软件建模和设计试题
- 格式:doc
- 大小:219.50 KB
- 文档页数:7

软件建模与分析复习题(C)一、单项选择题1、组成UML有三种基本的建筑块是:(A),事物和图A、关系B、类C、用例D、实体2、UML体系包括三个部分:UML基本构造块,(A)和UML公共机制A、UML规则B、UML命名C、UML模型D、UML约束3、UML中的事物包括:结构事物,分组事物,注释事物和(D)A、实体事物B、边界事物C、控制事物D、动作事物4、(A)模型的缺点是缺乏灵活性,特别是无法解决软件需求不明确或不准确的问题A、瀑布模型B、原型模型C、增量模型D、螺旋模型5、下面哪个不是UML中的静态视图(A)A.状态图B.用例图C.对象图D.类图6、(A)技术是将一个活动图中的活动状态进行分组,每一组表示一个特定的类、人或部门,他们负责完成组内的活动。
A、泳道B、分叉汇合C、分支D、转移7、下列关于状态图的说法中,正确的是(C)A.状态图是UML中对系统的静态方面进行建模的五种图之一。
B.状态图是活动图的一个特例,状态图中的多数状态是活动状态C.活动图和状态图是对一个对象的生命周期进行建模,描述对象随时间变化的行为。
D.状态图强调对有几个对象参与的活动过程建模,而活动图更强调对单个反应型对象建模8、对反应型对象建模一般使用(A)图A、状态图B、顺序图C、活动图D、类图9、类图应该画在Rose的哪种(B)视图中A、Use CaseViewB、Logic ViewC、ComponentViewD、Deployment View10、类通常可以分为实体类,(C)和边界类A、父类B、子类C、控制类D、祖先类11、顺序图由类角色,生命线,激活期和(B)组成A、关系B、消息C、用例D、实体12、(D)是系统中遵从一组接口且提供实现的一个物理部件,通常指开发和运行时类的物理实现A、部署图B、类C、接口D、组件13、关于协作图的描述,下列哪个不正确(B)A.协作图作为一种交互图,强调的是参加交互的对象的组织;B.协作图是顺序图的一种特例C.协作图中有消息流的顺序号;D.在ROSE工具中,协作图可在顺序图的基础上按“F5”键自动生成;14、组件图用于对系统的静态实现视图建模,这种视图主要支持系统部件的配置管理,通常可以分为四种方式来完成,下面哪种不是其中之一(B)A.对源代码建模B.对事物建模C.对物理数据库建模D.对可适应的系统建模15、一个对象和另一个对象之间,通过消息来进行通信。
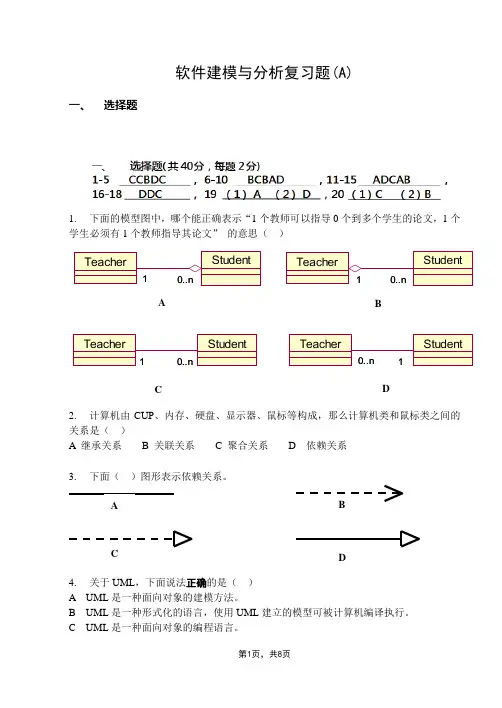
软件建模与分析复习题(A)一、 选择题1. 下面的模型图中,哪个能正确表示“1个教师可以指导0个到多个学生的论文,1个学生必须有1个教师指导其论文” 的意思( )2. 计算机由CUP 、内存、硬盘、显示器、鼠标等构成,那么计算机类和鼠标类之间的关系是( )A 继承关系B 关联关系C 聚合关系D 依赖关系3.下面( )图形表示依赖关系。
4. 关于UML ,下面说法正确的是( ) A UML 是一种面向对象的建模方法。
B UML 是一种形式化的语言,使用UML 建立的模型可被计算机编译执行。
C UML 是一种面向对象的编程语言。
A BC DD UML是一种面向对象的建模语言,但不是建模方法。
5.顺序图和交互图的关系,类似与下面的哪种关系()A 类和对象的关系B 类和参与者关系C Java和编程语言的关系D UML和Java的关系6.要对一个企业的工作流程建模,下面4种图中的()是最重要的。
A 交互图B 活动图C 状态图D 类图7.关于参与者,错误的说法是()A 参与者是与所建立的系统交互的人或物。
B 参与者可以是实际的人,也可以其他系统。
C 参与者是系统的一部分,是用例图的重要组成部分。
D 参与者之间可以存在泛化关系。
8.UML中关联的多重性是指()A 一个类有多个方法被另一个类调用。
B 一个类的实例对象能够与另一个类的多少个实例对象相关联。
C 一个类的某个方法被另一个类调用的次数。
D 两个类所具有的相同的方法和属性。
9.关于类图的说法正确的是()A 类图分为3个层次:对象层、特征层和关系层,其中对象层给出系统中所有反映问题域和系统责任的对象。
B 类图分为3个层次:对象层、特征层和关系层,其中特征层给出系统中所有反映问题域和系统责任的对象。
C 类图只是一种辅助模型,不如其他图重要。
D 类图定义了系统的功能需求,描述了系统的动态行为。
10.根据Coad/Yourdon的定义,面向对象的概念不包括()A 对象B 继承C 消息D 封装11.使用UML对系统进行动态建模,不能使用以下哪种图()A 类图B 顺序图C 状态图D 活动图12.UML的结构事物不包括()A 接口B 类C 协作D 状态机13.分析下面的顺序图,并指出哪种说法是正确的()A “求战”、“怎么办”以及“火烧连营”这3条消息并没有严格的次序,比如:“求战”消息有可能在“火烧连营”之前产生。

ug三维建模考试试题和答案UG三维建模考试试题一、单项选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. UG软件的全称是()。
A. UnigraphicsB. Unigraphics NXC. UGSD. NX2. UG中,创建一个长方体的命令是()。
A. ExtrudeB. SweepC. BoxD. Loft3. 在UG中,以下哪个命令用于创建圆()。
B. CylinderC. SphereD. Ellipse4. UG中,以下哪个命令用于创建草图()。
A. SketchB. WireframeC. CurveD. Surface5. 在UG中,以下哪个命令用于创建拉伸特征()。
A. ExtrudeB. RevolveC. SweepD. Loft6. UG中,以下哪个选项用于创建倒圆角()。
B. ChamferC. RoundD. Bevel7. 在UG中,以下哪个命令用于创建孔()。
A. HoleB. DrillC. PocketD. Counterbore8. UG中,以下哪个命令用于创建镜像特征()。
A. MirrorB. ReflectC. CopyD. Duplicate9. 在UG中,以下哪个命令用于创建拔模特征()。
B. TaperC. DraftingD. Taper Draft10. UG中,以下哪个选项用于创建阵列特征()。
A. PatternB. ArrayC. MirrorD. Repeat二、多项选择题(每题3分,共15分)11. UG软件可以应用于以下哪些领域()。
A. 机械设计B. 建筑设计C. 模具设计D. 航空设计A. LineB. ArcC. SplineD. Circle13. UG中,以下哪些命令用于修改特征()。
A. MoveB. CopyC. TransformD. Pattern14. 在UG中,以下哪些命令用于分析模型()。
A. MeasureB. AnalyzeC. CheckD. EvaluateA. LoftB. SweepC. BoundaryD. Ruled Surface三、判断题(每题1分,共10分)16. UG软件只能用于三维建模。

1.What is object technology? What do you perceive as object technology’s strength? It’s weakness?Object【A set of principles (abstraction, encapsulation, polymorphism) guiding software construction, together with languages, databases, and other tools that support those principles.】面向对象技术是一系列支持软件开发的原则(抽象,封装,多态性),以及支持这些原则的程序设计语言,数据库和其它工具。
【Reflects a single paradigm.Facilitates architectural and code reuse.Reflects real world models more closely.Encourages stability.Is adaptive to change】反映一个特定实例。
有利于构件和代码重用。
更加真实地反映现实世界模型。
具有更好的稳定性。
能适应需求的变化。
2.What is UML? List at least three benefits of developing with UML.【UML is Unified Modeling Language, it is a language for Visualizing, Specifying, Constructing, Documenting the artifacts of a software-intensive system. 】UML是统一建模语言,是一门用于对面向对象开发的产品进行可视化建模,说明,架构和文档编制的标准语言。

软件PD建模期末试题及答案一、题目描述:在软件PD建模课程的期末考试中,通常会包含多个题目,涉及不同的建模技巧和方法。
本文将为大家提供一份软件PD建模期末试题及答案,帮助大家更好地理解和掌握课程内容。
二、试题及答案:1. 题目:请解释什么是面向对象建模?并列举与面向对象建模相关的三个概念。
答案:面向对象建模是一种软件开发方法,通过将现实世界中的事物抽象为对象,并通过对象之间的交互来实现系统的设计和分析。
与面向对象建模相关的三个概念包括:1) 类:类是对象的蓝图或模板,描述了对象的属性和行为。
2) 对象:对象是类的一个实例,具有自己的状态和行为。
3) 继承:继承是指一个类可以从另一个类继承属性和方法的能力。
2. 题目:请解释什么是用例建模?并列举与用例建模相关的两个概念。
答案:用例建模是软件开发过程中的一项重要技术,用于描述系统与用户之间的功能需求和行为。
通过用例建模,可以清晰地了解系统的用例、参与者和它们之间的关系。
与用例建模相关的两个概念包括:1) 用例:用例是描述系统功能的一种技术,用于表示系统与外部参与者之间的交互。
2) 参与者:参与者是与系统进行交互的外部实体,可以是用户、其他系统或硬件设备。
3. 题目:请解释什么是活动图?并解释活动图的三个基本元素。
答案:活动图是用于描述系统行为的一种建模技术,通过图形化的方式表示系统中的各种活动和它们之间的关系。
活动图的三个基本元素包括:1) 活动节点:用于表示系统中的活动或操作,如计算、决策等。
2) 控制流:用于描述活动之间的顺序关系,表示活动之间的转换和流动。
3) 分支节点:用于表示在某个活动节点发生时,系统会根据一定的条件选择不同的路径。
4. 题目:请解释什么是状态图?并解释状态图的两个基本元素。
答案:状态图是一种描述系统状态和状态转换的建模技术,通过图形化的方式表示系统中对象的状态以及状态之间的转换。
状态图的两个基本元素包括:1) 状态:状态是对象在一段时间内的特定条件或情况,表示对象所处的状态。

计算机建模考试试题及答案一、选择题1. 下列哪项属于计算机建模的基本任务?A. 数据分析B. 系统设计C. 模型建立D. 编程实现2. 计算机建模的基本流程包括以下哪些步骤?A. 数据预处理、模型建立、模型求解、模型评价B. 数据采集、数据分析、模型建立、模型求解C. 数据分析、系统设计、模型建立、模型评价D. 数据预处理、数据分析、模型求解、模型评价3. 下列哪种方法可用于计算机建模吗?A. 数值方法B. 统计方法C. 人工智能D. 全部都对4. 计算机建模中常用的编程软件是什么?A. ExcelB. MATLABC. PythonD. SPSS5. 计算机建模的意义是什么?A. 帮助人们更好地理解和解决问题B. 提高数据分析的准确性C. 优化系统设计D. 扩展计算机的应用领域二、填空题1. 在计算机建模中,模型是对问题的抽象描述。
2. 计算机建模的基本要素包括数据、模型和算法。
3. 随着计算机技术的发展,计算机建模已经在许多领域得到广泛应用,如经济、环境、交通等。
4. 计算机建模可用于数据分析、系统仿真、决策支持等方面。
5. 在计算机建模中,模型求解是指通过计算机程序对建立的模型进行求解和分析。
三、解答题1. 请简述计算机建模的基本流程。
计算机建模的基本流程包括数据预处理、模型建立、模型求解和模型评价四个步骤。
首先,需要对收集到的数据进行清洗、整理和处理,以便为后续的分析和建模提供准确可靠的数据基础。
然后,根据问题的需求和特点,选择合适的建模方法和模型类型,并进行模型的参数设置和约束条件的确定。
接下来,通过编程实现模型,在计算机上进行求解和分析,得到相应的输出结果。
最后,对模型进行评价,检查模型的准确性和可靠性,评估模型的优缺点,为进一步改进和优化提供依据。
2. 请列举计算机建模中常用的方法和工具。
计算机建模中常用的方法包括数值方法、统计方法和人工智能等。
数值方法是一种基于数值计算的建模方法,通过数值计算的方式对模型进行求解和分析,常用的数值方法有数值积分、数值优化等。

软件工程基础1、软件就是程序,编写软件就是编写程序。
(×)2、软件危机的主要表现是软件需求增加,软件价格上升。
(×)3、C语言对面向对象的发展起到了重要作用。
(×)4、面向对象方法中的对象是客观世界中抽象出来的一个集合体。
(√)(5)面向对象可以保证开发过程中的需求变化完全不会导致系统结构的变化。
(×)(6)面向对象方法就是使用面向对象的程序设计语言进行编程(×)(7)对象的自治性是指的是对象是完全封闭的,不受任何外界影响。
(×)(8)类是面向对象程序中的构造单位,也是面向对象程序设计语言的基本成分。
(√)(1) 软件工程的概念是在( B )年被首次提出的。
A.1949B.1968C.1972D.1989(2)下列不属于软件工程的目标的一项是( C )。
A.提高软件产品质量B.提高软件产品的可靠性C.减少软件产品的需求D.控制软件产品的开发成本(3)软件危机产生的主要原因是( D )。
A.软件工具落后B.软件生产能力不足C.对软件认识不够D.软件本身的特点及开发方法(4)人们公认的第一门面向对象编程语言是( A )。
A.SimulaB.SmalltalkC.C++D.Java(5)下列编程语言中不支持面向对象的特性的是( B )。
A.C++B.ANSI CC.JavaD.Objective C(5)面向对象可以保证开发过程中的需求变化完全不会导致系统结构的变化。
(×)(6)面向对象方法就是使用面向对象的程序设计语言进行编程(×)(7)对象的自治性是指的是对象是完全封闭的,不受任何外界影响。
(×)(8)类是面向对象程序中的构造单位,也是面向对象程序设计语言的基本成分。
(√)(1) 软件工程的概念是在( B )年被首次提出的。
A.1949B.1968C.1972D.1989(2)下列不属于软件工程的目标的一项是( C )。

软件设计师考试题一、选择题1. 软件设计的原则包括以下哪些方面?A. 抽象化B. 模块化C. 封装性D. 所有以上2. 在软件开发过程中,需求分析的主要目的是什么?A. 确定软件的功能和性能B. 评估项目的可行性C. 制定项目开发计划D. 设计软件的架构3. UML(统一建模语言)中最常用的图有哪些?A. 用例图B. 类图C. 序列图D. 所有以上4. 面向对象设计中,继承的主要作用是什么?A. 提高代码的复用性B. 增强系统的安全性C. 降低系统的复杂性D. 提高系统的性能5. 在软件测试中,黑盒测试主要关注什么?A. 代码的正确性B. 功能的完整性C. 用户的体验D. 系统的稳定性二、填空题1. 软件设计模式是一套被广泛认可的__________解决方案。
2. 在软件开发中,__________和__________是确保软件质量的重要环节。
3. 设计模式中的单例模式确保一个类只有一个实例,并提供一个全局访问点。
4. 在进行软件需求分析时,通常需要创建__________图来帮助理解系统的功能需求。
5. 软件测试的目的是尽可能早地发现软件中的__________。
三、简答题1. 请简述软件设计文档的主要组成部分。
2. 描述软件开发生命周期(SDLC)的主要阶段。
3. 解释什么是软件架构,以及它在软件开发中的作用。
4. 讨论在软件设计中使用设计模式的优势。
5. 阐述单元测试在软件开发过程中的重要性。
四、论述题1. 分析软件开发中常见的几种设计模式,并举例说明它们在实际开发中的应用。
2. 论述软件需求分析的重要性,并提出有效的需求分析方法。
3. 探讨敏捷开发方法与传统瀑布开发模式的区别及其对软件设计的影响。
4. 讨论软件测试的不同类型及其在保证软件质量中的作用。
5. 评估当前软件设计领域的最新趋势,并预测它们对未来软件开发的潜在影响。
五、案例分析题阅读以下案例,并回答问题:某软件开发公司承接了一个电商平台的建设项目。

软件建模与分析复习题(B)一、单项选择题: 1. UML 的全称是 ( b )(A )Unify Modeling Language (B )Unified Modeling Language (C )Unified Modem Language(D )Unified Making Language2. 执行者(Actor )与用例之间的关系是( c )(A )包含关系(B )泛化关系 (C )关联关系 (D )扩展关系3.在类图中,下面哪个符号表示继承关系( c )4. 在类图中,“ #”表示的可见性是( b )(A )Public(B )Protected(C )Private(D )Package5.在类图中,下面哪个符号表示接口( c ) 6. 下面哪个视图属于UML 语言的交互图( d )(A )行为图(B )状态图(C )实现图(D )顺序图7. UML 语言包含几大类图形( d )(A )3(B )5(C )7(D )98. OMT 方法是由下面哪位科学家提出的( b )(A )Booch (B )Rumbaugh (C )Coad (D )Jacobson9. 下面那个类图的表示是错误的( d )10. 什么概念被认为是第二代面向对象技术的标志( a )(A )用例(B )UML 语言 (C )活动图 (D )组件图11. 下面哪个符号代表包图( a )(B) (A) (C) (D)StudentStudent name : String age: IntegerStudent getName () getAge ()Student Name : String Age:IntegergetName () getAge ()(B)(A) (C)(D)(B) (A) (C) (D)12. 生命线是UML 视图中哪个图形的组成部分( d )(A )类图(B )状态图(C )活动图(D )顺序图13. 在UML 的顺序图中,通常由左向右分层排列各个对象,正确的排列方法是( a )(A )执行者角色 控制类 用户接口 业务层后台数据库 (B )执行者角色 用户接口 控制类 业务层 后台数据库(C )执行者角色 控制类 用户接口 后台数据库 业务层 (D )执行者角色 用户接口业务层控制类后台数据库14. 多对象是UML 哪个视图中的概念( c )(A )类图(B )状态图(C )协作图(D )组件图15. 在类图中,哪种关系表达总体与局部的关系( d )(A )泛化(B )实现(C )依赖(D )聚合16. 在UML 中,接口有几种表达方式( a )(A )2(B )4(C )6(D )817. 下面哪个图形代表活动( d )18. 下面哪个UML 视图是描述一个对象的生命周期的(b )(A )类图 (B )状态图 (C)协作图(D )顺序 19.顺序图由类角色,生命线,激活期和( b )组成(A )关系 (B )消息 (C )用例 (D )实体 20. UML 中关联的多重度是指( b )(A )一个类有多个方法被另一个类调用(B )一个类的实类能够与另一个类的多个实类相关联 (C )一个类的某个方法被另一个类调用的次数 (D )两个类所具有的相同的方法和属性二、多项选择题1. 具有多重属性值的UML 图形包括( ) (A )类图 (B )对象图 (C )状态图(D )活动图 (E )部署图(B)(A(C)(D(B) (A)(C) (D)2.在UML的状态图中,转换通常由以下哪些部分构成()(A)动作(B)触发事件(C)源状态(D)目标状态(E)监护条件3.下面哪些图形可以清楚地表达并发行为()(A)类图(B)状态体(C)活动图(D)顺序图(E)实现图4.软件工程的三要素是()(A)方法(B)工具(C)模型(D)过程(E)语言5.可能具有状态机的对象包括()(A)类(B)子系统(C)用例(D)接口(E)协议6.UML的类图包含哪些抽象的层次()(A)概念层(B)说明层(C)实现层(D)业务层(E)控制层7.时序图的用途包括()(A)显示并发进程和激活(B)当不同的类之间存在多个简短的方法时,描述控制流的整体序列(C)显示在协作图中难于描述的事件序列(D)显示涉及类交互而与对象无关的一般形式(E)详细描述系统的瞬态图8.下面哪些图形可以清楚地表达并发行为()(A)类图(B)状态体(C)活动图(D)顺序图(E)实现图9.UML中,类的主要版型有()(A)角色类(B)业务类(C)边界类(D)控制类(E)实体类10.UML的类图包含哪些抽象的层次()(A)概念层(B)说明层(C)实现层(D)业务层(E)控制层三、简答题1. 什么是状态机,状态机由哪几部分组成?状态机是一种行为,说明对象在它的生命周期中响应事件所经历的状态序列以及它们对那些事件的响应。

1.What is object technology? What do you perceive as object technology’s strength? It’s weakness?OOT is such a technology that facing the objective world and the question realm and using the generally thinking way of human-beings to acknowledge the nature world to describe some things.OOT fit the thinking way of human-beings and easy to protect and functions’ addition and decrease are also become more convenient. And OOT’s reusing is more strengthen.weakness2. What is UML? List at least three benefits of developing with UML.UML(Unified Modeling Language)is used to proceeding the visual model of software dense system.(1)UML can help to express things exactly.(2)UML can help programmer to write a better code.(3)UML can accelerate the procedure’s development.3.What process characteristic best fit the UML? Describe each characteristic.4.What is a use-case driven process? What is use-case? What are the benefits of use case?It is the use-case become a guidance of program.Use-case is a description of system functions.Use-case can help us to get a general impression of the determined system.5.What is system’s architecture? What is an architecture-centric Process?System’s architecture is an overall construction of a system, it include the concept, the requirements and all of the detail in implementing the project. The architecture-centric process is a process that exploit a software use the system’s architecture.6.What is iteration? What are the benefits of Iterative Development?Iteration is a way of exploiting the software that finishing the software in several steps, and it need the customer present his advices after every step in order to ensure the product can fit to the requirements of the customer’s. Iteration can ensure a lower risk in a large project.7.What are the basic principles of OO technology? Describe each in detail.Abstraction, it report those important properties connect to the applications.Encapsulation, it can cover details of implementation and is the basis of the modularity.Modularity, it break complex part into simple piecesHierarchy, it provides a method that can let the son class to get data from father class.8.What is use case model? Which artifacts can be included in a use case model?9.List three types of relationships existed between different use cases and give examples.Generalization, Include, Extend.Generalization, apples and bananas can be generalized as fruit.Include, the banana peel is included in the banana.Extend, we can eat the banana, but we can also smash it and mixed it with yogurt and drink it, drinking is an extension.10.Explain the following diagram and their elements with examples.1) Use case diagram 2) Activity diagram 3) Sequence diagram 4) Collaboration diagram5) Class diagram 6) state chart diagram 7) Deployment diagram1)2)3)4)5)6)7)11.Describe the similarities and differences between the sequence diagram and collaborationdiagram.They are both interactive diagram, but collaboration diagram don’t care about when the information be transferred.12.Define the different relationships in class diagram: dependency, association, aggregation,composition, generalization.Dependency, is a connection during two classes, one class depend another class.Association, it let a class acquire another class’s functions and attributes.Aggregation, it is the association but those two classes are in different levels, one is entity but the other one is part.Composition, it is a kind of aggregation, it demands the object that represent the entity in responsible of the life cycle of the object that represent the part.Generalization, it represents the hierarchy between two classes.13.What is a node in deployment diagram? List two different types of nodes.Node in deployment diagram always represent a device .14.Describe the extensibility mechanisms of UML.15.What is the function of Stereotypes?Give two examples of stereotypes.16.Explain the six best practices of software engineering.1)Iteration 2)Manage requirements 3)Module-basis architecture 4)visualization modeling5) software quality’s confirmation 6)Control the changes of software.17.What is RUP? How many phases are there in RUP? Describe each phase’s purpose andmilestone.It is a programming exploitation methodology which is OOT and web-basis.Inception, Elaboration, Construction, TransitionInception: Constructing the business cases of system and confirm the edge of the project.Lifecycle objective.Elaboration: Analysis the problem domain.Lifecycle architecture.Construction: Product’s exploitation.Initial operation.Transition: Ensuring the software is usable to the customer.Product release. and briefly describe the “4+1”views of architecture.Ans:Which of the four views are:Logical View which is the logical relationship around the objects,Process View which is the view that show the actions of the objects or software actions,Deployment View which is to show the relatonship between the module of the objects and Implementation View which is the software implementations.And the one view can be Use-Case View.19.What is the difference between analysis and design?The analysis focus on understanding of de problem,but the design focus on the understanding of the solution.20.Please describe the whole process of OO analysis and design with UML.Ans:1.Build the requirement model-the plan for the reqiurement2.Build the basic model-Class diagram3.Build the assistant diagram4.Design the protocol of the model5.Prototype Development21.What is a layered architecture? Give examples of typical layers.Ans:A layered architecture can be descript as the “separation of responsibility which is to say that each layer is responsible for a finite amount of work.For instance,a company may has its enterprise architecture.The layers of the manager and the layers of the employees.They have the responsibilities themselves and they have their own layers.22.What are analysis mechanisms? What are design mechanisms? Give examples.Ans:Analysis mechanisms can be a process which may run through the whole analysis.And so does the design mechanisms.For instance,a analysis mechanisms may contains Auditing, Communication and so on.23.What is an analysis class? Name and describe the three analysis stereotypes. Give examples. Boundary Classes: Behavior that involves communication with an actorEntity Classes: Behavior that involves the data encapsulated within the abstractionControl Classes: Behavior specific to a use case or part of a very important flow of events24.What is Use-case realization? What‘s your understandings about the benefit of the use-caserealization structure.Ans:The Use-case realization is a method to realize the problem that we should analyse.The use-case realization structure helps to organize the model elements needed to realize the use cases in the design model.25.Describe the steps occurred in the use-case analysis.Ans:It may contain five steps: (1)Identify Use Cases,(2)Indentify Domain Class and relationships,(3)Define the System Sequence Diagram for each use case,(4)Produce an operation,(5)Draw a sequence diagram for each use case.26.What’s the package, and why we need package?Ans:Package is a universal mechanism that organize other elements of the models together.Why we need?If a system has a lot of structures and we have to know more about the structures,then we should point to the so many elements that the systems or the structureshave.And at that time we can find that this may big a complex and hard work.So the package has been developed for this. Package is a universal mechanism that organize other elements of the models together.So we can analyse the system from the bigger layers instead of the great number of the element.27.What is a subsystem? What is an interface? How does a subsystem differ from a package? Ans: A subsystem is a coherent and somewhat independent component of a larger system.It is an element of the model,and it contains the semantics of the packages and the classes.An interface can be an operation about the subsystem.A subsystem realizes one or more interfaces that define its behavior.28.What is the purpose of describing the run-time architecture? How to model the process view? Ans:Describing the run-time architecture’s purpose is:Analyze concurrency requirements,Identify processes and threads,Identify process lifecycles, Map processes onto the implementation and Distribute model elements amongProcesses.The Process View is an “architecturally significant” slice of theprocesses and threads of the Design Model.Processes can be modeled using:1. Active classes (Class Diagrams) and Objects(Interaction Diagrams)ponents (Component Diagrams)29.What is the purpose of describing the distribution? How to model the deployment view? Ans:The purpose is to Reduce processor load.For the Special processing requirements,Scaling concerns,Economic concerns and Distributed access to the system.The Deployment View is an “architecturally significant” slice of the Deployment Model.The deployment view will contain nodes and connections.Connection lines are used to connect the nodes that will be Physical run-time computational resource,Processor node and Device node.And connections may contain Communication mechanism,Physical medium and Software protocol30.Describe the 3 typical distribution patterns, C/S , B/Sand P2P.Ans:C/S:Client/Server, in network connections pattern, besides coordinated net, but also has another form network, namely client/server net, Client/Server. In the client/server network, the server is the network core, but the client is the network foundation, the client dependence server obtains the network resource which needs, but the server provides the network for the client to resources.B/S: Browser/Server,is called as Browser/Server patterns.It is developing as the development of Internet,it is improved from the C/S.P2P: Peer-to-peer network. According to the network in the shared resource way's difference, the local area network has two kind of configurations of organization: One kind is the peer-to-peer network (), another kind is the workstation/server structure. Between peer-to-peer network's computer may correspond mutually and the shared resource (document, peripheral device and so on); But in the workstation/server structure's network may the shared resource place on special purpose computer - server (server), between workstation not mutually direct shared resource. 31.What is the difference between the process models of agile and RUP?Ans: Rational Unified Process is a whole software process,but the process models of agile may bea process in an Architecture or in part of a software.That is to say the RUP may contain the process models of agile.。

一、基础操作题1. 如何在三维建模软件中新建一个场景?2. 如何在场景中添加一个立方体?3. 如何修改立方体的尺寸?4. 如何选择多个物体进行操作?5. 如何对选中的物体进行移动、旋转和缩放?6. 如何使用工具栏中的工具进行建模?7. 如何使用编辑面板对物体进行编辑?8. 如何使用材质编辑器为物体添加材质?9. 如何使用灯光工具添加灯光?10. 如何使用相机工具调整相机视角?二、建模技巧题1. 如何使用放样工具创建一个圆柱体?2. 如何使用布尔运算合并两个物体?3. 如何使用倒角工具为物体添加倒角?4. 如何使用切片工具切割物体?5. 如何使用阵列工具复制物体?6. 如何使用镜像工具创建镜像物体?7. 如何使用切割工具切割物体?8. 如何使用倒角工具为物体添加倒角?9. 如何使用放样工具创建一个圆锥体?10. 如何使用布尔运算切割物体?三、场景布置题1. 如何在场景中添加一个平面?2. 如何为平面添加材质?3. 如何在场景中添加一个球体?4. 如何为球体添加材质?5. 如何在场景中添加一个灯光?6. 如何调整灯光的强度和颜色?7. 如何在场景中添加一个摄像机?8. 如何调整摄像机的位置和视角?9. 如何在场景中添加一个天空盒?10. 如何调整天空盒的参数?四、高级建模题1. 如何使用曲面建模工具创建一个复杂的曲面?2. 如何使用NURBS建模工具创建一个曲面?3. 如何使用曲面编辑工具编辑曲面?4. 如何使用曲面细分工具优化曲面?5. 如何使用曲线建模工具创建一个曲线?6. 如何使用曲线编辑工具编辑曲线?7. 如何使用曲线细分工具优化曲线?8. 如何使用曲面和曲线结合创建一个复杂的模型?9. 如何使用参数化建模工具创建一个可调节尺寸的模型?10. 如何使用自定义工具创建一个独特的模型?五、渲染与动画题1. 如何设置渲染参数?2. 如何调整渲染输出格式?3. 如何使用渲染队列渲染场景?4. 如何使用渲染农场渲染场景?5. 如何调整渲染时间?6. 如何设置动画参数?7. 如何创建关键帧动画?8. 如何调整动画曲线?9. 如何使用动画控制器调整动画?10. 如何导出动画文件?六、材质与纹理题1. 如何创建自定义纹理?2. 如何将纹理应用到模型上?3. 如何调整纹理的坐标?4. 如何使用贴图映射?5. 如何创建和使用贴图贴面?6. 如何为材质添加透明度效果?7. 如何设置材质的反射和折射属性?8. 如何使用光照贴图增强材质效果?9. 如何创建和使用法线贴图?10. 如何调整材质的阴影效果?七、环境与特效题1. 如何创建雾效?2. 如何添加粒子效果?3. 如何设置粒子发射器?4. 如何创建爆炸效果?5. 如何添加雨滴效果?6. 如何设置环境光?7. 如何使用环境贴图?8. 如何创建动态水效果?9. 如何设置天空效果?10. 如何添加云彩效果?八、案例分析与改进题1. 分析一个现有三维模型的优点和不足。
软件设计与开发考试试题第一部分:单选题1. 下列哪个软件开发模型需要在项目开始前对需求进行详尽的分析和规划?A. 敏捷开发B. 瀑布模型C. 增量模型D. 螺旋模型2. 在软件设计中,哪种UML图用于展示系统中对象之间的交互关系?A. 用例图B. 类图C. 时序图D. 活动图3. 在敏捷开发中,下列哪个方法用于将需求划分为小的可交付的部分?A. SCRUMB. 极限编程C. 领域驱动设计D. 结构化分析4. 下列哪个软件开发模型强调不断迭代和反馈?A. 瀑布模型B. 螺旋模型C. 增量模型D. 敏捷开发5. 下列哪种测试类型主要用于评估软件系统的性能?A. 功能测试B. 集成测试C. 接口测试D. 性能测试第二部分:多选题1. 在软件设计中,下列哪些UML图常用于表示系统结构?A. 类图B. 用例图C. 包图D. 活动图2. 下列哪些开发模型适合于大型项目?A. 瀑布模型B. 敏捷开发C. 螺旋模型D. 增量模型3. 软件设计中涉及到的设计原则有哪些?A. 开闭原则B. 单一职责原则C. 里氏替换原则D. 接口隔离原则第三部分:简答题1. 请简要解释什么是软件设计模式?列举一个常用的设计模式并说明其用途。
2. 什么是敏捷开发?简要描述敏捷开发的原则和核心价值观。
3. 软件测试的目的是什么?简要描述测试用例的编写过程。
第四部分:编程题请结合实际编写一段代码,实现一个简单的软件功能,例如实现一个计算器程序或者学生信息管理系统。
请列出代码并注明每行代码的功能和作用。
以上为软件设计与开发考试试题,希望能帮助您检验所学知识。
祝您顺利通过考试!。
CAD三维建模练习题一、基本操作类1. 创建一个长方体,长、宽、高分别为100mm、50mm、200mm。
2. 绘制一个球体,半径为50mm。
3. 利用拉伸命令,将一个直径为100mm的圆拉伸成高度为50mm的圆柱体。
4. 使用旋转命令,将一个边长为50mm的正方形绕X轴旋转360度,形成旋转体。
5. 通过布尔运算,将两个长方体(尺寸分别为100mm×50mm×200mm和50mm×50mm×100mm)进行求和操作。
二、曲面建模类1. 创建一个半径为100mm的圆环面。
2. 绘制一个直径为200mm的圆锥面,高度为100mm。
3. 利用放样命令,创建一个直径为100mm、高度为200mm的圆台。
4. 通过扫掠命令,将一个直径为50mm的圆沿着一条螺旋线扫掠,形成螺旋体。
三、实体建模类1. 绘制一个尺寸为200mm×150mm×100mm的长方体,并在其上表面挖一个直径为50mm的圆孔。
2. 创建一个直径为100mm、高度为200mm的圆柱体,并在圆柱体侧面挖一个矩形槽(长100mm、宽50mm)。
3. 利用布尔差集操作,将两个球体(半径分别为50mm和30mm)进行差集运算。
4. 绘制一个六面体,尺寸为100mm×100mm×100mm,并将其对角线上的四个顶点切掉,形成八面体。
5. 创建一个直径为200mm、高度为100mm的圆锥体,并在圆锥体底面中心挖一个直径为50mm的圆孔。
四、装配体建模类1. 将上述长方体(尺寸为200mm×150mm×100mm)与圆柱体(直径100mm、高度200mm)进行装配。
2. 将球体(半径50mm)与圆锥体(直径200mm、高度100mm)进行装配,使球体位于圆锥体顶部。
3. 将圆环面(半径100mm)与圆台(直径100mm、高度200mm)进行装配。
4. 将螺旋体与长方体(尺寸为100mm×50mm×200mm)进行装配。