英语语言学导论复习题
- 格式:doc
- 大小:29.50 KB
- 文档页数:4
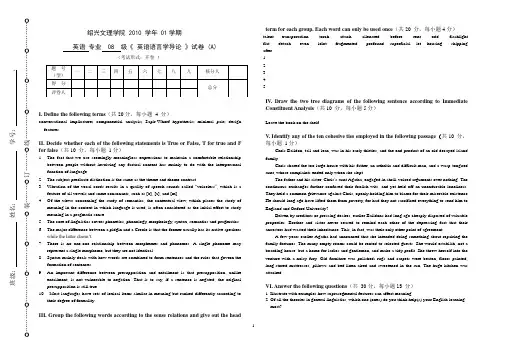
1绍兴文理学院 2010 学年 01学期英语 专业 08 级《 英语语言学导论 》试卷 (A)(考试形式:开卷 )I. Define the following terms (共20分,每小题 4 分)conversational implicature; componential analysis; Sapir-Whorf hypothesis; minimal pair; design featuresII. Decide whether each of the following statements is True or False, T for true and F for false (共10 分,每小题 1分)1. The fact that we use seemingly meaningless expressions to maintain a comfortable relationshipbetween people without involving any factual content has mainly to do with the interpersonal function of language.2.The subject-predicate distinction is the same as the theme and rheme contrast.3. Vibration of the vocal cords results in a quality of speech sounds called “voiceless ”, which is afeature of all vowels and some consonants, such as [b], [z], and [m].4. Of the views concerning the study of semantics, the contextual view, which places the study ofmeaning in the context in which language is used, is often considered as the initial effort to study meaning in a pragmatic sense.5. The core of linguistics covers phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics and pragmatics.6. The major difference between a pidgin and a Creole is that the former usually has its native speakerswhile the latter doesn’t.7. There is no one-one relationship between morphemes and phonemes. A single phoneme mayrepresent a single morpheme, but they are not identical.8. Syntax mainly deals with how words are combined to form sentences and the rules that govern theformation of sentences.9. An important difference between presupposition and entailment is that presupposition, unlikeentailment, is not vulnerable to negation. That is to say, if a sentence is negated, the original presupposition is still true.10. Most languages have sets of lexical items similar in meaning but ranked differently according totheir degree of formality.III. Group the following words according to the sense relations and give out the headterm for each group. Each word can only be used once (共20 分,每小题4分)talent transportation torch attach alienated before rent odd flashlight flat detach even idiot fragmented profound superficial let housing shipping after 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.IV . Draw the two tree diagrams of the following sentence according to Immediate Constituent Analysis (共10 分,每小题5分)Leave the book on the shelf.V . Identify any of the ten cohesive ties employed in the following passage (共10 分,每小题 1分)Chris Baildon, tall and lean, was in his early thirties, and the end-product of an old decayed island family.Chris shared the too large house with his father, an arthritic and difficult man, and a wasp-tongued aunt, whose complaints ended only when she slept.The father and his sister, Chris ’s aunt Agatha, engaged in shrill-voiced arguments over nothing. The continuous exchanges further confused their foolish wits, and yet held off an unendurable loneliness. They held a common grievance against Chris, openly holding him to blame for their miserable existence. He should long ago have lifted them from poverty, for had they not sacrificed everything to send him to England and Oxford University?Driven by creditors or pressing desires, earlier Baildons had long ago cheaply disposed of valuable properties. Brother and sister never ceased to remind each other of the depressing fact that their ancestors had wasted their inheritance. This, in fact, was their only other point of agreement.A few years earlier Agatha had announced that she intended doing something about repairing the family fortunes. The many empty rooms could be rented to selected guests. She would establish, not a boarding-house, but a home for ladies and gentlemen, and make a tidy profit. She threw herself into the venture with a noisy fury. Old furniture was polished; rugs and carpets were beaten, floors painted, long-stored mattresses, pillows and bed-linen aired and sweetened in the sun. The huge kitchen was attacked.VI. Answer the following questions (共 30分,每小题15 分)1. Illustrate with examples how suprasegmental features can affect meaning.2. Of all the theories in general linguistics, which one (ones) do you think help(s) your English learning most?。

Unit 3 The Units of EnglishF1. Phon etically, the stress of a compo und always falls on the first eleme nt, while the sec ond eleme nt receives sec on dary stress.F2. Words are the smallest meanin gful un its of Ian guage.T3. Just as a pho neme is the basic unit in the study of pho no logy, so is a morpheme the basic un it in the study of morphology.T4. The smallest meanin gful un its that can be used freely all by themselves are free morphemes.F5. Fore as in foretell is both a prefix and a bound morphemeT6. I nflectio nal morphemes man ifest various grammatical relati ons or grammatical categories such as nu mber, ten se, degree, and case.F7. Base refers to the part of word that rema ins whe n all in flect ional affixes are removedF8. There are rules that gover n which affix can be added to what type of stem to form a new word.Therefore, words formed accord ing to the morphological rules are acceptable words.T9. In most cases, prefixes cha nge the meaning of the base whereas suffixes cha nge the word-class of the base.F10. All words in En glish have a hierarchical structure.F11. Clippi ng is one of the three most importa nt devices of word-formati on inEn glish.T12. Idioms in En glish are modifiable in some grammatical ways.F13. The prese nee of con struct ions is unique to En glish.F14. Every En glish sentence has a subject.A1. Nouns, verbs and adjectives can be classified as _____________A lexical wordsB grammatical wordC fun ctio nD forwardsD2. The compound word “ bookstore ” is the place where books are sold. This in dicates that the meaning of a compo und ________________.A.is the sum total of the meaning of its comp onentsB.can always be worked out by look ing at the meanings of morphemesC.is the same as the meaning of a free phrase.D.None of the above.B3. The part of speech of the compo unds is gen erally determ ined by the part of speech of .A. the first eleme ntB. the sec ond eleme ntC. either the first or the sec ond eleme ntD. both the first and the sec ond eleme nts.A4. Morphemes that represe nt ten se, nu mber, gen der and case are called morphemeA in flecti onalB freeC fun ctio n wordsD derivati onalC5. ____________ is a branch of grammar which studies the in ternal structure of wordsand the rules by which words are formed.A. Syn taxB.GrammarC. Morphology D MorphemeC6. The meaning carried by the in flect ional morpheme is ____________ .A. lexicalB. morphemicC. grammaticalD. sema nticD7. Bound morphemes are those that ____________________ .A. have to be used in depe nden tlyB. can not be comb ined with other morphemesC. can either be free or boundD. has to be comb ined with other morphemesA8. ______ modifies the meaning of the stem, but usually do not cha nge the part ofspeech of the orig inal word.A. PrefixesB. SuffixesC. RootsD. AffixesB9. ____________ is ofte n thought to be the smallest meanin gful un its of Ian guage by thelin guists.A. WordsB. MorphemesC. Phon emesD. Senten cesB10. All of them are meanin gful except for __________________A lexemeB phon emeC morphemeD allomorphDiscuss the types of morphemes with examples.Free morphemes: They are the in depe ndent un its of meaning and can be used freelyall by themselves, for example, -” “theword “ bookish ” . Bound morphemes: They are those that cannot be used in depe nden tly but have to be comb ined with other morphemes, either free or bound, to form a word such as-ish ” in “ bookish ” . BoundMorphemes can be subdivided in to roots and affixes. A root is see n as part of a word; it can n ever sta nd by itself although it has a clear and defi nite meaning, such as “ genen the word“generate ” . Affixes are of two types: inflectional and derivatio nal. I nflect ional morphemes mani fest various grammatical relatio ns or grammaticalcategories such as-s” in the word “ books ” to indicate plurality of nouns. Derivati onal affixes are added to an exist ing form to create a word such as“ m-” in the word “ misinform ” . Derivational affixes can also be divided into prefixes and suffixes. Prefixes occur at the begi nning of a word such as - ” in “ dis the word “ dislike ” , while suffixes occur at the end of a word sieshBa's in the “word “ friendless ” .。
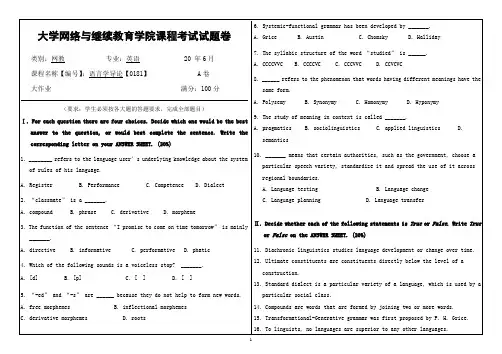
大学网络与继续教育学院课程考试试题卷类别:网教专业:英语 20 年6月课程名称【编号】:语言学导论【0181】 A卷大作业满分:100分(要求:学生必须按各大题的答题要求,完成全部题目)Ⅰ. For each question there are four choices. Decide which one would be the best answer to the question, or would best complete the sentence. Write the corresponding letter on your ANSWER SHEET. (20%)1. ________ refers to the language user’s underlying knowledge about the systemof rules of his language.A. RegisterB. PerformanceC. CompetenceD. Dialect2. “classmate” is a _______.A. compoundB. phraseC. derivativeD. morpheme3. The function of the sentence “I promise to come on time tomorrow” is mainly_______.A. directiveB. informativeC. performativeD. phatic4. Which of the following sounds is a voiceless stop? _______.A. [d]B. [p]C. []D. []5. “-ed” and “-s” are ______ because they do not help to form new words.A. free morphemesB. inflectional morphemesC. derivative morphemesD. roots 6. Systemic-functional grammar has been developed by _______.A. GriceB. AustinC. ChomskyD. Halliday7. The syllabic structure of the word “studied” is ______.A. CCCCVVCB. CCCCVCC. CCCVVCD. CCVCVC8. ______ refers to the phenomenon that words having different meanings have thesame form.A. PolysemyB. SynonymyC. HomonymyD. Hyponymy9. The study of meaning in context is called _______.A. pragmaticsB. sociolinguisticsC. applied linguisticsD.semantics10. _______ means that certain authorities, such as the government, choose aparticular speech variety, standardize it and spread the use of it across regional boundaries.A. Language testingB. Language changeC. Language planningD. Language transferⅡ. Decide whether each of the following statements is True or False. Write True or False on the ANSWER SHEET. (20%)11. Diachronic linguistics studies language development or change over time.12. Ultimate constituents are constituents directly below the level of aconstruction.13. Standard dialect is a particular variety of a language, which is used by aparticular social class.14. Compounds are words that are formed by joining two or more words.15. Transformational-Generative grammar was first proposed by P. H. Grice.16. To linguists, no languages are superior to any other languages.- 1 -- 2 -- 3 -。

《语言学导论》复习及各章节练习CHAPTERONEI.Designfeaturesoflanguage:productivity,duality,arbitrariness,anddisplacementII.Originoflanguage:•Themysteriousoriginofthelanguageorholyorigin•Bow-wow自然模声说•Yo-he-ho劳动号子说•Evolution进化说•Conventionalism约定俗成说•Innatism先天论•After-birthacquisition后天习得说•Gestures手势说•Embodiment体验说(Reality---cognition---language)III.Functionsoflanguage:informativefunction,interpersonalfunction,performativefunction,emotivefunction,phaticcommunion,recreationalfunctionandm etalingualfunctionIV.Linguisticsanditsbranches1.Sixperiodsoflinguistics•Philology传统语文学时期(19世纪前)•Historical&comparativelinguistics历史比较语言学时期(19世纪)•Structurallinguistics结构主义语言学时期(20世纪初)•Functionallinguistics系统功能主义语言学时期(20世纪中)•Transferredgenerativelinguistics转换生成语言学时期(20世纪中)•Cognitivelinguistics认知语言学时期(20世纪80年代)2.internalbranches:inrea-disciplinarydivisions(内部分支)1)Phonetics(语音学)studieshowspeechsoundsarepronounced,transmittedandperceived.2)Phonology(音系学)isthestudyoftherulesgoverningthestructure,distributionandsequencingofspeechsoundsandtheshapeofsyllables.(研究语音和音节的结构、分布和序列)3)Morphology(形态学)isconcernedwiththeinternalorganizationofwords.Itstudiestheminimalunitsofmeaning-morphemesandword-formationprocesses.4)Syntax(句法学)isthestudyoftherulesgoverningthewaysdifferentconstituentsarecombinedtoformsentencesinalanguage,orthestudyofinterre lationshipsbetweenelementsinsentencestructures.5)Semantics(语义学)isthestudyofhowmeaningisencodedinalanguage,oritisthestudyofmeaningoflinguisticunits,wordsandsentencesinparticular.6)Pragmatics(语用学)isthestudyofmeaningincontextorinuse.3.externalbranches:inter-disciplinarydivisions(外部分支:跨学科分支,即宏观语言学分支)1)Psycholinguisticsisthestudyoftheinterrelationoflanguageandmind.2)Sociolinguisticsstudiesthecharacteristicsoflanguagesvarieties,languagefunctionsandspeakersasthethreeinteractandchangewithi naspeechcommunity.3)Anthropologicallinguisticsstudiestheemergenceoflanguageandthedivergenceoflanguageoverthousandsofyears.4)Computationallinguisticsstudiestheuseofcomputerstoprocessorproducehumanlanguage.ChapterTwoPhonetics1.Sub-branchesofphoneticsArticulatoryphonetics:theproductionofspeechsoundsAcousticphonetics:thephysicalpropertiesofspeechsoundsAuditoryphoneticsorperceptualphonetics:theperceptivemechanismofspeechsounds2.GroupsofspeechsoundsConsonantsandvowels3.Waystodescribeconsonants1)positionofarticulation2)mannerofarticulation3)voicedorvoiceless4.Waystodescribevowels1)theheightoftongueraising(high,mid,low);2)thepositionofthehighestpartofthetongue(front,central,back)3)thelengthortensenessofthevowel(xorlongvs.short);4)lip-rounding(roundedvs.unrounded)ChapterThreePhonologyI.PhonemesandAllophones1.Phoneme:adistinctive,abstractsoundwithadistinctivefeature(具有区别意义的最小语音单位)2.Allophones:thevariantsofaphoneme(音位变体)3.Contrastivedistribution(对立分布):thetypicaltobefoundinMinimalPairs(最小对比对)。

英语专业导论试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 英语专业学生需要掌握的最基本的语言技能是:A. 阅读B. 写作C. 听力D. 口语答案:D2. 英语专业的核心课程之一是:A. 英语文学B. 英语翻译C. 商务英语D. 计算机科学答案:A3. 英语专业学生通常需要通过的英语水平考试是:A. TOEFLB. IELTSC. GRED. TEM-4答案:D4. 英语专业学生在学术研究中经常使用的数据库是:A. JSTORB. PubMedC. IEEE XploreD. ScienceDirect答案:A5. 英语专业学生在进行文学分析时,通常需要参考的文学理论包括:A. 马克思主义B. 女性主义C. 后殖民主义D. 所有以上选项答案:D6. 英语专业学生在进行跨文化交际学习时,需要了解的内容包括:A. 语言差异B. 文化习俗C. 社会规范D. 所有以上选项答案:D7. 英语专业学生在进行口译训练时,需要掌握的技能包括:A. 笔记技巧B. 同声传译C. 交替传译D. 所有以上选项答案:D8. 英语专业学生在进行写作训练时,通常需要遵循的写作原则包括:A. 清晰性B. 连贯性C. 逻辑性D. 所有以上选项答案:D9. 英语专业学生在进行翻译实践时,需要遵循的原则包括:A. 忠实性B. 通顺性C. 文化适应性D. 所有以上选项答案:D10. 英语专业学生在进行学术写作时,通常需要遵循的格式包括:A. MLAB. APAC. ChicagoD. 所有以上选项答案:D二、填空题(每空1分,共10分)11. 英语专业学生在进行文学研究时,经常使用的分析方法是________。
答案:文本分析12. 英语专业学生在进行语言教学时,常用的教学法包括________。
答案:交际法13. 英语专业学生在进行学术写作时,需要遵循的引用标准是________。
答案:MLA或APA14. 英语专业学生在进行口译训练时,需要掌握的口译类型包括________。

《语言学导论》平时测验1I. Fill in the blanks with the most suitable words. (24 points)1. Competence refers to an ideal language user’s underlying knowledge about the system of rules; and ______ refers to the ideal language user’s actual use of language in concrete situations.2.The design features of language are _________, duality, creativity and ________.3. ___________ transcription is used for the purpose of transcribing the minute difference between variations of the same sound. Take [ă]for example, to indicate that a vowel has been nasalized, we simply add a curved line to the top of the symbol [a].4. The four sounds /p/, /b/, /m/ and /w/ have one feature in common, i.e., they are all _______ sounds.5. Name the sound segments which matche the following descriptipns respectively.a._______ vocieless postalveolar fricative;b._________high back tense rounded vowel.6. A(n) ___________ is the smallest unit of sound that is of distinctive value. It is an abstract unit, a collection of distinctive phonetic features.7. _________ morphemes are those that cannot be used independently but have to be combined with other morphemes, either free or bound, to form a word8. Inflectional affixes very often only add a minute gammatical meaning to the stem, whereas ______ affixes often change the lexical meaning.9. According to structuralism, the ________ relation, or chain relation, is a relation beween one item and others in a sequence, or between elements which are all present.10. ((Poor) (John)) ((ran) (away)) is one representaion of ______________analysis, proposed by American linguist Bloomfield.II.Mark the choice that can best complete the statement. (24 points)1. _________ is a branch of grammar which studies the internal structure of words and the rules by which words are formed.A. SyntaxB. GrammarC. MorphologyD. Morpheme2.The study of a language as it changes though time is called ______ linguistics.A. diachronicB.synchronicC.functionalD.generative3. __________ is a voiced alveolar stop.A. /z/B. /d/C. /k/D. /b/4.______ has been widely accepted as the forefather of modern linguistics.A. ChomskyB. SaussureC. BloomfieldD. Halliday5. The different phones which can represent a phoneme in different phonetic environments are called the ____ of that phoneme.A. phonesB. soundsC. phonemesD. allophones6. Which vowel is different from others according to the kind of opening made at the lips?A. [i:]B. [כ]C. [e]D. [i]7. Since [p h] and [p=] are the variants of the phoneme /p/ and they never occur in the the samecontext, they are said to be ___________.A. in phonemic contrastB. in complementary distributionC. free variantsD. a minimal pair8. _________ are often thought to be the smallest meaningful unit of language in grammarby the linguists.A. WordsB. MorphemesC. PhonemesD. Sentences9. The English word “modernizers” is com posed of morphemes.A. fourB. threeC. twoD. five10. Based on the government and binding theory, the phrase “speak about the language” can be analysed as: “speak” is the head of this structure and __________“about the language”, and thus “speak” is the governor of “about thelanguage”.A. dominatesB. controlsC. c-commandsD. binds11. In Halliay’s view, the ______ function of language is realized in transitivity system in clauses as a representation of experience.A. interpersonalB. textualC. socialD. ideational12. In the sentence “She was a small woman, old and wrinkled”, the percentage of the function words is (nearly)______.A. 50%B. 40%C. 60%D. 70%III. Decide whether each of the following statements is True or False. Write T for True and F for False in the bracket before each of them. (16 points)1. ( ) The sentence “As the night fell, the wind rose.” doesn’t mean the same as “As the wind rose, the night fell”. This indicates a degree of non-arbitrariness about word order.2. ( ) In modern linguistics, diachronic study seems to enjoy priority over synchronic study.3. ( ) A voiceless consonant is produced without the obstruction of the airstream in the vocal tract.4. ( ) Inflectional suffixes never change the word class of the word they attach to.5. ( ) Recerived Pronunciation is the pronunciation accepted by most prople.6. ( ) All words contain a root morpheme.7. ( ) In terms of functional lingistics, Rheme is the element which serves as the starting point of the utterance, and the remainder of the utterance is called Residue.8. ( ) All syllables must have a nucleus but not all syllables contain an onset and a coda.IV. Define the following terms. (20 points)1. Parole---2. Coarticulation3. Inflection4. Deep structure5. Interpersonal functionV. Choose two from the following four questions and give your answers briefly. (16 points)1.Discuss about the distinctions between prescriptive and descriptive linguistics.2. How do you undertsatand the duality of language? Does the traffic lights have duality?3. To what extent is phonology related to phonetics and how do they differ?4. What are the methods for the formation of words in the English language? List at least four of them, and explain each of them with examples.。

英语语言学导论练习题英语语言学导论是一门研究英语语言结构、发展和使用的学科。
以下是一些练习题,旨在帮助学生更好地理解英语语言学的基本概念和理论。
练习题一:语音学1. 描述英语中的元音和辅音的区别。
2. 列举至少五种英语中的双元音,并说明它们的发音特点。
3. 解释“音位”和“音素”的区别,并给出例子。
练习题二:形态学1. 定义“形态学”并解释其在语言学中的重要性。
2. 举例说明英语中的派生词和复合词。
3. 描述英语中的不规则动词变化,并给出几个例子。
练习题三:句法学1. 简述句法研究的主要内容。
2. 用树状图表示一个简单英语句子的结构。
3. 解释“主语”、“谓语”和“宾语”在句子中的作用。
练习题四:语义学1. 定义“语义学”并解释其研究范围。
2. 描述“同义”和“反义”的概念,并给出英语例子。
3. 解释“语境”如何影响语言的意义。
练习题五:语用学1. 什么是语用学?它与语义学有何不同?2. 描述“指示语”、“礼貌原则”和“合作原则”在交际中的作用。
3. 举例说明如何在不同的社交场合中使用不同的语言风格。
练习题六:社会语言学1. 解释社会语言学研究的主要内容。
2. 讨论语言变异与社会身份之间的关系。
3. 描述双语现象及其对语言使用者的影响。
练习题七:心理语言学1. 心理语言学是如何研究语言的?2. 描述“语言习得”的过程及其理论。
3. 讨论“母语”和“第二语言”学习之间的差异。
练习题八:历史语言学1. 定义“历史语言学”并解释其研究目的。
2. 描述英语的发展历史和主要变化。
3. 讨论语言接触和借用对语言发展的影响。
完成这些练习题将有助于加深对英语语言学各个方面的理解,并提高分析和应用语言学理论的能力。
希望这些练习题能对你的学习有所帮助。

一、D: language acquisition device 语言习得机制2. Displacement: Displacement is that language can refer to the contexts removed from the immediate situations of the speaker. 移位法3、cultural transmission:文化传递性Animals call systems are genetically transmitted. Human languages are culturally transmitted.4. Interpersonal function: 人际关系Interpersonal function is the most important sociological use of language, by which people establish and maintain their status in a society. In addition, the ways in which people address others and refer to themselves indicate the various types of interpersonal relations. Finally, language marks our identity.5.Linguistics: Linguistics is defined as the systematic (or scientific) study of language 语言学6、Applied linguistics: Applied linguistics is a branch of study which apply linguistics to the research of other areas. 应用语言学7、Syntax: Syntax studies the rules governing the combination of words into sentences. 句法学8. morphology: Morphology is concerned with the internal organization of words. It studies the minimal units of meaning-morphemes and word-formation processes. 形态学二、1. Language acquisition and language learningLanguage acquisition is to get a language subconsciously and naturally with no great effort. Language learning is to get a language consciously with great efforts and usually under the teachers’ instruction.For instance, for most Chinese, their knowledge about their mother tongue-Chinese, is language acquisition, while their knowledge about English is language learning.2. Foreign language and second languageA language has gained official status in certain region or country is called second language, while foreign language has not.For example, for most Indians, English is their second language since English has gained official status in their country while English is regarded as foreign language in China.3. Expressive function and Evocative functionExpressive function is the use of language to reveal something about the feelings and attitudes of the speaker. In this function, language is used to evaluate, appraise and assert the speaker’s attitudes, etc.Evocative function is the use of language to create certain feelings in the hearer. It aims to amuse, startle, anger, soothe, worry or please.4. Phonetics and Phonology.Phonetics studies speech sounds, including the production of speech, that is, how speech sounds are actually made, transmitted and received, thedescription and classification of speech sounds, words and connected speech.Phonology is the branch of linguistics which studies the sound patterns of languages.5. Semantics and PragmaticsSemantics studies the meaning of languagePragmatics is the study of meaning in context.6. Synchronic and DiachronicSynchronic description takes a fixed instant as its point of observation. Diachronic linguistics is the study of a language through the course of its history.7. Langue and paroleLangue is the linguistic competence of the speaker. It refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all the members of a speech community.Parole is the actual phenomena or data of linguistics. It refers to the actualized language.Langue is abstract, stable, systematic and not actually spoken by anyone. Parole is specific, personal, subject to personal and situational constraints and always a naturally occurring event.petence and performance(语言能力和语言运用)A language user’s underlying knowledge about the system of rules iscalled his linguistic competence.Performance refers to the actual use of language in concrete situations.简答题:1. What are the design features of language?Arbitrariness任意性Duality二元性Creativity创造性Displacement移位性Culture transmission文化传递性Interchangeability互换性2. What is morpheme? Morpheme is the minimal unit of meaning. For example,“purify”consist of “pur” and“ify”,and the noun“disappearance” consist of three morphemes: appear, dis and ance. They all have meanings, and cannot be divided any more.3. What is phoneme? Example. Phoneme is the smallest linguistic unit of sound that can signal a difference in meaning. E.g.:/b/ /p/ /k/ /g/.4. What is the performative function of human language? Supply example s to illustrate.The performative function of language is primarily to change the social status of persons .It can also extend to the control of reality as on some magical or religions occasion .For example ,language is always used in the sentencing of criminals, the blessing of children and the naming of a ship at a launching ceremony.5. What are the basic three branches of phonetics?Articulatory phonetics, Acoustic phonetics, Auditory phonetics.6. Giving four branches of macrolinguistics.Psycholinguistics心理语言学sociolinguistics社会语言学Anthropological linguistics人类语言学Computational linguistics 计算语言学.7. What are the seven function of language.Informative信息功能interpersonal function人际功能performative 施为功能Emotive function感情功能phatic communion寒暄功能recreational function娱乐功能metalingual function元语言功能。

《英语语言学概论》精选试题11.Which of the following statements about language is NOT true?nguage is a systemnguage is symbolicC.Animals also have l anguagenguage is arbitrary2.Which of the following features is NOT one of the design features of language?A. SymbolicB. DualityC. ProductiveD. Arbitrary3.What is the most important function of language?A. InterpersonalB. PhaticC. InformativeD. Metalingual4.Who put forward the distinction between Langue and Parole?A. SaussureB. C homskyC. HallidayD. Anonymous5.According to Chomsky, which is the ideal user's internalized knowledge of his language?A. competenceB. paroleC. performanceD. langue6.The function of the sentence "A nice day, isn't it?" is .A. informativeB. phaticC. directiveD. performative7.Articulatory phonetics mainly studies .A.the physical properties of the sounds produced in speechB.the perception of soundsC.the combination of soundsD.the production of sounds8.The distinction between vowels and consonants lies in .A.the place of articulationB.the obstruction of airstreamC.the position of the tongueD.the shape of the lips9.Which is the branch of linguistics which studies the characteristics of speech sounds and provides methods for their description, classification and transcription?A. PhoneticsB. PhonologyC. SemanticsD. Pragmatics10.Which studies the sound systems in a certain language?A. PhoneticsB. PhonologyC. SemanticsD. Pragmatics11.Minimal pairs are used to .A.find the distinctive features of a languageB.find the phonemes of a languagepare two wordsD.find the allophones of languageually, suprasegmental features include ,length and pitch.A. phonemeB. speech soundsC. syllablesD. stress13.Which is an indispensable part of a syllable?A. CodaB. OnsetC. StemD. Peak三、判断1.The analyst collects samples of the language as it is used, not according to some views of how it should be used. This is called the prescriptive approach. F2.B road transcription is normally used by the phoneticians in their study of speech sounds. F台州学院考试题1.Articulatory Phonetics studies the physical properties of speech sounds.2.English is a typical intonation language.3.Phones in complementary distribution should be assigned to the same phoneme.4.Linguistic c is a native speaker’s linguistic knowledge of his language.1.The relationship between the sound and the meaning of a word is a .2.P refers to the realization of langue in actual u se.3.Linguistics is generally defined as t he s study of language.1.Which of the following branch of linguistics takes the inner structure of word as its main object of study?A. Phonetics.B. Semantics.C. M orphology.D. Sociolinguistics.3. Which of the following is a voiceless bilabial stop?A. [w].B. [m].C. [b].D. [p].6. What phonetic feature distinguishes the [p] in please and the [p] in speak?A.VoicingB. AspirationC. RoundnessD. Nasality11.Conventionally a is put in slashes.A. a llophoneB. phoneC. phonemeD. morphemenguage is tool of communication. The symbol “highway closed ”serves .A. an expressive functionB. an informative functionC. a performative functionD. a persuasive function14.Which of the following groups of words is a minimal pair?A. but/pubB. wet/whichC. cool/curlD. fail/find16.What are the dual structures of language?A. Sounds and letters.B. Sounds and m eaning.C. Letters and meaning.D. Sounds and symbols.19.Which of the following is one of the core branches of linguistics?A.Phonology.B.Psycho-linguistics.C.Sociolinguistics.D.Anthropology.IV. Translate the following linguistic terms: (10 points, 1 point each)A. From English to ChineseB. From Chinese to English1.acoustic phonetics6. 應用語言學2. closed class words4. distinctive featuresVI.Answer the following questions briefly. (20 points)1.Define phoneme. (4 points)2.Explain complementary distribution with an example.(5 points)3.What are the four criteria for classifying English vowels. (4 points)问答答案1. A contrastive phonological segment whose phonetic realizations are predictable by rules. (4 points)(or: A phoneme is a phonological unit; it is a unit that is of distinctive value.)2.The situation in which phones never occur in the same phonetic environment.(4 points)e.g. [p] and [p h] never occur in the same position. (1 point)3.the position of the tongue in the mouth(1 point), the openness of the mouth(1 point), the shape of the lips(1 point), and the length of the vowels. (1 point)Chapter 1 Introductions to LinguisticsI.Choose the best answer. (20%)nguage is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for humanA. contactB. communicationC. relationD. Community2.Which of the following words is entirely arbitrary?A. treeB. typewriterC. crashD. Bang3.The function of the sentence ―Water boils at 100 degrees Centigrade.‖ is.A. interrogativeB. directiveC. informativeD. Performative4.In Chinese when someone breaks a bowl or a plate the host or the people present are likely to say―碎碎(岁岁)平安‖as a means of controlling the forces which they believes feelmight affect their lives. Which functions does it perform?A. InterpersonalB. EmotiveC. PerformativeD. Recreational5.Which of the following property of language enables language users to overcome the barriers caused by time and place , due to this feature of language, speakers of a language arefree to talk about anything in any situation?A. TransferabilityB. DualityC. DisplacementD. Arbitrariness6.Study the following dialogue. What function does it play according to the functions of language?—Anice day, isn’t it?—Right! I really enjoy the sunlight.A. EmotiveB. PhaticC. PerformativeD. Interpersonal7.________ refers to the actual realization of the ideal language user’s knowledge of the rules of his language in utterances.A. PerformanceB. CompetenceC. LangueD. Parole8.When a dog is barking, you assume it is barking for something or at someone thatexists hear and now. It couldn’t be sorrowful for some lost love or lost bone. This indicat design feature of .A.cultural transmissionB.productivityC.displacementD. Duality9.answers such questions as how we as infants acquire our first language.A.PsycholinguisticsB.A nthropological linguisticsC.SociolinguisticsD.Applied linguistics10.deals with language application to other fields, particularly education.A.Linguistic theoryB.Practical linguisticsC.Applied linguisticsparative linguisticsII.Decide whether the following statements are true or false. (10%)11. Language is a means of verbal communication. Therefore, the communication way used by the deaf-mute is not language. F13.Speaking is the quickest and most efficient way of the human communication systems.nguage is written because writing is the primary medium for all languages. F15.We were all born with the ability to acquire language, which means the details language system can be genetically transmitted. F16.Only human beings are able to communicate. F17. F. de Saussure, who made the distinction between langue and parole in the early 20th century, was a French linguist. F18. A study of the features of the English used in Shake e s a p re’s time is an example of the diachronic 历时study of language. F19.Speech and writing came into being at much the same time in human history.F20. III.All the languages in the world today have both spoken and written forms.Fill in the blanks. (10%)Fnguage, broadly speaking, is a means of verbal_ communication.22.In any language words can be used in new ways to mean new things and can becombined into innumerable sentences based on limited rules. This feature is usually termed creativity_ .nguage has many functions. We can use language to talk about itself. This funct is .24.Theory that primitive man made involuntary vocal noises while performing heavywork has been c alled the yo-he-ho ________ theory.25.Linguistics is the systematic study of language.26.Modern linguistics is __ ________ in the sense that the linguist tries to discover what language is rather than lay down some rules for people to observe.27.One general principle of linguistic analysis is the primacy of over writing.28.The description of a language as it changes through time is a study.29.Saussure put forward two important concepts. refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all members of a speech community.30.Linguistic potential is similar to Saussure’s langue and Chomsky’s.I V.Explain the following terms, using examples. (20%)31.Design feature32.Displacementpetence34.Synchronic linguisticsV.Answer the following questions. (20%)35.Why do people take duality as one of the important design features of human language?Can you tell us what language will be if it has no such design feature? (南开大学,2004 )35.Duality makes our language productive. A large number of different units can be formed out o a small number of elements – for instance, tens of thousands of words out of a small set of sounds, around 48 in the case of the English language. And out of the huge number of words, there can be astronomical number of possible sentences and phrases, which in turn can combineto form unlimited number of texts. Most animal communication systems do not have this design feature of human language.If language has no such design feature, then it will be like animal communicational systemwhich will be highly limited. It cannot produce a very large number of sound combinations, e.g. words, which are distinct in meaning.Chapter 2 Speech SoundsI.Choose the best answer. (20%)1.Pitch variation is k nown as when its patterns are imposed on s entences.A. intonationB. toneC. pronunciationD. voice2.Conventionally a is put in slashes (/ /).A. allophoneB. phoneC. phonemeD. morpheme3.An aspirated p, an unaspirated p and an unreleased p are of the p phoneme.A. analoguesB. tagmemesC. morphemesD. allophones4.The opening between the vocal cords is sometimes referred to as .A. g lottisB. vocal cavityC. pharynxD. uvula6.A phoneme is a group of similar sounds called .A. minimal pairsB. allomorphsC. phonesD. allophones7.Which branch of phonetics concerns the production of speech sounds?A.Acoustic phoneticsB.Articulatory phoneticsC.Auditory phoneticsD.None of the above8.Which one is different from the others according to places of articulation?A. [n]B. [m]C. [ b ]D. [p]9.Which vowel is different from the others according to the characteristics of vowels?A. [i:]B. [ u ]C. [e]D. [ i ]10.What kind of sounds can we make when the vocal cords are vibrating?A. VoicelessB. V oicedC. G lottal s topD. ConsonantII.Decide whether the following statements are true or false. (10%)11.Suprasegmental phonology refers to the study of phonological properties of units larger thanthe segment-phoneme, such as syllable, word and sentence.12.The air stream provided by the lungs has to undergo a number of modification to acquire thequality of a speech sound.14.[p] is a voiced bilabial stop.15.Acoustic phonetics is concerned with the perception of speech sounds.16.All syllables must have a nucleus but not all syllables contain an onset and a coda.17.W hen pure vowels or monophthongs are pronounced, no vowel glides take place.18.According to the length or tenseness of the pronunciation, vowels can be divided into vs. lax or long vs. short.III.Fill in the blanks. (20%)21. Consonant sounds can be e ither ______ __ or _______ _, while all vowel sounds are .23. The qualities of vowels depend upon the position of the and the lips.25.Consonants differ from vowels in that the latter are produced without .26.In phonological analysis the words fail / veil are distinguishable simply because of the two phonemes /f/ - /v/. This is an example for illustrating .27.In English there are a number of _________ , which are produced by moving f rom one vowel position to another through intervening positions.28.refers to the phenomenon of sounds continually show the influence of their neighbors.29.is the smallest linguistic unit.IV.Explain the following terms, using examples. (20%)31.Sound assimilation32.Suprasegmental featureplementary distribution34.Distinctive featuresV.Answer the following questions. (20%)35.What is a coustic phonetics? (中国人民大学,2003 )36.What are the differences between voiced sounds and voiceless sounds in terms of articulation? (南开大学,2004 )VI.Analyze the f ollowing situation. (20%)37.Write the symbol that corresponds to each of the following phonetic descriptions; then give an English word that contains this sound. Example: voiced alveolar stop [d] dog. (青岛海洋大学,1999 )(1)voiceless bilabial unaspirated stop(2)low front vowel(3)lateral liquid(4)velar nasal(5)voiced interdental fricative32.Suprasegmental feature: The phonetic features that occur above the level of the segments are called suprasegmental features; these are the phonological properties of such units as the syllable, the word, and the sentence. The main suprasegmental ones includes stress, intonation, and tone.plementary distribution: The different allophones of the same phoneme never occur in the same phonetic context. When two or more allophones of one phoneme never occur in the same linguistic environment they are said to be in complementary distribution.34.Distinctive featureIst: refers to the features that can distinguish one phoneme from another. If we can group the phonemes into two categories: one with this feature and the other without, this feature is called a d istinctive feature.V. 35.Acoustic phonetics deals with the transmission of speech sounds through the air. When a speechsound is produced it causes minor air disturbances (sound waves). Various instruments are usedto measure the characteristics of these sound waves.36. When the vocal cords are spread apart, the air from the lungs passes between them unimpeded. Sounds produced in this way are described as voiceless; consonants [p, s, t] are produced in this way. But when the vocal cords are drawn together, the air from the lungs repeatedly pushes them apart as it passes through, creating a vibration effect. Sounds pr in this way are described as voiced. [b, z, d] are voiced consonants.11。

语⾔学导论期末考试试题(滨州学院外语系)语⾔学导论期末考试试题(滨州学院外语系)Ⅰ. Read each of the following statements carefully. Decide which one of the four choices best completes the statement and choose the letter A,B,C or D. (20%)1. _______ is best known and remembered for its contribution to phonology and the distinction between phonetics and phonology. The most influential scholar in this aspect is Trubetzkoy who published Principles of Phonology in 1939.A. The London SchoolB. Traditional grammarC. American StructuralismD. The Prague School2. Saussure believed that language is a system of signs. This sign is the union of a form and an idea,which Saussure called _______.A. langue and paroleB. signifier and signifiedC. speech and writingD. system and function3. Many modern linguists have criticized traditional grammarians for adopting a _____ approach to language study.A. synchronicB. diachronicC. prescriptiveD. descriptive4. The fact that different languages have different words for the same object is good proof that human language is_______.A. arbitraryB. rationalC. logicalD. cultural5. Palatal semi-vowel refers to the sound_______.A. [n]B. [h]C. [w]D. [j]6. A phoneme is a group of phonetically similar sounds called_______.A. minimal pairsB. allomorphsC. phonesD. allophones7. Morphemes that represent “tense”,“number”,“gender”,“case” and so forth are called_______morphemes.A. inflectionalB. boundC. freeD. derivational8. The English word “modernizers” is composed of_______morphemes.A. fourB. threeC. twoD. five9. “Unless I hear from her,I won’t leave this town” is a_______sentence.A. simpleB. coordinateC. complexD. compound10. In the phrase structure rule “S NP VP”,the arrow can be read as_______.A. is equal toB. consists ofC. hasD. generates11. In the following pairs of words,_______are a pair of complementary antonyms.A. old and youngB. male and femaleC. hot and coldD. buy and sell12. The stimulus-response theory was proposed by_______.A. FirthB. HallidayC. BloomfieldD. Chomsky13._______found that natural language had its own logic and thus concluded the famous Cooperative Principle.A. John AustinB. John FirthC. Paul GriceD. William Jones14. As far as the sentence “My bag is heavy” is concerned,linguists of pragmatics are more interested in its ______ meaning.A. literalB. logicalC. contextualD. grammatical15._______is defined as any regionally or socially definable human group identified by shared linguistic system.A. A speech communityB. A raceC. A societyD. A nation16. A speaker’s knowledge of the total set of rules,conventions,etc.,governing the skilled use of language in a society is termed ______.A. competenceB. performanceC. communicative competenceD. communicative strategy17. The phonemes /k/,/a:/ and /p/ are in ______ relations in the words /ka:p/ (carp)and /pa:k/ (park).A. synchronicB. syntagmaticC. diachronicD. paradigmatic18. The Prague School claims that a sentence may be analyzed from the functional side in terms of ______as well as from the grammatical side.A. theme and rhemeB. argument and predicateC. subject and predicateD. performative and constative19. In the proposition “Professor Green is a linguist”,the predicate linguist is a ______.A. no-place predicateB. one-place predicateC. two-place predicateD. three-place predicate20. The following conversation exchange clearly violates ______.A: Let’s get the kids something.B: Okey,but I veto I-C-E-C-R-E-A-M-S.A. maxim of QuantityB. maxim of QualityC. maxim of RelationD. maxim of MannerⅡ. Decide whether the following statements are true or false. Write T for true and F for false. (20%)1. By arbitrariness Saussure means that the forms of linguistic signs bear some natural relationship to their meaning.()2. Human language is,unlike animal communication systems,stimulus free.()3. Language marks our identity,physically in terms of age,sex,and voiceprints;geographically in terms of accents,dialects.()4. The sentencing of criminals is an example of emotive function of language.()5. Synchronic linguistic is the study of a language through the course of its history.()6. Pre-school children know virtually all the rules of language except for some subtleties. This means they have the underlying knowledge about the system of rules.()7. The sound〔z〕is a voiced alveolar stop.()8. The free variants of a phoneme shown in the different pronunciation of the same word,such as “tap” may be caused by habit,or individual preference,rather than by any distribution rule.()9. Voicing is a distinctive feature for English consonants.()10. A syllable that has no coda is called a closed syllable.()11. In English,inflectional affixes are mostly prefixes.()12. In the word “illegal”,“il” is an allomorph of the negativ e morpheme.()13. The word “girl” used to mean “young person of either sex”. Today it means “young woman”. This is an example of broadening of meaning.()14. The value of a linguistic sign is determined by the signs with which it can combine to form a syntagmatic relation,and the signs with which it can form a paradigmatic relation.()15. The phrase “five children” is an endocentric construction. ()16. Componential analysis can not help explain the sense relations of words.()17. The sentence I pour some liquid into the tube is a performative one.()18. The sentence like War is war is an example in which the Quality maxim is violated.()19. The weak version of the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis says that language is the shaper of our thinking patterns.()20. Malinowsky believed that the context of situation is indispensable for the understanding of the words.()Ⅲ. Explain the following linguistic terms or notions in English. (40%)1. Trace2. Displacement3. Stem4. Dissimilation5. Diacritics6. Theme7. Relational opposites8. Sapir-Whorf Hypotheses9. Predicate logic10. Conversational implicatureⅣ. Give brief answers to the following questions. (12+8=20)1. What are the main concerns of general linguistics?2. Explain the speech act theory with examples.试题标准答案及评分标准⽤纸课程名称语⾔学导论(B卷)Ⅰ. Read each of the following statements carefully. Decide which one of the four choices best completes the statement and choose the letter A,B,C or D. (120=20)1. A2. D3.A4. C5. B6. C7. D8. D9. D10. B11.A12. A13. C14. D15. C16. B17.C18. C19. B20.DⅡ. Decide whether the following statements are true or false. Write T for true and F for false. (120=20)1. T2. F3. T4. F5. T6. T7. F8. T9. F10. T11. F12. T13. F14. F15. T16. T17. F18. F19. T20. TⅢ. Explain the following linguistic terms and notions in English. (210=20)1. Trace—(By Chomsky)A phonetically null element to occupy the position from whicha syntactic element has been moved. That is,after the movement of an element,there will be a trace left in the original position.2. Displacement--It means that human lges enable their users to symbolize (refer to)objects,events and concepts which are not present (in time and space)at the moment of communication.3. Stem—Any morpheme or combination of morphemes to which an inflection affix can be added. A stem can be equivalent to a root or may contain a root and a derivational affix.4. Dissimilation-- It refers to the influence exercised by one sound segment on the production of another,so that the two sounds in a sequence become less alike or different.5. Diacritics--A set of symbols added to the letter symbols to make minute (slight)difference between variations of the same sound than the letters alone make possible.6. Theme--It refers to “that which is known or at least obvious in the given situation and from which the speaker proceeds”7. Relational opposites--Converse antonymy is typically seen in reciprocal social roles,kinship relations,temporal and spatial relations,there are always 2 entities involved,one presupposes the other.8. Sapir-Whorf Hypotheses--Our lge helps mould our way of thinking,and therefore,different lges may probably express our unique way of understanding the world. On the one hand,lge may determine our thinking patterns;on the other hand,similarity between lges is relative,the greater their structural differentiation is,the more diverse their conceptualization of the world will be.9. Predicate logic--It studies the internal structure of simple propositions. (Or,it deals with expressions containing predicates,arguments and quantifiers).10. Conversational implicature--It is a type of implied meaning,which can be deduced on the basis of the conventional meaning of words together with the context,under theguidance of the CP and its maxims. It is comparable to illocutionary force in that they are both concerned with the contextual meaning.IV. Give brief answers to the following questions. (12+8=20)1. What are the main concerns of general linguistics?General linguistics includes at least five parameters,namely,phonology,morphology,syntax,semantics and pragmatics. The following are the main branches of linguistics. (2)Phonetics studies the speech sounds,including the production of the speech.Phonology studies the rules governing the structure,distribution,and sequencing of speech sounds and the shape of syllables.(2 points)Morphology is concerned with the internal organization of words.It studies the minimal units of meaning ---morphemes and word-formation. (2)Syntax is about principles of forming and understanding correct English sentences. The form or structure of a sentence is governed by the rules of syntax. (2)Semantics studies how meaning is encoded in a language.(2)Pragmatics is the study of meaning in context. (2)2. Explain the speech act theory with examples.Speech act theory was put forward by J Austin in 1950s. His first shot at the theory is the claim that there are two types of sentences: performative and constatives. (2)The uttering of these sentences is the doing of an action.They are called performatives. (1) E.g. a. I name this ship the queen Elizabeth. b. I promise to finish the work in time. c. I bet you sixpence it will rain tomorrow. (2)While a sentence like this "I pour some liquid into the tube." is called constative. It is a description of what the speaker is doing at the time of speaking.(3)。

大三下语言学导论期末考试题目英语一、听力第一节(共5小题,每小题1分)听下面5段对话。
每段对话后有一个小题,从题中所给的A、B、C三个选项中选出最佳选项,并标在试卷的相应位置。
听完每段对话后,你都有10秒钟的时间来回答有关小题和阅读下一小题。
每段对话仅读一遍。
1、Who is the man talking about now?A.His girlfriend.B.His sister.C.His mother.2、What are they talking about?A.A traffic accident.B.A fire.C.A crime.3、Where does the conversation most probably take place?A.At a bookshop.B.At a kitchen.C.At a bank.4、Who was injured?A.George.B.George’s wife.C.George’s wife’s father.5、What do we learn from the conversation?A.Tony could not continue the experiment.B.Tony finished the experiment last night.C.Tony will go on with his experiment.第二节(共15小题,每小题1分)听下面5段对话或独白。
每段对话或独白后有几个小题,从题中所给的A、B、C三个选项中选出最佳选项,并标在试卷的相应位置。
听每段对话或独白前,你将有时间阅读各个小题,每小题5秒钟;听完后,各小题将给出5秒钟的作答时间。
每段对话或独白读两遍。
听第6段材料,回答第6至7题。
6、Where does this conversation most likely take place?A.In the street.B.At the woman’s home.C.Over the phone.7、What is the woman going to do tonight?A.Help her sister with English.B.Meet her friend at the station.C.Go to an exhibition with her parents.听第7段材料,回答第8至10题。
语言导论试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 语言的最小意义单位是:A. 音素B. 词C. 语素D. 句答案:C2. 下列哪个选项不是语言的功能?A. 信息传递B. 情感表达C. 娱乐消遣D. 社会规范答案:C3. 语言的起源可以追溯到:A. 古代文明B. 史前时代C. 现代文明D. 工业革命答案:B4. 语言学研究的主要对象是:A. 语言结构B. 文学作品C. 社会现象D. 历史事件答案:A5. 语言的演变主要受到以下哪个因素的影响?A. 社会变迁B. 科技发展C. 人口迁移D. 所有以上答案:D6. 语言的方言差异主要体现在:A. 词汇B. 语法C. 发音D. 所有以上答案:D7. 语言的标准化通常包括:A. 词汇的统一B. 语法的规范C. 语音的标准化D. 所有以上答案:D8. 语言的交际功能主要体现在:A. 信息的传递B. 情感的交流C. 思想的表达D. 所有以上答案:D9. 语言的符号性特征主要体现在:A. 语音和意义的结合B. 书写和意义的结合C. 符号和意义的结合D. 所有以上答案:C10. 语言的创造性主要表现在:A. 新词汇的创造B. 新语法结构的创造C. 新表达方式的创造D. 所有以上答案:D二、填空题(每题2分,共10分)1. 语言的______性是指语言能够表达无限多的意义。
答案:创造性2. 语言的______性是指语言能够传递信息、表达情感和思想。
答案:交际性3. 语言的______性是指语言能够随着社会的发展而不断变化。
答案:动态性4. 语言的______性是指语言能够通过符号来表达意义。
答案:符号性5. 语言的______性是指语言能够按照一定的规则来组织词汇和语法结构。
答案:规则性三、简答题(每题5分,共20分)1. 简述语言与思维的关系。
答案:语言与思维紧密相关,语言不仅是思维的工具,也是思维的表达形式。
语言的结构和词汇影响着人们的认知和思维方式,而思维的发展也推动了语言的丰富和变化。
Chapter 1 Invitations to LinguisticsI. Define the following terms.design features synchronic diachronic prescriptive descriptive arbitrariness duality displacement metalanguage competence phatic communion macrolinguistics performance langue parole II. Choose the best answer.1. Linguistics is the scientific study of __________.A. a particular languageB. the English languageC. human languages in generalD. the system of a particular language2. Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human __________.A. contactB. communicationC. relationD. community3. The function of the sentence “Water boils at 100 degrees Centigrade.” is __________.A. interrogativeB. directiveC. informativeD. performative4. In Chinese when someone breaks a bowl or a plate the host or the people present are likely to say“碎碎(岁岁)平安”as a means of controlling the forces which the believers feel might affect their lives. Which function does it perform?A. InterpersonalB. EmotiveC. PerformativeD. Recreational5. Which of the following property of language enables language users to overcome the barriers caused by time and place, due to this feature of language, speakers of a language are free to talk about anything in any situation?A. CreativityB. DualityC. DisplacementD. Arbitrariness6. Study the following dialogue. What function does it play according to the functions of language?—A nice day, isn’t it?— Right! I really enjoy the sunlight.A. EmotiveB. PhaticC. PerformativeD. Interpersonal7. __________ refers to the actual realization of the ideal language user’s knowledge of the rules of his language in utterances.A. PerformanceB. CompetenceC. LangueD. Parole8. When a dog is barking, you assume it is barking for something or at someone that exists here and now. It couldn’t be sorrowful for some lost love or lost bone. This indicates the design feature of __________.A. ArbitrarinessB. productivityC. displacementD. duality9. __________ answers such questions as how we as infants acquire our first language.A. PsycholinguisticsB. Anthropological linguisticsC. SociolinguisticsD. Applied linguistics10. ______ is the study of how language works in social interaction.A. SociolinguisticsB. PsycholinguisticsC. Cognitive linguisticsD. Neurolinguistics11. Which of the following words is entirely arbitrary?A. treeB. typewriterC. crashD. bang12. As modern linguistics aims to describe and analyze the language people actually use, and not to lay down rules for "correct" linguistic behavior, it is said to be ___.A. prescriptiveB. sociolinguisticC. descriptiveD. psycholinguistic13. The branch of linguistics that studies how context influences the way speakers interpret sentences is called ___.A. semanticsB. pragmaticsC. sociolinguisticsD. psycholinguistics14. The fact that different languages have different words for the same object is good proof that human language is ______.A. arbitraryB. non-arbitraryC. logicalD. non-productive15. The study of how words are combined to form sentences is called _______.A. phoneticsB. morphologyC. syntaxD. semantics16. ______ is the study of the linguistic meaning of words and sentences.A. SemanticsB. PragmaticsC. SyntaxD. MorphologyⅢ. Blank-filling.1. Language is a system of ________ ________ symbols used for human communication.2. Linguistics is generally defined as the ________ study of ________.3. If a linguistic study describes and analyzes the language people actually use, it is said to be ________; if it aims to lay down rules for “correct” behavior, it is said to be ________.4. In modern linguistics, ________ study seems to enjoy priority over ________ study. The reason is that successful studies of various states of a language would be the foundations of a historical study.5. Langue refers to the ________ linguistic system shared by all the members of a speech community; and parole refers to the ________ of langue in actual use.6. Chomsky de fines competence as the ideal user’s ________ of the rules of his language, and performance, the actual ________ of this knowledge in linguistic communication.7. “A rose by any other name would smell as sweet”. This famous quotation from Shakespeare illustrate that language has the design feature of ________.8. The property of ________ of language provides a speaker with an opportunity to talk about a wide range of things, free from barriers caused by separation in time and place.9. Language is a system, which consists of two sets of structures, one of ________, and the other of ________. This double articulation of language enables its users to talk about anything within their knowledge.10. An English speaker and a Chinese speaker are both able to use language,but they are not mutually intelligible, which shows that language is culturally ________.11. Human language is arbitrary. This refers to the fact that there is no logical or intrinsic connection between a particular sound and the __________ it is associated with.12. When language is used for establishing an atmosphere or maintaining social contact rather than exchanging information or ideas, its function is ______________ function.13. The features that define our human languages can be called __________ features.14. Saussure took a __________ view of language, while Chomsky looks at language from a __________ point of view.IV. Decide whether the following statements are true or false.1. Language is a means of verbal communication. Therefore, the communication way used by the deaf-mute is not language. ( )2. Speaking is the quickest and most efficient way of the human communication systems. ( )3. Language is written because writing is the primary medium for all languages. ( )4. Human capacity for language has a genetic basis, i.e. we are all born with the ability to acquire language and the details of a language system are genetically transmitted. ( )5. Only human beings are able to communicate. ( )6. F. de Saussure, who made the distinction between langue and parole in the early 20th century, was a French linguist. ( )7. A study of the features of the English used in Shakespeare’s time is an example of the diachronic study of language. ( )8. All the languages in the world today have both spoken and written forms. ( )9. Historical linguistics equals to the study of synchronic study. ( )10. Language is arbitrary by nature but it is not completely arbitrary. ()11. Language is the instrument of thought, record of facts, and people often feel need to speak their thoughts aloud. This indicates that language has an expressive function. ()12. A baby’s babbling, widespread use of verbal dueling, poetry writing as well as self-singing all show that language can be used to amuse the speaker.()13. The most important sociological use of language is the recreational function, by which people establish and maintain their status in society.()Ⅴ. Questions.1. A story by Robert Louis Stevenson contains the sentence “As the night fell, the wind rose.” Could this be expressed as “As the wind rose, the night fell?” If not, why? Does this indicate a degree of non-arbitrariness about word order?Yes. It is a case in point to illustrate non-arbitrariness about word order. When the two parts interchange, the focus and the meaning of the sentence is forced to change, because clauses occurring in linear sequence without time indicators will be taken as matching the actual sequence of happening. The writer’s original intention is distorted, and we can feel it effortlessly by reading. That is why systemic-functionalists and American functionalists think language is not arbitrary at the syntactic level.2. The recursive nature of language provides a theoretical basis for the creativity of language. Can you write a recursive sentence?3. There are many expressions in language which are meta-lingual or self-reflexive, namely, talking about talk and thinking about thinking, for instance, to be honest, to make a long story short, come to think of it, on second thought, can you collect a few more to make a list of these expressions? When do we use them most often?4. Comment on the following prescriptive rules. Do you think they are acceptable?(A) It is I.(B) It is me.You should say A instead of B because “be” should be followed by the nominative case, not the accusative according to the rules in Latin.(A) Who do you speak to?(B) Whom do you speak to?You should say B instead of A.(A) I haven’t done anything.(B) I haven’t done nothing.B is wrong because two negatives make a positive.5. Why do people take duality as one of the important design features of human language? Can you tell us what language will be if it has no such design feature? (南开大学,2004)Duality makes our language productive. A large number of different units canbe formed out of a small number of elements –for instance, tens of thousands of words out of a small set of sounds, around 40 in the case of the English language.And out of the huge number of words, there can be astronomical number of possible sentences and phrases, which in turn can combine to form unlimited number of texts. Most animal communication systems do not have this design feature of human language.If language has no such design feature, then it will be like animal communicational system which will be highly limited. It cannot produce a very large number of sound combinations, e.g. words, which are distinct in meaning.6. You may be familiar with the following proverbs. How do you perceive them according to the arbitrariness and conventionality of language?The proof of the pudding is in the eating.Let sleeping dogs lie.You can’t make a silk purse out of a sow’s ear.Rome was not built in a day.When in Rome, do as the Romans do.All roads lead to Rome.。
英语专业语言学导论考试试题一、选择题1、以下哪个选项不属于语言学的范畴?A.语音学B.句法学C.语义学D.政治学2、下列哪一项不是语言学的研究对象?A.语言的发音机制B.语言的语法结构C.语言的社交功能D.语言的生物属性3、哪种语言学理论认为语言是自然现象?A.行为主义理论B.先天语言能力理论C.进化语言学理论D.交际语言学理论二、简答题1、请简述语言学中的索绪尔假设是什么?并解释其对语言学研究的影响。
2、请阐述结构主义语言学的基本观点及其主要贡献。
3、请说明语言学中的“能指”和“所指”概念,并举例说明。
三、论述题1、请结合实例论述语言学中的“语境”概念,以及它在语言使用中的作用。
2、请阐述语言学中的“言语行为理论”,并说明其对语言习得和语言交际的指导意义。
四、分析题请分析以下这段话,并说明其中涉及了哪些语言学概念?“在这个句子中,主语是‘我’,谓语是‘喜欢’,宾语是‘巧克力’,这是一个简单的陈述句。
”(提示:句子结构、主谓宾、句法等)以下哪个不是教育技术学的主要研究对象?()教育技术学中的“技术”一词通常指的是()。
以下哪一项不是教育技术学的发展历程?()以下哪个理论是教育技术学中的基础理论?()请从技术角度说明教育技术学对教育的推动作用。
请论述教育技术学对教育改革的影响。
专业英语八级考试是针对英语专业学生的高难度语言考试,旨在测试学生的英语综合能力,包括听力、阅读、写作和翻译等方面的技能。
以下是一份专业英语八级考试试题的样例,供大家参考。
听一段录音材料,根据问题选择答案。
录音材料涉及一些学术领域的讨论,包括社会科学、自然科学等。
问题类型包括选择题和填空题。
阅读一篇文章,回答问题。
文章可能涉及一些学术领域的内容,包括社会科学、自然科学等。
问题类型包括选择题和问答题。
根据给定的主题写一篇文章,字数要求在500字左右。
文章主题可能涉及一些学术领域的内容,例如文化、历史、经济等。
文章需要结构清晰,语法正确,表达准确。
《语言学导论》复习思考题Ⅰ. In each question there are four choices. Decide which one would be the best answer to the question, or best completes the sentence. Write the corresponding letter on your ANSWER SHEET.1. According to Noam Chomsky, language is the product of_______.A. an innate faculty, unique to humansB. communicationC. environmental conditioningD. all of the above2. Which of the following statements is FALSE ________.A. Language is just for communication.B. Language is one of many ways in which we experience the world.^C. Language is a sign system.D. Language is arbitrary and conventional.3. Which one of the following statements about errors in foreign language learning in FALSE _________.A. Errors can not be avoided in foreign language learning.B. Errors tell the teacher how far towards the goal the learner has progressed and consequently what remains for him to learn.C. Errors are something bad that should not be allowed in foreign language learning.D. Errors provide the researcher with evidence of how language is learned or acquired, what strategies or procedures the learner is employing is his discovery of the language.4. The English language has______.【A. morphemesB. syntaxC. number agreementD. all of the above5. “He” and “she” are not examples of gender agreement in English, because_____.A. they are pronounsB. they need not agree with other words in an English sentenceC. they mark biological/social genderD. both b and c above6. A phoneme is_____.A. the smallest meaningful unit in language—B. the smallest unit in languageC. the same as an allophoneD. both b and c above7. Of the following, what are the two types of phonetics______.A. acoustic and electricB. arbitrary and auditoryC. articulatory and acousticD. allophonic and allomorphic8. /Wik/ is a transcription of_______.A. sickB. chickC. chicD. thick、9. The Black English sentence “I don't gotta do nothing” is consid ered incorrect because________.A. it contains a double negative and is thus inherently incorrectB. it is impossible to understandC. it is not associated with the upper class use of standard EnglishD. both a and b above10. The use of non-standard English persists because_______.A. the working class is incapable of speaking “correctly”【B. English is a complicated and therefore difficult language to masterC. subordinate groups use non-standard English to promote solidarityD. teachers do not properly stress the importance of standard English in schools11. True or false: Chinese has no inflections for grammatical case. ______.A. TrueB. False12. What is defined as 'the study of sentence structure' ______.A. MorphologyB. SemanticsC. PhonologyD. Syntax13. ______ refers to the fact that there is no necessary or logical relationship between a linguistic form and its meaning. ______.%A. DisplacementB. creativityC. arbitrarinessD. duality14. The study of a language at some point of time is called________.A. computational linguisticsB. sociolinguisticsC. diachronic linguisticsD. synchronic linguistics15. ________ refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all the members ofa speech communityA. LangueB. performanceC. competenceD. parole16. Traditional grammar is ________.A. descriptiveB. prescriptiveC. non-Latin-basedD. wrong^17. ______ is the branch of linguistics which studies the characteristics of speech sounds and provides methods for their description, classification and transcription.A. PhonologyB. Phonetic alphabetC. Corpus linguisticsD. Phonetics18. _____ is the minimal unit in the sound system of a language, which is of distinctive value.A. AllophoneB. PhoneC. PhonemeD. Morpheme19. Which of the following factors does not help to identify a word ______.A. Relative shortness uninterruptibilityC. A minimum free formD. Stability20. Speech act theory was initially developed by _______.~A. HallidayB. AustinC. SearleD. Grice21. The four major modes of semantic change are_______.A. extension, narrowing, elevation and degradationB. extension, generalization, elevation and degradationC. extension, narrowing, specialization and degradationD. extension, elevation, amelioration and degradation22. The relation between the two words “husband” and “wife” can be described as____.A. gradable antonymyB. converse antonymy|C. complementary antonymyD. synonymy23. “friendly” is a _______.A. compoundB. inflectional wordC. derivativeD. morpheme24. The construction “honest people” is _______.A. a coordinate constructionB. an exocentric constructionC. an endocentric constructionD. an immediate constituent25. The word “brunch” and “motel” are _______.-A. formed by blendingB. acronymsC. coined by back-formationD. clipped words26. The function of the sentence “A nice day, isn’t it” is _______.A. directiveB. informativeC. performativeD. phatic27. Which of the following sounds is a voiced bilabial stop ______.A. [m]B. [v]C. [p]D. [b]28. Which of the following sounds is a voiceless affricate _______.A. [w]B. [f]C. [tF]D. [dV];29. In the sentence “Can I have a bite to drink” the speaker may not have a problem with competence, but with_______.A. performanceB. utteranceC. syntaxD. context30. The phrase “Colorful ideas sleep furiously” is an example of_______.A. rapport talkB. indexical languageC. an ungrammatical but acceptable sentenceD. a grammatical but unacceptable sentence31. There are ______ morphemes in the word “children’s”!A. sixB. twoC. threeD. four32. The words “take” and “table” are called _______ because they can stand asa word by themselves.A. inflectional morphemesB. free morphemesC. stemsD. roots33. Identify the morphemes in the word 'unimaginative':A. un-im-ag-in-at-iveB. un-imaginativeC. un-imagin-ativeD. unimagin-ative34. Which of the following two-term sets shows the feature of complementarity _______.`A. Husband/ WifeB. Alive/DeadC. Hot/ ColdD. White/ Black35. The Whorf Hypothesis claims that________.A. language is full of “rich points”, whose meanings are difficult to translate into another languageB. abstract terms are easily translatableC. accents are part of identityD. language influences culture-specific ways of knowing36. The phrase ‘time is a commodity’ is an example of_______.A. The Whorf HypothesisB. A metaphoric system'C. A non-standard varietyD. A rich point37. The last phoneme in the word “hang” is a _______.A. glottalB. palatalC. dentalD. nasal38. Three places of articulation that involve the teeth and/or the lips are:A. palatal, velar, glottalB. bilabial, labiodental, dentalC. stop, fricative, affricativeD. nasal, lateral, semi vowel39. In the sentence 'I took my big brown cat to the vet yesterday', which of the following does not appear _______.A. AdjectiveB. PrepositionC. AdverbD. Conjunction-40. What is the meaning relationship between the two words “plant/grass” ______.A. HomonymyB. AntonymyC. HyponymyD. Allomorphs41. The syllabic structure of the word “linguistics” is ______.A. CVCCVCCVCCB. CVCCCVCCVCCC. CVCCVVCCVCCD. CVCVVCCVCC42. The phonetic transcription with diacritics is called _____.A. broad transcriptionB. International Phonetic AlphabetC. American English PronunciationD. narrow transcription(43. The Black English sentence “I don't gotta do nothing” is considered incorrect because:a) it contains a double negative and is thus inherently incorrectb) it is impossible to understandc) it is not associated with the upper class use of standard Englishd) both a and b above44. According to their ______, words can classified into closed-class and open-class words.A. variabilityB. membershipC. similaritiesD. functions45. When language is used to "do things", it serves the _____ function.|A. evocativeB. expressiveC. directiveD. performative46. "Classroom" is a _______.A. free morphemeB. derivativeC. compoundD. root.47. The phrase “time is a commodity” is an example of_______.A. The Whorf HypothesisB. A metaphoric systemC. A non-standard varietyD. A rich point48. _______ is a type of phonological process by which one sound takes on some or all the characteristics of a neighboring sound.A. AssimilationB. TransformationC. Code-switchingD. interference/49. _______ refers to the use of a native language pattern or rule which leads to an error or inappropriate form in the target language.A. InterlanguageB. Positive transferC. Negative transferD. Overgeneralization50. In the sentence “I took my big brown cat to the vet yesterday”, which of the following does not appear _______.A. AdjectiveB. PrepositionC. AdverbD. Conjunction51. _______ is that part of the meaning of word or phrase that relates it to phenomena in the real world or in a fictional or possible world.A. ConnotationB. Affective meaningC. DenotationD. Sense52. A linguist regards the changes in language and language use as ______.|A. unnaturalB. something to be fearedC. naturalD. abnormal53. The semantic components of the word “boy” can be expressed as _____.A. +human, +male, +adultB. +human, -male, +adultC. +human, -male, -adultD. +human, +male, -adult54. Conjunctions, preposition, pronouns and articles can be classified as ____.A. lexical wordsB. grammatical wordsC. pro-formsD. content words55. If two sounds are of no distinctive value, but are varieties of the same phoneme, they are called ______./A. phonesB. speech soundsC. allophonesD. morphs56. In the following sounds, _____ is a voiced stop.A. [b]B. [d]C. [p]D. [k]57. “You stand up” is transformed into “Stand up”. Which transformational rule is used according to TG Grammar _____.A. CopyingB. AdditionC. ReorderingD. Deletion58. The words such as TOFEL, NATO, UFO are _____.A. formed by blendingB. acronymsC. coined by back formationD. clipped words~59. The words such as “brunch”, “motel” are _______.A. formed by blendingB. acronymsC. coined by back formationD. clipped words60. ______ are produced when the obstruction is complete at first, then released slowly with friction resulting from partial obstruction.A. NasalsB. GlidesC. FricativesD. Affricatives61. “A fish is swimming in the pond” is transformed into “There is a fish swimming in the pond”. Which of the following transformational rules is used ______.A. CopyingB. AdditionC. ReorderingD. Deletion62. “The man put on his hat” is transformed into “The man put his hat on”. Which transformational rule is applied here _______.[A. CopyingB. AdditionC. ReorderingD. Deletion63. The function of the sentence “A nice day, isn’t it” is ______.A. directiveB. informativeC. emotiveD. phatic64. Which of the following sounds is a voiceless bilabial stop _____.A. [m]B. [f]C. [p]D. [b]65. Which of the following languages is a tone languageA. RussianB. ChineseC. EnglishD. French66. ________ speaking, no variety of language is better than or superior to others.《A. GenerallyB. SociallyC. PoliticallyD. Linguistically67. Grammar-based language learning and teaching fails partially because _____.A. still no precise information is obtained concerning how grammar can be learnedB. grammar can not be taught at allC. it is useless to teach grammar in language classesD. learners can learn better without grammarforeign language learners to achieve effective learning, the input should_____.A. not be so far beyond their reach that they are overwhelmed@B. be interesting and simpleC. not be so close to their current stage that they are not challenged at allD. Both A and C69. Interlanguage is _____.A. is produced by every foreign language learnersB. a mixture of the learner’s mother tongue and the target languageC. imperfect compared with the target language, but it is not mere translation from the learner’s native languageD. Both A and C》70. Error analysis may be carried out in order to______.A. identify strategies which learners use in language learningB. try to identify the causes of learner errors.C. obtain information on common difficulties in language learningD. All of the above.71. Many Chinese English learners may, at the beginn ing stage, produce “mans” and “photoes” as the plural forms of “man” and “photo”. This is most likely the result of _______ in the process of foreign language learning.A. Negative transferB. OvergeneralizationC. Positive transferD. mother tongue interference,72. Which of the following qualities is not the requirement of a good test _______.A. ObjectivityB. ReliabilityC. ValidityD. Both A and C73. Which of the following statements about machine translation is likely to be wrong _______.A. Machine translation has always been a chief concern in computational linguistics.B. There are areas where machine translation surpasses human translations.C. Sooner or later, machine translation will replace human translation completely.D. In some areas, human translations surpasses machine translation.74. Teaching culture in our language classes can _______.;A. get the students familiar with cultural differencesB. help the students transcend their own culture and see things as the members of the target culture willC. emphasize the inseparability of understanding language and understanding culture through various classroom practicesD. All of the above.75. According to Grice’s theory, a conversa tional implicature arises when the cooperative principle and its maxims are _______.A. strictly observedB. secretly and deliberately violatedC. blatantly or apparently violatedD. Both A and BⅡ. Match each of the following terms in Column A with one of the appropriate definitions in Column B. Write the corresponding letter on your ANSWER SHEET. …Part OneColumn A1. constituent2. complementary distribution3. design features4. diglossia5. displacement6. homonymy)7. language interference8. registers9. selectional restrictions10. semantic anomalyColumn BA. the phenomenon that human language can cope with any subject whatever, and it does not matter how far away the topic of conversation is in time and spaceB. the framework proposed by Hockett, which discusses the defining properties of human language as against animal communicationC. the restrictions on the type of noun that can be selected with each verb【D. the type of language which is selected as appropriate to a type of situationE. the phenomena that allophones occur in different phonetic environmentsF. a sociolinguistic situation where two varieties of a language exist side by side throughout the community, with each having a definite role to playG. the case that two, or more meanings may be associated with the same linguistic formH. the case that one of the arguments or the predicate of the main predication is self-contradictoryI. any linguistic form or group of linguistic forms that appears at the bottom of one of the lines in the tree diagram of the syntactic analysisJ. the use of elements from one language while speaking another.Part Two】Column A1. duality of structure2. free morphemes3. endocentric construction4. International Phonetic Alphabet5. Psycholinguistics6. the syntagmatic relation7. derivational morphemes"8. regional dialect9. sequential rules10. presuppositionColumn BA. the study of the relationship between language and mind.B. the bound morphemes which are conjoined to other morphemes (or words) to derive or form a new word\C. the organization of language into two levels: a lower level of sounds which combine to form a higher level of meaningful unitsD. a standardized and internationally accepted system of phonetic transcription.E. linguistic varieties used by people living in different regions.F. the rules which govern the combination of sounds in a particular language.G. one whose distribution is functionally equivalent, or approaching equivalence, to one of its constituentsH. the kind of meaning which the speaker doesn't assert but assumes the hearer can identify from the sentenceI. the morphemes which can constitute words by themselvesJ. the one between one item and others in a linear sequence, or between elements which are all present.Part ThreeColumn A2. blending3. compounds4. arbitrariness5. cultural transmission6. diachronic linguistics《7. distinctive features8. standard dialect9. ultimate constituent10. CreoleColumn BA. the study of the language development or change over timeB. the features that a phoneme has and that distinguish it from other phonemesC. the words that are produced by stringing together words>D. the smallest grammatical unit obtained through binary segmentationE. a particular variety of a language, not related to any particular group of language usersF. a language formed when a pidgin has become the primary language of a speech communityG. word formed by combining parts of other wordsH. the fact that the details of the linguistic system must be learned anew by each speakerI. the oppositeness of meaning between lexemesJ. a design feature of language which refers to the fact that there is no logical connection between the signifier and the signified of a sign.Part Four|Column A1. a proposition2. a speech community3. an utterance4. bilingualism5. constatives6. performatives7. registers?8. sociolect9. the Whorf-Sapir hypothesis10. utterance meaningColumn BA. the suggestion that different languages carve the world up in different ways, and that as a result their speakers think about it differentlyB. something conveyed by a sentence in a context other than its literal meaningC. varieties of language that are related to useD. a piece of language actually used in a particular context:E. the linguistic variety used by people belonging to a particular social classF. a community the members of which have or believe they have at least one common variety of languageG. what is expressed by a declarative sentence when that sentence is uttered to make a statementH. sentences which describe or state something; they are either true or falseI. the situation where at least two languages are used side by side by an individual or by a group of speakers, with each having a different role to playJ. sentences that do not describe things and cannot be said to be true or false Part FiveColumn A】1. an analytic proposition2. binary cutting3. connotation4. derivation5. lexicology6. logical semantics7. reference8. semantic feature<9. the chain relation10. the choice relationColumn BA. the relation holding between one item and others in a linear sequence, or between elements which are all presentB. the basic unit of meaning in a wordC. the study of the meaning of a sentence in terms of its truth conditionsD. one whose grammatical form and lexical meaning make it necessarily true, without reference to external criteriaE. the additional meanings that a word or phrase has beyond its central meaning 。
一、单选题1._______is defined as any regionally or socially definable human group identified by sharedlinguistic system.A、A speech communityB、A raceC、A societyD、A nation答案: C2._______found that natural language had its own logic and thus concluded the famous CooperativePrinciple.A、John AustinB、John FirthC、Paul GriceD、William Jones答案: C3.The phonemes /k/, /a:/ and /p/ are in ______ relations in the words /ka:p/ (carp) and /pa:k/(park).A、synchronicB、syntagmaticC、diachronicD、paradigmatic答案: C4.Morphemes that represent “tense”, “number”, “gender”, “case” and so forth arecalled_______morphemes.A、inflectionalB、boundC、freeD、derivational答案: D5.The English word “modernizers” is composed of_______morphemes.A、fourB、threeC、twoD、five答案: D6.A speaker’s knowledge of the total set of rules, conventions, etc., governing the skilled useof language in a society is termed ______.A、competenceB、performanceC、communicative competenceD、communicative strategy答案: B7.The Prague School claims that a sentence may be analyzed from the functional side in terms of______as well as from the grammatical side.A、theme and rhemeB、argument and predicateC、subject and predicateD、performative and constative答案: C8.As far as the sentence “My bag is heavy” is concerned, linguists of pragmatics are moreinterested in its ______ meaning.A、literalB、logicalC、contextualD、grammatical答案: D二、判断题1.The sentence I pour some liquid into the tube is a performative one.()A、正确B、错误答案:错误2.The sentencing of criminals is an example of emotive function of language.()A、正确B、错误答案:错误3.The weak version of the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis says that language is the shaper of our thinkingpatterns.()A、正确B、错误答案:正确4.Human language is, unlike animal communication systems, stimulus free.()A、正确B、错误答案:错误5.The sentence like War is war is an example in which the Quality maxim is violated.()A、正确B、错误答案:错误6.Synchronic linguistic is the study of a language through the course of its history.()A、正确B、错误答案:正确7.The sound〔z〕is a voiced alveolar stop.()A、正确B、错误答案:错误8.V oicing is a distinctive feature for English consonants.()A、正确B、错误答案:错误9.A syllable that has no coda is called a closed syllable.()A、正确B、错误答案:正确10.In the word “illegal”, “il” is an allomorph of the negative morpheme.()A、正确B、错误答案:正确三、名词解释1.Dissimilation答案: Dissimilation-- It refers to the influence exercised by one sound segment on the production of another, so that the two sounds in a sequence become less alike or different.2.Predicate logic答案: Predicate logic--It studies the internal structure of simple propositions. (Or, it deals with expressions containing predicates,arguments and quantifiers).3.Sapir-Whorf Hypotheses答案: Sapir-Whorf Hypotheses--Our lge helps mould our way of thinking, and therefore, different lges may probably express our unique way of understanding the world. On the one hand, lge may determine our thinking patterns; on the other hand, similarity between lges is relative, the greater their structural differentiation is, the more diverse their conceptualization of the world will be.4.Stem答案: Stem—Any morpheme or combination of morphemes to which an inflection affix can be added. A stem can be equivalent to a root or may contain a root and a derivational affix.四、问答题1.Explain the speech act theory with examples.答案: Speech act theory was put forward by J Austin in 1950s. His first shot at the theory is the claim that there are two types of sentences: performative and constatives. The uttering of these sentences is the doing of an action. They are called performatives. E.g. a. I name this ship the queen Elizabeth. b. I promise to finish the work in time. c. I bet you sixpence it will rain tomorrow.While a sentence like this "I pour some liquid into the tube." is called constative. It is a description of what the speaker is doing at the time of speaking.。
语言学导论复习一.名词解释1.Broad transcription(宽式音标):Broad transcription is the transcription with letter-symbols only. This is the transcription normally used in dictionaries and teaching textbooks for general purposes.ponential[.kɔmpə'nenʃəl]analysis(成分分析): Componential analysis is a way proposed by the structural semanticists[sə'mæntəsist] to analyze word meaning. The approach is based on the belief that the meaning of a word can be dissected into meaning components, called semantic features.3.Interlanguage(中介语;过渡语):Proposed by S. Pit Corder and Larry Selinker, the concept of interlanguage was established as learners’ independent system of the second language which is of neither the native language nor the second language, but a continuum [kən'tinjuəm]or approximation [ə.prɔksi'meiʃən] n. 接近,近似from his native language to the target language.petence & performance(语言能力和语言行为):Chomsky defines competence as the ideal user’s knowledge of the rules of his language, and performance the actual realization of this knowledge in linguistic communication.5. Context(语境): The notion of context is essential to the pragmatic study of language. It is generally considered as constituted by the knowledge shared by the speaker and the hearer, such as cultural background, situation, the relationship between the speaker and the hearer, etc.nguage Acquisition(语言习得):Language acquisition refers to the child’s acquisition of his mother tongue, i.e. how the child comes to understand and speak the language of his community.7.Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis [hai'pɔθisis](萨丕尔-沃尔夫假说):Sapir and Whorf, proclaimed that the structure of the language people habitually use influences the ways they think and behave. Sapir and Whorf believe that language filters过滤people’s perception感官,观念and the way they categorize分类experiences. This interdependence互相依赖of language and thought is now known as Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis.nguage Acquisition Device(语言习得机制):The linguist Noam Chomsky claims that human beings are biologically [baiə'lɔdʒikli] 生物学地programmed for language and that the language develops in thechild just as other biological functions such as walking. Originally Chomsky referred to this innate天生的ability as Language Acquisition Device, (also known as LAD).二.论述题1. What are the major views concerning the study of meaning?(1) The naming theory命名论One of the oldest notions concerning meaning, and also the most primitive one, was the naming theory proposed by the ancient Greek scholar Plato. The view holds that words are just names or labels称谓for things.(2) The conceptualist view 概念论This view holds that there is no direct link between a linguistic form and what it refers to (i.e. between language and the real world); rather, in the interpretation解释of meaning they arelinked through the mediation of concepts in the mind.(3)Contextualism语境论The view holds that meaning should be studied in terms of situation, use, context —elements closely linked with language behaviour.(4)Behaviorism行为主义论Behaviorists attempted to define the meaning of a language form as the“situation in which the speaker utters it and the response it calls forth唤起,引起in the hearer”.(Bloomfield)2. According to Austin, what are the three acts a person is possibly performing while making an utterance. Give an example.According to Austin, a speaker might be performing three acts when speaking: locutionary [ləu'kju:ʃənəri]act(言内行为), illocutionaryact(言外行为) , and perlocutionary act. (言后行为)A locutionary act is the act of uttering words, phrases and clauses. It is the act of conveying literal meaning by means of syntax, lexicon and phonology.An illocutionary act is the act of expressing the speaker’s intention; it is the act performed in saying something. A perlocutionary act is the act performed by or resulting from saying something; it is the consequence of, or the change brought about by the utterance; it is the act performed by saying something.For example:“You have left the door wide open.” The locutionary act is the saying of it with its literal meaning: you have left the door open. The illocutionary act can be a request of the hearer to close the door, or making a complaint, depending on the context. The perlocutionary act refers to the effect of the utterance. It can be the hearer’s closing the door or his refusal to comply with the request.3. What are the main features of human language that have been specified by C. Hockett to show that it is essentially different from animal communication system?Design features refer to the defining properties of human language that distinguish it from any animal system of communication.(1)Arbitrariness(任意性)This means that there is no logical connection between meanings and sounds. However, language is not entire arbitrary; certain words are motivated. Some compound words are also not entirely arbitrary. But non-arbitrary words make up only a small percentage of the vocabulary of a language.(2)Productivity (能产性)Language is productive or creative in that it makes possible the construction and interpretation of new signals by its users. Productivity is unique to human language.(3)Duality(二层性)Language is a system, which consists of two sets of structures, or two levels. At the lower or the basic level there is a structure of sounds, which are meaningless by themselves. But the sounds of language can be grouped and regrouped into a large number of units of meaning, which are found at the higher level of the system. This duality of structure of language enables its users to talk about anything within their knowledge.(4) Displacement(移位性)Language can be used to refer to contexts removed from the immediate situations of the speaker.(5) Cultural transmission(文化传承性)We were all born with the ability to acquire language, the details of any language system are not genetically transmitted, but instead have to be taught and learned. The process whereby凭借conj. language is passed on from one generation to the next is described as cultural nguage is culturally transmitted. In contrast, animal call systems are genetically transmitted基因遗传.。