)关系符号:如“=”是等号,“≈”是近似符号,“≠”是不等号,“>”是大于符号,“<”是小于符号,“→ ”表示变量变化的趋势,“∽”是相似符号,“≌”是全等号,“∥”是平行符号,“⊥”是垂直符号,“∝”是反比例符号,“∈”是属于符号,“C”或“C 下面加一横”是“包含”符号等。

各种数学符号的英语表达方式
英文标点符号怎么念,小编带大家一起来学习学习。
+ plus 加号;正号
- minus 减号;负号
±plus or minus 正负号
× multiplied by乘号
÷divided by 除号
= equal to 等于号
≠ not equal to不等于号
≡equivalent to 全等于号
≌equal to or approximately equal to 等于或约等于号≈ approximately equal to约等于号
< less than 小于号
> more than 大于号
≮not less than 不小于号
≯not more than 不大于号
≤less than or equal to 小于或等于号
≥more than or equal to 大于或等于号
% percent 百分之…
‰permill 千分之…
∞infinity 无限大号
∝varies as 与…成比例
√square root 平方根
∵since, because 因为
∴hence 所以
∷equals, as proportion 等于,成比例
∠angle 角
⌒semicircle 半圆
⊙circle 圆。

常用数学符号的英文表达English Expression of the Mathematical Symbol in Common Use第一部分英汉微积分词汇Part1 English-Chinese Calculus V ocabulary第一章函数与极限Chapter1 Function and Limit集合set元素element子集subset空集empty set并集union交集intersection差集difference of set基本集basic set补集complement set直积direct product笛卡儿积Cartesian product开区间open interval闭区间closed interval半开区间half open interval有限区间finite interval区间的长度length of an interval无限区间infinite interval领域neighborhood领域的中心centre of a neighborhood领域的半径radius of a neighborhood左领域left neighborhood右领域right neighborhood映射mappingX到Y的映射mapping of X ontoY满射surjection单射injection一一映射one-to-one mapping双射bijection算子operator变化transformation函数function 逆映射inverse mapping复合映射composite mapping自变量independent variable因变量dependent variable定义域domain函数值value of function函数关系function relation值域range自然定义域natural domain单值函数single valued function多值函数multiple valued function单值分支one-valued branch函数图形graph of a function绝对值函数absolute value符号函数sigh function整数部分integral part阶梯曲线step curve当且仅当if and only if(iff)分段函数piecewise function上界upper bound下界lower bound有界boundedness无界unbounded函数的单调性monotonicity of a function 单调增加的increasing单调减少的decreasing单调函数monotone function函数的奇偶性parity(odevity) of a function对称symmetry偶函数even function奇函数odd function函数的周期性periodicity of a function周期period反函数inverse function直接函数direct function复合函数composite function中间变量intermediate variable函数的运算operation of function基本初等函数basic elementary function初等函数elementary function幂函数power function指数函数exponential function对数函数logarithmic function三角函数 trigonometric function反三角函数 inverse trigonometric function 常数函数 constant function 双曲函数 hyperbolic function 双曲正弦 hyperbolic sine 双曲余弦 hyperbolic cosine 双曲正切 hyperbolic tangent反双曲正弦 inverse hyperbolic sine 反双曲余弦 inverse hyperbolic cosine 反双曲正切 inverse hyperbolic tangent 极限 limit数列 sequence of number 收敛 convergence 收敛于 a converge to a 发散 divergent极限的唯一性 uniqueness of limits收敛数列的有界性 boundedness of aconvergent sequence子列 subsequence函数的极限 limits of functions函数()f x 当x 趋于x 0时的极限 limit of functions ()f x as x approaches x 0 左极限 left limit 右极限 right limit单侧极限 one-sided limits水平渐近线 horizontal asymptote 无穷小 infinitesimal 无穷大 infinity铅直渐近线 vertical asymptote 夹逼准则 squeeze rule单调数列 monotonic sequence高阶无穷小 infinitesimal of higher order 低阶无穷小 infinitesimal of lower order 同阶无穷小 infinitesimal of the same order 等阶无穷小 equivalent infinitesimal 函数的连续性 continuity of a function 增量 increment函数()f x 在x 0连续 the function ()f x is continuous at x 0左连续 left continuous 右连续 right continuous区间上的连续函数 continuous function 函数()f x 在该区间上连续 function ()f x is continuous on an interval 不连续点 discontinuity point第一类间断点 discontinuity point of the first kind第二类间断点 discontinuity point of the second kind初等函数的连续性 continuity of the elementary functions定义区间 defined interval最大值 global maximum value (absolute maximum)最小值 global minimum value (absolute minimum)零点定理 the zero point theorem 介值定理 intermediate value theorem第二章 导数与微分Chapter2 Derivative and Differential 速度 velocity匀速运动 uniform motion 平均速度 average velocity瞬时速度 instantaneous velocity 圆的切线 tangent line of a circle 切线 tangent line切线的斜率 slope of the tangent line 位置函数 position function 导数 derivative 可导 derivable函数的变化率问题 problem of the change rate of a function导函数 derived function 左导数 left-hand derivative 右导数 right-hand derivative 单侧导数 one-sided derivatives()f x 在闭区间【a,b 】上可导 ()f x isderivable on the closed interval [a,b] 切线方程 tangent equation 角速度 angular velocity 成本函数 cost function 边际成本 marginal cost 链式法则 chain rule隐函数implicit function显函数explicit function二阶函数second derivative三阶导数third derivative高阶导数nth derivative莱布尼茨公式Leibniz formula对数求导法log- derivative参数方程parametric equation相关变化率correlative change rata微分differential可微的differentiable函数的微分differential of function自变量的微分differential of independent variable微商differential quotient间接测量误差indirect measurement error 绝对误差absolute error相对误差relative error第三章微分中值定理与导数的应用Chapter3 MeanValue Theorem of Differentials and the Application of Derivatives罗马定理Rolle’s theorem费马引理Fermat’s lemma拉格朗日中值定理Lagrange’s mean value theorem驻点stationary point稳定点stable point临界点critical point辅助函数auxiliary function拉格朗日中值公式Lagrange’s mean value formula柯西中值定理Cauchy’s mean value theorem洛必达法则L’Hospital’s Rule0/0型不定式indeterminate form of type 0/0不定式indeterminate form泰勒中值定理Taylor’s mean value theorem泰勒公式Taylor formula余项remainder term拉格朗日余项Lagrange remainder term 麦克劳林公式Maclaurin’s formula佩亚诺公式Peano remainder term 凹凸性concavity凹向上的concave upward, cancave up凹向下的,向上凸的concave downward’concave down拐点inflection point函数的极值extremum of function极大值local(relative) maximum最大值global(absolute) mximum极小值local(relative) minimum最小值global(absolute) minimum目标函数objective function曲率curvature弧微分arc differential平均曲率average curvature曲率园circle of curvature曲率中心center of curvature曲率半径radius of curvature渐屈线evolute渐伸线involute根的隔离isolation of root隔离区间isolation interval切线法tangent line method第四章不定积分Chapter4 Indefinite Integrals原函数primitive function(antiderivative) 积分号sign of integration被积函数integrand积分变量integral variable积分曲线integral curve积分表table of integrals换元积分法integration by substitution分部积分法integration by parts分部积分公式formula of integration by parts有理函数rational function真分式proper fraction假分式improper fraction第五章定积分Chapter5 Definite Integrals曲边梯形trapezoid with曲边curve edge窄矩形narrow rectangle曲边梯形的面积area of trapezoid with curved edge积分下限lower limit of integral积分上限upper limit of integral积分区间integral interval分割partition积分和integral sum可积integrable矩形法rectangle method积分中值定理mean value theorem of integrals函数在区间上的平均值average value of a function on an integvals牛顿-莱布尼茨公式Newton-Leibniz formula微积分基本公式fundamental formula of calculus换元公式formula for integration by substitution递推公式recurrence formula反常积分improper integral反常积分发散the improper integral is divergent反常积分收敛the improper integral is convergent无穷限的反常积分improper integral on an infinite interval无界函数的反常积分improper integral of unbounded functions绝对收敛absolutely convergent第六章定积分的应用Chapter6 Applications of the Definite Integrals元素法the element method面积元素element of area平面图形的面积area of a luane figure直角坐标又称“笛卡儿坐标(Cartesian coordinates)”极坐标polar coordinates抛物线parabola椭圆ellipse旋转体的面积volume of a solid of rotation旋转椭球体ellipsoid of revolution, ellipsoid of rotation曲线的弧长arc length of acurve 可求长的rectifiable光滑smooth功work水压力water pressure引力gravitation变力variable force第七章空间解析几何与向量代数Chapter7 Space Analytic Geometry and Vector Algebra向量vector自由向量free vector单位向量unit vector零向量zero vector相等equal平行parallel向量的线性运算linear poeration of vector 三角法则triangle rule平行四边形法则parallelogram rule交换律commutative law结合律associative law负向量negative vector差difference分配律distributive law空间直角坐标系space rectangular coordinates坐标面coordinate plane卦限octant向量的模modulus of vector向量a与b的夹角angle between vector a and b方向余弦direction cosine方向角direction angle向量在轴上的投影projection of a vector onto an axis数量积,外积,叉积scalar product,dot product,inner product曲面方程equation for a surface球面sphere旋转曲面surface of revolution母线generating line轴axis圆锥面cone顶点vertex旋转单叶双曲面revolution hyperboloidsof one sheet旋转双叶双曲面revolution hyperboloids of two sheets柱面cylindrical surface ,cylinder圆柱面cylindrical surface准线directrix抛物柱面parabolic cylinder二次曲面quadric surface椭圆锥面dlliptic cone椭球面ellipsoid单叶双曲面hyperboloid of one sheet双叶双曲面hyperboloid of two sheets旋转椭球面ellipsoid of revolution椭圆抛物面elliptic paraboloid旋转抛物面paraboloid of revolution双曲抛物面hyperbolic paraboloid马鞍面saddle surface椭圆柱面elliptic cylinder双曲柱面hyperbolic cylinder抛物柱面parabolic cylinder空间曲线space curve空间曲线的一般方程general form equations of a space curve空间曲线的参数方程parametric equations of a space curve螺转线spiral螺矩pitch投影柱面projecting cylinder投影projection平面的点法式方程pointnorm form eqyation of a plane法向量normal vector平面的一般方程general form equation of a plane两平面的夹角angle between two planes 点到平面的距离distance from a point to a plane空间直线的一般方程general equation of a line in space方向向量direction vector直线的点向式方程pointdirection form equations of a line方向数direction number直线的参数方程parametric equations of a line两直线的夹角angle between two lines垂直perpendicular直线与平面的夹角angle between a line and a planes平面束pencil of planes平面束的方程equation of a pencil of planes行列式determinant系数行列式coefficient determinant第八章多元函数微分法及其应用Chapter8 Differentiation of Functions of Several Variables and Its Application一元函数function of one variable多元函数function of several variables内点interior point外点exterior point边界点frontier point,boundary point聚点point of accumulation开集openset闭集closed set连通集connected set开区域open region闭区域closed region有界集bounded set无界集unbounded setn维空间n-dimentional space二重极限double limit多元函数的连续性continuity of function of seveal连续函数continuous function不连续点discontinuity point一致连续uniformly continuous偏导数partial derivative对自变量x的偏导数partial derivative with respect to independent variable x高阶偏导数partial derivative of higher order二阶偏导数second order partial derivative 混合偏导数hybrid partial derivative全微分total differential偏增量oartial increment偏微分partial differential全增量total increment可微分differentiable必要条件necessary condition充分条件sufficient condition叠加原理superpostition principle全导数total derivative中间变量intermediate variable隐函数存在定理theorem of the existence of implicit function曲线的切向量tangent vector of a curve法平面normal plane向量方程vector equation向量值函数vector-valued function切平面tangent plane法线normal line方向导数directional derivative梯度gradient数量场scalar field梯度场gradient field向量场vector field势场potential field引力场gravitational field引力势gravitational potential曲面在一点的切平面tangent plane to a surface at a point曲线在一点的法线normal line to a surface at a point无条件极值unconditional extreme values 条件极值conditional extreme values拉格朗日乘数法Lagrange multiplier method拉格朗日乘子Lagrange multiplier经验公式empirical formula最小二乘法method of least squares均方误差mean square error第九章重积分Chapter9 Multiple Integrals二重积分double integral可加性additivity累次积分iterated integral体积元素volume element三重积分triple integral直角坐标系中的体积元素volume element in rectangular coordinate system 柱面坐标cylindrical coordinates柱面坐标系中的体积元素volume element in cylindrical coordinate system球面坐标spherical coordinates球面坐标系中的体积元素volume element in spherical coordinate system反常二重积分improper double integral曲面的面积area of a surface质心centre of mass静矩static moment密度density形心centroid转动惯量moment of inertia参变量parametric variable第十章曲线积分与曲面积分Chapter10 Line(Curve)Integrals and Surface Integrals对弧长的曲线积分line integrals with respect to arc hength第一类曲线积分line integrals of the first type对坐标的曲线积分line integrals with respect to x,y,and z第二类曲线积分line integrals of the second type有向曲线弧directed arc单连通区域simple connected region复连通区域complex connected region格林公式Green formula第一类曲面积分surface integrals of the first type对面的曲面积分surface integrals with respect to area有向曲面directed surface对坐标的曲面积分surface integrals with respect to coordinate elements第二类曲面积分surface integrals of the second type有向曲面元element of directed surface高斯公式gauss formula拉普拉斯算子Laplace operator格林第一公式Green’s first formula通量flux散度divergence斯托克斯公式Stokes formula环流量circulation旋度rotation,curl第十一章无穷级数Chapter11 Infinite Series一般项general term部分和partial sum余项remainder term等比级数geometric series几何级数geometric series公比common ratio调和级数harmonic series柯西收敛准则Cauchy convergence criteria, Cauchy criteria for convergence正项级数series of positive terms达朗贝尔判别法D’Alembert test柯西判别法Cauchy test交错级数alternating series绝对收敛absolutely convergent条件收敛conditionally convergent柯西乘积Cauchy product函数项级数series of functions发散点point of divergence收敛点point of convergence收敛域convergence domain和函数sum function幂级数power series幂级数的系数coeffcients of power series 阿贝尔定理Abel Theorem收敛半径radius of convergence收敛区间interval of convergence泰勒级数Taylor series麦克劳林级数Maclaurin series二项展开式binomial expansion近似计算approximate calculation舍入误差round-off error,rounding error欧拉公式Euler’s formula魏尔斯特拉丝判别法Weierstrass test三角级数trigonometric series振幅amplitude角频率angular frequency初相initial phase矩形波square wave谐波分析harmonic analysis 直流分量direct component基波fundamental wave二次谐波second harmonic三角函数系trigonometric function system 傅立叶系数Fourier coefficient傅立叶级数Forrier series周期延拓periodic prolongation正弦级数sine series余弦级数cosine series奇延拓odd prolongation偶延拓even prolongation傅立叶级数的复数形式complex form of Fourier series第十二章微分方程Chapter12 Differential Equation解微分方程solve a dirrerential equation 常微分方程ordinary differential equation 偏微分方程partial differential equation,PDE微分方程的阶order of a differential equation微分方程的解solution of a differential equation微分方程的通解general solution of a differential equation初始条件initial condition微分方程的特解particular solution of a differential equation初值问题initial value problem微分方程的积分曲线integral curve of a differential equation可分离变量的微分方程variable separable differential equation隐式解implicit solution隐式通解inplicit general solution衰变系数decay coefficient衰变decay齐次方程homogeneous equation一阶线性方程linear differential equation of first order非齐次non-homogeneous齐次线性方程homogeneous linear equation非齐次线性方程non-homogeneous linearequation常数变易法method of variation of constant暂态电流transient stata current稳态电流steady state current伯努利方程Bernoulli equation全微分方程total differential equation积分因子integrating factor高阶微分方程differential equation of higher order悬链线catenary高阶线性微分方程linera differential equation of higher order自由振动的微分方程differential equation of free vibration强迫振动的微分方程differential equation of forced oscillation串联电路的振荡方程oscillation equation of series circuit二阶线性微分方程second order linera differential equation线性相关linearly dependence线性无关linearly independce二阶常系数齐次线性微分方程second order homogeneour linear differential equation with constant coefficient二阶变系数齐次线性微分方程second order homogeneous linear differential equation with variable coefficient特征方程characteristic equation无阻尼自由振动的微分方程differential equation of free vibration with zero damping 固有频率natural frequency简谐振动simple harmonic oscillation,simple harmonic vibration微分算子differential operator待定系数法method of undetermined coefficient共振现象resonance phenomenon欧拉方程Euler equation幂级数解法power series solution数值解法numerial solution勒让德方程Legendre equation微分方程组system of differential equations常系数线性微分方程组system of linera differential equations with constant c。
×times sign multiplication 2 × 3 = 6 ·multiplication dot multiplication 2 · 3 = 6÷division sign /division 6 ÷ 2 = 3obelus/ division slash division 6 / 2 = 3–horizontal line division / fractionmod modulo remainder calculation 7 mod 2 = 1. period decimal point, decimal2.56 = 2+56/100separatora b power exponent 23= 8a^b caret exponent 2 ^ 3= 8√a square root √a ·√a = a√9 = ±33√a cube root 3√a ·3√a ·3√a = a3√8 = 24√a fourth root 4√a ·4√a ·4√a ·4√a = a4√16 = ±2n√a n-th root (radical) for n=3, n√8 = 2% percent1% = 1/100 10% × 30 = 3‰per-mille1‰ = 1/1000 = 0.1%ppm per-million1ppm = 1/1000000ppb per-billion 1ppb = 1/1000000000 10ppb × 30 = 3×10-7ppt per-trillion 1ppt = 10-1210ppt × 30 = 3×10-10Geometry symbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example ∠angle formed by two rays ∠ABC = 30°measuredABC = 30°anglespherical angle AOB = 30°∟right angle = 90°α = 90°°degree 1 turn = 360°α = 60°deg degree 1 turn = 360deg α = 60deg′prime arcminute, 1° = 60′α = 60°59′″double prime arcsecond, 1′ = 60″α = 60°59′59″line infinite lineAB line segment line from point A to point Bray line that start from point Aarc arc from point A to point B= 60°⊥perpendicular perpendicular lines (90° angle) AC ⊥ BC| | parallel parallel lines AB | | CD≅congruent to equivalence of geometric shapes and size ∆ABC≅∆XYZ ~ similarity same shapes, not same size ∆ABC~ ∆XYZ Δtriangle triangle shape ΔABC≅ΔBCD |x-y| distance distance between points x and y | x-y | = 5πpi constant π = 3.141592654...is the ratio between the circumference and diameter of acirclec = π·d = 2·π·rrad radians radians angle unit 360° = 2π rad c radians radians angle unit 360° = 2πcgrad gradians / gons grads angle unit 360° = 400 gradg gradians / gons grads angle unit 360° = 400 g Algebra symbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning /definitionExample[a,b] closed interval [a,b] ={x | a≤x≤b}x∈[2,6]∆delta change /difference∆t = t1 - t0∆discriminant Δ =b2 - 4ac∑sigma summation -sum of allvalues in rangeof series∑ x i= x1+x2+...+x n∑∑sigma doublesummation∏capital pi product -product of allvalues in rangeof series∏ x i=x1∙x2∙...∙x ne e constant / Euler's number e =2.718281828...e = lim (1+1/x)x , x→∞γEuler-Mascheroni constantγ =0.527721566...φgolden ratio golden ratioconstantπpi constant π =3.141592654...is the ratiobetween thecircumference anddiameter of acirclec = π·d = 2·π·rLinear Algebra SymbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example ·dot scalar product a · b×cross vector product a × bA⊗B tensor product tensor product of A and B A⊗B inner product[ ] brackets matrix of numbers( ) parentheses matrix of numbers| A | determinant determinant of matrix Adet(A) determinant determinant of matrix A|| x || double vertical bars normA T transpose matrix transpose (A T)ij = (A)jiA†Hermitian matrix matrix conjugate transpose (A†)ij = (A)ji A*Hermitian matrix matrix conjugate transpose (A*)ij = (A)ji A-1inverse matrix A A-1 = Irank(A) matrix rank rank of matrix A rank(A) = 3 dim(U) dimension dimension of matrix A rank(U) = 3 Probability and statistics symbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition ExampleP(A) probabilityfunctionprobability of event A P(AP(A∩B) probability ofeventsintersectionprobability that ofevents A and BP(A∩BP(A∪B) probability ofevents union probability that ofevents A or BP(A∪BP(A | B) conditionalprobabilityfunctionprobability of event Agiven event BoccuredP(A | Bf (x) probabilitydensity function(pdf)P(a ≤ x ≤ b) = ∫f (x) dxF(x) cumulative F(x) = P(X≤ x)distribution function (cdf)μpopulationmean mean of populationvaluesμ = 10E(X) expectationvalue expected value ofrandom variable XE(X) = 10E(X | Y) conditionalexpectation expected value ofrandom variable Xgiven YE(X | Y=2) = 5var(X) variance variance of randomvariable Xvar(X) = 4σ2variance variance ofpopulation valuesσ2 = 4std(X) standarddeviation standard deviation ofrandom variable Xstd(X) = 2σX standarddeviation standard deviationvalue of randomvariable XσX=2median middle value of random variable xcov(X,Y) covariance covariance ofrandom variables Xand Ycov(X,Y) = 4corr(X,Y) correlation correlation ofrandom variables Xand Ycorr(X,YρX,Y correlation correlation ofrandom variables Xand YρX,Y∑summation summation - sum of all values in range of series∑∑doublesummationdouble summationBin (n,p) binomialdistributionf (k) = n C k p k(1-p)n-kPoisson(λ)Poissondistributionf (k)= λk e-λ / k!Geom(p) geometricdistributionf (k) = p(1-p) kHG(N,K,n) hyper-geometric distributionBern(p) Bernoulli distributionCombinatorics SymbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Examplen! factorial n! = 1·2·3·...·n5! = 1·2·3·4·5 = 120 n P k permutation 5P3 = 5! / (5-3)! = 60 n C kcombination 5C3 = 5!/[3!(5-3)!]=10Set theory symbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example{ } set a collection of elements A = {3,7,9,14},B = {9,14,28}A ∩B intersection objects that belong to set A and setBA ∩B = {9,14}A ∪B union objects that belong to set A or setBA ∪B ={3,7,9,14,28}A ⊆B subset subset has fewer elements orequal to the set{9,14,28} ⊆{9,14,28}A ⊂B proper subset / strict subset has fewer elements than {9,14} ⊂subset the set {9,14,28}A ⊄B not subset left set not a subset of right set {9,66} ⊄{9,14,28}A ⊇B superset set A has more elements or equalto the set B{9,14,28} ⊇{9,14,28}A ⊃B proper superset / strictsupersetset A has more elements than setB{9,14,28} ⊃{9,14}A ⊅B not superset set A is not a superset of set B {9,14,28} ⊅{9,66}2A power set all subsets of A power set all subsets of AA =B equality both sets have the same members A={3,9,14}, B={3,9,14}, A=BA c complement all the objects that do not belong to set AA \B relative complement objects that belong to A and not toBA = {3,9,14},B = {1,2,3},A-B = {9,14}A -B relative complement objects that belong to A and not toBA = {3,9,14},B = {1,2,3},A-B = {9,14}A ∆B symmetric difference objects that belong to A or B butnot to their intersectionA = {3,9,14},B = {1,2,3},A ∆B ={1,2,9,14}A ⊖B symmetric difference objects that belong to A or B butnot to their intersectionA = {3,9,14},B = {1,2,3},A ⊖B ={1,2,9,14}a∈A element of set membership A={3,9,14}, 3 ∈Ax∉A not element of no set membership A={3,9,14}, 1 ∉A(a,b) ordered pair collection of 2 elementsA×B cartesian product set of all ordered pairs from A andB|A| cardinality the number of elements of set A A={3,9,14},|A|=3#A cardinality the number of elements of set A A={3,9,14},#A=3aleph-null infinite cardinality of natural numbers setaleph-one cardinality of countable ordinal numbers setØ empty set Ø = { } C = {Ø} universal set set of all possible values0natural numbers / wholenumbers set (with zero) 0= {0,1,2,3,4,...} 0 ∈01natural numbers / wholenumbers set (withoutzero)1= {1,2,3,4,5,...} 6 ∈1 integer numbers set = {...-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,...} -6 ∈rational numbers set = {x | x=a/b, a,b∈} 2/6 ∈real numbers set = {x | -∞ < x <∞}∈complex numbers set= {z | z=a+bi,-∞<a<∞,-∞<b<∞}6+2i∈Logic symbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example ·and and x·y^ caret / circumflex and x ^ y& ampersand and x & y+ plus or x + y∨reversed caret or x∨y | vertical line or x | yx' single quote not - negation x'x bar not - negation x¬not not - negation ¬x! exclamation mark not - negation ! x⊕circled plus / oplus exclusive or - xor x⊕y ~ tilde negation ~ x⇒implies⇔equivalent if and only if (iff)↔equivalent if and only if (iff)∀for all∃there exists∄there does not exists∴therefore∵because / sinceCalculus & analysis symbolsSymbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example limit limit value of a functionεepsilon represents a very small number,ε→0near zeroe e constant / Euler'snumber e = 2.718281828...e = lim(1+1/x)x ,x→∞y ' derivative derivative - Lagrange's notation (3x3)' = 9x2y '' second derivative derivative of derivative (3x3)'' = 18xy(n)nth derivative n times derivation (3x3)(3) = 18 derivative derivative - Leibniz's notation d(3x3)/dx = 9x2second derivative derivative of derivative d2(3x3)/dx2 = 18xnth derivative n times derivationtime derivative derivative by time - Newton's notationtime secondderivativederivative of derivativeD x y derivative derivative - Euler's notationD x2y second derivative derivative of derivativepartial derivative ∂(x2+y2)/∂x = 2x ∫integral opposite to derivation ∫f(x)dx∫∫double integral integration of function of 2variables∫∫f(x,y)dxdy∫∫∫triple integral integration of function of 3variables∫∫∫f(x,y,z)dxdydz∮closed contour / lineintegral∯closed surfaceintegral∰closed volumeintegral[a,b] closed interval [a,b] = {x | a ≤ x ≤ b}(a,b) open interval (a,b) = {x | a < x < b}i imaginary unit i≡ √-1 z = 3 + 2i z* complex conjugate z = a+bi→z*=a-bi z* = 3 - 2i z complex conjugate z = a+bi→z = a-bi z = 3 - 2i ∇nabla / del gradient / divergence operator ∇f (x,y,z) vectorunit vectorx * y convolution y(t) = x(t) * h(t)Laplace transform F(s) = {f (t)}Fourier transform X(ω) = {f (t)}δdelta function∞lemniscate infinity symbol。
常⽤数学符号⼤全数学符号及读法⼤全常⽤数学输⼊符号:≈≡≠=≤≥<>±+-× ÷/∫?ⅴ∞ⅸⅹ∑∏?∩ⅰ??//?‖ⅶ√()【】{}ⅠⅡ??ⅷαβγδεδεζΓ⼤写⼩写英⽂注⾳国际⾳标注⾳中⽂注⾳Ααalpha alfa 阿⽿法Ββbeta beta 贝塔Γγgamma gamma 伽马Γδdeta delta 德⽿塔Δεepsilon epsilon 艾普西隆Εδzeta zeta 截塔Ζεeta eta 艾塔Θζtheta ζita 西塔Ηηiota iota 约塔Κθkappa kappa 卡帕ⅸιlambda lambda 兰姆达Μκmu miu 缪Νλnu niu 纽Ξµxi ksi 可塞Ονomicron omikron 奥密可戎ⅱπpi pai 派Ρξrho rou 柔ⅲζsigma sigma 西格马Σηtau tau 套Τυupsilon jupsilon ⾐普西隆Φθphi fai 斐Υχchi khai 喜Φψpsi psai 普西Χωomega omiga 欧⽶i -1的平⽅根f(x) 函数f在⾃变量x处的值sin(x) 在⾃变量x处的正弦函数值exp(x) 在⾃变量x处的指数函数值,常被写作e x a^x a的x次⽅;有理数x由反函数定义ln x exp x 的反函数a x同 a^xb a 以b为底a的对数; b logba = acos x 在⾃变量x处余弦函数的值tan x 其值等于 sin x/cos xcot x 余切函数的值或 cos x/sin xsec x 正割含数的值,其值等于 1/cos xcsc x 余割函数的值,其值等于 1/sin xasin x y,正弦函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = sin y acos x y,余弦函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = cos y atan x y,正切函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = tan y acot x y,余切函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = cot y asec x y,正割函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = sec y acsc x y,余割函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = csc yζ⾓度的⼀个标准符号,不注明均指弧度,尤其⽤于表⽰atan x/y,当x、y、z⽤于表⽰空间中的点时i, j, k 分别表⽰x、y、z⽅向上的单位向量(a, b, c) 以a、b、c为元素的向量(a, b) 以a、b为元素的向量(a, b) a、b向量的点积a?b a、b向量的点积(a?b) a、b向量的点积|v| 向量v的模|x| 数x的绝对值表⽰求和,通常是某项指数。
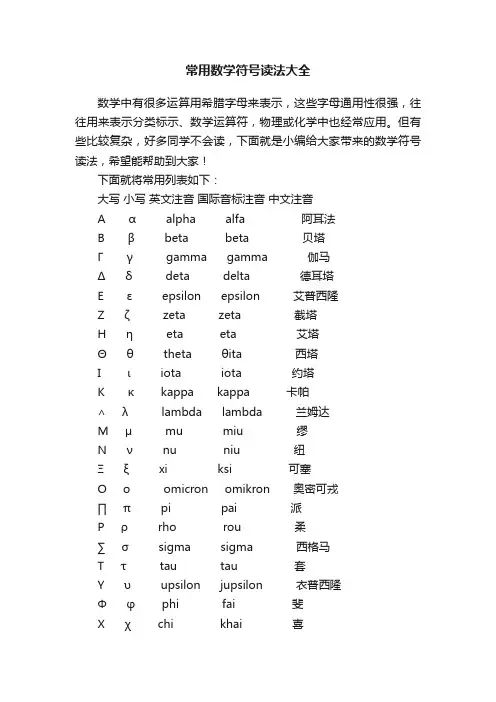
常⽤数学符号读法⼤全 数学中有很多运算⽤希腊字母来表⽰,这些字母通⽤性很强,往往⽤来表⽰分类标⽰、数学运算符,物理或化学中也经常应⽤。
但有些⽐较复杂,好多同学不会读,下⾯就是⼩编给⼤家带来的数学符号读法,希望能帮助到⼤家!下⾯就将常⽤列表如下: ⼤写⼩写英⽂注⾳国际⾳标注⾳中⽂注⾳ Αα alpha alfa 阿⽿法 Ββ beta beta 贝塔 Γγ gamma gamma 伽马 Δ δ deta delta 德⽿塔 Εε epsilon epsilon 艾普西隆 Ζζ zeta zeta 截塔 Ηη eta eta 艾塔 Θθ theta θita 西塔 Ιι iota iota 约塔 Κκ kappa kappa 卡帕 ∧λ lambda lambda 兰姆达 Μ µ mu miu 缪 Νν nu niu 纽 Ξξ xi ksi 可塞 Οο omicron omikron 奥密可戎 ∏π pi pai 派 Ρρ rho rou 柔 ∑ σ sigma sigma 西格马 Ττ tau tau 套 Υυ upsilon jupsilon ⾐普西隆 Φφ phi fai 斐 Χχ chi khai 喜 Ψψ psi psai 普西 Ωω omega omiga 欧⽶伽 · 数学符号: (1)数量符号:如:i,2+i,a,x,⾃然对数底e,圆周率π。
(2)运算符号:如加号(+),减号(-),乘号(×或·),除号(÷或/),两个集合的并集(∪),交集(∩),根号(√),对数(log,lg,ln),⽐(:),微分(dx),积分(∫)等。
(3)关系符号:如“=”是等号,“≈”是近似符号,“≠”是不等号,“>”是⼤于符号,“<”是⼩于符号,“→”表⽰变量变化的趋势,“∽”是相似符号,“≌”是全等号,“∥”是平⾏符号,“⊥”是垂直符号,“∝”是反⽐例符号,“∈”是属于符号,“C”或“C下⾯加⼀横”是“包含”符号等。
几何符号∻‖ⅶ∼∺∵∳△2 代数符号ⅴ∧∨~∫∴∶∷∲ⅵ∯3运算符号×÷ⅳ±4集合符号∪∩ⅰ5特殊符号ⅲπ(圆周率)6推理符号|a| ∻∱△ⅶ∩∪∴∵±∷∶ⅰⅬⅭⅮⅯ↖↗↘↙‖∧∨&; §∽∾∿≀≁≂≃≄≅≆ΓΔΘ∧ΞΟⅱⅲΦΧΨΩα β γ δ ε δ ε ζ η θ ι κ λμ ν π ξ ζ η υ θ χ ψ ωⅠⅡⅢⅣⅤⅥⅦⅧⅨⅩⅪⅫⅰⅱⅲⅳⅴⅵⅶⅷⅸⅹⅰⅱⅲ↚ⅳⅴⅵ↛ⅶ↜‖∧∨∩∪∫∬∭∮∯∰∱∲∳∲∴∵∶∷∶∷∸∹⊕∺∻⊿∼℃上述符号所表示的意义和读法(中英文参照)+plus 加号;正号-minus 减号;负号±plus or minus 正负号×is multiplied by 乘号÷is divided by 除号=is equal to 等于号∴is not equal to 不等于号∵is equivalent to 全等于号∳is approximately equal to 约等于∲is approximately equal to 约等于号<is less than 小于号>is more than 大于号∶is less than or equal to 小于或等于∷is more than or equal to 大于或等于%per cent 百分之…ⅵinfinity 无限大号ⅳ(square) root 平方根X squared X的平方X cubed X的立方∮since; because 因为∭hence 所以ⅶangle 角∼semicircle 半圆∺circle 圆○circumference 圆周△triangle 三角形∻perpendicular to 垂直于∪intersection of 并,合集∩union of 交,通集∫the integral of …的积分ⅲ(sigma) summation of 总和°degree 度′minute 分〃second 秒#number …号。
数学符号及读法大全常用数学输入符号:≈≡≠=≤≥<>≮≯∷±+-× ÷/∫∮∝∞∧∨∑∏∪∩∈∵∴//⊥‖∠⌒≌∽√()【】{}ⅠⅡ⊕⊙∥αβγδεζηθΔ大写小写英文注音国际音标注音中文注音Ααalpha alfa 阿耳法Ββbeta beta 贝塔Γγgamma gamma 伽马Δδdeta delta 德耳塔Εεepsilon epsilon 艾普西隆Ζζzeta zeta 截塔Ηηeta eta 艾塔Θθtheta θita 西塔Ιιiota iota 约塔Κκkappa kappa 卡帕∧λlambda lambda 兰姆达Μμmu miu 缪Ννnu niu 纽Ξξxi ksi 可塞Οοomicron omikron 奥密可戎∏πpi pai 派Ρρrho rou 柔∑σsigma sigma 西格马Ττtau tau 套Υυupsilon jupsilon 衣普西隆Φφphi fai 斐Χχchi khai 喜Ψψpsi psai 普西Ωωomega omiga 欧米i -1的平方根f(x) 函数f在自变量x处的值sin(x) 在自变量x处的正弦函数值exp(x) 在自变量x处的指数函数值,常被写作e x a^x a的x次方;有理数x由反函数定义ln x exp x 的反函数a x同 a^xlogb a 以b为底a的对数; b logba = acos x 在自变量x处余弦函数的值tan x 其值等于 sin x/cos xcot x 余切函数的值或 cos x/sin xsec x 正割含数的值,其值等于 1/cos xcsc x 余割函数的值,其值等于 1/sin xasin x y,正弦函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = sin y acos x y,余弦函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = cos y atan x y,正切函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = tan y acot x y,余切函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = cot y asec x y,正割函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = sec y acsc x y,余割函数反函数在x处的值,即 x = csc yθ角度的一个标准符号,不注明均指弧度,尤其用于表示atan x/y,当x、y、z用于表示空间中的点时i, j, k 分别表示x、y、z方向上的单位向量(a, b, c) 以a、b、c为元素的向量(a, b) 以a、b为元素的向量(a, b) a、b向量的点积a•b a、b向量的点积(a•b) a、b向量的点积|v| 向量v的模|x| 数x的绝对值Σ表示求和,通常是某项指数。
+ plus 加号;正号
- minus 减号;负号
± plus or minus 正负号
× is multiplied by 乘号
÷ is divided by 除号
=is equal to 等于号
≠ is not equal to 不等于号
≡ is equivalent to 全等于号
≌is equal to or approximately equal to 等于或约等于≈ is approximately equal to 约等于号
<is less than 小于号
>is more than 大于号
≮is not less than 不小于号
≯is not more than 不大于号
≤ is less than or equal to 小于或等于号
≥ is more than or equal to 大于或等于号
% per cent 百分之…
‰ per mill 千分之…
∞ infinity 无限大号
∝varies as 与…成比例
√ (square) root 平方根
∵since; because 因为
∴hence 所以
∷equals, as (proportion) 等于,成比例
∠angle 角
⌒semicircle 半圆
⊙circle 圆
○ circumference 圆周
π pi 圆周率
△ triangle 三角形
⊥perpendicular to 垂直于
∪union of 并,合集
∩ intersection of 交,通集∫ the integral of …的积分
∑ (sigma) summation of 总和
° degree 度
′ minute 分
〃second 秒
℃Celsius system 摄氏度
{ open brace, open curly 左花括号
} close brace, close curly 右花括号
( open parenthesis, open paren 左圆括号
) close parenthesis, close paren 右圆括号
() brakets/ parentheses 括号
[ open bracket 左方括号
] close bracket 右方括号
[] square brackets 方括号
. period, dot 句号,点
| vertical bar, vertical virgule 竖线
& ampersand, and, reference, ref 和,引用
* asterisk, multiply, star, pointer 星号,乘号,星,指针
/ slash, divide, oblique 斜线,斜杠,除号
// slash-slash, comment 双斜线,注释符
# pound 井号
\ backslash, sometimes escape 反斜线转义符,有时表示
转义符或续行符
~ tilde 波浪符
. full stop 句号
, comma 逗号
: colon 冒号
; semicolon 分号
? question mark 问号
! exclamation mark (英式) exclamation point (美式)
' apostrophe 撇号
- hyphen 连字号
-- dash 破折号
... dots/ ellipsis 省略号
" single quotation marks 单引号
"" double quotation marks 双引号
‖ par allel 双线号
& ampersand = and
~swung dash 代字号
§ section; division 分节号
→ arrow 箭号;参见号。