英国文学史及作品选读课件Chapter 1The Anglo-Saxon Period (450-1066)
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:963.00 KB
- 文档页数:3



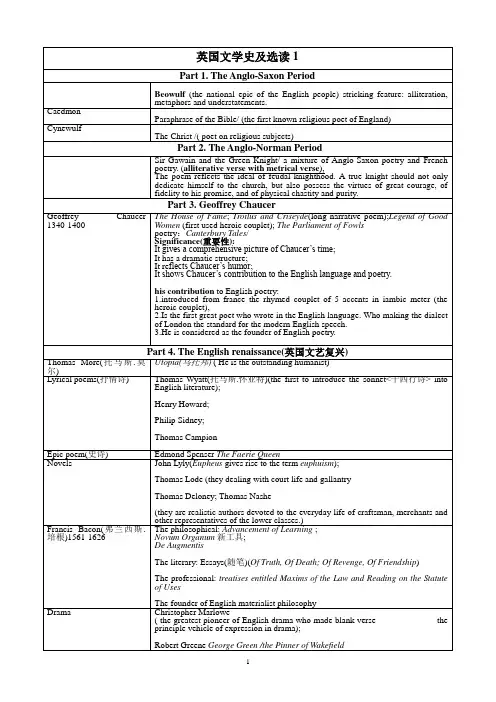
英国文学史及选读1Part 1. The Anglo-Saxon PeriodBeowulf (the national epic of the English people) stricking feature: alliteration, metaphors and understatements. CaedmonParaphrase of the Bible/ (the first known religious poet of England) Cynewulf The Christ /( poet on religious subjects)Part 2. The Anglo-Norman PeriodSir Gawain and the Green Knight/ a mixture of Anglo-Saxon poetry and French poetry. (alliterative verse with metrical verse ), The poem reflects the ideal of feudal knighthood. A true knight should not only dedicate himself to the church, but also possess the virtues of great courage, of fidelity to his promise, and of physical chastity and purity.Part 3. Geoffrey Chaucer Geoffrey Chaucer 1340-1400The House of Fame ; Troilus and Criseyde (long narrative poem);Legend of Good Women (first used heroic couplet); The Parliament of Fowls poetry :Canterbury Tales / Significance(重要性): It gives a comprehensive picture of Chaucer’s time ; It has a dramatic structure; It re flects Chaucer’s humor ; It shows Chaucer’s contribution to the English language and poetry. his contribution to English poetry: 1.introduced from france the rhymed couplet of 5 accents in iambic meter (the heroic couplet), 2.Is the first great poet who wrote in the English language. Who making the dialect of London the standard for the modern English speech. 3.He is considered as the founder of English poetry. Part 4. The English renaissance(英国文艺复兴)Thomas More(托马斯.莫尔) Utopia(乌托邦) ( He is the outstanding humanist) Lyrical poems(抒情诗) Thomas Wyatt(托马斯.怀亚特)(the first to introduce the sonnet<十四行诗> into English literature); Henry Howard; Philip Sidney; Thomas Campion Epic poem(史诗) Edmond Spenser The Faerie Queen Novels John Lyly(Eupheus gives rise to the term euphuism ); Thomas Lode (they dealing with court life and gallantry Thomas Deloney; Thomas Nashe (they are realistic authors devoted to the everyday life of craftsman, merchants and other representatives of the lower classes.) Francis Bacon(弗兰西斯.培根)1561-1626 The philosophical: Advancement of Learning ; Novum Organum 新工具; De Augmentis The literary: Essays(随笔)(Of Truth, Of Death; Of Revenge, Of Friendship ) The professional: treatises entitled Maxims of the Law and Reading on the Statute of Uses The founder of English materialist philosophy Drama Christopher Marlowe ( the greatest pioneer of English drama who made blank verse the principle vehic le of expression in drama); Robert Greene George Green /the Pinner of WakefieldWilliamShakespeare1564-1616 (37plays, two narrative poems, 154sonnets) The Tempest暴风风雨;The Two Gentlemen of Verona维罗纳二绅士;The Mercy Wives of Windsor温莎的风流妇人;Measure for Measure恶有恶报;The Comedy of Errors错中错;Much Ado about Nothing无事自扰;Love’s Labour’s Lost空爱一场;A Midsummer Night’s Dream仲夏夜之梦;The Merchant of Venice威尼斯商人;As You Like It如愿;The Taming of the Shrew驯悍记;All’s Well That Ends Well皆大欢喜;Twelfth Night第十二夜;The Winter’s Tale冬天的故事;The Life and Death of King John/Richard the Second/Henry the Fifth/Richard the Third约翰王/理查二世/亨利五世/理查三世;The First/Second Part of King Henry the Fourth亨利四世(上、下);The First/Second/Third Part of King Henry the Sixth亨利六世(上、中、下); The Life of King Henry the Eighth亨利八世;Troilus and Cressida脱爱勒斯与克莱西达;The Tragedy of Coriolanus考利欧雷诺斯;Titus Andronicus泰特斯·安庄尼克斯;Romeo and Juliet罗密欧与朱丽叶;Timon of Athens雅典的泰门;The Life and Death of Julius Caesar;朱利阿斯·凯撒;The Tragedy of Macbeth麦克白;The Tragedy of Hamlet哈姆雷特/王子复仇记;King Lear李尔王;Othello奥塞罗;Antony and Cleopatra安东尼与克利欧佩特拉;Cymbeline辛白林;Pericles波里克利斯;Venus and Adonis维诺斯·阿都尼斯;Lucrece露克利斯;The Sonnets十四行诗The Great Comedie(伟大的喜剧)s: A Midsummer Night’s Dream; The Merchant of V enice; As You Like It ;Twelfth Night;The Great Tragedies(伟大的悲剧): The Tragedy of Hamlet; Othello; King Lear; The Tragedy of Macbeth;The Later Comedies(romances): Pericles; Cymbeline; The Winter’s Tale; The Tempest;Part 5. The English Bourgeois revolution period and RestorationJohn Milton1608-1674 Shorter poems: L‘Allegro欢乐的人;Il Penseroso沉思的人;Comus科马斯;Lycidas;Principle pamphlets: Areopagitica论出版自由; Eikonoklastes; Defense for theEnglish people;Poem: Paradise Lost (The poem was written in blank verse); Paradise Regained;John Bunyan1628-1688 The Pilgrim’s Progress(It is the greatest English allegory, its style is simple and biblical)John Donne1572-1631 Poetry(love lyrics & religious poems);Sonnets(The founder of the Metaphysical school of poetry)John Dryden Critic, poet and playwright of restoration periodPart 6. The eighteenth CenturyThe Age of Enlightenment or The Age of ReasonEnlightenment Alexander Pope;Joseph Addison&Richard Steele The Spectator;Jonathan Swift;Daniel Defoe;Henry Fielding;Richard B. Sheridan;Oliver Goldsmith;Edward Gibbon;Samuel JohnsonPope exercised the greatest influence on the 18th century poetry;Swift is the most outstanding personality, Gulliver’s TravelsNeoclassicism John Dryden, Alexander Pope, Jonathan Swift, Joseph Addison, Richard Steele, Henry Fielding, Samuel Johnson, Oliver Goldsmith, Edward Gibbon The Decline & Fall of theRoman Empire Neoclassical poetry, as represented by Dryden, Pope & Johnson, reachedits stylistic perfection during the periodModern Realistic Novel Defoe Robinson Crusoe,Richardson,Fielding, Sterne, Goldsmith, T.G..Smollet’s satirical novel The adventures of Roderick RandomFielding and Smollet are the real founders of the genre of the bourgeois realistic novel in England and Europe.Richardson displays the innermost life of an individual, Pamela or Virtue Rewarded, he History of a Young Lady, The History of Sir Chares GrandionGothic Novel The real originator of English Gothic novel was Horace Walpole Castle of Otranto;Mary Shelley Frankenstein;Ann Radcliff The Mysteries of UdolphoSentimentalism Novels: Laurence Stern Sentimental Journey;Tristram Shandy;Oliver Goldsmith The Vicar of WakefieldPoetry: Thomas Gray’s An Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard;Goldsmith’s The Deserted Village;George Crabbe The VillageSatire Pope , Swift, Richard B. Sheridan School for ScandalPre-Romanticism in poetry, which was ushered in by Percy Macpherson & Chatterton, and represented by William Blake&Robert Burns。






British literatureLecture 1About the authors•Social background•Life experience•Point of view (political/ literary)•Poet / novelist / dramatist (playwright) / essayist (prose writer) •Achievement/ contribution•Social status (position)•Representative worksAbout the works•Synopsis (the plots/ stories)•Theme•Characters (heroes/ protagonist/ antagonist)•Social significance/ importance•Artistic features: techniques•figures of speech (修辞)•Simile, metaphor, personification, symbol, irony, paradox, metonymy, synecdoche, overstatement/ understatement , alliteration and so on•Find the definition of the above termsThe period of English Literature•I. Early and Medieval English Literature•II. The English Renaissance (14th-16th century)•III. The Period of Bourgeois Revolution andRestoration (17th C.)•IV. Neoclassical Period--- The Age of Reason andEnlightenment (18th C.)•V. Romantic period( early 19th--- wwII)•VI. Critical Realism ( Victoria Period/ the second halfof the 19th C. )•VII. Modern Period (20 th C.)2. Early and Medieval LiteratureQuestions:1.The literature forms of Anglo-Saxon period?2.what’s the “England national epic”?3. The story of “Beowulf”4. What are the three battles of Beowulf ?5. The definition of “epic”6. The literature forms of Anglo-Norman period?7. What is “romance”?8.The class feature of the RomanceEpic (Heroic Poetry): This term is applied to great and lengthy narrative poems describing some important national enterprise or the adventures of distinguished heroes. (史诗)eg:Homer Odyssey《奥德赛》Dante’s Divine Comedy《十日谈》Milton Paradise Lost《失乐园》Romance: it was a long composition, sometimes in verse, sometimes in prose, describing the life and adventures of a noble hero.Class Feature of the Romance: the theme of loyalty to king and lord was repeatedly emphasized in romances, as loyalty was the corner-stone of feudal morality, without which the whole structure of feudalism would collapse.Sir Gawain and Green Knight 《高文爵士和緑衣骑士》3. ChaucerLife:⏹Born in a middle-classfamily in London⏹Is said to have studied atOxford and Cambridge⏹Became a man of affaires, undertaking various diplomatic missions to the Continent as courtier, diplomat and civil servant⏹Died in 1400,buried in Westminster Abbey, there established the poets’ corner Westminster Abbey (西敏寺)⏹An Abbey of monk on the bank of the Thames. The state church in England.⏹It was destroyed and rebuilt several times.⏹Chaucer w as first buried in the Abbey, then established “Poets’ corner”.⏹It is an honor for a poet or his monument to be buried there.Literary Career:⏹His experience gave him chance to obtain a good knowledge of Latin, French and Italian.⏹Three periods:The first period consists of works translated from French, as “The Romaunt of the Rose”The second consists of works adapted from the Italian, as “Troilus and Criseyde.”(based on Boccacio’s poem Filostrato)The third includes “The Canterbury Tales”, which is purely English.⏹Translator⏹“The father (founder) of English poetry” -- John Dryden⏹“Founder of English realism” -- GorkyThe first short-story teller and first morden poet in E.L.Forerunner of humanismThe City Canterbury⏹Canterbury is a city and metropolitan district in Kent England, and an important Romantown.⏹The capital of the Saxon Kingdom of Kent.The Canterbury Tales 《坎特伯雷故事集》⏹A collection of stories⏹Pilgrim, pilgrimage⏹The Tabard Inn, a tavern in Southwark, near London.⏹A gigantic plan of 124 stories, but only 24 were written.⏹The verse models Boccaccio’s Decameron in formThe Prologue (楔子)⏹A prologue is an introduction or preface, often in verse, to a literary work, esp. a play ⏹The prologue provides a framework for the tales. There is an intimate connection between the tale and the prologue, both complementing each other.The Gneral Prologue (the original version)Whan that Aprill, with his shoures sooteThe droghte of March hath perced to the roote,And bathed every veyne in swich licourOf which vertu engendred is the flour;Whan zephirus eek with his sweete breethInspired hath in every holt and heethThe tendre croppes, and the yonge sonneHath in the Ram his halve cours yronne,And smale foweles maken melodye.Heroic Couplet (Iambic pentameter英雄双韵体⏹A pair of rhymed lines of verse of equal length, in the form of ten syllables and five stresses in each line. It was first used by Chaucer. Its master is Alexander Pope.⏹Alliteration(头韵)An alliterative verse, certain accented words in a line begin the same consonants sound. Alliteration is the opposite of rhyme by which the similar sounds occur at the end of the syllables.Contribution⏹He presents a panoramic picture of English life in the Middle Ages.⏹He brought a realistic tone to English literary creation. All his characters are true to life ⏹He introduced Rhymed stanzas, instead of the old Anglo-Saxon (alliterative verse)⏹He first wrote in the current English form of the time. His poetry is acknowledged as the literary language of the country, which is usually called middle English.The language of Chaucer⏹Middle English --- is closer to Old English, the language of the Anglo-Saxons, and Norman French, the language of William the ConquerorFeatures in Chaucer’s writing⏹Rhymed stanzas of various type⏹Simplicity in characterization⏹Satirical and humorous tone⏹narrativeAbout the prioress⏹Higher orders of the religious group⏹Speaks French-- the aristocratic language⏹Tenderness, pity, gentility⏹Overly concern about her personal appearance ⏹Satiric tone。

英国文学史及选读Chapter1英国文学史及选读Chapter1发布人:圣才学习网发布日期:2010-08-16 17:32 共270人浏览[大] [中] [小]The Anglo-Saxon PeriodI. Fill in the blanks.1.After the fall of the Roman Empire and athe withdrawl of Roman troops from Albion,the aboriginal __ population of the larger part of the island was soon conquerered and almost totally exterminated by the Teutonic tribes of ____,_____ ,and _____ who came from the continent and settled in the island,naming its central part a,or England.2.For nearly ______ years prior to the coming of the English,British had been a Roman province. In _____,the Rome withdrew their legions from Britain to protect herself against swarms of Teutonic invaders.3.The literature of early period falls naturally into teo divisions,and ____.The former represents the poetry which ____the Anglso-Saxons probably brought with them in the form of _____ ,the crude material out of which literature was slowly developed on English soil;the later represents the writings developed under the teaching of ______ .4._____can be justly termed England’s national epic and its hero _____---one of the national heros of the English people.5.The Song of Beowulf reflects events which took place on the ______ approximately at the beginning of the_____century,when the forefathers of the Jutes lived in the southern part of the _____ and maintained close relations with kindred tribes,e.g.with the ______ who lived on the other side of the straits.6.Among the early Anglo-Saxon poets we may mention______ who lived in the latter half of the ______ century and who wrote a poetic Paraphase of the Blible.7.____ is the first known religious poets of England. He is known as the father of English song.8.The didac tic poem “The Christ” was produced by ________.II. Choose the best answer for each blank.9.The most important work of _______ is the Anglo-Saxon Chronicles,which is regarded as the best monument of the old English prose.a. Alfred the Greatb. Caedmonc. Cynewulfd. Venerable Bede2. Who is the monster half-huamn who had mingled thirty warriors in The Song of Beowulf?a. Hrothgat.b. Heorot.c. Grendel.d. Beowulf.3. _____ is the first important religious poet in English Literature.a. Cynewulfb.Caedmonc. Shakepeare.d. Adam Bede4. The epic,The Song of Beowulf,represents the spirit of ______.a. monksb. romanticistsc. sentimentalistd. paganIII. Decide whether the following statements are true or false and write your answers in the brackets.1. ()The author of The Song of Beowulf is Cynewulf.2. ()The setting of The Song of Beowulf is in Scotland.3. ()Alfred the Great compiles The Anglo-Saxon Chronicles.4. ()Venerable Bede wrote The Ecclesiastical History of the English People.5. ()The author of Paraphase is Caedmon.IV. Define the liretary terms listed below.Alliteration Epic.V. Answer the following questions.1.What do you know about the Teutors.2.Please give a brief description of The Song of Boewulf.英国文学史及选读Chapter2发布人:圣才学习网发布日期:2010-08-16 17:31 共93人浏览[大] [中] [小]The Anglo-Norman PeriodI. Fill in the following blanks.1.In the year___,at the battle of ___,the ____ headed by William,Duke of Normandy,defeated the Anglo-Saxons.2.The literature which Normans brought to England is remarkable for its bright,____ tales of _______ and _______,in marked contrast with the ___ and ______ of Anglo-Saxon poetry.3.English literature is also a combination of ____and _____ elements.4.In the 14th century,the two most important writers are ___ and Chaucer.5.In the 15th century,there is only one important prose writer whose name is _____. He wrote an important work called Morte d’ Arthur.II. Define the leterature terms listed below.1.Canto2.legend3.Arthurian Legend.III. Read the excerpt of Sir Gawain and the Green Knight carefully,and then make a brief comment on it.IV. Answer the following questions.1.What is the consequence of the Norman Conquest?2.Make a brief survey of the middle English literature.英国文学史及选读Chapter3发布人:圣才学习网发布日期:2010-08-16 17:31 共68人浏览[大] [中] [小]Geoffrey ChaucerI. Fill in the following blanks.1.Chaucer’s masterpiece is _____,one of the most famous works in all literature.2.Chaucer created in The Canterbury Tales a strikingly brilliant and picturesque panorama of _______.3.There are various kinds of ballads _______,______,______,_____,and ______.4.Bishop ____ was among the first to take a literary interest in ballads.5.The name of the “jolly innkeeper” in The CanterburyTales is ______,who proposes that each pilgrim of the ____ should tell two tales on the way to Canterbury and two more on the way back.6.In contradistinction to the ______ verse of Anglo-Saxon poetry,Chaucer chose the metrical form which laid the foundation of the English _____ verse.II. Choose the best answer.1.Who is the “father of English poetry” and one of the greatest narrative poets of England?a. Christopher Marlowb. Geoffrey Chaucerc. W. Shakespeared. Alfred the Great2. Chaucer’s earlist work of any length is his “______” a transl ation of the French “Roman de la Rose” by Gaillaume de Lorris and Jean de Meung,which was a love allegory enjoying widespread popularity in the 13th and 14th centuries not only in France but throught Europe.a. Troilus and Criseydeb. A Red,Red Rosec. Romance of the Rosed. Piers the Plowman3. In his literary development,Chaucer was influenced by three literatures,which one is not true?a. French literature.b. Italian literaturec. English literatured. American literatureIII. Decide whether the following statements are true or false and write your answers in the brackets.1. ()The 32 pilgrims,according to Chaucer’s plan,was to exceed that of Baccoccio’s Decameron.2. ()The Prologue is a splendid masterpiece of Romantic portray,the first of its kind in the history of English literature.3. ()The Canterbury Tales is a vivid and brilliant reflection of 15th century in England.4. ()Chaucer’s poetry traces out a path to the literature of English Renaissance.IV. Define the leterary terms listed below.1.Romance.2.Fable.3.BalladV. Anwer the following question.1.What is the social significance of The Canterbury Tales ?英国文学史及选读Chapter4发布人:圣才学习网发布日期:2010-08-16 17:30 共66人浏览[大] [中] [小]The RenaissanceI. Complete each of the following statements with a proper word or phrase according to the textbook.1.Shakespeare’s first priginal play written in about 1590 was _________.2.Hamlet,Othello,King Lear,and _______ are generally regarded as Shakespeare’s four great tragedies.3.The Tragical History of Doct or Faustus is one of _______’s best known sonnets.4.Absolute monarchy in England reached its summit during the reign of ______.5.Bacon’s works may be divided into three classes,the ______,the _______,the _______ works.6.Together with the development of bourgeois relationships and formation of the English national state this period is marked by a flourishing of national culture known as the_________.7.Edmund Spenser was the author of the greatest epic poem of _______.II. Find out the author and his works.⑴The author and their works1. ()Thomas More a. Gorge Green2. ()Enmund Spenser b. Eupheus3. ()John Lyly c.The Fairy Queen4. ()Marlowe d. Utopia5. ()Robert Greene e. The Jew of Malta⑵The characters in the play1. ()Desdemona a. The Merchant of Venice2. ()Cordelia b. As you like it3. ()Juliet c.Hamlet4. ()Ophelia d. King Lear5. ()Portia e. Othello6. ()Rosalind f. Romeo and JulietIII. Define the leterary terms listed below.1.Renaissance2.sonnet3.Spenserian Stanza4.Humanism5.dramatic irony6.tragedy7.allusionIV. Answer the following questions.1.Give a summary about the English literature during the Renaissance period.2.What is the main idea of Hamlet?3.Give a brief introduction to Thomas More’s Utopia.4.Wh en were Shakespeare’s main tragedies written?what did he write about in his tragedies?英国文学史及选读Chapter5发布人:圣才学习网发布日期:2010-08-16 17:29 共40人浏览[大] [中] [小]Chapter Five The Period of Revolution and RestorationI. Complete each of the following statements with a proper word or phrase according to th etextbook.1.The 17th century was a period when ______ impeded the further development of capitalism in England and the ______ could no longer bear the sway of _______.2.England became a commomwealth under the leadership of _______.3.The Glorious Revolution in _____ meant three things the supremacy of ________,the beginning of _______,and the final truiumph of the principle of _______.4.Restoration created a literature of its own,that was often ______ and _______,but on the whole _______ and _______.5.The first thing to strik e the reader is Donne’s extraordinary _____ and penetrating_______. The next is the ______ which marks certain of the lighter poems and which represents a conscious reation from the extreme _______ of woman encouraged by the Petrachan tradition.6.Parad ise Lost presents the author’s view in an ______,_______ form. It is based on the _______legend of the imaginary progenitors of the human race-______,and _______,and involves God and his eternal adversary _____in its plot.7.Bunyan’s most important wo rk is _________,written in the old-fashioned,medieval form of ________ and _________.8.Christia has two objects,---to get rid of his ______,which holds the sins and fears of his life,and to make his way.II. Find out the work from column A and its content from column B.1. ()II Penseroso a. defense of the Revolution2. ()Lycidas b. Satan against God3. ()Comas c. about dear friend4. ()Areopagitica d. happiness5. ()Eikonolastes e. meditation6. ()Defense for the English People f. masque7. ()Paradise Lost g. attack on the censorship8. ()L’Allegro h. justifying the excutionIII.Define the leterature terms listed below.1 .Blank Verse2. Three Unities3. Conceit4. Stanza5. Elegy6 .Allegory7. GenreLiterary CriticismIV. Answer the following questions.1.What are the different aspects between the literature of Elizabeth period and that of the Revolution period?2.Give a brief analysis of Satan,the central figure in ParadiseLost.3.Why do people say Samson is Milton?4.In your opinion,why is “The Pilgrim’s P rogress” successful?英国文学史及选读Chapter6发布人:圣才学习网发布日期:2010-08-16 17:29 共34人浏览[大] [中] [小]The Age of Enlightenment EnglandI. Complete each of the following statements with a proper word or phrase according to th etextbook.1.The Revolution of 1688,which banished the last of the _____ kings,marks the end of the long struggle for political freedom in England.2.Another feature of the age was the rapid development of _________.3.It is simply for convenience that we study 18th century writings in three main divisions:the reign of so-called _____,the revival of _______ poetry,and the beginnings of the _______.4.The philosophy of the nlighteners,though ________ ________ and _________ in its essence,did not exclude senses,or sentiments,as a means of perception and learning.5.The most outstanding figure of English sentimentalism was ________.6.The Tarler and _______ _________ were Steele and Addison’s chief contribution to English literature.7.Robinson Crusoe is largely an ______ ________ ________ story,rather than the study of ______ _______ which Defoe probably intended it to be.8.Gulliver’s adventures begins with ______________,who are so small that Gulliver isa giant among them.9.The poem,which Addison named ______ _______,was hailed throughout England as a great work.10.In the essays of the 16th century,French writer ____ set the model for more familiar,personal and discursive discussion.11.Fielding’s laternovels are _______________,was inspired by the success of Ri chardson’s novel Pamela.12.As________,Goldsmith is among the best of the century.13. The greatest of _______ poets is Robert Burns.II. Match the theirs works in column A writers/genres with in column B.⑴1. ()The Deserted Village a. Thomas Gary2. ()The Village b. George Crabble3. ()Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard c. Oliver Goldsmith4. ()The Seasons d. James Thomson5. ()The Rape of the Lock e. William Blake6. ()The Chimney Sweeper f. Alexander Pope7. () A Red,Red Rose g. Robert Burns⑵1. ()A Sentimental Journey a. Daniel Defoe2. ()The Vicar of Wakefield b. Jonathan Swift3. ()The School for Scandal c.John Bunyan4. ()The History of a Young Lady d. Horace Walpole5. ()Tom Jones e. Laurence Sterne6. ()The Adventures of Peregrine Pickle f. Oliver Goldsmith7. ()Robinson Crusoe g. Richard B. Sheridam8. ()Gulliver’s Tra vels h. Samuel Richardson9. ()The Castle of Otranto i. T. G. Smollet10.()The Pilgrim’s Progress j. Fielding.⑶1. ()The Vicar of Wakefield a. essay2. ()She Stoops to Conquerb. poem3. ()The Citizen of the world c. novel4. ()The Deserted Village d. comedyIII.Define the leterature terms listed below.1.Enlightenment Movement2.Realistic Novel3.Gothic novel4.Heroic Couplet5.Mock Epic6.Bildungsroman7.Epitaph8.Farce9.Imagism10.RhymeIV. Answer the following questions.1.What is Pope’s position in English literature?2.What are the features of Sterne’s novels?3.What are the narrative festures of Gulliver’s Travel?4.What is Dr. Johnson’s comment on Addison’s prose?5.What is Fielding’s style?6.Why is Burn’s poetry important?英国文学史及选读Chapter7发布人:圣才学习网发布日期:2010-08-16 17:28 共27人浏览[大] [中] [小]The Romantic PeriodI. Fill in the following blanks.1.With the publication of William Wordworth’s _____ in Collaboration with S. T. Coleridge,________ began to bloom and found a firm place in the history of English literature.2.The most important and decisive factor in the develoment of literature is _____,English Romanticism was greatly influenced by the _______ and _______.3.The greatest historical novelist _____ was produced in the Romantic Age.4.Byron is chiefly known for his two long poems,one is Childe Harold’s Pilgrimage,the other is ________.5.Shelley’s poem _______ (1816),is vaguely autobiographical acount of a youn g poet’s unsuccessful attempt to recapture his envisional ideal.6.Ode to a Nightingale was written by _______.II. Decide whether the following statements are true or false.1. The Romantics emphasized the special qualities of each individual’s mind.2.The brilliant literary criticiam Biographis literaria is written by Samuel Johnson.III. Write the author of the following literary works.1. Song of Innocence2. The Prelude3. Kubla Khan4. Don Juan5. Prometheus Unbound6. Ode to the West Wind7. Ode on a Greciam Urn8. Pride and Prejudice9. Poor RelationsIV. Match the authors in column A with the works in columnB.1. Dante a. I Wandered Lonely as a Cloud2.Byron b. Ode to a Nightingale3. Wordsworth c. Gain4. Keats d. Prometheus Unbound5. Shelley e. Divine ComedyV. Define the following terms.1.Romanticism/doc/a410999246.htmlke poetsVI. Answer the following questions.1.How does Wordsworth define the poet?2.What kinds of stylistic devices are used in Ode to the West Wind?3.Co mment on Austen’s writing festures.英国文学史及选读Chapter7发布人:圣才学习网发布日期:2010-08-16 17:28 共27人浏览[大] [中] [小]The Romantic PeriodI. Fill in the following blanks.1.With the publication of William Wordworth’s _____ in Collaboration with S. T. Coleridge,________ began to bloom and found a firm place in the history of English literature.2.The most important and decisive factor in the develomentof literature is _____,English Romanticism was greatly influenced by the _______ and _______.3.The greatest historical novelist _____ was produced in the Romantic Age.4.Byron is chiefly known for his two long poems,one is Childe Harold’s Pilgrimage,the other is ________.5.Shelley’s poem _______ (1816),is vaguely autobiographical acount of a young poet’s unsuccessful attempt to recapture his envisional ideal.6.Ode to a Nightingale was written by _______.II. Decide whether the following statements are true or false.1. The Romantics emphasized the special qualities of each individual’s mind.2.The brilliant literary criticiam Biographis literaria is written by Samuel Johnson.III. Write the author of the following literary works.1. Song of Innocence2. The Prelude3. Kubla Khan4. Don Juan5. Prometheus Unbound6. Ode to the West Wind7. Ode on a Greciam Urn8. Pride and Prejudice9. Poor RelationsIV. Match the authors in column A with the works in columnB.1. Dante a. I Wandered Lonely as a Cloud2.Byron b. Ode to a Nightingale3. Wordsworth c. Gain4. Keats d. Prometheus Unbound5. Shelley e. Divine ComedyV. Define the following terms.1.Romanticism/doc/a410999246.htmlke poetsVI. Answer the following questions.1.How does Wordsworth define the poet?2.What kinds of stylistic devices are used in Ode to the West Wind?/doc/a410999246.htmlment on Austen’s writing festures.英国文学史及选读Chapter9发布人:圣才学习网发布日期:2010-08-16 17:26 共37人浏览[大] [中] [小]The 20TH Century LiteratureI. Fill in the following blanks.1.Those “novels of character and enviorement” by T homas Hardy are the most representative of him as both a _______ and a critical realist writer.2.The trilogy “The Forsyte Saga” consists of The Man of Propert y,In Chancery and_________./doc/a410999246.htmlwrence first novel,_________________,was received with respect.4.Virginia Woolf’s novel ________________,published in 1925,made her reputation as an important psychological writer.5._________is the m ost outstanding stream of consciousnessnovelist.II. Define the literary terms.1.Imagism2.ModernismIII. Find the relevant match from column B for each item in column A.1. James Joyce a. Neo-classicism2. Ezra Pound b. An active romantic3. William Wordsworth c. Humanism4. Oscar Wilde d. Transcendantalism5. Walter Scott e. A radical enlightenner6. Alezander Pope f. Imagism7. Johanthan Swift g. Aestheticism8. Percy Bysshe Shelley h. A lake Poet9. William Shakespeare i. Stream of consciousness10. Henry,David Thoreau j. A historical novelistIV. Give a brief comment on the c haracteristic of Hardy’s novels.。