JSP排课管理系统
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:111.00 KB
- 文档页数:10
基于Servlet、JSP的学⽣管理系统(附完整源码)起因最近重温servlet,想到了⼤学时期⽤同⼀个“学⽣管理系统”⽔了⼏门课的课程设计,不免感慨万千。
周末简单的写了个界⾯,建了⼏张表,做了⼀个⼩系统(试图找⼀找当年划⽔的感觉,可惜没找到)。
写的⽐较简单,不过做个普通的课程设计应该够了,需要的可以⾃取。
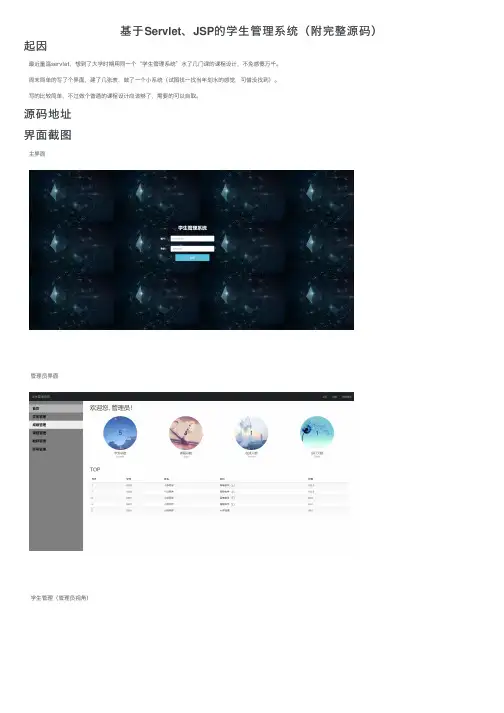
源码地址界⾯截图主界⾯管理员界⾯学⽣管理(管理员视⾓)添加系统⽤户(管理员视⾓)学⽣主页学⽣个⼈信息⽬录结构运⾏环境tomcat9jdk1.8其他依赖jar包见WEB-INF下⾯的lib⽂件夹。
涉及技术:Servlet、JSP、BootStrap、Jquery(较少)主要功能系统有两个⾓⾊,管理员和学⽣。
做的⽐较简单,没有建额外的⾓⾊表、权限表,仅仅⽤了⼀个字段区分。
管理员可以管理学⽣信息、教师信息、可以添加系统⽤户,录⼊成绩,具有增删改查的⼀切权限。
学⽣只能查看⾃⼰的分数,个⼈档案等。
代码分析⾸页数据统计系统运⾏时常、当前在线⼈数,这两个功能⽤到了servlet的组件,监听器。
通过继承ServletContextListener, HttpSessionListener, HttpSessionAttributeListener等接⼝,可以完成对servlet上下⽂、session的创建销毁等关键节点的监听。
在线⼈数,必然是登录成功的⼈数。
⽽session是有⼈访问页⾯就会创建,所以我们不能根据session的创建和销毁来统计在线⼈数。
在登陆成功后,会在session⾥添加⼀个变量,我们可以监听这⼀⾏为。
当设置session变量的时候,在线⼈数+1移除session变量的时候,在线⼈数-1。
当然这种做法还是有问题的,⽐如直接关闭浏览器,不点注销,数据统计就会失效,这⾥不做深⼊探究。
再来说说系统运⾏时长,我的思路是servlet上下⽂创建的时候,记录下那个时刻的时间戳。
后⾯⽤到的时候,直接⽤当前的时间戳减去保存的时间戳,就可以计算出相隔的毫秒数,也就可以得到天数。


排课管理系统建设方案一、项目背景记得那些年里,学校的课程安排总是让人头疼。
老师们为了排课,不惜熬夜,甚至有时候还要吵架。
这就是我们的项目背景:一个急需改善的排课现状。
二、项目目标我们的目标很简单,就是通过建立一个高效、智能的排课管理系统,让老师们从繁琐的排课工作中解放出来,让他们有更多的时间去关注教学质量和学生的成长。
三、系统架构1.前端设计前端设计要简洁、易用。
就像那些年流行的APP一样,要让老师们一眼就能看懂,上手就能用。
考虑到老师们年龄层次的不同,我们采用扁平化设计,降低操作难度。
2.后端设计后端设计要稳定、高效。
就像那些年我们一起开发的系统一样,要能够承受大量的数据请求,保证系统运行稳定。
我们采用分布式架构,提高系统的并发处理能力。
3.数据库设计数据库设计要合理、安全。
就像那些年我们一起学习的数据库知识一样,要确保数据的完整性和一致性。
我们采用关系型数据库,结合NoSQL数据库,实现数据的高效存储和查询。
四、功能模块1.排课管理这个模块是核心,就像那些年我们手动排课一样,要实现课程的自动安排。
我们可以根据老师的教学任务、学生的选课情况,自动课程表。
2.教师管理这个模块要实现对教师信息的管理,就像那些年我们熟悉的教师档案一样,包括教师的基本信息、教学任务、课程安排等。
3.学生管理这个模块要实现对学生的管理,就像那些年我们的学生档案一样,包括学生的基本信息、选课情况、成绩管理等。
4.课程管理这个模块要实现对课程的管理,就像那些年我们的课程表一样,包括课程的开设、调整、查询等功能。
5.统计分析五、实施计划1.需求分析这个阶段要充分了解学校的排课需求,就像那些年我们调研市场需求一样,收集各方面的意见,确保系统功能的完整性。
2.系统设计这个阶段要根据需求分析,进行系统架构和模块设计,就像那些年我们一起画的系统架构图一样,明确各部分的职责和关系。
3.系统开发这个阶段要按照设计文档,进行系统开发,就像那些年我们一起编程一样,攻克一个个难题,实现系统功能。

学生选课管理系统java+数据库简介学生选课管理系统是一个基于Java编程语言和数据库开发的系统,旨在提供学生选课的便捷和教务管理的智能化。
该系统具有课程管理、学生管理、教师管理、选课关联等功能模块,可以实现学生选课、教师管理课程、生成选课报表等操作。
功能模块1. 课程管理•提供课程信息录入和编辑功能,包括课程号、课程名称、授课教师等信息。
2. 学生管理•支持学生信息的录入、查询、修改和删除,学生信息包括学号、姓名、性别、年级等。
3. 教师管理•实现对教师信息的管理,可以录入教师信息、查询教师信息、修改和删除教师信息。
4. 选课关联•学生可以根据课程列表进行选课操作,系统会检查选课的合法性,避免时间冲突等问题。
数据库设计系统采用关系型数据库存储数据,设计了以下表结构: 1. 课程表:存储课程的信息,包括课程号、课程名称、授课教师等字段。
2. 学生表:存储学生的信息,包括学号、姓名、性别、年级等字段。
3. 教师表:存储教师的信息,包括教师号、姓名、职称等字段。
4. 选课表:记录学生选课的信息,包括学号、课程号、选课状态等字段。
技术实现系统使用Java语言开发,结合数据库技术进行数据存储和查询。
通过编写DAO(Data Access Object)层实现数据访问,实现了数据的持久化和业务逻辑的分离。
在用户界面方面,可以使用Swing或JavaFX等技术实现交互界面,使用户可以方便地操作系统功能。
总结学生选课管理系统是一个方便学生选课和教务管理的工具,通过Java编程语言和数据库技术的结合,实现了课程管理、学生管理、教师管理和选课关联等功能。
系统设计合理,可以提高选课效率,降低管理成本,是教育管理的重要辅助工具。
以上是对学生选课管理系统的介绍,希望能够为你对这一类型系统的理解提供帮助。


JSP员工管理系统1. 简介JSP员工管理系统是一个用于管理企业员工信息的系统,通过该系统可以方便地进行员工信息的录入、查询、更新和删除等操作。
该系统采用JSP(JavaServer Pages)作为前端开发技术,使用MySQL作为后端数据库存储员工信息。
2. 功能模块JSP员工管理系统主要包括以下几个功能模块:2.1 登录功能用户可以使用用户名和密码登录系统。
系统会验证用户名和密码的准确性,若验证通过,则跳转到首页;否则,提示用户重新输入。
2.2 首页登录成功后,用户将进入系统的首页。
首页主要展示系统的基本信息和各个功能模块的入口。
2.3 员工信息管理功能该功能模块实现了对员工信息的增删改查操作。
用户可以通过表单输入员工的基本信息,包括姓名、年龄、性别、职位等,并且可以对已有员工信息进行修改和删除。
用户还可以通过关键词查询员工信息,系统将返回匹配的员工列表。
2.4 统计功能系统提供了一些统计功能,包括员工人数统计、各个职位的人数统计、员工年龄段的分布统计等。
用户可以通过选择不同的统计维度和筛选条件来获取相应的统计结果。
2.5 权限管理功能该功能模块实现了对系统用户的权限管理。
系统管理员可以添加、删除和修改用户的权限,设置用户能够访问的功能模块和操作。
3. 技术架构JSP员工管理系统的技术架构如下:•前端采用JSP作为开发技术,使用HTML和CSS进行页面设计和样式布局。
•后端采用Java语言开发,使用Servlet作为控制器,处理用户的请求,并调用相应的服务层进行业务逻辑处理。
•数据库采用MySQL存储员工信息,通过JDBC(Java Database Connectivity)与后端进行交互。
•通过Tomcat作为应用服务器部署和运行系统。
4. 数据库设计系统的数据库设计如下:4.1 员工表(employee)列名数据类型主键描述id int是员工IDname varchar(50)员工姓名age int员工年龄gender varchar(10)员工性别position varchar(50)员工职位entry_date date入职日期4.2 用户表(user)列名数据类型主键描述id int是用户ID username varchar(50)用户名password varchar(50)密码role varchar(50)用户角色5. 系统部署系统的部署步骤如下:1.配置Java开发环境和Tomcat服务器环境。

jsp管理系统源码JSP管理系统源码是一项用于构建和管理动态网页的技术。
它允许开发人员在Java中嵌入HTML代码,并通过在服务器上运行Java代码生成动态内容。
通过结合JSP和Java代码,可以构建强大且功能丰富的管理系统。
JSP管理系统源码的开发过程需要一定的技术知识和经验。
首先,开发人员需要掌握Java编程语言和JavaWeb开发的基本概念。
其次,他们需要了解JSP的语法和标签,以及如何在JSP文件中嵌入Java代码。
此外,他们还需要学习如何与数据库进行交互,以便存储和检索数据。
JSP管理系统源码通常由多个组件组成,包括前端界面、后端逻辑和数据库。
前端界面是用户与系统进行交互的地方,它呈现数据和提供操作选项。
开发人员可以使用HTML和CSS来设计和布局前端界面,通过JSP标签嵌入动态内容。
后端逻辑是处理用户请求并执行相应操作的地方,例如验证用户身份、查询数据库和生成动态页面。
开发人员可以使用Java编写后端逻辑,并通过JSP标签将其嵌入到JSP文件中。
数据库用于存储和检索数据,开发人员可以使用SQL语句与数据库进行交互。
在开发JSP管理系统源码时,开发人员应遵循良好的编程实践和安全性原则。
他们应该对用户输入进行验证和过滤,以防止潜在的安全漏洞,如SQL注入和跨站脚本攻击。
此外,他们还应使用适当的身份验证和授权机制来保护系统的敏感功能和数据。
JSP管理系统源码可以用于各种各样的应用,例如学生管理系统、图书管理系统、库存管理系统等。
根据具体的需求和功能,开发人员可以进一步扩展和定制源码,以满足特定的业务需求。
总之,JSP管理系统源码是一种强大而灵活的技术,用于构建和管理动态网页。
开发人员可以利用JSP的特性和Java的功能,创建功能丰富且安全可靠的管理系统。
但是,为了开发出高质量的源码,开发人员需要具备相关的技术知识和经验,并遵循编程实践和安全性原则。
只有这样,我们才能开发出满足用户需求的优秀JSP管理系统源码。

JSP学生选课系统-课程设计JSP学生选课系统052 1. 一、实训目的计算机应用实训是计算机科学与技术专业重要的实践性教学课程,安排在毕业前最后一学期进行。
通过本次应用实训,使学生对结合学习过的知识,对软件开发过程进一步理解,并掌握按照软件工程的思想,进行程序开发设计的过程,同时培养学生严谨、科学的工作作风,为今后从事计算机工作打下必要的基础。
通过本次实训,使学生掌握程序设计中需求分析、概要设计、详细设计的方法和过程,并通过实际学习,利用Eclipse3+MyEclipse6+JDK6开发环境,实现基于JSP环境下采用Model1模式程序的编制。
2. 二、设计题目编号题目备注1 图书管理系统2 人事管理系统3 教材管理系统4 学生管理系统5 工资管理系统6 库存管理系统7 IC卡管理系统8 科技文献管理系统3. 三、分组原则原则上每组人数不超过5人,在班级内部采用自愿组合的形式,但班级内部两个不同小组不允许选择同一题目。
4. 四、实训要求1、认真听讲。
2、遵守实训时间安排。
3、按时上机,认真练习。
4、认真书写实训报告。
时间安排表:序实习内容总天数讲课操作机动备注号1 布置题目,查找资料 1 0.3 0.72 需求分析与设计3 2 13 数据库设计及答辩 1 0.5 0.54 JSP程序设计 8 4 45 报告撰写 1 0.1 0.96 成绩评定及答辩 1 0.1 0.9合计(天数) 15 7 81. 六、成绩评定成绩包括出勤纪律、分析设计、程序编制和实训报告4个部分。
由实训指导教师科学评定成绩,各项成绩按比例累加得到实训总成绩。
实训各项占总成绩比例如下:出勤纪律:10%分析设计:20%程序编制:50%实训报告:20%注:其中平时成绩和实训报告具有一票否决权,其一不及格总成绩为不及格。
1、本实训是一门综合程序设计课程,在本实训期间,每一部分内容都是教师先讲解,让学生了解之后再进行练习。
2、本实训注重在规定的时间内完成设计内容,目的在于加强学生的动手能力。

注册-登录小实验1.0 JDK的安装 (2)2.0 Tomcat 的安装 (3)3.0 Eclipse 3.2 安装 (5)3.1 MyEclipse 的安装 (5)3.0.1 java jdk 的导入! (6)3.0.2Tomcat 的配制 (6)3.0.3 用 MyEclipse 新建一个项目 (8)3.0.5 在应程序中使用 Tomcat (8)4.0 登录——注册小实验 ! (10)4.0.1 新建一个项目 (10)4.0.2登录 (12)前台界面设计 (12)后台处理程序 (13)验证试验是否成功: (16)4.1.0 注册 (16)1.0 JDK的安装环境变量的设置set path =D:\Sun\j2sdk1.4.2_16;%paht%2.0 Tomcat 的安装设置安装路径设置用户名和密码选择你jdk 安的装的位置测试你的Tomcat 安装是否成功在IE 地址栏上输入:localhost:8080/如果不成功可以重复做一下!!3.0 Eclipse 3.2 安装Eclipse 放到你要想要放的位置就行了!!我放的是D:\Sun选择Workbeach 进入!3.1 MyEclipse 的安装MyEclipse是一个Exe安装文件,有安装向导,直接双击安装,选择完Eclipse 安装目录3.0.1 java jdk 的导入!File —> Properties —>Java Build Path3.0.2Tomcat 的配制1. Window-﹥Preference…,2. MyEclipse-﹥Application Servers-﹥Tomcat 5JDK ?3.0.3 用 MyEclipse 新建一个项目New —> Project —>MyEclipse —>Web Projecet3.0.5 在应程序中使用 Tomcat选中WebTest工程的根目录,右键菜单MyEclipse-﹥Add and Remove Projects Deployments…,在打开的对话框中确保Projects为WebTest,点击Add按钮,在弹出对话框的Server中选择Tomcat !选中项目如:点击OK!!到此 Java web开发环境配置成功!!!大家就来小试牛刀吧!4.0 登录——注册小实验 !4.0.1 新建一个项目File —> New —>Project —>MyEclipse—>Web Project添加一个Jsp 右键 webRoot : New—>JSP 名称MyJsp .jsp4.0.2登录前台界面设计代码如下:<% page contentType="text/html; charset=gb2312" language="java" import="java.sql.*" errorPage="" %><!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"><html> <head><title>Register Test!</title></head><body> 登录界面!! <br><form method="post" action="cheklogin.jsp" name="form"><table width="183" height="85" border="1"><tr><td>User:</td><td><input type="text" name="user" size="13"></td></tr><tr><td>Password:</td><td><input type="Password" name="password" size="13" > </td></tr><tr><td><input type="Submit" name="bt1" text="OK" value="登录"> </td><td><a href="do_register.jsp" target="_parent">新用户注册<br></a></td></tr></table></form></body></html>后台处理程序添加一个Jsp 右键 webRoot : New—>JSP 名称cheklogin .jsp代码如下:<% page contentType="text/html; charset=gb2312" language="java" import="java.sql.*" errorPage="" %><%String path = request.getContextPath();String basePath =request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServ erPort()+path+"/";%><!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"><html><head><base href="<%=basePath%>"><title>My JSP 'cheklogin.jsp' starting page</title><meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"><meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"><meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"><meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"><!--<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">--></head><body><%String usr = request.getParameter("user");String pwd = request.getParameter("password");//String usr = "hurui";//String pwd = "free889";Connection con = null;Statement sm = null;ResultSet rs = null;try{Class.forName(".informix.jdbc.IfxDriver").newInstance(); //装载jdbc 驱动String url ="jdbc:informix-sqli://192.168.5.249:9003/testuser:informixserver=iser vice_online_net"; // 定义数据库连接URLcon = DriverManager.getConnection(url,"informix","informix"); //获取数据连接实例sm = con.createStatement(); //获取Statement 的实例rs = sm.executeQuery("select * from new_test_user wherelogin='"+usr+"' and password='"+pwd+"'"); //执行查询语句,并返回给结果集}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace( );}//添加表格%><table border="1" width="80%"><tr><td>你的用户名是:</td><td>你的密码是:</td></tr><%while (rs.next()) { //循环输出产品信息String var_name=rs.getString(1);String var_val=rs.getString(2);%><tr><%if(usr == var_name || pwd ==var_val){System.out.println("success!");}%><td><%= var_name %></td><td><%= var_val %></td></tr><%}rs.close();sm.close();con.close();%></body></html>验证试验是否成功:输入:用户名:admin密码:111114.1.0 注册数据库:iservice_online_net表:new_test_user表结构:用户名对应字段: login密码对应字段: password<%Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");String url="jdbc:odbc:Test";Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection(url,"sa"," ");if(!con.isClosed()){System.out.println("正确连接!");}else{System.out.println("连接不正确!");}con.close();%>当然也是可以不用到上面表字段就可以完成简单注册,是否使用,看你使用数据库的习惯!。

本科生毕业设计(论文)外文翻译毕业设计(论文)题目:基于JSP的高校选排课系统的设计与实现外文题目:Overview of JSP Technology译文题目:JSP技术概述学院:软件学院专业:软件工程学生姓名:学生班级:软件工程1102班学生学号:指导教师:Overview of JSP TechnologyAutor: Zambon Giulio/ Sekler MichaelSource: Springer-Verlag New York Inc1.Benefits of JSPJSP pages are translated into servlets. So, fundamentally, any task JSP pages can perform could also be accomplished by servlets. However, this underlying equivalence does not mean that servlets and JSP pages are equally appropriate in all scenarios. The issue is not the power of the technology, it is the convenience, productivity, and maintainability of one or the other. After all, anything you can do on a particular computer platform in the Java programming language you could also do in assembly language. But it still matters which you choose.JSP provides the following benefits over servlets alone: It is easier to write and maintain the HTML. Your static code is ordinary HTML: no extra backslashes, no double quotes, and no lurking Java syntax.You can use standard Web-site development tools. Even HTML tools that know nothing about JSP can be used because they simply ignore the JSP tags.You can divide up your development team. The Java programmers can work on the dynamic code. The Web developers can concentrate on the presentation layer. On large projects, this division is very important. Depending on the size of your team and the complexity of your project, you can enforce a weaker or stronger separation between the static HTML and the dynamic content.Now, this discussion is not to say that you should stop using servlets and use only JSP instead. By no means. Almost all projects will use both. For some requests in your project, you will use servlets. For others, you will use JSP. For still others, you will combine them with the MVC architecture . You want the appropriate tool for the job, and servlets, by themselves, do not complete your toolkit.2. Advantages of JSP Over Competing TechnologiesA number of years ago, Marty was invited to attend a small 20-person industry roundtable discussion on software technology. Sitting in the seat next to Marty was James Gosling, inventor of the Java programming language. Sitting several seats away was a high-level manager from a very large software company in Redmond, Washington. During the discussion, the moderator brought up the subject of Jini, which at that time was a new Java technology. The moderator asked the manager what he thought of it, and the manager responded that it was too early to tell, but that it seemed to be an excellent idea. He went on to say that they would keep an eye on it, and if it seemed to be catching on, they would follow his company's usual "embrace and extend" strategy. At this point, Gosling lightheartedly interjected "You mean disgrace and distend."Now, the grievance that Gosling was airing was that he felt that this company would take technology from other companies and suborn it for their own purposes. But guess what? The shoe is on the other foot here. The Java community did not invent the idea of designing pages as a mixture of static HTML and dynamic code marked with special tags. For example, ColdFusion did it years earlier. Even ASP (a product from the very software company of the aforementioned manager) popularized this approach before JSP came along and decided to jump on the bandwagon. In fact, JSP not only adopted the general idea, it even used many of the same special tags as ASP did..So, the question becomes: why use JSP instead of one of these other technologies? Our first response is that we are not arguing that everyone should. Several of those other technologies are quite good and are reasonable options in some situations. In other situations, however, JSP is clearly better. Here are a few of the reasons.2.1Versus .NET and Active Server Pages (ASP)NET is well-designed technology from Microsoft. is the part that directly competes with servlets and JSP. The advantages of JSP are two fold.First, JSP is portable to multiple operating systems and Web servers; you aren't locked into deploying on Windows and IIS. Although the core .NET platform runs on a few non-Windows platforms, the ASP part does not. You cannot expect to deploy serious applications on multiple servers and operating systems. For some applications, this difference does not matter. Forothers, it matters greatly.Second, for some applications the choice of the underlying language matters greatly. For example, although .NET's C# language is very well designed and is similar to Java, fewer programmers are familiar with either the core C# syntax or the many auxiliary libraries. In addition, many developers still use the original version of ASP. With this version, JSP has a clear advantage for the dynamic code. With JSP, the dynamic part is written in Java, not VBScript or another ASP-specific language, so JSP is more powerful and better suited to complex applications that require reusable components.You could make the same argument when comparing JSP to the previous version of ColdFusion; with JSP you can use Java for the "real code" and are not tied to a particular server product. However, the current release of ColdFusion is within the context of a J2EE server, allowing developers to easily mix ColdFusion and servlet/JSP code.2.2 Versus PHPPHP (a recursive acronym for "PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor") is a free, open-source, HTML-embedded scripting language that is somewhat similar to both ASP and JSP. One advantage of JSP is that the dynamic part is written in Java, which already has an extensive API for networking, database access, distributed objects, and the like, whereas PHP requires learning an entirely new, less widely used language. A second advantage is that JSP is much more widely supported by tool and server vendors than is PHP.2.3 Versus Pure ServletsJSP doesn't provide any capabilities that couldn't, in principle, be accomplished with servlets. In fact, JSP documents are automatically translated into servlets behind the scenes. But it is more convenient to write (and to modify!) regular HTML than to use a zillion println statements to generate the HTML. Plus, by separating the presentation from the content, you can put different people on different tasks: your Web page design experts can build the HTML by using familiar tools and either leave places for your servlet programmers to insert the dynamic content or invoke the dynamic content indirectly by means of XML tags.Does this mean that you can just learn JSP and forget about servlets? Absolutely not! JSPdevelopers need to know servlets for four reasons:JSP pages get translated into servlets. You can't understand how JSP works without understanding servlets.JSP consists of static HTML, special-purpose JSP tags, and Java code. What kind of Java code? Servlet code! You can't write that code if you don't understand servlet programming.Some tasks are better accomplished by servlets than by JSP. JSP is good at generating pages that consist of large sections of fairly well structured HTML or other character data. Servlets are better for generating binary data, building pages with highly variable structure, and performing tasks (such as redirection) that involve little or no output.Some tasks are better accomplished by a combination of servlets and JSP than by either servlets or JSP alone.2.4 ersus JavaScriptJavaScript, which is completely distinct from the Java programming language, is normally used to dynamically generate HTML on the client, building parts of the Web page as the browser loads the document. This is a useful capability and does not normally overlap with the capabilities of JSP (which runs only on the server). JSP pages still include SCRIPT tags for JavaScript, just as normal HTML pages do. In fact, JSP can even be used to dynamically generate the JavaScript that will be sent to the client. So, JavaScript is not a competing technology; it is a complementary one.It is also possible to use JavaScript on the server, most notably on Sun ONE (formerly iPlanet), IIS, and BroadVision servers. However, Java is more powerful, flexible, reliable, and portable.3. Misconceptions About JSPForgetting JSP Is Server-Side Technology,Here are some typical questions Marty has received (most of them repeatedly).Our server is running JDK 1.4. So, how do I put a Swing component in a JSP page?How do I put an image into a JSP page? I do not know the proper Java I/O commands to read image files.Since Tomcat does not support JavaScript,how do I make images that are highlighted when the user moves the mouse over them?Our clients use older browsers that do not understand JSP. What should we do?When our clients use "View Source" in a browser, how can I prevent them from seeing the JSP tags?All of these questions are based upon the assumption that browsers know something about the server-side process. But they do not. Thus:For putting applets with Swing components into Web pages, what matters is the browser's Java version—the server's version is irrelevant. If the browser supports the Java 2 platform, you use the normal APPLET (or Java plug-in) tag and would do so even if you were using non-Java technology on the server.You do not need Java I/O to read image files; you just put the image in the directory for Web resources (i.e., two levels up from WEB-INF/classes) and output a normal IMG tag.You create images that change under the mouse by using client-side JavaScript, referenced with the SCRIPT tag; this does not change just because the server is using JSP.Browsers do not "support" JSP at all—they merely see the output of the JSP page. So, make sure your JSP outputs HTML compatible with the browser, just as you would do with static HTML pages.And, of course you need not do anything to prevent clients from seeing JSP tags; those tags are processed on the server and are not part of the output that is sent to the client.Confusing Translation Time with Request Time,A JSP page is converted into a servlet. The servlet is compiled, loaded into the server's memory, initialized, and executed. But which step happens when? To answer that question, remember two points: The JSP page is translated into a servlet and compiled only the first time it is accessed after having been modified.Loading into memory, initialization, and execution follow the normal rules for servlets.The most frequently misunderstood entries are highlighted. When referring to the table, note that servlets resulting from JSP pages use the _jspService method (called for both GET and POST requests), not doGet or doPost. Also, for initialization, they use the jspInit method, not the init method.JSP page translated into servlet Servlet compiled Servlet loaded into server's memory jspInit called _jspService called.JSP技术概述作者:赞邦.朱利奥/赛克勒.迈克尔出处: 施普林格出版社(纽约公司)1.JSP的好处JSP页面最终会转换成服务程序。

学生选课管理系统JavaWeb课程设计一、概述学生选课管理系统是一种用于管理学生选课信息的系统,能够实现学生注册、登录、选课、退选等功能。
本文将介绍基于JavaWeb技术设计学生选课管理系统的实现方案。
二、系统设计1. 系统结构学生选课管理系统主要包括学生管理模块、课程管理模块和选课管理模块。
2. 数据库设计系统数据库主要包括学生信息表、课程信息表、选课信息表等。
各表之间通过外键进行关联。
三、功能模块设计1. 学生管理模块•学生注册:学生可以通过系统注册账号。
•学生登录:学生可以使用注册账号登录系统。
•学生信息查看:学生可以查看个人信息。
2. 课程管理模块•课程信息查看:学生可以查看系统中所有课程信息。
•课程详情查看:学生可以查看课程的详细信息。
3. 选课管理模块•选课:学生可以选择感兴趣的课程进行选课。
•退选:学生可以退选已经选修的课程。
四、功能实现系统采用JavaWeb技术实现,包括前端页面的设计和后端逻辑的实现。
1. 前端设计系统前端页面采用HTML、CSS和JavaScript进行设计,主要包括学生登录页面、学生信息页面、课程信息页面等。
2. 后端实现系统后端采用Java语言开发,使用Servlet实现业务逻辑。
通过数据库连接池实现与数据库的交互,实现学生信息的增删改查,课程信息的查询和选课功能。
五、系统展望未来可以进一步完善系统功能,添加成绩管理模块、教师管理模块等,提升系统的全面性和实用性。
六、总结学生选课管理系统是一种重要的教务管理系统,本文设计了基于JavaWeb技术的学生选课管理系统方案,通过前后端的设计和实现,实现了学生信息管理、课程管理和选课功能。
希望该系统能够为学生选课提供便利,为教务管理提供支持。
密级:NANCHANG UNIVERSITY学士学位论文THESIS OF BACHELOR(2010—2014年)题目基于Java Web的高校排课系统的设计与实现学院:信息工程学院系信管系专业班级:学生姓名:学号:指导教师:职称:起讫日期:2014.2.16—2014.5.30基于Java Web排课系统的设计与实现摘要排课问题是一个NP完全问题,是一个多约束的、多目标的组合优化问题。
而传统的手工排课的方式,不仅繁琐、极易出错,而且不能全面地考虑对教学资源的合理利用。
因此,设计一个能够根据约束条件,自动安排课程的智能排课系统,是现在高校教务管理的迫切需求。
本文通过对排课系统的分析,阐述了基于Java Web平台下的排课系统的Web 解决方案。
本系统采用了B/S结构,采用了基于JSP Model2的MVC设计模式,大大简化了系统开发的困难。
本文选用了遗传算法来解决排课问题,阐述了遗传算法的基本原理与算法流程,以及在排课问题中的具体实现。
关键词:排课系统;MVC;JSP Model2 ;Java WebCourse Arrangement System Design andImplementation Based on WebAbstractCourse timetabling problem is a NP complete problem, and is a combinatorial optimization problem with a variety of constraints and a multiobjective optimization. the traditional manual method , is not only tedious and error-prone, and can not fully take the reasonable use of the teaching resources into consideration. Therefore, designing a course arrangement system that can arrange the course arrangement automatically according to the constraints is the urgent demand of university educational administration management now.Through the analysis of the curriculum arrangement system, this paper expounds the web solutions of curriculum arrangement system based on Java Web platform . This system adopts B/S structure, and using the MVC design pattern based on JSP Model2,greatly simplifying the difficulties of system development. This paper use genetic algorithm to solve the course timetabling problem, and expounds the basic principle of genetic algorithm , the algorithm flow, and the concrete implementation in the problem.Keyword: Course Arrangement System;MVC;JSP Model2;Java Web目录摘要 (I)Abstract (II)第一章绪论 (1)1.1 课题背景与意义 (1)1.2 国内外发展现状 (1)1.3 本文的研究目标 (2)第二章相关开发技术 (3)2.1 网络结构 (3)2.2 JSP技术 (3)2.3 MVC模式介绍 (5)2.4本章小结 (6)第三章排课系统分析与设计 (7)3.1 排课系统需求分析 (7)3.2 排课系统功能架构分析 (9)3.3 数据库设计 (12)第四章排课系统算法设计 (18)4.1 遗传算法介绍 (18)4.2 排课系统算法设计 (19)4. 3 本章小结 (26)第五章排课系统实现与测试 (27)5.1登录模块实现与测试 (27)5.2 基本信息管理模块实现与测试 (28)5.3 手动排课模块实现与测试 (29)5.4 自动排课模块实现与测试 (30)5.5 课表查询模块实现实现与测试 (30)5.6 本章小结 (31)第六章总结与展望 (32)6.1 总结 (32)6.2 展望 (32)参考文献 (33)致谢 (35)第一章绪论1.1 课题背景与意义随着我国在校大学生人数快速增长,教学资源相对紧缺,合理安排课程变得尤为重要。
基于JSP的信息管理系统设计与实现信息管理系统是一种用于管理和处理各种信息的软件系统,它可以帮助用户高效地组织、存储、检索和分析信息。
随着互联网的发展,信息管理系统在各个领域得到了广泛的应用,如学校教务管理系统、企业人事管理系统、图书馆借阅管理系统等。
本文将介绍基于JSP (JavaServer Pages)技术的信息管理系统的设计与实现过程。
一、系统需求分析在设计信息管理系统之前,首先需要进行系统需求分析,明确系统的功能和性能需求。
一般来说,信息管理系统需要具备以下基本功能:用户管理:包括用户注册、登录、权限管理等功能。
信息录入:用户可以录入各种类型的信息,如学生信息、员工信息、图书信息等。
信息查询:用户可以根据条件查询所需的信息。
信息统计:系统可以对录入的信息进行统计分析,并生成报表。
界面友好:系统界面应该简洁美观,操作方便。
二、系统设计1. 技术选型在本文中,我们选择使用JSP作为开发技术,JSP是一种动态网页开发技术,它可以将Java代码嵌入到HTML页面中,实现页面动态生成。
同时,我们还会使用Servlet作为控制器,负责处理用户请求和调用业务逻辑。
2. 数据库设计在设计信息管理系统时,数据库设计是至关重要的一环。
我们需要根据系统需求设计合理的数据库表结构,保证数据存储的有效性和完整性。
以学生信息管理系统为例,可能涉及到学生表、课程表、成绩表等。
3. 系统架构基于JSP的信息管理系统通常采用MVC(Model-View-Controller)架构模式。
其中,Model负责数据处理和业务逻辑,View负责页面展示,Controller负责接收用户请求并调度Model和View。
三、系统实现1. 环境搭建首先,我们需要搭建开发环境,包括安装JDK(Java Development Kit)、Tomcat服务器以及数据库(如MySQL)。
然后创建一个Web项目,并配置好相关环境。
2. 编码实现接下来,我们开始编写代码实现系统功能。
引言计算机已经成为我们学习和工作的得力助手:今天,计算机的价格已经十分低廉,性能却有了长足的进步。
它已经被应用于许多领域,计算机之所以如此流行的原因主要有以下几个方面:首先,计算机可以代替人工进行许多繁杂的劳动;其次,计算机可以节省许多资源;第三,计算机可以大大的提高人们的工作效率;第四,计算机可以使敏感文档更加安全,等等。
在高校中用计算机管理排课的意义现在我国的高校校中排课的管理水平还停留在纸介质的基础上,这样的机制已经不能适应时代的发展,因为它浪费了许多人力和物力,在信息时代这种传统的管理方法必然被计算机为基础的信息管理所取代。
我希望可以在这方面有所贡献。
改革的总设计师邓小平同志说过"科学技术是第一生产力",我希望能用我四年的所学编制出一个实用的程序来帮助高校进行更有效的课程管理。
第一章系统概述1.1 排课背景排课管理系统是一个教育单位不可缺少的部分,它的内容对于学校的决策者和管理者来说都至关重要,所以排课管理系统应该能够为用户提供充足的信息和快捷的查询手段。
但一直以来人们使用传统人工的方式管理文件排课,这种管理方式存在着许多缺点,如:效率低、保密性差,另外时间一长,将产生大量的文件和数据,这对于查找、更新和维护都带来了不少的困难。
随着科学技术的不断提高,计算机科学日渐成熟,其强大的功能已为人们深刻认识,它已进入人类社会的各个领域并发挥着越来越重要的作用。
作为计算机应用的一部分,使用计算机对排课信息进行管理,具有着手工管理所无法比拟的优点。
例如:检索迅速、查找方便、可靠性高、存储量大、保密性好、寿命长、成本低等。
这些优点能够极大地提高排课管理的效率,也是企业的科学化、正规化管理,与世界接轨的重要条件。
1.2排课系统的意义终上所述,开发这样一套排课管理软件成为很有必要的事情。
我们所开发的这排课管理软件归纳起来,好处大约有以下几点:1.可以存储历届的排课,安全、高效;2.只需一到二名排课录入员即可操作系统,节省大量人力;3.可以按照录入人员的输入来自动生成课程表,并尽量减少冲突等情况发生。
JavaWeb学生选课管理系统一、引言学生选课管理系统是在学校教务管理中非常重要的一个系统。
随着计算机技术的发展,采用JavaWeb技术开发学生选课管理系统已成为一种常见的选择。
本文将介绍如何使用JavaWeb技术开发一个简单的学生选课管理系统。
二、系统功能需求学生选课管理系统的主要功能包括学生登录、浏览课程、选课、退课等。
下面将逐一介绍这些功能的实现方法。
1. 学生登录学生登录是学生进入选课系统的入口。
学生需要输入自己的学号和密码进行登录。
系统需要验证学生输入的学号和密码是否正确,并根据验证结果进行相应的处理。
2. 浏览课程学生登录成功后,系统需要展示可选的课程列表给学生浏览。
课程信息包括课程编号、课程名称、课程学分等。
学生可以通过浏览课程列表了解每门课程的具体信息。
3. 选课学生可以从课程列表中选择感兴趣的课程进行选课。
系统需要记录学生所选课程的信息,并更新相应的学生选课记录。
4. 退课学生可以在选课期间自由地退选已选的课程。
系统需要删除学生的选课记录,并更新相关的课程信息。
三、系统架构学生选课管理系统的整体架构采用三层结构,包括表现层(Presentation Layer)、业务逻辑层(Business Logic Layer)和数据访问层(Data Access Layer)。
1. 表现层表现层是系统与用户之间的交互界面,使用HTML、CSS和JavaScript等技术进行开发。
通过表现层,学生可以进行登录、浏览课程、选课、退课等操作。
2. 业务逻辑层业务逻辑层负责处理系统的核心业务逻辑,包括学生登录验证、课程信息查询、选课和退课等功能的实现。
该层使用Java语言编写,可以使用Java的框架(如Spring、Struts等)简化开发。
3. 数据访问层数据访问层负责与数据库进行交互,包括学生信息、课程信息、选课记录等数据的读取和存储。
该层使用Java的持久层框架(如MyBatis、Hibernate等)进行开发,简化数据库访问操作。
学生在线选课系统--JSP课程设计姓名:彭仁欢学号:20140130202专业:计算机信息管理教师:吴志强2013年6月27日目录一、实验目的 (1)二、队员分析 (1)三、系统流程图 (1)四、E-R图 (2)五、程序代码(前台显示模块)与运行结果 (2)六、数据库操作 (13)七、设计心得 (21)八、设计结果 (22)一、设计目的本次实验课程设计是打算设计一个小型的学生在线选课系统,用于给学生网上在线直接选好课程然后学校能加更好的管理各们课程,本次课程设计也是基于jsp环境下进行设计的,学生运用JSP与SQL Server2000所学知识来进行开发,以此使得学生更加深刻地掌握这些语言与操作。
了解JSP对于数据库的操作,让学生能更加深刻的了解JSP的程序开发。
二、设计分析1、要求:建立一个学生选课系统2、功能:选课的增删改查,选课课程开课与截止的新闻发布的增删改查,管理员的一些后台管理等功能。
3、运行软件:Tomacat、SQL Server20004、运行环境:Windows XP系统三、系统流程图四、 E-R图五、程序代码(前台模块)与运行结果1、新闻列表代码:<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"><html xmlns="/1999/xhtml"><%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=gb2312"%><%@ page import="java.sql.*" %><%Connection con;Statement sql;ResultSet rs;try{ Class.forName("com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver");}catch(Exception e){ out.print(e);}try { String uri= "jdbc:sqlserver://127.0.0.1:1433;DatabaseName=text";String user="sa";String password="danmo0410.";con=DriverManager.getConnection(uri,user,password);sql=con.createStatement();rs=sql.executeQuery("SELECT top 10 * FROM dm_new ORDER BY dm_time");%><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" /> <link href="style/index.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"><title>无标题文档</title></head><body><table width="850" border="0" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0"><tr><td width="580" height="185" style="background:url(images/1_01.gif)no-repeat"></td><td width="270" height="185" style="background:url(images/1_02.gif) no-repeat"></td></tr><tr><td height="353" colspan="2" style="background:url(images/1_05.gif) no-repeat"><div id="header"><ul><li><a href="index.jsp">首页</a></li><li><a href="course.jsp">选课列表</a></li><li><a href="view.jsp">查看选课</a></li><li><a href="admin.jsp">管理中心</a></li></ul></div><div id="center"><h3>学校通知</h3><dl><% while(rs.next()){ %><dd style="background:url(images/gaoshi.gif) no-repeat center left;"><a href="index_aritle.jsp?id=<% out.print(rs.getInt("dm_id"));%>"><em><%out.print(rs.getDate("dm_time"));%></em><%out.print(rs.getString("dm_title"));%></a></dd><%}%></dl></div></td></tr><tr><td colspan="2" height="55" style="background:url(images/1_06.gif) no-repeat"> </td></tr></table></body></html><%con.close();}catch(SQLException e){ out.print(e);}%>2、查看新闻代码:<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"><html xmlns="/1999/xhtml"><%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=gb2312"%><%@ page import="java.sql.*" %><% String id=request.getParameter("id");%><% Connection con;Statement sql;ResultSet rs;try{ Class.forName("com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver");}catch(Exception e){ out.print(e);}try { String uri= "jdbc:sqlserver://127.0.0.1:1433;DatabaseName=text";String user="sa";String password="danmo0410.";con=DriverManager.getConnection(uri,user,password);sql=con.createStatement();rs=sql.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM dm_new WHERE dm_id="+id+"");%><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" /> <link href="style/aritle.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"><title>无标题文档</title></head><body><table width="850" border="0" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0"><tr><td width="580" height="185" style="background:url(images/1_01.gif) no-repeat"></td><td width="270" height="185" style="background:url(images/1_02.gif) no-repeat"></td></tr><tr><td height="353" colspan="2" style="background:url(images/1_05.gif) no-repeat"><div id="header"><ul><li><a href="index.jsp">首页</a></li><li><a href="course.jsp">选课列表</a></li><li><a href="view.jsp">查看选课</a></li><li><a href="admin.jsp">管理中心</a></li></ul></div><div id="center"><h3>新闻查看</h3><dl><% if(rs.next()){ %><dd><strong>标题:</strong><% out.print(rs.getString("dm_title"));%> <strong>时间:</strong></strong><% out.print(rs.getDate("dm_time"));%></dd><dd><strong>内容:</strong><% out.print(rs.getString("dm_content"));%></dd><%}%><dd><a href="index.jsp"><input class="submit" type="submit" value="返回"></a></dd></dl></div></td></tr><tr><td colspan="2" height="55" style="background:url(images/1_06.gif) no-repeat"> </td></tr></table></body></html><%con.close();}catch(SQLException e){ out.print(e);}%>3、选课列表代码:<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"><html xmlns="/1999/xhtml"><%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=gb2312"%><%@ page import="java.sql.*" %><% Connection con;Statement sql;ResultSet rs;try{ Class.forName("com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver");}catch(Exception e){ out.print(e);}try { String uri= "jdbc:sqlserver://127.0.0.1:1433;DatabaseName=text";String user="sa";String password="danmo0410.";con=DriverManager.getConnection(uri,user,password);sql=con.createStatement();rs=sql.executeQuery("SELECT top 10 * FROM dm_class"); %><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" /> <link href="style/index.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"><title>无标题文档</title></head><body><table width="850" border="0" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0"><tr><td width="580" height="185" style="background:url(images/1_01.gif) no-repeat"></td><td width="270" height="185" style="background:url(images/1_02.gif) no-repeat"></td></tr><tr><td height="353" colspan="2" style="background:url(images/1_05.gif) no-repeat"><div id="header"><ul><li><a href="index.jsp">首页</a></li><li><a href="course.jsp">选课列表</a></li><li><a href="view.jsp">查看选课</a></li><li><a href="admin.jsp">管理中心</a></li></ul></div><div id="center"><h3>在线选课</h3><dl><% while(rs.next()){%><dd style="background:url(<% out.print(rs.getString("dm_face"));%>) no-repeat center left;"><a href="course_aritle.jsp?id=<% out.print(rs.getInt("dm_id"));%>"><em><%out.print(rs.getDate("dm_time"));%></em><%out.print(rs.getString("dm_class"));%></a></dd><%}%></dl></div></td> </tr> <tr><td colspan="2" height="55" style="background:url(images/1_06.gif) no-repeat"> </td></tr></table></body></html><%con.close();}catch(SQLException e){ out.print(e);}%>4、进行选课代码:<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"><html xmlns="/1999/xhtml"><%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=gb2312"%><%@ page import="java.sql.*" %><% String id=request.getParameter("id");%><% Connection con;Statement sql;ResultSet rs;try{ Class.forName("com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver");}catch(Exception e){ out.print(e);}try { String uri= "jdbc:sqlserver://127.0.0.1:1433;DatabaseName=text";String user="sa";String password="danmo0410.";con=DriverManager.getConnection(uri,user,password);sql=con.createStatement();rs=sql.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM dm_class WHERE dm_id="+id+"");%><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" /> <link href="style/aritle.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"><title>无标题文档</title></head><body><table width="850" border="0" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0"><tr><td width="580" height="185" style="background:url(images/1_01.gif) no-repeat"></td><td width="270" height="185" style="background:url(images/1_02.gif) no-repeat"></td></tr><tr><td height="353" colspan="2" style="background:url(images/1_05.gif) no-repeat"><div id="header"><ul><li><a href="index.jsp">首页</a></li><li><a href="course.jsp">选课列表</a></li><li><a href="view.jsp">查看选课</a></li><li><a href="admin.jsp">管理中心</a></li></ul></div><div id="center"><h3>新闻查看</h3><dl><% if(rs.next()){ %><dd><strong>标题:</strong><% out.print(rs.getString("dm_class"));%> <strong>时间:</strong></strong><% out.print(rs.getDate("dm_time"));%> <strong>已报人数:</strong></strong><%out.print(rs.getInt("dm_renshu"));%></dd><dd><strong>内容:</strong><% out.print(rs.getString("dm_content"));%></dd><%}%><dd><a href="course.jsp"><input class="submit" type="submit" value="返回"></a></dd></dl><h3>写入信息</h3><dl class="write"><form action="course_ceshi.jsp" method="post"><input type="hidden" name="renshu" value="<% out.print(rs.getString("dm_renshu"));%>" /><input type="hidden" name="kehao" value="<% out.print(rs.getString("dm_id"));%>" /><input type="hidden" name="kecheng" value="<% out.print(rs.getString("dm_class"));%>" /><dd>学号:<input type="text" name="xuehao" />(*学号只能为数字*)</dd><dd>姓名:<input type="text" name="username" />(*输入你的姓名*)</dd><dd>性别:<input type="radio" name="sex" value="男" checked="checked"/>男<input type="radio" name="sex" value="女"/>女</dd><dd>专业:<input type="text" name="classes" />(*输入你的专业*)</dd><dd><input class="name" type="submit" value="提交" /></dd> </form></dl></div></td></tr><tr><td colspan="2" height="55" style="background:url(images/1_06.gif) no-repeat"> </td></tr></table></body></html><%con.close();}catch(SQLException e){ out.print(e);}%>5、查询选课代码<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"><html xmlns="/1999/xhtml"><%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=gb2312"%><%@ page import="java.sql.*" %><%Connection con;Statement sql;ResultSet rs;try{ Class.forName("com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver");}catch(Exception e){ out.print(e);}try { String uri= "jdbc:sqlserver://127.0.0.1:1433;DatabaseName=text";String user="sa";String password="danmo0410.";con=DriverManager.getConnection(uri,user,password);sql=con.createStatement();rs=sql.executeQuery("SELECT top 8 * FROM dm_class ORDER BY dm_time ");%><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" /> <link href="style/view.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"><title>无标题文档</title></head><body><table width="850" border="0" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0"><tr><td width="580" height="185" style="background:url(images/1_01.gif) no-repeat"></td><td width="270" height="185" style="background:url(images/1_02.gif) no-repeat"></td></tr><tr><td height="353" colspan="2" style="background:url(images/1_05.gif) no-repeat"><div id="header"><ul><li><a href="index.jsp">首页</a></li><li><a href="course.jsp">选课列表</a></li><li><a href="view.jsp">查看选课</a></li><li><a href="admin.jsp">管理中心</a></li></ul></div><div id="center"><h3>查询选课</h3><dl><form action="view_aritle.jsp" method="post"><dd class="cha">输入学号:<input name="name" type="text"/><input type="submit" value="查询"/></dd></form><form action="view_aritle_a.jsp" method="post"><dd class="cha">输入课程:<input name="classname" type="text"/><input type="submit" value="查询"/></dd></form></dl><h3 style="clear:both;">课程详细</h3><dl><% while(rs.next()){ %><dd class="xi" style="background:url(images/gaoshi.gif) no-repeat center left;"><a href="view_aritle_b.jsp?id=<% out.print(rs.getInt("dm_id"));%>"><em><%out.print(rs.getDate("dm_time"));%></em><%out.print(rs.getString("dm_class"));%></a></dd><%}%></dl></div></td></tr><tr><td colspan="2" height="55" style="background:url(images/1_06.gif) no-repeat"> </td></tr></table></body></html><%con.close();}catch(SQLException e){ out.print(e);}%>六、数据库操作建立3张表:1.dm_class:课程表2.dm_new:新闻表3.dm_student:学生选课表七、设计结果本次课程设计—-学生在线选课系统,运用JSP命令以及数据库连接操作,使得程序运行成功。