写作语法一_五大基本句型+句子成分+名词性从句
- 格式:doc
- 大小:45.00 KB
- 文档页数:5

句子的基本成分和结构(Cherry)英语十大词类顺口溜:名代动形副,介连冠感数1 名词单复数,可数不可数。
2 代词主宾格,反身无主格。
3 动词情系助,及物不及物。
4 含有形容词,关键比较级。
5 副词时地频,有些有比较。
6 介词短语多,时间地点等。
7 连词分两类,并列和从属。
8 冠词有两种,定冠不定冠。
9 感叹词表感情,喜怒和哀乐。
10 数词记两种,基数和序数句子种类:按句子的用途1)陈述句(肯定、否定):He is six years old. She didn’t hear of you before.2)疑问句(一般、特殊、选择、反意):Do they like skating? How old is he?Is he six or seven years old? Mary can swim, can’t she?3)祈使句(肯定;否定): (Please) Be careful, boys. Don’t/Never talk in class!4)感叹句: How clever the boy is! What a clever boy he is!按句子的结构1)简单句:只有一个主语(或并列主语)和一个谓语(或并列语).He often reads English in the morning.Tom and Mike are American boys.She likes drawing and often draws pictures for the wall newspapers.2) 并列句:由并列连词(and, but, or等)或分号(;)把两个或两个以上的简单句连在一起构成。
You help him and he helps you.The future is bright; the road is tortuous. 前途是光明的,道路是曲折的。
3)复合句:由when, where, why, how, because等从属连词连接主从句并且从句在主句中充当一个成分的句子称为主从复合句。

句子成分及五大基本句型思考:英语句子由什么组成的?I am a student.1.单词分类?2.如何将单词组成句子?3.句子分类?主语+谓语主语+谓语+宾语主语+谓语+宾语+宾语主语+谓语+宾语+宾补主语+系语+表语名词性从句:主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句、同位语从句定语从句:限制性定语从句、非限制性定语从句状语从句:时间状从,地点状从、原因状从、目的状从、结果状从、条件状从、让步状从、方式状从、比较状从词类1.名词Noun (n.):表示人或事物的名称的词。
如:student,mistake,distance 2.动词V erb (v.) :表示动作或状态的词。
如:love,succeed,enjoy3.代词Pronoun (pron.):用来代替名词,数词等。
如:she, he, they 4.形容词Adjective (adj.):修饰名词,表示人或事物的特征。
如:beautiful,wonderful5.副词Adverb (adv.):修饰动词,形容词,副词等,表示动作特征。
如:slowly,always,frequently 6.数词Numeral (num.):表示数目多少或顺序。
如:one,first,hundred,thousand 7.介词Preposition (prep.):用在名词或代词前,说明它与别的词的关系。
如:of,with,for8.冠词Article(art.):用在名词前,帮助说明名词所指的范围。
如:a, an ,the9.感叹词Interjection(int.):表示感叹语气的词。
如:oh, wow, oops 10.连词Conjunction(conj.):起连接作用的词,词与词,短语与短语,句子与句子之间。
如:and,but ,because句子成分组成句子的各个部分1.主语(subject):是谓语动作或状态的执行者,是句子叙述的主体。
表明这句话说的是谁和什么。


句子成份及五种基本句型湖北黄石三中:李毓missliyu@一. 句子成份:句子的组成部分叫句子成份。
英语的基本成分有八种:主语(Subject)、谓语(Predicate)、表语(Predicative)、宾语(Object)、定语(Attribute)、状语(Adverbial)、补语(Complement)和同位语(Appositive)。
句子的直接成分是由主语和谓语构成。
主语:是一个句子叙述的主体,说的是“什么人即who”或“什么事物即what”。
一般位于句首。
是由名词(词组)、主格代词(词组)、动名词(词组)、不定式(短语)、名词性从句构成。
谓语:说明主语所做的动作或具有的特征和状态。
是由动词或动词短语构成。
一般放在主语之后。
在结构上变化多样。
可分为简单谓语(由一个动词或动词短语构成)和复合谓语(1.由情态动词或其它助动词+动词原形或动词的某种形式构成2.由系动词+表语构成)。
动词可分为及物动词vt、不及物动词vi、连系动词link. v、助动词aux.v.(协助主要动词构成时态、语态,是语法功能词,自身没有词义,不可单独使用,必须和其他实义动词一起构成谓语。
没有对应的汉译)、情态动词mod.v. (本身有一定的词义,表示说话人的情绪、态度或语气的动词,只能和实义动词原形构成谓语。
不能单独作谓语)及物动词:有的vt后必须带宾语(叫单宾及物动词)如:like ,hate等;有的及物动词后带双宾(叫双宾及物动词)如give, lend等;有的及物动词后带复合宾语即宾语和宾补(叫复合宾语及物动词)如find, see, consider等. 当其宾语作主语,可变被动语态不及物动词:其后不能直接接宾语,可单独作谓语,无被动语态;有的不及物动词后可接相应的介词,其功能相当于vt,后可接宾语,若当其宾语作主语,可变被动语态。
连系动词:后接表语或补语。
※不同谓语结构决定着不同的句型。
某些动词既是及物动词又是不及物动词。
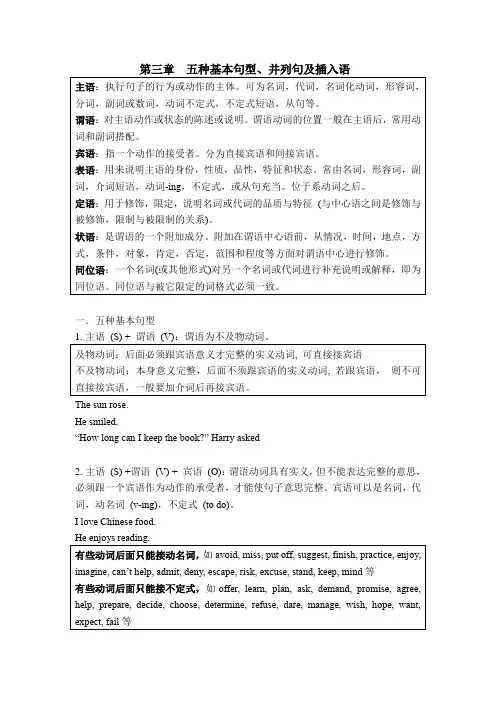
一.五种基本句型The sun rose.He smiled.“How long can I keep the book?” Harry asked2.主语(S) +谓语(V) + 宾语(O):谓语动词具有实义,但不能表达完整的意思,必须跟一个宾语作为动作的承受者,才能使句子意思完整。
宾语可以是名词,代词,动名词(v-ing),不定式(to do)。
I love Chinese food.3.主语(S) + 系动词(V) + 表语(P):系动词有以下几类:①表示主语的状态,特征:be, feel, look, sound, taste, smell, seem, appear等。
To do this job is not easy.The cat is under the table.In fact, fossil fuel is in a terrible short supply.Seeing is believing.The meal looks delicious.This medicine tastes bitter.He seemed to be feeling very exhausted last week.She appears (to be) a very pious person.There appears to be a misunderstanding.②表示主语从一种状态变成另一种状态:go, come, turn, become, grow, fall, get 等His hair turned grey in a few days.Global shortage of fresh water has become a heated topic.The professor got angry.The boy fell asleep quickly.The leaves turned yellow.P.S: go作为系动词时一般表贬义,如go hungry/ mad/ crazy/ bad/ sour/ wrong等。

英语基础语法一、词类:英语词类分十种:名词、形容词、代词、数词、动词、副词;介词、连词、感叹词、冠词1、名词(n.):表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。
如:boy, morning, bag, ball, class, orange.2、代词(pron.):主要用来代替名词。
如:who, she, you, it .3、形容词(adj..):表示人或事物的性质或特征。
如:good, right, white, orange .4、数词(num.):表示数目或事物的顺序。
如:one, two, three, first, second, third, fourth.5、动词(v.):表示动作或状态。
如:am, is,are,have,see .6、副词(adv.):修饰动词、形容词或其他副词,说明时间、地点、程度等。
如:now, very, here, often, quietly, slowly.7、冠词(art..):用在名词前,帮助说明名词。
如:a, an, the.8、介词(prep.):表示它后面的名词或代词与其他句子成分的关系。
如in, on, from, above, behind.9、连词(conj.):用来连接词、短语或句子。
如and, but, before .10、感叹词(interj..)表示喜、怒、哀、乐等感情。
如:oh, well, hi, hello.二、句子成分:英语句子成分分为七种:主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、表语、补足语。
1、主语是句子所要说的人或事物,回答是“谁”或者“什么”。
通常用名词或代词担任。
如:I’m Miss Green.(我是格林小姐)2、谓语动词说明主语的动作或状态,回答“做(什么)”。
主要由动词担任。
如:Jack cleans the room every day. (杰克每天打扫房间)3、表语在系动词之后,说明主语的身份或特征,回答是“什么”或者“怎么样”。

名词性从句语法总结名词性从句是在句子中充当名词成分的从句,它可以在句子中作主语、宾语、表语、定语等成分。
名词性从句包括主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和定语从句。
在使用名词性从句时,需要注意从句的引导词和从句本身的语法结构。
下面对名词性从句的语法规则进行总结:1. 主语从句。
主语从句在句子中充当主语成分,常常由连接词 that, whether, if, who, whom, whose, what, which, when, where, why, how 等引导。
例如:What he said is true.(他说的是真的。
)。
Whether we can go camping depends on the weather.(我们能否去野营取决于天气。
)。
2. 宾语从句。
宾语从句在句子中充当宾语成分,常常由连接词 that, whether, if, who, whom, whose, what, which, when, where, why, how 等引导。
例如:I know who did it.(我知道是谁干的。
)。
She asked me where I was going.(她问我要去哪里。
)。
3. 表语从句。
表语从句在句子中充当表语成分,常常由连接词 that, whether, who, whom, whose, what, which 等引导。
例如:The problem is that we don't have enough time.(问题在于我们没有足够的时间。
)。
Her wish is that she can travel around the world.(她的愿望是能够环游世界。
)。
4. 定语从句。
定语从句在句子中充当定语成分,用来修饰某个名词或代词。
常常由连接词that, who, whom, whose, which, when, where 等引导。

句子成分分析名词性从句形容词性从句和副词性从句的句子结构剖析在语法学中,句法分析是对句子结构的研究和解析,包括句子成分和句子成分之间的关系。
本文将对名词性从句、形容词性从句和副词性从句这三种常见的从句进行句子结构剖析,以帮助读者更好地理解和运用这些从句。
1. 名词性从句名词性从句在句子中担任名词的成分,通常用来作主语、宾语、表语或同位语。
它可以由连接词"that"引导,也可以由"wh-"系列引导(如who、whom、whose、which、what等),甚至可以由whether或if引导。
名词性从句的句子结构较为简单,通常是一个完整的句子,与主句之间存在一定的从属关系。
下面是一些例子:- 主语从句:That he is late surprises me.(他迟到了让我吃惊。
)- 宾语从句:I know who did it.(我知道是谁干的。
)- 表语从句:My wish is that he may succeed.(我希望他能成功。
)- 同位语从句:The fact that she passed the exam excited her.(她通过了考试的事实让她很激动。
)2. 形容词性从句形容词性从句用来修饰名词或代词,并且起到形容词的作用。
一般由关系代词(如who、whom、whose、which、that等)引导。
形容词性从句常位于被修饰词后面,起到限定或描述的作用。
下面是一些例子:- The book that is on the table is mine.(在桌子上的那本书是我的。
)- The person who borrowed my phone is my friend.(借了我的手机的人是我的朋友。
)- I like the movie which is based on a true story.(我喜欢那部根据真实故事改编的电影。

七大句子成分五大基本句型四大语法要点三大复杂句七大句子成分、五大基本句型、四大语法要点、三大复杂句句子是语言最基本的单位,它是传达思想的主要手段。
了解句子的构成成分、句型类型和语法要点对于提高中文写作能力至关重要。
本文将详细介绍七大句子成分、五大基本句型、四大语法要点以及三大复杂句,帮助读者更好地理解和运用这些句子结构。
一、七大句子成分句子成分是构成句子的基本单位,包括主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、补语和同位语。
这些成分在句子中负责承担不同的语义和语法作用。
1. 主语:句子中起主要说明作用的成分,通常回答“谁做了什么”。
例如:小明(主语)在公园里玩耍(谓语)。
2. 谓语:句子中表示动作或状态的核心成分,通常回答“做了什么”。
例如:小明在公园里(状语)玩耍(谓语)。
3. 宾语:句子中接在动词后面,接受动作的对象,通常回答“做了什么”。
例如:小明在公园里玩耍(谓语)风筝(宾语)。
4. 定语:句子中修饰主语或宾语的成分,通常回答“是什么样的”。
例如:小明在美丽的(定语)公园里玩耍。
5. 状语:句子中修饰动词、形容词、副词等的成分,通常回答“如何”、“在哪里”、“为什么”等问题。
例如:小明在公园里(状语)欢快地玩耍(谓语)。
6. 补语:句子中用来补充说明主语或宾语的成分,通常回答“是什么”。
例如:小明是一个活泼的男孩(补语)。
7. 同位语:句子中与主语、宾语等成分并列的解释说明成分。
例如:小明,一位来自中国的学生(同位语),喜欢玩耍。
以上七大句子成分构成了句子的基本框架,理解并熟练运用它们是进行正常沟通和书写的基础。
二、五大基本句型基本句型是指句子的结构类型,它们是主谓句、主谓宾句、主谓表句、主系表句和主语从句。
了解和掌握这些句型对于写作和阅读理解都非常重要。
1. 主谓句:句子中只包含主语和谓语成分的简单句。
例如:小明(主语)在公园里玩耍(谓语)。
2. 主谓宾句:句子中包含主语、谓语和宾语成分的简单句。

五大基本句型1.主(n./pron./to do sth/doing sth/主语从句)——谓(vi.如:come, go, arrive, stay, work, fall, rise, die, happen, fail, appear,lie,sit,stand,last)(1).The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.(2).Your brother has gone home.(3).We work hard at English.2.主-------谓(vt.如:visit, spend, forget, raise,have,seat,astonish,satisfy,embarass)-----宾(n./ pron./to do sth/doing sth/宾语从句)(1).I study chemistry and he studies physics.(2).I have never seen such an interesting film.(3).He doesn't know what to read.3.主-------谓(vt.)------间接宾语(sb)-------直接宾语(sth.)(1).Give sb sth=Give sth to sb: send, pass, hand, show(2).Buy sb sth=Buy sth for sb: make, get, cook, call, find(3).Ask sb sth=Ask sth of sb(1).Will you lend me your bike?(2).Peter bought Mary a new dress.(3).Please get him some hot water.(4).Will you tell us sth about your school life?(5).This little boy is always asking the teacher all sorts of questions.(6).Pass me the paper, please.John is teaching Mary how to ride a bicycle.4.主-----谓(vt.)-------宾-------补(n./adj/adv/介词短语/to do sth----如:ask, tell, order,want, wish, encourage, allow, forbid/Do sth----如:“四看”、“二听”、“一感觉”;have, let 与make /Doing sth/Done by sb.)(1).I saw her enter the lab.(2).Nathan Hale felt his heart beating fast.(3).We elected him our school headmaster.(4).The students often keep their classroom clean and tidy.I'll have the bike repaired.I heard him singing happily in the next room.That man made the boy obey him.He painted the door red.She found her bike stolen.let me have a look. We call her Xiao li.We asked them to stay for lunch.I wish you to go with me.Don't keep your mother waiting.suddenly she saw a wallet lying on the ground.When he woke up, he found himself tied down.5.主-----系(be/look,smell,taste,sound,feel/prove,remain,stay,keep/turn,get,become,make)----表。

句子成分一.动词基本分类:1.实义动词包括及物(vt)和不及物(vi)vt 直接带宾语He likes English. V i 不需带宾语Did he come yesterday? 若要带宾语中间需加介词He arrived at the airport .2. 连系动词如:be/ look/sound/keep/taste/smell/taste/seem/become/turn/remain (依然)…3. 助动词:本身无意义,要与实义动词组成谓语。
如:do/does/will/would/have/hasHe has gone to Beijing. He will leave for Beijing.4情态动词:can/could/ may/might…二.副词一般修饰动词/形容词/副词基本分类:1 时间副词now/ago/once/already…2 地点副词here/downstairs/back /outside/ off…3 方式副词carefully/fast/suddenly…4 程度副词almost/very/so/much/deeply…5 频度副词always/ usually/sometimes…三.句子成分:构成句子的各个部分。
A.主语- 可由以下表示:1.名词:American music has become more and more popular.2.代词:Who is the man standing over there?3.数词:One-third of the students are girls.4.不定式:To swim in the river is a great pleasure.= It is a great pleasure to swim in the river (It 是形式主语) 5.动名词:Smoking does harm to the health.6.从句:When we are going to have the test is clear.B. 谓语在句中一般由动词充当1.He practices running every morning.2.He has caught a cold.3.We may keep the book for two weeks.C. 表语一般位于系动词之后可由以下表示:1.代词:Is it yours/ It is mine.2.形容词:The weather has turned cold.3.分词:The teacher is pleased with my work.4.不定式:His job is to teach English.5.动名词:His hobby is playing football.D. 宾语一般位于Vt 或介词之后可由以下表示:1.名词:He is going to buy a dictionary.2.代词:We should learn from him.3.不定式:He decided not to see me.4.动名词:He practices running every morning.分类:分为直接宾语(动作的承受者,通常指物)和间接宾语(动作所向的人或物,通常指人)He sent me a present.=He sent a present to me. (me 间宾/ a present 直宾)He bought her a map= He bought a map for her.有些Vt 如:make/have/get/let/find/call/see/notice/hear/watch除了跟有一个宾语外,还要有一个宾语补足语来说明宾语的状态才能使句子完整。
第一编第一讲正确使用5种基本句型如果一篇文章中有较多的语法错误,即使词汇再亮、句式再高,也只能是欲盖弥彰、难掩其丑,将直接被打入低分“冷宫”。
“欲想得高分,先保基本分”。
所以,我们先从写对句子学起。
第一讲正确使用5种基本句型基本句型(一) 简约却不简单的“主谓”结构(一)主谓结构中谓语常用来表示主语的动作或状态。
这种句型中的谓语动词为不及物动词,后面可以跟副词、介词短语、状语从句等。
但不能接宾语,也没有被动语态。
常见的不及物动词有:arrive, come, lie, shine, live, walk, fall, rise, happen, exist, ride, occur, agree, write等。
它的基本结构是:主语+谓语(vi.)(+状语)①The_sun was shining.太阳在照耀着。
②He usually swims at weekends.他经常在周末游泳。
③I am writing to give my thanks to you.我写信向你表示感谢。
④In the environment, teachers_and_students are living happily and working hard.在这种环境下,师生们生活快乐,工作努力。
[应用体验1] 翻译句子(主语+不及物动词)①他从早到晚地努力工作。
He_works_hard_from_morning_till_night.②接下来的几周,我们的友谊发展地很快。
Our_friendship_developed_fast_over_the_following_weeks.③本周五晚自习之后我们将于8:00在学生俱乐部集合。
We'll_gather_at_the_Students'_Club_at_8:00_p.m.this_Friday,_after_the_evening_classes.④我们同意周末帮老人做一些家务活。
句子成分讲解摘要:句子成分主语谓语宾语宾语补足语表语定语状语同位语句子分类简单句复合句并列复合句主从复合句五大基本句型主谓主系表主谓宾主谓宾宾补主谓间宾直宾练习一、句子成分I met my best friend Tom at the station yesterday.I主语、met谓语、friend宾语、my best定语、Tom同位语、at the station地点状语、yesterday时间状语主语:定义:主语是谓语所表示的动作的发出者。
主语一般位于句子开头,且不能省略。
作主语的成分:名词Jane is good at playing the piano.代词She went out in a hurry.数词Four plus four is eight.动词不定式To see is to believe.动名词Smoking is bad for health.the+形容词The young should respect the old.从句What he has said is true.注意:在倒装句、疑问句、感叹句中,句子主语可放在谓语之后eg.Do you like it?在祈使句中,主语you常常省略。
eg.Don’t move.谓语:定义:主语的动作或主语所具有的特征和状态, 一般在主语之后。
分类:简单谓语:由一个动词或动词短语构成He likes reading.When he reads books,he often listens to music.复合谓语:由情态动词或其他助动词+动词原形构成☆基本助动词be、do、haveI can swim.She has finished the homeworkI don’t like apples.由系动词加表语构成I am a student. I am beautiful.宾语定义;谓语动词的对象或承受者。
一般位于及物动词或者介词后。
英语句子成分分析句子是按照一定的语法规律组成的,表达一个完整的意义.一个句子一般由两部分构成,即主语部分和谓语部分,这两部分也叫做句子的主要成分。
句子的次要成分包括宾语,定语,状语,表语等。
句子成分是句子中起一定功用的组成部分。
1)主语:是一句的主体,是全句述说的对象,常用名词,数词或代词担任,一般放于句首。
如:Students study. (学生学习)We are friends.(我们是朋友)这两句话中单词students是个名词,we是代词,它们在句中做主语。
2)谓语:是对主语加以陈述,表示主语的行为或状态,常用动词或者动词词组担任,放在主语的后面。
如:Students study. (学生学习。
)We are friends. (我们是朋友)这两句话中单词study和are都是动词,study叫做实意动词,are叫做be动词,它们在句中作谓语.3)宾语:表示行为的对象,常由名词或者代词担任。
放在及物动词或者介词之后。
如:They are teachers. ( 他们是老师.)I play with him。
(我和他一起玩。
)这两句话中单词teachers是名词,单词him是带词,它们在句中作宾语.4)定语:是用来说明或者限制名词的成分,常用形容词或者相当于形容词的短语或从句担任.形容词放在名词之前,相当于形容词的短语或从句放在名词的后面。
如:This is a red sun。
(这是个红太阳。
)He is a tall boy.(他是个高个子男孩。
)这两句话中单词red和 tall都是形容词,它们作定语。
5)状语是用来说明动词,形容词,副词或整个句子的成分。
常由副词担任.修饰动词时可以放在动词之前,也可以放在动词之后;修饰形容词或副词时放在它们之前。
如:The students study hard. (这些学生学习努力.)I often write to him. (我常给他写信。
)The bag is too heavy. (这个书包太重了。
1.基本的句子分类和句子核心成分简单句,复合句(用连词直接连接的两个完整的简单句,“串联句”),复杂句(主从复合句,“并联句”)不管是什么句子,既然叫做“句子”,那么意味着成分必须完整没有缺失。
既然是句子,不管是主句还是从句,都必须有谓语动词。
而且任何一个句子中,有且只有一个谓语动词。
“非谓语动词”---v-ing现在分词,v-ed过去分词,to-do改错:There are many people claim that education is quite crucial for the young generations.修改一:who claim that…修改二:claiming that…修改三:去掉there are2.5大基本句型:简单句的分类主语+谓语(常常在后面接一个副词修饰谓语动词)Time flies.//I ran.//You jump; I jump.主语+谓语+宾语I want you.//I borrow books.//I love you.主语+系动词(可接名词和形容词):be动词+感官动词(look/sound/smell/taste/feel)+get/become/turn/grow/appear/fall(asleep)/keep/stay/remain/maintain/exist(th ere exist…=there be…)…+表语(主语补足语)主语+谓语+双宾语主语+谓语+复合宾语(主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语,宾语补足语是对宾语的进一步说明,一般是名词和形容词)He gave me a book.I call him Jack.I push the door open.区别双宾语和复合宾语:双宾语的两个宾语之间没有必然的逻辑关系,而复合宾语的两个成分之间是有逻辑关系的,中间可以加be动词来进行甄别。
3.句子基本成分的概念的建立和强化主语---是一句话的中心,整句话都谈它的情况。
最简单的形式是名词。
谓语---是主语的主要情况,可表示动作,也可表示状态。
只能是动词。
宾语---表示动作的承受者,也可表示动作的结果。
最简单的形式就是名词。
表语---也叫主语补足语,和系动词一道构成谓语。
定语---修饰名词、代词。
最简单的定语就是形容词:a beautiful flower//a standardized test状语---修饰动词、形容词或副词。
最简单的状语就是副词:increase rapidly//extremely wealthy//very well4.句子翻译练习:1)这个经济危机最初在美国爆发。
The economic crisis//depression(衰退)broke out originally in America.2)跟他讲话就像对牛弹琴。
It is/seems like/is like talking to a wall/deaf that when you talk to him.It is…(主语)that/who…Taking to him is like talking to a wall. //Seeing is believing.3)忽略这个事情可能会导致严重后果。
Ignoring/To ignore/The ignorance of this matter may lead to serious consequences.4)价格会升高是确定的。
The increasing price is certain.An increase in the price is certain.It is certain that the price will increase...is certain.The price will increase.That the price will increase is certain. = It is certain that the price will increase.5)送小孩出国留学对于不少家庭来说是个沉重的经济负担.It is a heavy economic financial burden that sending children to study abroad for many families.6)大学生做兼职可以减轻父母的经济负担。
减轻:lessen/alleviate//release7)政府应该意识到他们的首要职责(primary responsibility)是帮助人民消除贫困(poverty/impoverishment )、疾病(illnesses)和文盲(illiteracy)。
Literacy/numeracy skills=be equipped with basic literacy and numeracy skills有文化,有基本的文化素养8)这个观点是年幼的孩子比青少年更容易掌握一门语言。
This point of view is a language that younger children…句型:主系表This point of view is that it is easier for younger children to master/acquire/have a good grasp of a language than teenagers.表语从句There is a fact that…同位语从句Some people believe that…宾语从句That it is easier for younger children to master a language than teenagers is obvious.= It is obvious that…主语从句名词性从句:表语从句、同位语从句、宾语从句、主语从句5.考官范文例题:Some people think that parents should teach children how to be agood member of society. Others, however, believe that school is the place to learn this. Discuss both these views and give your own opinion.P1 A child’s education has never been about learning information and basic skills only. It has always included teaching the next generation how to be good members of society. Therefore, this cannot be the responsibility of the parents alone.P2:In order to be a good member of any society the individual must respect and obey the rules of their community and share their values. Educating children to understand the need to obey rules and respect others always begins in the home and is widely thought to be the responsibility of parents. They will certainly be the first to help children learn what is important in life, how they are expected to behave and what role they will play in their world.6.可以作主语/宾语/表语/同位语的所有成分➢名词The economic crisis first broke out in the United States.➢动名词短语doing文段里面的句子,或:Talking to him is talking to a wall.➢带to不定式to do sthTo ignore this might have serious consequences.➢主语从句: 分三种形式1)由that引导的主语从句她成为一个艺术家主要是由于他父亲的影响。
That she became an artist may have been due to her father’s influence.价格将会上升是一定的。
That prices will go up is certain.//It is certain that prices will go up.2)由连接代词或连接副词引导的主语从句: 连接代词包括who,which; 连接副词包括when,why,how,whether他什么时候回来很大程度上取决于天气。
When he will be back depends much on whether.这是怎样做的是一个谜。
How this was done was a mystery.派谁去还没有决定。
Who is to be sent there hasn’t been decided.我们能够成功还要拭目以待。
Whether we will succeed remains to be seen.3)由关系代词what引导的主语从句你应该做的是选择一家公司进行投资。
What you should do is to choose a company to invest in.P3: However, learning to understand and share the value system of a whole society cannot be achieved just in the home. Once a child goes to school, they are entering a wider community where teachers and peers will have just as much influence as their parents do at home. At school, children will experience working and living with people from a whole variety of backgrounds from the wider society. This experience should(教他们如何相互合作以及如何对他们的社区做贡献)________________________________________________________________________________ ___________表语从句例子:这个问题是谁应该对发生了的事情负责。