有限元四面体网格划分-英文
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:1.91 MB
- 文档页数:7




Preference :Structural 结构分析Thermal 热分析Fluid 流场分析Electromagnetic 电磁场分析Preprocessor 前处理器Element type 单元类型Structural Mass 结构质量Link 杆Beam 梁Pipe 管道Solid 实体Quad 4 node 4 节点四边形单元Quad 8 node 8 节点四边形单元Brick 8 node 8 节点六面体单元Brick 20 node 20 节点六面体单元Tet 4 node 4 节点四面体单元Tet 10 node 10 节点四面体单元Shell 板壳Contact 接触Option 选择Full integration 完全积分Reduced integration 减缩积分Plane stress 平面应力Plane strain 平面应变Axisymmetric 轴对称Plane strs w/thk 平面应力(输入厚度)Real constant 实常数Thickness 厚度Beam 梁Cross-sectional area 横截面积Area moment of inertia 截面惯性矩Torsional moment of inertia 截面极惯性矩Beam height 梁高Material Props 材料特性Material model 材料模型Structural 结构Linear 线性Elastic 弹性Isotropic 各向同性EX 弹性模量PRXY 泊松比Orthotropic 各向正交Anisotropic 各向异性NonlinearDensity 密度(质量)Thermal expansion 热膨胀系数Damping 阻尼Friction coefficient 摩擦系数Thermal 传热CFD 计算流体动力学Electromagneties 电磁学Acoustics 声学Fluid 流体Section 截面Beam 梁Modeling 建模Create 创造Keypoint 关键点(几何)On Working Plane 在工作平面上On Active CS 在激活的坐标系上Hard point 硬点Line 线Straight Line 直线Arc 弧Through 3 KPs 通过3 点By End KPs & Rad 由端点和半径By Cent & Radius 由圆心和半径Full Circle 整圆Spline 样条Spline thru Locs 由点的坐标建立样条曲线Spline thru KPs 由关键点的坐标建立样条曲线Fillet 倒角Area 面,面积Triangle 三角形Square 矩形Pentagon 五边形Hexagon 六边形Heptagon 七角形Octagon 八角形Corner 角Center 中心Dimension 尺寸,维数Annulus 环状Arbitrary 任意Through KPs 通过关键点生成面By Lines 由线生成面Rectangle 四边形By 2 Corners 由2 个角点生成面By Centr & Cornr 由中心和角点生成面By Dimensions 由尺寸生成面Circle 圆面Solid Circle 实体圆面Annulus 圆环面Partial Annulus 部分环面By End Points 由端点生成圆面Polygon 多边形Volume 体Block 块体Cylinder 圆柱体Hollow 空心圆柱体Solid 固体,实体Prism 三棱体Sphere 球体Cone 圆锥体Node 节点Fill between Nds 在两个节点中填充节点Element 单元Attribute 特性Boolean 布尔运算Intersect 相交Add 加Subtract 减Divide 切分Glue 粘接Overlap 搭接Partition 分割Meshing 分网(离散化)Quadrilateral 四边形Triangle 三角形Hexahedral 六面体Tetrahedral 四面体Sweep 扫略Mapped 映射Surface load 表面力Body load 体积力Reaction 反力Force/ Moment 力/力矩Torque 扭矩Shear 剪力Pressure 压力Temperature 温度Inertia 惯性Angular velocity 角速度Angular acceleration 角加速度Gravity 重力Displacement 位移Constraint 约束Boundary condition 边界条件Symmetry B.C. 对称边界条件Antisymmetry B.C. 反对称边界条件Deflection 变形Coordinate System 坐标系Global 整体坐标系Local 局部坐标系Cartesian 笛卡尔(直角)坐标系Cylindrical 柱坐标系Spherical 球坐标系Element 单元坐标系Nodal 节点坐标系Active Cs 激活坐标系Select 选择Entity 实体List 列表Plot 绘图Plot control 绘图控制Work plane 工作平面Parameter 参数Resume 开始DB 数据库Elastic 弹性Plastic 塑性Linear 线性Nonlinear 非线性Contact 接触Delete 删除Couple 耦合Couple DOFS 耦合自由度Coincident node 重合节点Constraint equation 约束方程Solution 求解Static 静力学分析Modal 模态分析Harmonic 谐响应分析Transient 瞬态动力学分析Spectrum 谱分析Buckling 屈曲分析(稳定性分析)Postprocessor 后处理器Deformed shape 变形Contour plot 等高绘图DOF solution 自由度解Component 分量X-component ofdisplacement X 方向位移Displacement vector sum 位移矢量和Stress 应力X-component of stress X 方向正应力XY shear stress XY 剪应力Principal stress 主应力Stress intensity 应力强度Von Mises stress Mises 等效应力(基于第四强度理论)Bending stress 弯曲应力Axial direct stress 轴向应力Strain 应变Initial strain 初应变Frequency 频率。





第27章MasterFEM 教程:自由网格划分本篇介绍了划分二维单元和实体单元的方方法。
用户将学会:∙划分二维单元。
∙根据曲率设置网格密度。
∙分配局部单元密度。
∙运用maximum area plane方法划分网格。
∙划分实体单元。
开始前必备知识:熟悉MasterFEM界面和创建零件。
熟悉在模型文件中管理零件。
熟悉拉伸特征和旋转特征的布尔运算。
熟悉仿真分析流程。
设置1/4如果还没有运行一个新的模型文件,创建一个新文件并命名。
FileOpen·1·打开模型文件菜单确信用户是在以下工作状态和任务当中:设置工作单位为毫米(mm)OptionsUnitsmm (milli newton)设置2/4工作内容:按照以下尺寸草绘封闭线框(拉伸距离50mm)。
提示:·2·工作内容:命名此零件提示:名称: Part设置3/4工作内容:创建此模型的有限元模型提示:创建有限元模型菜单OK注意事项:零件没有明显的改变,但是在抽屉里(Manage Bins)双击带省略号的零件名称就会看到对应的有限元模型文件。
设置4/4保存模型文件。
FileSave警告!如果软件提示用户保存模型文件,用户应选择:·3·No记住:只有教程中提示保存模型文件,而不是软件提示保存的时候,用户才可以执行保存文件操作。
为什么:在上一次保存以后的错误操作不能撤销恢复,用户可以选择重新打开文件,恢复到上一次保存时的状态。
提示:重新打开模型文件的快捷键:按Control-Z。
表面划分壳单元1/4本节介绍在表面上运用默认属性创建二维单元的方方法,后面将会介绍如何控制单元长度和局部密度。
当几何尺寸改变后,和几何相关的有限元模型也会自动更新。
表面划分壳单元2/4工作内容:在表面上定义单元属性,单元厚度为10mm的四边形壳单元。
怎样做:·4·选取表面Define Mesh 菜单Define Free Meshing Options 菜单Curvature Based Length:不要关闭Define Mesh 菜单.为什么:10mm长的单元至少能在25mm长的短边上定义两个单元,关闭Curvature-based选项是为了和下面的操作比较此参数的效果如何。
有限元、力学专业词汇汇总拉力tensile force 正应力normal stress 切应力shear stress静水压力hydrostatic pressure 集中力concentrated force 分布力distributed force 线性应力应变关系linear relationship between stress andstrain弹性模量modulus of elasticity 横向力lateral force transverse force轴向力axial force 拉应力tensile stress 压应力compressive stress平衡方程equilibrium equation 静力学方程equations of static比例极限proportional limit 应力应变曲线stress-strain curve 拉伸实验tensile test‘屈服应力yield stress 极限应力ultimate stress 轴shaft 梁beam纯剪切pure shear 横截面积cross-sectional area 挠度曲线deflection curve 曲率半径radius of curvature 曲率半径的倒数reciprocal of radius of curvature纵轴longitudinal axis 悬臂梁cantilever beam 简支梁simply supported beam微分方程differential equation 惯性矩moment of inertia 静矩static moment扭矩torque moment 弯矩bending moment弯矩对x的导数 derivative of bending moment with respect to x弯矩对x的二阶导数the second derivative of bending moment with respect to x静定梁statically determinate beam 静不定梁statically indeterminate beam相容方程compatibility equation 补充方程complementary equation中性轴neutral axis 圆截面circular cross section两端作用扭矩twisted by couples at two ends 刚体rigid body 扭转角twist angle 静力等效statically equivalent 相互垂直平面mutually perpendicular planes通过截面形心through the centroid of the cross section 一端铰支pin support at one end 一端固定fixed at one end 弯矩图bending moment diagram剪力图shear force diagram 剪力突变abrupt change in shear force、旋转和平移rotation and translation虎克定律hook’s law边界条件boundary condition 初始位置initial position、力矩面积法moment-area method 绕纵轴转动rotate about a longitudinal axis 横坐标abscissa 扭转刚度torsional rigidity 拉伸刚度tensile rigidity剪应力的合力resultant of shear stress 正应力的大小magnitude of normal stress 脆性破坏brittle fail 对称平面symmetry plane 刚体的平衡equilibrium of rigid body 约束力constraint force 重力gravitational force实际作用力actual force 三维力系three-dimentional force system合力矩resultant moment 标量方程scalar equation、矢量方程vector equation 张量方程tensor equation 汇交力系cocurrent system of forces任意一点an arbitrary point 合矢量resultant vector 反作用力reaction force反作用力偶reaction couple 转动约束restriction against rotation平动约束restriction against translation 运动的趋势tendency of motion绕给定轴转动rotate about a specific axis 沿一个方向运动move in a direction控制方程control equation 共线力collinear forces 平面力系planar force system 一束光a beam of light 未知反力unknown reaction forces 参考框架frame of reference大小和方向magnitude and direction 几何约束geometric restriction刚性连接rigidly connected 运动学关系kinematical relations运动的合成superposition of movement 固定点fixed point平动的叠加superposition of translation 刚体的角速度angular speed of a rigid body 质点动力学particle dynamics 运动微分方程differential equation of motion 工程实际问题practical engineering problems 变化率rate of change 动量守恒conservation of linear momentum 定性的描述qualitative description点线dotted line 划线dashed line 实线solid line 矢量积vector product点积dot product 极惯性矩polar moment of inertia 角速度angular velocity角加速度angular acceleration infinitesimal amount 无穷小量definite integral 定积分a certain interval of time 某一时间段kinetic energy 动能conservative force 保守力damping force 阻尼力coefficient of damping 阻尼系数free vibration 自由振动periodic disturbance 周期性扰动viscous force 粘性力forced vibration 强迫震动general solution 通解particular solution 特解transient solution 瞬态解steady state solution 稳态解second order partial differential equation 二阶偏微分方程external force 外力internal force 内力stress component 应力分量state of stress 应力状态coordinate axes 坐标系conditions of equilibrium 平衡条件body force 体力continuum mechanics 连续介质力学displacement component位移分量additional restrictions 附加约束compatibility conditions 相容条件mathematical formulations 数学公式isotropic material 各向同性材料sufficient small 充分小state of strain 应变状态unit matrix 单位矩阵dilatation strain 膨胀应变the first strain invariant 第一应变不变量deviator stress components 应力偏量分量resonance frequency 谐振频率the first invariant of stress tensor 应力张量的第一不变量bulk modulus 体积模量constitutive relations 本构关系linear elastic material 线弹性材料mathematical derivation 数学推导 a state of static equilibrium 静力平衡状态Newton‘s first law of motion 牛顿第一运动定律directly proportional to 与……成正比stress concentration factor 应力集中系数state of loading 载荷状态st venant’ principle 圣维南原理uniaxial tension 单轴拉伸cylindrical coordinates 柱坐标buckling of columns 柱的屈曲critical value 临界值stable equilibrium 稳态平衡unstable equilibrium condition 不稳定平衡条件critical load 临界载荷a slender column细长杆fixed at the lower end下端固定free at the upper end上端自由critical buckling load 临界屈曲载荷potential energy 势能fixed at both ends 两端固定hinged at both ends 两端铰支tubular member 管型杆件transverse dimention 横向尺寸stability of column 柱的稳定axial force 轴向力elliptical hole 椭圆孔plane stress 平面应力nominal stress 名义应为principal stress directions 主应力方向axial compression 轴向压缩dynamic loading 动载荷dynamic problem 动力学问题inertia force 惯性力resonance vibration 谐振static states of stress 静态应力dynamic response 动力响应time of contact 接触时间length of wave 波长。
abaqus中英文ABAQUS专业术语中英文对照前后处理器模块——ABAQUS/CAE几何体建模——GeometryGeometry Creation Tools(几何体生成工具)2-D Sketcher(二维草图)Sketch T ools and Options(草图工具和选项)Geometry Import/Export(几何体导入和导出)Geometry Repair T ools(几何体修补工具)Mesh Edit(网格编辑)模型装配——AssemblyInstance Tools(实例工具)Sets and Surfaces(集合和表面)Display Groups(显式组)Merge/Cut T ools(合并/剪切操作)定义材料性质——PropertiesMaterial Models(材料模型)General(一般性质)Elasticity(弹性性质)Electrical properties(电性质)Mass diffusion(质量扩散)Plasticity(塑性性质)Pore fluid properties(孔隙流体性质)Thermal properties(热性质)Gasket(垫片)Acoustic medium(声学介质)Equation of state (EOS) materials(状态方程)User materials(用户自定义材料)Hyperelastic material evaluation(超弹性材料评估)Sections(截面性质)Solid(实体)homogeneous(各向同性的), generalized plane strain(广义平面应变的Shell(壳)homogeneous(各向同性的), composite(复合材料壳单元), membrane (薄膜),surface (rebar layers)(带钢筋层的曲面)Beam(梁) beam(梁), truss(杆)Point(点)mass(质量单元), rotary inertia(转动惯量), damping(阻尼), capacitance(电容)Gasket(垫片)Beam section profiles(梁截面形状)Skin(蒙皮)Orientations(材料方向)分析流程功能——AnalysisGeneral, Linear and Nonlinear Analyses(通用,线性和非线性分析)Static stress/displacement analysis(静力分析)Viscoelastic/viscoplastic response(粘弹/粘塑响应)Dynamic stress/displacement analysis(动力分析)Heat transfer analysis(热传导分析)Mass diffusion analysis(质量扩散分析)Acoustic analysis(声学分析)Coupled problems(耦合问题)– Thermo-mechanical(热固)– Thermo-electrical(热电)– Piezoelectric(压电)– Pore fluid flow-mechanical(孔隙流动)– Thermo-mechanical mass diffusion(热-固-质量扩散)– Shock and acoustic-structural(冲击和声固耦合)Linear Perturbation Analyses(线性摄动分析)Static stress/displacement analysis(应力位移静力分析)– Linear static stress/displacement analysis(应力位移线性静力分析)– Eigenvalue buckling estimates(特征值屈曲分析)Dynamic stress/displacement analysis(应力位移动力学分析)– Natural frequency extraction(自振频率提取)– Complex eigenvalue extraction(复频率提取)– Transient response via modal superposition(通过模态叠加法计算瞬态响应)–Steady-state response to harmonic loading (简谐载荷下的稳态响应)– Response spectrum analysis(响应谱分析)– Random response analysis(随机响应分析)Analysis Controls(分析控制)Output Requests(输出请求)定义约束和接触——Constraints and InteractionsContact(接触)General contact (ABAQUS/Explicit)(通用接触)Surface-to-surface contact(面面接触)Self-contact(自接触)Contact Properties(接触性质)Constraints(约束)Thermal(热)Loads(载荷)Mechanical(机械)Bolt load(螺栓预紧力)Thermal(热)Acoustic(声场)Fluid(流体)Electrical(电)Mass diffusion(质量扩散)Fields(场)Multiple load cases(多工况)Connectors(连接单元)Boundary Conditions(边界条件)Nodal(节点位移)Velocity(速度)Acceleration(加速度)Velocity/angular velocity(角速度)Submodel(子模型)Pore pressure(孔压)Electric potential(电势)Temperatures(温度)网格划分——MeshingMesh Seeding(网格种子)Structured Meshing(结构化分网)Surface Meshing(表面分网)Solid Meshing(实体分网)Virtual Topology(虚拟拓扑)单元库——Element Library Beam(梁单元)Truss(杆单元)Connector(连接单元)Shell(壳单元)Membrane(薄膜单元)Continuum(实体单元)Elbow(弯管单元)Gasket(垫片单元)Pipe(管道单元)后处理——VisualizationModel plotting(模型图)Deformed, contour, vector/tensor, path, tickmark, overlay, material orient ations, X–Y plots(变形图,云图、矢量/张量图、材料方向图、X-Y曲线图等)Animations(动画)Stress linearization(应力线性化)Tabular data reports(数据报表)Probe/query tools(查询工具)Diagnostics visualization(结果诊断)过程自动化——Process AutomationPython scripting(Python脚本)GUI toolkit(用户界面工具包)Macro manager(宏管理器)隐式求解器模块——ABAQUS/STANDARD分析类型——Analysis TypesGeneral, Linear and Nonlinear Analyses(通用,线性和非线性分析) Static stress/displacement analysis(静力分析)Direct cyclic analysis(直接载荷循环分析)Viscoelastic/viscoplastic response(粘弹性和粘塑性)Dynamic stress/displacement analysis(动力学分析)Steady-state transport analysis(稳态传输分析)Heat transfer analysis(热传导分析)Mass diffusion analysis(质量扩散分析)Acoustic analysis(声场分析)Coupled analysis(耦合分析)Linear Perturbation Analyses(线性摄动分析)分析和建模技术——Analysis and Modeling Techniques求解技术——Solution Techniques材料定义——Material DefinitionsElastic Mechanical Properties(弹性机械性质)Inelastic Mechanical Properties(非弹性机械性质)Additional Material Properties(其他材料性质)单元库——Element LibraryContinuum(实体单元)Membranes(薄膜单元)Beams(梁单元)Pipes(管道单元)Elbows(弯管单元)Frame Elements(框架单元)Trusses(杆单元)Gasket Elements(垫片单元)Inertial Elements(惯性单元)Rigid Elements(刚体单元)Capacitance Elements(热容单元)Connector Elements(连接单元)Springs, Dashpots, Flexible Joints(弹簧,阻尼器,柔性接头)Distributed Coupling(分布耦合)Special-Purpose Elements(特殊用途单元)User-Defined Elements(用户自定义单元)预设条件——Prescribed Conditions约束和接触——Constraints and Interactions Kinematic Constraints(自由度约束)Surface-Based Contact Modeling(基于表面的接触建模)Element-Based Contact Modeling(基于单元的接触建模)Cavity Radiation(空腔辐射)用户子程序——User Subroutines显式求解器模块——ABAQUS/EXPLICIT分析类型——Analysis Types非线性显示动力学分析分析和建模技术——Analysis and Modeling Techniques 材料定义——Material DefinitionsElastic Mechanical Properties(弹性机械性质)Inelastic Mechanical Properties(非弹性机械性质)Additional Material Properties(其他材料性质)单元库——Element LibraryContinuum(实体单元)Structural(结构单元)Inertial Elements(惯性单元)Rigid Elements(刚体单元)Capacitance Elements(热容单元)Connector Elements(连接单元)Springs, Dashpots(弹簧和阻尼器)预设条件——Prescribed Conditions约束和接触——Constraints and InteractionsKinematic Constraints(自由度约束)Contact Modeling(接触建模)。
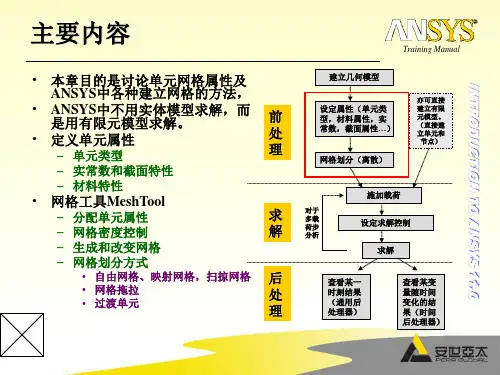
对于有限元分析来说,网格划分是其中最关键的一个步骤,网格划分的好坏直接影响到解算的精度和速度。
网格化有三个步骤:定义单元属性(包括实常数)、在几何模型上定义网格属性、划分网格。
定义网格的属性主要是定义单元的形状、大小。
单元大小基本上在线段上定义,可以用线段数目或长度大小来划分,可以在线段建立后立刻声明,或整个实体模型完成后逐一声明。
采用Bottom-Up方式建立模型时,采用线段建立后立刻声明比较方便且不易出错。
例如声明线段数目和大小后,复制对象时其属性将会一起复制,完成上述操作后便可进行网格化命令。
网格化过程也可以逐步进行,即实体模型对象完成到某个阶段就进行网格话,如所得结果满意,则继续建立其他对象并网格化。
网格的划分可以分为自由网格(free meshing)、映射网格(mapped meshing)和扫略网格(sweep meshing)等。
一、自由网格划分自由网格划分是自动化程度最高的网格划分技术之一,它在面上可以自动生成三角形或四边形网格,在体上自动生成四面体网格。
通常情况下,可利用ANSYS的智能尺寸控制技术(SMARTSIZE 命令)来自动控制网格的大小和疏密分布,也可进行人工设置网格的大小(AESIZE、LESIZE、KESIZE、ESIZE等系列命令)并控制疏密分布以及选择分网算法等(MOPT命令)。
对于复杂几何模型而言,这种分网方法省时省力,但缺点是单元数量通常会很大,计算效率降低。
同时,由于这种方法对于三维复杂模型只能生成四面体单元,为了获得较好的计算精度,建议采用二次四面体单元(92号单元)。
如果选用的是六面体单元,则此方法自动将六面体单元退化为阶次一致的四面体单元,因此,最好不要选用线性(一阶次)的六面体单元(没有中间节点,比如45号单元),因为该单元退化后为线性的四面体单元,具有过大的刚度,计算精度较差;如果选用二次的六面体单元(比如95号单元),由于其是退化形式,节点数与其六面体原型单元一致,只是有多个节点在同一位置而已,因此,可以利用TCHG命令将模型中的退化形式的四面体单元变化为非退化的四面体单元(如92号单元),减少每个单元的节点数量,提高求解效率。
第五章四面体网格膨胀概述Training Manual •四面体网格划分算法•Patch Conforming的膨胀选项–算法–前处理和后处理–高级选项–冲突避免•Patch Independent 划分P t h I d d t–损伤外貌y–Proximity 细化–Curvature 细化•作业5.1 三通搅拌器的膨胀四面体网格(Patch Conforming)(P t h C f i)•作业5.2 汽车多支管的流体和结构网格划分(Patch Independent)(Patch Independent)四面体网格划分算法Training Manual •Patch Conforming–默认时考虑所有的面和边(尽管在收缩控制和虚拟拓扑时会改变且默认损伤外貌基于最小尺寸限制)–适度简化CAD (如. native CAD, Parasolid, ACIS, 等.)在体部件中结使扫共体棱柱体格–在多体部件中可能结合使用扫掠方法生成共形的混合四面体/棱柱和六面体网格–有高级尺寸功能–表面网格体网格•Patch Independent–对CAD 有长边的面, 许多面的修补, 短边等有用.–内置defeaturing/simplification 基于网格技术–基于ICEM CFD 四面体/棱柱Octree 方法–体网格表面网格Patch Conforming 四面体膨胀Training Manual •基本设置包括膨胀选项,前处理和后处理膨胀算法膨胀选项–平滑过渡Training Manual •平滑过渡(默认)–使用局部四面体单元尺寸计算每个局部的初始高度和总高度以达到平滑的体积变化比。
每个膨胀的三角形都有一个关于面积计算的初始高度,在节点处平均。
这意味着对一均匀网格,初始高度大致相同,而对变化网格初始高度也是不同的。
–过渡比•膨胀层最后单元层和四面体区域第一单元层间的体尺寸改变•当求解器设置为CFX时, 默认的Transition Ratio是0.77. 对其它物理选项, 包括SolverPreference设置为Fluent的CFD, 默认值是0.272.•因为Fluent求解器是单元为中心的,其网格单元等于求解器单元, 而CFX求解器是顶点为中心的,求解器单元是双重节点网格构造的,因此会发生不同的处理膨胀选项–厚度选项Training Manual •总厚度–创建常膨胀层,用Number of Layers的值和Growth Rate控制以获得Maximum Thickness值控制的总厚度。