移动蜂窝网络架构说明
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:1.19 MB
- 文档页数:21
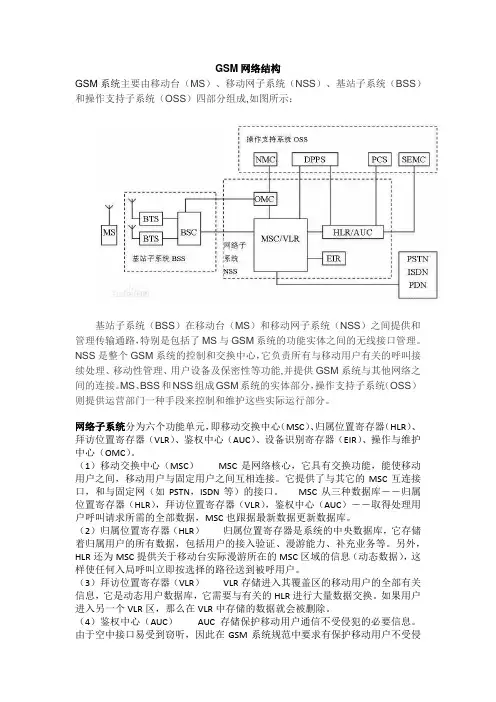
GSM网络结构GSM系统主要由移动台(MS)、移动网子系统(NSS)、基站子系统(BSS)和操作支持子系统(OSS)四部分组成,如图所示:基站子系统(BSS)在移动台(MS)和移动网子系统(NSS)之间提供和管理传输通路,特别是包括了MS与GSM系统的功能实体之间的无线接口管理。
NSS是整个GSM系统的控制和交换中心,它负责所有与移动用户有关的呼叫接续处理、移动性管理、用户设备及保密性等功能,并提供GSM系统与其他网络之间的连接。
MS、BSS和NSS组成GSM系统的实体部分,操作支持子系统(OSS)则提供运营部门一种手段来控制和维护这些实际运行部分。
网络子系统分为六个功能单元,即移动交换中心(MSC)、归属位置寄存器(HLR)、拜访位置寄存器(VLR)、鉴权中心(AUC)、设备识别寄存器(EIR)、操作与维护中心(OMC)。
(1)移动交换中心(MSC)MSC是网络核心,它具有交换功能,能使移动用户之间,移动用户与固定用户之间互相连接。
它提供了与其它的MSC互连接口,和与固定网(如PSTN,ISDN等)的接口。
MSC从三种数据库――归属位置寄存器(HLR),拜访位置寄存器(VLR),鉴权中心(AUC)――取得处理用户呼叫请求所需的全部数据,MSC也跟据最新数据更新数据库。
(2)归属位置寄存器(HLR)归属位置寄存器是系统的中央数据库,它存储着归属用户的所有数据,包括用户的接入验证、漫游能力、补充业务等。
另外,HLR还为MSC提供关于移动台实际漫游所在的MSC区域的信息(动态数据),这样使任何入局呼叫立即按选择的路径送到被呼用户。
(3)拜访位置寄存器(VLR)VLR存储进入其覆盖区的移动用户的全部有关信息,它是动态用户数据库,它需要与有关的HLR进行大量数据交换。
如果用户进入另一个VLR区,那么在VLR中存储的数据就会被删除。
(4)鉴权中心(AUC)AUC存储保护移动用户通信不受侵犯的必要信息。
由于空中接口易受到窃听,因此在GSM系统规范中要求有保护移动用户不受侵犯的措施,如用户的鉴权,传输信息加密等,而鉴权信息和密钥就存储在AUC 中。

蜂窝移动通信系统组成(二)引言概述:蜂窝移动通信系统是一种基于蜂窝网络的无线通信系统,由多个基站和用户设备组成。
在上一篇文章中,我们介绍了蜂窝移动通信系统的基本原理和组成部分。
在本文中,我们将进一步探讨蜂窝移动通信系统的组成,包括信道管理、移动管理、呼叫管理、资源管理和安全管理。
正文:一、信道管理1. 频率复用技术:介绍频率复用技术如频分复用(FDMA)和时分复用(TDMA),以提高频谱利用率。
2. 多址复用技术:介绍多址复用技术如码分多址(CDMA)和分组调度多址(TD-CDMA),以支持多用户同时传输数据。
3. 带宽分配:介绍如何通过动态频率分配(DFCA)和动态信道分配(DCA)等技术,根据用户需求分配信道资源。
二、移动管理1. 基站切换:介绍移动用户在不同基站之间切换的过程,包括小区搜索、测量和切换决策等步骤。
2. 手机定位:介绍如何通过不同定位技术如GPS和无线定位等,确定移动用户的位置信息。
3. 用户鉴权和注册:介绍用户鉴权和注册过程,以确保只有合法用户能够接入系统并进行通信。
三、呼叫管理1. 呼叫建立:介绍呼叫建立过程,包括寻呼、呼叫请求和呼叫确认等步骤。
2. 呼叫保持与转移:介绍呼叫保持和呼叫转移等功能,以支持用户在通话中保持或转移呼叫。
3. 呼叫释放:介绍呼叫释放过程,包括正常释放、异常释放和强制释放等情况。
四、资源管理1. 功率控制:介绍功率控制技术,以确保系统中各个用户设备的发送功率在合理范围内,保证通信质量。
2. 频率管理:介绍频率管理技术,以平衡系统中不同用户设备之间的频率资源,避免干扰。
3. 带宽管理:介绍带宽管理技术,以合理分配系统中的带宽资源,满足不同用户的通信需求。
五、安全管理1. 用户身份认证:介绍用户身份认证技术,以确保只有合法用户能够接入系统并进行通信。
2. 数据加密与解密:介绍数据加密与解密技术,以保证用户数据的机密性和完整性。
3. 防止恶意攻击:介绍常见的恶意攻击方式如拒绝服务攻击(DDoS)和干扰攻击,并提供相应的防护措施。

蜂窝网络技术的架构和协议标准介绍一、引言近年来,随着移动通信技术的快速发展,蜂窝网络已经成为人们生活中不可或缺的一部分。
无论是以前的2G、3G网络,还是现在的4G 及将来的5G网络,它们都以蜂窝网络技术为基础。
本文将介绍蜂窝网络技术的架构和协议标准,以帮助读者更好地了解和使用移动通信。
二、蜂窝网络架构蜂窝网络由基站、核心网和用户设备三个主要组成部分构成。
基站是蜂窝网络的基础设施,通过无线信号覆盖一定范围内的区域,提供通信服务。
核心网是蜂窝网络的中枢,负责处理数据传输、用户认证以及网络管理等功能。
用户设备则是终端用户使用的具备无线通信能力的设备,如手机、平板电脑等。
三、蜂窝网络协议标准蜂窝网络的协议标准是实现蜂窝网络的一套规范,以确保不同厂商的设备可以互相兼容和通信。
在2G时代,GSM(Global System for Mobile Communications)是主流的蜂窝网络协议标准。
它采用了时分多址技术,使得多个用户可以在同一频率上同时进行通话或数据传输。
随着技术的不断进步,3G时代引入了UMTS(Universal Mobile Telecommunications System)作为新的蜂窝网络标准。
UMTS采用了分时分频多址技术,使得多用户可以在同一频率上进行通信,从而提高了网络容量和传输速率。
同时,UMTS还引入了IP协议,使得语音和数据可以通过Internet进行传输。
当前最流行的蜂窝网络标准是4G LTE(Long Term Evolution)。
它采用了OFDM(正交频分多址)和MIMO(多输入多输出)等先进技术,大幅提升了网络的速度和容量。
与3G相比,4G LTE能够实现更高的传输速率和更低的时延,使得高清视频、在线游戏等应用更加流畅。
而在不久的将来,5G网络将成为主流的蜂窝网络标准。
目前,5G的技术标准正在全球范围内制定中。
5G将利用更高的频率和更大的带宽,提供更高的网络容量和更低的时延。

无线通信中的移动网络和蜂窝网络架构无线通信是指通过无线电波或红外线等无线信号传递信息的通信方式。
在现代社会中,无线通信已经成为人们生活中不可或缺的一部分。
其中,移动网络和蜂窝网络是最为常见的两种无线通信网络架构。
本文将详细介绍移动网络和蜂窝网络的定义、工作原理以及各自的优缺点,并共分以下几个方面进行阐述。
一、移动网络的定义和工作原理1. 移动网络是指通过无线电信号实现通信的网络,可以实现人与人、人与物之间的远程通信。
2. 移动网络基于无线电技术,将数据传输通过无线电信号进行,通过无线传感器、无线终端等设备实现信息的发送和接收。
3. 移动网络由移动通信基站、传输网络和核心网三个部分构成。
4. 移动网络的工作原理是将数据划分为小的数据包,然后通过无线网络传输给接收方,并在接收方将这些数据包重组成完整的信息。
二、蜂窝网络的定义和工作原理1. 蜂窝网络是移动网络的一种,是借用了蜂窝式建筑物的概念来构建网络架构。
2. 蜂窝网络将地理区域划分为多个相互独立的小区域,每个小区域由一个蜂窝基站负责提供信号覆盖。
3. 蜂窝网络通过不同频段的信号避免产生干扰,并将用户数据传输到核心网中的目标用户。
4. 蜂窝网络的工作原理是将接入用户的数据传输到蜂窝基站,然后再由蜂窝基站转发到核心网,最终到达目标用户。
三、移动网络和蜂窝网络的优缺点1. 移动网络的优点:a. 覆盖范围广:移动网络可以实现全球范围内的移动通信,让人们在任何时候、任何地点都能保持联系。
b. 便利性高:移动网络不需要布线,无需固定设备,可以随时随地连接,极大地方便了人们的生活。
c. 可扩展性强:移动网络可以根据需求进行扩展,适用于大范围的用户,能够满足日益增长的通信需求。
2. 移动网络的缺点:a. 受信号干扰:由于信号传播存在一定的干扰,造成了信号质量的下降,影响了通信质量。
b. 安全隐患:移动网络通信过程中面临更多的数据泄露和黑客攻击的风险,需要加强安全保护。

蜂窝网络服务功能介绍蜂窝网络蜂窝网络或移动网络(Cellular network)是一种移动通信硬件架构,把移动电话的服务区分为一个个正六边形的小子区,每个小区设一个基站,形成了形状酷似蜂窝的结构,因而把这种移动通信方式称为蜂窝移动通信方式。
蜂窝网络又可分为模拟蜂窝网络和数字蜂窝网络,主要区别于传输信息的方式。
蜂窝网络组成部分蜂窝网络组成主要有以下三部分:移动站,基站子系统,网络子系统。
移动站就是网络终端设备,比如手机或者一些蜂窝工控设备。
基站子系统包括移动基站(大铁塔)、无线收发设备、专用网络(一般是光纤)、无线的数字设备等等的。
基站子系统可以看作是无线网络与有线网络之间的转换器。
蜂窝和频率重用蜂窝网络蜂窝:将一块大的区域划分为多个小的蜂窝,使用多个小功率发射器代替一个大功率发射机。
一般使用正六边形来描述蜂窝形状。
频率复用:每一个蜂窝使用一组频道。
如果两个蜂窝相隔足够远,则可以使用同一组频道。
簇(cluster):由N个蜂窝组成的蜂窝组,使用了全部的频率资源频率复用因子(reusefactor):1/N对于正六边形的蜂窝,N=i +i*j+j ,i》=1,j》=1,当i》1时,j0或当j》1时,i0.因此,N=3,4,7,9,12.。
蜂窝的几何表示蜂窝通常使用正六边形来表示。
为什么是正六边形而不是圆?顶点到几何中心等距的多边形中,能够完整(无重叠)地覆盖某一区域可能的几何形状有:正方形、等边三角形和正六边形三种形状。
在正方形、等边三角形和正六边形中,正六边形的面积最大。
蜂窝坐标系使用(i,j)表示某一蜂窝的坐标。
例如:蜂窝A的坐标为(2,1)。
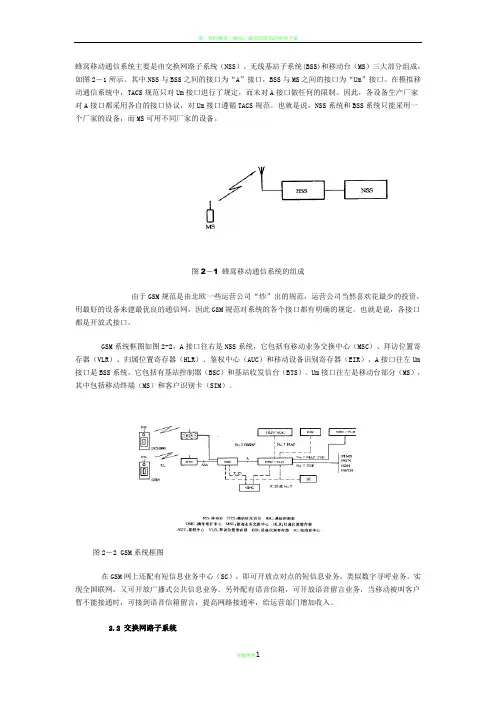
蜂窝移动通信系统主要是由交换网路子系统(NSS)、无线基站子系统(BSS)和移动台(MS)三大部分组成,如图2-1所示。
其中NSS与BSS之间的接口为“A”接口,BSS与MS之间的接口为“Um”接口。
在模拟移动通信系统中,TACS规范只对Um接口进行了规定,而未对A接口做任何的限制。
因此,各设备生产厂家对A接口都采用各自的接口协议,对Um接口遵循TACS规范。
也就是说,NSS系统和BSS系统只能采用一个厂家的设备,而MS可用不同厂家的设备。
图2-1 蜂窝移动通信系统的组成由于GSM规范是由北欧一些运营公司“炒”出的规范,运营公司当然喜欢花最少的投资,用最好的设备来建最优良的通信网,因此GSM规范对系统的各个接口都有明确的规定。
也就是说,各接口都是开放式接口。
GSM系统框图如图2-2,A接口往右是NSS系统,它包括有移动业务交换中心(MSC)、拜访位置寄存器(VLR)、归属位置寄存器(HLR)、鉴权中心(AUC)和移动设备识别寄存器(EIR),A接口往左Um 接口是BSS系统,它包括有基站控制器(BSC)和基站收发信台(BTS)。
Um接口往左是移动台部分(MS),其中包括移动终端(MS)和客户识别卡(SIM)。
图2-2 GSM系统框图在GSM网上还配有短信息业务中心(SC),即可开放点对点的短信息业务,类似数字寻呼业务,实现全国联网,又可开放广播式公共信息业务。
另外配有语音信箱,可开放语音留言业务,当移动被叫客户暂不能接通时,可接到语音信箱留言,提高网路接通率,给运营部门增加收入。
2.2 交换网路子系统交换网路子系统(NSS)主要完成交换功能和客户数据与移动性管理、安全性管理所需的数据库功能。
NSS 由一系列功能实体所构成,各功能实体介绍如下:MSC:是GSM系统的核心,是对位于它所覆盖区域中的移动台进行控制和完成话路交换的功能实体,也是移动通信系统与其它公用通信网之间的接口。
它可完成网路接口、公共信道信令系统和计费等功能,还可完成BSS、MSC之间的切换和辅助性的无线资源管理、移动性管理等。
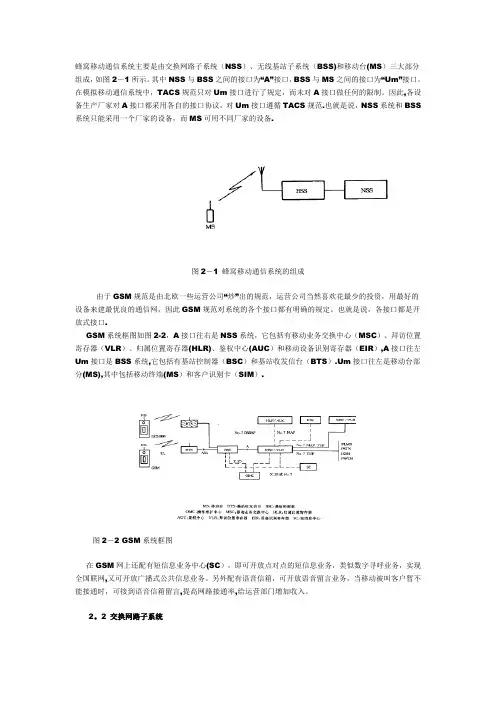
蜂窝移动通信系统主要是由交换网路子系统(NSS)、无线基站子系统(BSS)和移动台(MS)三大部分组成,如图2-1所示。
其中NSS与BSS之间的接口为“A”接口,BSS与MS之间的接口为“Um”接口。
在模拟移动通信系统中,TACS规范只对Um接口进行了规定,而未对A接口做任何的限制。
因此,各设备生产厂家对A接口都采用各自的接口协议,对Um接口遵循TACS规范.也就是说,NSS系统和BSS 系统只能采用一个厂家的设备,而MS可用不同厂家的设备.图2-1 蜂窝移动通信系统的组成由于GSM规范是由北欧一些运营公司“炒”出的规范,运营公司当然喜欢花最少的投资,用最好的设备来建最优良的通信网,因此GSM规范对系统的各个接口都有明确的规定。
也就是说,各接口都是开放式接口.GSM系统框图如图2-2,A接口往右是NSS系统,它包括有移动业务交换中心(MSC)、拜访位置寄存器(VLR)、归属位置寄存器(HLR)、鉴权中心(AUC)和移动设备识别寄存器(EIR),A接口往左Um接口是BSS系统,它包括有基站控制器(BSC)和基站收发信台(BTS).Um接口往左是移动台部分(MS),其中包括移动终端(MS)和客户识别卡(SIM).图2-2 GSM系统框图在GSM网上还配有短信息业务中心(SC),即可开放点对点的短信息业务,类似数字寻呼业务,实现全国联网,又可开放广播式公共信息业务。
另外配有语音信箱,可开放语音留言业务,当移动被叫客户暂不能接通时,可接到语音信箱留言,提高网路接通率,给运营部门增加收入。
2。
2 交换网路子系统交换网路子系统(NSS)主要完成交换功能和客户数据与移动性管理、安全性管理所需的数据库功能. NSS 由一系列功能实体所构成,各功能实体介绍如下:MSC:是GSM系统的核心,是对位于它所覆盖区域中的移动台进行控制和完成话路交换的功能实体,也是移动通信系统与其它公用通信网之间的接口。
它可完成网路接口、公共信道信令系统和计费等功能,还可完成BSS、MSC之间的切换和辅助性的无线资源管理、移动性管理等。

数字蜂窝移动通信系统的基本组成及各部分的作用数字蜂窝移动通信系统的基本组成及各部分的作用随着移动通信技术的飞速发展,数字蜂窝移动通信系统已经成为了我们生活中不可或缺的一部分。
这一系统以其高效率、便捷性和广泛的覆盖范围,为人们提供了无线通信和数据传输的便利。
但是,对于普通用户来说,对数字蜂窝移动通信系统的基本组成以及各部分的作用,往往显得有些陌生。
本文将通过深度和广度兼具的方式,全面评估数字蜂窝移动通信系统的基本组成及各部分的作用,帮助读者更好地了解这一重要的通信系统。
一、数字蜂窝移动通信系统的基本组成数字蜂窝移动通信系统是由多个基本部分组成的复杂系统,其中包括基站系统、核心网和移动终端三个部分。
1. 基站系统基站系统是数字蜂窝移动通信系统中最为重要的组成部分之一,其主要包括基站、无线传输子系统和控制器等多个子系统。
基站是通信系统中的一个核心设备,用于对移动终端进行信号的发送和接收。
无线传输子系统则负责信号的传输和解调工作,保障了通信的稳定性和可靠性。
控制器则起到了对基站和移动终端的控制和管理作用,确保通信系统的正常运行。
2. 核心网核心网是数字蜂窝移动通信系统的另一个重要组成部分,其主要功能是对移动通信数据进行传输和交换。
它由移动交换中心、业务支撑系统和数据传输网等多个子系统构成。
移动交换中心是数字蜂窝移动通信系统中的核心设备,用于对移动通信数据进行交换和路由。
业务支撑系统则用于提供各种业务支持和管理服务,保障了通信系统的正常运行。
数据传输网则负责对移动通信数据进行传输和交换,确保了通信数据的安全性和稳定性。
3. 移动终端移动终端是数字蜂窝移动通信系统中的另一重要组成部分,其主要包括手机、数据卡和调频器等设备。
手机是人们日常生活中最为常见的移动终端设备,用于进行语音通话、发送和数据传输等多种通信功能。
数据卡则是用于将移动通信数据传输到移动终端设备中的重要设备,它能够确保移动终端设备能够正常、稳定地进行通信。

蜂窝移动通信系统的组成蜂窝移动通信系统的组成概述蜂窝移动通信系统是一种基于无线电技术的通信系统,它由多个小区组成,每个小区都有一个基站来提供无线电信号覆盖。
在这种系统中,用户可以通过移动设备进行通信,包括语音、短信、数据传输等。
蜂窝移动通信系统的组成主要包括以下几个方面:1. 基站子系统基站子系统是整个蜂窝移动通信系统最核心的部分。
它由基站控制器(BSC)、基站传输子系统(BTS)和天线子系统(AS)三部分组成。
BSC是整个基站子系统的核心控制单元,它负责对所有的BTS进行管理和控制。
通过BSC,可以实现对小区内所有终端设备的呼叫控制、资源分配、话务管理等功能。
BTS是指基站传输子系统,它是连接用户终端设备和网络之间的桥梁。
每个BTS都包含多个射频单元(TRX),每个TRX都可以支持多个频道。
通过BTS,可以实现对用户终端设备的接入、呼叫处理等功能。
AS是指天线子系统,它主要用于向用户终端设备提供无线电信号覆盖。
每个小区都会有一个AS,它可以包含多个天线。
2. 移动交换中心移动交换中心(MSC)是整个蜂窝移动通信系统的核心控制单元,它负责对所有的基站进行管理和控制。
通过MSC,可以实现对整个网络的呼叫控制、资源分配、话务管理等功能。
在蜂窝移动通信系统中,MSC也扮演着一个重要的角色。
它不仅负责对用户终端设备进行管理和控制,还负责与其他网络进行互联互通。
3. 鉴权中心鉴权中心(AUC)是用于保证用户身份安全的关键单元。
在蜂窝移动通信系统中,每个用户终端设备都有一个唯一的标识码(IMSI),这个标识码与用户的身份信息相关联。
当用户终端设备接入网络时,AUC会对其进行身份验证,并将验证结果传递给MSC。
通过这种方式,可以保证只有合法用户才能够接入网络。
4. 认证中心认证中心(HLR)是用于存储和管理用户信息的关键单元。
在蜂窝移动通信系统中,每个用户都会有一个对应的HLR记录其身份信息、服务状态、位置等信息。

蜂窝网络技术的架构和协议标准介绍蜂窝网络是我们生活中常见的移动通信技术,它提供了便捷的通信服务,让我们能够随时随地进行电话和数据传输。
本文将介绍蜂窝网络技术的基本架构和协议标准,以帮助读者更好地了解这一技术。
一、蜂窝网络的基本架构蜂窝网络是一种将网络覆盖区域划分为多个小区的无线通信系统,每个小区都配备了一座基站。
这些基站通过专用的信号进行通信,将用户的通信数据传输到目标位置。
这种架构的设计主要是为了解决移动通信中无线波传播距离有限的问题。
蜂窝网络的基本架构由三个层次组成,分别是手机终端、基站子系统和核心网。
手机终端作为用户的接入设备,通过无线信号与基站进行通信。
基站子系统则负责信号的传输和处理,其中包括基站控制器和基站发射机。
核心网则是整个网络的中枢,负责用户数据的路由和管理。
二、蜂窝网络的协议标准蜂窝网络采用了一系列的协议标准来规范通信过程,确保设备之间的互通性和数据的安全性。
其中最为重要的协议是GSM(Global System for Mobile Communications,全球移动通信系统)和LTE (Long Term Evolution,长期演进)。
GSM标准是蜂窝网络的第一代技术,它于20世纪80年代初开始研发,并于90年代初正式商用。
GSM标准采用了时分多址(TDMA)技术,将频谱分成多个时隙,每个时隙只允许一个用户进行通信。
这种技术有效地提高了频谱利用率,支持更多用户同时接入网络。
随着移动通信技术的快速发展,LTE标准被提出并广泛应用。
LTE是蜂窝网络的第四代技术,它采用了OFDM(Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing,正交频分复用)技术,能够更高效地利用频谱资源,在减少通信时延的同时提供更高的传输速率。
同时,LTE还支持多天线技术,可以有效地抑制信号干扰,提高通信质量。
除了GSM和LTE,蜂窝网络还包括其他一些协议标准,如UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System,通用移动通信系统)和WiMAX(Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access,全球微波互操作性)。

蜂窝移动通信系统组成(一)引言概述:蜂窝移动通信系统是现代通信技术的重要组成部分,在实现移动通信的无缝连接和高速数据传输方面发挥了关键作用。
本文将探讨蜂窝移动通信系统的组成,帮助读者更好地了解这一技术。
正文内容:1. 蜂窝移动通信系统的基本原理- 蜂窝移动通信系统是基于无线电技术的通信系统,通过划分地理区域为小单元,每个小单元称为蜂窝,从而实现无缝的移动通信。
- 蜂窝移动通信系统利用无线基站与移动设备之间的无线信道进行信息的传输和接收。
1.1. 手机用户与基站通信- 手机用户通过手机设备与所在区域内的基站进行通信。
- 基站接收并解码来自手机用户的信息,然后将其传输到目标基站或其他通信网络中。
1.2. 基站间的无缝切换- 蜂窝移动通信系统中的基站之间通过无缝切换实现用户在移动过程中的通信连续性。
- 当用户从一个蜂窝区域移动到另一个蜂窝区域时,通信系统会自动将用户的通信连接从一个基站切换到另一个基站。
2. 蜂窝移动通信系统的关键组成部分- 蜂窝移动通信系统由多个关键组成部分组成,以实现高效的通信传输和数据处理。
2.1. 基站- 基站是蜂窝移动通信系统中的核心设备,用于接收和发送电波以实现与手机用户之间的通信。
- 基站通常由天线、收发信机、射频设备、控制单元等组成。
2.2. 移动设备- 移动设备是指用户所使用的手机等设备,它们通过无线电波与基站进行通信。
- 移动设备拥有自己的信号处理器、天线和操作系统,用于接收和发送通信信号。
2.3. 传输网络- 传输网络是蜂窝移动通信系统中的另一个重要组成部分,用于连接不同基站之间的通信流量。
- 传输网络经常使用光纤、卫星连接等技术来传输数据。
2.4. 控制中心- 控制中心是蜂窝移动通信系统的核心控制单元,负责调度和管理整个通信系统的运行。
- 控制中心包括信令网关、移动交换中心和运营支持系统等。
2.5. 用户接口- 用户接口是蜂窝移动通信系统与用户之间的桥梁,用于用户通过移动设备与通信系统进行交互。
蜂窝移动通信系统组成蜂窝移动通信系统是一种广泛应用于现代通信领域的无线通信技术。
它由多个组成部分构成,包括基站子系统、核心网子系统以及移动终端设备。
本文将对蜂窝移动通信系统的组成进行详细介绍。
一、基站子系统基站子系统是蜂窝移动通信系统的核心组成部分,负责无线信号的传输和接收。
它包括以下几个主要组件:⑴基站基站是蜂窝移动通信系统中的无线发射和接收设备,负责与移动终端进行信号的传输和接收。
它通常由天线、射频(Radio Frequency)模块、数字信号处理器等组件构成。
⑵基站控制器(BSC)基站控制器负责控制基站的运行和管理。
它与基站之间通过无线或有线连接进行通信,可以同时控制多个基站。
基站控制器的主要功能包括呼叫控制、信道分配、功率控制等。
⑶传输网(Transit Network)传输网是蜂窝移动通信系统中用于传输数据和信号的网络。
它由多种传输介质组成,如光纤、微波等。
传输网负责将来自基站的信号传输至核心网子系统。
二、核心网子系统核心网子系统是蜂窝移动通信系统中的中心部分,负责处理和管理移动通信的核心功能。
它由以下几个主要组件组成:⑴移动交换中心(MSC)移动交换中心是核心网子系统中的一个重要组成部分,负责呼叫控制、信令传输等功能。
它与基站控制器相互连接,管理呼叫的接入和传输。
⑵主数据管理(Home Location Register,HLR)主数据管理是核心网子系统中的一个数据库,用于存储和管理移动用户的基本信息,如用户号码、位置信息等。
⑶位置注册(Visitor Location Register,VLR)位置注册是核心网子系统中的一个数据库,用于存储和管理目前正在访问某一地区的移动用户信息。
⑷计费中心(Billing Center)计费中心负责统计和计费移动通信服务的使用情况。
它与移动交换中心、主数据管理等组件进行数据交换,相应的通信费用信息。
三、移动终端设备移动终端设备是蜂窝移动通信系统的用户侧,用于与基站进行通信和连接。
蜂窝移动通信网络的架构与优化随着移动科技的不断发展和普及,蜂窝移动通信网络已经成为了当代社会中最重要的通讯方式之一,并得到了广泛的应用。
作为一种新兴的移动通信技术,蜂窝移动通信网络凭借着其技术独特性和广泛的应用场景,开启了移动通信时代的新篇章。
本文将从蜂窝移动通信网络的架构和优化两个方面进行探讨。
一、蜂窝移动通信网络的架构蜂窝移动通信网络是指以一定的频段划分,将城市或者区域分为若干个覆盖范围相互独立的、有机组合的小区,小区间相互配合完成各自的通信功能,并提供一种低成本、高速率、高可靠性、可移动性和经济效益较高的通信方式。
传统的蜂窝移动通信网络主要由三个部分组成:基站、移动终端以及核心网。
基站是指在各小区内设置的通信设备,通过无线电波与移动终端进行通讯,而移动终端则是利用基站提供的信号进行通讯的终端设备,核心网则是整个移动通讯网络的控制中心,负责控制和管理整个网络的运行。
根据不同的通信标准,蜂窝移动通信网络可以分为2G、3G、4G和5G等几代。
2G通信网络主要使用GSM标准,采用TDMA 技术进行多用户并发通信,这种信道复用方式能够提高系统的频谱利用效率,从而降低资费。
3G通信网络主要采用WCDMA或CDMA2000标准,引入了高速数据传输技术,实现了数据与语音的共存。
4G通信网络使用LTE标准,采用OFDM技术、MIMO 技术、Small Cell技术等技术手段,实现了高速、高效、高质的无线宽带服务。
5G通信网络则是一种全新的、基于物联网的通信技术,具有低时延、高带宽、高可靠性、高密度连接、低功耗等特点,是未来智能化社会的重要构成组成部分。
二、蜂窝移动通信网络的优化蜂窝移动通信网络的优化是指通过一系列的技术手段和策略,提高网络的性能和服务质量,同时降低系统的运营成本。
具体的优化策略包括以下几个方面:1.信号优化:蜂窝移动通信网络中,信号的强度和质量对通讯的质量有着直接的影响。
因此,对信号的强度和质量进行优化,可以有效地提高通信的稳定性和可靠性。
蜂窝网络技术的架构和协议标准介绍引言:近年来,蜂窝网络技术的快速发展对我们的生活产生了深远的影响。
但是,很多人对于蜂窝网络的架构和协议标准了解甚少。
本文将深入探讨蜂窝网络技术的架构以及协议标准,帮助读者更好地理解并应用于实际生活中。
一、蜂窝网络的基本架构蜂窝网络由基站和移动设备组成,基站负责与移动设备进行通信,而移动设备则通过基站连接到互联网。
基站之间通过各种通信链路进行连接,形成了覆盖范围广泛的网络。
在蜂窝网络中,基站根据网络规模和需求布置,可以分为宏基站和微基站。
宏基站覆盖范围较大,一般用于城市和乡村地区;微基站覆盖范围较小,可以满足密集人群聚集的地区需求。
二、蜂窝网络的协议标准为了保证蜂窝网络的运行效率和互操作性,国际电信联盟(ITU)和3GPP(第三代合作伙伴计划)制定了一系列的协议标准,以确保不同厂商的设备能够实现互相通信和兼容。
1. GSM(Global System for Mobile Communications)标准GSM是全球范围内最为广泛采用的蜂窝通信协议标准之一。
其主要用于移动电话通信,实现了语音和短信的传输。
GSM标准采用时分多址技术,将频谱划分为不同的时隙,并通过对时隙进行分配和调度来实现多个用户之间的通信。
2. CDMA(Code Division Multiple Access)标准与GSM不同,CDMA是一种基于编码的多址技术。
CDMA标准将语音和数据转换为数字信号,并通过编码和解码技术实现多用户在同一个频道上同时传输。
由于其抗干扰能力较强,CDMA被广泛应用于3G和4G网络中。
3. LTE(Long-Term Evolution)标准LTE是一种4G无线通信标准,具有高速数据传输、低时延和强大的网络承载能力。
LTE使用OFDMA(正交频分多址)和MIMO(多输入多输出)技术,提供了更高的覆盖范围和传输速率。
4. 5G标准随着技术的发展,5G标准被制定出来,作为下一代蜂窝网络技术的发展方向。
蜂窝网络技术的架构和协议标准介绍蜂窝网络技术是现代移动通信中最基本的网络技术之一。
它的发展为人们在任何时间、任何地点都能够实现无线通信提供了可能。
本文将从蜂窝网络的架构和协议标准两个方面进行介绍。
一、蜂窝网络架构蜂窝网络的架构是由一系列基站和核心网组成的。
基站是网络中与用户直接接触的部分,负责提供无线信号覆盖,进行无线信号传输和接收。
核心网是网络中的控制中心,负责处理信令传输、用户管理以及数据交换。
在蜂窝网络架构中,基站被划分为多个蜂窝,每个蜂窝覆盖一定的区域。
这样的划分可以提高网络的覆盖范围和容量。
每个蜂窝中都有一个基站控制器(BSC)负责管理该蜂窝中的若干个基站。
同时,蜂窝网络还采用了移动交换中心(MSC)来处理电话呼叫和数据传输。
MSC负责连接不同的蜂窝,实现用户之间的通信。
另外,为了增加网络的容量和覆盖范围,蜂窝网络还引入了辅助交换中心(AUC)、网关GPRS支持节点(SGSN)和服务GPRS支持节点(GGSN)等设备。
二、蜂窝网络协议标准为了实现不同设备之间的互通和协同工作,蜂窝网络采用了一系列的协议标准。
其中,最重要的就是GSM(Global System for Mobile Communications)标准。
GSM是一种全球移动通信系统,是蜂窝网络中最早被采用和推广的一种标准。
它规定了无线信号的传输方式、信道的分配方式以及呼叫控制和数据传输等方面的协议。
GSM标准的推出为蜂窝网络的发展奠定了基础。
除了GSM,蜂窝网络还采用了一些其他的协议标准。
如GPRS (General Packet Radio Service)和EDGE(Enhanced Data ratesfor GSM Evolution)标准,它们在GSM的基础上增加了数据传输和互联网接入等功能。
而在3G时代,蜂窝网络引入了UMTS(Universal Mobile Telecommunications System)和CDMA2000(Code Division Multiple Access)等协议标准,实现了更高的数据传输速率和更多的业务功能。
蜂窝移动通信组网技术一、引言1-1 文档目的本文档旨在详细介绍蜂窝移动通信组网技术,以便读者对该技术有全面的了解。
1-2 文档范围本文档主要涵盖蜂窝移动通信组网技术的基本概念、网络架构、无线接入技术、核心网络技术等方面的内容。
二、蜂窝移动通信基础知识2-1 蜂窝通信原理介绍蜂窝通信的基本原理,包括频率复用、移动台切换、覆盖范围等。
2-2 移动通信标准介绍蜂窝移动通信的标准,如GSM、CDMA、LTE等。
三、蜂窝移动通信网络架构3-1 网络架构概述介绍蜂窝移动通信网络的整体架构,包括基站子系统、核心网等。
3-2 基站子系统详细介绍基站子系统的组成部分,包括基站控制器、基站收发设备等。
3-3 核心网络介绍核心网络的组成部分,包括移动交换中心、业务支持系统等。
四、蜂窝移动通信无线接入技术4-1 无线接入技术概述介绍蜂窝移动通信中的无线接入技术,包括调制解调、信道编码等。
4-2 蜂窝覆盖技术介绍蜂窝通信的覆盖范围扩展技术,包括室内覆盖、微蜂窝等。
五、蜂窝移动通信核心网络技术5-1 移动交换中心介绍移动交换中心的功能和作用,包括寻呼、呼叫控制等。
5-2 业务支持系统介绍业务支持系统的组成部分,包括计费系统、用户数据管理系统等。
六、附件本文档附有以下附件:1-蜂窝移动通信组网技术相关图表和示意图。
2-相关文献和资料。
注释:1-蜂窝通信:一种将有限的频率资源划分为若干个小区的无线通信方式,使不同的用户可以同时使用同一频率。
2-频率复用:将有限的频率资源划分为若干个频率小区,以实现多用户同时通信。
3-移动台切换:当移动台从一个小区进入另一个小区时,需要进行切换以确保通信的连续性。
G蜂窝网络架构分析引言随着移动通信技术的快速发展,第五代移动通信系统(5G)已经成为通信领域的研究热点。
5G网络作为下一代移动通信系统,相比第四代移动通信系统(4G)在速度、延迟、连接数等方面都有了显著的提升。
而在5G蜂窝网络架构中,G蜂窝网络架构以其高效、灵活、可靠的特点备受。
本文将对G蜂窝网络架构进行详细分析,介绍其组成部分、协议过程、优点与不足以及应用前景。
概述G蜂窝网络架构是5G网络架构的一种,它由多个基站、蜂窝和信道组成,每个基站覆盖一定数量的蜂窝,每个蜂窝则包含一组信道。
G 蜂窝网络架构采用了先进的信号处理技术和网络协议,使得用户能够在不同基站和蜂窝之间无缝切换,保障了网络的连续性和稳定性。
组成部分1、基站基站是G蜂窝网络架构中的重要组成部分,它负责管理一定区域的蜂窝,与蜂窝内的终端设备进行通信。
基站包含了无线收发信机、天线、电源等设备,能够实现对信号的发送、接收、处理等功能。
同时,基站还具备对终端设备的注册、认证和管理等功能,能够有效地保护网络的安全性和稳定性。
2、蜂窝蜂窝是G蜂窝网络架构中的另一个重要组成部分,它是由一组信道组成的覆盖区域。
每个蜂窝都包含多个信道,信道之间存在一定的频率间隔,以避免信号干扰。
蜂窝的大小和形状可以根据实际需要进行调整,通常取决于基站和地理位置等因素。
3、信道信道是G蜂窝网络架构中的基本单元,它承载着无线信号的传输。
信道可以分为控制信道和数据信道两类,控制信道用于传输信令和同步信号,而数据信道则用于传输用户数据。
信道的质量直接影响到网络的性能和可靠性。
协议过程在G蜂窝网络架构中,数据的传输过程主要包括以下步骤:1、信令传输当终端设备进入蜂窝覆盖范围后,需要通过信令与基站进行通信。
信令传输包含了设备注册、认证、连接建立等过程,以确保终端设备能够合法地接入网络。
2、数据传输数据传输是G蜂窝网络架构的核心功能之一。
在数据传输过程中,终端设备将数据发送到基站,然后由基站将数据传输到目标位置。
INFO-H-507 Mobile and Wireless Networks Cellular Systems EngineeringCellular Concept •Proposed by Bell Labs in 1971•Geographic Service divided into smaller cells •Neighboring cells do not use same set of frequencies to prevent interference •Often approximate coverage area of a cell by an idealized hexagon •Increase system capacity by frequency reuse Cellular Concept! Proposed by Bell Labs in 1971! Geographic Service divided into smaller “cells”! Neighboring cells do not use same set of frequencies to prevent interference! Often approximate coverage area of a cell by an idealized hexagon ! Increase system capacity by frequency reuse 2Less colours as possible -> the available BW is fixed -> BW of each div is limitedmodular -> extendablethe capacity can be expressed: bps/cell | bps/km^2 | Erlang/cell | Erlang/km^2•Deploy a large number of low-power transmitters(Base Stations) each having a limited coverage area•Reuse the spectrum several times in the area to be covered to increase capacity•issues•Capacity(traffic load)in a cell•One measure=number of communication channels that are available •Performance•Call blocking probability,handoff dropping probability,throughput etc.•Interference•Why not a large radio tower and large service area?•Number of simultaneous users would be very limited(to total number of traffic channels T)•Mobile handset would have greater power requirement •Cellular concept-small cells with frequency reuse•Advantages•Lower power handsets•Increases system capacity with frequency reuse•Drawbacks•Cost of cells•Handoffs between cells must be supported•Need to track user to route incoming call/message/dataT ypes of Interference•TDMA/FDMA based systems•Co-channel interference•Interference from signals transmitted by another cell using the sameradio spectrum•Adjacent channel interference•Interference from signals transmitted in the same cell with overlappingspectral sidelobes•CDMA systems•Interference from within the cell•Interference from outside the cellClustering in TDMA/FDMA•Adjacent cells CANNOT use the same channels•Co-channel interference will be too severe•The available spectrum is divided into chunks(sub-bands)that are distributed among the cells•Cells are grouped into clusters•Each cluster of cells employ the entire available radio spectrum•The spatial allocation of sub-bands has to be done to minimizeinterferenceCellular Concept(cont’)•Let T=total number of duplex channelsK cells=size of cell cluster(typically4,7,9,12,21)N=T/K=number of channels per cell•For a specific geographic area,if clusters are replicated M times, then total number of channels•System capacity=M⇥T•Choice of K determines distance between cells using the samefrequencies termed co-channel cells•K depends on how much interference can be tolerated by mobilestations and path lossCell Design -Reuse Pattern•Example:cell cluster size K =7,frequency reuse factor =1/7;•Assume T =490total channels,N =T /K =70channels per cell9! Example: cell cluster size K = 7, frequency reuse factor = 1/7; ! Assume T = 490 total channels, N = T/K = 70 channels per cell B A E C D G F B A E CD G F BA E C D G FAssume T = 490 total channels,K = 7, N = 70 channels/cellClusters are replicated M=3timesSystem capacity = 3x490 = 1470total channelsHex is used -> approximation of circle -> seamlessly fitGeometry of a hexagonal cell (1)π/6RSource: Ian Groves, Fundamentals of Communications (lecture notes)•Unit scale is the distance between neighboring cell centers •For cell radius R,one has2R cos(⇡/6)=1and R=1/p3.•T ofind the distance r to any point P(u,v),do(u,v)to(x,y) transformation:x=u cos(⇡/6)y=v+u sin(⇡/6)r2=x2+y2=u2cos2(⇡/6)+v2+u2sin2(⇡/6)+2uv sin(⇡/6) which yieldsr=p u2+v2+uv•Hexagonal cells will be grouped in clusters of cells•clusters pave the surface as a repetitive pattern of order6(hexagonalsymmetry)•the coordinates,in the(u,v)system,of any adjacent cell is of the form(i,j)where i,j2Z.•an equivalent cluster radius R c can be derived from the distance D •start from a reference cell and move i hexagons along the u-axis thenj hexagons along the v-axis.g Co-channel cells (continued)distance ihe u directiondistance j alongrectionter size K = i2 2,AuAAAAAAD=r(i,j)=p i2+j2+ijR c=Dp3=p i2+j2+ij p3•The number of cells in a cluster is given by N=Area(cluster)Area(cell)•Single cell area is6times the area of a triangle with equal edges R:Area(cell)=6⇥12✓R d2◆=6⇥12R p3R2!=3p32R2•Following similar reasoning,the cluster area is:Area(cluster)=3p32(R c)2•And,finally,N=R2c R2=i2+j2+ijExamplesMore Examples171324 3 1 4 212 3 4 1 3 1 4 2 6 7 5 1 11111K = 4 (i =2, j =0)K = 7 (i =2, j =1)2 9 8 67 1 310111245 6586798 12453 10 1112491011 K = 12 (i =2, j =2)interference:x6only count the 1^st tierReuse factor•The frequency reuse factor Q isgiven by:Q =D R=p 3Nand can interpreted as the rate at which the same frequency can be used in the network.•NB:reuse factor is sometimesdefined as 1/N directlyPossible Cluster Sizes (N ) and Frequency reuse factor (Qi j N Q 101 1.7321133204 3.464217 4.583309 5.196221263113 6.2454016 6.92832197.5541217.93750258.663327942289.165•In general,SIR =PdesiredP i P interf ,iSIR Calculation 21SITE ASITE BRSSI, dBmC/I Distancerd-60-90 -120signal-interference-ratio•Now consider a mobile at the edge of cell,distance R from transmitter(downlink only)with power P t.•Number offirst-tier(dominant)co-channel cells is i=6(always)•Averagefirst tier co-channel cell is distance D awayThe SIR can approximated as followsSIR[dB]⇡10log✓P t R ↵6P t D ↵◆=10log✓16Q↵◆=10↵log(Q) 7.86:Hex faces D: distance between same cells, z.B 1 to 1 in 1st tier•The SIR is independent of cell size!SIR Calculation (2)•For ↵=4,one has the following values2011 / 201217S /I for different cluster sizesFor ν=4i j N Q S/I 101 1.732 1.742113311.28204 3.46413.78217 4.58318.64309 5.19620.832212623.333113 6.24524.024016 6.92825.8232197.5527.3241217.93728.1950258.6629.73327930.3742289.16530.693 4 712 13195101520 2530cluster size KS r i n d BS r as a function of the cluster size23•trade-off to be found in cellular systems:•if N decreases,the SIR drops and the quality decreases•if N increases,less channels are available per cell (see also “trunkingefficiency”in Erlang chapter)more cells -> better S/I-> less resource / area (density) z.B bps/cell=> tradeoffSIR Calculation (exercises)•Consider a GSM cellular system•typical SIR requirement of 18dB•Suburban propagation environment with ↵=4•solving the SIR for D /R givesDR=(6SIR )1/↵.Remember D /R =p 3N ,which results in N =13(6SINR )2/↵.•a margin of 18dB =10log (x )and x =63.0957.ThereforeN =6.4857•Since N must be an integer,you round up to nearest feasible clustersize N =7.SIR Calculation (3)•T ypical values for GSM system•one cell with a SIR 18dB,the average N is between 7and 9•sometimes N =3with dynamic frequency re-allocation•If the traffic load increases in a given zone•increase the available channels (buy more frequencies)•decrease N while keeping the SIR acceptable•reduce cell size through the value of R (increases the number of basestations and cost of deployment/operation)for GSM, for a communication, a freq is occupied -> more densely a cell is -> more communication is supported<= low speed <= low SIRlarge cell => low density cell => low resource for each cellumbrella cellumbrella cell is a big cell, which covers a group of cell,in case the resource is saturated by one of the covered cell,Cell Sectoring •Use directional antennas toreduce interference•Divide each BS (i.e.,hexagon)in k of sectors•Radio propagation is focused in certain directions•increases the number of cells Nbut also cuts the interferers in k •No new base station has to beset upCell Sectoring! Use directional antennas to reduce interference ! Radio propagation isfocused in certaindirections ! Antenna coverage isrestricted to part of acell called a sector ! By reducinginterference, the cluster size can be reduced (J s is reduced, and so wecan reduce N ) 33Cell Sectoring •For a 3sector antenna:•each sector uses 1/3of the allocated channels •mobile is interfered by 2first-tier base stations instead of 6,i.e.,SIR sectorized =SIR omni +10log 3=SIR omni +4.8[dB]NETWORKS OB_Propa +Cellular eng_ d. 2./0age 6tiq e l stimation précéd n e est simpliste et I affectés par problèmes de propagation ondes directes, réfléchies,….fading)/I égradé par les autres cellules des clusters voisins qui tilisent la m me fréqu nce et nterfèrent ./I amélioré par ifférentes fonctionnalités (e.g. supportées par le GSM)(1)contrôle de puissance des mobiles 2) DTX : “discontinuous transmission”3) Frequency hopping 4) HO and ver)BS3 BS secteurmportant économie en sites (BS)F2,F5F1,F4 F3,F6 3 secteursid d beille éalité•Results for a 18.6[dB]of SIR requirement:•omni antenna:N =7•3-sectors antenna N =4•The capacity increase is 7/4⇡1.75times 21/21the antenna is directional != omni=> 6/3 = 2 interference ONLY drawbacks:1) handover between freqs 2) splitting the freqs => reduce the local cap 3) for a whole cell{f_1 … f_6} <= 7 Erlangs for a 3BS cell{f_1,f_2; f_3,f_4; f_5, f_6} <= 3*3 erlangsresource problem。