教育类的中英文文献对照
- 格式:doc
- 大小:48.50 KB
- 文档页数:13

Addresses地址Autobiography自传Bibliography参考书目Biography传记Books and Documents书籍和文档Case Reports案例报告Classical Article经典的文章Clinical Conference临床会议Clinical Study临床研究Clinical Trial临床试验Clinical Trial, Phase I第一阶段的临床试验Clinical Trial, Phase II二期临床试验Clinical Trial, Phase III III期临床试验Clinical Trial, Phase IV临床试验,第四阶段Comment评论Comparative Study比较研究Congresses代表大会Consensus Development Conference共识发展会议Consensus Development Conference, NIH发展会议共识,国家卫生研究院Controlled Clinical Trial控制临床试验Corrected and Republished Article纠正和转载文章Dataset数据集Dictionary字典Directory目录Duplicate Publication重复发布Editorial编辑Electronic Supplementary Materials电子辅料English Abstract英语文摘Evaluation Studies评价研究Festschrift纪念文集Government Publications政府出版物Guideline指导方针Historical Article历史的文章Interactive Tutorial交互式教程Interview面试Introductory Journal Article介绍性的期刊文章Journal Article期刊文章Lectures讲座Legal Cases法律案件Legislation立法Letter信Meta-Analysis荟萃分析Multicenter Study多中心研究News新闻Newspaper Article报纸文章Observational Study观察性研究Overall整体Patient Education Handout病人教育讲义Periodical Index期刊索引Personal Narratives个人故事Portraits肖像Practice Guideline实践指南Pragmatic Clinical Trial务实的临床试验Published Erratum发布错误Randomized Controlled Trial随机对照试验Research Support, American Recovery and Reinvestment Act研究支持,美国复苏和再投资法案。

英文课程库翻译对照(参考)一、学院/开课单位基础医学院:Preclinical Medicine School 临床医学院:Clinical Medical College 人文学院:College of Humanities 中药学院:College of Traditional Chinese Pharmacy针灸学院:College of Acupuncture and Moxibustion管理学院:School of Management护理学院:College of Nursing信息中心:Information Center 研究生部:Graduate faculty二、课程类别选修课:Selected Course必修课:Required Course专业基础课:Special Core Course专业课:Professional Course学位课:Degree course公共课:Public Course补本科课程:Supplement Undergraduate Courses三、专业名称1、中医:中医基础理论:Basic Theory of TCM中医临床基础:TCM Clinical Foundation中医医史文献:TCM History and Document 方剂学:Science of Formulae of Chinese Herbs中医诊断学:Diagnostics of TCM中医内科学:Traditional Chinese Internal Medicine中医外科学:Surgery of TCM中医儿科学:Pediatrics of TCM中医妇科学:Gynecology of TCM中医骨伤科学:Orthopedics & Traumatology of TCM 中医五官科学:Otorhinolaryngology of TCM 针灸推拿学:Acupuncture & Moxibustion 民族医学:Ethnomedicine/ Medicine of Chinese Minorities临床中药学:Clinical Pharmacology of TCM 中医养生康复学:Health-preserving & Rehabilitation of TCM中医护理学:Nursing of TCM2、中西医结合:中西医结合基础:The basis of Integrative Medicine中西医结合临床:Clinical Science of Integrative Medicine3、药学:药物分析学:Pharmacoanalysis微生物与生化药学:Microbial and Biochemical Pharmacy4、中药学:临床中药学:Clinical Pharmacology of TCM 中药化学:Chemistry of Chinese Meteria Medica中药药理学:Pharmacology of Chinese Meteria Medica中药制药学:Pharmaceutics of Chinese Meteria Medica中药生药学:Pharmacognostics of Chinese Meteria Medica5、公共管理:社会医学与卫生事业管理:Social Medical and Health Service Management四、学位类型科学学位:Science degree临床专业学位:Clinical professional degree五、学位层次:本科学位:Bachelor degree 硕士学位:Master's degree 博士学位:Doctor's degree/ Ph.D六、课程名称:1、公共课科学社会主义理论:Theories of Scientific Socialism自然辩证法:Nature Dialectics 现代科技革命与马克思主义:Modern Science and Technology Revolution and Marxism硕士英语:English for Master’s Degree 博士英语:English for Doctor’s Degree 博士日语:Japanese for Doctor’s Degree 博士二夕卜英语:Second Foreign Language for Doctor's Degree (English) 计算机应用:Application of Computer 医用统计学:Medical Statistics 名师大讲堂:Academician Lectures 科研思路与方法:Scientific Ideas and Methods/ Research Courses汉语水平考试:HSK2、专业课/专基课/选修课/学位课(1)基础医学院课程内经专题讲座:Forums and Lectures of Internal Classic难经学术思想:Academic Thoughts of NanJing中国古代哲学:Ancient Chinese Philosophy 中医基础专论:Monography of Basic TCM Theories伤寒论专题讲座:Treatise on Cold Diseases 金匮要略专题讲座:Treatise on Golden Chamber温病学专题讲座:Treatise on Warm Diseases中医训诂考据学:TCM Textology Exegesis 中国医学史:History of TCM 中医文献学:Philology of TCM 文献检索:Literature Retrieval 各家学说:Various Schools of TCM 中医医案:Medical Records of TCM 中医处方方法学:Prescription Methodology of TCM 中医辨证学:TCM Syndrome Differentiation 中医诊断古籍选读:Selected ancient readings of TCM Diagnosis中医内科学(中诊专业):Traditional Chinese Internal Medicine临床中药学:Clinical Pharmacology of TCM 神经生理学:Neurophysiology生物化学:Biochemistry生物化学实验:Biochemistry Experiment 医学分子生物学:Medical Molecular Biology分子生物学实验:Molecular Biology Experiment实验动物学:Experimental Zoology 神经解剖学:Neuroanatomy 局部解剖学:Medical Topography 头面部局部解剖学:Craniotopography医用细胞学基础:Medical Foundation of Cytology组织细胞分子学实验:Histiocyte Molecular Experiment病理生理学:Pathophysiology医学免疫学:Medical Immunology临床流行病学(DME):Clinical Epidemiology (DME)DME:Design, Measurement and Evaluation中医基础理论(补本科):The Basic Theory of TCM中医养生学概论:Introduction to TCM Health-preserving中医康复学概论:Introduction to TCM Rehabilitation中医饮食营养学:Nutriology of TCM循证医学:Evidence-based Medicine 核酸研究技术在中医药学的应用:Application of Nucleic Acid Research Techniques in TCM(2)临床医学院中医内科学专题讲座:Treatises on Traditional Chinese Internal Medicine 中医内科杂病研究:Miscellaneous Internal Diseases of TCM中医外科学专题讲座:Treatises on Traditional Chinese Surgery中医妇科学专题讲座:Treatises on TCM Gynecology中医儿科学专题讲座:Treatises on TCM Pediatrics西医内科学:Internal Medicine中西医结合内科学专题讲座:Treatises on Integrative Internal Medicine中西医结合外科学专题讲座:Treatises on Integrative Surgery中西医结合妇科学专题讲座:Treatises on Integrative Gynecology中西医结合五官科学专题讲座:Treatises on Integrative Otorhinolaryngology 针灸推拿学专题讲座:Treatises on Acupuncture and Massage中西医结合骨伤科专题讲座:Treatises on Integrative Orthopedics and Traumatology 中西医结合儿科学专题讲座:Treatises on Integrative Pediatrics 西医外科学:Surgery 临床病理学基础:Basic Theories of Clinical Pathology(3)针灸学院针灸学:Acupuncture 中医推拿学:Chinese Massage 实验针灸学:Experimental Acupuncture 针灸医籍各家学说:Various Schools of Acupuncture masterpieces 中医气功学:Qigong of TCM 针灸现代研究进展(博士):Modern Research Progress of Acupuncture and Moxibustion针刀疗法:Acupotomology therapy(4)管理学院高级统计学(一):Advanced Statistics (1)卫生经济理论与方法:Health Economic Theory and Method 社会医学:Social Medicine现代医院管理:Modern Hospital Management 卫生改革与卫生经济政策:Health Reform and Health Economic Policy卫生机构会计实务:Accounting Practice in Health Institution高等教育学:Higher Pedagogy教育管理学:Science of Educational Management药事管理学:Science of Pharmacy Administration药品知识产权实务:Pharmaceutical Intellectual Property Practice高级数据库开发:Advanced Database Development高级网络技术:Advanced Network TechnologyQOL (生存质量)测量与评价:QOL Measurement and Evaluation 社会与发展心理学:Social and Developmental Psychology 宏微观经济分析:Macro and Micro Economic Analysis 现代企业管理:Modern Enterprise Management 医院质量与标准化管理:Hospital Quality and Standardized Management 财务分析与管理:Financial Analysis and Management高级统计学(二):Advanced Statistics (1)卫生事业管理:Health Service Management流行病学:Epidemiology卫生统计数据库分析与应用:HealthStatistics Database Analysis and Application 经济法律通论(民法、诉讼法、合同法):General Theory of Economic Laws(Civil law, procedural law and contract law)知识产权法:Intellectual Property Law 药品质量管理:Drug Quality Control 药事法学:Law of Pharmaceutical Affairs 计算机统计软件应用:Computer statistics software applications组织行为学:Science of Organizational Behavior人力资源管理:Human ResourceManagement技术经济学:Technical Economics 医药营销:Pharmaceutical Marketing 企业战略管理:Enterprise Strategic Management决策支持系统(信息管理):Decisionsupport systems (informationmanagement)教育心理学:Education Psychology 电子商务:E-commerce项目管理:Project Management 古代管理思想研究:Study on Ancient ManagementThought 论文写作:Essay writing健康教育与健康促进:Health Education andHealth Promotion现代管理理论:Modern ManagementTheory公共关系与危机管理:Public Relations andCrisis Management卫生服务成本研究与应用:Research andApplication on Cost of Health Services(5)中药学中药学专论:Monography of Science ofChinese Materia Medica分析测试技术:Analysis and TestTechnology中药化学专论:Monography of Chinese Pharmaceutical Chemistry 中药药理学专论:Monography of Traditional Chinese Pharmacology 中药制药学专论:Monography of Traditional Chinese Pharmaceutics 中药生药学专论:Monography of Traditional Chinese Pharmacognostics临床中药学专论Monography of Clinical Science of Chinese Materia Medica 结构有机化学:Structure of Organic Chemistry波谱分析:Spectrum Analysis药性导论:Introduction of Drug Property 本草文献学:Philology of Chinese Materia Medica中医学选读:TCM Selected Readings 中药成分分析:Analysis of Chinese Materia Medica Components中药信息学:Informatics of Chinese Materia Medica中药炮制学专论:Monography of Processing Chinese Materia Medica中成药学专论:Monography of Science of Chinese Patent Drug生物药剂学:Biological Pharmacology 药用植物学专论:Monography of Medicinal Botany分子生药学:Molecular Pharmacognostics 植物化学分类:Classification of Plant Chemistry中药资源学专论:Monography of Chinese Materia Medica Resources中药显微鉴定:Microscopic Identification of Chinese Materia Medica中药品种论述:Chinese Varieties Treatise 中药生物技术:Chinese Biotechnology 生物制药专题:Special Subject on Biopharmaceutics药理学进展:Advancements of Pharmacology中药药效毒理研究思路与方法:Research Ideas and methods of Chinese Materia Medica Effect and Toxicology物理药剂学:Physical Pharmacology科研思路与方法(中药专业):Scientific ideas and Methods (for Chinese Materia Medica Profession)微生物与生化药学专论:Monography of Microbial and Biochemical Pharmacology 分子细胞生物学专论:Monography of Molecular Cell Biology中药生物技术应用:Biotechnology Applications in Chinese Materia Medica 蛋白质工程:Protein Engineering 计算机辅助药物设计:Computer-aided drug design微生物与生化药学研究方法:Microbial and Biochemical Pharmaceutical Research Methods药物分析专论:Monography of Drug Analysis药品质量控制:Drug Quality Control 中药成分体内代谢与分析:Vivo Metabolism and Analysis of Chinese Materia Medica Components 计算药物分析:Analysis of Drug Calculation生物药物分析:Biopharmaceutical Analysis 新药设计学:Science of New Drug Designing中药药理学:Chinese Pharmacology(6)护理学院护理研究进展:Nursing Research Progress 护理理论:Nursing Theory 护理教育:Nursing Education 中医临床护理概论:Introduction to TCM Clinical Nursing护理心理学:Nursing Psychology本翻译有不尽之处,欢迎各位老师同学提供更好的翻译建议!研究生部培养办2010-7-13。


endnote中英文对照参考文献EndNote是一种文献管理软件,它可以帮助研究者整理和管理引用的参考文献,以及在写作时自动引用这些文献。
在使用EndNote时,一个研究者需要做的第一件事情就是建立自己的文献库。
建立文献库之后,研究者就可以开始收集他们需要引用的文献并将其添加到文献库中。
在EndNote中,参考文献可以根据不同的格式进行引用,比如APA、MLA等。
对于不同格式的参考文献,EndNote也提供了相应的引用模板,用户只需根据约定好的格式将需要引用的文献信息填写到模板中即可。
下面是一些关于文献引用的例子。
书籍:参考文献:作者. (年份). 书名. 出版地点:出版社。
例如:Collins, J. (2009). Good to great. New York: HarperCollins.期刊文章:参考文献:作者. (年份). 文章标题. 期刊名称, 卷号(期号), 页数.例如:Smith, J. (2010). The effects of climate change on Arctic ecosystems. Nature, 463(7282), 1117-1121.网页:参考文献:作者. (年份). 网页标题 [类型]. 来源. 网址.例如:World Health Organization. (2020). Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak [online]. Available from:https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2020-DON146 [Accessed 26 August 2020].最后,需要注意的是,在使用EndNote时,一定要小心引用的文献是否真实可靠。
因为一个糟糕或伪造的文献引用可能会在你的学术研究和论文中带来严重的后果。
因此,学术研究者需要始终保持谨慎和严谨的态度。

哲学Philosophy马克思主义哲学Philosophy of Marxism中国哲学Chinese Philosophy外国哲学Foreign Philosophies逻辑学Logic伦理学Ethics美学Aesthetics宗教学Science of Religion科学技术哲学Philosophy of Science and Technology经济学Economics理论经济学Theoretical Economics政治经济学Political Economy经济思想史History of Economic Thought经济史History of Economic西方经济学Western Economics世界经济World Economics人口、资源与环境经济学Population, Resources and Environmental Economics应用经济学Applied Economics国民经济学National Economics区域经济学Regional Economics财政学(含税收学)Public Finance (including Taxation)金融学(含保险学)Finance (including Insurance)产业经济学Industrial Economics国际贸易学International Trade劳动经济学Labor Economics统计学Statistics数量经济学Quantitative Economics中文学科、专业名称英文学科、专业名称国防经济学National Defense Economics法学Law法学Science of Law法学理论Jurisprudence法律史Legal History宪法学与行政法学Constitutional Law and Administrative Law刑法学Criminal Jurisprudence民商法学(含劳动法学、社会保障法学) Civil Law and Commercial Law (including Science of Labour Law and Science of Social Security Law )诉讼法学Science of Procedure Laws经济法学Science of Economic Law环境与资源保护法学Science of Environment and Natural Resources Protection Law国际法学(含国际公法学、国际私法学、国际经济法学、) International law (including International Public law, International Private Law and International Economic Law)军事法学Science of Military Law政治学Political Science政治学理论Political Theory中外政治制度Chinese and Foreign Political Institution科学社会主义与国际共产主义运动Scientific Socialism and InternationalCommunist Movement中共党史(含党的学说与党的建设) History of the Communist Party of China(including the Doctrine of China Party and Party Building)马克思主义理论与思想政治教育Education of Marxist Theory and Education in Ideologyand Politics国际政治学International Politics国际关系学International Relations外交学Diplomacy社会学Sociology社会学Sociology人口学Demography人类学Anthropology民俗学(含中国民间文学) Folklore (including Chinese Folk Literature) 民族学Ethnology民族学Ethnology马克思主义民族理论与政策Marxist Ethnic Theory and Policy中国少数民族经济Chinese Ethnic Economics中国少数民族史Chinese Ethnic History中国少数民族艺术Chinese Ethnic Art教育学Education教育学Education Science教育学原理Educational Principle课程与教学论Curriculum and Teaching Methodology教育史History of Education比较教育学Comparative Education学前教育学Pre-school Education高等教育学Higher Education成人教育学Adult Education职业技术教育学Vocational and Technical Education特殊教育学Special Education教育技术学Education Technology心理学Psychology基础心理学Basic Psychology发展与心理学Developmental and Educational Psychology应用心理学Applied Psychology体育学Science of Physical Culture and Sports体育人文社会学Humane and Sociological Science of Sports运动人体科学Human Movement Science体育教育训练学Theory of Sports Pedagogy and Training民族传统体育学Science of Ethnic Traditional Sports文学Literature中国语言文学Chinese Literature文艺学Theory of Literature and Art语言学及应用语言学Linguistics and Applied Linguistics汉语言文字学Chinese Philology中国古典文献学Study of Chinese Classical Text中国古代文学Ancient Chinese Literature中国现当代文学Modern and Contemporary Chinese Literature中国少数民族语言文学Chinese Ethnic Language andLiterature比较文学与世界文学Comparative Literature and World Literature 外国语言文学Foreign Languages and Literatures英语语言文学English Language and Literature俄语语言文学Russian Language and Literature法语语言文学French Language and Literature德语语言文学German Language and Literature日语语言文学Japanese Language and Literature印度语言文学Indian Language and Literature西班牙语语言文学Spanish Language and Literature阿拉伯语语言文学Arabic Language and Literature欧洲语言文学European Language and Literature亚非语言文学Asian-African Language and Literature外国语言学及应用语言学Linguistics and Applied Linguistics inForeign Languages新闻传播学Journalism and Communication新闻学Journalism传播学Communication艺术学Art艺术学Art Theory音乐学Music美术学Fine Arts设计艺术学Artistic Design戏剧戏曲学Theater and Chinese Traditional Opera电影学Film广播电视艺术学Radio and television Art舞蹈学Dance历史学History历史学History史学理论及史学史Historical Theories and History of Historical Science考古学及博物馆学Archaeology and Museology历史地理学Historical Geography历史文献学(含敦煌学、古文字学) Studies of Historical Literature (including Paleography and Studies of Dunhuang)专门史History of Particular Subjects中国古代史Ancient Chinese History中国近现代史Modern and Contemporary Chinese History世界史World History理学Natural Science数学Mathematics基础数学Fundamental Mathematics计算数学Computational Mathematics概率论与数理统计Probability and Mathematical Statistics应用数学Applied mathematics运筹学与控制论Operational Research and Cybernetics物理学Physics理论物理Theoretical Physics粒子物理与原子核物理Particle Physics and Nuclear Physics原子与分子物理Atomic and Molecular Physics等离子体物理Plasma Physics凝聚态物理Condensed Matter Physics声学Acoustics光学Optics无线电物理Radio Physics化学Chemistry无机化学Inorganic Chemistry分析化学Analytical Chemistry有机化学Organic Chemistry物理化学(含化学物理)Physical Chemistry (including Chemical Physics) 高分子化学与物理Chemistry and Physics of Polymers天文学Astronomy天体物理Astrophysics天体测量与天体力学Astrometry and Celestial Mechanics地理学Geography自然地理学Physical Geography人文地理学Human Geography地图学与地理信息系统Cartography and Geography Information System大气科学Atmospheric Sciences气象学Meteorology大气物理学与大气环境Atmospheric Physics and Atmospheric Environment 海洋科学Marine Sciences物理海洋学Physical Oceanography海洋化学Marine Chemistry海洋生理学Marine Biology海洋地质学Marine Geology地球物理学Geophysics固体地球物理学Solid Earth Physics空间物理学Space Physics地质学Geology矿物学、岩石学、矿床学Mineralogy, Petrology, Mineral Deposit Geology 地球化学Geochemistry古生物学与地层学(含古人类学)Paleontology and Stratigraphy (including Paleoanthropology)构造地质学Structural Geology第四纪地质学Quaternary Geology生物学Biology植物学Botany动物学Zoology生理学Physiology水生生物学Hydrobiology微生物学Microbiology神经生物学Neurobiology遗传学Genetics发育生物学Developmental Biology细胞生物学Cell Biology生物化学与分子生物学Biochemistry and Molecular Biology生物物理学Biophysics生态学Ecology系统科学Systems Science系统理论Systems Theory系统分析与集成Systems Analysis and Integration科学技术史History of Science and Technology工学Engineering力学Mechanics一般力学与力学基础General and Fundamental Mechanics固体力学Solid Mechanics流体力学Fluid Mechanics工程力学Engineering Mechanics机械工程Mechanical Engineering机械制造及其自动化Mechanical Manufacture and Automation机械电子工程Mechatronic Engineering机械设计与理论Mechanical Design and Theory车辆工程Vehicle Engineering光学工程Optical Engineering仪器科学与技术Instrument Science and Technology精密仪器及机械Precision Instrument and Machinery测试计量技术及仪器Measuring and Testing Technologies and Instruments 材料科学与工程Materials Science and Engineering材料物理与化学Materials Physics and Chemistry材料学Materialogy材料加工工程Materials Processing Engineering冶金工程Metallurgical Engineering冶金物理化学Physical Chemistry of Metallurgy钢铁冶金Ferrous Metallurgy有色金属冶金Non-ferrous Metallurgy动力工程及工程热物理Power Engineering and Engineering Thermophysics 工程热物理Engineering Thermophysics热能工程Thermal Power Engineering动力机械及工程Power Machinery and Engineering流体机械及工程Fluid Machinery and Engineering制冷及低温工程Refrigeration and Cryogenic Engineering化工过程机械Chemical Process Equipment电气工程Electrical Engineering电机与电器Electric Machines and Electric Apparatus电力系统及其自动化Power System and its Automation高电压与绝缘技术High Voltage and Insulation Technology电力电子与电力传动Power Electronics and Power Drives电工理论与新技术Theory and New Technology of Electrical Engineering电子科学与技术Electronics Science and Technology物理电子学Physical Electronics电路与系统Circuits and Systems微电子学与固体电子学Microelectronics and Solid State Electronics电磁场与微波技术Electromagnetic Field and Microwave Technology信息与通信工程Information and Communication Engineering通信与信息系统Communication and Information Systems信号与信息处理Signal and Information Processing控制科学与工程Control Science and Engineering控制理论与控制工程Control Theory and Control Engineering检测技术与自动化装置Detection Technology and Automatic Equipment系统工程Systems Engineering模式识别与智能系统Pattern Recognition and Intelligent Systems导航、制导与控制Navigation, Guidance and Control计算机科学与技术Computer Science and Technology计算机软件与理论Computer Software and Theory计算机系统结构Computer Systems Organization计算机应用技术Computer Applied Technology建筑学Architecture建筑历史与理论Architectural History and Theory建筑设计及其理论Architectural Design and Theory城市规划与设计(含风景园林规划与设计)Urban Planning and Design (including Landscape Planning and Design)建筑技术科学Building Technology Science土木工程Civil Engineering岩土工程Geotechnical Engineering结构工程Structural Engineering市政工程Municipal Engineering供热、供燃气、通风及空调工程Heating, Gas Supply, Ventilating and Air Conditioning Engineering防灾减灾工程及防护工程Disaster Prevention and Reduction Engineering and Protective Engineering桥梁与隧道工程Bridge and Tunnel Engineering水利工程Hydraulic Engineering水文学及水资源Hydrology and Water Resources水力学及河流动力学Hydraulics and River Dynamics水工结构工程Hydraulic Structure Engineering水利水电工程Hydraulic and Hydro-Power Engineering港口、海岸及近海工程Harbor, Coastal and Offshore Engineering测绘科学与技术Surveying and Mapping大地测量学与测量工程Geodesy and Survey Engineering摄影测量与遥感Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing地图制图学与地理信息工程Cartography and Geographic Information Engineering化学工程与技术Chemical Engineering and Technology化学工程Chemical Engineering化学工艺Chemical Technology生物化工Biochemical Engineering应用化学Applied Chemistry工业催化Industrial Catalysis地质资源与地质工程Geological Resources and Geological Engineering矿产普查与勘探Mineral Resource Prospecting and Exploration地球探测与信息技术Geodetection and Information Technology地质工程Geological Engineering矿业工程Mineral Engineering采矿工程Mining Engineering矿物加工工程Mineral Processing Engineering安全技术及工程Safety Technology and Engineering石油与天然气工程Oil and Natural Gas Engineering油气井工程Oil-Gas Well Engineering油气田开发工程Oil-Gas Field Development Engineering油气储运工程Oil-Gas Storage and Transportation Engineering纺织科学与工程Textile Science and Engineering纺织工程Textile Engineering纺织材料与纺织品设计Textile Material and Textiles Design纺织化学与染整工程Textile Chemistry and Dyeing and Finishing Engineering服装设计与工程Clothing Design and Engineering轻工技术与工程The Light Industry Technology and Engineering制浆造纸工程Pulp and Paper Engineering制糖工程Sugar Engineering发酵工程Fermentation Engineering皮革化学与工程Leather Chemistry and Engineering交通运输工程Communication and Transportation Engineering道路与铁道工程Highway and Railway Engineering交通信息工程及控制Traffic Information Engineering & Control交通运输规划与管理Transportation Planning and Management载运工具运用工程Vehicle Operation Engineering船舶与海洋工程Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering船舶与海洋结构物设计制造Design and Construction of Naval Architecture and Ocean Structure轮机工程Marine Engine Engineering水声工程Underwater Acoustics Engineering航空宇航科学与技术Aeronautical and Astronautical Science and Technology飞行器设计Flight Vehicle Design航空宇航推进理论与工程Aerospace Propulsion Theory and Engineering航空宇航器制造工程Manufacturing Engineering of Aerospace Vehicle人机与环境工程Man-Machine and Environmental Engineering兵器科学与技术Armament Science and Technology武器系统与运用工程Weapon Systems and Utilization Engineering兵器发射理论与技术Armament Launch Theory and Technology火炮、自动武器与弹药工程Artillery, Automatic Gun and Ammunition Engineering军事化学与烟火技术Military Chemistry and Pyrotechnics核科学与技术Nuclear Science and Technology核能科学与工程Nuclear Energy Science and Engineering核燃料循环与材料Nuclear Fuel Cycle and Materials核技术及应用Nuclear Technology and Applications辐射防护及环境保护Radiation and Environmental Protection农业工程Agricultural Engineering农业机械化工程Agricultural Mechanization Engineering农业水土工程Agricultural Water-Soil Engineering农业生物环境与能源工程Agricultural Biological Environmental and Energy Engineering 农业电气化与自动化Agricultural Electrification and Automation林业工程Forestry Engineering森林工程Forest Engineering木材科学与技术Wood Science and Technology林产化学加工工程Chemical Processing Engineering of Forest Products环境科学与工程Environmental Science and Engineering环境科学Environmental Science环境工程Environmental Engineering生物医学工程Biomedical Engineering食品科学与工程Food Science and Engineering食品科学Food Science粮食、油脂及植物蛋白工程Cereals, Oils and Vegetable Protein Engineering农产品加工及贮藏工程Processing and Storage of Agriculture Products水产品加工及贮藏工程Processing and Storage of Aquatic Products农学Agriculture作物学Crop Science作物栽培学与耕作学Crop Cultivation and Farming System作物遗传育种学Crop Genetics and Breeding园艺学Horticulture果树学Pomology蔬菜学Olericulture茶学Tea Science农业资源利用学Utilization Science of Agricultural Resources土壤学Soil Science植物营养学Plant Nutrition植物保护学Plant Protection植物病理学Plant Pathology农业昆虫与害虫防治Agricultural Entomology and Pest Control农药学Pesticide Science畜牧学Animal Science动物遗传育种与繁殖Animal Genetics, Breeding and ReproductionScience动物营养与饲料科学Animal Nutrition and Feed Science草业科学Practaculture Science特种经济动物饲养学(含蚕、蜂等)The Rearing of Special-type EconomicAnimals (including Silkworm, Honeybees, etc.)兽医学Veterinary Medicine基础兽医学Basic Veterinary Medicine预防兽医学Preventive Veterinary Medicine临床兽医学Clinical Veterinary Medicine林学Forestry林木遗传育种学Forest Tree Genetics and Breeding森林培育学Silviculture森林保护学Forest Protection森林经理学Forest Management野生动植物保护与利用Wildlife Conservation and Utilization园林植物与观赏园艺Ornamental Plants and Horticulture水土保持与荒漠化防治Soil and Water Conservation and Desertification Combating水产学Fisheries Science水产养殖学Aquaculture Science捕捞学Fishing Science渔业资源学Science of Fisheries Resources医学Medicine基础医学Basic Medicine人体解剖与组织胚胎学Human Anatomy, Histology and Embryology免疫学Immunology病原生物学Pathogenic Organisms病理学与病理生理学Pathology and Pathophysiology法医学Forensic Medicine放射医学Radiation Medicine航空航天与航海医学Aerospace and Nautical medicine临床医学Clinical Medicine内科学(含心血管病学、血液病学、呼吸系病学、消化系病学、内分泌与代谢病学、肾脏病学、风湿病学、传染病学)Internal medicine (including Cardiology, Hematology, Respiratory, Gastroenterology, Endocrinology and Metabolism, Nephrology, Rheuma-tology, Infectious Diseases)儿科学Pediatrics老年医学Geriatrics神经病学Neurology精神病与精神卫生学Psychiatry and Mental Health皮肤病与性病学Dermatology and Venereology影像医学与核医学Imaging and Nuclear Medicine临床检验诊断学Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics护理学Nursing外科学(含普通外科学、骨外科学、泌尿外科学、胸心血管外科学、神经外科学、整形外科学、烧伤外科学、野战外科学)Surgery (General Surgery, Orthopedics, Urology, Cardiothoracic Surgery, Neurosurgery, Plastic Surgery, Burn Surgery, Field Surgery)妇产科学Obstetrics and Gynecology眼科学Ophthalmic Specialty耳鼻咽喉科学Otolaryngology肿瘤学Oncology康复医学与理疗学Rehabilitation Medicine & Physical Therapy运动医学Sports Medicine麻醉学Anesthesiology急诊医学Emergency Medicine口腔医学Stomatology口腔基础医学Basic Science of Stomatology口腔临床医学Clinical Science of Stomatology公共卫生与预防医学Public Health and Preventive Medicine流行病与卫生统计学Epidemiology and Health Statistics劳动卫生与环境卫生学Occupational and Environmental Health营养与食品卫生学Nutrition and Food Hygiene儿少卫生与妇幼保健学Maternal, Child and Adolescent Health卫生毒理学Hygiene Toxicology军事预防医学Military Preventive Medicine中医学Chinese Medicine中医基础理论Basic Theories of Chinese Medicine中医临床基础Clinical Foundation of Chinese Medicine中医医史文献History and Literature of Chinese Medicine方剂学Formulas of Chinese Medicine中医诊断学Diagnostics of Chinese Medicine中医内科学Chinese Internal Medicine中医外科学Surgery of Chinese Medicine中医骨伤科学Orthopedics of Chinese Medicine中医妇科学Gynecology of Chinese Medicine中医儿科学Pediatrics of Chinese Medicine中医五官科学Ophthalmology and Otolaryngoloy of Chinese Medicine针灸推拿学Acupuncture and Moxibustion and Tuina of Chinese medicine民族医学Ethnomedicine中西医结合医学Chinese and Western Integrative Medicine中西医结合基础医学Basic Discipline of Chinese and Western Integrative中西医结合临床医学Clinical Discipline of Chinese and Western Integrative Medicine药学Pharmaceutical Science药物化学Medicinal Chemistry药剂学Pharmaceutics生药学Pharmacognosy药物分析学Pharmaceutical Analysis微生物与生化药学Microbial and Biochemical Pharmacy药理学Pharmacology中药学Science of Chinese Pharmacology军事学Military Science军事思想学及军事历史学Military Thought and Military History军事思想学Military Thought军事历史学Military History战略学Science of Strategy军事战略学Military Strategy战争动员学War Mobilization战役学Science of Operations联合战役学Joint Operation军种战役学(含第二炮兵战役学)Armed Service Operation (including Operation of Strategic Missile Force)战术学Science of Tactics合同战术学Combined-Arms Tactics兵种战术学Branch Tactics军队指挥学Science of Command作战指挥学Combat Command军事运筹学Military Operation Research军事通信学Military Communication军事情报学Military Intelligence密码学Cryptography军事教育训练学(含军事体育学)Military Education and Training (including Military Physical Training) 军制学Science of Military System军事组织编制学Military Organizational System军队管理学Military Management军队政治工作学Science of Military Political Work军事后勤学与军事装备学Science of Military Logistics and Military Equipment军事后勤学Military Logistics后方专业勤务Rear Special Service军事装备学Military Equipment管理学Management Science管理科学与工程Management Science and Engineering工商管理学Science of Business Administration会计学Accounting企业管理学(含财务管理、市场营销学、人力资源管理学)Corporate Management (including Financial Management, Marketing, and Human Resources Management)旅游管理学Tourist Management技术经济及管理学Technology Economy and Management农林经济管理学Agricultural and Forestry Economics & Management农业经济管理学Agricultural Economics & Management林业经济管理学Forestry Economics & Management公共管理学Science of Public Management行政管理学Administration Management社会医学与卫生事业管理学Social Medicine and Health Management教育经济与管理学Educational Economy and Management社会保障学Social Security土地资源管理学Land Resource Management图书馆、情报与档案学Science of Library, Information and Archival图书馆学Library Science情报学Information Science档案学Archival ScienceC++ 程序设计Programming With C++Java程序设计Java ProgrammingVLSI测试与可测试性设计Testing and Testable Design of VLSI Systems安全信息系统概论Introduction to Secure Information Systems编译程序高级教程Compilers:An Advances Course变革管理Change Management并行处理Parallel Process博士学位英语Doctoral English Program程序的形式验证Formal Verification of Programs抽象代数Abstract Algebra处理器体系结构前沿Frontier Processors Architecture代数拓扑Algebraic Topology当代西方财务管理理论与实务Contemporary Corporate Finance-Theory and Practice 德语(二外)German电子商务与网络营销Electronic Commerce and Cyber-Marketing多媒体计算机技术Multimedia Computer Technology多媒体计算机技术及应用Multimedia:technologies&Applications泛函分析Functional Analysis分布式操作系统Distributed Operating Systems分布式多媒体计算机系统Distributed Multimedia Computer Systems风险投资与创业计划Venture CapitalVenture Capital and Business Plan复变函数与积分变换Function of Complex Variable and Integral Transform高等数理统计Mathematical Statistics高级管理学Advanced Management高级计算机网络Advanced Computer Networks高级人工智能Advanced Artificial Intelligence高级软件工程Advanced Course on Software Engineering高性能计算机系统High Performance Computer Systems管理会计学Management Accounting管理信息系统Management Information System管理学基础Basic Management广义相对论基础Introduction to General Relativity规划论Mathmatical Programming国际企业管理International Enterprise Management国家税收The National Tax会计学Accounting会计学原理Principles of Financial Accounting机器人学概论Introduction to Robotics计算机控制理论及应用Computer Controll Theory and Application计算机视觉Computer Vision计算机算法设计与分析The Design and Analysis of Computer Algorithms计算机体系结构Computer System Architecture计算机通信网络安全Computer Communication Network Security计算机图形学Computer Graphics计算机图形学在生命科学中的应用Computer Graphics and applications in life sciences 计算机网络Computer Networks计算机网络导论Computer Network Introduction计算机网络设计与性能分析Computer Network Design and Performance Analysis计算机网络体系结构Computer Networks Architecture计算机系统性能评价Performance Evaluation of Computer Systems计算语言学Computational Linguistics技术创新管理Technology Management技术和工程哲学Philosophy of Technology and Engineering近世代数Modern Algebra纠错编码理论Coding Theory矩阵分析Matrix Analysis决策分析Decision Analysis科技战略导论Introduction of Science & Technology Strategy科学技术史History of Science and Technology科学社会学Sociology of Science科学社会主义理论与实践Theory and Practice of Scientific Socialism科学哲学导论Introduction to Philosophy of Science可持续发展的理论与实践Sustainable Development in Theory and Practice可计算性与计算复杂性Computability and Complexity of Computing李群和李代数Lie Groups and Lie Algebras量子场论Quantum Field Theory量子力学Quantum Mechanics量子统计Quantum Statistical Mechanics论语研读The Study on the Analects of Confucius美学理论与鉴赏Aesthetic Theories and the Appreciation of Art密码学Cryptography面向对象程序设计--C++ Object-Oriented Programming模式识别Pattern Recognition and Inteligence System企业资源计划(ERP) Enterprise Resource Planning情报研究与信息咨询Information Research and Information Consultation群论Group Theory人工智能理论与实现Artificial Intelligence Theory and Implemention人工智能原理The principles of Artificial Intelligence认知心理学Cognitive Psychology日语(二外)Japanese软件工程software Engineering软件开发和程序设计方法学Software Development and Programming Methodology神经计算Neural Computing审计学Auditing生产与运作管理Production and Operation Management实验心理学Experimental Psychology数据库技术Database Technology数理逻辑Mathematical Logic数学模型及其应用Mathematical Models and Its Applications数学物理方程Differential Equations in Mathematical Physics数值分析Numerical Analysis数值计算方法Numerical Computing Methods数值线性代数Numerical Linear Algebra数字集成系统设计Design of Digital Integrated System数字图书馆研究Digital Libraries数字图象处理Digital Image Processing硕士学位英语MS English Program随机过程Stochastic Processes随机数学概论Introduction to Mathematics of Randomness投资学Financial Investments图书馆自动化系统The Library Automation System图与网络流理论Graph Theory and Network Flow Theory微分方程数值解Numerical Solutions of Differential Equations微分几何Differential Geometry微分流行Differentiable Manifolds微观经济学基础Fundamentals of MicroEconomics文献信息学理论与实践Theory and Practice of Documentary Information系统辨识System Identification先进计算机和软件技术系统讲座Topics in advanced computer and software technology 现代计算机代数Modern Computer Algebra现代情报学理论与方法Introduction of Modern Information Science现代数字通信Modern Digital Communication现代数字信号处理Advanced Digital Signal Processing现代通信原理Modern Communication System Principles现代图书馆学理论与方法Linear Algebra Theory现代西方哲学Western Contemporary Philosophy线性代数学Theories and Methods of Mo线性系统控制理论Linear System Control Theory项目管理Project Management心理多元统计分析Multivariate Statistic Analysis for Psychology心理评估Psychological Assessment心理学研究方法Research Method of Psychology信号检测与估计Signal Detection and Estimation信息工程Information Engineering信息经济学Information Economy信息论与编码Information Theory and Coding信息政策与法律Information policy and law信息咨询理论与方法Theory and Method of Information Consultation形式语言与自动机理论Formal language and Automata theory形式语义学引论Introduction to Formal Semantics遥感图像处理Remote Sensing Image Processing应用概率论Applied Probability Theory应用软件开发工具Computer aided tools for system modeling&programming应用统计学Applied Statistics英美社会与文化Society and Culture in Britain and America营销管理Marketing Management有限元方法的数学基础The Mathematical Bases of Finite Element Methods语音交互技术基本原理Fundamental of Speech Interaction Technology运作管理Operation Management战略管理Strategic Management战略信息管理Strategic Information Management张量分析Matrix and Tensor Analysis证券投资概论Introduction to Security Investment智能控制理论基础及应用Intelligent Control-Fundamentals and Applications中国现代作家研究Modern Chinese Writers Study中外伦理思想流派Thoughts of Ethics in West and East自然辨证法Dialectics of Nature自然辨证法与科技革命Dialectics of Nature and Scientific and Technical Revolution 组合数学Combinatorial Mathematics组合优化Combinatorial Optimization最优化计算方法Optimization Computing Methods最优化算法Algorithms for Optimization最优控制理论Optimum Control Theory生物物理学Biophysics真空冷冻干燥技术Vacuum Freezing & Drying Technology16位微机16 Digit MicrocomputerALGOL语言ALGOL LanguageBASIC 语言BASIC LanguageBASIC 语言及应用BASIC Language & ApplicationC 语言C LanguageCAD 概论Introduction to CADCAD/CAM CAD/CAMCOBOL语言COBOL LanguageCOBOL语言程序设计COBOL Language Program DesigningC与UNIX环境C Language & Unix EnvironmentC语言与生物医学信息处理C Language & Biomedical Information Processing dBASE Ⅲ课程设计C ourse Exercise in dBASE ⅢFORTRAN语言FORTRAN LanguageIBM-PC/XT Fundamentals of Microcomputer IBM-PC/XTIBM-PC微机原理Fundamentals of Microcomputer IBM-PCLSI设计基础Basic of LSI DesigningPASCAL大型作业PASCAL Wide Range WorkingPASCAL课程设计Course Exercise in PASCALX射线与电镜X-ray & Electric MicroscopeZ-80汇编语言程序设计Z-80 Pragramming in Assembly Languages板壳理论Plate Theory板壳力学Plate Mechanics半波实验Semiwave Experiment半导体变流技术Semiconductor Converting Technology半导体材料Semiconductor Materials半导体测量Measurement of Semiconductors半导体瓷敏元件Semiconductor Porcelain-Sensitive Elements半导体光电子学Semiconductor Optic Electronics半导体化学Semiconductor Chemistry半导体激光器Semiconductor Laser Unit半导体集成电路Semiconductor Integrated Circuitry半导体理论Semiconductive Theory半导体器件Semiconductor Devices半导体器件工艺原理Technological Fundamentals of Semiconductor Device半导体物理Semiconductor Physics半导体专业Semiconduction Specialty半导体专业实验Specialty Experiment of Semiconductor薄膜光学Film Optics报告文学专题Special Subject On Reportage报刊编辑学Newspaper & Magazine Editing报纸编辑学Newspaper Editing泵与风机Pumps and Fans泵与水机Pumps & Water Turbines毕业设计Graduation Thesis编译方法Methods of Compiling编译技术Technique of Compiling编译原理Fundamentals of Compiling变电站的微机检测与控制Computer Testing & Control in Transformer Substation变分法与张量Calculus of Variations & Tensor变分学Calculus of Variations变质量系统热力学与新型回转压Variable Quality System Thermal Mechanics & Neo-Ro 表面活性物质Surface Reactive Materials并行算法Parallel Algorithmic波谱学Wave Spectrum材料的力学性能测试Measurement of Material Mechanical Performance材料力学Mechanics of Materials财务成本管理Financial Cost Management财政学Public Finance财政与金融Finance & Banking财政与信贷Finance & Credit操作系统Disk Operating System操作系统课程设计Course Design in Disk Operating System操作系统原理Fundamentals of Disk Operating System策波测量技术Technique of Whip Wave Measurement测量原理与仪器设计Measurement Fundamentals & Meter Design测试技术Testing Technology测试与信号变换处理Testing & Signal Transformation Processing产业经济学Industrial Economy产业组织学Industrial Organization Technoooligy场论Field Theory常微分方程Ordinary Differentical Equations超导磁体及应用Superconductive Magnet & Application超导及应用Superconductive & Application超精微细加工Super-Precision & Minuteness Processing城市规划原理Fundamentals of City Planning城市社会学Urban Sociology成组技术Grouping Technique齿轮啮合原理Principles of Gear Connection冲击测量及误差Punching Measurement & Error冲压工艺Sheet Metal Forming Technology抽象代数Abstract Algebra传动概论Introduction to Transmission传感器与检测技术Sensors & Testing Technology传感器原理Fundamentals of Sensors传感器原理及应用Fundamentals of Sensors & Application传热学Heat Transfer传坳概论Introduction to Pass Col船舶操纵Ship Controling船舶电力系统Ship Electrical Power System船舶电力系统课程设计Course Exercise in Ship Electrical Power System 船舶电气传动自动化Ship Electrified Transmission Automation船舶电站Ship Power Station船舶动力装置Ship Power Equipment船舶概论Introduction to Ships船舶焊接与材料Welding & Materials on Ship船舶机械控制技术Mechanic Control Technology for Ships船舶机械拖动Ship Mechamic Towage船舶建筑美学Artistic Designing of Ships船舶结构力学Structual Mechamics for Ships船舶结构与制图Ship Structure & Graphing船舶静力学Ship Statics船舶强度与结构设计Designing Ship Intensity & Structure船舶设计原理Principles of Ship Designing船舶推进Ship Propeling船舶摇摆Ship Swaying船舶阻力Ship Resistance船体建造工艺Ship-Building Technology船体结构Ship Structure船体结构图Ship Structure Graphing船体振动学Ship Vibration创造心理学Creativity Psychology磁测量技术Magnetic Measurement Technology磁传感器Magnetic Sensor磁存储设备设计原理Fundamental Design of Magnetic Memory Equipment 磁记录技术Magnetographic Technology磁记录物理Magnetographic Physics磁路设计与场计算Magnetic Path Designing & Magnetic Field Calculati磁盘控制器Magnetic Disk Controler磁性材料Magnetic Materials磁性测量Magnetic Measurement磁性物理Magnetophysics磁原理及应用Principles of Catalyzation & Application大电流测量Super-Current Measurement大电源测量Super-Power Measurement大机组协调控制Coordination & Control of Generator Networks大跨度房屋结构Large-Span House structure大型锅炉概况Introduction to Large-Volume Boilers大型火电机组控制Control of Large Thermal Power Generator Networks大学德语College German大学俄语College Russian大学法语College French大学日语College Japanese。

中西方教育差异文献1. "Chinese Education: Selected Documents" by Ruth Hayhoe这本书搜集了一系列关于中国教育的文献,涵盖了教育体制、课程改革和教育政策等方面的内容。
2. "Chinese Learners and Western Education" by David Watkins本书研究了中国学生在西方教育体系中的经历和适应情况,探讨了中西方教育差异对学生学习和发展的影响。
3. "The Globalisation of Chinese Education: Perspectives from the Field" by Jane Knight该书从实地研究的角度分析了中国教育的全球化趋势,比较了中西方教育体系的异同,并探讨了全球化对中国教育的影响。
4. "Cultures of Schooling: Pedagogies for Cultural Difference and Social Access" by Mary Kalantzis and Bill Cope这本书讨论了中西方文化差异对教育的影响,并提供了一些跨文化教育的教学策略和方法。
5. "Educational Trends in a Changing China: Comparative Perspectives on Education Reforms and Practices" edited by Shibao Guo and Yan Guo该书汇集了多位学者的研究,比较了中国教育改革和实践与其他国家的差异,深入探讨了中西方教育制度的异同。
6. "Chinese Education and Society: A Bibliographic Guide" byMarjorie Bingham Wescoat这本书提供了关于中国教育和社会的文献索引,为研究者提供了研究中国教育的重要参考资源。
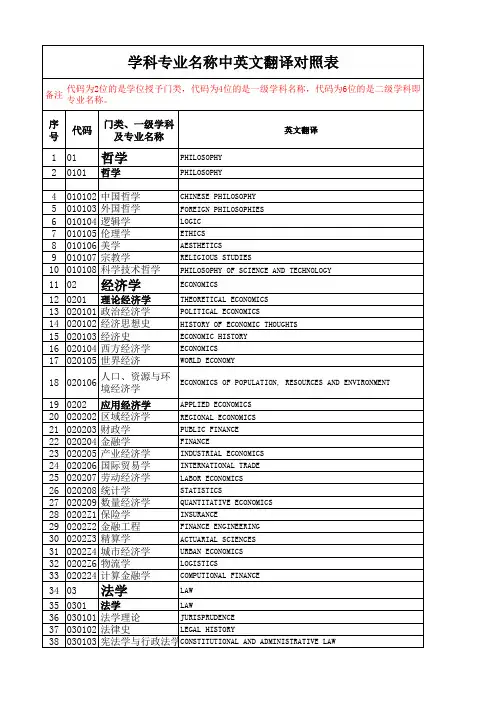
备注序号代码门类、一级学科及专业名称英文翻译101哲学 PHILOSOPHY 20101哲学 PHILOSOPHY 4010102中国哲学 CHINESE PHILOSOPHY 5010103外国哲学FOREIGN PHILOSOPHIES 6010104逻辑学 LOGIC 7010105伦理学 ETHICS 8010106美学 AESTHETICS 9010107宗教学 RELIGIOUS STUDIES 10010108科学技术哲学 PHILOSOPHY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 1102经济学 ECONOMICS 120201理论经济学 THEORETICAL ECONOMICS 13020101政治经济学 POLITICAL ECONOMICS 14020102经济思想史 HISTORY OF ECONOMIC THOUGHTS 15020103经济史 ECONOMIC HISTORY 16020104西方经济学ECONOMICS 17020105世界经济WORLD ECONOMY 18020106人口、资源与环境经济学ECONOMICS OF POPULATION, RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT 190202应用经济学 APPLIED ECONOMICS 20020202区域经济学 REGIONAL ECONOMICS 21020203财政学 PUBLIC FINANCE 22020204金融学 FINANCE 23020205产业经济学 INDUSTRIAL ECONOMICS 24020206国际贸易学 INTERNATIONAL TRADE 25020207劳动经济学 LABOR ECONOMICS 26020208统计学 STATISTICS 27020209数量经济学 QUANTITATIVE ECONOMICS 280202Z1保险学INSURANCE 290202Z2金融工程FINANCE ENGINEERING 300202Z3精算学ACTUARIAL SCIENCES 310202Z4城市经济学URBAN ECONOMICS 320202Z6物流学LOGISTICS 33020224计算金融学COMPUTIONAL FINANCE 3403法学 LAW 350301法学 LAW 36030101法学理论 JURISPRUDENCE 37030102法律史LEGAL HISTORY 38030103宪法学与行政法学C ONSTITUTIONAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE LAW 学科专业名称中英文翻译对照表代码为2位的是学位授予门类,代码为4位的是一级学科名称,代码为6位的是二级学科即专业名称。

中英文翻译论文参考文献一、中英文翻译论文期刊参考文献[1].言、意、象——翻译与言外之意.《兰州大学学报(社会科学版)》.被北京大学《中文核心期刊要目总览》收录PKU.被南京大学《核心期刊目录》收录CSSCI.2015年2期.刘新慧.[2].中英文翻译中文化空缺现象及翻译策略.《华东交通大学学报》.被中信所《中国科技期刊引证报告》收录ISTIC.2009年4期.王显涛.[3].论商品包装的中英文翻译—以对等理论问指导.《当代教育实践与教学研究(电子刊)》.2015年12期.孙一博.[4].中英文翻译中的文化语境研究.《佳木斯教育学院学报》.2013年10期.陈真.[5].中英文翻译中文化空缺现象及翻译对策.《海外英语《海外英语《中国药师》.被中信所《中国科技期刊引证报告》收录ISTIC.2012年2期.李杨华.邵寅.二、中英文翻译论文参考文献学位论文类[1].论商务合同翻译之转换法.被引次数:1作者:封云.法律英语翻译与实践西南政法大学2009(学位年度)[2].CETranslationofBusinessContracts:FromtheGermanFunctionalistPe rspective.作者:杜艳.外语语言学及应用语言学西南政法大学2009(学位年度)[3].MomentinPeking及其两个汉译本对文化负载词语的处理.被引次数:1 作者:尚路平.外国语言学及应用语言学兰州大学2009(学位年度)[4].国际标准翻译研究——基于ISO9001和ISO14001的翻译.作者:刘艳华.外国语言学及应用语言学对外经济贸易大学2007(学位年度)[5].ChineseEnglishTranslationofMedicalTexts:ErrorsandStrategies. 作者:李春慧.外国语言学与应用语言学第四军医大学2009(学位年度)[6].连接成分的显化:基于语料库的中英文翻译文本对比.被引次数:2 作者:刘鼎甲.英语语言文学燕山大学2009(学位年度)[7].AComparativeStudyofChineseandEnglishFigureofSpeechandTranslat ion.作者:吴兰青.外国语言学及应用语言学西南财经大学2005(学位年度)[8].国俗词汇的可译性及其实现手段——从文化图式视角.作者:刘鹏.英语语言文学山东师范大学2005(学位年度)[9]中英文翻译机制的实验研究——概念通路和词汇通路的探讨.作者:王璐璐.基础心理学北京师范大学2005(学位年度)[10]DiscourseCohesionAComparativeStudybetweentheTwoChineseVersion sofMomentinPeking.作者:杨佳.外国语言学及应用语言学东北大学2009(学位年度)三、中英文翻译论文专著参考文献[1]基于多层过滤的统计机器翻译.周玉.宗成庆.徐波,2004第二届全国学生计算语言学研讨会[2]船舶规范、公约和决议翻译的技巧.庄韵,2012首届“苏浙闽粤桂沪”航海学会学术研讨会[3]电脑辅助中医翻译之实践.唐国顺,2008第18届世界翻译大会[4]口筆譯硏究典藏分析:以中港台及日韓大學爲例.楊承淑,2008第18届世界翻译大会[5]中国“理工大学”校名英译思考与商榷.潘月明.郭秀芝,2008第18届世界翻译大会[6]中华民族热中英文的高榷.张荫民,2004第七次汉字书同文学术研讨会[7]化合物名称中译英自动翻译系统的研究.徐挺军.陈维明,2008第九届科学数据库与信息技术学术讨论会[8]医学院校学生专业英语翻译技能的培训.林生趣.张书旭,2008第18届世界翻译大会[9]互文性视阈下的中药说明书结构词翻译研究.刘艾娟.都立澜.李晓莉.陈铸芬.翟书娟,2015世界中医药学会联合会翻译专业委员会第六届学术年会[10]传译昆曲经典,弘扬中华文化《昆曲精华》的翻译回顾.周福娟.汤定军,20062006年全国翻译高层研讨会。

学前教育英文文献学前教育是指为幼儿提供的早期教育和培养,旨在促进幼儿全面发展。
以下是一些关于学前教育的英文文献,供您参考:1. Barnett, W. S. (2011). Effectiveness of early educational intervention. Science, 333(6045), 975-978.This article discusses the effectiveness of early educational interventions in promoting positive outcomes for children in various areas of development.2. Pianta, R. C., & Walsh, D. J. (1996). High-risk children in schools: Constructing sustaining relationships. Routledge.This book explores the importance of building and maintaining supportive relationships with high-risk children in schools, emphasizing the role of early education in fostering positive connections.3. Zigler, E., & Bishop-Josef, S. J. (2006). The cognitive child versus the whole child: Lessons from 40 years of Head Start. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 27(2), 114-118.This journal article reflects on the lessons learned from the Head Start program over 40 years, highlighting the importance of considering both cognitive and holistic aspects of child development in early education.4. Rimm-Kaufman, S. E., & Pianta, R. C. (2000). An ecological perspective on the transition to kindergarten: A theoretical framework to guide empirical research. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 21(5), 491-511.This article presents an ecological perspective on the transition to kindergarten,offering a theoretical framework to guide empirical research on the factors influencing successful transitions in early education.5. Bowman, B. T., Donovan, M. S., & Burns, M. S. (Eds.). (2001). Eager to learn: Educating our preschoolers. National Academies Press.This book provides a comprehensive review of research on early childhood education, covering topics such as curriculum, assessment, teacher qualifications, and the importance of family involvement.这些文献涵盖了学前教育的不同方面,包括早期干预的有效性、建立与高风险儿童的关系、认知与整体发展的重要性、过渡到幼儿园的生态视角以及学前教育的课程、评估和家庭参与等。

体育教育中英文对照外文翻译文献体育教育中英文对照外文翻译文献(文档含英文原文和中文翻译)译文:长沙市社区篮球运动的发展现状与对策研究摘要采用文献资料法、逻辑分析法、调查访问法、数理统计法对长沙市社区篮球运动的研究,表明长沙市社区篮球运动的发展并不乐观、没有跟上时代的步伐、与时俱进。
表现在社区篮球场地奇缺,社区体育指导员没有专门的人员担任、没有社区体育指导的专业知识,全民健身的宣传力度不够、人们的全民健身意识淡薄,政府的投入力度等等方面还不够。
建议加大全民健身的宣传力度,以增强社区居民的健身意识;加强社区内篮球场地的建设;建立健全的社会指导员培训机构;每个社区都引进专业的社会指导员;将学校、社区、企业单位的体育场馆进行综合的利用;注重在建设体育场馆的质量和位置;大力发展社区的作用,由社区组织一些社区内或是社区之间的篮球比赛,以营造体育运动的氛围。
关键词:篮球运动;社区;现状;对策AbstractWith the methods of documentation, logic analysis, investigation and interview, mathematical statistics; and through the study on community's basketball of Changsha , indicate that the development of community's basketball of Changsha is pessimistic , and without following the paces of the times . Display in the areas of that community basketball field in exceedingly short supply, community sports instructor having not special personnel, community professional knowledge being rare, no enough propaganda strength of nationwide fitness programs, the thin consciousness of nationwide fitness programs, and input power of government wait a moment for to be enougheven. Propose strengthening the propaganda strength of nationwide fitness programs, in order to strengthen community residents' consciousness of building up body; Strengthen the construction of the basketball field in the community; Set up sound social instructor's training organization; Each community introduces the specialized social instructor; Carry on comprehensive use gymnasiums and stadiums of school , community and enterprise ; Pay attention to building quality and position of the gymnasiums and stadiums; The function of the community should pay more effective role, more basketball match in some communities or between the community should be organized by community, in order to build an atmosphere of sports activity.Keywords: Basketball Movement; Community; Current; Countermeasure.20 世纪80 年代中期以来,随着我国经济和社会的发展,城市经济体制的改革和城市管理体制改革的推进,城市社区和社区体育得以迅速的发展。

船舶工程学院College of Shipbuilding Engineering建筑工程学院College of Civil Engineering动力与能源工程学院College of Power and Energy Engineering自动化学院College of Automation水声工程学院College of Underwater Acoustic Engineering计算机科学与技术学院College of Computer Science and Technology机电工程学院College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering信息与通信工程学院College of Information and Communications Engineering 经济管理学院School of Economics and Management材料科学与化学工程学院College of Material Science and Chemical Engineering 理学院College of Science人文社会科学学院College of Humanities and Social Sciences核科学与技术学院College of Nuclear Science and Technology外语系Foreign Languages Department体育军事训练部Physical Education Department中文学科、专业名称英文学科、专业名称哲学 Philosophy马克思主义哲学 Philosophy of Marxism中国哲学 Chinese Philosophy外国哲学 Foreign Philosophies逻辑学 Logic伦理学 Ethics美学 Aesthetics宗教学 Science of Religion科学技术哲学 Philosophy of Science and Technology经济学 Economics理论经济学 Theoretical Economics政治经济学 Political Economy经济思想史 History of Economic Thought经济史 History of Economic西方经济学 Western Economics世界经济 World Economics人口、资源与环境经济学 Population, Resources and Environmental Economics应用经济学 Applied Economics国民经济学 National Economics区域经济学 Regional Economics财政学(含税收学) Public Finance (including Taxation)金融学(含保险学) Finance (including Insurance)产业经济学 Industrial Economics国际贸易学 International Trade劳动经济学 Labor Economics统计学 Statistics数量经济学 Quantitative Economics中文学科、专业名称英文学科、专业名称国防经济学 National Defense Economics法学 Law法学 Science of Law法学理论 Jurisprudence法律史 Legal History宪法学与行政法学 Constitutional Law and Administrative Law刑法学 Criminal Jurisprudence民商法学(含劳动法学、社会保障法学) Civil Law and Commercial Law (including Science of Labour Law and Science of Social Security L aw )诉讼法学 Science of Procedure Laws经济法学 Science of Economic Law环境与资源保护法学 Science of Environment and Natural Resources Protection Law国际法学(含国际公法学、国际私法学、国际经济法学、) International law (including International Public law, International Private Law and International Economic Law)军事法学 Science of Military Law政治学 Political Science政治学理论 Political Theory中外政治制度 Chinese and Foreign Political Institution科学社会主义与国际共产主义运动 Scientific Socialism and InternationalCommunist Movement中共党史(含党的学说与党的建设) History of the Communist Party of China(including the Doctrine of China Party and Party Building)马克思主义理论与思想政治教育 Education of Marxist Theory and Education in Ideology and Politics 国际政治学 International Politics国际关系学 International Relations外交学 Diplomacy社会学 Sociology社会学 Sociology人口学 Demography人类学 Anthropology民俗学(含中国民间文学) Folklore (including Chinese Folk Literature)民族学 Ethnology民族学 Ethnology马克思主义民族理论与政策 Marxist Ethnic Theory and Policy中国少数民族经济 Chinese Ethnic Economics中国少数民族史 Chinese Ethnic History中国少数民族艺术 Chinese Ethnic Art教育学 Education教育学 Education Science教育学原理 Educational Principle课程与教学论 Curriculum and Teaching Methodology教育史 History of Education比较教育学 Comparative Education学前教育学 Pre-school Education高等教育学 Higher Education成人教育学 Adult Education职业技术教育学 V ocational and Technical Education特殊教育学 Special Education教育技术学 Education Technology心理学 Psychology基础心理学 Basic Psychology发展与心理学 Developmental and Educational Psychology应用心理学 Applied Psychology体育学 Science of Physical Culture and Sports体育人文社会学 Humane and Sociological Science of Sports运动人体科学 Human Movement Science体育教育训练学 Theory of Sports Pedagogy and Training民族传统体育学 Science of Ethnic Traditional Sports文学 Literature中国语言文学 Chinese Literature文艺学 Theory of Literature and Art语言学及应用语言学 Linguistics and Applied Linguistics汉语言文字学 Chinese Philology中国古典文献学 Study of Chinese Classical Text中国古代文学 Ancient Chinese Literature中国现当代文学 Modern and Contemporary Chinese Literature中国少数民族语言文学 Chinese Ethnic Language and Literature比较文学与世界文学 Comparative Literature and World Literature 外国语言文学 Foreign Languages and Literatures英语语言文学 English Language and Literature俄语语言文学 Russian Language and Literature法语语言文学 French Language and Literature德语语言文学 German Language and Literature日语语言文学 Japanese Language and Literature印度语言文学 Indian Language and Literature西班牙语语言文学 Spanish Language and Literature阿拉伯语语言文学 Arabic Language and Literature欧洲语言文学 European Language and Literature亚非语言文学 Asian-African Language and Literature外国语言学及应用语言学 Linguistics and Applied Linguistics in Foreign Languages新闻传播学 Journalism and Communication新闻学 Journalism传播学 Communication艺术学 Art艺术学 Art Theory音乐学 Music美术学 Fine Arts设计艺术学 Artistic Design戏剧戏曲学 Theater and Chinese Traditional Opera电影学 Film广播电视艺术学 Radio and television Art舞蹈学 Dance历史学 History历史学 History史学理论及史学史 Historical Theories and History of Historical Science考古学及博物馆学 Archaeology and Museology历史地理学 Historical Geography历史文献学(含敦煌学、古文字学) Studies of Historical Literature (including Paleography and Studies of Dunhuang)专门史 History of Particular Subjects中国古代史 Ancient Chinese History中国近现代史 Modern and Contemporary Chinese History世界史 World History理学 Natural Science数学 Mathematics基础数学 Fundamental Mathematics计算数学 Computational Mathematics概率论与数理统计 Probability and Mathematical Statistics应用数学 Applied Mathematics运筹学与控制论 Operational Research and Cybernetics物理学 Physics理论物理 Theoretical Physics粒子物理与原子核物理 Particle Physics and Nuclear Physics原子与分子物理 Atomic and Molecular Physics等离子体物理 Plasma Physics凝聚态物理 Condensed Matter Physics声学 Acoustics光学 Optics无线电物理 Radio Physics化学 Chemistry无机化学 Inorganic Chemistry分析化学 Analytical Chemistry有机化学 Organic Chemistry物理化学(含化学物理) Physical Chemistry (including Chemical Physics) 高分子化学与物理 Chemistry and Physics of Polymers天文学 Astronomy天体物理 Astrophysics天体测量与天体力学 Astrometry and Celestial Mechanics地理学 Geography自然地理学 Physical Geography人文地理学 Human Geography地图学与地理信息系统 Cartography and Geography Information System大气科学 Atmospheric Sciences气象学 Meteorology大气物理学与大气环境 Atmospheric Physics and Atmospheric Environment 海洋科学 Marine Sciences物理海洋学 Physical Oceanography海洋化学 Marine Chemistry海洋生理学 Marine Biology海洋地质学 Marine Geology地球物理学 Geophysics固体地球物理学 Solid Earth Physics空间物理学 Space Physics地质学 Geology矿物学、岩石学、矿床学 Mineralogy, Petrology, Mineral Deposit Geology 地球化学 Geochemistry古生物学与地层学(含古人类学) Paleontology and Stratigraphy (including Paleoanthropology)构造地质学 Structural Geology第四纪地质学 Quaternary Geology生物学 Biology植物学 Botany动物学 Zoology生理学 Physiology水生生物学 Hydrobiology微生物学 Microbiology神经生物学 Neurobiology遗传学 Genetics发育生物学 Developmental Biology细胞生物学 Cell Biology生物化学与分子生物学 Biochemistry and Molecular Biology生物物理学 Biophysics生态学 Ecology系统科学 Systems Science系统理论 Systems Theory系统分析与集成 Systems Analysis and Integration科学技术史 History of Science and Technology工学 Engineering力学 Mechanics一般力学与力学基础 General and Fundamental Mechanics固体力学 Solid Mechanics流体力学 Fluid Mechanics工程力学 Engineering Mechanics机械工程 Mechanical Engineering机械制造及其自动化 Mechanical Manufacture and Automation机械电子工程 Mechatronic Engineering机械设计与理论 Mechanical Design and Theory车辆工程 Vehicle Engineering光学工程 Optical Engineering仪器科学与技术 Instrument Science and Technology精密仪器及机械 Precision Instrument and Machinery测试计量技术及仪器 Measuring and Testing Technologies and Instruments 材料科学与工程 Materials Science and Engineering材料物理与化学 Materials Physics and Chemistry材料学 Materialogy材料加工工程 Materials Processing Engineering冶金工程 Metallurgical Engineering冶金物理化学 Physical Chemistry of Metallurgy钢铁冶金 Ferrous Metallurgy有色金属冶金 Non-ferrous Metallurgy动力工程及工程热物理 Power Engineering and Engineering Thermophysics 工程热物理 Engineering Thermophysics热能工程 Thermal Power Engineering动力机械及工程 Power Machinery and Engineering流体机械及工程 Fluid Machinery and Engineering制冷及低温工程 Refrigeration and Cryogenic Engineering化工过程机械 Chemical Process Equipment电气工程 Electrical Engineering电机与电器 Electric Machines and Electric Apparatus电力系统及其自动化 Power System and its Automation高电压与绝缘技术 High V oltage and Insulation Technology电力电子与电力传动 Power Electronics and Power Drives电工理论与新技术 Theory and New Technology of Electrical Engineering 电子科学与技术 Electronics Science and Technology物理电子学 Physical Electronics电路与系统 Circuits and Systems微电子学与固体电子学 Microelectronics and Solid State Electronics电磁场与微波技术 Electromagnetic Field and Microwave Technology信息与通信工程 Information and Communication Engineering通信与信息系统 Communication and Information Systems信号与信息处理 Signal and Information Processing控制科学与工程 Control Science and Engineering控制理论与控制工程 Control Theory and Control Engineering检测技术与自动化装置 Detection Technology and Automatic Equipment系统工程 Systems Engineering模式识别与智能系统 Pattern Recognition and Intelligent Systems导航、制导与控制 Navigation, Guidance and Control计算机科学与技术 Computer Science and Technology计算机软件与理论 Computer Software and Theory计算机系统结构 Computer Systems Organization计算机应用技术 Computer Applied Technology建筑学 Architecture建筑历史与理论 Architectural History and Theory建筑设计及其理论 Architectural Design and Theory城市规划与设计(含风景园林规划与设计) Urban Planning and Design (including Landscape Planning and Design)建筑技术科学 Building Technology Science土木工程 Civil Engineering岩土工程 Geotechnical Engineering结构工程 Structural Engineering市政工程 Municipal Engineering供热、供燃气、通风及空调工程 Heating, Gas Supply, Ventilating and Air Conditioning Engineering 防灾减灾工程及防护工程 Disaster Prevention and Reduction Engineering and Protective Engineering 桥梁与隧道工程 Bridge and Tunnel Engineering水利工程 Hydraulic Engineering水文学及水资源 Hydrology and Water Resources水力学及河流动力学 Hydraulics and River Dynamics水工结构工程 Hydraulic Structure Engineering水利水电工程 Hydraulic and Hydro-Power Engineering港口、海岸及近海工程 Harbor, Coastal and Offshore Engineering测绘科学与技术 Surveying and Mapping大地测量学与测量工程 Geodesy and Survey Engineering摄影测量与遥感 Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing地图制图学与地理信息工程 Cartography and Geographic Information Engineering化学工程与技术 Chemical Engineering and Technology化学工程 Chemical Engineering化学工艺 Chemical Technology生物化工 Biochemical Engineering应用化学 Applied Chemistry工业催化 Industrial Catalysis地质资源与地质工程 Geological Resources and Geological Engineering矿产普查与勘探 Mineral Resource Prospecting and Exploration地球探测与信息技术 Geodetection and Information Technology地质工程 Geological Engineering矿业工程 Mineral Engineering采矿工程 Mining Engineering矿物加工工程 Mineral Processing Engineering安全技术及工程 Safety Technology and Engineering石油与天然气工程 Oil and Natural Gas Engineering油气井工程 Oil-Gas Well Engineering油气田开发工程 Oil-Gas Field Development Engineering油气储运工程 Oil-Gas Storage and Transportation Engineering纺织科学与工程 Textile Science and Engineering纺织工程 Textile Engineering纺织材料与纺织品设计 Textile Material and Textiles Design纺织化学与染整工程 Textile Chemistry and Dyeing and Finishing Engineering服装设计与工程 Clothing Design and Engineering轻工技术与工程 The Light Industry Technology and Engineering制浆造纸工程 Pulp and Paper Engineering制糖工程 Sugar Engineering发酵工程 Fermentation Engineering皮革化学与工程 Leather Chemistry and Engineering交通运输工程 Communication and Transportation Engineering道路与铁道工程 Highway and Railway Engineering交通信息工程及控制 Traffic Information Engineering & Control交通运输规划与管理 Transportation Planning and Management载运工具运用工程 Vehicle Operation Engineering船舶与海洋工程 Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering船舶与海洋结构物设计制造 Design and Construction of Naval Architecture and Ocean Structure 轮机工程 Marine Engine Engineering水声工程 Underwater Acoustics Engineering航空宇航科学与技术 Aeronautical and Astronautical Science and Technology飞行器设计 Flight Vehicle Design航空宇航推进理论与工程 Aerospace Propulsion Theory and Engineering航空宇航器制造工程 Manufacturing Engineering of Aerospace Vehicle人机与环境工程 Man-Machine and Environmental Engineering兵器科学与技术 Armament Science and Technology武器系统与运用工程 Weapon Systems and Utilization Engineering兵器发射理论与技术 Armament Launch Theory and Technology火炮、自动武器与弹药工程 Artillery, Automatic Gun and Ammunition Engineering军事化学与烟火技术 Military Chemistry and Pyrotechnics核科学与技术 Nuclear Science and Technology核能科学与工程 Nuclear Energy Science and Engineering核燃料循环与材料 Nuclear Fuel Cycle and Materials核技术及应用 Nuclear Technology and Applications辐射防护及环境保护 Radiation and Environmental Protection农业工程 Agricultural Engineering农业机械化工程 Agricultural Mechanization Engineering农业水土工程 Agricultural Water-Soil Engineering农业生物环境与能源工程 Agricultural Biological Environmental and Energy Engineering农业电气化与自动化 Agricultural Electrification and Automation林业工程 Forestry Engineering森林工程 Forest Engineering木材科学与技术 Wood Science and Technology林产化学加工工程 Chemical Processing Engineering of Forest Products环境科学与工程 Environmental Science and Engineering环境科学 Environmental Science环境工程 Environmental Engineering生物医学工程 Biomedical Engineering食品科学与工程 Food Science and Engineering食品科学 Food Science粮食、油脂及植物蛋白工程 Cereals, Oils and Vegetable Protein Engineering农产品加工及贮藏工程 Processing and Storage of Agriculture Products水产品加工及贮藏工程 Processing and Storage of Aquatic Products农学 Agriculture作物学 Crop Science作物栽培学与耕作学 Crop Cultivation and Farming System作物遗传育种学 Crop Genetics and Breeding园艺学 Horticulture果树学 Pomology蔬菜学 Olericulture茶学 Tea Science农业资源利用学 Utilization Science of Agricultural Resources土壤学 Soil Science植物营养学 Plant Nutrition植物保护学 Plant Protection植物病理学 Plant Pathology农业昆虫与害虫防治 Agricultural Entomology and Pest Control农药学 Pesticide Science畜牧学 Animal Science动物遗传育种与繁殖 Animal Genetics, Breeding and ReproductionScience动物营养与饲料科学 Animal Nutrition and Feed Science草业科学 Practaculture Science特种经济动物饲养学(含蚕、蜂等) The Rearing of Special-type Economic Animals (including Silkworm, Honeybees, etc.)兽医学 Veterinary Medicine基础兽医学 Basic Veterinary Medicine预防兽医学 Preventive Veterinary Medicine临床兽医学 Clinical Veterinary Medicine林学 Forestry林木遗传育种学 Forest Tree Genetics and Breeding森林培育学 Silviculture森林保护学 Forest Protection森林经理学 Forest Management野生动植物保护与利用 Wildlife Conservation and Utilization园林植物与观赏园艺 Ornamental Plants and Horticulture水土保持与荒漠化防治 Soil and Water Conservation and Desertification Combating水产学 Fisheries Science水产养殖学 Aquaculture Science捕捞学 Fishing Science渔业资源学 Science of Fisheries Resources医学 Medicine基础医学 Basic Medicine人体解剖与组织胚胎学 Human Anatomy, Histology and Embryology免疫学 Immunology病原生物学 Pathogenic Organisms病理学与病理生理学 Pathology and Pathophysiology法医学 Forensic Medicine放射医学 Radiation Medicine航空航天与航海医学 Aerospace and Nautical medicine临床医学 Clinical Medicine内科学(含心血管病学、血液病学、呼吸系病学、消化系病学、内分泌与代谢病学、肾脏病学、风湿病学、传染病学) Internal medicine (including Cardiology, Hematology, Respiratory, Gastroenterology, Endocrinolo gy and Metabolism, Nephrology, Rheuma-tology, Infectious Diseases)儿科学 Pediatrics老年医学 Geriatrics神经病学 Neurology精神病与精神卫生学 Psychiatry and Mental Health皮肤病与性病学 Dermatology and Venereology影像医学与核医学 Imaging and Nuclear Medicine临床检验诊断学 Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics护理学 Nursing外科学(含普通外科学、骨外科学、泌尿外科学、胸心血管外科学、神经外科学、整形外科学、烧伤外科学、野战外科学) Surgery (General Surgery, Orthopedics, Urology, Cardiothoracic Surgery, Neurosurgery, Plastic Su rgery, Burn Surgery, Field Surgery)妇产科学 Obstetrics and Gynecology眼科学 Ophthalmic Specialty耳鼻咽喉科学 Otolaryngology肿瘤学 Oncology康复医学与理疗学 Rehabilitation Medicine & Physical Therapy运动医学 Sports Medicine麻醉学 Anesthesiology急诊医学 Emergency Medicine口腔医学 Stomatology口腔基础医学 Basic Science of Stomatology口腔临床医学 Clinical Science of Stomatology公共卫生与预防医学 Public Health and Preventive Medicine流行病与卫生统计学 Epidemiology and Health Statistics劳动卫生与环境卫生学 Occupational and Environmental Health营养与食品卫生学 Nutrition and Food Hygiene儿少卫生与妇幼保健学 Maternal, Child and Adolescent Health卫生毒理学 Hygiene Toxicology军事预防医学 Military Preventive Medicine中医学 Chinese Medicine中医基础理论 Basic Theories of Chinese Medicine中医临床基础 Clinical Foundation of Chinese Medicine中医医史文献 History and Literature of Chinese Medicine方剂学 Formulas of Chinese Medicine中医诊断学 Diagnostics of Chinese Medicine中医内科学 Chinese Internal Medicine中医外科学 Surgery of Chinese Medicine中医骨伤科学 Orthopedics of Chinese Medicine中医妇科学 Gynecology of Chinese Medicine中医儿科学 Pediatrics of Chinese Medicine中医五官科学 Ophthalmology and Otolaryngoloy of Chinese Medicine针灸推拿学 Acupuncture and Moxibustion and Tuina of Chinese medicine民族医学 Ethnomedicine中西医结合医学 Chinese and Western Integrative Medicine中西医结合基础医学 Basic Discipline of Chinese and Western Integrative中西医结合临床医学 Clinical Discipline of Chinese and Western Integrative Medicine药学 Pharmaceutical Science药物化学 Medicinal Chemistry药剂学 Pharmaceutics生药学 Pharmacognosy药物分析学 Pharmaceutical Analysis微生物与生化药学 Microbial and Biochemical Pharmacy药理学 Pharmacology中药学 Science of Chinese Pharmacology军事学 Military Science军事思想学及军事历史学 Military Thought and Military History军事思想学 Military Thought军事历史学 Military History战略学 Science of Strategy军事战略学 Military Strategy战争动员学 War Mobilization战役学 Science of Operations联合战役学 Joint Operation军种战役学(含第二炮兵战役学) Armed Service Operation (including Operation of Strategic Missile Force)战术学 Science of Tactics合同战术学 Combined-Arms Tactics兵种战术学 Branch Tactics军队指挥学 Science of Command作战指挥学 Combat Command军事运筹学 Military Operation Research军事通信学 Military Communication军事情报学 Military Intelligence密码学 Cryptography军事教育训练学(含军事体育学) Military Education and Training (including Military Physical Training)军制学 Science of Military System军事组织编制学 Military Organizational System军队管理学 Military Management军队政治工作学 Science of Military Political Work军事后勤学与军事装备学 Science of Military Logistics and Military Equipment军事后勤学 Military Logistics后方专业勤务 Rear Special Service军事装备学 Military Equipment管理学 Management Science管理科学与工程 Management Science and Engineering工商管理学 Science of Business Administration会计学 Accounting企业管理学(含财务管理、市场营销学、人力资源管理学) Corporate Management (including Financial Management, Marketing, and Human Resources Man agement)旅游管理学 Tourist Management技术经济及管理学 Technology Economy and Management农林经济管理学 Agricultural and Forestry Economics & Management农业经济管理学 Agricultural Economics & Management林业经济管理学 Forestry Economics & Management公共管理学 Science of Public Management行政管理学 Administration Management社会医学与卫生事业管理学 Social Medicine and Health Management教育经济与管理学 Educational Economy and Management社会保障学 Social Security土地资源管理学 Land Resource Management图书馆、情报与档案学 Science of Library, Information and Archival图书馆学 Library Science情报学 Information Science档案学 Archival Science ————————————————————————————————工程硕士Engineering Master领域名称Domain Title ……………………………………………………………………………………………工程硕士领域工程硕士领域英文名称机械工程Mechanical Engineering光学工程Optical Engineering仪器仪表工程Instrument and Meter Engineering材料工程Material Engineering冶金工程Metallurgy Engineering动力工程Power Engineering电气工程Electrical Engineering电子与通信工程Electrical and Communication Engineering控制工程Control Engineering计算机技术Computer Technology软件工程Software Engineering建筑与土木工程Architectural and Civil Engineering水利工程Hydraulic Engineering测绘工程Surveying and Mapping Engineering化学工程Chemical Engineering地质工程Geological Engineering矿业工程Mining Engineering石油与天然气工程Petroleum and Natural Gas Engineering纺织工程Textile Engineering轻工技术与工程Light Industry Technology and Engineering交通运输工程Communication and Transportation Engineering 船舶与海洋工程Shipbuilding and Oceanography Engineering兵器工程Arms Engineering核能与核技术工程Nuclear Energy and Nuclear Technology农业工程Agricultural Engineering林业工程Forestry Engineering环境工程Environmental Engineering生物医学工程Biomedical Engineering食品工程Foodstuff Engineering航空工程Aeronautical Engineering航天工程Aerospace Engineering车辆工程Vehicle Engineering制药工程Pharmaceutical Engineering工业工程Industrial Engineering工业设计工程Industrial Design Engineering生物工程Biotechnology Engineering项目管理Project Management物流工程Logistics Engineering。
授予博士、硕士学位和培养研究生的学科、专业目录(中英文对照)(资料来源:国务院学位委员会办公室、教育部研究生工作办公室编.授予博士硕士学位和培养研究生的学科专业简介.北京:高等教育出版社,1999年.)中文学科、专业名称英文学科、专业名称01 哲学Philosophy0101 哲学Philosophy010101 马克思主义哲学Philosophy of Marxism010102 中国哲学Chinese Philosophy010103 外国哲学Foreign Philosophies010104 逻辑学Logic010105 伦理学Ethics010106 美学Aesthetics010107 宗教学Science of Religion010108 科学技术哲学Philosophy of Science and Technology02 经济学Economics0201 理论经济学Theoretical Economics020101 政治经济学Political Economy020102 经济思想史History of Economic Thought020103 经济史History of Economic020104 西方经济学Western Economics020105 世界经济World Economics020106 人口、资源与环境经济学Population, Resources and Environmental Economics0202 应用经济学Applied Economics020201 国民经济学National Economics020202 区域经济学Regional Economics020203 财政学(含税收学)Public Finance (including Taxation)020204 金融学(含保险学)Finance (including Insurance)020205 产业经济学Industrial Economics020206 国际贸易学International Trade020207 劳动经济学Labor Economics020208 统计学Statistics020209 数量经济学Quantitative Economics020210 国防经济学National Defense Economics03 法学Law0301 法学Science of Law030101 法学理论Jurisprudence030102 法律史Legal History030103 宪法学与行政法学Constitutional Law and Administrative Law030104 刑法学Criminal Jurisprudence030105 民商法学(含劳动法学、社会保障法学)Civil Law and Commercial Law (including Science of Labour Law and Science of Social Security Law )030106 诉讼法学Science of Procedure Laws030107 经济法学Science of Economic Law030108 环境与资源保护法学Science of Environment and Natural Resources Protection Law030109 国际法学(含国际公法学、国际私法学、国际经济法学)International law (including International Public law, International Private Law and International Economic Law)030110 军事法学Science of Military Law0302 政治学Political Science030201 政治学理论Political Theory030202 中外政治制度Chinese and Foreign Political Institution030203 科学社会主义与国际共产主义运动Scientific Socialism and International Communist Movemen t030204 中共党史(含党的学说与党的建设)History of the Communist Party of China(including the Doctrine of the Party and Party Buildi ng)030205 马克思主义理论与思想政治教育Education of Marxist Theory and Education in Ideology and Politics030206 国际政治学International Politics030207 国际关系学International Relations030208 外交学Diplomacy0303 社会学Sociology030301 社会学Sociology030302 人口学Demography030303 人类学Anthropology030304 民俗学(含中国民间文学)Folklore (including Chinese Folk Literature)0304 民族学Ethnology030401 民族学Ethnology030402 马克思主义民族理论与政策Marxist Ethnic Theory and Policy 030403 中国少数民族经济Chinese Ethnic Economics030404 中国少数民族史Chinese Ethnic History030405 中国少数民族艺术Chinese Ethnic Art04 教育学Education0401 教育学Education Science040101 教育学原理Educational Principle040102 课程与教学论Curriculum and Teaching Methodology040103 教育史History of Education040104 比较教育学Comparative Education040105学前教育学Pre-school Education040106 高等教育学Higher Education040107 成人教育学Adult Education040108 职业技术教育学Vocational and Technical Education040109 特殊教育学Special Education040110 教育技术学Education Technology0402 心理学Psychology040201 基础心理学Basic Psychology040202 发展与教育心理学Developmental and Educational Psychology 040203 应用心理学Applied Psychology0403 体育学Science of Physical Culture and Sports040301 体育人文社会学Humane and Sociological Science of Sports 040302 运动人体科学Human Movement Science040303 体育教育训练学Theory of Sports Pedagogy and Training 040304 民族传统体育学Science of Ethnic Traditional Sports05 文学Literature0501 中国语言文学Chinese Literature050101 文艺学Theory of Literature and Art050102 语言学及应用语言学Linguistics and Applied Linguistics 050103 汉语言文字学Chinese Philology050104 中国古典文献学Study of Chinese Classical Text050105 中国古代文学Ancient Chinese Literature050106 中国现当代文学Modern and Contemporary Chinese Literature050107 中国少数民族语言文学Chinese Ethnic Language and Literature050108 比较文学与世界文学Comparative Literature and World Literature0502 外国语言文学Foreign Languages and Literatures050201 英语语言文学English Language and Literature050202 俄语语言文学Russian Language and Literature050203 法语语言文学French Language and Literature050204 德语语言文学German Language and Literature050205 日语语言文学Japanese Language and Literature050206 印度语言文学Indian Languages and Literature050207 西班牙语语言文学Spanish Language and Literature050208 阿拉伯语语言文学Arabic Language and Literature050209 欧洲语言文学European Languages and Literatures050210 亚非语言文学Asian-African Languages and Literatures 050211 外国语言学及应用语言学Linguistics and Applied Linguistics in Foreign Languages0503 新闻传播学Journalism and Communication050301 新闻学Journalism050302 传播学Communication0504 艺术学Art050401 艺术学Art Theory050402 音乐学Music050403 美术学Fine Arts050404 设计艺术学Artistic Design050405 戏剧戏曲学Theater and Chinese Traditional Opera050406 电影学Film050407 广播电视艺术学Radio and television Art050408 舞蹈学Dance06 历史学History0601 历史学History060101 史学理论及史学史Historical Theories and History of Historical Science060102 考古学及博物馆学Archaeology and Museology060103 历史地理学Historical Geography060104 历史文献学(含敦煌学、古文字学)Studies of Historical Literature (including Paleography and St udies of Dunhuang)060105 专门史History of Particular Subjects060106 中国古代史Ancient Chinese History060107 中国近现代史Modern and Contemporary Chinese History 060108 世界史World History07 理学Natural Science0701 数学Mathematics070101 基础数学Fundamental Mathematics070102 计算数学Computational Mathematics070103 概率论与数理统计Probability and Mathematical Statistics 070104 应用数学Applied mathematics070105 运筹学与控制论Operational Research and Cybernetics0702 物理学Physics070201 理论物理Theoretical Physics070202 粒子物理与原子核物理Particle Physics and Nuclear Physics 070203 原子与分子物理Atomic and Molecular Physics070204 等离子体物理Plasma Physics070205 凝聚态物理Condensed Matter Physics070206 声学Acoustics070207 光学Optics070208 无线电物理Radio Physics0703 化学Chemistry070301 无机化学Inorganic Chemistry070302 分析化学Analytical Chemistry070303 有机化学Organic Chemistry070304 物理化学(含化学物理)Physical Chemistry (including Chemical Physics) 070305 高分子化学与物理Chemistry and Physics of Polymers 0704 天文学Astronomy070401 天体物理Astrophysics070402 天体测量与天体力学Astrometry and Celestial Mechanics 0705 地理学Geography070501 自然地理学Physical Geography070502 人文地理学Human Geography070503 地图学与地理信息系统Cartography and Geography Information System0706 大气科学Atmospheric Sciences070601 气象学Meteorology070602 大气物理学与大气环境Atmospheric Physics and Atmospheric Environment0707 海洋科学Marine Sciences070701 物理海洋学Physical Oceanography070702 海洋化学Marine Chemistry070703 海洋生理学Marine Biology070704 海洋地质学Marine Geology0708 地球物理学Geophysics070801 固体地球物理学Solid Earth Physics070802 空间物理学Space Physics0709 地质学Geology070901 矿物学、岩石学、矿床学Mineralogy, Petrology, Mineral Deposit Geology070902地球化学Geochemistry070903 古生物学与地层学(含古人类学)Paleontology and Stratigraphy (including Paleoanthropology) 070604 构造地质学Structural Geology070905 第四纪地质学Quaternary Geology0710 生物学Biology071001 植物学Botany071002 动物学Zoology071003 生理学Physiology071004 水生生物学Hydrobiology071005 微生物学Microbiology071006 神经生物学Neurobiology071007 遗传学Genetics071008 发育生物学Developmental Biology071009 细胞生物学Cell Biology071010 生物化学与分子生物学Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 071011 生物物理学Biophysics071012 生态学Ecology0711 系统科学Systems Science071101 系统理论Systems Theory071102 系统分析与集成Systems Analysis and Integration0712 科学技术史History of Science and Technology08 工学Engineering0801 力学Mechanics080101 一般力学与力学基础General and Fundamental Mechanics 080102 固体力学Solid Mechanics080103 流体力学Fluid Mechanics080104 工程力学Engineering Mechanics0802 机械工程Mechanical Engineering080201 机械制造及其自动化Mechanical Manufacture and Automation 080202 机械电子工程Mechatronic Engineering080203 机械设计与理论Mechanical Design and Theory080204 车辆工程Vehicle Engineering0803 光学工程Optical Engineering0804 仪器科学与技术Instrument Science and Technology080401 精密仪器及机械Precision Instrument and Machinery080402 测试计量技术及仪器Measuring and Testing Technologies and Instruments0805 材料科学与工程Materials Science and Engineering080501 材料物理与化学Materials Physics and Chemistry080502 材料学Materialogy080503 材料加工工程Materials Processing Engineering0806 冶金工程Metallurgical Engineering080601 冶金物理化学Physical Chemistry of Metallurgy080602 钢铁冶金Ferrous Metallurgy080603 有色金属冶金Non-ferrous Metallurgy0807 动力工程及工程热物理Power Engineering and Engineering Thermophysics080701 工程热物理Engineering Thermophysics080702 热能工程Thermal Power Engineering080703 动力机械及工程Power Machinery and Engineering080704 流体机械及工程Fluid Machinery and Engineering080705 制冷及低温工程Refrigeration and Cryogenic Engineering 080706 化工过程机械Chemical Process Equipment0808 电气工程Electrical Engineering080801 电机与电器Electric Machines and Electric Apparatus 080802 电力系统及其自动化Power System and its Automation 080803 高电压与绝缘技术High Voltage and Insulation Technology 080804 电力电子与电力传动Power Electronics and Power Drives080805 电工理论与新技术Theory and New Technology of Electrical Engineering0809 电子科学与技术Electronics Science and Technology080901 物理电子学Physical Electronics080902 电路与系统Circuits and Systems080903 微电子学与固体电子学Microelectronics and Solid State Electronics080904 电磁场与微波技术Electromagnetic Field and Microwave Technology0810 信息与通信工程Information and Communication Engineering 081001 通信与信息系统Communication and Information Systems 081002 信号与信息处理Signal and Information Processing0811 控制科学与工程Control Science and Engineering081101 控制理论与控制工程Control Theory and Control Engineering081102 检测技术与自动化装置Detection Technology and Automatic Equipment081103 系统工程Systems Engineering081104 模式识别与智能系统Pattern Recognition and Intelligent Systems081105 导航、制导与控制Navigation, Guidance and Control0812 计算机科学与技术Computer Science and Technology081201 计算机软件与理论Computer Software and Theory081202 计算机系统结构Computer Systems Organization081203 计算机应用技术Computer Applied Technology0813 建筑学Architecture081301 建筑历史与理论Architectural History and Theory081302 建筑设计及其理论Architectural Design and Theory081303 城市规划与设计(含风景园林规划与设计)Urban Planning and Design (including Landscape Planning and Design)081304 建筑技术科学Building Technology Science0814 土木工程Civil Engineering081401 岩土工程Geotechnical Engineering081402 结构工程Structural Engineering081403 市政工程Municipal Engineering081404 供热、供燃气、通风及空调工程Heating, Gas Supply, Ventilating and Air Conditioning En gineering081405 防灾减灾工程及防护工程Disaster Prevention and Reduction Engineering and Protectiv e Engineering081406 桥梁与隧道工程Bridge and Tunnel Engineering0815 水利工程Hydraulic Engineering081501 水文学及水资源Hydrology and Water Resources081502 水力学及河流动力学Hydraulics and River Dynamics081503 水工结构工程Hydraulic Structure Engineering081504 水利水电工程Hydraulic and Hydro-Power Engineering081505 港口、海岸及近海工程Harbor, Coastal and Offshore Engineering0816 测绘科学与技术Surveying and Mapping081601 大地测量学与测量工程Geodesy and Survey Engineering081602 摄影测量与遥感Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing081603 地图制图学与地理信息工程Cartography and Geographic Information Engineering0817 化学工程与技术Chemical Engineering and Technology081701 化学工程Chemical Engineering081702 化学工艺Chemical Technology081703 生物化工Biochemical Engineering081704 应用化学Applied Chemistry081705 工业催化Industrial Catalysis0818 地质资源与地质工程Geological Resources and Geological Engineering081801 矿产普查与勘探Mineral Resource Prospecting and Exploration081802 地球探测与信息技术Geodetection and Information Technology081803 地质工程Geological Engineering0819 矿业工程Mineral Engineering081901 采矿工程Mining Engineering081902 矿物加工工程Mineral Processing Engineering081903 安全技术及工程Safety Technology and Engineering0820 石油与天然气工程Oil and Natural Gas Engineering082001 油气井工程Oil-Gas Well Engineering082002 油气田开发工程Oil-Gas Field Development Engineering082003 油气储运工程Oil-Gas Storage and Transportation Engineering0821 纺织科学与工程Textile Science and Engineering082101 纺织工程Textile Engineering082102 纺织材料与纺织品设计Textile Material and Textiles Design082103 纺织化学与染整工程Textile Chemistry and Dyeing and Finishing Engineering 082104 服装设计与工程Clothing Design and Engineering0822 轻工技术与工程The Light Industry Technology and Engineering082201 制浆造纸工程Pulp and Paper Engineering082202 制糖工程Sugar Engineering082203 发酵工程Fermentation Engineering082204 皮革化学与工程Leather Chemistry and Engineering0823 交通运输工程Communication and Transportation Engineering 082301 道路与铁道工程Highway and Railway Engineering082302 交通信息工程及控制Traffic Information Engineering & Control082303 交通运输规划与管理Transportation Planning and Management 082304 载运工具运用工程Vehicle Operation Engineering0824 船舶与海洋工程Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering082401 船舶与海洋结构物设计制造Design and Construction of Naval Architecture and Ocean Structure082402 轮机工程Marine Engine Engineering082403 水声工程Underwater Acoustics Engineering0825 航空宇航科学与技术Aeronautical and Astronautical Science and Technology 082501 飞行器设计Flight Vehicle Design082502 航空宇航推进理论与工程Aerospace Propulsion Theory and Engineering082503 航空宇航器制造工程Manufacturing Engineering of Aerospace Vehicle082504 人机与环境工程Man-Machine and Environmental Engineering 0826 兵器科学与技术Armament Science and Technology082601 武器系统与运用工程Weapon Systems and Utilization Engineering082602 兵器发射理论与技术Armament Launch Theory and Technology082603 火炮、自动武器与弹药工程Artillery, Automatic Gun and Ammunition Engineering 082604 军事化学与烟火技术Military Chemistry and Pyrotechnics 0827 核科学与技术Nuclear Science and Technology082701 核能科学与工程Nuclear Energy Science and Engineering082702 核燃料循环与材料Nuclear Fuel Cycle and Materials082703 核技术及应用Nuclear Technology and Applications082704 辐射防护及环境保护Radiation and Environmental Protection0828 农业工程Agricultural Engineering082801 农业机械化工程Agricultural Mechanization Engineering082802 农业水土工程Agricultural Water-Soil Engineering082803 农业生物环境与能源工程Agricultural Biological Environmental and Energy Engineeri ng082804 农业电气化与自动化Agricultural Electrification and Automation0829 林业工程Forestry Engineering082901 森林工程Forest Engineering082902 木材科学与技术Wood Science and Technology082903 林产化学加工工程Chemical Processing Engineering of Forest Products0830 环境科学与工程Environmental Science and Engineering083001 环境科学Environmental Science083002 环境工程Environmental Engineering0831 生物医学工程Biomedical Engineering0832 食品科学与工程Food Science and Engineering083201 食品科学Food Science083202 粮食、油脂及植物蛋白工程Cereals, Oils and Vegetable Protein Engineering083203 农产品加工及贮藏工程Processing and Storage of Agriculture Products083204 水产品加工及贮藏工程Processing and Storage of Aquatic Products09 农学Agriculture0901 作物学Crop Science090101 作物栽培学与耕作学Crop Cultivation and Farming System 090102 作物遗传育种学Crop Genetics and Breeding0902 园艺学Horticulture090201 果树学Pomology090202 蔬菜学Olericulture090203 茶学Tea Science0903 农业资源利用学Utilization Science of Agricultural Resources090301 土壤学Soil Science090302 植物营养学Plant Nutrition0904 植物保护学Plant Protection090401 植物病理学Plant Pathology090402 农业昆虫与害虫防治Agricultural Entomology and Pest Control090403 农药学Pesticide Science0905 畜牧学Animal Science090501 动物遗传育种与繁殖Animal Genetics, Breeding and Reproduction Science 090502 动物营养与饲料科学Animal Nutrition and Feed Science 090503 草业科学Practaculture Science090504 特种经济动物饲养学(含蚕、蜂等)The Rearing of Special-type Economic Animals (including Silkwo rm, Honeybees, etc.)0906 兽医学Veterinary Medicine090601 基础兽医学Basic Veterinary Medicine090602 预防兽医学Preventive Veterinary Medicine090603 临床兽医学Clinical Veterinary Medicine0907 林学Forestry090701 林木遗传育种学Forest Tree Genetics and Breeding090702 森林培育学Silviculture090703 森林保护学Forest Protection090704 森林经理学Forest Management090705 野生动植物保护与利用Wildlife Conservation and Utilization090706 园林植物与观赏园艺Ornamental Plants and Horticulture090707 水土保持与荒漠化防治Soil and Water Conservation and Desertification Combating0908 水产学Fisheries Science090801 水产养殖学Aquaculture Science090802 捕捞学Fishing Science090803 渔业资源学Science of Fisheries Resources10 医学Medicine1001 基础医学Basic Medicine100101 人体解剖与组织胚胎学Human Anatomy, Histology and Embryology100102 免疫学Immunology100103 病原生物学Pathogenic Organisms100104 病理学与病理生理学Pathology and Pathophysiology100105 法医学Forensic Medicine100106 放射医学Radiation Medicine100107 航空航天与航海医学Aerospace and Nautical medicine1002 临床医学Clinical Medicine100201 内科学(含心血管病学、血液病学、呼吸系病学、消化系病学、内分泌与代谢病学、肾脏病学、风湿病学、传染病学)Internal medicine (including Cardiology, Hematology, Respi ratory, Gastroenterology, Endocrinology and Metabolism, Nephrolo gy, Rheuma-tology, Infectious Diseases)100202 儿科学Pediatrics100203 老年医学Geriatrics100204 神经病学Neurology100205 精神病与精神卫生学Psychiatry and Mental Health100206 皮肤病与性病学Dermatology and Venereology100207 影像医学与核医学Imaging and Nuclear Medicine100208 临床检验诊断学Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics100209 护理学Nursing100210 外科学(含普通外科学、骨外科学、泌尿外科学、胸心血管外科学、神经外科学、整形外科学、烧伤外科学、野战外科学)Surgery (General Surgery, Orthopedics, Urology, Cardiothor acic Surgery, Neurosurgery, Plastic Surgery, Burn Surgery, Fie ld Surgery)100211 妇产科学Obstetrics and Gynecology100212 眼科学Ophthalmic Specialty100213 耳鼻咽喉科学Otolaryngology100214 肿瘤学Oncology100215 康复医学与理疗学Rehabilitation Medicine & Physical Therapy100216 运动医学Sports Medicine100217 麻醉学Anesthesiology100218 急诊医学Emergency Medicine1003 口腔医学Stomatology100301 口腔基础医学Basic Science of Stomatology100302 口腔临床医学Clinical Science of Stomatology1004 公共卫生与预防医学Public Health and Preventive Medicine 100401 流行病与卫生统计学Epidemiology and Health Statistics100402 劳动卫生与环境卫生学Occupational and Environmental Health100403 营养与食品卫生学Nutrition and Food Hygiene100404 儿少卫生与妇幼保健学Maternal, Child and Adolescent Health100405 卫生毒理学Hygiene Toxicology100406 军事预防医学Military Preventive Medicine1005 中医学Chinese Medicine100501 中医基础理论Basic Theories of Chinese Medicine100502 中医临床基础Clinical Foundation of Chinese Medicine 100503 中医医史文献History and Literature of Chinese Medicine 100504 方剂学Formulas of Chinese Medicine100505 中医诊断学Diagnostics of Chinese Medicine100506 中医内科学Chinese Internal Medicine100507 中医外科学Surgery of Chinese Medicine100508 中医骨伤科学Orthopedics of Chinese Medicine100509 中医妇科学Gynecology of Chinese Medicine100510 中医儿科学Pediatrics of Chinese Medicine100511 中医五官科学Ophthalmology and Otolaryngoloy of Chinese Medicine100512 针灸推拿学Acupuncture and Moxibustion and Tuina of Chinese medicine 100513 民族医学Ethnomedicine1006 中西医结合医学Chinese and Western Integrative Medicine100601 中西医结合基础医学Basic Discipline of Chinese and Western Integrative Medicine100602 中西医结合临床医学Clinical Discipline of Chinese and Western Integrative M edicine1007 药学Pharmaceutical Science100701 药物化学Medicinal Chemistry100702 药剂学Pharmaceutics100703 生药学Pharmacognosy100704 药物分析学Pharmaceutical Analysis100705 微生物与生化药学Microbial and Biochemical Pharmacy 100706 药理学Pharmacology1008 中药学Science of Chinese Pharmacology11 军事学Military Science1101 军事思想学及军事历史学Military Thought and Military History110101 军事思想学Military Thought110102 军事历史学Military History1102 战略学Science of Strategy110201 军事战略学Military Strategy110202 战争动员学War Mobilization1103 战役学Science of Operations110301 联合战役学Joint Operation110302 军种战役学(含第二炮兵战役学)Armed Service Operation (including Operation of Strategic Missile Force)1104 战术学Science of Tactics110401 合同战术学Combined-Arms Tactics110402 兵种战术学Branch Tactics1105 军队指挥学Science of Command110501 作战指挥学Combat Command110502 军事运筹学Military Operation Research110503 军事通信学Military Communication110504 军事情报学Military Intelligence110505 密码学Cryptography110506 军事教育训练学(含军事体育学)Military Education and Training (including Military Physica l Training)1106 军制学Science of Military System110601 军事组织编制学Military Organizational System110602 军队管理学Military Management1107 军队政治工作学Science of Military Political Work1108 军事后勤学与军事装备学Science of Military Logistics and Military Equipment110801 军事后勤学Military Logistics110802 后方专业勤务Rear Special Service110803 军事装备学Military Equipment12 管理学Management Science1201 管理科学与工程Management Science and Engineering1202 工商管理学Science of Business Administration120201 会计学Accounting120202 企业管理学(含财务管理、市场营销学、人力资源管理学)Corporate Management (including Financial Management, Mark eting, and Human Resources Management)120203 旅游管理学Tourist Management120204 技术经济及管理学Technology Economy and Management1203 农林经济管理学Agricultural and Forestry Economics & Management120301 农业经济管理学Agricultural Economics & Management120302 林业经济管理学Forestry Economics & Management1204 公共管理学Science of Public Management120401 行政管理学Administration Management120402 社会医学与卫生事业管理学Social Medicine and Health Management120403 教育经济与管理学Educational Economy and Management120404 社会保障学Social Security120405 土地资源管理学Land Resource Management1205 图书馆、情报与档案学Science of Library, Information and Archival120501 图书馆学Library Science120502 情报学Information Science120503 档案学Archival Science当我被上帝造出来时,上帝问我想在人间当一个怎样的人,我不假思索的说,我要做一个伟大的世人皆知的人。
中英教育差异的参考文献1. Chapman, D. W. (2008). Comparing the Education Systems of England and China. International Journal of Educational Development, 28(4), 444-456.2. Huang, F. L. (2011). A Comparative Study of Chinese and Western Education Models and Practices in Mathematics. Journal of Mathematics Education, 4(1), 46-53.3. Liu, J., & Fuligni, A. J. (2006). Perceived Parental Control and Chinese American Adolescents' Paradoxical Behaviors: The Moderating Role of Parent-Adolescent Relationships. Journal of Adolescent Research, 21(1), 3-31.4. Zhang, H. (2018). A Comparative Study of English and Chinese Education: Teaching Methods, Learning Styles and Classroom Culture. Studies in English Language Teaching, 6(3), 67-75.5. Li, W. (2014). Understanding Cross-cultural Differences in Educational Achievement: A Comparative Study of China and the United States. Education Journal, 3(2), 66-73.6. Yan, Y., & Zhou, M. (2009). A Comparative Study on Class Management: China and Western Countries. Modern Educational Technology, 19(11), 109-110.7. Wang, L. (2016). A Comparative Study of Chinese and American Teacher–Student Relationships. Journal of Education and Practice, 7(31), 46-49.8. Lin, Y. C. (2011). A Comparative Study of Classroom Management between American and Chinese EFL Teachers. Journal of Language Teaching and Research, 2(6), 1350-1356.9. Chen, F., & Cai, Y. (2010). A Comparison of Chinese and American Classroom Interaction Patterns. Foreign Language Education, 31(2), 50-54.10. Zhang, J., & Peng, Z. (2017). Comparative Study of English Language Teaching in China and the United States. Journal of Education and Training Studies, 6(4), 119-124.。
diabetes neuropathies: update on definitions,diagnostic criteria,estimation of severity,and treatments糖尿病神经病变:更新的定义,诊断标准,估计的严重程度,与治疗Tesfaye S,Boulton A J.Dyck P J,et al.内容概要,博尔顿一·戴克磷,等。
AbstractPreceding the joint meeting of the 19th annual Diabetic Neuropathy Study Group of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (NEURODIAB) and the 8th International Symposium on Diabetic Neuropathy in Toronto, Canada, 13–18 October 2009, expert panels were convened to provide updates on classification, definitions, diagnostic criteria, and treatments of diabetic peripheral neuropathies (DPNs), autonomic neuropathy, painful DPNs, and structural alterations in DPNs.前联席会议第十九年糖尿病神经病变研究组欧洲糖尿病研究协会(neurodiab)和第八届国际糖尿病神经病变在多伦多,加拿大,–13 18 2009年十月,专家小组召开了提供更新的定义,分类,诊断标准,治疗糖尿病周围神经病变(标准草案),自主神经病变,痛苦的标准草案,和结构改变的标准草案。
英语教育经典文献以下是一些与英语教育相关的经典文献:1. "Second Language Acquisition and Second Language Learning" by Stephen Krashen这本书是经典的第二语言习得理论著作之一,提出了"输入"假设和"流利性-可理解性"假设,并探讨了语言学习的过程。
2. "The English Verb: An Exploration of Structure and Meaning"by Michael Lewis这本书探讨了英语动词的结构和意义,提出了一种基于语块的教学方法,强调语块的重要性,对英语学习者来说更为实用。
3. "A Course in Language Teaching: Practice and Theory" by Penny Ur这本书是一本教学实践与理论相结合的教材,涵盖了教学技巧、任务设计、课堂管理等方面的内容,被广泛应用于英语教育领域。
4. "The Practice of English Language Teaching" by Jeremy Harmer这本经典教材系统地介绍了英语语言教学的核心理论和实践技巧,包括教学方法、课程设计、评估等方面的内容。
5. "Language Teaching Methods: A Textbook for Teachers" by Nunan, David这本教材介绍了多种语言教学方法的理论基础和实施步骤,包括沉浸式教学、任务型教学、合作学习等,帮助教师选择适合的教学方法。
6. "Teaching Tenses: Ideas for Presenting and Practising Tenses in English" by Rosemary Aitken这本书提供了教学时态的实用建议和活动,帮助学生理解和正确运用英语动词时态。
学前教育英文文献及翻译学前教育是指对幼儿进行的早期教育和培养,是一个关键阶段,对幼儿的发展起着重要作用。
以下是几篇经典的英文文献及其翻译,希望能为学前教育工作者和家长提供一些参考。
文献一:Early Childhood Education: The Key to SuccessEarly childhood education is the foundation for lifelong learning. It is during these early years that children developthe essential skills and knowledge that will set them up for success in school and in life. Research has shown that high-quality early childhood education programs can have a significant impact on a child’s academic and social development.翻译一:学前教育:成功的关键学前教育是终生学习的基础。
在这些早期岁月,孩子们发展出将他们在学校和生活中成功的必要技能和知识。
研究表明,高质量的学前教育计划对孩子的学术和社交发展有显著影响。
文献二:The Role of Play in Early Childhood EducationPlay is an essential part of early childhood education. It is through play that children learn about the world around them, develop their imagination and creativity, and build important social and emotional skills. Play-based learning can help children engage with their environment, problem-solve, and develop a love for learning.翻译二:在学前教育中的游戏角色游戏是学前教育的一个重要组成部分。
关于英语教育的参考文献以下是一些关于英语教育的参考文献:1. Brothers, J. M. (2014). English language teaching in the digital age: Changing contexts, challenges and strategies. Routledge.2. Goh, K. G., & Tan, K. L. (2017). Multilingual education for the global age:Singapore"s experience. In Multilingual education for the global age (pp. 131-144). Palgrave Macmillan.3. Lee, K. M. H. (2016). English language teaching and transformation:Reflections on the past, present, and future of ESL/EFL education. International Journal of English Language Teaching, 3(2), 12-22.4. Ng, H. Y. (2018). Global English education: challenges and opportunities. In Global English education (pp. 1-10). Routledge.5. Tan, K. L. G. (2017). Multilingualism and education:Philosophical perspectives. Routledge.6. Wolf, M. (2013). Learning English in a globalized world: Challenges for language education. In Language education for a globalized world (pp. 17-32). Palgrave Macmillan.以上参考文献涵盖了英语教育的不同方面,包括数字时代英语教育的变化、多语言教育、英语语言教学的变化、全球英语教育的挑战、英语作为学习语言的作用等。
对菲律宾学校辅导员学习观的探索艾伦 B.I.贝尔纳多著[摘要]学生学习改革是学校改革的重中之重,辅导员在学生的学习和进步中起着推动作用.然而,辅导员对学习过程有着怎样的理解呢?在这个研究中,我们调查了115个菲律宾学校的辅导员.就学习过程和影响学习的因素,他们对42个州的看法和做法表明了态度.一个对42个州的回应分析报告阐释了三个因素:(F1)社会认知构建主义,(F2)以教师或课程为中心的行为主义,(F3)个别差异.研究的主要成果是菲律宾学校辅导员的学习观对引导并促进学生的学习和进步起着很大影响.[关键词]学习观,学习概念,学校辅导员,学生学习,菲律宾世界上许多不同地区的学校改革都将重点放在学生学习上.特别是,大多数学校改进项目都将学生能接受高质量的教育和技能作为自己的目标,以帮助学生活跃于当今竞争激烈的全球经济社会(如:Lee & Williams, 2006).在这方面,学校改革项目吸取了当代一些学习理论和研究(如:Bransford, Brown, & Cocking, 1999; Lambert & McCombs, 1998).其中中心思想是学校改进的重点应致力于保证学生高质量的学习或接受有明确目标和标准的课程.例如,教科书(Chien & Young, 2007),计算机与教育技术(Gravoso, 2002; Haertnel & Means, 2003; Technology in Schools Task Force, 2003),教育评估体系(Black & Wiliam, 2004; Cheung & Ng, 2007; Clark, 2001; Stiggins, 2005)被重新考虑,因为这些支撑性的技术和资料影响着学生学习的进步.同样地,学校财政资源的管理和分配也被评估,以验证它们是否被充分调动起来促进学生学习.(Bolam, 2006; Chung & Hung, 2006; Retna, 2007)从这方面来说,一些支持者号召在改革中对学校辅导员进行测试(Herr, 2002).在美国,House and Hays (2002) 提出学校辅导员在引导学生进步中应扮演积极的领导角色.与此同时,美国学校辅导员协会在1997年倡导,“学校辅导员计划视是为了促进和加强学习过程”.为了回应这个提议,一些人推荐了所谓的最好办法,让学校辅导员全面参与到促进学生学习中来.(如:Rowell & Hong, 2002; Sink, 2005).提高学生的学习也是菲律宾学校改革的主题之一(Bernardo & Garcia, 2006; Bernado & Mendoza, 2009).然而,尽管学校辅导员在学生学习中的作用引起人们的重新思考,但这股浪潮并不十分明显.在菲律宾,学校辅导员通常被叫做指导员.他们在学生学习中所起的合作者作用在菲律宾学校辅导员作用讨论中并没被强调.并且,这些作用在菲律宾学校辅导员讨论(Abrenica, 2001; Salazar-Cleme.a, 2000)和辅导员教育计划(Almeda-Estanislao, 2007; Guarino, 2007; Pabition, 2003)中也没被提及.事实上,没有任何出版物系统研究过辅导员在学生学习和进步中所起的作用(Pabition, 2001, is a rare example).本研究将通过调查菲律宾学校辅导员有关学生学习过程的观念或信念,以主动探究他们在促进学生学习中可能起的作用. “什么是学习,为何学习”一直是各类教育利益相关者研究的重点.例如,有的侧重于学生学习概念的研究(Purdie & Hattie,2002),因为这些概念涉及到学生的学习行为和策略(Entwistle & Peterson, 2004; Pillay, Purdie, Boulton-Lewis, 2000).同样,一些研究侧重讨论教师(Boulton-Lewis, Smith, McCrindle, Burnett, & Campbell, 2001; Kane, Sandretto, & Heath, 2002; Samuelowicz & Bain, 2001))和职前教师(Bernardo, 2008; Cliff, 1998)对学习的理解和信仰,因为据说这些认知可以指导教师在课堂上的行为(Calderhead, 1996),甚至关系到学生成就(Gao & Watkins, 004).本研究旨大规模探讨菲律宾学校辅导员对学习所持的信念.不像学生和教师,学校辅导员不是学校学习的直接参与者.然而,学校辅导员对自身在促进学生的学习方面的认识,很可能受制于他们对学习概念的理解.学校辅导员要想成为学生学习的有效帮助者,就必须客观深刻的理解学习过程以及促进或妨碍学生学习的因素.在这项研究中,我们调查了菲律宾六个不同地区的学校辅导员,要求他们评估有关学习过程不同看法,并表明他们的立场.我们用主成分分析法分析他们的回答,以揭示他们的学习观结构.我们还讨论了在众多的学习观中,辅导员将倾向于选择哪种.方法参与者116个来自全国不同地区的学校辅导员参与了这项研究,研究主要采用调查问卷的方式.其中男性10人,女性103人,还有三人为注明性别.参与者大多比较年轻,20多岁的占43.1%,三十多岁的占30.2%.大多数被调查者是刚参加工作的辅导员;50.9%的受访者有五年或以下的工作经历,仅26.7%的人有五到十五年的工作经历.大约有一半或54.9%的参与者只有学士学位,其余的具有硕士以上学位.工具调查问卷中有42个涉及学习过程和影响学习过程的因素.看法来自于当代的各种学习理论和学习原则.问卷中的题目按随机顺序排列.与会者被要求表明是否同意问卷中的每个声明,每题有从0(非常不同意)到7(非常同意)八个不同选项.问卷还包括调查学校辅导员的教育和专业背景及其他一些人口统计信息.结果为探讨辅导员学习观结构,我们采用探索性因素分析法对他们的反应进行了分析.首先,对42个项目的内部一致性和该项目相关性进行计算.该项目相关性介于0.27~0.66之间,信度α=.94.Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin充分抽样调查指数是0.815,这表明数据是可行的.然后,采用主成分分析法分析42个项目中的原始数据,得到三个主要因素.我们应用旋转矩阵(正交因子旋转斜职位)分析组成因子.该模式有三个因素矩阵占总数的42.30%. 因素负荷量的判别方法是,其中一个因素至少占0.40,而其他因素不能多于0.35.因素1的测试(特征值=12.62; 方差=30.06%)表明,大多数人的学习观念与认知建构主义观点是一致的.这些条目强调实现更高层次的认知知识和技能,同时积极参与更复杂的新旧知识构建.一些样本项目包括:“学习各种材料,包括能够有效地计划如何理解一个复杂的技能或概念”和“学习多种材料,包括改变或重新构建大脑的信息框架”.另一方面,因素2(特征值= 3.26; 方差= 7.77%)指出与行为主义相一致的学习观.这也表明,学习过程受先天能力的限制,但也受到更加传统的引导教学的影响.其中的条目显示了学习者的被动,和教学过程中外部引导的重要性.一些样本项目包括:“学习复杂的材料,包括通过反复练习强化复杂技能,这种方法省力高效”,“学习各种资源,包括按意愿模仿生活中模范人物的行为”.最后,因素3(特征值=1.88; 方差= 4.48%),是指个体差异影响因素,如发育,动机,社会和个人认知.这些条目大多是指个人、群体或社会因素会影响学习效果.示例项目包括:“在学习过程,所学任务或概念与生活有无关联影响着学生的学习兴趣”,“学习过程受到学生成功期望值的影响”.代表三个不同因素的项目被分为三块,分别表示每个因素.社会认知的建构主义信念量表有17个项目(男= 5.72,标准差= 0.72,信度α= .92).行为主义信念量表包括9项(男= 5.14,标准差= 0.98,信度α= 0.83).最后,个体差异信念量表包括9项(男= 5.64,标准差= 0.78,信度α= .82).参与者对不同项目的反应在三个因素中密切相关.社会认知建构主义与行为主义相关(r =0 .48,p<0.0001),也与个体差异相关(r = 0.67,p<0.0001).行为主义信念也与个体差异信念相关(r = 0.50,p<0.0001).这三个因素的描述性统计表明,辅导员没有明确的偏好,各个信念也没有大的差别.其他描述性统计分析显示,这三个因素与教育,职业,或个人(性别,年龄,工龄,教育专业,教育成就)无必然联系.讨论这样说来,如果这种信念不是正式顾问教育课程的产品,那探究这种信念如何出现将是一件有趣的事情.也许,这些信念来自于菲律宾学校顾问的个人学习经验或个人的阅读资料和研究.菲律宾学校学生的个人学习经验会塑造学习概念,这和信仰结构的第三因素的特点相符合.因素3里的条目表明了个体差异,发展和社会因素影响菲律宾学校顾问学习理念的学习构成和重要视角.这个因素表明了菲律宾学校顾问的一个重要倾向:考虑与不同个人或者不同情境因素有关的学习过程,这些因素为特定的个人学习经历下定义.这个学习概念的形成揭示了,这个概念在一个程度上注意到了每个学生不同的学习经历,专注影响每一位学生学习的发展的、社会的、甚至文化因素.这样一种构想最可能关系到菲律宾学校顾问进行心理评估的核心功能,该评估突显出个体差异.基本的咨询技巧也同样需要顾问去探究特定的因素,这些因素决定那些不被看好的学生、荣誉学生和其他顾问在职业生涯中遇到的特殊学生的学习结果和经历.即使这项研究的结果只是初步探测,但是它提示了有用的类别或构建,来用于研究菲律宾顾问推动和促进菲律宾籍学生的学习的更方面能力.前面的讨论凸显了与第三因素相关的学习观念是如何与学校顾问的基本职能和功能相密切联系.与前两个因素或视角相对应的学习理念也可能与处理学生的学习需求的特定选择相关.那些强烈坚信社会构建主义学习信念的学校顾问很可能对一些学习问题进行概念,这些问题关于学习策略的积极使用,计划和其他的自律的学习模式,以及影响学生学习能力和动机的个人和社会因素.此外,社会建构主义学习理念可能与是开发更强的机构和学生自主决定的努力相联系.另一方面,那些坚信行为学习理念的顾问倾向于对学习问题从以下方面概念:适当的内部和外部的强化有效的学习行为,他们会把注意力集中在分析教师、父母、同辈、甚至是学生们自己如何应对各种有效和无效的学生学习行为.因此,行为主义学习信念可能改变特定的外部事件,并影响到以扬长避短为目的的学生学习环境.在这一点上面,学校顾问的学习信念和专业实践的关系仍然是推测性的,因为这项研究并没有试图收集关于专业操作的数据.未来的研究可以聚焦于这重要的一点,同样的,一些对教师和学生的学习理念相关的研究与教师实践(Calderhead,1996;高和沃特金斯,2004年)和学生学习行为(·恩特威斯尔&彼得森,Purdie,2003;Pillay,Boulton-Lewis,2000年)相关.这项研究的一个重要贡献在于它提供了一个有用的工具,这具有很高的内部一致性的价值.该工具可用于研究学校顾问不同的学习理念如何联系学生的学业表现(例如,失败,成绩不良等)、咨询及其它帮助学生提高学习成绩,甚至建立自己的专业职能的策略.由于世界不同地区的学校顾问在积极推动和促进学生的学习,那么考虑学校顾问提及的过程有关的认知, 这是很重要的.从菲律宾学校顾问的例子,研究表明了对学习过程下定义的角度,可以提供相关的专业职能,加强学习.这项研究的结果走出了一个小但重要的一步,其能够更加有效地对菲律宾学校顾问如何发挥其功能去提高学生的学习方法下定义.Exploring Filipino School Counselors’Beliefs about LearningAllan B. I. Bernardo[Abstract]School reform efforts that focus on student learning require school counselors to take on important new roles as advocates of student learning and achievement. But how do school counselors understand the process of learning? In this study, we explore the learning beliefs of 115 Filipino school counselors who indicated their degree of agreement with 42 statements about the process of learning and the factors that influence this process. A principal components analysis of the responses to the 42 statements suggested three factors: (F1) social-cognitive constructivist beliefs, (F2) teacher-/curriculum-centered behaviorist beliefs, and (F3) individual difference factors. The preliminary results are briefly discussed in terms of issues related to how Filipino school counselors’ conceptions of learning may guide their strategies for promoting student learning and achievement.[Key words] beliefs about learning, conceptions of learning, school counselors, student learning, PhilippinesSchool reform efforts in different parts of the world have focused on students’ learning. In particular, most school improvement programs now aim to ensure that students acquire the high-level knowledge and skills that help them to thrive in today’s highly competitive global economy (e.g., Lee & Williams, 2006). In this regard, school reform programs draw from various contemporary theories and research on learning (e.g., Bransford, Brown, & Cocking, 1999; Lambert & McCombs, 1998). The basic idea is that all school improvement efforts should be directed at ensuring students achieve high levels of learning or attainment of well-defined curricular objectives and standards. For example, textbooks (Chien & Young, 2007), computers and educational technology (Gravoso, 2002; Haertnel & Means, 2003; Technology in Schools Task Force, 2003), and educationalassessment systems (Black & Wiliam, 2004; Cheung & Ng, 2007; Clark, 2001; Stiggins, 2005) are being reconsidered as regards how they can effectively provide scaffolds and resources for advancing student learning. Likewise, the allocation and management of a school’s financial resources are assessed in terms of whether these are effec tively mobilized and utilized towards improving student learning (Bolam, 2006; Chung & Hung, 2006; Retna, 2007).In this regard, some advocates have also called for an examination of the role of school counselors in these reform efforts (Herr, 2002). In the United States, House and Hayes (2002) challenged school counselors to take proactive leadership roles in advocating for the success of all students in schools. In this line, the American School Counselor Association (1997) has advocated that “the purpose of a counseling program in a school setting is to promote and enhance the learning process.” In response to this thrust, many have documented and advocated best practices that would allow school counselors to fulfill their new roles in enhancing student learning (e.g., Rowell & Hong, 2002; Sink, 2005).The improvement of student learning has also been an important theme in school reform efforts in the Philippines (Bernardo & Garcia, 2006; Bernardo & Mendoza, 2009). However, the push for rethinking the roles of school counselors in improving student learning has not been as pronounced. School counselors, who are often called guidance counselors in the Philippines, and their functions and competencies as collaborators in the promotion of student learning in achievement have not been highlighted in discussions on the functions of Philippine school counselors (Abrenica, 2001; Salazar-Cleme.a, 2000). These functions and competencies are also not mentioned in discussions on the perceived competencies of Philippine school counselors (Almeda-Estanislao, 2007; Guarino, 2007; Pabiton, 2003), or in the counselor education programs (Wong-Fernandez, 2000, 2001). In fact, there is hardly any published research that looks into the role of school counselors in improving student learning and achievement (Pabiton, 2001, is a rare example).The present study aims to initiate inquiry into the possible roles of Philippine school counselors in promoting student learning, by looking into school counselors’ conceptions or beliefs regarding the learning process. Conceptions and beliefs aboutlearning has been an important focus of research among various education stakeholders. For example, research has focused on students’ conceptions of learning (Purdie & Hattie, 2002) as these con ceptions are related to the students’ learning behaviors and strategies (Entwistle & Peterson, 2004; Pillay, Purdie, Boulton-Lewis, 2000). Similarly, research has also focused on conceptions and beliefs about learning of teachers (Boulton-Lewis, Smith, McCrindle, Burnett, & Campbell, 2001; Kane, Sandretto, & Heath, 2002; Samuelowicz & Bain, 2001) and pre-service teachers (Bernardo, 2008; Cliff, 1998) as these cognitions are said to guide teachers practices in the classroom (Calderhead, 1996) and may even be related to student achievement (Gao & Watkins, 2004). This study aims to extend this line of inquiry by exploring the beliefs about learning of school counselors in the Philippines.School counselors are not the direct participants in the learning processes in schools, unlike students and teachers. Nevertheless, how school counselors conceive of their roles in promoting student learning is likely to be shaped by their own conceptions regarding the learning process. If school counselors are to be effective agents in facilitating students learning, they should have a deep and principled understanding of the processes of learning, and the factors that may promote or hinder these processes. In this study, we inquired into the beliefs about learning of practicing school counselors in six different regions of the Philippine by asking them to assess different statements regarding the learning process and indicate their agreement with such statements. Their responses were analyzed using principal components analysis in order to reveal the structure of their beliefs about learning, and possible options for school counselors in relation to the various dimensions of the learning beliefs are discussed.MethodParticipantsOne-hundred sixteen school counselors from six different regions of the country participated in the study by answering a questionnaire on conceptions of learning. Ten of the participants were male, 103 female, and three did not indicate their gender. Most of the participants are relatively young; 43.1% of the participants were in their 20s, and 30.2% were in their 30’s. Most of the participants are also relatively new in their present positionsas counselors; 50.9% of the participants have been in their present positions for five years for less and 26.7% have been in their positions for 6 to 15 years. About half or 54.9% of the participants have only a bachelor’s degree, and the rest have master’s degrees. InstrumentA questionnaire was designed to include 42 statements regarding the learning process and factors that affect this process. The statements were derived from different contemporary theories and principles regarding learning. The items were arranged in one random sequence in the questionnaire. The participants were asked to indicate whether they agree or disagree with each statement in the questionnaire, using a scale from 0 (very strongly disagree) to 7 (very strongly agree). The questionnaire also included questions referring to the school counselors’ educational and professional background and some other demographic information.ResultsTo explore the structure of the school counselors’ beliefs about learning, their responses were analyzed using an exploratory factor analysis. First, the internal consistency of the entire 42-item scale was computed and the item-total correlations were computed. The item-total correlations ranged from .27 to .66, Cronbach’s α = .94. The Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin measure of sampling adequacy was .815 indicating that the data are factorable. The raw data on the 42 items were then analyzed using principal components analysis, and the scree plot suggested three factors. The component matrix was rotated using the promax rotation (orthogonal factors are rotated to oblique positions). The pattern matrix with three factors accounted for 42.30% of the variance. The factor loadings were determined by considering items with loading of at least .40 in one factor and not more than .35 in either of the other factors.An examination of the items in Factor 1 (Eigenvalue = 12.62; % of variance = 30.06) indicates that most of the items refer to conceptions of learning that are consistent with cognitive constructivist views of learning. These items emphasize the importance of attaining higher level cognitive knowledge and skills, and the importance of active processes that relate old and new knowledge in the process of constructing more complexknowledge representations. Some sample items include: “Learning complex material involves being able to effectively plan how to understand a comp lex skill or concept” and “Learning complex material involves changing or reorganizing how one represents information in the mind.”On the other hand, the items in Factor 2 (Eigenvalue = 3.26; % of variance = 7.77) refer to conceptions of learning consistent with behaviorist conceptions of learning, that also suggest that learning processes are constrained by innate capabilities but are shaped by more traditional instructional processes. The items in this factor also suggest a passive role of the learner, and the importance of external instructional processes in advancing learning. Some sample items include: “Learning complex material involves the consistent practice and reinforcement of complex skills so that this is executed fast and without error” and “L earning complex material involves the imitation of desired behaviors from models in the environment.”Finally, the items in Factor 3 (Eigenvalue = 1.88; % of variance = 4.48) refer to factors that influence individual differences in learning, such as developmental, motivational, social, and individual cognitive styles. Most of the items in this factor refer to one or more personal or social factors that may influence the outcomes of the learning process. Example items include: “The learning process is infl uenced by whether the task and concepts to be learned are relevant to the learner’s personal interest” and “The learning process is influenced by the learner’s expectations for success and failure in learning.”The different items that loaded into the three factors were combined form three scales that represented each of the three factors. The social-cognitive constructivist beliefs scale consisted of 17 items (M=5.72, SD = .72, Cronbach’s α = .92). The behaviorist beliefs scale consisted of 9 items (M = 5.14, SD = .98, Cronbach’s α = .83). Finally, individual difference beliefs scale consisted of another 9 items (M = 5.64, SD = .78, Cronbach’s α = .82). The participants’ responses to the items in the three factors were highly related. Social-cognitive constructivists beliefs were correlated with behaviorist beliefs (r = .48, p < .0001), and with individual difference beliefs (r = .67, p < .0001). Behaviorist beliefs were also correlated with individual difference beliefs (r = .50,p< .0001). The descriptive statistics for the three factors suggest that there is no clear preference for one set of beliefs or another, nor is there a clear distinction made among the beliefs. Other descriptive statistical analysis revealed that the responses for the three factors were not associated with any of the educational, professional, or demographic variables such as sex, age, years in the profession, educational concentration/major, or educational attainment.DiscussionThis exploratory study reveals that Filipino school counselors’ beliefs about learning are organized in terms of fairly coherent systems of principles and factors that are consistent with both traditional (behaviorist) and contemporary (constructivist) approaches to understanding learning. One could speculate that the beliefs are organized in ways that reflect formal instruction regarding theories of learning, however, research on the guidance and counseling or counselor education curriculum in the Philippines (Wong-Fernandez, 2000, 2001) indicates that such concepts are not given emphasis at all. Thus, it is unlikely that the Filipino counselors’ beliefs about learning merely replicate the structure of formal courses on learning.In this regard, it would be interesting to inquire into how such beliefs actually emerge if it is not likely to be a product of the formal counselor education curriculum. Perhaps, the beliefs emerge from reflections about the Filipino school counselors’ personal learning experiences or personal readings and studies. That the personal experiences of Filipino school counselors may shape their conceptions of learning seems consistent with the features of the third factor in the structure of their beliefs. The items in Factor 3 indicate that ideas regarding individual difference, developmental and social factors that influence learning comprise and important dimension of the Filipino school counselors’ beliefs about learning. The factor indicates an important predisposition among Filipino school counselors to think about the learning process in relation to the various personal and contextual factors that define the specific experiences of each learner. This conceptualization of learning reveals a degree of sensitivity to the distinctiveness in the learning experiences of each student, and mindfulness about the various developmental,social, and even cultural factors that influence the learning of each individual student. Such a conceptualization most likely relates to the Filipino school counselors’ core function of psychological assessment, which highlights individual difference variables. Basic counseling techniques also require the school counselors to inquire into specific factors that determine the learning outcomes and experiences of underachieving students, honor students, and other distinct cases that the school counselors are likely to encounter in their professional practice.Even as the results of the study are exploratory and preliminary, the results indicate useful categories or constructs to begin studying aspects of the Filipi no counselors’ capacity to engage the function of promoting and enhancing Filipino students’ learning. The preceding discussion highlights how learning beliefs associated with the third factor are likely to be associated with some fundamental competencies and functions of school counselors. Learning beliefs corresponding to the first two factors or dimensions may also be related to specific options for dealing with students’ learning needs. School counselors who hold strong social-cognitive constructivist learning beliefs are likely to conceptualize learning problems in terms of the use of active learning strategies, planning and other self-regulatory learning approaches, and possible personal and social factors that influence the students’ ability and motiv ation to implement these strategies. Moreover, social-cognitive constructivist learning beliefs might be associated with efforts to develop stronger agency and self-determination on the part of the student. On the other hand, school counselors who hold strong behaviorist learning beliefs are likely to conceptualize learning problems in terms of problems with appropriate internal and external reinforcements to effective learning behaviors, and are likely to focus on analyzing how teachers, parents, peers, and even the students themselves respond to various effective and ineffective learning behaviors of the student. Thus, behaviorist learning beliefs might be associated with interventions that will involve changing certain external contingencies in the studen ts’ learning environment for the purpose of shaping and strengthening good learning behaviors and extinguishing bad ones.The relationship between school counselors’ learning beliefs and their professionalapproaches and practices remains speculative at this point, as the study did not attempt to gather data on these professional practices. Future research studies can focus on this important point, in the same way that some research on teachers’ and students’ beliefs about learning are associated with teacher practices (Calderhead, 1996; Gao & Watkins, 2004) and student learning behaviors (Entwistle & Peterson, 2004; Pillay, Purdie, Boulton-Lewis, 2000). One important contribution of the study is that it provides a useful instrument with high internal consistency values for doing so. The instrument may be used to study how school counselors’ different conceptualizations of learning may be related to their attributions for students’ academic performance (e.g., failure, underachievement, etc.), to the counseling and other intervention strategies they adopt for helping students improve on their learning achievement levels, and even to how they construct their professional functions vis-à-vis student learning.As school counselors in different parts of the world strive to define more active roles in promoting and enhancing student learning, it is important to consider the relevant cognitions that school counselors might have related to the process. In the case of Filipino school counselors, the study indicates dimensions of conceptualizations about the learning process that may provide the foundation for concretizing the school counselors’ professional functions related to enhancing learning. The results of this study represent a small but important step towards more effectively conceptualizing approaches for how Filipino school counselors may engage this function of enhancing learning among Filipino students.。